AP MACRO 1.2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What does the circular flow model represent?
The flow of money, goods, services, and resources between households, firms, government, banks, and the foreign sector
Who are the five key participants in the circular flow?
Households, firms, government, foreign sector, banking sector
How do households participate in the economy?
Demand goods/services, supply capital, pay taxes. and demand exports
How do firms participate in the economy?
Produce goods/services, demand resources from households, sell exports abroad
What are governments main roles in the circular flow?
Collects taxes, provides public goods, builds infrastructure
What happens when the government spends more than it collects in taxes?
Budget deficit
How does the foreign sector affect the circular flow?
imports= leakage, exports=injection
How does the banking sector affect the circular flow?
Savings = leakage (money not spent) , Loans= injection (fund investment & consumption)
What are injections?
Spending that adds to economic activity
What are leakages?
Money leaving the flow (taxes, savings, imports)
What is GDP
The total market value of all goods/services produced in a country in one year
Why are spending, income, and output equal in GDP?
Every dollar spent is a dollar earned, and every good bought was produced.
What is the expenditure approach equation for GDP
GDP= C+I+G+Xn
What are the three approaches to measuring GDP?
Expenditure, income, output
What does I (investment) include
Firm spending on capital equipment + household spending on new homes
What does "G" (Government Spending) include and exclude?
Includes government purchases of goods/services; excludes transfer payments
What does Xn (Net Exports) equal
Exports-Imports
What is called when imports > exports
Trade deficit (negative Xn)
What is it called when exports > imports?
Trade surplus (positive Xn)
Which statement is true about the circular flow diagram of an economy?
The market for factors of production connects spending by firms to household income.
A short-run increase in national income could be caused by a decrease in which of the following?
imports
What does Nominal GDP measure?
The value of a nations output in current prices for that year
Why can nominal GDP be misleading?
inflation or deflation can make GDP appear to change even if its actual output doesnt
What is Real GDP?
GDP adjusted for changes in the price level, showing actual output
How does inflation affect nominal vs. real GDP?
Inflation exaggerates nominal GDP; real GDP corrects for this to reflect true output
What is the GDP Deflator?
A price index used to convert nominal GDP into real GDP by adjusting for changes in the price level.
The consumer price index (CPI) does not measure the true cost of inflation because
improvements in the quality of goods or services are not fully reflected
In what way is the GDP deflator similar to the consumer price index?
Both can be used to adjust nominal values to real values.
Which of the following necessarily occurs during an economic recession?
Real gross domestic product decreases.
The CPI compares the cost of a basket of goods in the current year to the cost of the same basket in the ______ year.
Base
The correct CPI formula is
(Current ÷ Base) × 100
Which of the following formulas is used to find the inflation rate between two years?
(y2 –y1) ÷ (y1 × 100
If nominal GDP increases but real GDP stays the same, what does that?
Prices increased (inflation)
The GDP Deflator measures
The ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP
The formula for the GDP Deflator is
Nominal GDP ÷ Real GDP × 100
“Nominal” GDP means GDP measured in _____
Current-year prices
Which statement is true about the circular flow diagram of an economy?Which statement is true about the circular flow diagram of an economy?
The market for factors of production connects spending by firms to household income.
Which statement best describes the law of demand?
a decrease in the price of a product will increase the quantity demanded of that product,
What causes movement along the demand/supply curve?
A change in the price of the good itself
What causes shifts to the demand/supply curve?
changes in consumer income, tastes, population, the prices of related goods, and expectations
During which phase of the business cycle is unemployment typically at its lowest?
During the expansionary phase
Labor Force equation
Employed + Unemployed
Labor Force Participation Rate Formula
(Labor Force/ Civilian non-instiutionalized population)x100
Unemployment Rate Formula
(Unemployed/Labor Force) x 100
Which of the following will happen when the actual inflation rate exceeds the expected inflation rate?
This will harm lenders with fixed-interest rate loans.
Real GDP equation
real gdp = (nominal GDP/ GDP deflator ) x 100
The output gap is measured by which of the following?
The difference between actual and potential
Which of the following will occur in a competitive market when the price of a good is less than the equilibrium price?
Price will increase to eliminate the shortage and restore equilibrium.
If the wage rate of workers producing a good decreases, then which of the following will most likely occur?
The supply of the good will increase.
Which of the following describes the relationship between price and quantity demanded according to the law of demand?
Negative relationship, illustrated by a downward-sloping demand curve

Based on the graph provided, which segment represents only the expansionary phase of the business cycle?
TV
Real Wage formula is
( Nominal Wage ) / (Price Level)
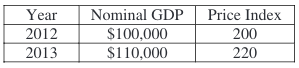
The table above shows the nominal gross domestic product (GDP) and the price index for an economy during the period 2012 and 2013. Which of the following would have occurred from 2012 to 2013?
Real GDP did not change.
Which of the following would be true if the actual rate of inflation were less than the expected rate of inflation?
People who borrowed funds at the nominal interest rate during this time period would lose.
If prices (inflation) increase at a faster rate than output
nominal GDP will rise
When nominal GDP decreases while real GDP rises
the price level must have decreased.
Which of the following changes in the supply of and the demand for a good will definitely result in a decrease in both the equilibrium price and quantity of the good?
No change, Decrease
The term “value added” for a firm is best defined as which of the following?
The firm’s sales minus the cost of inputs purchased from other firms
GDP is an imperfect measure of a nation’s economic performance because it does not account for which of the following?
Goods produced at home for personal consumption
The cyclical unemployment rate is
the difference between the actual unemployment rate and the natural rate of unemployment.