HSCI 442
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:37 AM on 1/19/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
1
New cards
EDTA
* used in blood storage
* anticoagulant
* chelates to ions in blood to prevent clotting
* anticoagulant
* chelates to ions in blood to prevent clotting
2
New cards
RPMI-1640
* Roswell Park Memorial Institute Medium
* is a cell culture media
* supports cell growth and vitality
* is a cell culture media
* supports cell growth and vitality
3
New cards
FBS
* fetal bovine serum
* contains proteins and nutrients that support cell vitality
* contains proteins and nutrients that support cell vitality
4
New cards
HBSS
* Hank's Buffered Salt Solution
* composed of inorganic salts and supplemented with glucose
* used to wash cells
* promotes cell vitality and maintains optimal pH (7-7.4)
* composed of inorganic salts and supplemented with glucose
* used to wash cells
* promotes cell vitality and maintains optimal pH (7-7.4)
5
New cards
PBS
* Phosphate Buffered Saline
* a physiological balanced salt solution used as a rinse in cell culture
* used in dilutions, washing cell suspensions, and rinsing
* maintains pH
* a physiological balanced salt solution used as a rinse in cell culture
* used in dilutions, washing cell suspensions, and rinsing
* maintains pH
6
New cards
D-PBS
* Dulbecco's Phosphate-Buffered Saline
* used for dilutions, rinsing cells and as a buffer
* maintains pH
* typically contains lower in phosphate concentration and may include calcium, magnesium, or chloride
* used for dilutions, rinsing cells and as a buffer
* maintains pH
* typically contains lower in phosphate concentration and may include calcium, magnesium, or chloride
7
New cards
cold D-PBS
- slows down the metabolic processes of cells and keep the cells from dying
8
New cards
RBC lysis buffer
* lyses erythrocytes in single cell suspensions of hematopoietic tissues (e.g., spleen and human peripheral blood) w/ minimal effects on lymphocytes
* contains ammonium chloride
* contains ammonium chloride
9
New cards
trypan blue
* a viability stain used to differentiate dead cells (blue) from living cells (clear)
* binds to dead cells
* cell counter accounts for 1:2 dilution of cells in trypan blue
* binds to dead cells
* cell counter accounts for 1:2 dilution of cells in trypan blue
10
New cards
DMSO
* dimethyl sulfoxide
* cryoprotectant for cells
* penetrates the cell membrane by forming pores and thus prevents intracellular ice formation by reducing the water content inside the cell
* cryoprotectant for cells
* penetrates the cell membrane by forming pores and thus prevents intracellular ice formation by reducing the water content inside the cell
11
New cards
blood smear steps
1. place a small drop of blood on a clean slide--hold a second slide at a 30-40 degree angle on the slide in front of the drop
2. maintain contact and move second slide back to contact the drop, let the blood spread across the second slide by capillary action
3. maintain firm contact with the bottom slide and push the top slide in one motion to produce the smear
12
New cards
Wright's stain
* a combination of eosin (red) and methylene blue
* allows differentiation between white and red blood cells
* allows differentiation between white and red blood cells
13
New cards
Flow Staining Buffer
- contains HBSS and Pen/Step solution (antibiotic)
14
New cards
live/dead cell stain
* dye binds to dead cells--allow them to be removed from the analysis
* light sensitive
* light sensitive
15
New cards
Fc receptor blocking
* TruStain FcX PLUS anti-mouse CD16/32
* decreases non-specific antibody binding
* usually added when staining lymphocytes for flow cytometry
* decreases non-specific antibody binding
* usually added when staining lymphocytes for flow cytometry
16
New cards
anti-CD45R/B220 antibody
binds to B cells
17
New cards
anti-CD8 antibody
binds to CD8 T cells
18
New cards
antibody titration
allows researchers to determine the amount of necessary antibody needed for optimal stain resolution
19
New cards
paraformaldehyde
* PFA- formaldehyde in aqueous solution
* fixes cells in place
* fixes cells in place
20
New cards
anti-CD4 antibody
binds to CD 4 T cells
21
New cards
anti-NK antibody
binds to NK cells
22
New cards
cyanine dye blocking solution
* True-Stain Monocyte Blocker
* blocks non-specific binding of PE and APC
* blocks non-specific binding of PE and APC
23
New cards
compensation controls
* corrects for fluorescence spillover
* removes the signal of any given fluorochrome from all detectors except the one devoted to measuring that dye
* removes the signal of any given fluorochrome from all detectors except the one devoted to measuring that dye
24
New cards
FMO
* fluorescence minus one
* way of creating positive gates
