Oral Pathology All Exams
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
Which of the following tissues listed will develop from the ectoderm layer of the embryo?
A. epidermis
B. muscle
C. liver
D.dermis
A. epidermis
Environmental agents and factors that include infections, drugs, and radiation are considered:
A. primordium
B. somites
C. ectopic
D. teratogens
D. teratogens
The process of _______ is the development of the differing structure or shape for each organ or system.
A. morphodifferentiation
B. cytodifferentiation
C. histodifferentiation
D. proliferation
A. morphodifferentiation
The primitive streak forms in the embryonic disc, causing:
A. initiation of palatal development
B. bilateral symmetry
C. fusion of the mandibular processes
D. disintegration of the oropharyngeal membrane
E. creation of a second embryonic layer
B. bilateral symmetry
Differentiated mesoderm gives rise to the ______ that are located on both sides of the developing nervous system.
A. neural folds
B. Somites
C. pharyngeal pouches
D. neural crest cells
B. Somites
How many X-type of chromosomes enables the embryo to become a female when present?
A. one
B. two
C. three
D. four
B. two
By the end of the first week of prenatal development, the blastula stops traveling and undergoes:
A. implantation
B. disintegration
C. migration
D. amniocentesis
A. implantation
The fertilized egg is called a:
A. blastocyst
B. morula
C. zygote
D. embryo
C. zygote
During which week of prenatal development does the neural plate differentiate?
A. second week
B. third week
C. fourth week
D. fifth week
E. seventh week
B. third week
Which of the following structures initially forms during the third week of prenatal development?
A. Primitive streak
B. bilaminar embryonic disc
C. embryo blast layer
D. trophoblast layer
A. Primitive streak
Which developmental period is considered the most critical period of prenatal development?
A. preimplantation
B. fetal
C. embryonic
D. fertilization
C. embryonic
The neural tube from early prenatal development will form which of the following structures?
A. heart
B. spinal cord
C. face
D. digestive tract
E. vertebral column
B. spinal cord
This is the first physiologic process involved in prenatal development. During this process the action of one group of cells on another leads to the establishment of the developmental pathway in the responding tissue.
A. proliferation
B. induction
C. differentiation
D. morphogenesis
E. maturation
B. induction
Neural crest cells migrate from which embryonic structures?
A. stomodeum
B. first brachial arch
C. neural folds
D. frontonasal process
E. hypoblast layer
C. neural folds
Which period of prenatal development is characterized by increased cellular differentiation?
A. unattached conceptus
B. preimplantation period
C. embryonic period
D. fetal period
C. embryonic period
T/F Oral epithelium is derived from ectoderm as a result of embryonic folding?
true
which of the following facial structures is formed from the mandibular arch?
A. forehead
B. lower face
C. philtrum
D. nose
E. second brachial arch
B. lower face
The frontonasal process is a swelling that appears over the developing brain in the embryo and forms the:
A. forehead
B. otic placodes
C. mandibular arch
D. neck area
E. brachial arches
A. forehead
T/F Facial development is completed during the twelfth week of prenatal development.
true
T/F The stacked bilateral swellings of tissue that appear inferior to the stomodeum and include the mandibular arch are the brachial pouches.
false
Which of the following phrases concerning the second brachial arch is CORRECT?
A. it is called the mandibular arch
B. it contains Reicherts cartilage
C. it forms into the muscles of mastication
D. it is associated with the trigeminal nerve
B. it contains Reicherts cartilage
A type of cleft lip can result from the lack of fusion between:
A. mandibular and maxillary processes
B. medial nasal and maxillary processes
C. lateral nasal and medial nasal processes
D. two lateral nasal processes
E. lateral nasal and maxillary processes
B. medial nasal and maxillary processes
The philtrum of the upper lip forms from the:
A.mandibular processes
B. medial nasal processes
C. lateral nasal processes
D. nasal placodes
E. maxillary processes
B. medial nasal processes
From which structure is the palatine tonsillar tissue derived?
A. first brachial arch
B. second brachial arches
C. first pharyngeal pouches
D. second pharyngeal pouches
D. second pharyngeal pouches
The disintegration of the oropharyngeal membrane enlarges the:
A. nasal pits
B. stomodeum
C. anus
D. pharyngeal pouches
B. stomodeum
T/F The placodes are rounded areas of specialized, thickened ectoderm found at the location of developing special sense organs.
true
T/F The stomodeum initially appears as a shallow depression in the embryonic surface ectoderm at the cephalic end.
true
T/ F The overall growth of the face is in a superior and posterior direction in relationship to the cranial base.
false
In which week of prenatal development does facial development begin in the embryo?
