Tissue Integrity- Basic of Wounds Guest Ppt
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Notes-2025by Lizzie Wounds
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Epidermis
found thickest on the palms of your hands and soles of your feet (1.5mm thick)
SQ or Hypodermis
deepest layer of the skin
storing fat
contains blood vessels
hair follicle roots and nerves
Forming Scar Tissue
not the same as normal skin tissue
appears often discolored and lacks sweat glands and hair
Areas that experience repeated friction or pressure
can form tough, thick skin known as a callus
examples: hands of tennis players and fingertips of guatarists
Old Wives Tale of Wound Healing (not true tales)
leaving a wound open to air good for it
use hydrogen peroxide to clean a wound
scabs are good
One of two: Epidermal
thin, avascular
regenerates every 4-6 weeks
function-maintains a barrier
includes 5 sublayers
Two of two: Dermal
provides strength, support, blood, and oxygen to the skin
attached to epidermal layer with rete pegs
contains collagen, fibroblasts, elastic fibers
Four Phases of Wound Healing:
Hemostasis
Inflammation
Proliferation
Remodeling
Phase 1: Hemostasis of Wound Healing
stops bleeding
day 1 to 3
Phase 2: Inflammation of Wound Healing
Day 3 to 20
New Framework for blood vessel growth
Phase 3: Proliferation or Granulation
Week 1 to 6
pulls the wound closed
Phase 4: Remodeling or Maturation
Week 6 to 2 years
final proper tissue
Factors that affect wound healing and treatment guidelines
Wound Assessment
Wound Size
Tissue Quality
Drainage
External Factors:
blood flow
infection
clinical status
Wound Considerations:
cause of the wound
what does the wound “need”?
who is caring for the wound
role of bacteria in the wound
Acute Wounds:
Surgical Incisions
Closed/Open
Skin tears
Moisture Associated Skin Damage (MASD)
Medical Adhesive related skin injury
burn
Chronic Wounds:
Pressure Ulcer/Injury
Arterial Ulcer
Venous Ulcer
Diabetic/Neuropathic Ulcer
Surgical Incisions: Closed
Sutures
Staples
Glue
Steri Strips
Surgical Incisions: Open
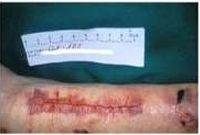