* samples are stained with all the fluorophores in your panel, minus one of them
* way of creating positive gates
* samples are stained with all the fluorophores in your panel, minus one of them
25
New cards
Luria-Bertani
* lysogeny broth
* rich media used for bacteria growth
* rich media used for bacteria growth
26
New cards
Escherichia coli O127:H6 strain E2348/69
27
New cards
spectrophotometer
- measures bacteria concentration at optical density 600 nm- OD(600 nm) = 1x10^8 cells/ml
28
New cards
DMEM
* Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium
* supports cell growth
* lower glucose concentration than RPMI
* supports cell growth
* lower glucose concentration than RPMI
29
New cards
ovalbumin
egg white protein
30
New cards
sodium azide
* preservative
* prevents microbial contamination
* can be added to produce good storage buffer
* prevents microbial contamination
* can be added to produce good storage buffer
31
New cards
IgG
most abundant antibody found in the plasma
32
New cards
IgG1
most abundant and versatile
33
New cards
IgG2
* 1:1 mix of IgG2b and IgG2c
* no IgGa because mice lack the gene encoding antibody
* responds to bacterial capsular polysaccharide antigens
* no IgGa because mice lack the gene encoding antibody
* responds to bacterial capsular polysaccharide antigens
34
New cards
Tween (PBS-T)
* helps to prevent non-specific antibody binding
* to remove unbound antibody
* to remove unbound antibody
35
New cards
Casein (PBS-C)
* blocking buffer
* used for blocking excess binding sites on membrane and microplates in antibody-based detection
* used for blocking excess binding sites on membrane and microplates in antibody-based detection
36
New cards
alkaline-phosphatase (AP)
* enzyme bound to antibody in ELISA (secondary antibody)
* uses the substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate which produces a water-soluble yellow reaction product
* uses the substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate which produces a water-soluble yellow reaction product
37
New cards
p-nitrophenyl phosphate
* pNPP- substrate for AP
* produces a water-soluble yellow reaction product
* light sensitive reaction
* produces a water-soluble yellow reaction product
* light sensitive reaction
38
New cards
ELISA
* enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
* can be indirect or direct
* can be indirect or direct
39
New cards
immune system: anatomic barriers
* skin
* oral mucosa
* respiratory epithelium
* intestine
* oral mucosa
* respiratory epithelium
* intestine
40
New cards
innate immune defenses
* complement
* macrophages
* granulocytes
* natural killer cells
* macrophages
* granulocytes
* natural killer cells
41
New cards
adaptive immune defenses
* b cells
* t cells
* t cells
42
New cards
leukocytes
white blood cells
43
New cards
thrombocytes
platelets
44
New cards
erythrocytes
red blood cells
45
New cards
blood smear
a thin layer of blood smeared on a microscope slide and then stained in such a way to allow the various blood cells to be examine microscopically
46
New cards
purpose of blood smears
* look for parasites (e.g., malaria)
* hematological problems (e.g., sickle cell)
* cancer (e.g., leukemia)
* effects of chemotherapy
* hematological problems (e.g., sickle cell)
* cancer (e.g., leukemia)
* effects of chemotherapy
47
New cards
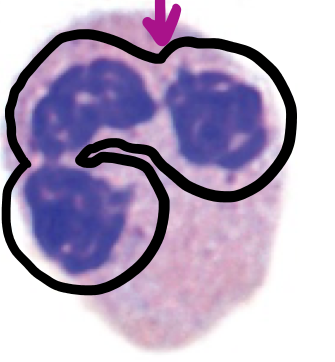
neutrophil
**role:** phagocytosis and killing of microorganisms
* granulocyte
* multi-lobed nucleus (normally 3-5)
* numerous small/purple granules
* constitutes 50-70% of white blood cells (i.e., most abundant)
* stay in circulation and are not present in healthy tissue
* generate inflammatory response
* granulocyte
* multi-lobed nucleus (normally 3-5)
* numerous small/purple granules
* constitutes 50-70% of white blood cells (i.e., most abundant)
* stay in circulation and are not present in healthy tissue
* generate inflammatory response
48
New cards
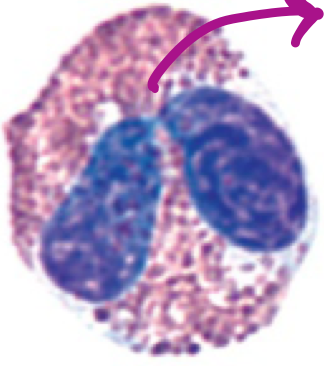
eosinophil
**role:** killing of antibody-coated parasites through release of granule contents
* bi-lobed nucleus (normally red/pink)
* numerous closely packed orange/red granules
* 1-4% of white blood cells
* increased in parasitic infections
* bi-lobed nucleus (normally red/pink)
* numerous closely packed orange/red granules
* 1-4% of white blood cells
* increased in parasitic infections
49
New cards
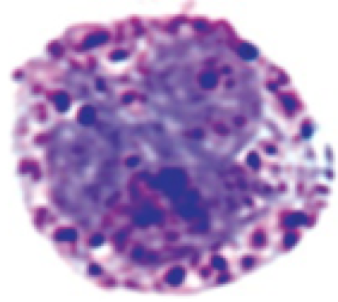
basophil
**role:** controlling immune response to parasites
* densely packed, large purpose cytoplasmic granules
* kidney-shaped nucleus (difficult to see)
* constitutes less than 1% of white blood cells
* increased during asthma
* densely packed, large purpose cytoplasmic granules
* kidney-shaped nucleus (difficult to see)
