Hypertension – Mechanisms & Medications
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The 5 meds we learned for antihypertension
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are antihypertensives?
Medications whose purpose is to lower blood pressure
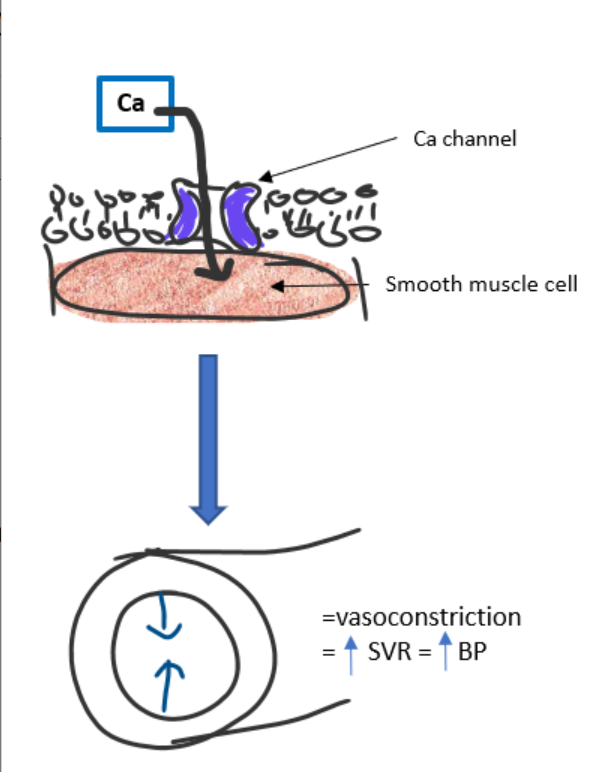
What happens when calcium enters vascular smooth muscle?
calcium enters smooth muscle
muscle contracts
vasoconstriction
increased SVR (afterload)
increased BP
(Ca channel open → vessel tightens → ↑ SVR → ↑ BP)
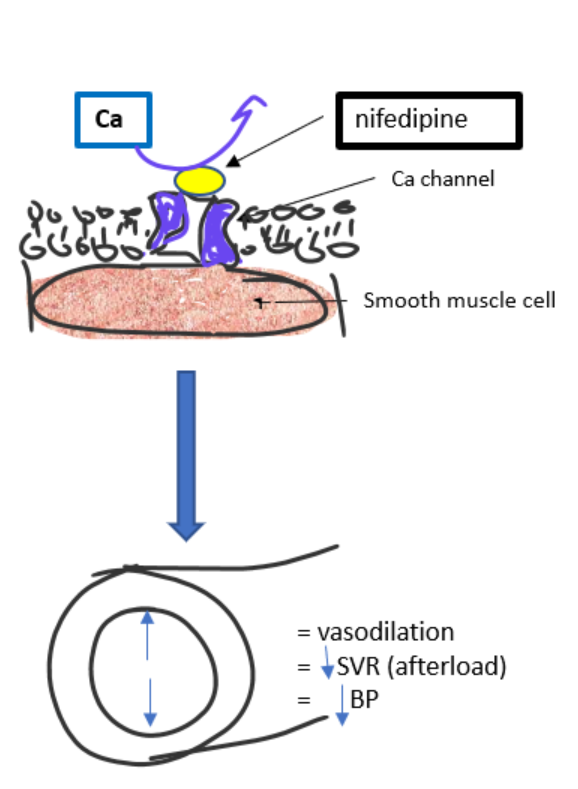
How do calcium channel blockers (nifedipine) lower blood pressure?
block calcium entry into vascular smooth muscle
prevent contraction
cause vasodilation
decrease SVR (afterload)
decrease BP
acts mainly on arterioles
What are the adverse effects of calcium channel blockers (nifedipine)?
