agec5001 intro & economic thinking about the environment
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
positive externality
a benefit received by a third party as an indirect effect of the actions of an involved party (ex: getting your flu shot to benefit the public’s health)
negative externality
a cost imposed on a third party as an indirect effect of the actions of an involved party (ex: pollution from a factory affecting local residents’ health)
negative externalities lead to…
overproduction
public goods
goods that are non-excludable & non-rivalrous in consumption (ex: public parks, clean air)
private goods
goods that are excludable & rivalrous in consumption (ex: cars, houses)
common pool resource
a resource that non-excludable but rivalrous (ex: fisheries, forests)
tragedy of the commons
MC > MB = over consumption & resource depletion
solutions to the tragedy of commons
gov regulation, private property rights, community management
weak sustainability
natural capital is substitutable for man-made capital
strong sustainability
natural capital is not substitutable, critical natural capital must be preserved
sustainable development
development that meets the needs of the present w/out compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) theory
environmental quality first deteriorates, then improves with economic development
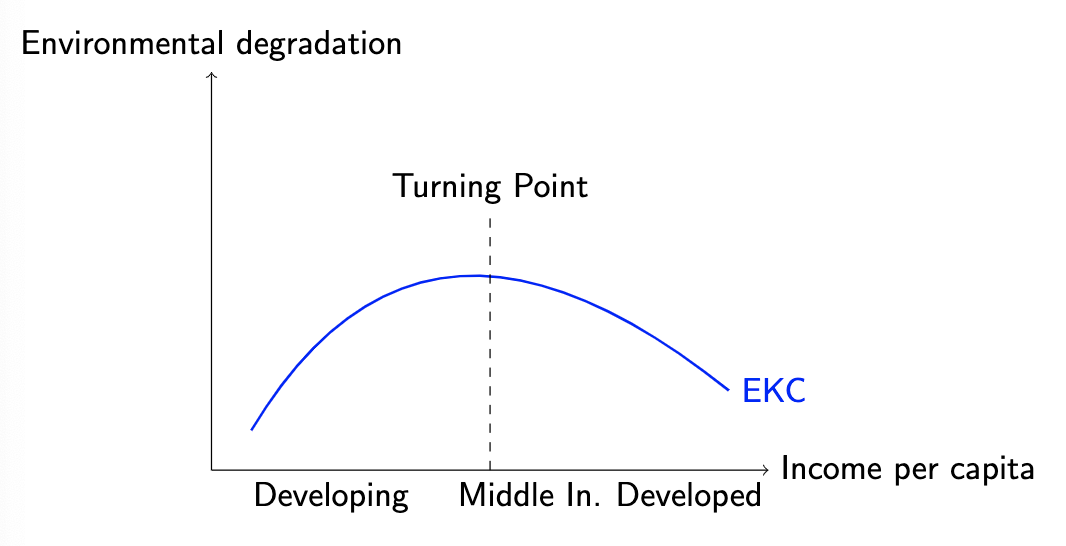
cost-benefit analysis
compares C&Bs of policies
market-based instruments
taxes, subsidies, cap & trade; harnessing market forces for environmental goals
regulatory approaches
standards, bans, mandates; common & control policies
valuation methods
revealed vs. stated preferences; puts prices on environmental goods
why is environmental valuation difficult?
many environmental goods don’t have market prices