Physiology Lecture #6- Cardiovascular response to exercise
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What are the major functions of the cardiovascular system?
delivery of O2
removal of CO2
transport of hormones
thermoregulation
maintenance of acid-base balance
immune function
What are the 2 divisions of the CV system?
Pulmonary circuit and Systemic circuit
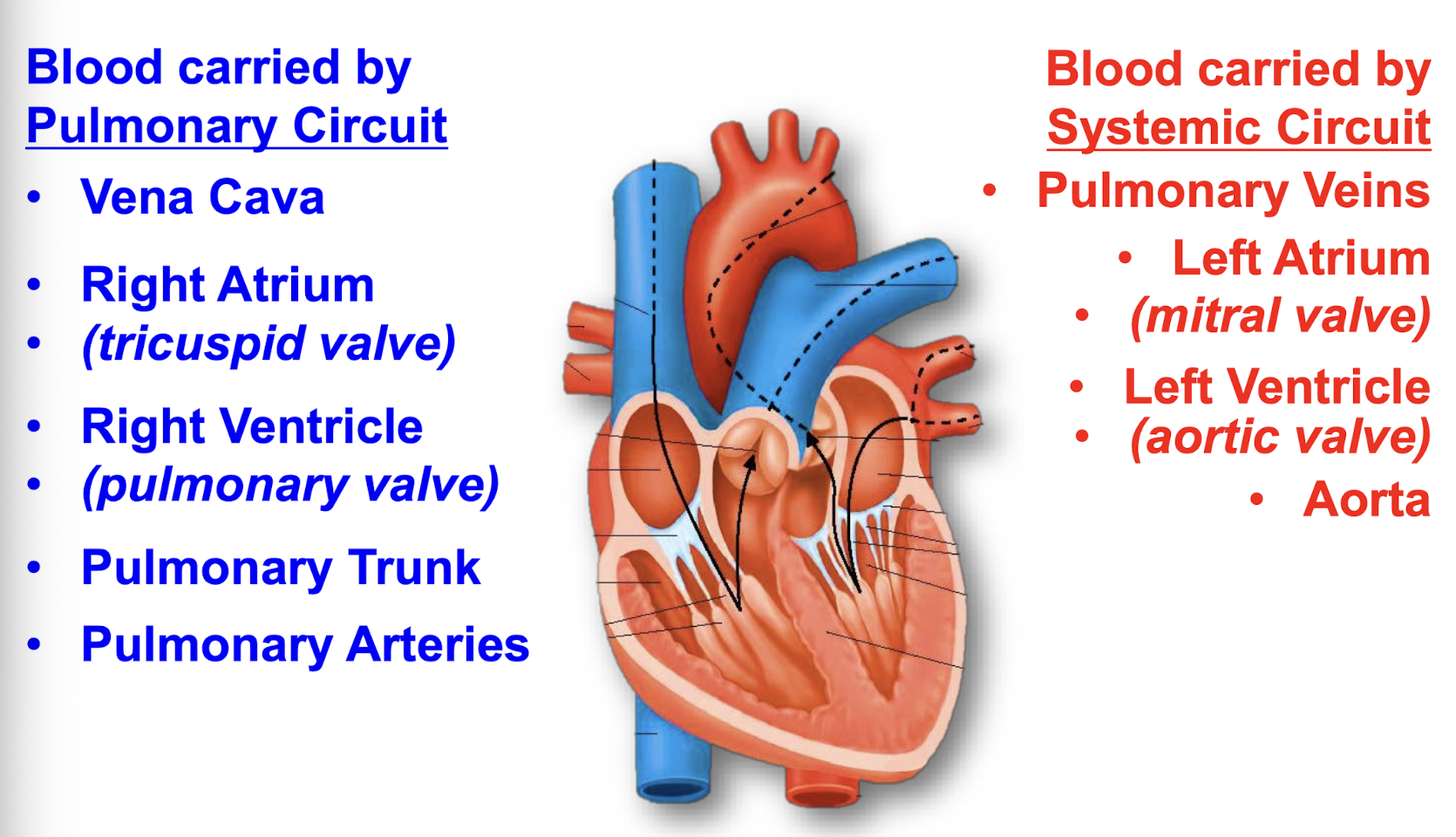
Pulmonary circuit
right side of heart
pulmonary arteries, veins, & capillary beds
Systemic circuit
left side of the heart
arteries, veins, & capillary beds
O2 to the rest of the body
What are the 4 chambers of the heart?
