Food Animal Repro
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Dairy vs calf-cow
o For dairies: tighter 12-month calving intervals maximize milk production and ensure cows are bred back soon after calving.
o For beef cow-calf: aim for a compact calving window (spring calving, fall weaning) to produce uniform calf crops and market groups.
Age at first calving
Heifers should calve by ~24 months. Earlier calving (without compromising growth) means more lifetime productivity.
Why are extra days open important?
Costs money! $2-5 per day to feed the animal
Natural cover (bulls)
Used more so in calf-cow operations. The bulls detect estrus, less labor is required.
Risks of natural cover
Variable conception, STI transmission, bull maintenance cost
Heat detection + AI
Required careful observation since standing heat only lasts 12-18hrs. Can use tail paint or activity monitors to improve success
What is the AM-PM rule?
If cow shows heat in the morning, inseminate that evening
Timed AI example
o Example: Ovsynch (GnRH → PGF → GnRH → AI).
o Why it works: synchronizes follicular waves and luteal regression, so ovulation timing is predictable.
Timed AI limitation
Less effective in anestrus cows (no CL to regress)
CIDR synch (progesterone implant + PGF)
o Supplies progesterone, resets ovarian cycle, prevents persistent follicles.
o More reliable than Ovsynch in non-cycling cows.
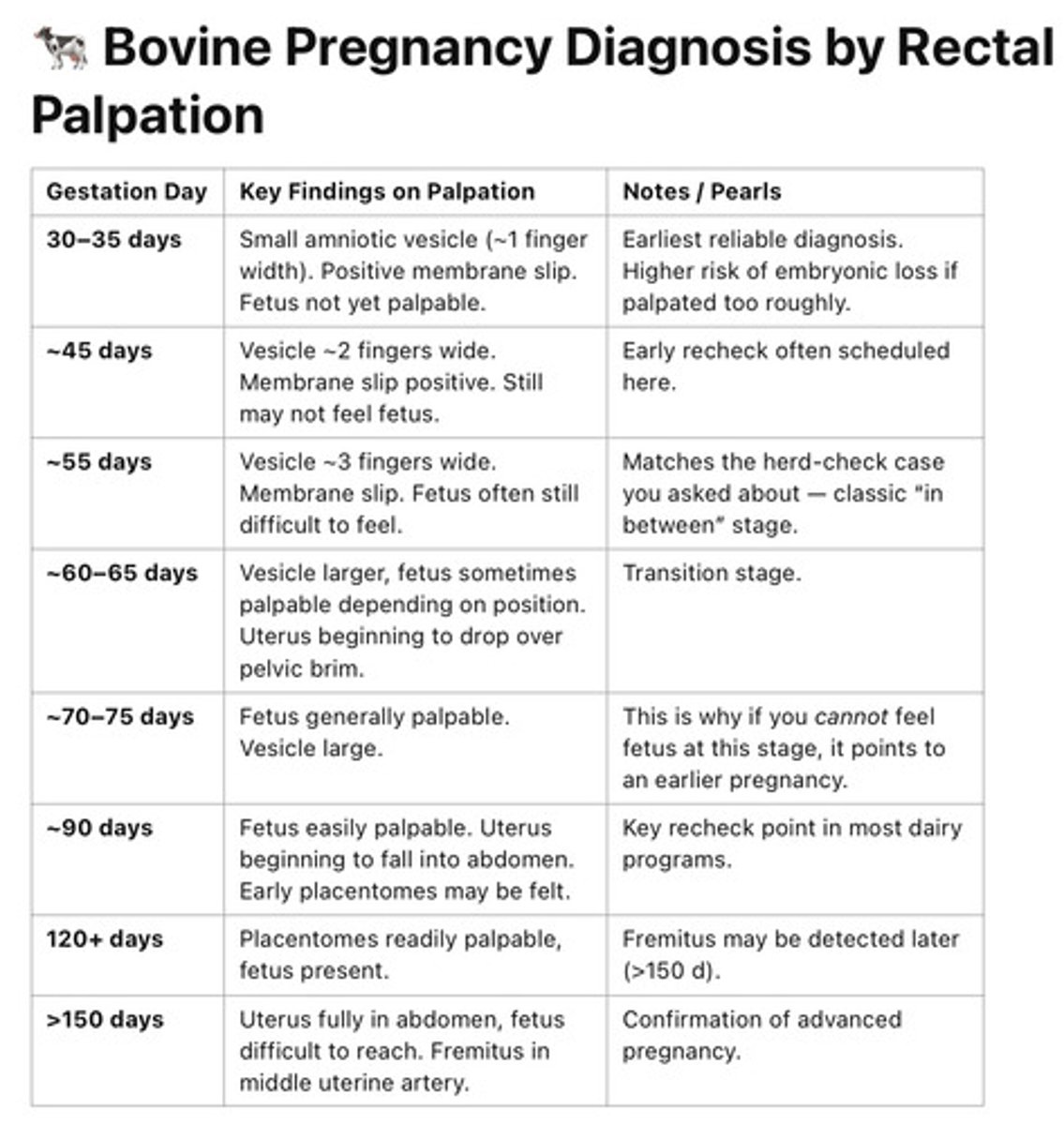
Rectal palpation pregnancy detection
o Can detect as early as ~30-35 days (amnionic vesicle, membrane slip).
o Risk: very early palpation may increase embryonic loss.
Ultrasound pregnancy detection
o Accurate at 28-32 days.
o Can identify twins, nonviable embryos, and fetal sex (>60 days).
o Why often preferred: early, safe, and provides more information.