A. second
B. fourth
C. fifth
D. eighth
B. fourth
The mandibular arch during the embryonic period is the:
A. fusion of the two mandibular processes
B. swelling found superior to the stomodeum
C. structure that gives rise to the lateral nasal process
D. posterior portion of the hard palate
A. fusion of the two mandibular processes
T/F The secondary palate will give rise to the anterior third of the hard palate.
false
The tongue develops from multiple swellings derived from:
A. the outer portions of the maxillary process
B. the inferior growth of the inter maxillary segment
C. palatal shelves of the maxillary process
D. first and second pharyngeal pouches
E. the first four brachial arches
E. the first four brachial arches
Which of the following structures is initially formed during the fifth week of prenatal development?
A. neural tube
B. mandibular arch
C. palatal processes
D. inter maxillary segment
D. inter maxillary segment
T/F The intermaxillary segment gives rise to the secondary palate.
false
T/F Tongue development begins as a triangular median swelling, the tubercular impair
true
This is a V-shaped groove on the tongue that marks the border of the base and body of the tongue.
A. median lingual sulcus
B. lingual frenum
C. median palatine suture
D. sulcus terminalis
D. sulcus terminalis
T/F The foramen cecum is the beginning of the thymus
false
If the palatal shelves are unable to fuse properly during prenatal development, there may be formation of a:
A. cleft lip
B. ankyloglossia
C. cleft palate
D. spina bifida
C. cleft palate
The fusion of the two palatal shelves with the primary palate is dependent on the:
A. ingrowth from the maxillary arch
B. change in position of the paranasal sinuses
C. continued vertical growth of all the processes
D. Change in the position of the tongue
D. Change in the position of the tongue
T/F The tongue develops during the fourth to eight weeks of prenatal development.
true
T/F The copula is formed from the fusion of mesenchyme of mainly the third and parts of the fourth brachial arches.
true
T/F The nasal cavity forms at the same time as the palate.
true
During which week of prenatal development is the palate completed?
A. fifth
B. eighth
C. tenth
D. twelfth
D. twelfth
What portion of the final palate does the secondary palate give rise to?
A. 1/3rd of the hard palate
B. entire hard palate
C. only the soft palate region
D. posterior 2/3rds of hard and soft palate
D. posterior 2/3rds of hard and soft palate
When is the palate formed?
A. during the fourth week of prenatal development
B. in the embryonic period
C. during one week of prenatal development
D. spanning both the embryonic and fetal periods
D. spanning both the embryonic and fetal periods
What is the angled portion of the ameloblast that secretes the enamel matrix?
A. inner enamel epithelium
B. depolarized reameloblasts
C. tomes process
D. disintegrating basement membrane
C. tomes process
Where does the dental lamina begin to form initially in the developing dental arches?
A. near the midline
B. adjacent to the mental foramen
C. over the region of the future molars
D. adjacent to the developing temporomandibular joint
A. near the midline
The dental lamina is an embryonic structure that develops from the:
A. oral epithelium
B. mesenchyme
C. neural crest cells
D. endodermal layer
A. oral epithelium
Which of the following embryonic structures becomes the dentinoenamel junction?
A. inner cells of the dental papilla
B. outer cells of the dental papilla
C. outer enamel epithelium of the enamel organ
D. inner enamel epithelium of the enamel organ
E. basement membrane between the enamel organ and the dental papilla
E. basement membrane between the enamel organ and the dental papilla
T/F Three embryological structures, the enamel organ, dental papilla, and dental sac, are now considered together to be the tooth germ.
true
Which portion of the tooth germ is the primary source of the periodontal ligament?
A. dental sac
B. Herwigs epithelial root sheath
C. stratum intermedium
D. central cells of dental papilla
E. outer cells of the dental papilla
A. dental sac
The initiation stage of odontogenesis MAINLY involves the process of:
A. differentiation
B. proliferation
C. induction
D. morphogenesis
C. induction
Which of the following permanent teeth can be considered nonsuccedaneous?