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Right atrium
Receives blood from superior and inferior vena cava
Right ventricle
receives blood from right atrium
Left atrium
receives blood from pulmonary veins (from the lungs)
Left ventricle
receives blood from left atrium, delivers blood to the systemic circuit via the aorta
more force
What are the 4 valves of the heart and what is their purpose?
Tricuspid valve
Pulmonary valve
Mitral valve
Aortic valve
Stop back flow of blood
Tricuspid valve (right A-V valve)
Between right atrium and right ventricle
Pulmonary valve (semilunar valve)
Between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
Bicuspid/mitral valve (left A-V valve)
Between left atrium and left ventricle
Aortic Valve (semilunar valve)
Between left ventricle and aorta
What are the 3 layers of the heart wall?
endocardium
myocardium
epicardium
Characteristics of skeletal muscle
Appearance: long, unbranched, multinucleated
Type of activity: contracts as needed to produce precise movement
Fiber type: Type I, IIa, IIx
Contraction Type: voluntary
Activation Type: Motor units control group of fibers
Characteristics of Cardiac Muscle
Appearance: shorter, branches connected by intercalated discs, single nucleus
Type of Activity: Continuous rhythmic contractions
Fiber type: striated with one fiber type, similar to type I fibers with multiple mitochondria & large capillary density
Contraction type: involuntary
Activation type: No motor units, contracts as one unit with gap junctions
Why doesn’t the heart get sore?
more you fill it, more forceful contraction
but you can’t eccentrically train it muscles which causes soreness
increased volume of movement doesn’t put that much increased demand on the heart to make it get sore
Coronary circulation
The system of blood vessels that supplies oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle itself
Includes:
Left and Right coronary arteries
marginal artery
circumflex artery
left anterior descending/interventricular artery
Posterior interventricular artery
path of blood through the heart
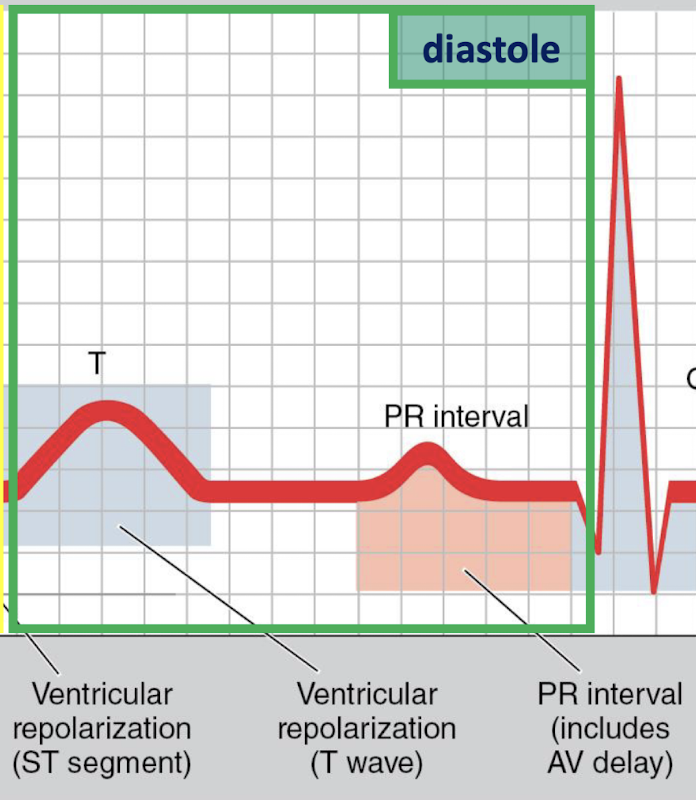
When is systole on an ECG?
QRS complex and ST segment

When is diastole on an ECG?
T Wave and PR interval
What happens in diastole?
pressure in ventricles is low
filling with blood from atria
A-V valves open
What happens in systole?
pressure in ventricles rise
blood ejected into pulmonary and systemic circulation
semilunar valves open
What makes the Lub and Dub heart sounds?
First: closing of A-V valves
Second: closing of aortic and pulmonary valves
What makes up the intrinsic conduction system of the heart?