Skin Tears: Category I Linear type/Flap Type
w/o tissue loss either linear or with a flap that closes the tear to within an approximation of 1mm of the wound edges
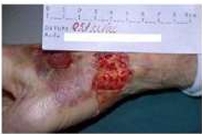
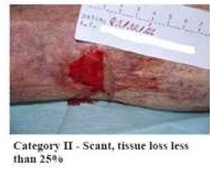
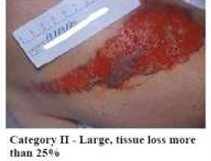
Skin Tears: Category II
Partial tissue loss, considered scant when the loss is 25% or less and moderate
or loss when the tissue loss is more than 25%
Skin Tears: Category III
Complete tissue loss nor epidermal flap covering the injury
Moisture Associated Skin Damage (MASD)
Intertriginous skin Damage (ITD)
in b/w skin folds
Think “in the depth”
Common locations are sacral slit, inframammary, under pannus
can be with or without a fungal component
Incontinence Associated Dermatitis (IAD)
caused from urinary and/ or bowel incontinence
Periwound dermatitis
from wound drainage
Peristomal dermatitis
from stoma output on skin
Medical Adhesive Related Skin Injury (MARSI)
Skin injury
results when skin to adhesive attachment is stronger than skin cell to skin cell attachment
as a result: the epidermal layers separate, or the epidermis separates completely from the dermis
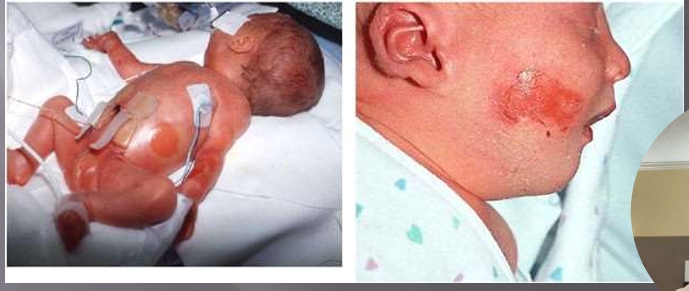
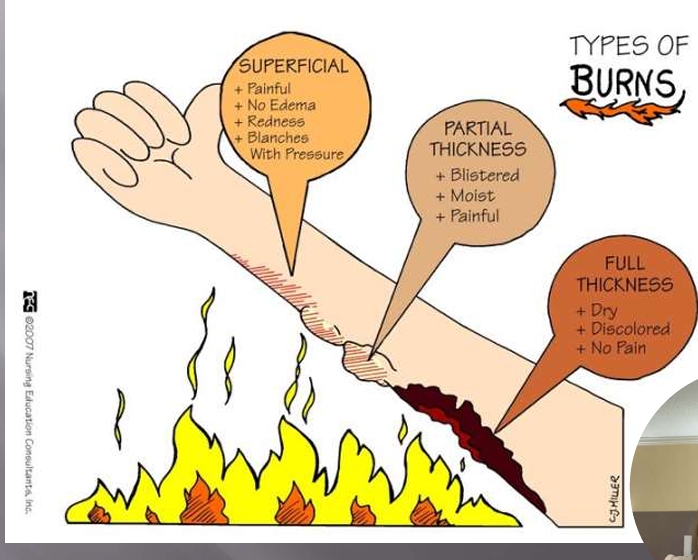
First-Degree (Superficial) Burns
affect only the epidermis, or outer layer of skin
burn site: red, painful, dry, and with no blisters
Example: Mild sunburn
long-term tissue damage is rare and usually consists of an increase or decrease in the skin color
Second-degree (partial thickness) burns
involves the epidermis and part of the dermis layer of skin
burn site appears red, blistered, and may be swollen and painful
Third-Degree (full thickness) burns
destroy the epidermis and dermis and may go into the subcutaneous tissue
burn site may appear white or charred
Fourth-Degree Burns:
damage underlying bones, muscles, and tendons
no pain nerve endings are destroyed
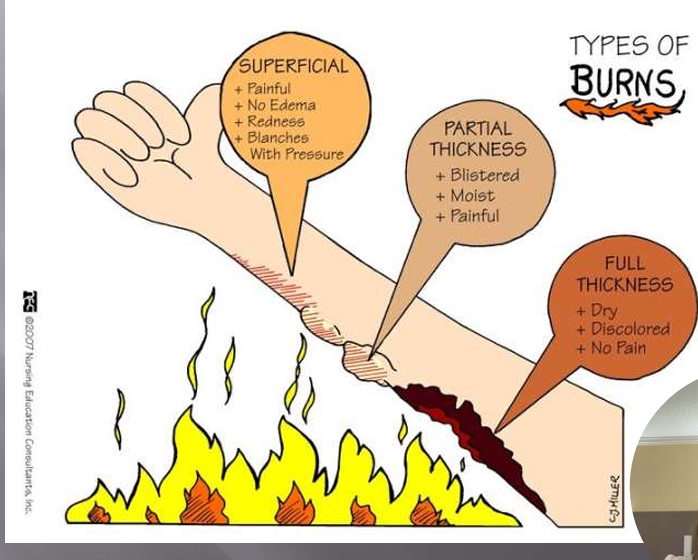
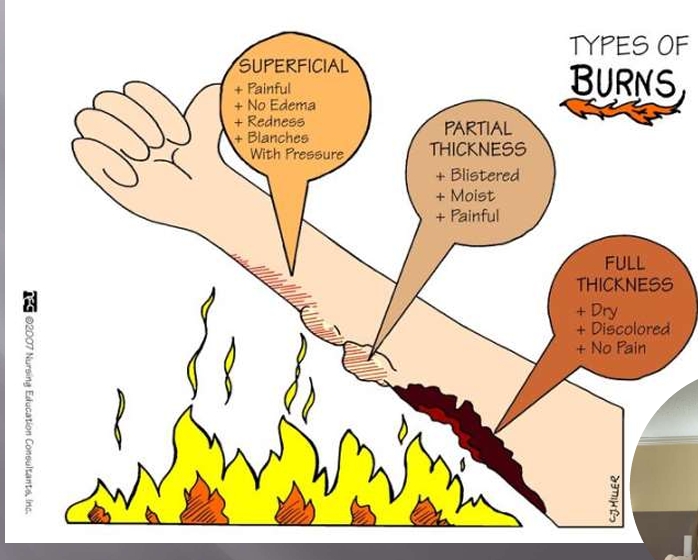
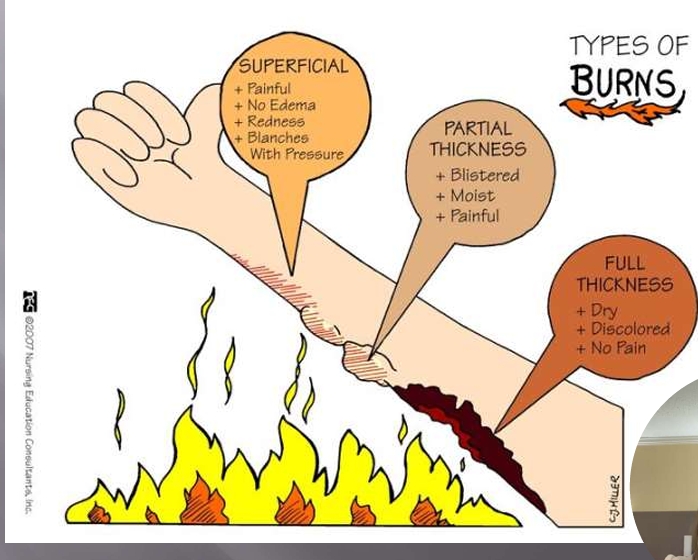
First-Degree Burn (Superficial)
painful
no edema
redness
blanches with pressure