* constitutes less than 1% of white blood cells
* increased during asthma
50
New cards
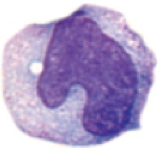
monocyte
**role:** circulating precursor cell to macrophage
* very fine, dark cytoplasmic granules
* kidney-shaped nucleus
* 2-10% of white blood cells
* round-ish shape
* located in blood
* continually turning over to macrophages in adulthood
* very fine, dark cytoplasmic granules
* kidney-shaped nucleus
* 2-10% of white blood cells
* round-ish shape
* located in blood
* continually turning over to macrophages in adulthood
51
New cards
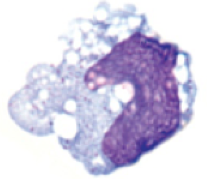
macrophage
**role:** phagocytosis and killing of microorganisms; activation of t cells and initiation of immune response
* large, irregular shape
* very large cytoplasm
* small nucleus
* cytoplasmic granules present
* found in tissue; become resident in tissues during childhood
* large, irregular shape
* very large cytoplasm
* small nucleus
* cytoplasmic granules present
* found in tissue; become resident in tissues during childhood
52
New cards
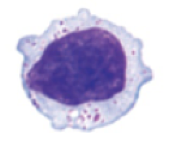
large lymphocyte
**role:** kills cells infected with certain viruses
* cytoplasmic granules
* irregular shaped nucleus
* natural killer cell
* cytoplasmic granules
* irregular shaped nucleus
* natural killer cell
53
New cards
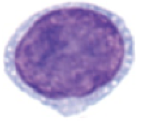
small lymphocyte
**role:** production of antibodies (b cells); cytotoxic and helper functions (t cells)
* little visible cytoplasm
* large, round nucleus
* small
* uniformly shaped
* no granules
* little visible cytoplasm
* large, round nucleus
* small
* uniformly shaped
* no granules
54
New cards
thick blood smear
* too large blood drop
* angle too high
* angle too high
55
New cards
thin blood smear
* too small blood drop
* angle too low
* angle too low
56
New cards
dependents of good blood smear
* size of the blood drop
* angle applied to the spreader
* speed/steadiness in pushing the spreader
* angle applied to the spreader
* speed/steadiness in pushing the spreader
57
New cards
qualities of good blood smear
* takes up 1/2-3/4 of the entire slide
* tongue-shaped
* lateral edges of smear are visible
* smooth without (many) irregularities
* tongue-shaped
* lateral edges of smear are visible
* smooth without (many) irregularities
58
New cards
bi-variate dot plots
* can see relationship between markers
* can see sub-populations in 2 dimensions instead of one
* can see sub-populations in 2 dimensions instead of one
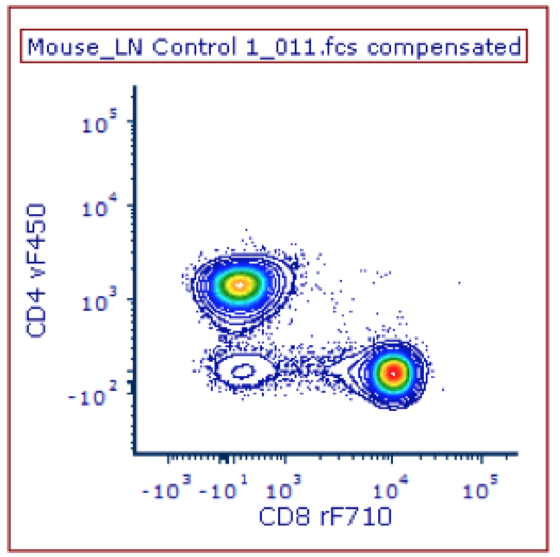
59
New cards
forward and side scatter
* show in linear scale; **exceptions**: small things like bacteria, extracellular vesicles, and nuclei
* provides gating of lymphocytes/exclusion of dead cells
* provides gating of lymphocytes/exclusion of dead cells
60
New cards
flow cytometry: log scale
* use for dynamic ranges
* compresses scale to get nice, round populations
* compresses scale to get nice, round populations
61
New cards
live/dead gating
* removes dead cells from sample
* dead cells can soak up antibody and give false positives
* dead cells can soak up antibody and give false positives
62
New cards
double positive events
can occur due to debris in sample or presence of dead cells
63
New cards
fluorescence parameters
* uses log scale; exception for low single increase
* provides gating of specific cell markers
* provides gating of specific cell markers
64
New cards
median fluorescence intensity (MFI)
* used to assess levels of target protein expression
* use median for log data
* use mean for linear data only
* use median for log data
* use mean for linear data only
65
New cards
MFI fold-change
* used to compare the expression level of antigen/marker between samples
* fold change = MFI (sample) / MFI (control) = times increase in marker
* can compare fold-change in MFI between treatments/samples
* fold change = MFI (sample) / MFI (control) = times increase in marker
* can compare fold-change in MFI between treatments/samples
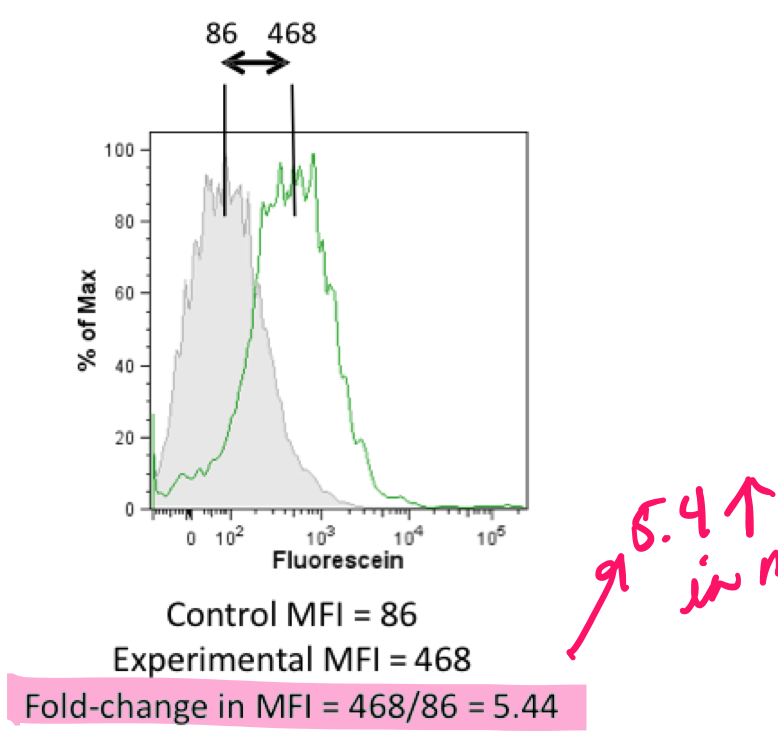
66
New cards
flow cytometry antibody titration
* ensures cells are not over or under-stained
* over-stain = non-specific staining
* under-stain = insufficient detection of target/molecule
* over-stain = non-specific staining
* under-stain = insufficient detection of target/molecule
67
New cards
flow cytometry
* measurements of cells/particles in liquid suspension
* simultaneous measurement of one or more characteristics of single cells as they pass through a laser
* simultaneous measurement of one or more characteristics of single cells as they pass through a laser
68
New cards
forward scatter
a measure of the relative cell size
69
New cards
side scatter
measures the relative complexity of the cell (e.g., granules, nucleus, etc.)
