Diffusion and Osmosis Quiz
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Semi-permeable
the cell membrane is semi-permeable meaning it only allows certain molecules to pass through easily
(Semi- Permeable) Cells must exchange _____ and ______ with its environment, must cross the ____ __________
food and wastes
cell membrane
(Semi-Permeable) Water and gases (____) can move freely, proteins and carbohydrates (______) cannot
Small
Large
1.) Diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration (down the concentration gradient)
Occurs faster at higher temps
Smaller molecules move faster than larger ones
Example of diffusion
Drop of red dye in water, all water will turn red
(Diffusion) Passive transport-
no energy required
2.) Osmosis
The diffusion (high to low) of WATER through a semi-permeable membrane (move water)
Passive transport
3 types of osmosis
Everything wants to be even, balanced (Homeostasis)
Hypertonic Solution
When comparing 2 solution, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes is HYPERTONIC
Means “above strength
Solution has a high solute concentration than cell
Water is pulled out from the cell to equalize the solution and the cell will shrivel
15%?
Hypotonic Solution
When comparing 2 solutions, the solution with the lower concentration of solutes
Means “below strength” low strength
Solution has a lower solute concentration than cell
Water goes into cell causing it to swell
Isotonic
Concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside
Water moves in and out of the solution at the same rate
(Cell and solution its in are equal)
What is Facilitated Diffusion and what is an example
Movement of specific molecules across cell membrane through protein channels
Passive transport!
Ex. Red blood cells have a channel that’s specially designed for glucose to get in and out of the cell (otherwise glucose would be too large to do this)
Active transport
Using energy to move across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
Low to high concentration is needed for big particles or ions (charged) particles positive or negative)
(Active transport) the movement of macromolecules such as proteins or polysaccharides into or out of the cell is called ____ _______
Bulk Transport (This is for big stuff-take out the trash)
What are the two types of bulk transport
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Smaller particles move with a ________ ________
Protein Pump
Endocytosis
Cell membrane folds into a pouch (vesicle) and encloses the particle (endo—→ into)
Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis are types of endocytosis
Pinocytosis-
Phagocytosis-
Ingesting liquids
Ingesting solids (food)
Exocytosis
Wastes and cell produces leave cell (opposite of endocytosis)
________ is always first but if it doesn’t work then ______ is the second option
Diffusion
Osmosis
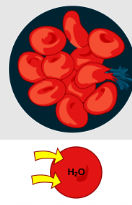
Is this hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic
Hypotonic

Is this hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic
Hypertonic
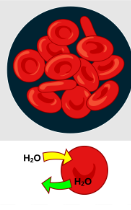
Is this hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic
Isotonic
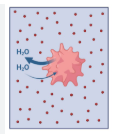
Is this solution Hypertonic, Hypotonic, or Isotonic
Hypertonic Solution
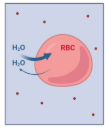
Is this solution Hypertonic, Hypotonic, or Isotonic
Hypotonic Solution
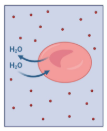
Is this solution Hypertonic, Hypotonic, or Isotonic
Isotonic Solution
For active energy what can it move materials from
Low to high concentration which makes it need energy to move materials because it moves opposite of the gradient
For Passive energy what can it move materials from
It moves materials from high to low and requires no energy because it moves with the gradient which allows it in the end to reach an equilibrium