A. incisors
B. canines
C. premolars
D. molars
D. molars
Which embryonic structure is specifically responsible for the development of the root?
A. stellate reticulum
B. enamel organ
C. stratum intermedium
D. cervical loop
E. successional dental lamina
D. cervical loop
What is the term used for the movement of the nuclei within the inner enamel epithelium as the tissue forms preameloblasts?
A. dentinogenesis
B. repolarization
C. disintegration
D. maturation
B. repolarization
Hertwigs epithelial root sheath is entirely composed of:
A. all layers of the enamel organ
B. enamel organ and dental papilla
C. inner and outer cells of the dental papilla
D. inner and outer enamel epithelium
E. dental papilla and dental sac
D. inner and outer enamel epithelium
How many buds in the dental lamina appear along the maxillary arch during odontogenesis of the primary dentition?
A. 5
B. 10
C. 15.
D. 20
B. 10
The outer cells of the dental papilla are induced to differentiate into:
A. pulp tiissue
B. preameloblasts
C. odontoblasts
D. cementoblasts
E. ameloblasts
C. odontoblasts
Which stage of tooth formation occurs for the primary dentition during the eleventh and twelfth week of prenatal development?
A. bell stage
B. initiation stage
C. cap stage
D. bud stage
A. bell stage
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the enamel organ?
A. stellate reticulum
B. stratum intermedium
C. odontoblastic layer
D. outer epithelial cells
E. inner epithelial cells
C. odontoblastic layer
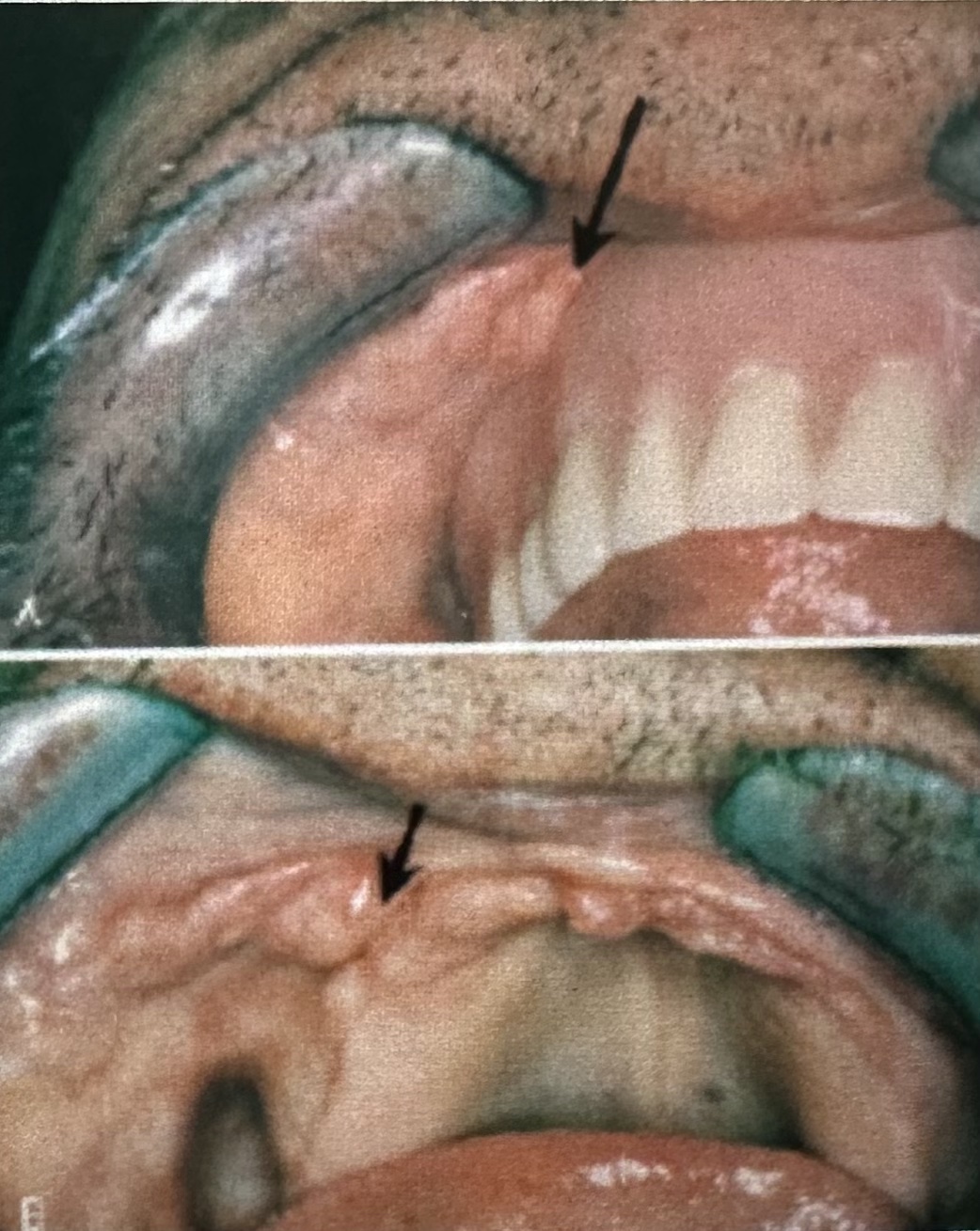
the accurate diagnosis for this lesion is:
a. palatal papillomatosis
b. gingival hyperplasia
c. chronic hyperplastic pulpitis
d. epulis fissuratum
d. epulis fissuratum
which type of inflammation occurs when the injury is minimal and brief and its source is removed from the tissue?
