2C- Cells and the immune system
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
describe how a phagocyte destroys a pathogen present in the blood and how this leads to the formation of an APC
phagocyte recognises antigen on a pathogen
phagocyte engulfs the pathogen in its cytoplasm forming a phagosome
lysosomes containing hydrolytic enzymes (lysozymes) fuse with the phagosome and hydrolyse the pathogen
the phagocyte presents the pathogens antigen on its cell surface to activate other immune cells
give 3 types of cells that can stimulate an immune response
cells from other organisms/ transplants
abnormal/ cancerous body cells
cells infected by a virus
describe the structure of an antibody
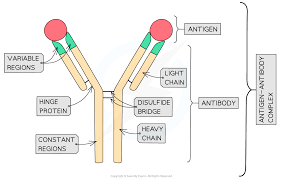
what is the role of a disulphide bridge in forming a proteins quaternary structure
joins two different polypeptides together
describe the structure of HIV
lipid envelope
don’t need to know about integrase

describe how HIV is replicated
attachment proteins attach to receptors on helper T cells/ lymphocyte
nucleic acid/ RNA enters the cell
reverse transcriptase converts RNA to DNA
viral proteins, enzymes and capsid are produced
viral particles are assembled and released from the host cell
define an antigen
a foreign protein
that stimulated an immune response
define an antibody
a protein specific to an antigen
produced by B cells
describe how to presentation of a viral antigen leads to the secretion of an antibody against the virus
helper T cells will bind to the antigen on the APC
Th cells stimulate a specific B cell to undergo clonal selection and divides by mitosis
this forms many plasma cells that are exact copy’s of the B cell and rapidly produce monoclonal antibody’s
define passive immunity, and what are the two methods to this type of immunity
a type of immunity provided by being given antibody’s made by a different organism
natural- a baby getting antibody’s from its parent through placenta and breast milk
artificial- becoming immune from being injected with antibody’s from another organism e.g. antivenom
define active immunity, and what are the two methods to this type of immunity
immunity that is created by your own immune system after being exposed to an antigen and creating its own antibody’s
natural- immunity after catching a disease
artificial- through vaccination, being injected with an attenuated form of the virus
contrast active and passive immunity
Active immunity-
requires exposure to an antigen
takes a while for protection to develop
memory cells are produced
protection is long term
Passive immunity-
doesn’t require exposure to antigen
protection is immediate
memory cells aren’t produced
protection is short term as antibody’s are broken down
define a cellular immune response
the T-cells and other immune system cells that interact with e.g. phagocytes
define a humoral immune response
B-cells, clonal selection and the production of monoclonal antibody’s
when a person is bitten by a venomous snake they are injected with a toxin. antivenom is used as a treatment. Antivenom contains antibody’s against the snake toxin. this is an example of passive immunity.
explain how the treatment with antivenom works and why it is essential o use passive immunity rather than active
in passive immunity/ the antivenom, antibody’s bind to the toxins antigen causing it to be destroyed
active immunity would be too slow as there aren’t many B-cells