Sinoatrial Node
Atrioventricular node
AV bundle (bundle of his)
R/L bundle branches
Purkinje fibers

Extrinsic control of heart activity: parasympathetic nervous system
reaches heart via vagus nerve
carries impulses to SA, AV nodes
releases Ach, hyperpolarizes cells
decreases HR & force of contraction
Decrease HR below intrinsic HR
intrinsic HR = 100 beats/min
normal resting HR = 60-100 beats/min
elite endurance athlete have 35 beats/min
Extrinsic control of heart activity: Sympathetic nervous system
opposite effect of parasympathetic
carries impulses to SA, AV nodes
releases norepinephrine, facilitates depolarization
increase HR, force of contraction
endocrine system can exert similar effect
Increases HR above intrinsic HR
determines HR during physical, emotional stress
sympathetic stimulation can increase HR to max of 250 bpm
What are the 3 basic phases of an ECG?
P wave: atrial depolarization
QRS complex: ventricular depolarization
T-Wave: ventricular repolarization
Systole
Contraction phase, chambers expel blood (QRS to T-wave)
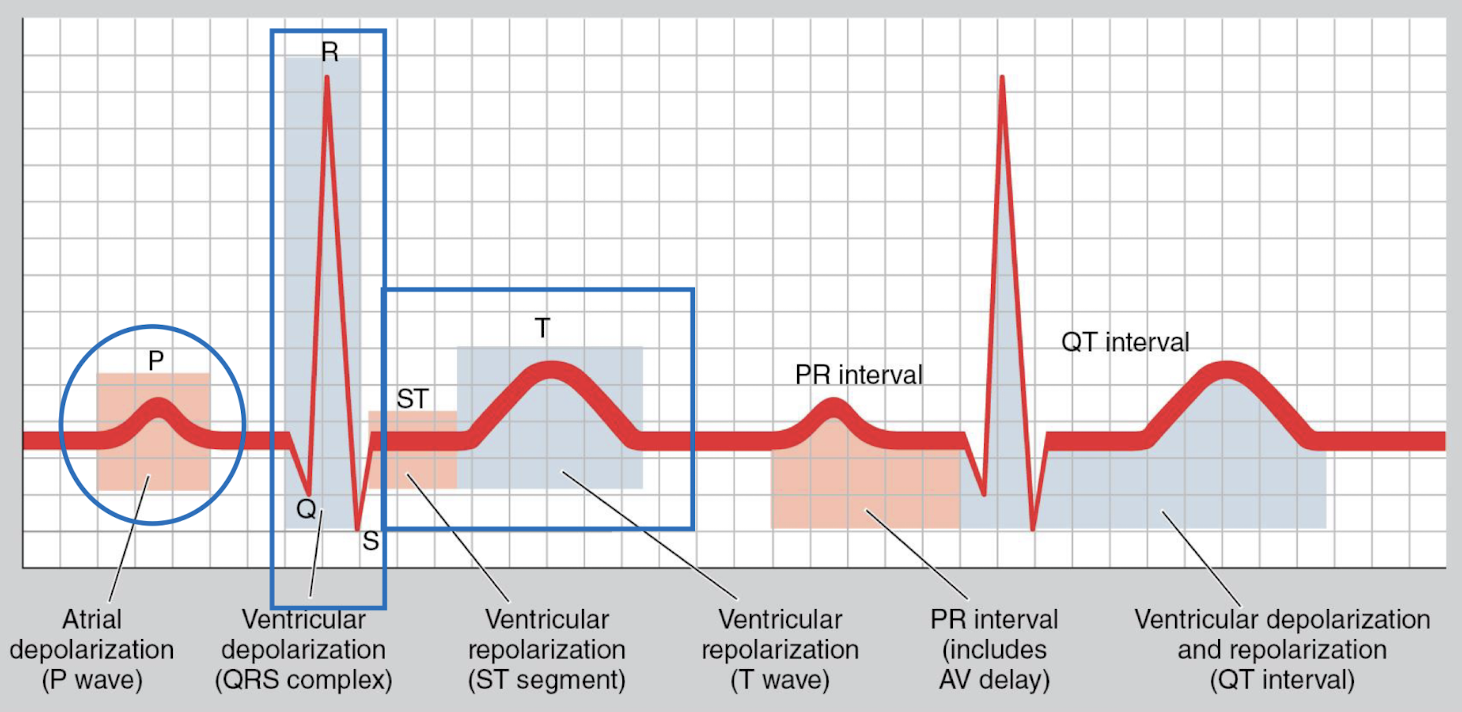
Diastole
Relaxation phase, chambers fill with blood (T-wave to QRS
How much blood is ejected from ventricles/beat?
