Chem
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Chemical kinetics
The study of reaction rates (speed of reaction)
Factors that influence the reaction rate
1. concentration of reactants
2. nature of the reaction (amount of activation energy)
3. temperature
4. reaction mechanism
5. presence of catalyst
Collision Theory
1. reactions occur when there are collisions between reactants
2. BUT not all collisions lead to a reaction
- molecules must be properly oriented (collision geometry)
- only molecules with enough kinetic energy (KE) to break the bonds will result in a reaction
- molecules with low KE (KE < Ea) will bounce off each other
Activation Energy (Ea)
1. always positive
2. depends on the nature of reaction (low Ea= fast; high Ea = slow)
3. independent of concentration/temperature
activated complex
intermediate between reactants and products (psuedo-molecule)
catalyst
lowers activation energy without being consumed in the reaction
reaction rate
a positive quantity that expresses how the concentration (Molarity) of a reactant or product changes with time
reaction rate & temperature
as temperature increases, rate increases (in general)
reversible reactions
reactions that do not go to completion
equilibrium system
the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate (speed) and the concentration of reactants and products remain constant
equilibrium is a dynamic process
at equilibrium the forward and reverse reactions are still occuring (dynamic), even though the concentrations remain constant
Stresses alter equilibrium
When a system is at equilibrium, it will stay that way until something changes this condition
Pressure effects on equilibrium
when pressure is increased, the stress is relieved by favoring the reaction with fewer gas molecules (fewer gas molecules = lower pressure)
Stresses on equilibrium
1. temperature
2. concentration
3. pressure
Le Chatelier's Principle
When a system at equilibrium is disturbed by applying a stress, a new equilibrium position is attained to relieve the stress
equilibrium constant
the ratio of product concentration to the reactant concentration at equilibrium (no units)
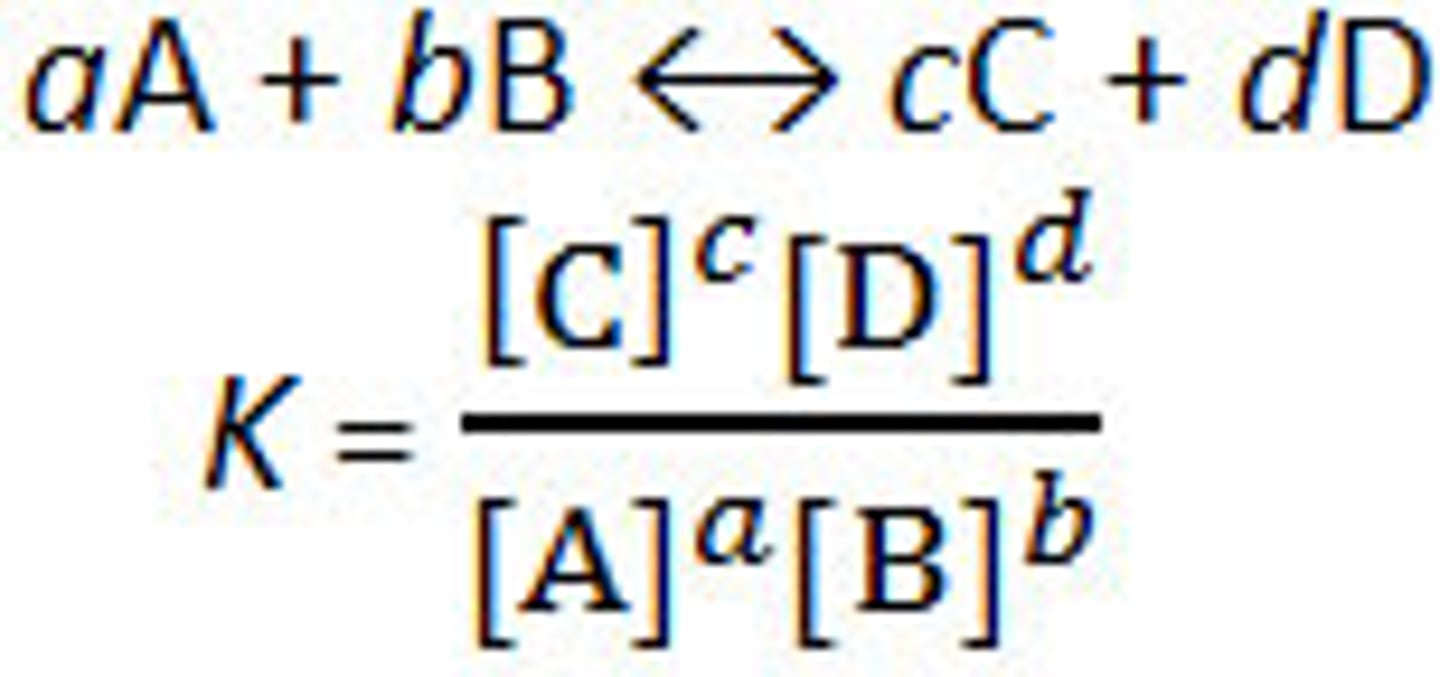
Meaning of equilibrium constant
∙ Keq > 1: products are favored (forward reaction)
∙ Keq < 1: reactants are favored (reverse reaction)
The Haber-Bosch Process