a. acute
b. chronic
c. local
d. systmeic
a. acute
which type of cell is the first to arrive at the site of injury and is the primary cell type involved in acute inflammation?
a. macrophage
b. neutrophil
c. plasma cell
d. mast cell
b. neutrophil
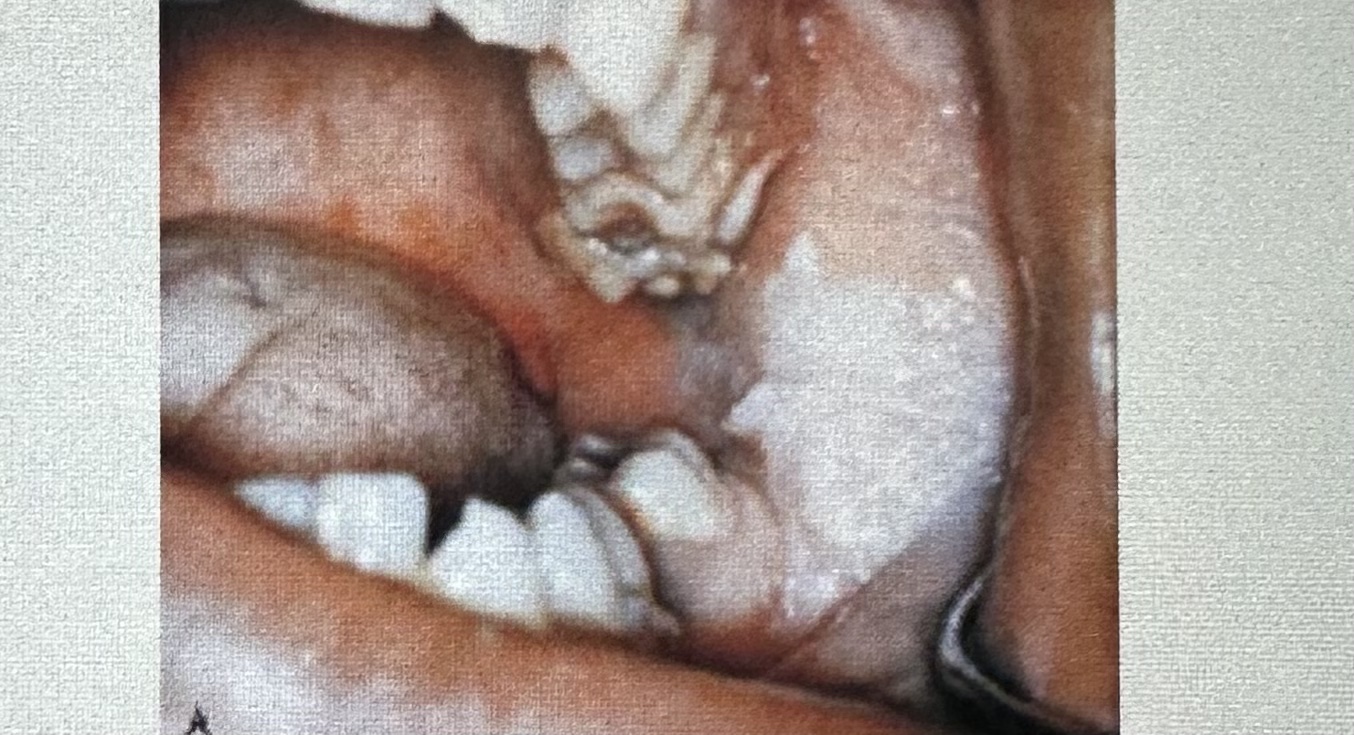
A patient comes to the office for an emergency visit. The patient complains of a toothache in the left mandibular posterior area. On clinical examination you notice a gray-to-white patch on the left posterior buccal mucosa. On questioning, the patient tells you that this area is also painful. After reviewing the patients medical history, you question the patient regarding his recent use of:
A. hydrogen peroxide
B. aspirin
C. antibiotics
D. mouthwash
B. aspirin
Serous exudate is composed of:
A. tissue debris and many white blood cells
B. suppuration
C. plasma fluids and proteins with a few white blood cells
D. plasma fluids and red blood cells