Second Degree Burn (Partial Thickness)
blistered
moist
painful
Third-Degree Burn (Full-thickness)
dry
discolored
no pain
Chronic Wounds
have high levels of inflammatory markers
high bacteria count
failed to progress in 30 days
often long healing items complicated by infections
Pressure Injury
localized injury to the skin and/or underlying tissue usually over a bony prominence,
or under a medical device, as a result of pressure,
or pressure in combination with shear and or friction
Common Sites for Pressure Injuries
Back of the head
shoulder
elbow
buttocks
heel
ear
hip
thigh
leg
rib cage
knees
toes
sacrum
Braden Scale: Sensory Perception
measures the person’s ability to detect and respond to discomfort or pain related to pressure on parts of their body
ability to feel pain
level of consciousness of a patient (can they react to the pressure)
Braden Scale: Moisture
excessive and continuous skin moisture can pose a risk to compromise the integrity of the skin by causing the skin tissue to become macerated
risk for epidermal erosion
assesses the degree of moisture the skin is exposed to
Braden Scale: Activity
looks at a patient’s level of physical activity since very little or no activity can encourage atrophy of muscles and breakdown of tissue
Braden Scale: Mobility
looks at the capability of a patient to adjust their position independently
assesses physical competency to move and can involve the client’s willingness to move
Braden Scale: Nutrition
assessment of a client’s nutritional status looks at their normal patterns of daily nutrition
eating only portions of meals or having imbalanced nutrition can indicate a high risk in this category
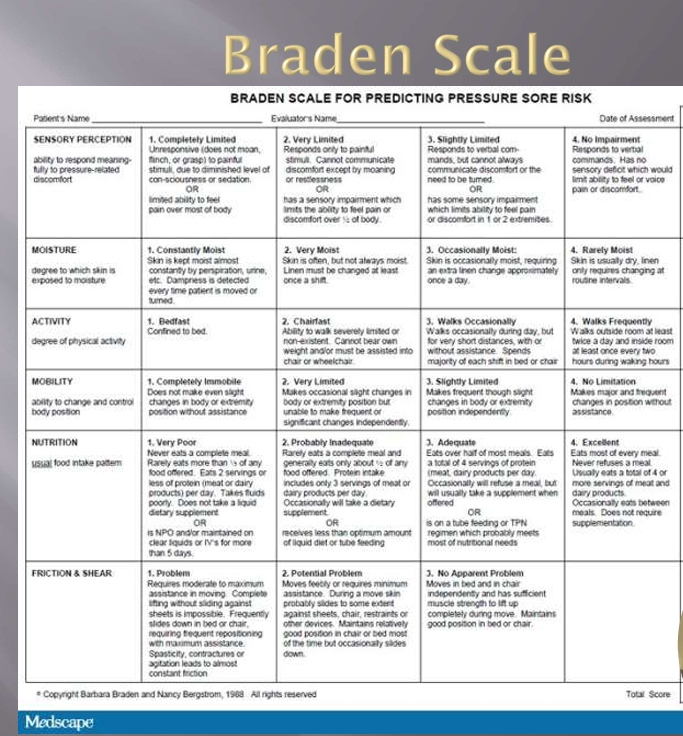
Braden Scale: Friction and Shear
amount of assistance a client need and the degree of sliding on beds or chairs that they experience
assess sliding motion can cause shear
shear is the skin and bone moving in the opposite direction causing breakdown of cell membranes and capillaries
Risk Factors
intrinsic vs extrinsic
can they tolerate the pressure or shearing
incontinent
over age 75
vascular status
feeling?
