Final Pathology Review Part 1
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
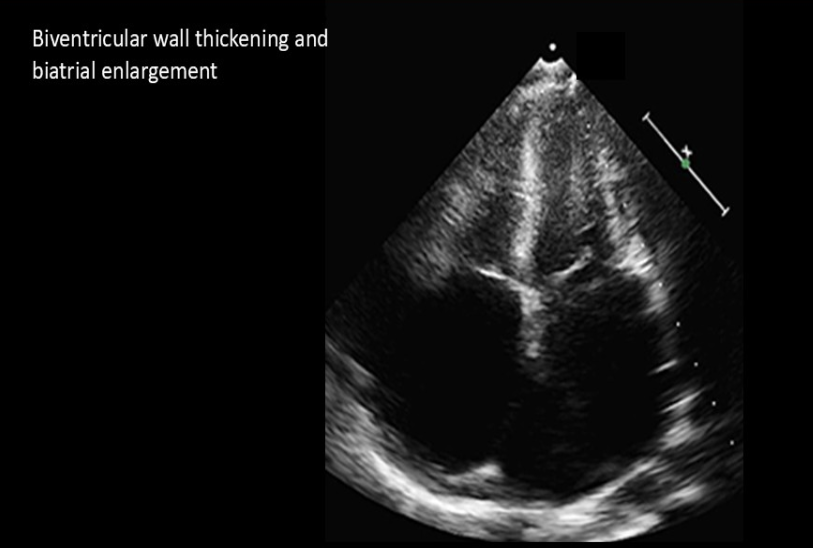
Normal LV size
Biventricular hypertrophy
Significant biatrial enlargement
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Average EF% with HCM
70-80%
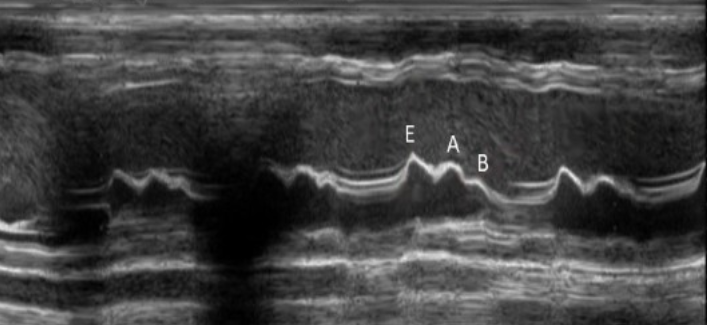
Increased LVEDP seen with DCM will demonstrate?
B bump
Most common echo finding in HIV patients
Pericardial effusion

Expansion of the LV apex with basal hyperkinesis
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
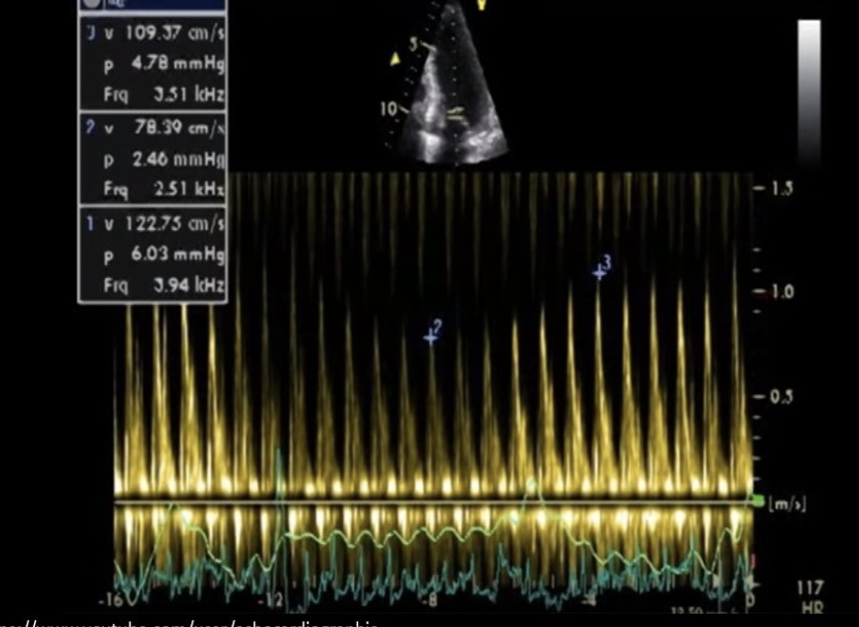
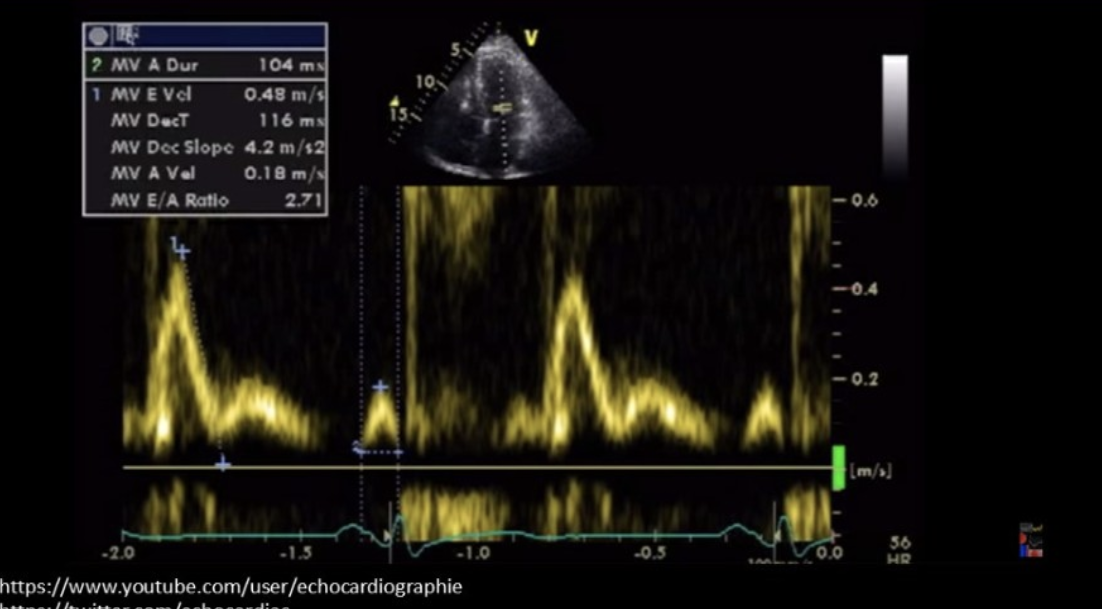
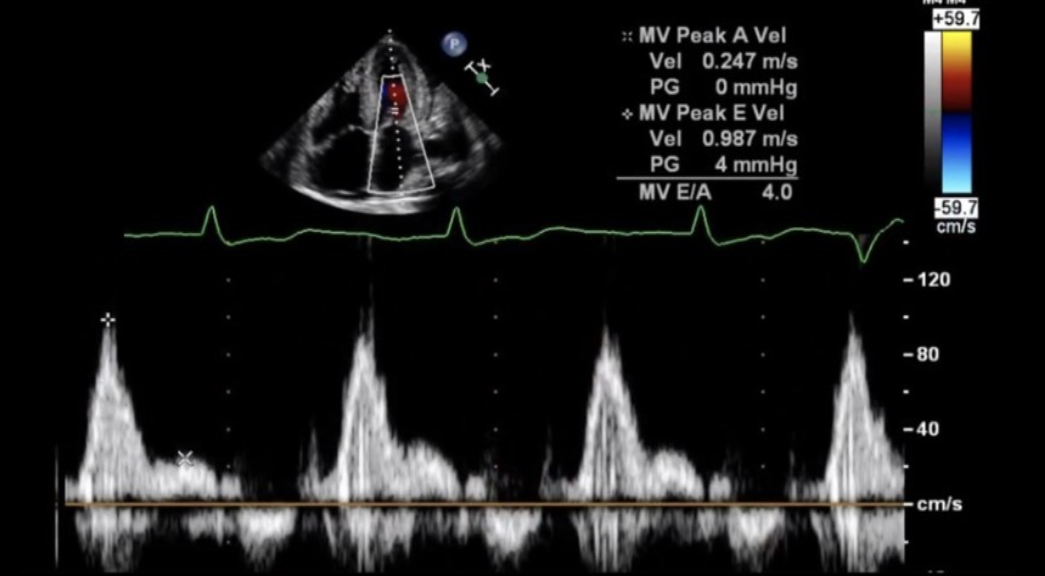
Which cardiac abnormality is consistent with the Doppler tracing?
Constrictive pericarditis
Widespread ST elevation
Trace MR
Trace TR