adverse effects: tachycardia, dizziness
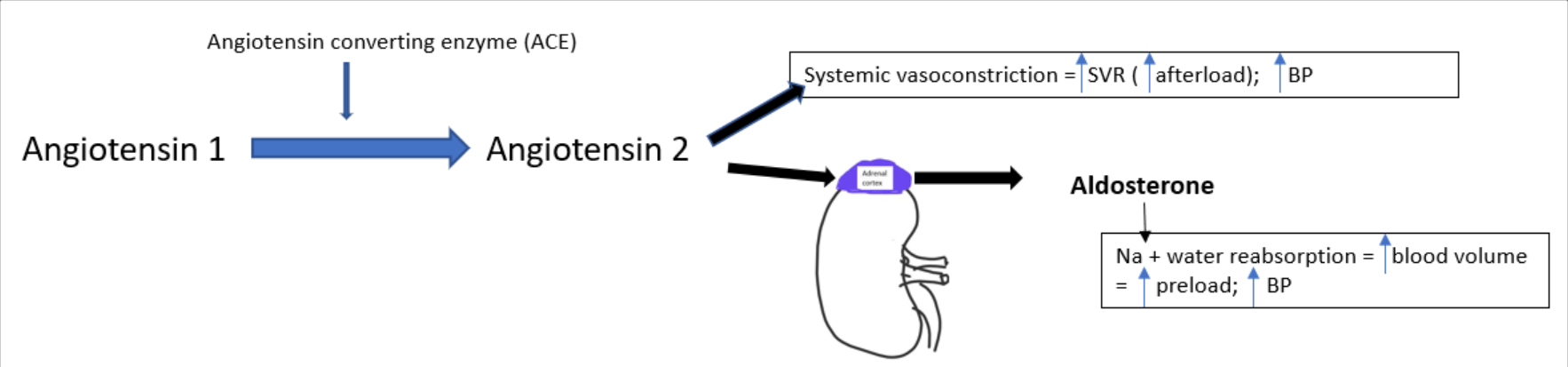
What are the effects of angiotensin II?
vasoconstriction = ↑ SVR , ↑ BP
stimulates aldosterone release (from the adrenal cortex)
aldosterone → Na⁺ & water reabsorption
increased BV = ↑ preload , ↑ BP
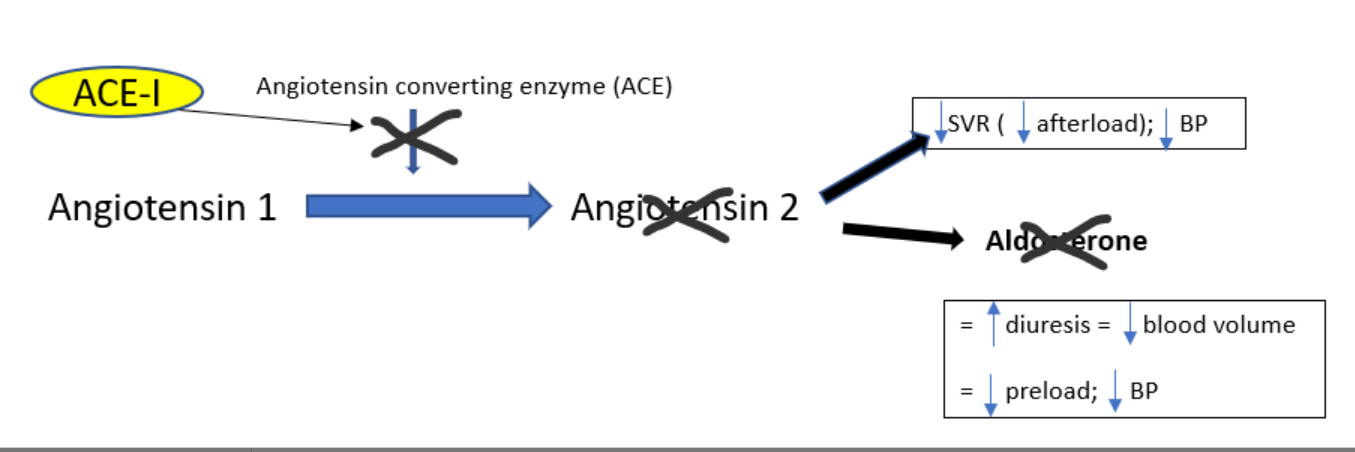
How to ACE inhibitors (enalapril) lower blood pressure?
