1.1 Data Structures
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Data Structure
A group/collection of related data items/elements
Benefits of data structure
i. It is a convenient or best way of organising data relating to a
real problem.
ii. It may be efficient to deal with various elements as one item.
Types of data structures
i. Array.
ii. Record.
iii. Stack
iv. Queue
v. Linked List
vi. Binary Tree
vii. Hash Table
Array
A data structure that stores elements of the same type
How is an array element accessed?
Array element are accessed via indexes or subscripts
Arrays have a fixed or predetermined number of elements. True/Flase
True
Record
A record is a data structure that consists of a fixed number of variables, called fields. Every field has an identifier (field name) and a data type. Each field in a record can have a different data type. Records are often used to represent complex data types by grouping related information together.
Stack
A stack is a container of objects that are inserted and removed according to the last-in, first-out (LIFO) or first-in, last-out (FILO) principle.
It is a limited-access data structure where elements can be
added and removed from the stack only at the top.
A stack can be used as recursive data structure
A stack is either empty or it consists of a top and the rest, which is a stack
What does push do in a stack?
Add an element to the top of a stack
What does pop do in a stack?
Removes an element from the top of the stack
When does an overflow occur in a stack?
When an attempt is made to add to a full stack
When does undeflow occur in a stack?
When an attempt is made to pop an empty stack.
What could stack be used for?
They can be used for:
i. store subprogram return addresses.
ii. store recursion values.
iii. Store short-term arithmetical results.
iv. Enable the undo function.
Pushing onto a stack algorithm
If stackPointer < stackMaixmum, then:
stackPointer = stackPointer + 1
stackArray(stackPointer) = dataItem
Else:
Output "Stack is full, your data has been saved."
Popping from a stack algorithm
If stackPointer > 0, then:
dataItem = stackArray (stackPointer)
stackPointer = stackPointer - 1
Else:
Output "Stack is empty, no data can be
retrieved"
Queue
A queue is a container of objects that are inserted and removed according to the first-in-first-out (FIFO) principle.
Data items are added at the end of queue and removed from the front
What could a queue be used for?
They could be used for:
i. A printer queue.
ii. A keyboard buffer.
iii. Task Scheduling
iv. Traffic Management
How to implement a queue?
The data for a queue would be stored in an array. Two pointers would keep track of the front and back of the queue as data is added and removed. (front pointer and Back pointer)
Adding to a queue algorithm
if backPointer < queueSize then
backPointer = backPointer + 1
queueArray[backPointer] = dataItem
else
output "Queue is full. Your data has not been saved."
end if
Removing from a queue algorithm
if frontPointer <> backPointer then
queueArray[frontPointer] = Null
frontPointer = frontPointer + 1
else
output "Queue is empty. No data can be retrieved."
end if
Linked List
A linked list is a set of data elements, where each element contains the data itself and a pointer to the memory address next element.
It's a dynamic data structure, as it can grow and shrink in size after declaration.
Each element in a linked list is known as a node; the first element is the head note, which is null in an empty list.
The last node in a linked list has a pointer to null.
A node cannot be directly accessed and each node needs to be traversed until the correct node is accessed (sequential access)
Benefits of linked lists
i. New items can be inserted into a linked list without rearranging all the other elements. By updating pointers
ii. If they are programmed dynamically, they use memory more efficiently
iii. Dynamic Size
Drawbacks of Linked List
i. A Linked list is more complex to program or manipulate
than an array
ii. Extra Programming is required to access the data in the
opposite direction.
iii. Can only be accessed in a linear manner. (sequential access)
iv. Use more data due to nodes
Binary Tree
Is a data structure made up of nodes and branches, with each node containing data and having one or two branches.
What is the node at the top called?
Root Node
How is a binary search tree created?
The data is added in the order it occurs. The first data item (no matter what it is) becomes the root node. Additional nodes are added on the left if they are less than (or equal to) the root and to the right if they are greater than the root.
Binary Tree Traversal
The process of visiting each node in a binary tree in a specific order
Preorder Traversal
Visiting the root node, then the left subtree, and finally the right subtree.
It can be used to copy files or create a copy of the tree as it starts with the root node and goes down.
Dot on left
Inorder Traversal
Visiting the left subtree, then the root node, and finally the right subtree.
It can be used to search.