Mild pericardial effusion
Pericarditis
Layer most affected by Staphylococcus Aureus
Endocardium
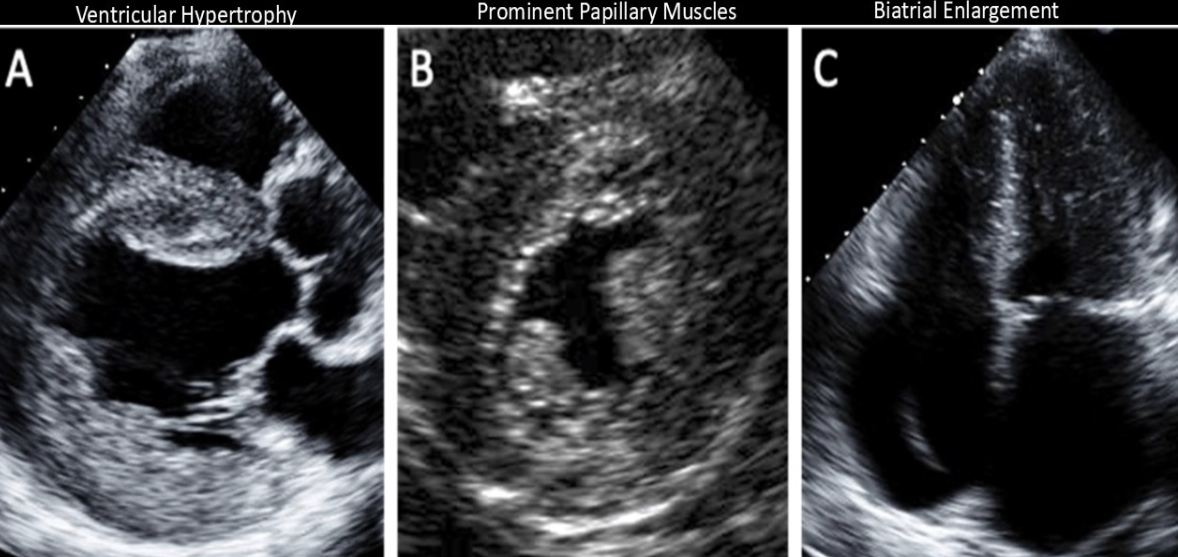
LVH
Prominent papillary muscles
Hyperechoic endocardial layer
Conduction defects
Fabry disease
Refers to an arterial pulse waveform with alternating strong and weak beats
Pulsus alternans
Preferred method of diagnosis of constrictive pericarditis
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiomyopathy strongly associated with diabetes
DCM
Most common type of infiltrative cardiomyopathy to develop restrictive cardiomyopathy
Amyloidosis
Restrictive filling pattern
Tall E wave
Small A wave
Decreased deceleration time
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Heterogeneous speckled appearance of the myocardium of the RV and LV consistent with?