block conversion of angiotensin I → angiotensin II
↓ vasoconstriction → ↓ SVR (afterload)
↓ aldosterone = ↑ diuresis
↓ blood volume = ↓ preload
↓ BP
What are the adverse effects of ACE inhibitors (enalapril)?
adverse effects: dry cough, dizziness, hyperkalemia(increased potassium in the blood)
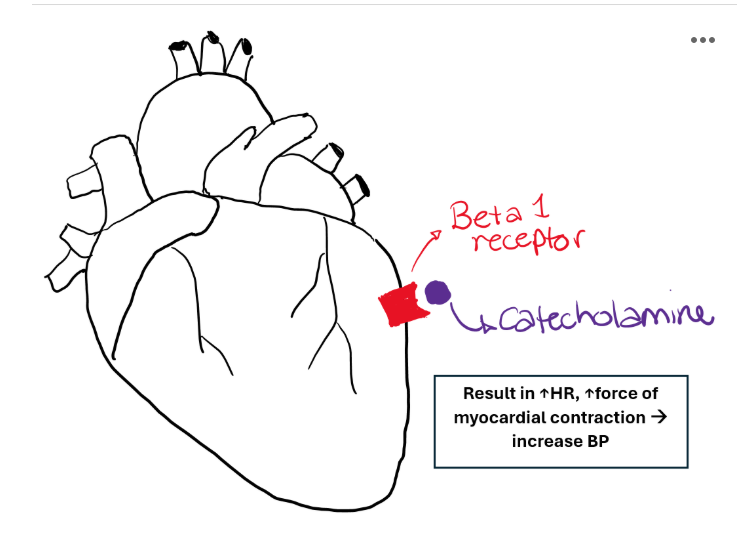
What happens when beta-1 receptors are stimulated?
Located in the heart
↑ heart rate
↑ force of contraction
↑ cardiac output
↑ blood pressure
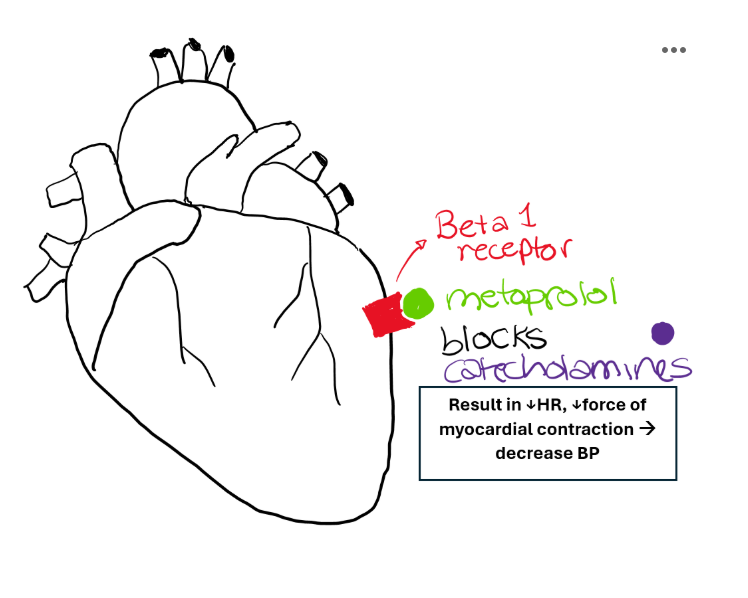
How do beta blockers (metoprolol) lower blood pressure?
Block beta-1 receptors in the heart
↓ heart rate
↓ contractility
↓ cardiac output
↓ BP
suppress activity of renin
What are the adverse effects of beta blockers (metoprolol)?