The process of "fixing" nitrogen from the atmosphere in the form of ammonia
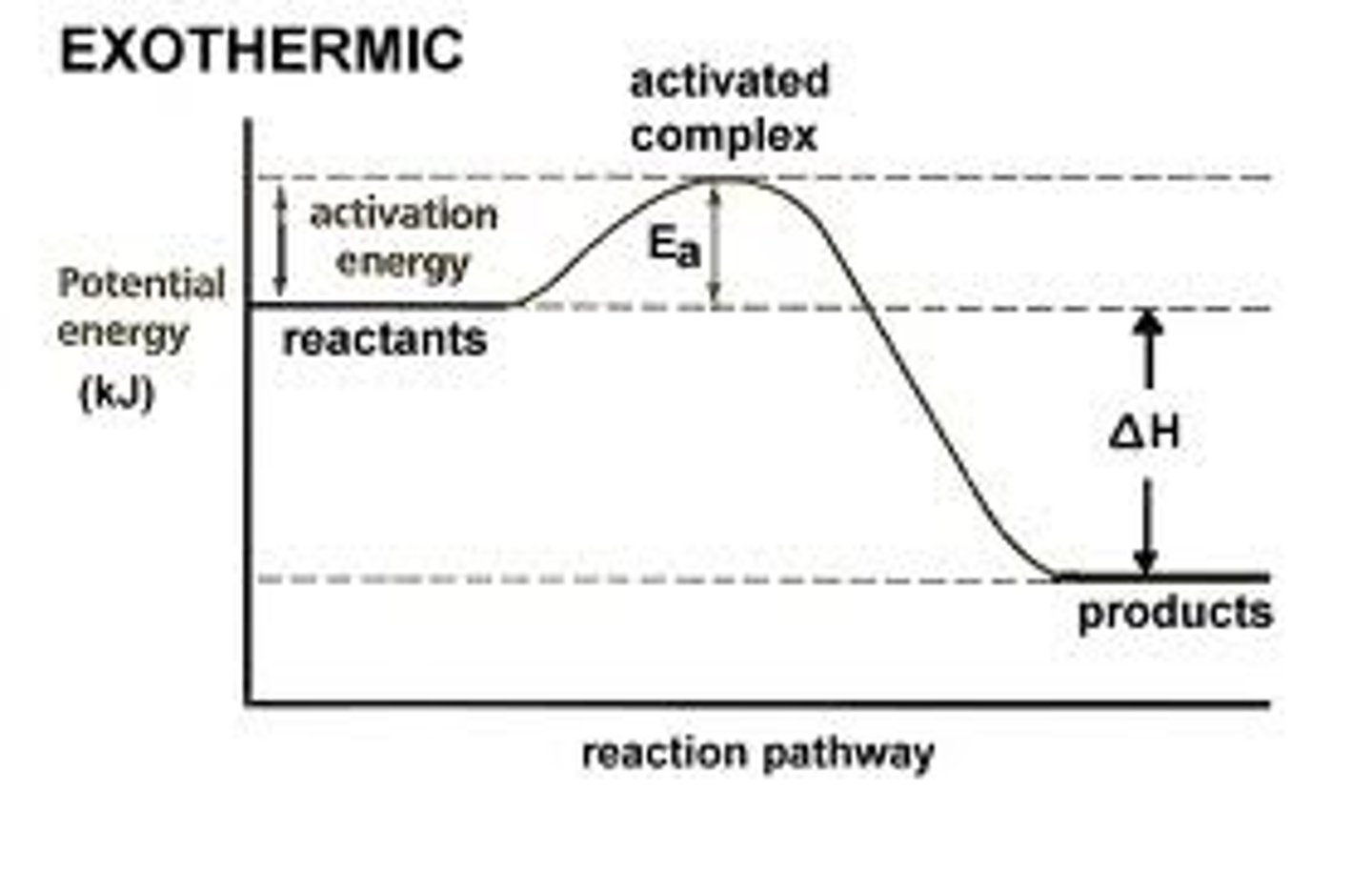
Exothermic Reaction (graph)
- fast because of low Ea
- change in temperature is negative
- releases energy
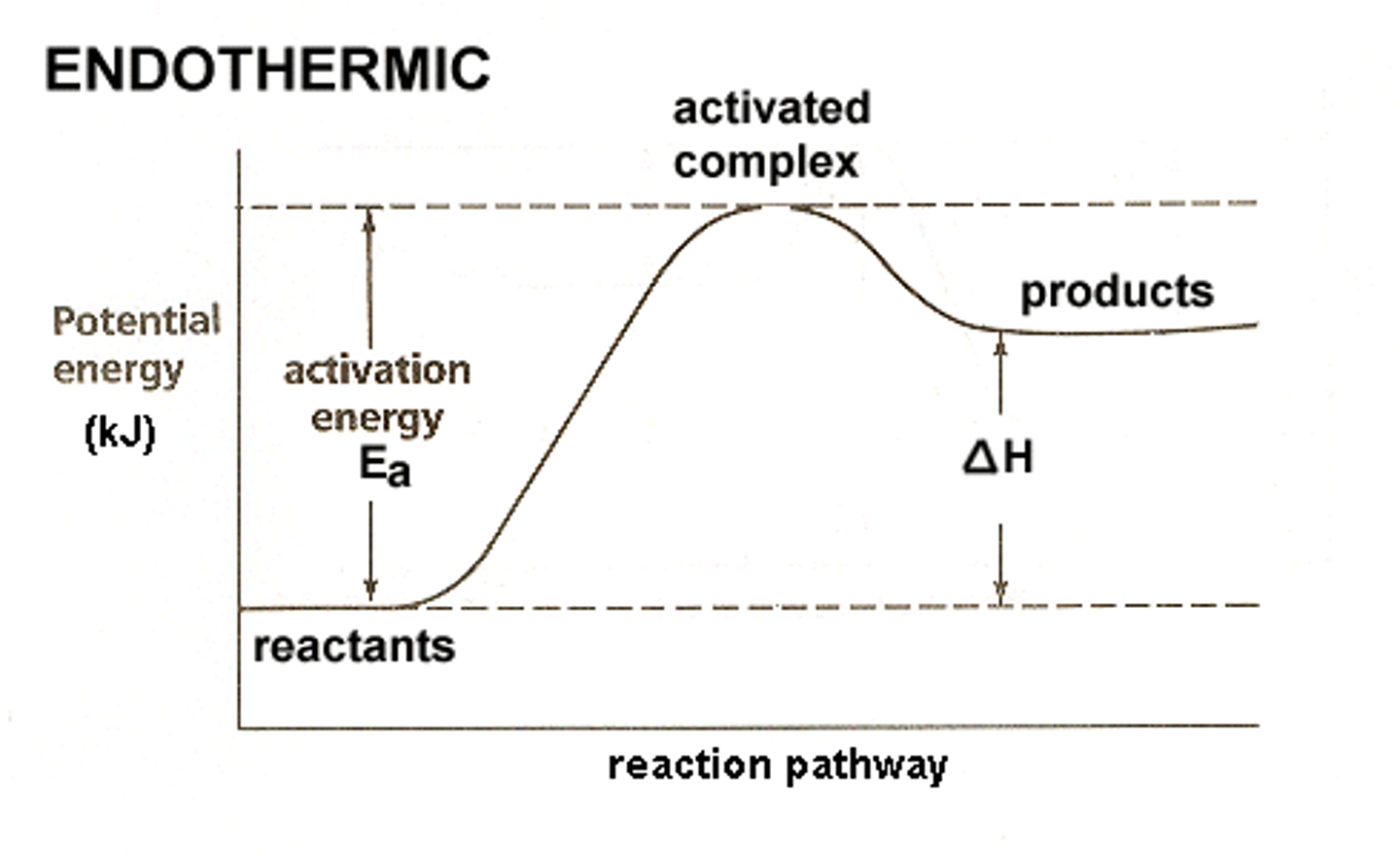
Endothermic Reaction (graph)
- slow because it needs a lot of Ea
- change in temperature is positive
- absorbs energy
branch of chemistry concerned with reaction rates and reaction mechanisms
kinetics
states that in order for a reaction to occur, the reactants must collide with one another with a sufficient amount of kinetic energy, as well as the correct orientation in space in order for them to combine
collision theory
successful collision
effective collision
factors that affect the collision of reactants
nature, concentration, surface area(solids), pressure (gases), temperature, catalysts
bond type affects the...of reactants
reaction rate
reacts faster than molecular reactants, as the particles within water are separated and therefore more accessible, and ionic bonds typically have fewer bonds to rearrange
aqueous ionic solutions
dependent on the amount of particles within the substance
concentration
greater concentration results in...
