AVBS3001- AGENTS OF DISEASE
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Goals of this Unit- Name infectious diseases, What are their features, Recognise pathogenic traits
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
Define Disease
A change in the state of **health** of a host resulting in the **inability** of the host or part thereof, to **carry out normal function due to the actions of an agents.**
2
New cards
Define Clinical disease
Change that is obvious with readily detectable signs of dysfunction or illness
* You can visible see symptoms
* You can visible see symptoms
3
New cards
Define Subclinical disease
Not readily detectable signs of dysfunction or illness, rather subtle changes in productivity, growth and fitness which may only be detectable using laboratory tests
4
New cards
Can a disease be subclinical to clincal
An animal can easily change from subclinical to clinical depending on the environment of the animal is situated on
5
New cards
What agents cause disease
* physical agents
* genetic or inherited
* Chemical agents
* Infectious agents
* Most common
* Can invade and multiply in/on a host
* Produce chemicals in the host or its environment (toxins)
* Multi-cellular, single cell or non-cellular
* Transmissible (direct or in-direct)
* Infectious agents are the most significant
* genetic or inherited
* Chemical agents
* Infectious agents
* Most common
* Can invade and multiply in/on a host
* Produce chemicals in the host or its environment (toxins)
* Multi-cellular, single cell or non-cellular
* Transmissible (direct or in-direct)
* Infectious agents are the most significant
6
New cards
How can we protect animals from infectious
* Understanding infectious agents that affect animals
* How they interact with the host and the environment
* Creating strategies to favour the HOST
* Breed and age
* Vax and worming
* Feed and shelter
* Biosecurity and control of animal/human movement
* How they interact with the host and the environment
* Creating strategies to favour the HOST
* Breed and age
* Vax and worming
* Feed and shelter
* Biosecurity and control of animal/human movement
7
New cards
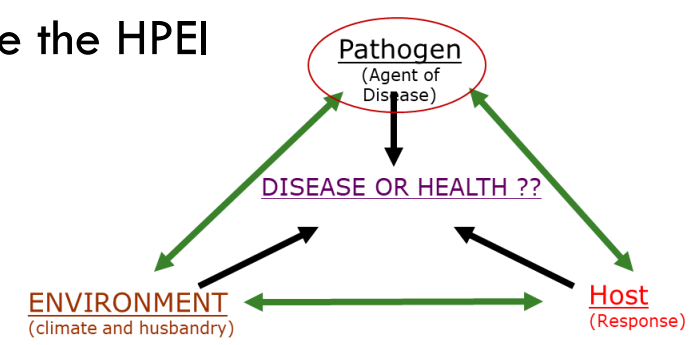
Factors that influence the Host pathogen environment interaction (HPEI)
* The pathogen itself; agent of disease
* The effect on the host; pathology
* Host response; immunity, inflammation and repair
* Environment; the external world relates to the host and the pathogen
Disease will result when the interactions favour the pathogen and a pathological host response
* The effect on the host; pathology
* Host response; immunity, inflammation and repair
* Environment; the external world relates to the host and the pathogen
Disease will result when the interactions favour the pathogen and a pathological host response
8
New cards
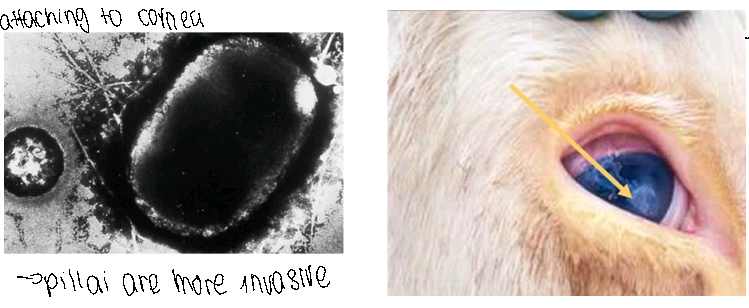
Disease manifestation can give us a clue about the identity of the infectious causative agent
Moraxella catarrhalis
* It contains a special feature inn attaching to the cornea
* The pillai of this pathogen gives it the ability to infect and attach to the cow’s eye causing the cloudiness -→ pilla are more invasive
* The pink causes cornea cloudus
* It contains a special feature inn attaching to the cornea
* The pillai of this pathogen gives it the ability to infect and attach to the cow’s eye causing the cloudiness -→ pilla are more invasive
* The pink causes cornea cloudus
9
New cards
Understanding HPEI
1. Diagnose the cause of an infectious disease
* Through sample collection
* Or culture and detection methods
\
2. Provide effective treatment of animals
* Antibiotics
3. Prevention and control
* By understanding the environment!!
* Survival in the environment
* Husbandry and stock density
* Housing and feed
* Climate
* Vaccination
\
Understanding HPEI -→ Better infectious disease management
\
10
New cards
Define Infection
Infectious agent is present within or on the animal. The agent may multiple, grow or invade the host.