Infiltrative cardiomyopathy
HF with preserved EF%
Significant diastolic dysfunction
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
What causes the AV to close mid systole?
LVOT obstruction
Equal diastolic pressures in the RV and LV
Constrictive pericarditis
Cardiac tamponade causes?
Restrictive diastolic filling
Biventricular wall thickening
Mild pericardial effusion
Thickening of all four valve leaflets
Amyloidosis
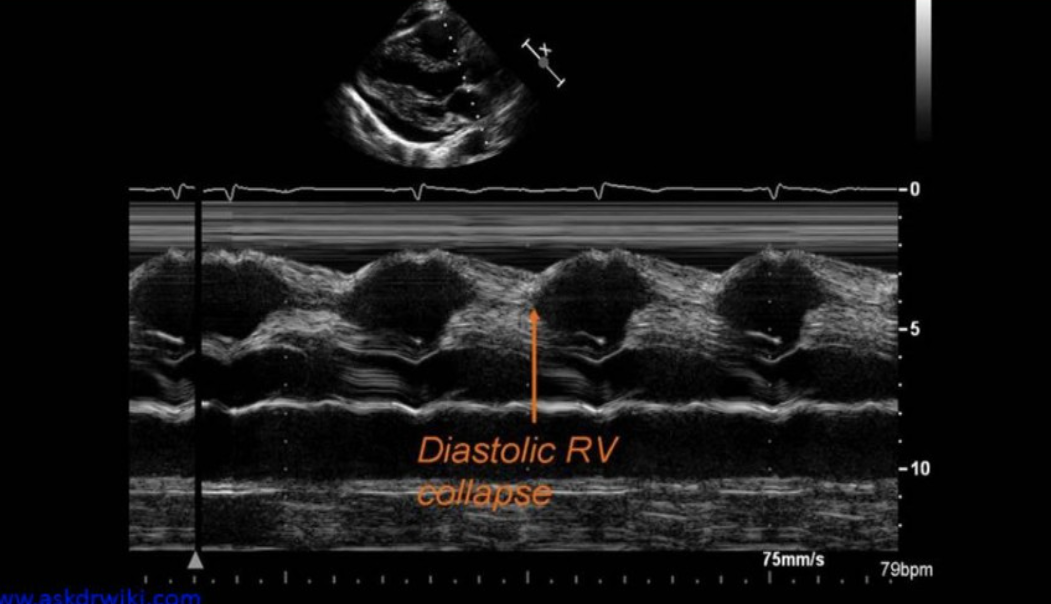
Most important cardiac structure that should be evaluated with suspected tamponade
RV free wall
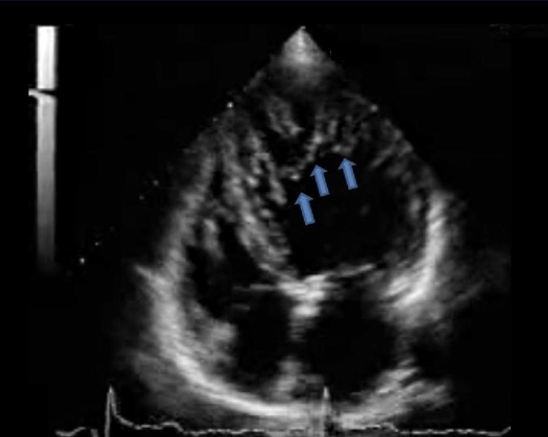
Irregular contour
Abnormal motion
Large trabeculations
Non-compaction cardiomyopathy
How does restrictive cardiomyopathy affect pulmonary venous flow?
Increased diastolic (D) and blunted systolic (S)
Dagger shaped waveform with high systolic velocity and late systolic peak reflects a dynamic obstruction
HOCM
Most common pattern of LVH with HCM
Isolated IVS hypertrophy
Acute transient stress-induced cardiomyopathy
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
What would cause you to suspect cardiac tamponade?
Becks triad
Typical treatment for advanced pericarditis
Pericardectomy
A valve ring abscess is usually a sign of what cardiac disorder?