C. plasma fluids and proteins with a few white blood cells
The major cause of a mucocele is:
A. a sialolith
B. salivary duct obstruction
C. trauma to a minor duct
D. allergic reaction
C. trauma to a minor duct
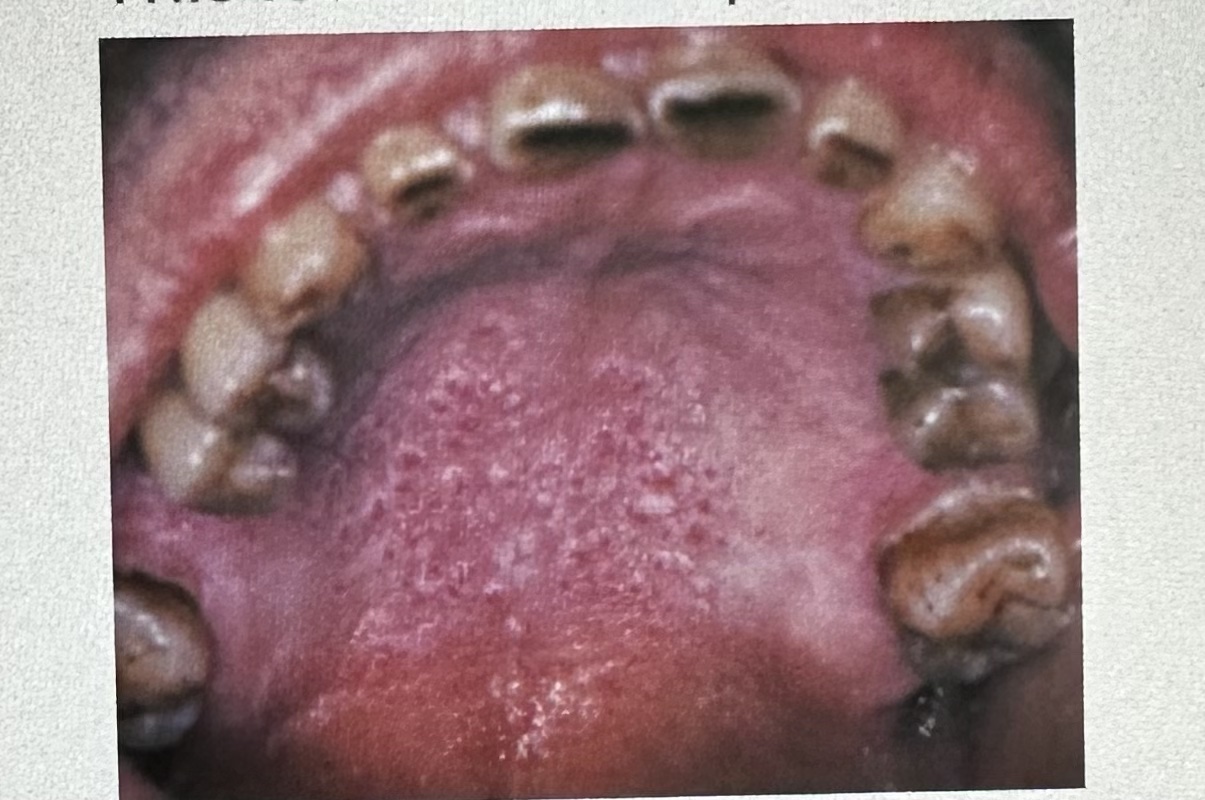
This lesion on the palate is typically associated with heavy pipe and cigar smoking and is called:
A. tobacco pouch keratosis
B. necrotizing sialometaplasia
C. nicotine stomatitis
D. frictional keratosis
C. nicotine stomatitis
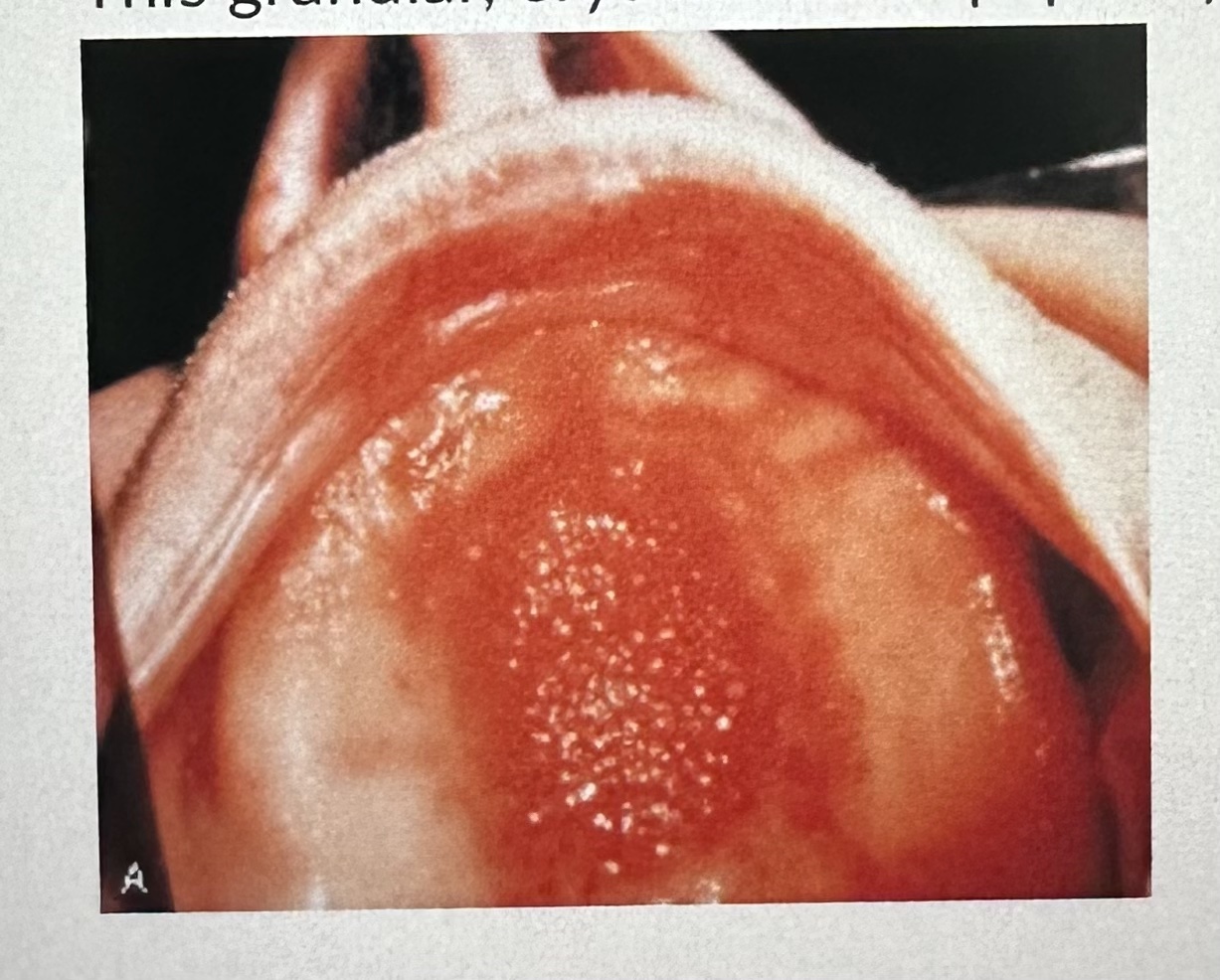
This granular, erythematous papillary surface of the palatal vault was caused by:
A. poor oral hygiene
B. an ill-fitting suction area of a maxillary denture
C. the denture flange
D. soaking the denture in caustic rinses
B. an ill-fitting suction area of a maxillary denture
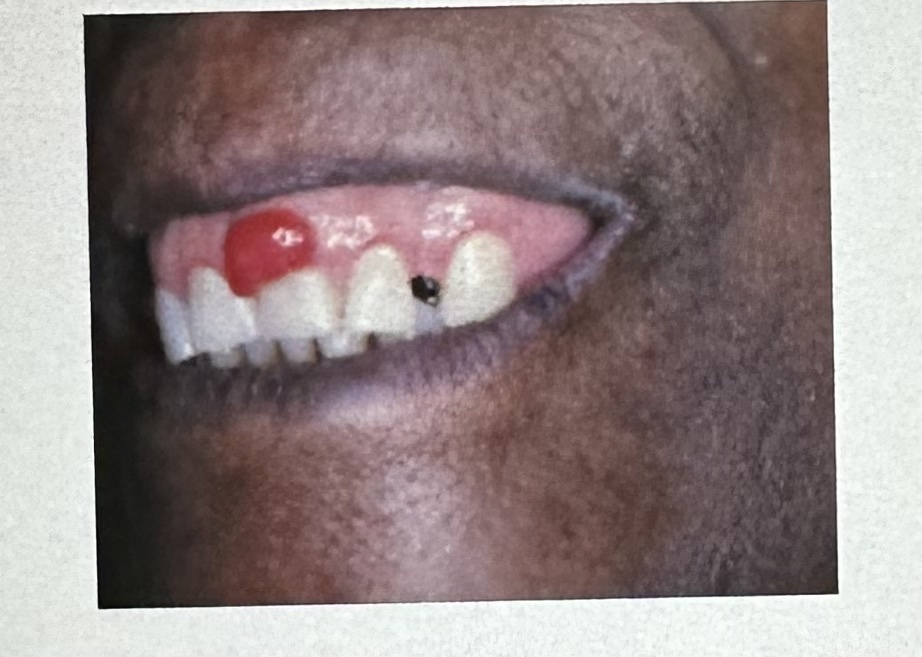
This sessile-based lesion is on the gingiva of a 13-year -old female. It is soft to palpation and bleeds easily.