Dot on bottom
Postorder Traversal
Visiting the left subtree, then the right subtree, and finally the root node
It can be used to delete a tree from branch to root.
Dot on right
When a binary tree is converted into an array what should empty nodes be set to?
Null or a rogue value (-1)
How do we convert a binary tree into an array
Using breadth first traversal to go line by line putting each item in the array and it works out so indexing of branches are 2n+1 or 2n+2 (starts at 0)
Hash Table
A hash table is a data structure that can map keys to values.
A hash table uses a hash function (key) to compute index to store and retrieve data in a table. With each key having a unique associated value
What is a hashing algorithm?
A process that includes mathematical hashing function. Data of any given length is converted into a compressed numerical has value of a fixed length. This then determines the index position the data is stored in.
Hash Function and the main goal of disribution
Takes a key as input and produces a hash code, which is an index in the table, the goal is to evenly distribute keys and minimise collsions.
Modulo (MOD)
A mathematical function that returns the remainder of a division operation
How is a MOD hash function generated?
Take the length of the value to be entered and divide by the size of the table, or use the MOD function to generate the index number. The index number is the reminder. (e.g. 1235 MOD 97 would give the index for the number in an array of 97 length)
What type of number is better for a MOD function
A prime number generally as there will be less collsions
What is a hash table?
The array where values are stored. Each element corresponds to a ‘bucket’ that can hold multiple key value pairs
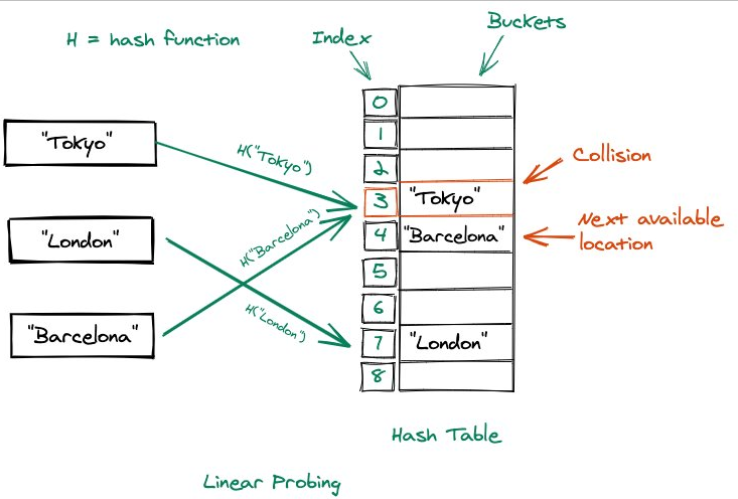
What is Collision Resolution
Collisions occur when two different keys hash to the same index, which creates a collision as it is not possible to store more than one set of data in an index
Methods for handling these include
Chaining (Using linked lists for each array index)
Open addressing (Finding the next available slot)
What is clustering?
When consecutive solts in an array become filled due to collisions which results in an overflow
How is clustering Resolved (What are the collision resoultions)?
Open addressing - When a collision occurs you try to fin dht enext available slot in the array
Linear probing (Checking the next slot)
Quadratic intervals (Checking in quadratic intervals 1,4,9 etc)
Double Hashing (using a second function to determine the next slot
Chaining - using linked lists at each index to store collided elements, reducing the chances of clustering.
What is primary and secondary clustering?
Primary - Occurs as a result of oppen adressing which can lead to longer probing sequences
Secondary Clustering - Occurs in chaining when multiple keys hash to the same index, leading to longer chains that can impact performance
What needs to be considered when implementing and hash table?
The size of the array to store all data but not waste space
This is determined by the load factor which is the number of spaces occupied divided by the number of buckets
The optimal load factor is about 0.75
What is vital for a suitable hash function?
The same hash value for the same key
Uniform distribution of hash values
Minimised collisions and clustering
Fast to compute
How can we predict collisions?
Hash function quality - a good function minimises clustering and ensures even distribution so less collisions
Load factor - a higher load factor will lead to more collisions
Collision resolution strategy - Chaining is generally better
Number of buckets - largers arrays reduce the collisions but increase memory
Pros and cons of chaining?
+dynamic
+simple
+never fills up
+less sensitive to load factor
-can affect search times
-more memory
-takes additional time (can degrade performance with secondary clustering)
Pro and con of quadratic over linear probing?