Infective endocarditis
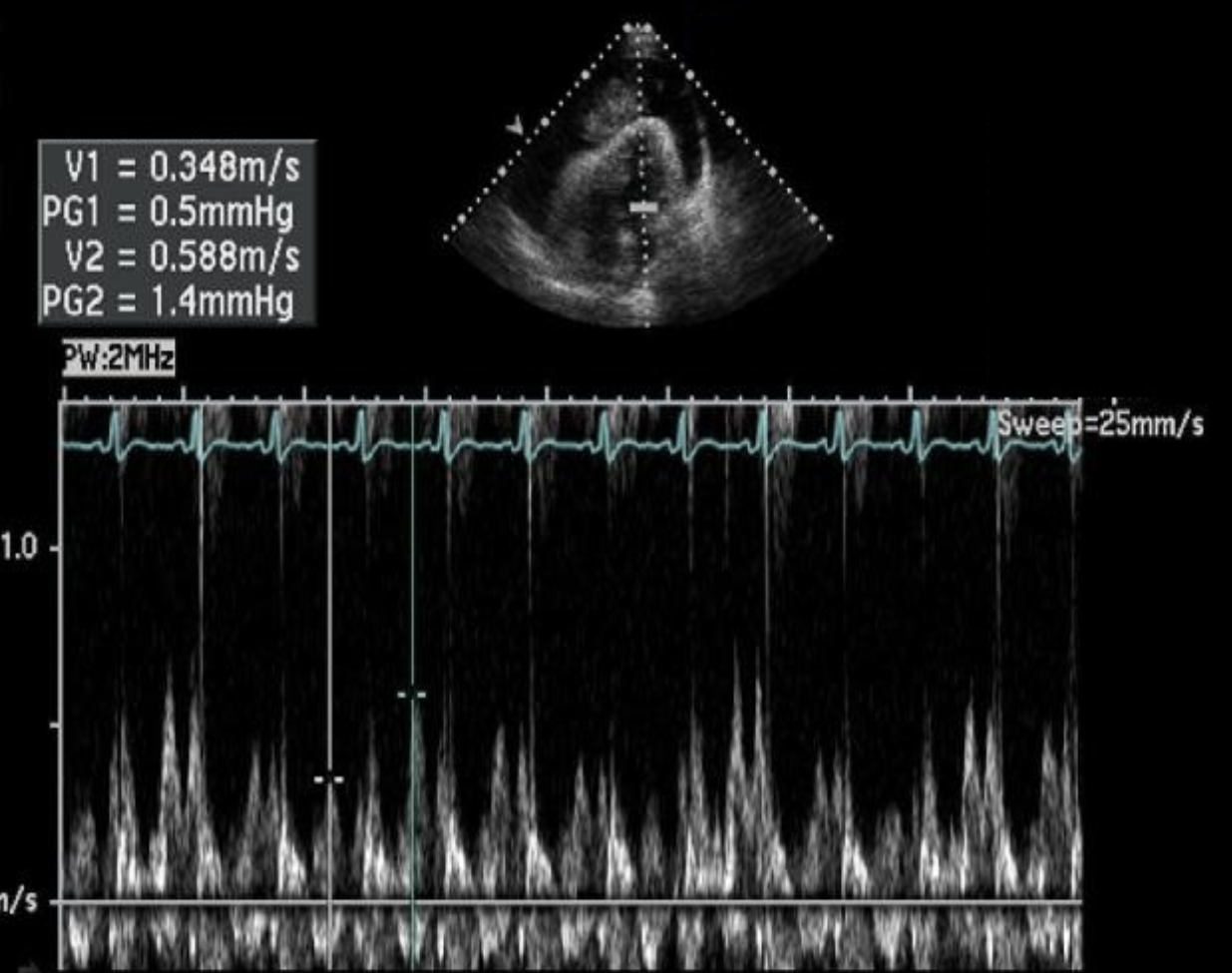
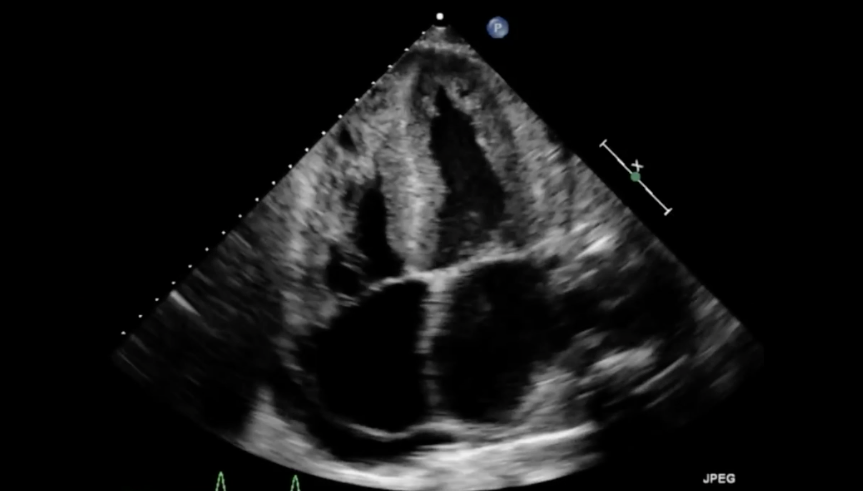
What are the calipers measuring?
Abnormal respiratory variation in the E velocity of the MV due to cardiac tamponade
Early stages of infiltrative cardiomyopathy are commonly associate with which type of diastolic dysfunction?
Grade 1
What effect does DCM have on HR?
Increases
HCM has associated?
MR
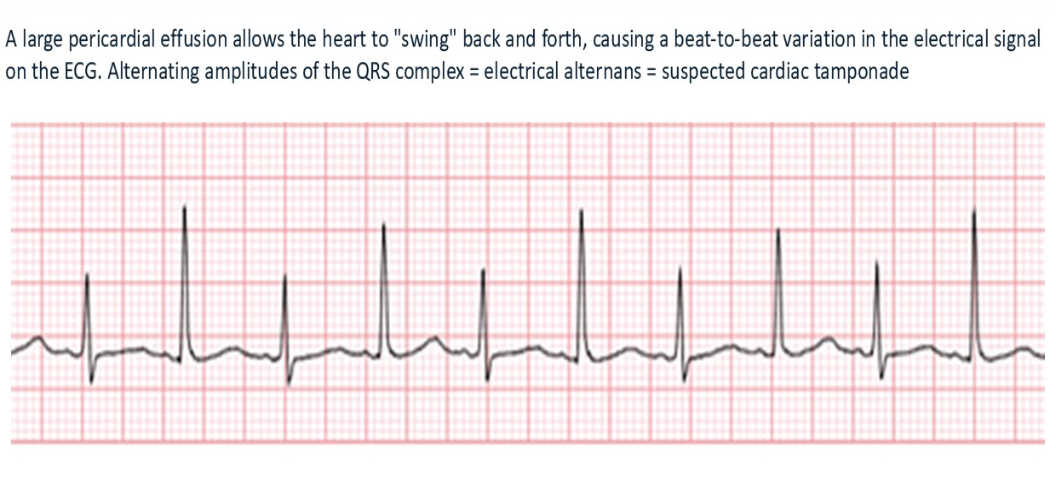
Electrical alternans is a common finding with?