nutritional status?
having skins?
external factors
External Factors that Mitigate the risk factors
repositioning
specialty mattresses
wicking pads
barrier
nutrition
proper moisture management
of pressure bony prominences
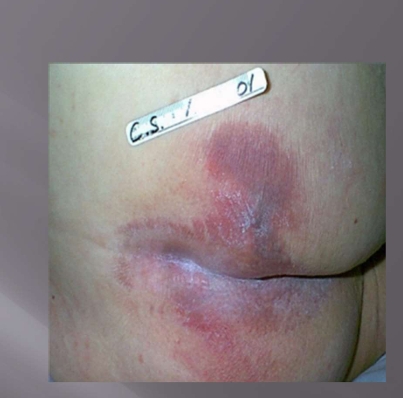
Pressure Injury Stage 1
intact skin with non-blanchable redness of a localized area
usually over bony prominence
darkly pigmented skin may not have visible blanching; its color may differ from the surrounding area
must touch to determine
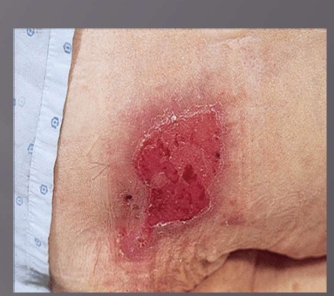
Pressure Injury Stage 2
partial thickness loss of dermis presenting as a shallow open ulcer with a red, pink wound bed, no slough
present as an intact or open/ruptured serum-filled blister
shiny or dry shallow ulcer without slough or bruising
This stage should not be used to
describe skin tears, tape
burns, perineal dermatitis,
maceration or excoriation.
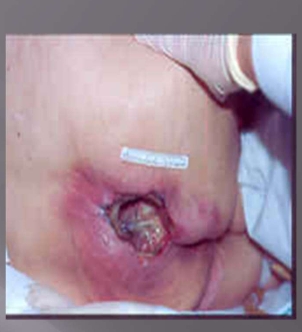
Pressure Injury Stage 3
Full thickness tissue loss
SQ fat may be visible but bone, tendon or muscle are not exposed
slough may be present but does not obscure the depth of tissue loss
include undermining and tunneling
depth varies by anatomical location
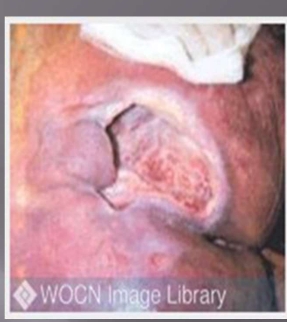
Pressure Injury Stage 4
Full-thickness tissue loss with exposed bone, tendon, or muscle
Slough or eschar may be present on some parts of the wound bed=
include undermining and tunneling
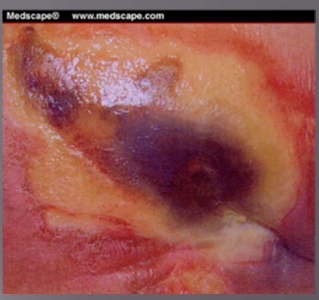
Pressure Injury- Deep Tissue Injury (sDTI)
Purple or maroon localized area of discolored intact skin or blood-filled blister
due to damage of underlying soft tissue from pressure and/or shear
the area may be preceded by tissue that is painful, firm, mushy, boggy, warner or cooler as compared to adjacent tissue
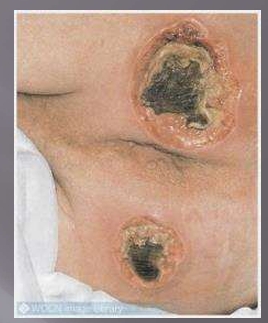
Pressure Injury- Unstageable
full thickness tissue loss
base of the ulcer is covered by slough (yellow, tan, gray, green, brown)
and/or eschar (tan, brown, black) in the wound bed
Pressure Injury Prevention
Support surfaces
Repositioning/ offloading
Moisture control
Toilet Scheduling