70
New cards
flow cytometry antibodies
* artificially conjugated to fluorochromes
* bind to specific surface molecules on target cells
* bind to specific surface molecules on target cells
71
New cards
longpass (LP) filter
* allow wavelengths longer than the filter rating to pass through
* reflects shorter wavelengths
* reflects shorter wavelengths
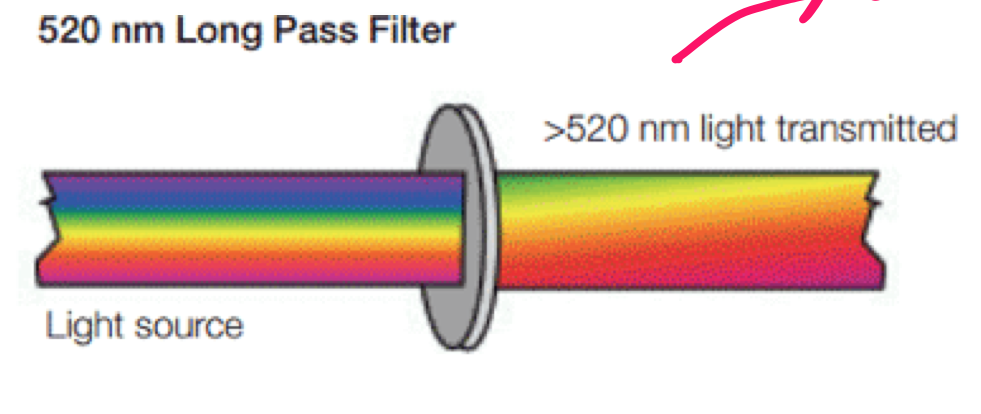
72
New cards
bandpass (BP) filter
* allow a relatively narrow range or band of light to pass through filter
* wavelengths outside range are reflected
* typically designated by 2 numbers
* wavelengths outside range are reflected
* typically designated by 2 numbers
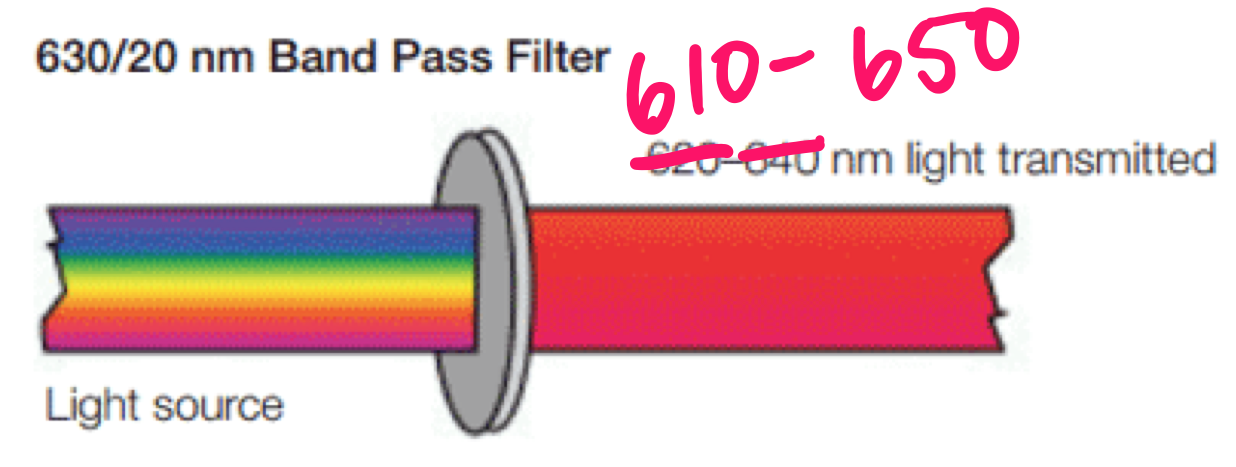
73
New cards
flow cytometry steps
1. emission of conjugated ab
2. detection of fluorescence
3. conversion to light into voltage
4. measure height, area, and width of light pulse
5. FCS file with raw data generated
6. data plotted
74
New cards
flow cytometry histograms
* shows the distribution of values for a specific parameter
* cannot see the relationship between 2 populations
* can miss sub-populations that have similar values in one parameter
* often used for MFI (represents half way mark of one population)
* cannot see the relationship between 2 populations
* can miss sub-populations that have similar values in one parameter
* often used for MFI (represents half way mark of one population)
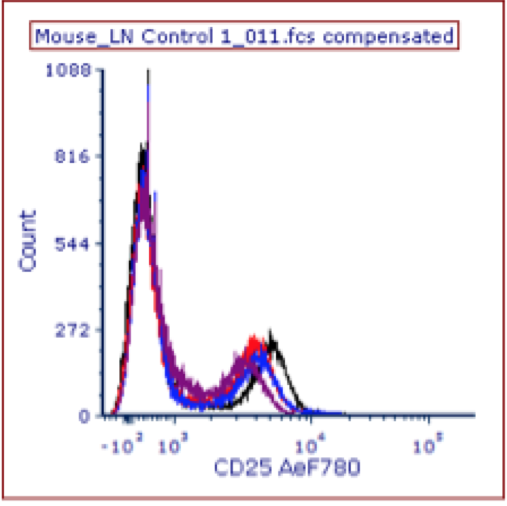
75
New cards
FMO
* fluorescence minus one
* controls are samples stained with all the fluorophores, minus one of them
* used to set the upper boundary for background signal using control, and thus can identify and gate positive populations in multicolor experiments