Cardiac tamponade
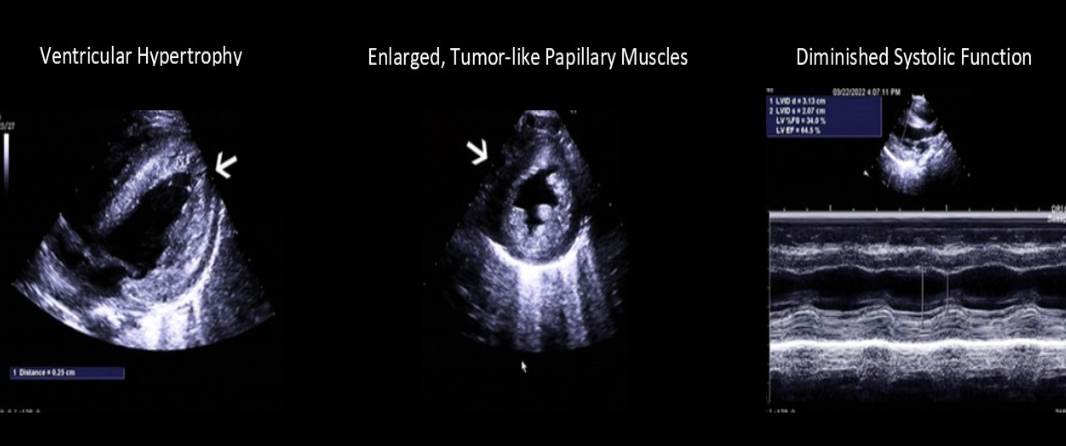
Autosomal recessive disease
Abnormal storage of glycogen
Increased ventricular thickening
Pompe disease
Chemotherapy
Decreased EF%
Global hypokinesis
New onset of SOB
Pericardial effusion
Infection only affects the cardiac valves with no involvement of myocardium or other cardiac structures
Marantic endocarditis
Pulsus paradoxus is commonly seen with?
Constrictive pericarditis and cardiac tamponade
Name a complication of DCM
Stroke
What would cause an increase in the murmur associated with hypertrophic subaortic stenosis?
Amyl nitrite administration
Who would benefit from the placement of an intra-aortic balloon pump?
DCM
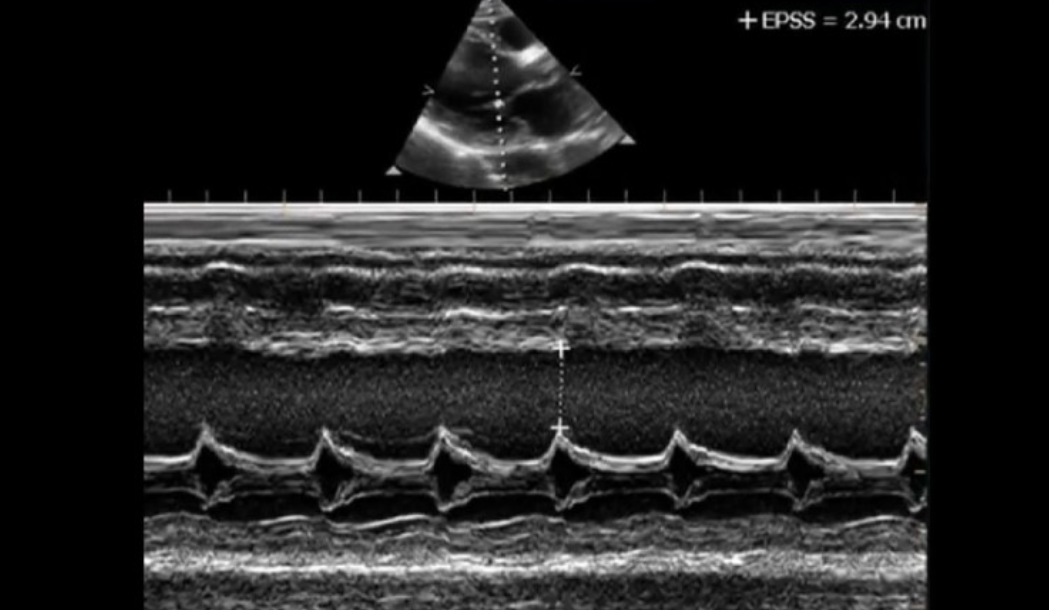
What m-mode measurement will increase in patients with DCM?
EPSS
Average EF% with DCM
10-20%
Non-dilated LV
Thick walled LV
EF 63%
E/A 2.1
E/E 19
Moderate biatrial enlargement
Moderate pulmonary HTN
RVH
Dilated IVC
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Dilated IVC and HPVs are commonly associated with?
Constrictive pericarditis and cardiac tamponade
In cardiac tamponade, the RV free wall will collapse during diastole except in patients with?
Pulmonary HTN
Most common complication seen with septal myectomy performed to correct ASH
VSD
Tachycardia
Dyspnea
Orthopnea
Lower extremity edema
DCM
Common finding with infiltrative cardiomyopathy, endocarditis and a recent MI
Pericardial effusion
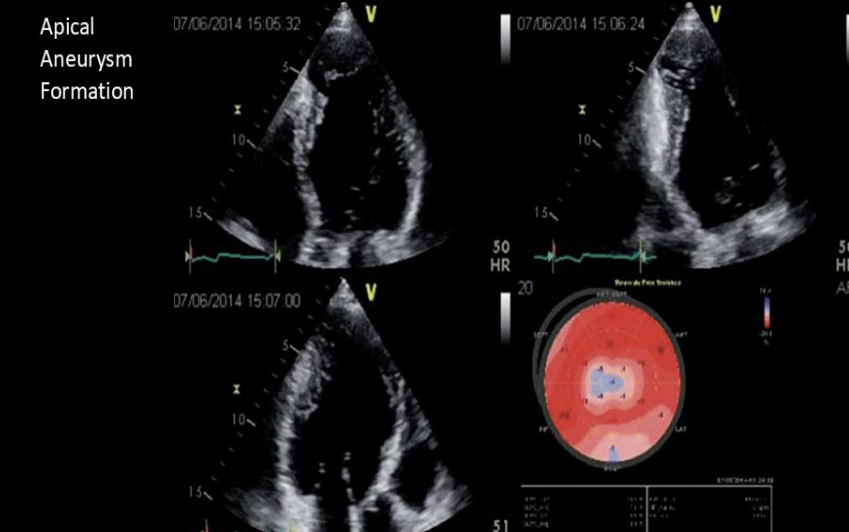
What are you looking for after a recent diagnosis of Chagas disease?