Regular Risk assessments
Minimize friction and shearing forces
Nutrition/Hydration
Barriers
Arterial Ulcers
consequences of obstruction or stenosis of an arterial lumen
interferes with blood transport to peripheral capillary bed
local ischemia results in necrosis and ulceration
Arteral Ulcers
Usually found tips of toes
wound bed pale or necrotic
little to no exudate
painful
diminished or absent pulses
Venous Ulcers
Venous HTN
Failure of Venomotor Pump Mechanism
Obstructed deep veins
Valvular dysfunction
faulty calf muscle pump
Backflow into superficial system
Venous Ulceration
drain a ton
Venous Ulcers
between ankles and knees
wound base dark red or may be covered with slough
moderate to large amounts of exudate
wound edges are irregular
edema is common
good pulses
Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Round, punched out lesions
High infection rate
associated with neuropathy
minimal drainage
painless
when infected lots of drainage
Wound Assessment
location
type of wound
size of wound
condition of the wound bed
characteristics of wound exudate
wound margins and peri wound skin
pain
nutritional status
Characteristics of healthy granulation tissue
Healthy:
bright red
moist
shiny
doesn’t bleed easily
Characteristics of unhealthy granulation tissue:
dark red/ bluish discoloration or pale
dehydrated
dull
bleeds easily
Dressing Selection
Appropriate for the wound type, tissue, depth and exudate volume
Maintain moist wound healing to reduce friction at wound surface
Minimizes pain and trauma when removing
Remains intact longer to reduce the need for frequent dressing changes
Optimizes wound bed preparation
Preserves peri-wound skin
reevaluate the dressing if it is causing pain or bleeding/trauma to wound or surrounding skin
soaking is required for removal
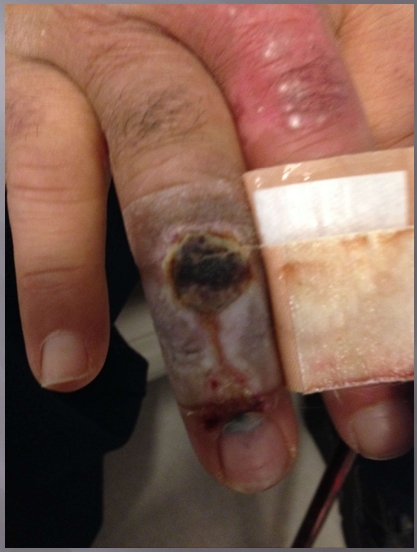
What injury is this?
Arterial ulcer (on the finger!) and a MASD
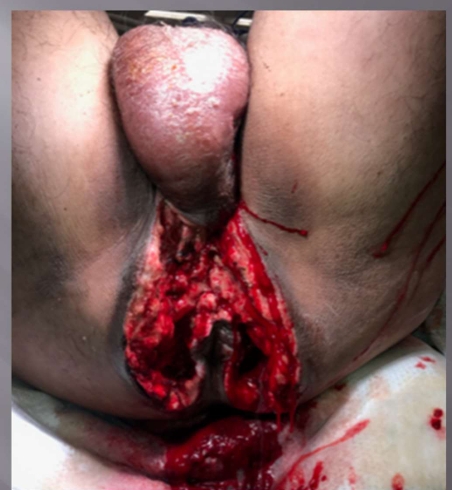
What injury is this?
Fournier gangrene (poorly controlled diabetic) in his perinium
Tx: VAC
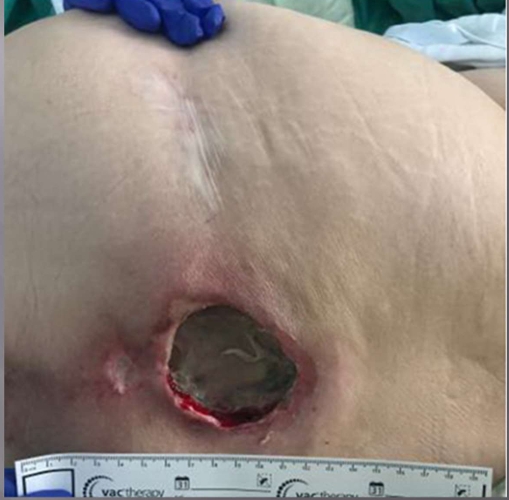
What is the inury?