* shows the background and contributions from neighbouring fluorescence spillover
* can create gates with control and then apply to test sample
* controls are samples stained with all the fluorophores, minus one of them
* used to set the upper boundary for background signal using control, and thus can identify and gate positive populations in multicolor experiments
* shows the background and contributions from neighbouring fluorescence spillover
* can create gates with control and then apply to test sample
76
New cards
fluorophore spectrum
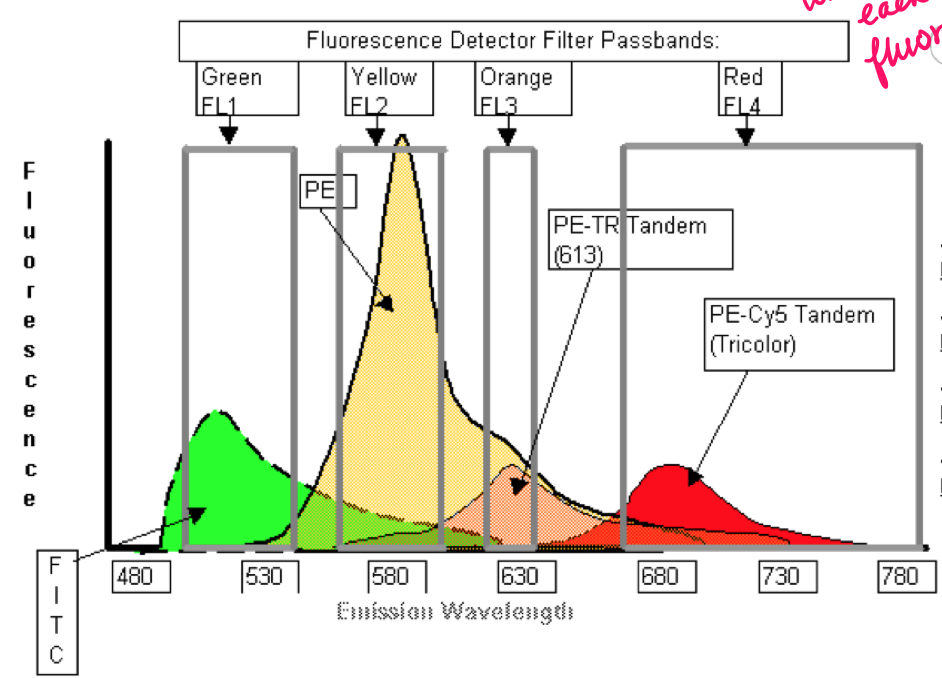
77
New cards
hematopoietic stem cell
cell by which all lymphoid cells are derived
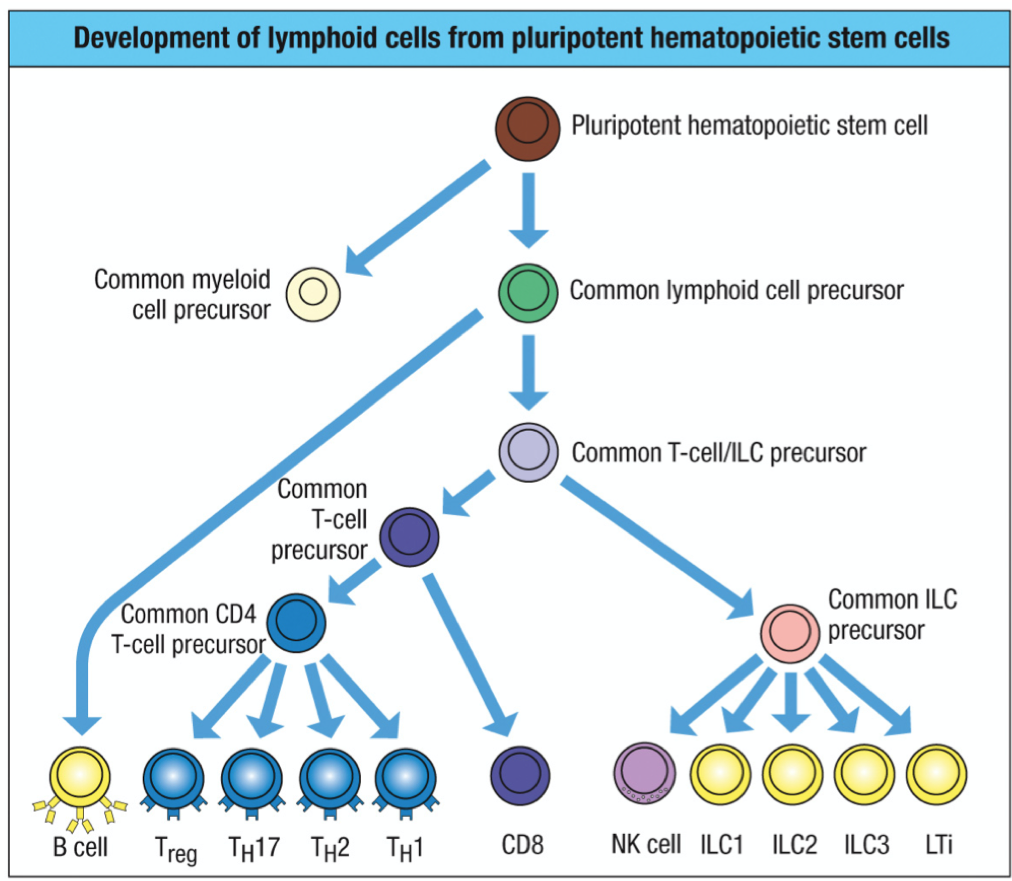
78
New cards
doublet discrimination
* helps remove events that are 2 or more cells stuck together
* reduces the contribution to false positive or double positive events
* set axis to FSC-A vs FSC-H, FSC-A vs FSC-W, SSC-A vs SSC-W, or SSC-A vs SSC-H
* reduces the contribution to false positive or double positive events
* set axis to FSC-A vs FSC-H, FSC-A vs FSC-W, SSC-A vs SSC-W, or SSC-A vs SSC-H
79
New cards
positive control
* standardize gating procedure and observe staining profile
* treated to induce positivity
* useful for rare positive populations or when expression is variable between sample
* treated to induce positivity
* useful for rare positive populations or when expression is variable between sample
80
New cards
biological controls
* e.g., Stim vs Unstim, T0 vs Time Course, Treated vs. Untreated
* any control you need to prove your hypothesis?
* any control you need to prove your hypothesis?
81
New cards
unstained control
used to evaluate inherent background and autofluorescence
82
New cards
common gating control
* FMO control