A. peripheral giant cell granuloma
B. pyogenic granuloma
C. traumatic neuroma
D. irritation fibroma
B. pyogenic granuloma
A wedge-shaped defect at the cervical area of a tooth, the cause of which is related to microfracture of the tooth structure in areas of concentration of stress, is called:
A. attrition
B. erosion
C. abrasion
D. abfraction
D. abfraction
An example of an irreversible cellular response that occurs during tissue injury is:
A. atrophy
B. hypertrophy
C. hyperplasia
D. necrosis
D. necrosis
Which of the following is defined as an increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ?
A. hypertrophy
B. atrophy
C. hyperplasia
D. repair
C. hyperplasia
The most common site for the pulp polyp is:
A. the occlusal surface of a large open carious tooth
B. the apex of the tooth
C. the gingival margin of the tooth
D. deep in the pulp canal
A. the occlusal surface of a large open carious tooth
During the microscopic event of inflammation, pain may be caused by which of the following?
A. phagocytosis
B. leukocytosis
C. exudate formation
D. anaphylaxis
C. exudate formation
Hyperemia is responsible for which two clinical signs of inflammation?
A. emigration and pain
B. heat and erythema
C. transudation and redness
D. swelling and chemotaxis
B. heat and erythema
A ranula is located on the:
A. lower lip
B. retromolar area
C. floor of the mouth
D. buccal mucosa
C. floor of the mouth
Which of the following cysts is characteristically associated with a tooth that is nonvital on pulp testing?
A. dentigerous
B. radicular
C. dermoid
D. residual
B. radicular
Which lymphocyte matures without passing through the thymus and later can develop into a plasma cell that produces antibodies?
A. T-lymphocyte
B. B-lymphocyte
C. macrophage
D. LE cell
B. B-lymphocyte
In which type of immune response do B-lymphocytes and antibodies play the predominant role?
