Chapter 4 - Personality & values
Personality
@@Personality@@: sum total of ways in which an individual reacts and interacts with others.
- Measuring personality can be used in hiring decisions and forecasting who is better for a job.
- Personality determinants
- Heredity: factors determined at conception; one’s biological, physiological and inherent psychological makeup.
- Individuals personality has to do with heredity and the environment.
- Personality traits: enduring characteristics that describe an individual’s behavior.
@@Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)@@: personality test that taps four characteristics and classifies people into 1 of 16 personality types.
- 4 characteristics
- Extroverted VS introverted
- Sensing VS intuitive
- Thinking VS feeling
- Judging VS perceiving
- Weakness: it forces people into being one way or the other, there is no in-between you are either introverted or extroverted.
- Strength: good tool that provides career guidance and increases self-awareness.
@@Big Five personality model@@: personality assessment model that taps 5 basic dimensions
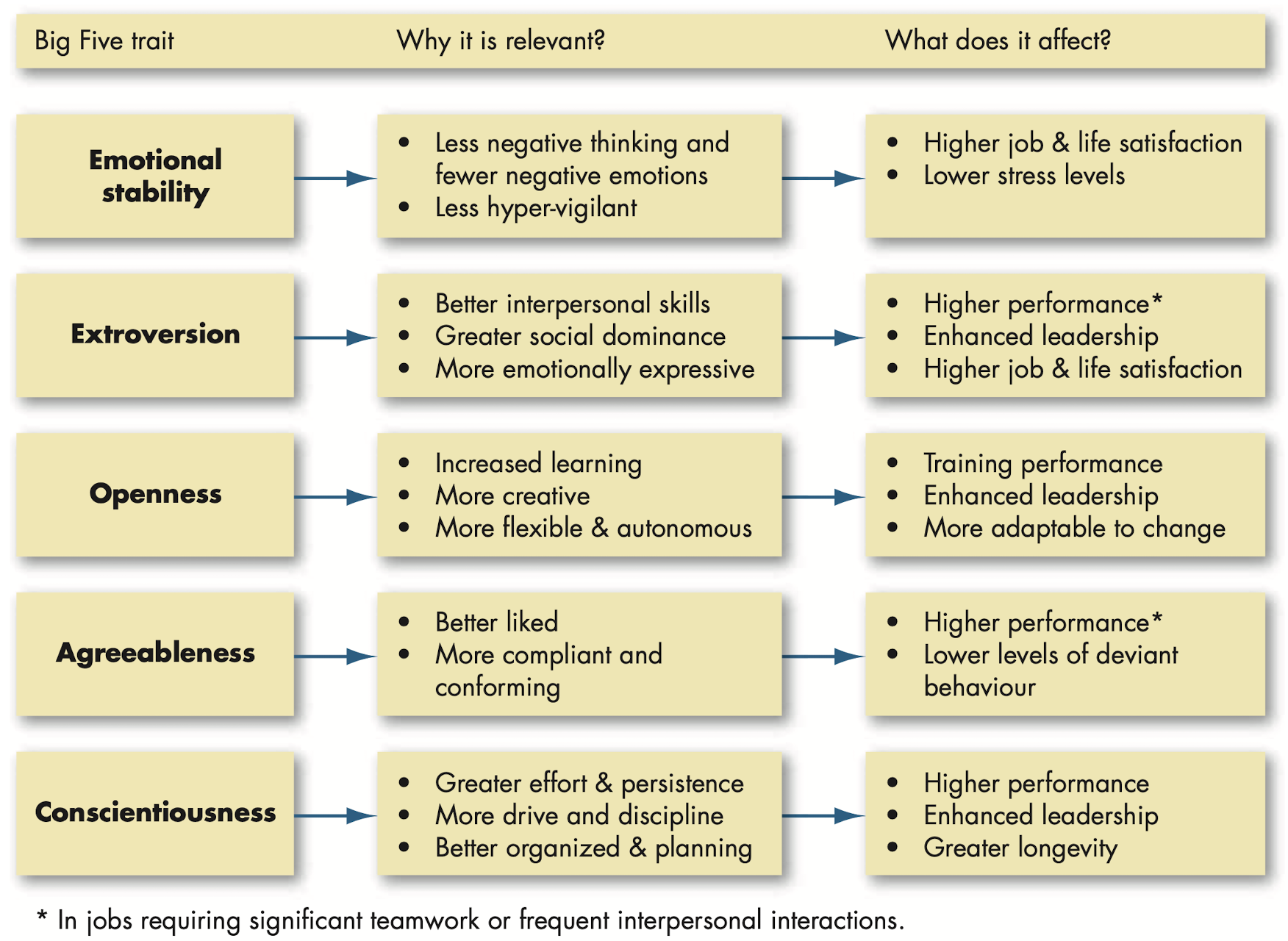
Extroversion: personality dimension that describes someone who is sociable, gregarious and assertive.