* positive control
* biological control
* unstained control
* positive control
* biological control
* unstained control
83
New cards
when is compensation required
when there is spectral overlap between 2 or more fluorophores
84
New cards
requirements when there is spectral overlap between fluorophores
* compensation
* for all fluorophores and live/dead stain
* FMO controls
* for all fluorophores and live/dead stain
* FMO controls
85
New cards
general gating strategy
1. lymphocytes
2. FSC single cells
3. SSC single cells
4. live cells
5. positive population
86
New cards
phagocytosis
* involved in innate response
* process in which phagocytes recognize, ingest, and kill pathogens
* pathogen uptake is usually through membrane receptors (e.g., complement, FC, scavenger receptor)
* process in which phagocytes recognize, ingest, and kill pathogens
* pathogen uptake is usually through membrane receptors (e.g., complement, FC, scavenger receptor)
87
New cards
phagocyte
cell which ingests and kills invading pathogens
* macrophages (mononuclear phagocytes)
* neutrophils (polymorphonuclear cells; PMNs)
* dendritic cells
* macrophages (mononuclear phagocytes)
* neutrophils (polymorphonuclear cells; PMNs)
* dendritic cells
88
New cards
Fc receptor
* located on phagocytes
* activated by IgG1 and IgG3 antibodies bound to pathogen
* interaction enables or accelerates phagocytosis
* activated by IgG1 and IgG3 antibodies bound to pathogen
* interaction enables or accelerates phagocytosis
89
New cards
3 cautions while working with spectrophotometer
1. avoid bubbles down in the cuvette
1. can affect the wavelength measurement
2. avoid touching the bottom of the cuvette to prevent smudges
3. throw out each use cuvette--they are not sterile