Hormone assays pregnancy detection
o Progesterone (d21-24): high = CL present, but not specific for pregnancy.
o PAG tests (BioPryn, DG29): sensitive/specific but can stay positive after abortion/parturition.
Freemartinish
o Female twin to a male; ~90% sterile.
o Why: male hormones + anti-Müllerian hormone from shared placenta suppress female tract development.
Other anomalies leading to incomplete tracts and infertility
unicornuate uterus, hypoplasia, segmental aplasia
Types of anestrus
o Behavioral anestrus: cycling but silent heats (esp. high producers).
o True anestrus: no CL, minimal follicles. Common in underfed heifers or early lactation cows.
Why do cows have anestrus?
energy deficiency suppresses GnRH/LH pulses
What is cystic ovarian disease?
Fluid-filled structure >3 cm or persisting >10-14 days
Follicular cyst
thin-walled, low P4, high estrogen
Luteal cyst
thick-walled, high P4 → anestrus
Why are cysts important?
Prolongs interval to conception, lowers fertility.
Cyst treament
-Transvaginal ultrasound guided cyst ablation
-GnRH then PGF 7-10 days later
-CIDR-synch — most reliable way to treat
Granulosa cell tumor
o Most common ovarian neoplasm.
o May produce steroids → abnormal behavior.
o Treatment: surgical removal → normal fertility if contralateral ovary intact.
Retained fetal membranes
>24 hrs, often immune dysfunction, dysfunction, milk fever, Vit E/Se deficiency,, possibly PGF deficiency
Retained fetal membranes treatment
Takes 8 days for the villous attachments to necrose. Stay out of the uterus, leave the membranes, and monitor rectal temp. If rectal temp >103, begin treatment for metritis with systemic antibiotics
Retained fetal membranes consequences
Expensive, delayed conception, and comorbidities (metritis, ketosis, LDA, pyometra)
Metritis
o <10 DIM, foul discharge, large flaccid uterus, systemic illness possible.
o Treat with systemic antibiotics if febrile/sick (e.g., ceftiofur).
Metritis protocol
watch discharge and temp for first 10 days in milk. If abnormal discharge AND sick/fever = give antibiotics. Can use flunixin only if endotoxic
Endometritis
o >26 DIM, purulent discharge, enlarged cervix, no systemic signs. Cervix > 7.5cm
o Delays conception, ↑ culling.
o Treatment: hormonal (PGF), intrauterine therapies (limited evidence).
Pyometra
o pus-filled uterus + persistent CL, cow is anestrus.
o Why: infection at first ovulation prevents PGF release → CL persists.
o Treatment = PGF to lyse CL, evacuate uterus.
Relationship of uterine diseases
o RFM → metritis → endometritis → pyometra (continuum).
o All reduce fertility, extend days open, ↑ culling risk.
Diagnostic approach to infertility
1. Rule out pregnancy.
2. Evaluate anatomy (congenital issues, adhesions).
3. Assess ovarian function (cycling vs. anestrus, cystic).
4. Review history (nutrition, disease, calving).
5. Consider bull infertility if herd-level problem.
Early embryonic death
<40 days; appears as open. Up to 20% loss is normal
Abortion
40-260 days; ~3-4% pregnancies; 80% infectious
Premature delivery
260 days-term; calf may survive
Stillbirth
full-term but born dead. Often dystocia/asphyxia.
Neonatal death
survive <24 hrs; congenital, dystocia, or infectious.
Venereal transmission abortion
Trichomoniasis and campylobacter venerealis
Trichomoniasis
protozoa from carrier bulls → EED, pyometra, repeat breeders, test and cull bulls. Reportable. Cull positive bulls and test with preputial scraping
Campylobacter venerealis
-Presents very similarly to trich. Prologned estrus cycle/return to heat
-Culture/histopath, vaccinate!
-SS fetus or C jejune causes sporadic abortion in cattle and CAN infect humans
Reportable infectious cause of abortion
Brucella abortus and trichomonas
Brucella abortus
zoonotic, eradicated in most US herds, but persists in wildlife (Yellowstone). Causes 5-7 mo abortions, leathery placenta. Milk ring test, vaccinate calves
BVDV
fetal infection outcomes vary with gestation (EED, PI calves, congenital defects). If suspect, collect ear notch from all calves before the next breeding season!
IBR (herpesvirus)
abortion storms, autolyzed fetuses. Shed in semen. Vaccinate
Lepto
late-term abortion, hemolytic disease, poor conception (esp. L. hardjo in first lactation animal). Vaccinate
Neospora caninum
abortion storms, vertical transmission → lifelong carriers. Diagnose with histopath of fetal brain
Mycotic abortion
thickened placenta, dermatitis on fetus
Diagnostic work up of abortions
• History: stage of gestation, herd vaccination, environment, nutrition.
• Samples: placenta (best tissue), fetus, dam's blood (paired serology), herd-mates' samples.
• Expectations: only ~25-40% of bovine abortions get a definitive diagnosis, even with full work-up.
• Why limited success: tissue often autolyzed, multiple causes possible, and many sporadic toxins/stresses leave no trace.
Puberty
when cow reaches 45% mature body weight
When to breed cow
when she is 55% mature body weight and 90% mature body height
When to calve cow
when she is 85% mature body weight and 95% mature body height
Post partum onset of cyclicity
• Direct correlation to energy balance!!! First ovulation is 15-25 days but can be 50-70 days if she is energy deficient
• It is also LH dependent
• Number of pre-breeding ovulations is directly correlated with subsequent conception rate
Rectal palpation CHART