DCM and apical aneurysm
Dilated LV with normal wall thickness
Reduced function
Hemochromatosis
Positional and respiratory variation in chest pain
Pericarditis
Most common cause of DCM
Alcoholism
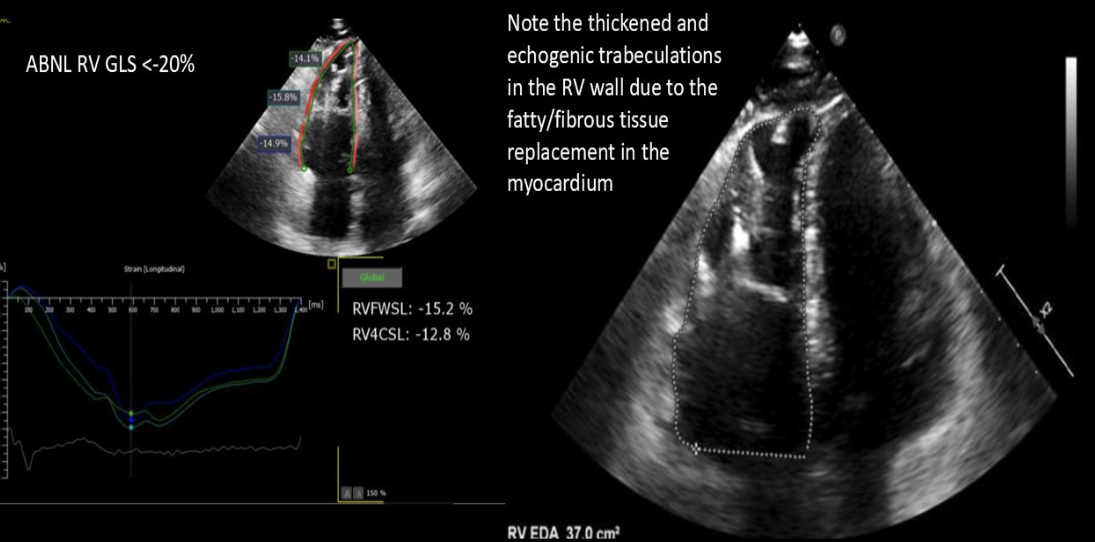
Fatty and fibrous tissue replacement of the myocardium of the RV
Arrhythmogenic RV cardiomyopathy
What effect will DCM have on LVOT velocity?
Decreased CO
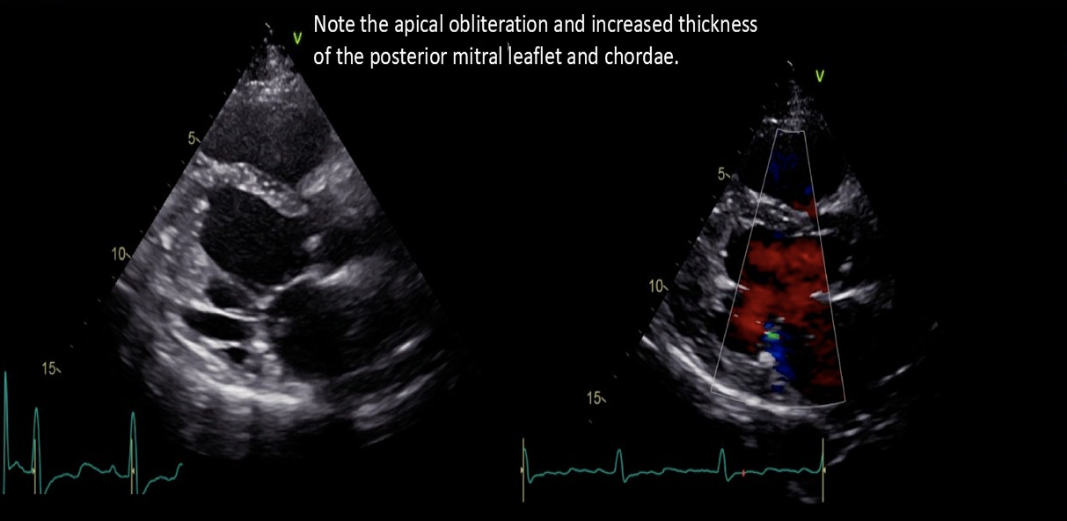
Endocardial thickening
Fibrous tissue overgrowth LV apex
Diastolic dysfunction
Endomyocardial fibrosis
Suspected cardiac emboli causing new onset of left hemiparalysis
High fever
Heroin addiction
Vegetation on the MV
Endocarditis typically causes the formation of vegetations on the?
Ventricular side of the AV and atrial side of the MV
Double diamond sign
DCM
Fever of 103
IV drug use
Recent onset of extreme dyspnea
Emboli lodged right bronchial artery
Vegetation on the TV
VSD found in LVOT near AV
Membranous VSD
MVP and bicuspid AV are associated with?
Coarctation
What can increase the number of microbubbles crossing the IAS during saline contrast exam?