Pressure Injury
Stage 4 (bone or tendon) and Unstagable (slough)
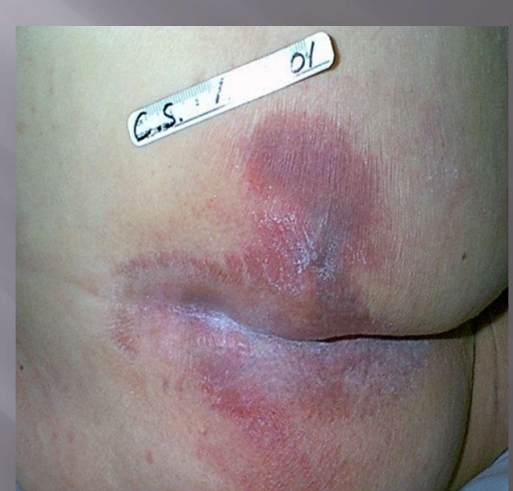
What injury is this?
Stage 1
non-blanchable
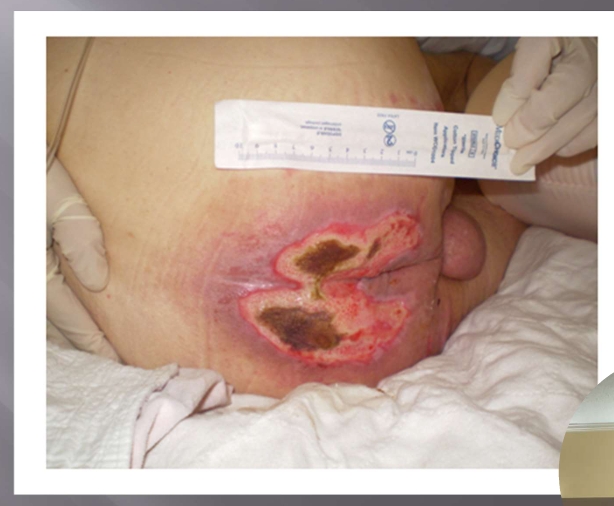
What Injury?
Incontinence Associated Dermatitis which became a unstageable pressure injury
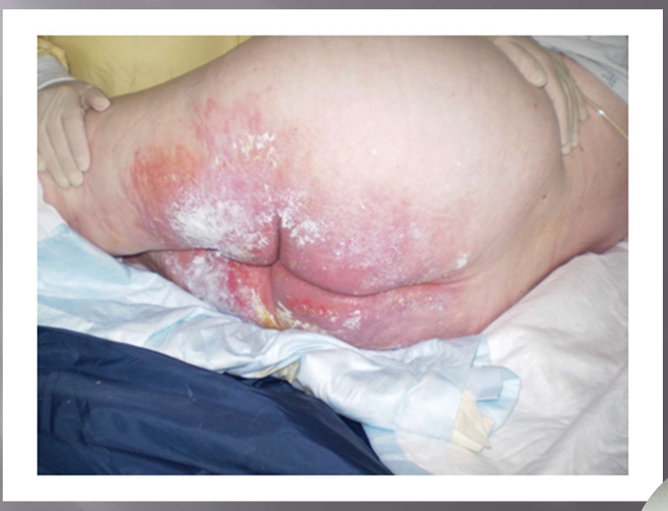
What injury?
Incontinence Associated Dermatitis
frequently loss stool (c diff)
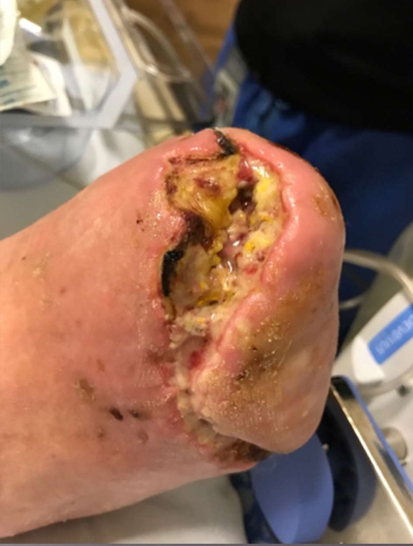
What Injury?
yellow tissue, irregular edges,
Post-surgical wound: Dhesis
Negative Pressure Wound therapy
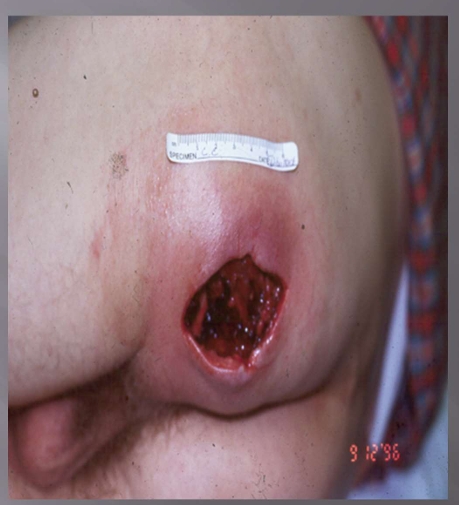
What injury?