increased collision rates
in solids, a greater amount of exposed surface area will result in__________, as a greater amount of a substance exposed will result in a greater amount base to collide off of
increased collision rates
temperature's correlation with collission
increased temperature results in high collision rates
pressure's correlation with collission
increased pressure (in gases only) results in higher collission rates
temperatures correlation with collision with gases
increased temperature in gases results in lower rates of collision
reduce the activation energy required for a reaction to occur, without sacrificing any other components
ex:) flint, matches, etc
catalyst
the amount of energy absorbed or released during a chemical reaction
enthalpy
bond forming reactions, energy is released as a product of the reaction; in this type of reaction, the potential energy of the products is less than that of the reactants, as excess energy is leaving the reaction as a product; features a negative change of heat on the reference teable
exothermic reactions
energy will appear on the right side in this type of reaction
exothermic
bond breaking reactions; in this reaction, heat is absorbed, as energy is required to join the reactants together; the potential heat of the products is greater than that of the potential heat of the reactants; features a positive change of heat on the reference table
endothermic reactions
energy will appear on the left side of this reaction
endothermic reactions
change of heat on the reference table
Table I
occurs in most reactions
both endothermic and exothermic reactions
the potential energy of the products will appear higher in this graph, as heat is aborbed into the products
endothermic reactions
the potential energy of the products will appear lower in this graph, as heat is released by the reactants into the products
exothermic reactions
the minimum amount of energy that colliding particles must have in order to react
activation energy
point at which the reaction has reached is maximum potential energy, and has reached the required amount of energy for the reaction to begin; following this point, the reaction may begin
activation complex
lowers the activation energy by finding an alternate reaction pathway/mechanism; it doesn't alter anything, and any stored energy isn't used up
catalyst
featured within reactions when the rated of forward and reverse reactions are equal; reversible chemical reaction (has the ability to both synthesize and decompose)
equilibrium reactions
must remain constant within reactions at equilibrium
concentrations (amounts of particles)
requires a closed system, or controlled environment for this to occur; meaning no reactant, product, or means of energy may escape, for the reaction to occur
equilibrium reactions
forms of stress that may alter an equilibrium reaction
changes in temperature, pressure, or concentration
what are the two brands of equilibrium
chemical equilibrium and physical equilibrium
physical equilibrium that exists between two phases of matter; the substance remains the same, with just the phase of the substance altering between
ex:) water at its melting and freezing points;will remain in both the solid and liquid phases
phase equillibirum
physical equilibrium which exists only in saturated solutions; the rate of dissolving is equal to the rate of recrystallization; will fluctuate between hat of a solid and aqueous state, with the substance itself remaining chemically identical to the other
solution equilibrium
equilibrium reaction in which a chemically distinct product is produced from two separate reactants
chemical equilibrium
within a chemical reaction, a ____________ and __________ cannot exist, as they both result in a loss of product
insoluble solid in an aqueous solution, uncontained gas
when a system at equilibrium is subjected to a stress, the system will shift to the left or right in order to relieve the stress, thus creating a new equilibrium
Chatelier's principle
shift to right
forward shift
shift to left
reverse shift
indicates molar concentration
brackets
as a result of excess molecular amounts, either more reactants or products will be produced within an equilibrium reaction
increase in concentration
no shift permitted despite pressure changes
identical amounts of particles on each side
decreases the time needed to reach equilibrium
catalyst
once at equilibrium, the catalyst increases both forward and backward reaction time.....