Ask patient to cough
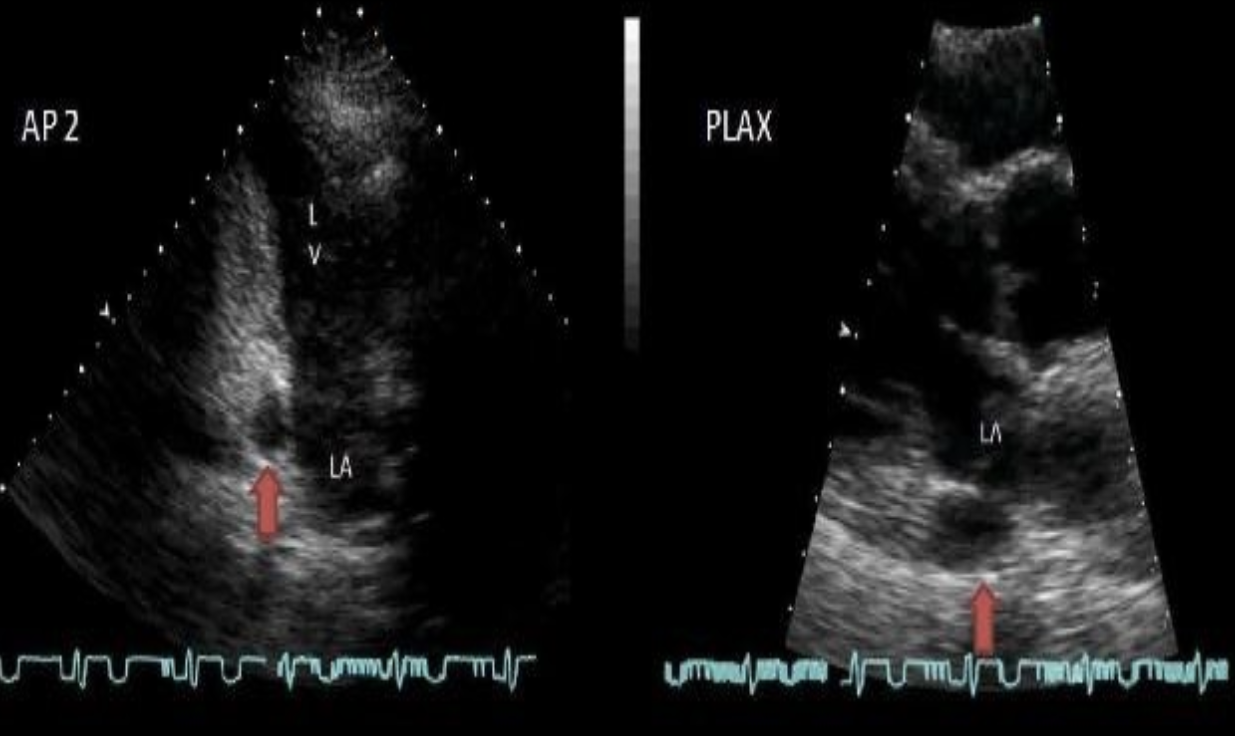
Dilated coronary sinus associated with?
Persistent left SVC
ASD located close to atrioventricular valves and associated with cleft MV
Septum primum
Continuous murmur
Normal brachial pressures bilaterally
Decreased pedal pulses
Coarctation distal to the left subclavian artery
Most commonly occurring congenital defect
VSD
Most commonly detected congenital heart defect in adults
Bicuspid AV
Doppler evaluation of the abdominal aorta in severe cases of coarctation will demonstrate?
Low velocity monophasic flow
Discolored nail beds
Clubbed fingers
Dyspnea
TOF
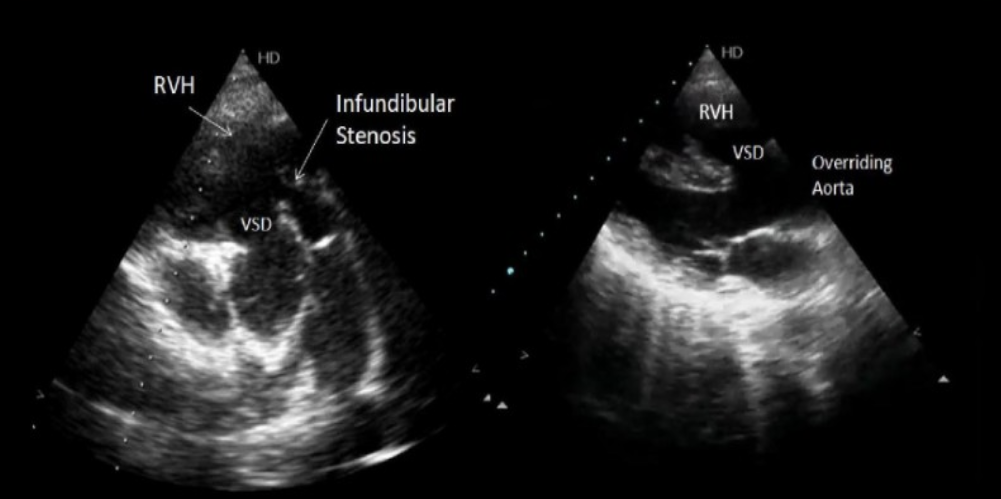
VSD
Overriding aorta
Infundibular stenosis
RVH
TOF
Large ASDs can lead to?
RV volume overload and flattened IVS
Most common location for the formation of coarctation
Isthmus
Anomalous origin of the coronary artery most commonly associated with?
Bicuspid AV and TOF
In cases of pulmonary atresia, what must be present to survive after birth?
PDA
Unable to demonstrate two vessels exiting the ventricles
Truncus arteriosus
Eisenmenger syndrome most likely to occur with?