adverse effects: bradycardia, orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, rebound of hypertension if stops taking meds abruptly
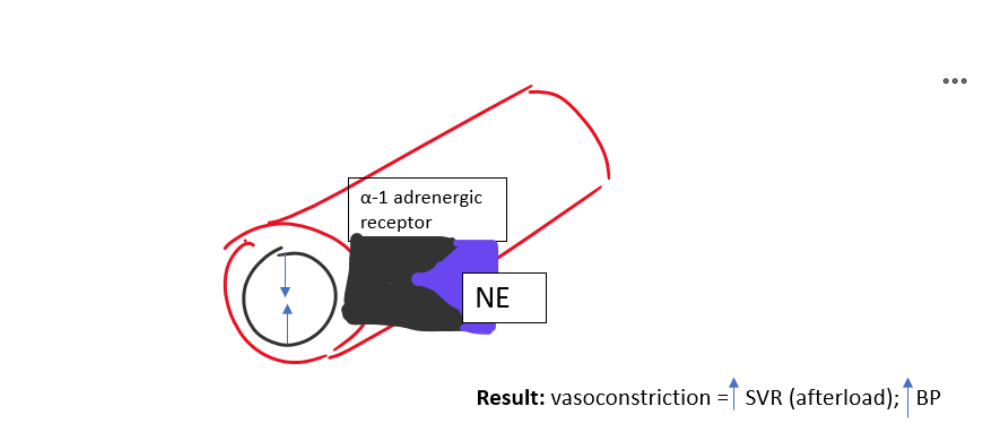
What happens when alpha-1 receptors are stimulated?
Located on blood vessels
Causes vasoconstriction
↑ SVR (afterload)
↑ blood pressure
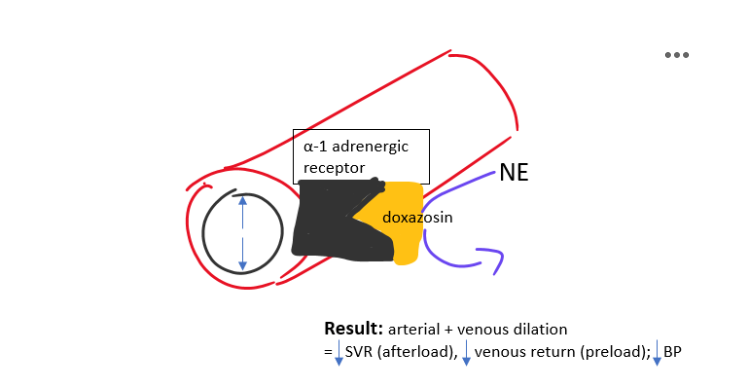
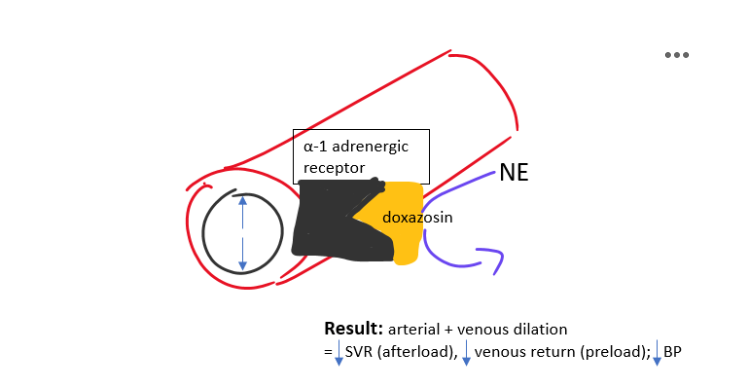
How do alpha-1 blockers (doxazosin) lower blood pressure?
Block alpha-1 receptors
Prevent vasoconstriction
Cause arterial & venous dilation
↓ SVR (afterload)
↓ venous return (preload)
↓ BP
What are the adverse effects of alpha-1 blockers (doxazosin)?
adverse effects:
orthostatic hypotension (common)
dizziness
How does ASA (antiplatelet medication) (aspirin) help prevent heart attack, stroke, cardiovascular disease and blood clots?
Antiplatelet medication
Inhibits platelet aggregation
Prevents clot formation
Reduces risk of MI and stroke
Why is ASA (antiplatelet medication) used in patients with hypertension or heart disease?
Hypertension damages blood vessels
Damaged vessels increase clot risk
ASA prevents platelet clumping
Reduces risk of cardiovascular events
Inhibits COx-1in platelets (preventing platelet
What is the adverse effect of ASA (antiplatelet medication)?
GI bleeding
suffix -pril = what
ACE inhibitor
suffix -olol means what
Beta-1 receptor
suffix -zosin means what
Alpha-1 receptor
suffix -pine means what
Ca+ channel blocker