Abscess (had a boil, I and D done)
Wound filler
wet to dry
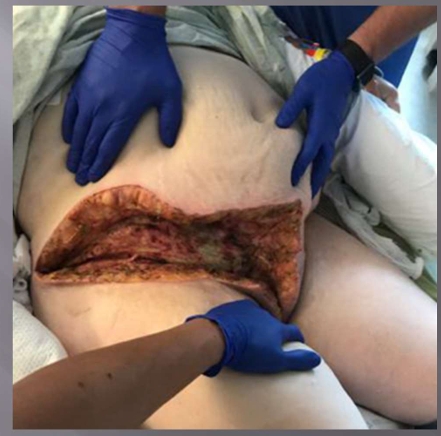
What injury?
Forinere gangrewre ??(infection froi labaia rto right flank
I and D proeedcuree to wash out
Negative 2PRessure Wound PRessure Woiudn therayp
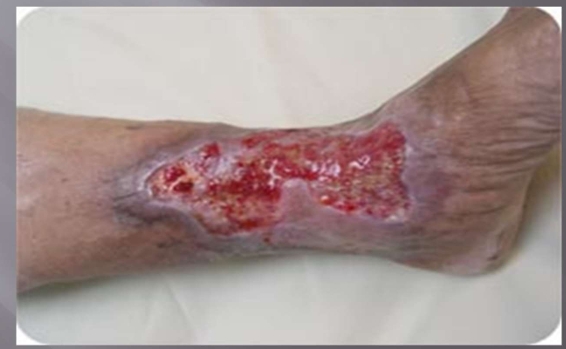
What injury?
Venous leg ulcer
Tx: absorptive dressings, Compression therapy
the most common leg ulcer in the US
makes up 60% of chronic wounds are leg ulcers
WEAR COMPRESSION SOCKS
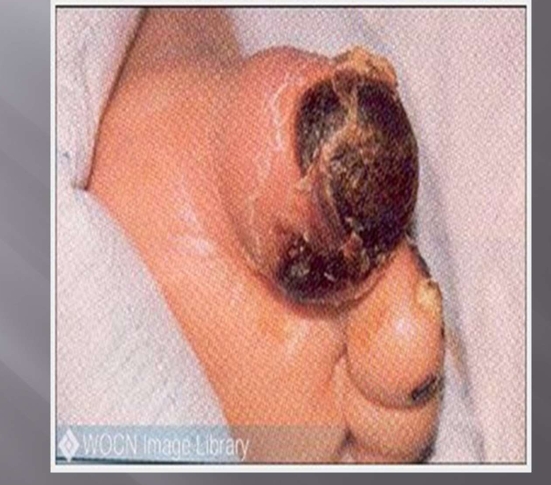
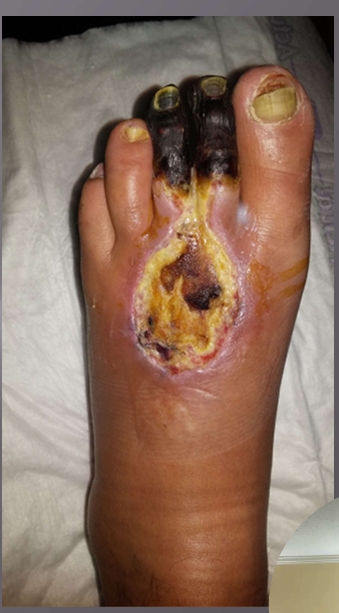
What injury?
Arterial ulcer (tip/top)
tip of the toe is turning black before the base of the toe
Must call vascular surgeon
no way to treat it, goal is to keep it dry once developed, and prevent wet gangrene
also control pain
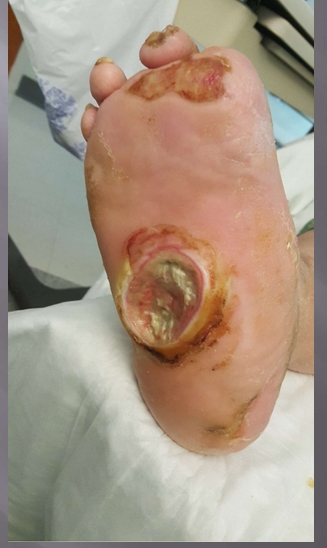
What injury?