~2/3 of blood is ejected from ventricle/beat
Heart rate
beats per minute
stroke volume
volume of blood pumped per contraction
SV= EDV-ESV
cardiac output
total volume of blood pumped by the ventricle per minute
Q=HRxSV
End-diastolic volume
volume of blood in ventricle just before contraction
End-systolic volume
volume of blood in ventricle just after contraction (what’s left over)
Cardiac output (CO)
Blood pumped by the heart per minute (L/min)
CO= HRxSV
Male= 5.0 L/min
Female= 4.0 L/min
what are the 4 factors to determine SV?
volume of venous blood returned to the heart (EDV, preload)
ventricular distensibility
ventricular contractility
aortic pressure (afterload)
Male and female stroke volume
Male= 70mL
Female= 50mL
Regulation of stroke volume
volume returned to the heart
end diastolic volume ‘preload’
volume of blood in ventricles at the end of diastole
primarily influenced by venous return
ventricular distensibility
frank-starling mechanism
Strength of ventricular contraction
Aortic Pressure
pressure the heart must pump against to eject blood
impedes ejection of blood from the left ventricle
Frank-Starling Mechanism
the force of contraction of cardiac muscle is proportional to its initial resting length
SV= EDV-ESV
Ejection Fraction
proportion of blood pumped out of the left ventricle with each beat
averages 60% at rest
clinical relevance- systolic heart failure
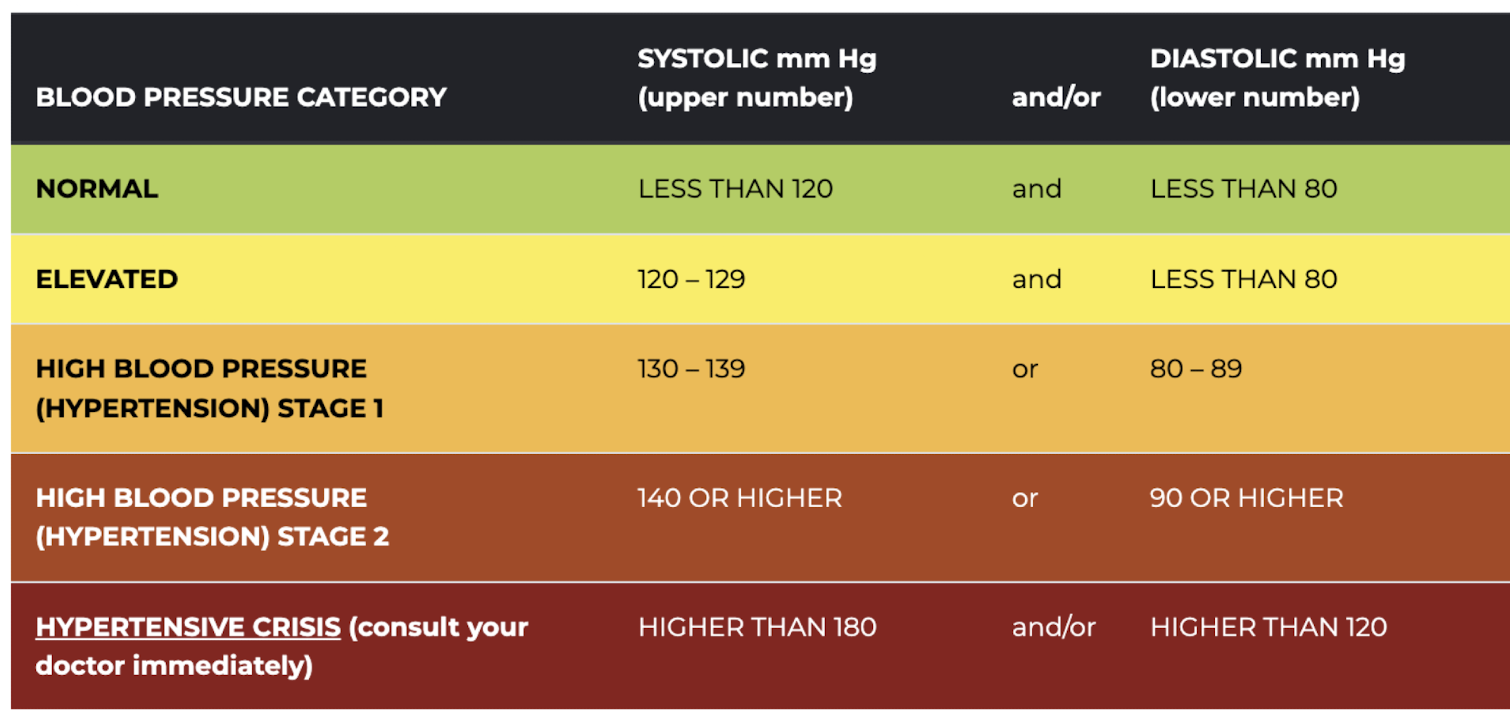
Systolic blood pressure
highest pressure within the vascular system
generated during cardiac contraction
Diastolic blood pressure
lowest pressure within the vascular system
when the heart is relaxed
indication of peripheral resistance
Blood pressure measurement
locate brachial artery
place cuff on upper arm
place stethoscope over brachial a. just below antecubital space
inflate cuff to between 180-200mg
gradually release pressure
note pressure when you hear first beat
note pressure when you hear the sound disappear
Blood pressure chart
Venous return
deoxygenated blood returned to the heart via the superior and inferior vena cava
valves prevent backflow of blood
low pressure system
venous pooling- clinical implications
Factors influencing venous return
valves in the veins
vasocontriction
muscle pump action

Artery characteristics
thick strong wall
high pressure
endothelial lining
smooth muscle
outer layer of connective tissue
Vein characteristics
thinner wall than artery
low pressure
endothelial lining
smooth muscle
large lumen
also have valves
Pressure gradient
Blood flow: high pressure → low pressure
100 mmHg
Resistance to blood flow equation

What can effect blood flow?
blood viscosity
vessel length
vessel radius
Blood flow equation