equally
naturally occurring reactions; typically favor the formation of products and exothermic reactions; favors simpler products in greater quantities
spontaneous reactions
features a low enthalpy (exothermic reactions) and a high entropy (chaos)
spontaneous reactions
low enthalpy and high entropy
always spontaneous
high enthalpy and low entropy
never spontaneous
low enthalpy and low entropy
dependent on temperature
high enthalpy and high entropy
dependent on temperature
kinetics
study of how fast a chemical reaction is occurring and describes the rate of change in the concentrations of the reactants and products over time in chemical rxn
collision theory
reaction is most likely to occur if the reactant particles collide with sufficient energy and proper orientation
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Temperature
temp increases, rate of chemical rxn increases
higher temps=particles collisions more frequently and with more energy
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Surface Area
surface area increase=rate of rxn increase
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Concentration
concentration increase= rate of rxn increase
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Pressure (gas only)
pressure increase=rate of rxn increase and more effective collisions
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Presence of a catalyst
catalyst presence=rate of rxn increase
gives an alternate reaction pathway which requires less energy than the normal
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Nature of Reactants
Ions in water = fast
gases are FASTER than solids and liquids
ions FASTER than molecules
Catalyst & alternate reaction pathway
lower activation energy
endothermic chemical reaction
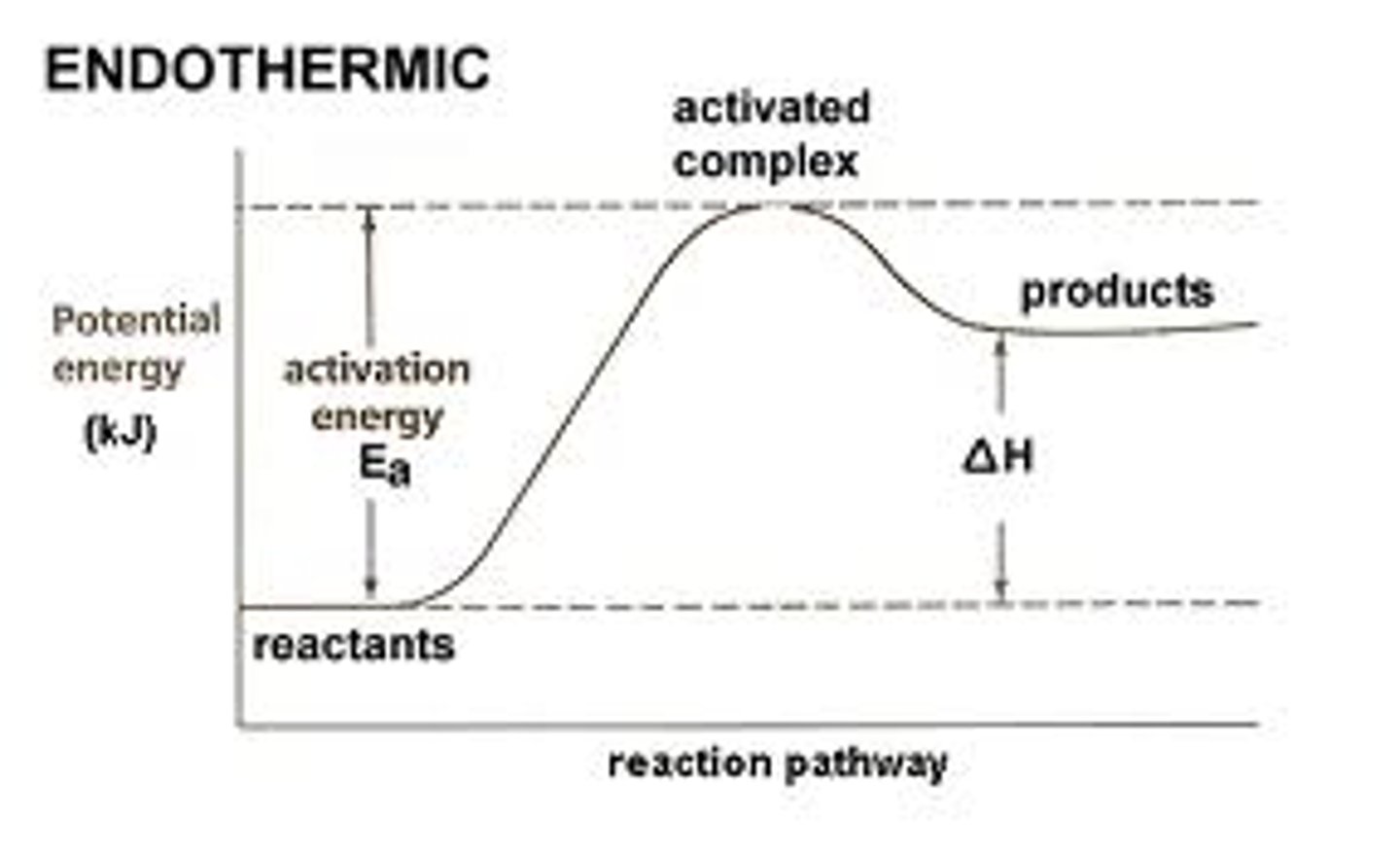
exothermic chemical reaction
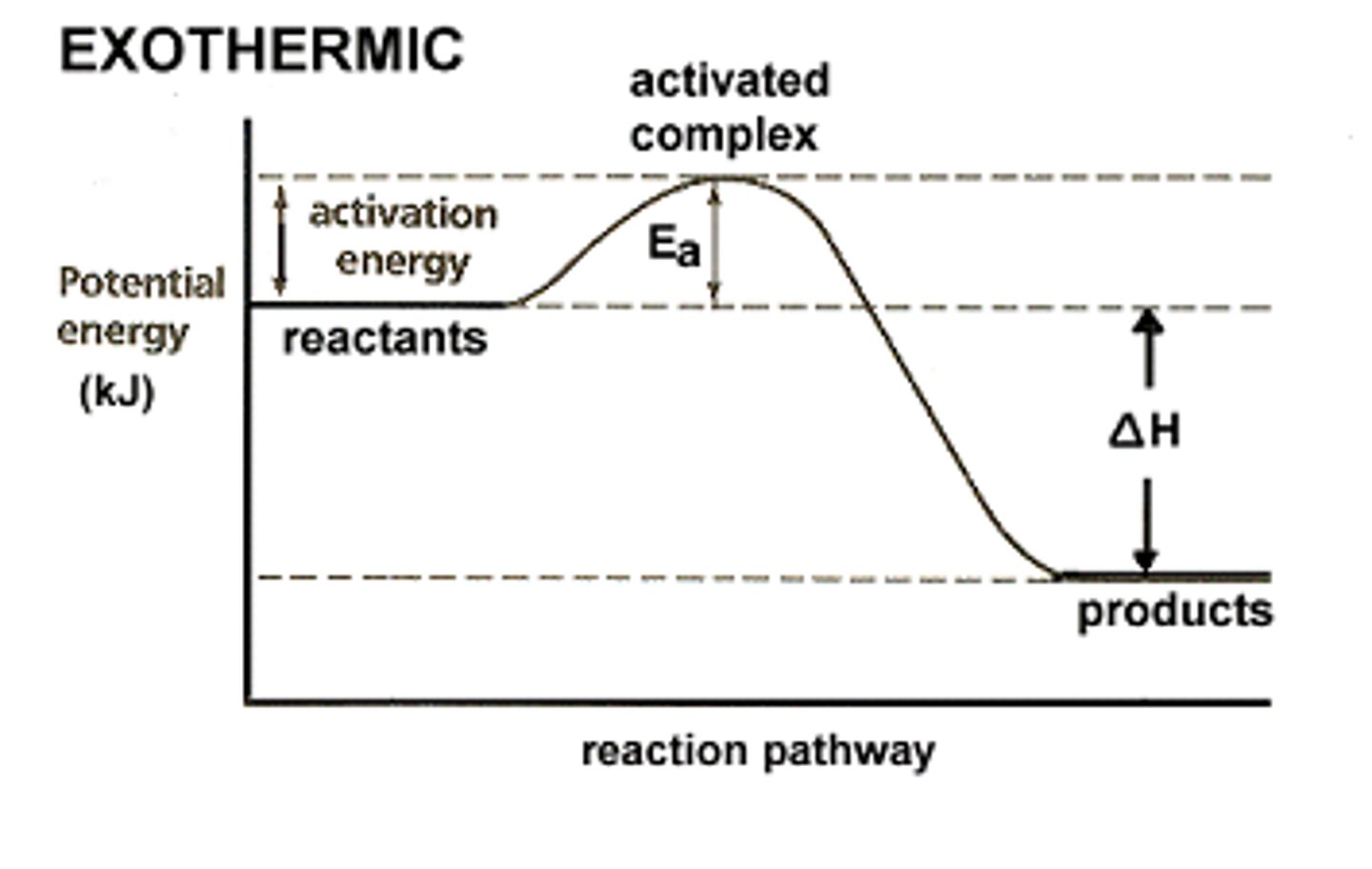
Heat of Reaction
- change in enthalpy
△H = PE products - PE reactants
-△H=exothermic
+△H=endothermic
Reaction Mechanisms
series of rxn steps that have to occur for a rxn to go to completion that are determined by experimentation
intermediates
species produced in one step that become reactants in a subsequent step
Reaction Rate Laws
rate = k [A][B]
k (specific rate constant)
depends on the size, speed, and kind of molecule at a given temperature
rate law experssion
rate of chemical rxn is proportional to the product of the [ ] of reactants raised to the power of the coefficents
rate of multi-step rxns
product of the [ ] of the reactants in the slowest step
equilibrium
- rates of forward = rate of reverse
- concentrations of reactants and products stay CONSTANT
Solution Equilibrium
when a solution is saturated
Phase equilibrium
rate of condensation/melting = rate of evaporation/freezing
chemical equilibrium