90
New cards
antibody hypervariable regions (complementary determining region)
* 3 heavy chain regions
* more variability than light chain
* HCDR3 has greater variability due to location in antigen binding region (middle/centre)
* 3 light chain regions
* less variable than heavy chain
* LCDR3 has greater variability due to location in antigen binding region (middle/centre)
* total of 6 binding interactions per antibody arm
* more variability than light chain
* HCDR3 has greater variability due to location in antigen binding region (middle/centre)
* 3 light chain regions
* less variable than heavy chain
* LCDR3 has greater variability due to location in antigen binding region (middle/centre)
* total of 6 binding interactions per antibody arm
91
New cards
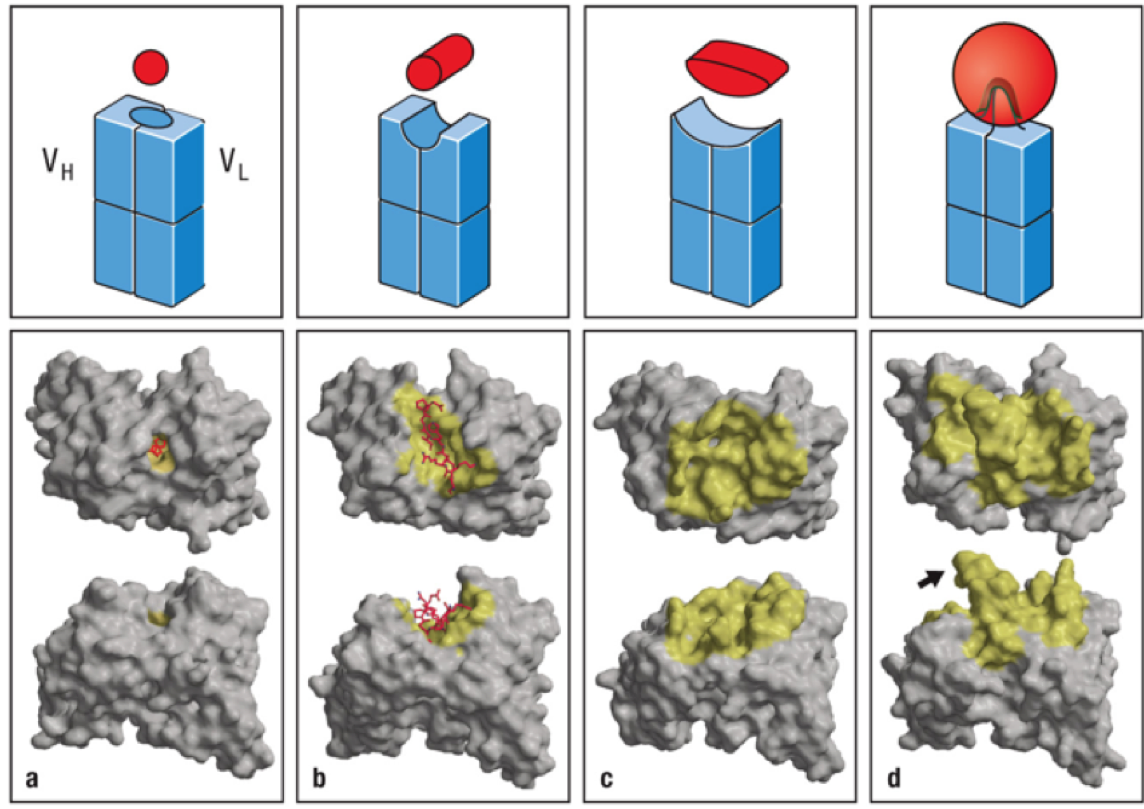
antibody-antigen binding shapes
* hapin
* a
* antigen nestles into antibody
* for small molecules
* peptide
* b and c
* antibody forms a groove/canyon
* dimple/crevasse
* d
* antibody points out towards antigen
* a
* antigen nestles into antibody
* for small molecules
* peptide
* b and c
* antibody forms a groove/canyon
* dimple/crevasse
* d
* antibody points out towards antigen
92
New cards
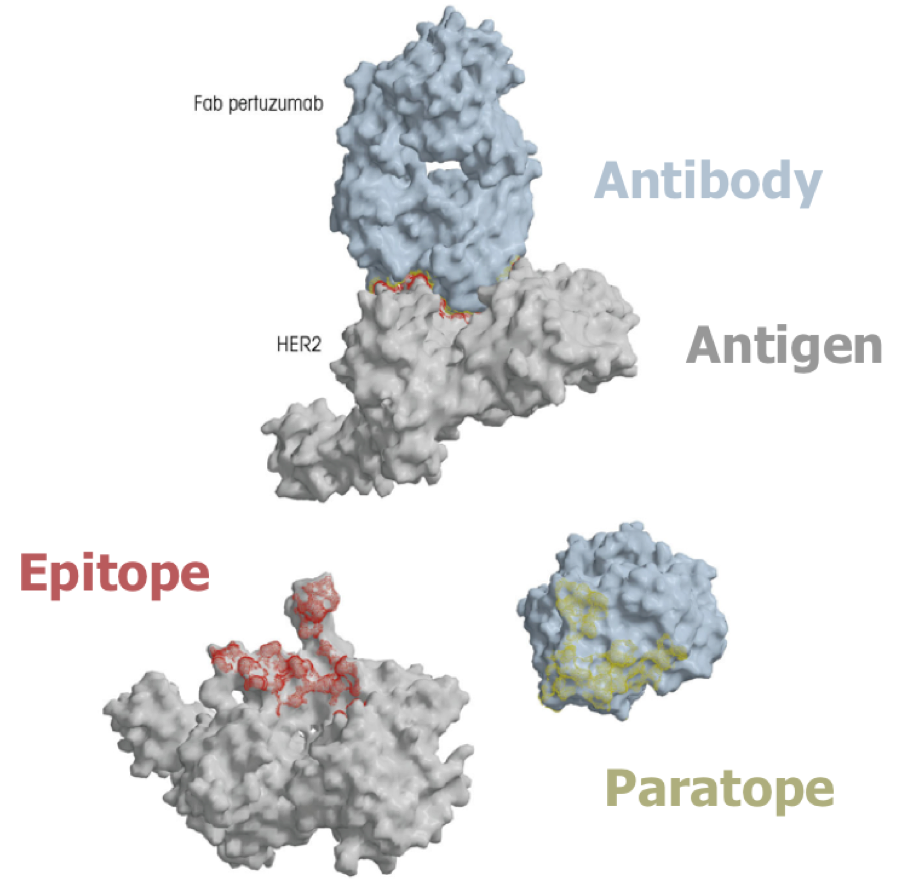
epitope
site on antigen to which the antibody binds
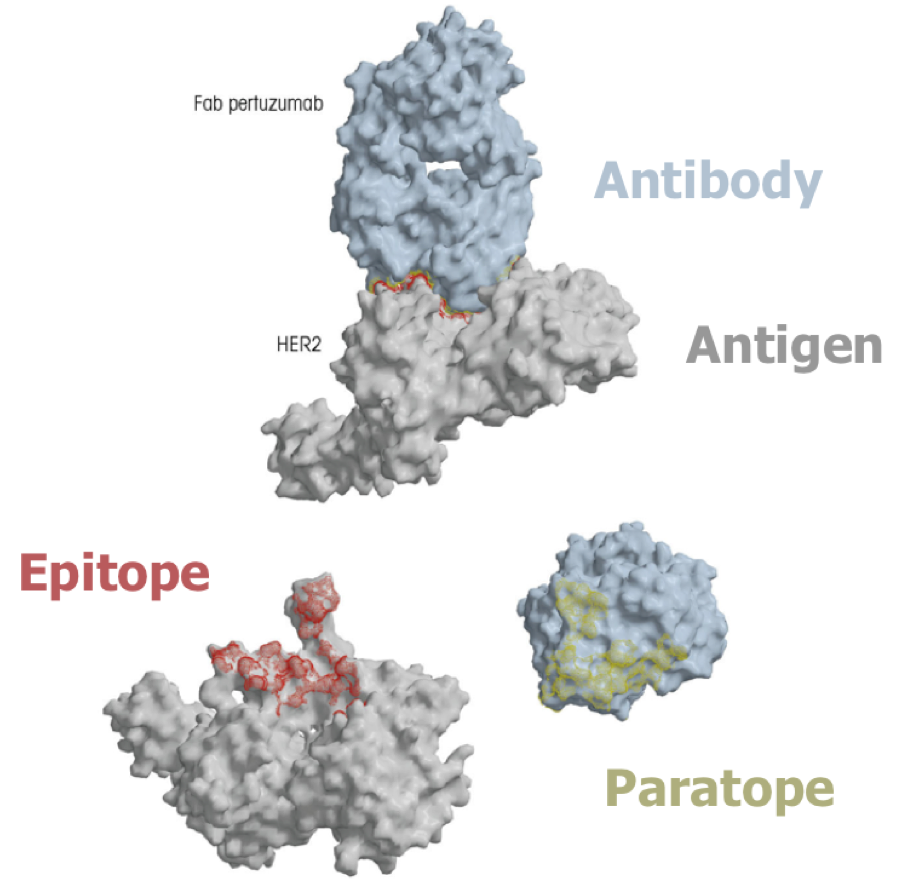
93
New cards
paratope
imprint on antibody of where the antigen was bound
94
New cards
epitope shapes
1. **conformational determinant**
2. **linear determinant**
3. **neoantigenic determinant**
95
New cards
conformational determinant
* binding is determined on antigen folding; folded peptide chain affects 3D spacing of residues that for epitopes