Blood flow= change in pressure/ resistance
Vasoconstriction
radius of the vessel decreases, decreasing blood flow
Vasodilation
radius of the vessel increases, increasing blood flow
Estimated HRmax
HRmax= 220-age in years
HRmax= 208-(0.7x age in years)
HR and Exercise
HR increases in direct proportion to increase in exercise intensity
Steady-State Heart Rate
Constant workload: HR increases rapidly until it reaches a plateau (steady state)
Increase in workload: HR increases to new steady-state value in 2-3 minutes
With exercise training: decreased steady-state heart rate for given submaximal workload
Stroke volume and acute exercise
SV increases directly with increasing work rate
untrained: SV plateaus at ~40-60% of VO2 max
trained individuals: can increase max SV at higher intensity levels
Increased preload, decreased afterload, increased contractility
Increased preload leads to…
Increased…
plasma volume
venous return
ventricular volume
Decreased afterload leads to…
decreased arterial constriction
increased max muscle blood flow
Increased stroke volume during exercise
Frank-starling mechanism: enhanced cardiac filling during diastole (preload)
Decreased total peripheral resistance: (afterload) due to increased vasodilation
Neurohormonal Influence: increased ventricular contractility due to increased sympathetic stimulation
Stroke volume with endurance training
Increases…
SV at rest
SV at a given submax work level
SV at max exercise intensity
trained individual: If heart rate decreases and stroke volume increases, what is the net effect of CO? (CO=HRxSV)
stays the same
During max exercise…
significant increase in CO secondary to increased max SV
Response to acute exercise
Increased HR, SV, CO
Response to endurance training
decreased HR at rest
decreased HR w/ given submax work rate
faster recovery HR
increased SV at rest
increased SV with given submax work rate
CO at rest and w/ given submax exercise work rate → little change
Heart size and endurance training
increases size of left ventricle as a result of ventricular filling
increases thickness of left ventricle wall
more forceful contraction
Blood pressure and acute exercise
increases systolic BP in proportion to exercise intensity
no significant change to diastolic BP during acute dynamic exercise; may decrease
BP response and endurance training
decreased systolic BP at rest & for a given submax exercise work rate
decreased diastolic BP at rest & for a given submax exercise work rate
Blood flow and acute exercise
Increased:
muscle blood flow
skin blood flow
Decreased:
kidney blood flow
splanchnic blood flow (liver, stomach, intestines)
What is the major contributor to redistribution of blood flow?
sympathetic nervous system