A. cell-mediated immunity
B. immune complex
C. humoral immunity
D. passive immunity
C. humoral immunity
An example of natural passive immunity would occur when:
A. antibodies from a mother pass through the placenta to the developing fetus
B. a microorganism cause a disease
C. a person receives a vaccination
D. a person is immunized
A. antibodies from a mother pass through the placenta to the developing fetus
Which one of the following is an example of type I hypersensitivity?
A. immune complexes formed between microorganisms and antibody in the circulating blood
B. asthma
C. autoimmune hemolytic anemia
D. serum sickness
B. asthma
What is the most common precipitating factor in the development of aphthous ulcers?
A. allergy
B. trauma
C. systemic disease
D. citrus foods
B. trauma
Certain recurrent ulcers appear on movable mucosa. They are discrete, round-to-oval ulcers that are up to 1 cm in diameter and exhibit a yellowish-white fibrin center surrounded by an erythematous halo. They are called:
A. major aphthous ulcers
B. sutton disease
C. herpetiform aphthous ulcers
D. minor aphthous ulcers
D. minor aphthous ulcers
Wickham striae is a term used to describe the oral mucosal lesions of:
A. linea alba
B. frictional keratosis
C. lichen planus
D. erythema multiforme
C. lichen planus
A certain condition, thought to be a hypersensitivity reaction, is characterized by skin and mucous membrane lesions. The skin lesions are referred to as a target, iris, or bulls eye lesions. The lip and mucosal lesions are more extensive and painful and often appear bloody and crusted. The intraoral lesions are extensive superficial ulcerations. The onset is explosive. On the basis of these clinical features, you suspect:
A. erythema multiforme
B. fixed drug reaction
C. behcet syndrome
D. angioedema
A. erythema multiforme
An example of an immunopathologic condition in which ones own body cells are no longer tolerated is:
A. contact mucositis
B. angioedema
C. autoimmune disease
D. contact dermatitis
C. autoimmune disease
Anaphylaxis occurs as a result of what type of hypersensitivity?
A. type I
B. type II
C. type III
D. type IV
A. type I
The most common oral manifestation of Sjogren syndrome is:
A. xerostomia
B. xerophthalmia
C. epimyoepithelial islands
D. aphthous ulcers
A. xerostomia
The most characteristic skin lesion in systemic lupus erythematous is described as:
A. a blister
B. urticaria
C. a butterfly rash
D. a bulla
C. a butterfly rash
T/F The immune response differs from the inflammatory response because it has the capacity for memory and responds more quickly to a foreign substance if encountered again.
true
Along with phagocytosis, the macrophage acts to process antigen material and present it on its surface to the T-helper cell. This stimulates both types of lymphocytes to travel from the lymphoid tissue or surrounding blood vessels to the injury site.
A. both statements are true
B. both statements are false
C. the first statement is true; the second is false
D. the first statement is false; the second is true
A. both statements are true
Which of the following is a condition that involves a deficiency in number, function, or interrelationships of the involved white blood cells and their products?
A. autoimmune disease
B. leukocytosis
C. immunodeficiency
D. anaphylaxis
C. immunodeficiency
The gray-white opalescent film seen on the buccal mucosa of 85% of black adults is a variant of normal that requires no treatment and is called:
A. linea alba
B. leukoedema
C. leukoplakia
D. white sponge nevus
B. leukoedema
Which papillae are elongated in the condition called black hairy tongue?
A. circumvallate
B. foliate
C. filiform
D. fungiform
C. filiform
Which of the following would be described as a segment that is part of the whole?
A. bulla
B. vesicle
C. lobule
D. pustule
C. lobule
A lesion with a sessile base is described as:
A. an ulcer
B. stemlike
C. pedunculated
D. flat and broad
D. flat and broad
Which one of the following is not diagnosed through clinical appearance?
A. mandibular tori
B. fordyce granules
C. black hairy tongue
D. compound odontoma
D. compound odontoma
Which one of the following conditions would most likely respond to therapeutic diagnosis?
A. angular cheilitis
B. amelogenesis imperfecta
C. paget disease
D. starve bone cyst
A. angular cheilitis
A lesion with a stemlike base is described as:
A. sessile
B. macular
C. pedunculated
D. lobulated
C. pedunculated
A small, circumscribed lesion, usually less than 1 cm in diameter, that is elevated or protrudes above the surface of normal surrounding tissue is a:
A. papule
B. macule
C. vesicle
D. bulla
A. papule