PDA or ASD
History of systolic murmur
Muscular VSD and secundum ASD
Associated with sinus venosus ASD
PAPVR
When evaluating VSD repair, what should be obtained to demonstrate success of the procedure?
SPAP
If all four pulmonary veins do not connect to the LA
TAPVR
If at least one pulmonary vein does not connect to the LA
PAPVR
ASD most commonly associated with Ebstein anomaly
Secundum ASD
Electrical abnormality commonly associated with Ebstein anomaly
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
Complex CHD that corrects itself
Corrected or L-transposition
Murmur associated with ASD
Systolic murmur with fixed split S2

Apical displacement of one or more tricuspid leaflets
Ebstein anomaly
Pulmonary artery forms as a branch of the LV
Aorta forms as a branch of the RV
Transposition
Inlet VSD
Common atrioventricular valve
Ostium primum ASD
Trisomy 21
Complete endocardial cushion defect
Flow moving through PFO from the RA to LA is related to what CHD?
Ebstein anomaly
First screening exam performed to asses for critical CHD
Pulse oximetry
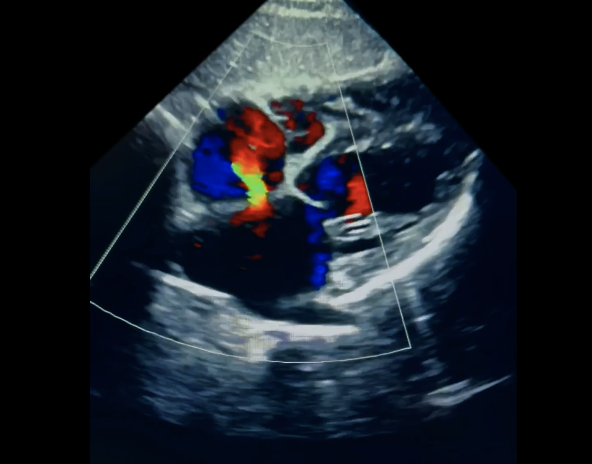
Name the ASD demonstrated
Ostium secundum
VSD patch
RVOT stent
Moderate PI
RV enlargement
TOF repair
In cases of PDA, normal cardiac pressures can be assumed when?
PPG from the shunt equals 100 mmHg
Holt Oram Syndrome most commonly associated with?
ASD
Murmur associated with bicuspid AV
Systolic ejection click after S1
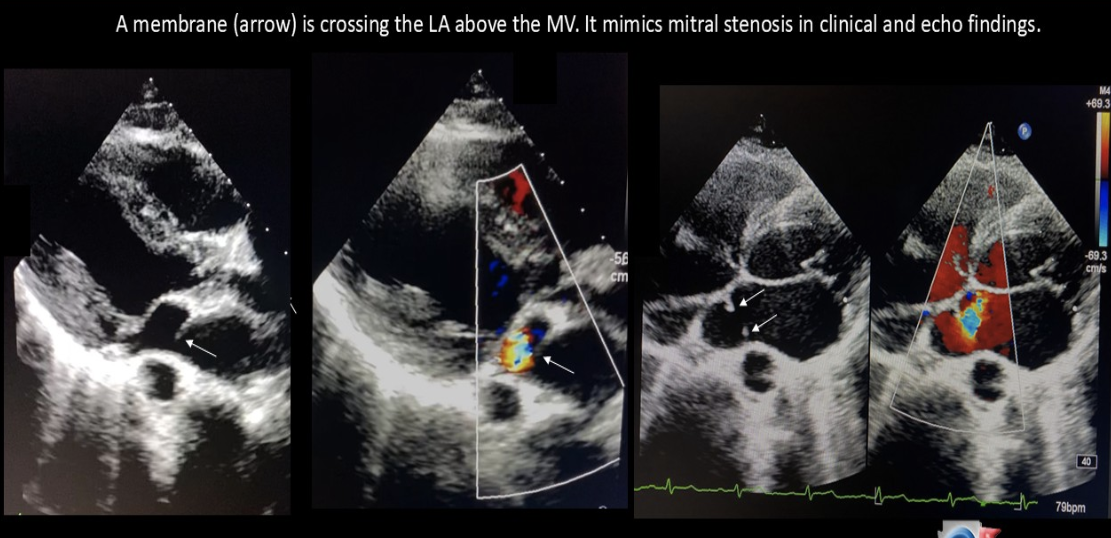
Cor triatriatum of the LA can lead to which flow complication?
Restricted pulmonary venous flow
Prolapse of the right aortic cusp most commonly seen with what type of VSD?
Outlet VSD
Conduit connecting the IVC to the RPA
Fontan procedure
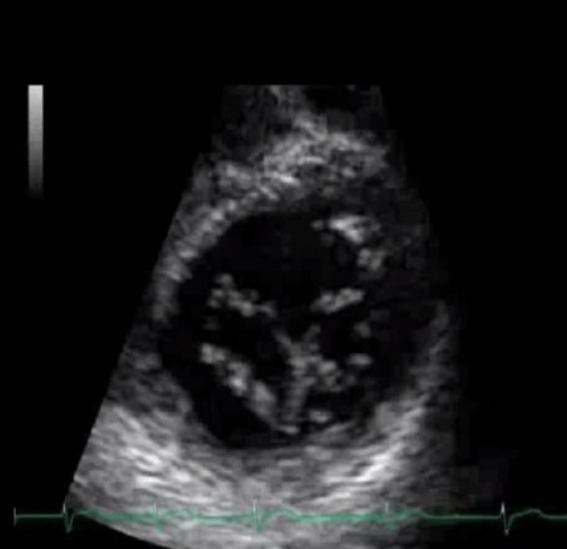
Two openings in the MV
Double outlet MV