Diabetic foot ulcer
poorly controlled, collapsed arch of the foot, its down instead of up
podiatric surgeon is needed
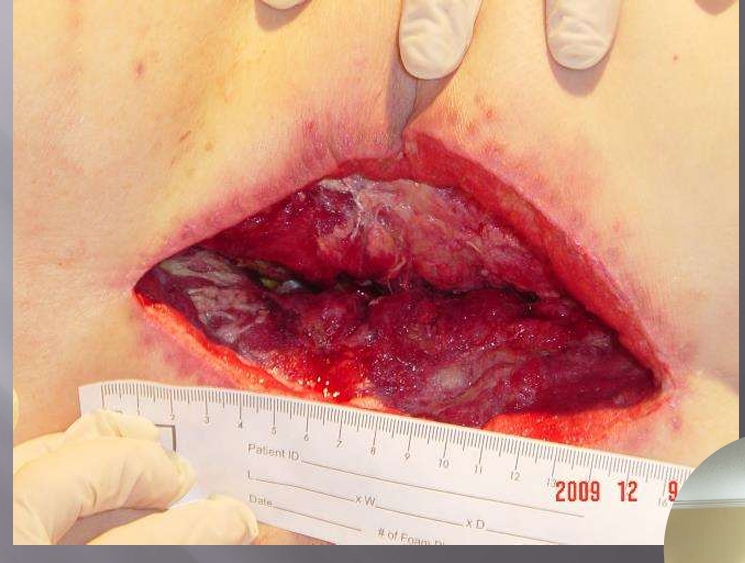
What injury?
Surgical incision that was left open for 3 days, lumbar incision, with hardware in
Tx: insulation negative pressure therapy
Veraflow Therapy: keep it as clean and bacteria free as quick as possible
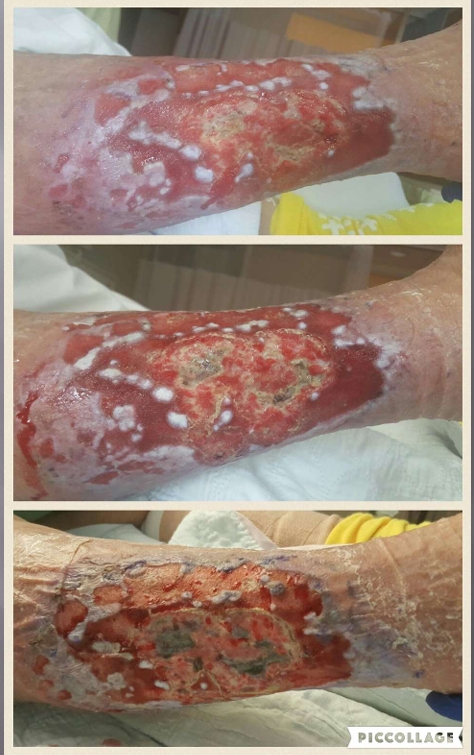
What injury?
Atypical wound
antimicrobial cleaning, IV antibiotics, compression therapy
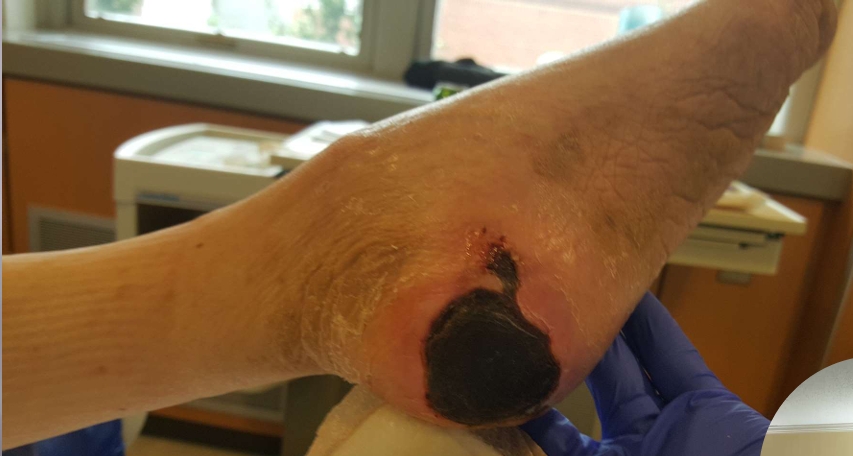
What injury?
Unstageable pressure injury of the heel
don’t properly offload the heel
Acceptable to OTA, black eschar over a heel pressure injury you can leave it intact, acts a biological dressing, ew
if the edges separates or become unstable can remove it