+Less primary clustering
-Need a lower load factor (May not work above 50%)
Explain double hashing
A second hashing function is used to find the step size for the data to move. For example
1st hash (h1): 35 MOD 10 = 5 (A collision occurs) 2nd hash (h2): 7 - ((35) MOD 7) = 7 - 0 = 7 New index (i = 1)= (h1(35) + i) x h2(35) MOD 10 = 2
If another collision occurs for the new index you would increment i until a space is found
What is rehashing?
Dynamically resizing the array to accomodate more elements. It requires creating a new array, recalculating hash values, and redistributing keys.
Why may rehashing become necessary?
When the load factor exceeds a certain threshold rehashing to help maintain a low and manageable load factor
To avoid clustering - it may occur over time due to insertions and deletions that cause more collisions and chains. Rehashing will more evenly distribute keys
Adapting to a change in data size - ensure the table is efficient will the change in data size
Time complexity control - Insterting or deleting elements involves recalculating hash values and resolving collisions and as load factor increases the operations become more time consuming
What are key hash table operations?
Insertion - insert a key-value pair using a hash function to generate an index
Search - search fora value based on a key with the hash function generating the index and recieving the value
Deletion - deleting a value using the hash function for the index and using a collision resolution strategy isf needed
What are the benefits of hash tables?
Fast retrieval - Fast retrival based on keys and hash functions
Adaptability - dynamic resizing allowing for efficient memory use.
What are considerations that are needed for hash tables?
Collision handling - effective collision resolution is vital for maintaining performance
Hash function quality - A good hash function will evenly distribute keys
What are some uses for hash functions?
Database indexing - fast retrival of data
Caching - keys represent instructions
Symbol tables in compliers
Distributed systems
Cyrptography - quick verification of user credentials without exposing passwords
Network routing
Caching in web servers
Pros and Cons of Arrays?
+Can store many elements
+Allows Random access and indexing means no traversal so can use an index to directly access an element
+Efficient searching and sorting
- Chance of memory wastage
-Deleting an element require traversal
-Fixed Length so once it is full you cannot add more
How to do 2D and 3D arrays?
new[,] array = new int[10][10]
What are array operations
Searching - Find a particular element
Sorting - Arrange elements in and order
Traversing - Processing every element sequentially
Characteristics of an array?
Elements are same data type and memory size
Each element has a unique index
Stores large data under a single variable name
Stored in contiguous (Consecutive) memory and each element has its own memory location
Binary tree operations
Inserting, Removing, and Deleting Elements.
Traversing (Search)
Types of binary tree traversal
Depth-First Search (DFS) Algorithm (Pre- In- Post- Order)
Breadth-First Search (BFS) Algorithm (Level Order)
What is Level order Traversal
Visit nodes level by level, left to right, until you finish
Benefits of Binary Trees
Memory Efficient - Contiguous memory allows for efficient use of space when full
Sequential access - Easy to iterate, which improves performance
Simplified Indexing - Index(i), Left node is 2i+1, Right node is 2i+2 (Allows for them to be used in an array)
Limitations of binary Trees?
Fixed size - difficult to make bigger and memory inefficient
Inefficient for dynamic operations - frequent insertions and deletions can make maintaining contiguous structure computationally expensive
Wasted space if the tree is sparsely populated
What is contiguous memory
A method of allocating memory where data elements are stored in consecutive memory locations, improving access speeds and efficiency.
Linked List Operations
Insertion (Append (Add End), Prepend (Add Start), Insert (Add at a position))
Deletion (On any position with updating memory locations)
Traversal (Searching through nodes)
Linked list uses?
Implementation of Data Structures: Hash tables, stacks in data structures, and queues are just a few of the significant data structures that may be implemented using the linked list data structures.
Memory Management: To efficiently allocate and reallocate memory, Linked Lists data structures can be utilised in memory management systems.
File Systems: File systems can be represented using linked lists data structures. A node represents each file or directory; the links signify the parent-child relationships between the files and directories.
Graphs and Charts: Graphs can be represented by Linked Lists data structure, where each node is a vertex, and the links are the edges that connect them.
Making music playlists: Linked List data structures are frequently used to build music playlists. A node represents each song, and the connections between the nodes indicate the order in which the songs are played.
Picture Processing Method: Picture processing methods can be implemented using linked lists, where a node represents each pixel.