* non-linear; does not need to be a single protein (could be a quaternary structure)
* ab-ag binding is lost with denaturation
* non-linear; does not need to be a single protein (could be a quaternary structure)
* ab-ag binding is lost with denaturation
96
New cards
linear determinant
1. epitope is in same line sequence; does not depend on folding and does not need to be in consecutive sequence
2. accessible: ab can access epitope while antigen is folded
3. inaccessible: ab cannot access epitope while antigen is folded; only accessible through denaturation
4. ab-ag binding is not lost with denaturation
97
New cards
neoantigenic determinant
1. epitope does not exist in native protein/antigen
2. epitope is generated through a process that alters the structure, makeup or presentation of the protein (e.g., proteolysis)
98
New cards
adjuvants
added to vaccines to promote a greater immune response to vaccination
* Alum
* CpG-ODN
\*\* increase immunogenicity with slow release and when combined with bacteria
* Alum
* CpG-ODN
\*\* increase immunogenicity with slow release and when combined with bacteria
99
New cards
CpG oligonucleotides (ODNs)
* synthetic oligonucleotides
* contain unmethylated CpG dinucleotides in specific sequences (CpG motifs)
* activate toll-like receptor 9, leading to strong immunostimulatory effects
* contain unmethylated CpG dinucleotides in specific sequences (CpG motifs)
* activate toll-like receptor 9, leading to strong immunostimulatory effects
100
New cards
indrect ELISA required reagents
* antigen
* pure or semi-pure
* test solution containing antibody
* enzyme conjugate that binds Ig of immunized species
* pure or semi-pure
* test solution containing antibody
* enzyme conjugate that binds Ig of immunized species