Agreeableness: personality dimension that describes someone who is good natured, cooperative and trusting.
Conscientiousness: personality dimension that describes someone who is responsible, dependable, persistent and organized.
Emotional stability: personality dimension that characterizes someone as calm, self confident, secure (positive) VS nervous, depressed and insecure (negative).
Openness to experience: personality dimension that characterizes someone in terms of imagination, sensitivity and curiosity.
How do the Big Five Traits predict behavior at work?
Other personality traits relevant to OB
Core-self evaluation: degree to which an individual likes/dislikes himself/herself as capable and effective, and whether the person feels in control of his/her environment or powerless over the environment.
Machiavellianism: degree to which an individual is pragmatic, maintains emotional distance and believes that ends can justify means.
Narcissism: tendency to be arrogant, have a grandiose sense of self importance, require excessive admiration and have a sense of entitlement.
Self-monitoring: personality trait that measures an individual's ability to adjust his/her behavior to external, situational factors.
Risk-taking → managers in large organizations may be more willing to take risks than entrepreneurs.
Type A personality: aggressive involvement in a chronic, incessant struggle to achieve more and more in less and less time and if necessary against the opposing efforts of other things other people
- Are always moving, walking and eating rapidly
- Feel impatient with the rate at which most events take place
- Strive to think or do two of more things at once
- Cannot cope with leisure time
- Are obsessed with numbers, measuring their success in terms of how many or how much of everything they acquire
Proactive personality: people who identify opportunities, show initiative, take action and persevere until meaningful change occurs.
Personality and situations
Situation-strength theory: theory indicating that the way personality translates into behavior depends on the strength of the situation.
Trait Activation Theory (TAT): theory that predicts that some situations, events or interventions “activate” a trait more than others.
Values
- @@Values@@: basic convictions that a specific mode of conduct or end-state of existence is personally or socially preferable to an opposite or converse mode of conduct or end-state of existence.
- @@Value system@@: hierarchy based on a ranking of an individual’s values in terms of their intensity.
- Classifying values
- @@Terminal values@@: desirable end-states of existence; the goals a person would like to achieve during their lifetime.
- @@Instrumental values@@: preferable modes of behavior or means of achieving one’s terminal values.
- Contemporary work values
- More importance on challenge and advancement, career progression, job satisfaction, personal growth and autonomy also, loyalty and trust.
Linking an individual’s personality and values to the workplace
- @@Personality-job fit@@: theory that identifies six personality types and proposes that the fit between personality type and occupational environment determines satisfaction and turnover.
- @@Person-organization fit@@: theory that people are attracted to and selected by organizations that match their values and leave when there is not compatibility.
Global implications
- Hofstede’s framework for assessing cultures
- @@Power distance@@: national culture attribute that describes the extent to which a society accepts that power in institutions and organizations is distributed unequally.
- @@Individualism VS collectivism@@
- Individualism: national culture attribute that describes the degree to which people prefer to act as individuals rather than as members of groups.
- Collectivism: national culture attribute that describes a tight social framework in which people expect others in groups of which they are a part to look after them and protect them.
- @@Masculinity VS femininity@@
- Masculinity: national culture attribute that describes the extent to which the culture favors traditional masculine work roles of achievement, power, and control. Societal values are characterized by assertiveness and materialism.
- Femininity: national culture attribute that indicates little differentiation between male and female roles; a high rating indicates that women are treated as the equals of men in all aspects of the society.
- @@Uncertainty avoidance@@: national culture attribute that describes the extent to which a society feels threatened by uncertain and ambiguous situations and tries to avoid them.
- @@Long-term orientation VS short-term orientation@@
- Long-term orientation: national culture attribute that emphasizes the future, thrift and persistence.
- Short-term orientation: national culture attribute that emphasizes the present and accepts change.
- GLOBE framework for assessing cultures
- Similar to Hofstede’s, but with 2 added dimensions:
- @@Humane orientation@@
- @@Performance orientation@@