concetration of reactants and products remain constant
rates of forward and reverse are equal
equilibrium expression
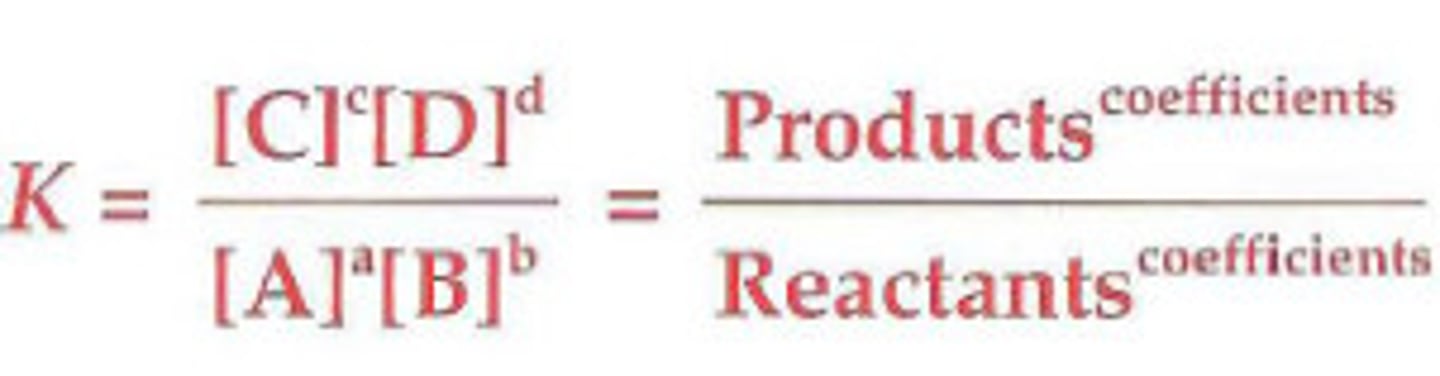
Keq
shows the extent to which the reactants are converted to products
AT EQUILIBRIUM
RATES of opposing rxns are EQUAL
solubility product constant
Ksp
values are always SMALL
Le Chatelier's Principle
if stress to a system at equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift to reduce of alleviate the stress
Stressors of system @ equilibrium
- concentration
- temperature
- pressure (only gases)
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products are on the right:
add reactant
right
the other reactants DECREASE as products INCREASE
trying to balance the products by making more so shifts right
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products are on the right:
add product
left
the other reactants INCREASE as products DECREASE
trying to balance the reactants side by making more so shifts left
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products are on the right:
remove reactant
left
the product DECREASES as the reactants INCREASE
trying to balance the reactants side since there isnt enough reactant to make the product
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products are on the right:
remove product
right
the product INCREASES as the reactants DECREASE
trying to balance products side to make more products