\
Infection =/ Disease
HPEI determines the disease/ health status resulting from an infection
\
Infection =/ Disease
HPEI determines the disease/ health status resulting from an infection
11
New cards
Define Carrier
Can be an animal, often resistant to disease development, but able to spread an infectious agent to others.
12
New cards
Define Parasitism
When a symbiotic relationship between an organism and the host causes harm in the host (DISEASE).
* Any organism that cause harm to the host it inhabits can be classified as a parasite
* Infectious agents can be said to have parasitic properties that enable them to be pathogen (i.e) cause disease
* Any organism that cause harm to the host it inhabits can be classified as a parasite
* Infectious agents can be said to have parasitic properties that enable them to be pathogen (i.e) cause disease
13
New cards
Host-infectious agent relos
* parasitism
* Mutualism
* Commensalism
\
* Mutualism
* Commensalism
\
14
New cards
Define Mutualism
When the symbiotic relationship between an organism and the host results in benefits to both.
ie. the rumen microflora → ferments plant CHO -→ Energy for rumination
The bacteria needs the host in order for survival and likewise
ie. the rumen microflora → ferments plant CHO -→ Energy for rumination
The bacteria needs the host in order for survival and likewise
15
New cards
Define Commensalism
When the symbiotic relationship exists between an organism and the host results in no obvious harm to the host
* No obvious harm
* Shows some benefit for the host e.g bacterial found normally on your skin such as Staphylococcus aureus
* No obvious harm
* Shows some benefit for the host e.g bacterial found normally on your skin such as Staphylococcus aureus
16
New cards
Mutualistic and commensally can turn towards parasitism
Changes in host and environmental factors
* Lactic acidosis in cattle occurs with sudden introduction of high grain diets and overgrowth of Streptococcus bovis
* Cut and abrasions on the skin resulting in Staphylococcus aureus dermatitis
* Lactic acidosis in cattle occurs with sudden introduction of high grain diets and overgrowth of Streptococcus bovis
* Cut and abrasions on the skin resulting in Staphylococcus aureus dermatitis
17
New cards
What are the consequences of animal infectious diseases
* Animal productivity and diversity
* Supply and demand
* Farming industries
* Food safety and security
* Ecological balance
* Impact upon public health
* Indirectly and directly
* Financial
* Nutritional
* Psychological
* Supply and demand
* Farming industries
* Food safety and security
* Ecological balance
* Impact upon public health
* Indirectly and directly
* Financial
* Nutritional
* Psychological
18
New cards
Zoonosis
Diseases caused by unfectious agents that can be transmitted between animal and human
* 75% of emerging human infectious disease have an animal origin
* Swine flu, Avian influenza and COVID
* 75% of emerging human infectious disease have an animal origin
* Swine flu, Avian influenza and COVID
19
New cards
Causation
Infectious diseases are caused by the action of an infectious agents in the host.
20
New cards
Factors that influence disease risk
* **Host Factors**
* Animal species
* Genotype
* age
* Nutritional status
* reproductive status
* Past exposure/immunity -→ often protects the host, but may sensitive the host (allergic reaction)
* Concurrent disease/injuries
* Immune competence → Lack of passive transfer of antibodies increases risk of infectious disease in neonates
* Behaviours
* **Parasitic factors**
* Strains and virulence - virulence is a measure of pathogenicity → more virulent, less bias needed to cause disease and associated disease severity
* Higher does → greater chance of disease
* Methods and duration of exposure
* route and length of expsoure can influence host response
* Properties of virulence factors
* adapt to the host
* ability to invade and evade host host responses
* trigger pathology
* Often associated with virulence
* **Environmental factors**
* Climate- feed availbility, drought, rain, humidity and insects
* Topography
* Population density - spread of disease
* Food, water, soil and air - source of infectious agent
* Animal species
* Genotype
* age
* Nutritional status
* reproductive status
* Past exposure/immunity -→ often protects the host, but may sensitive the host (allergic reaction)
* Concurrent disease/injuries
* Immune competence → Lack of passive transfer of antibodies increases risk of infectious disease in neonates
* Behaviours
* **Parasitic factors**
* Strains and virulence - virulence is a measure of pathogenicity → more virulent, less bias needed to cause disease and associated disease severity
* Higher does → greater chance of disease
* Methods and duration of exposure
* route and length of expsoure can influence host response
* Properties of virulence factors
* adapt to the host
* ability to invade and evade host host responses
* trigger pathology
* Often associated with virulence
* **Environmental factors**
* Climate- feed availbility, drought, rain, humidity and insects
* Topography
* Population density - spread of disease
* Food, water, soil and air - source of infectious agent
21
New cards
How do we establish causation
Establishing evidence of a disease process associated with a pathogen
* **Substantial**
* The mere present of an agent is usually not enough
* Significant concentration and specific responses relating to virulence traits
* Need to make biological sense
* SLIDE 37 lec 1
* **Substantial**
* The mere present of an agent is usually not enough
* Significant concentration and specific responses relating to virulence traits
* Need to make biological sense
* SLIDE 37 lec 1
22
New cards
23
New cards
How do we establish casaution