1.3 -Toxicology in Public Health and Environmental Health
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Who is most impacted by the environment?
Low and middle income countries bear the greatest share of environmental disease
How do contaminants travel in the environment?
Soil/waste
Groundwater
Landfill gas
Offsite sources
Exposure routes
What are the routes of exposure to environmental contaminants?
Inhalation (lungs)
Ingestion (GI tract)
Dermal (skin)
Clinical practice: additional routes such as injection
How are chemicals absorbed through the respiratory tract?
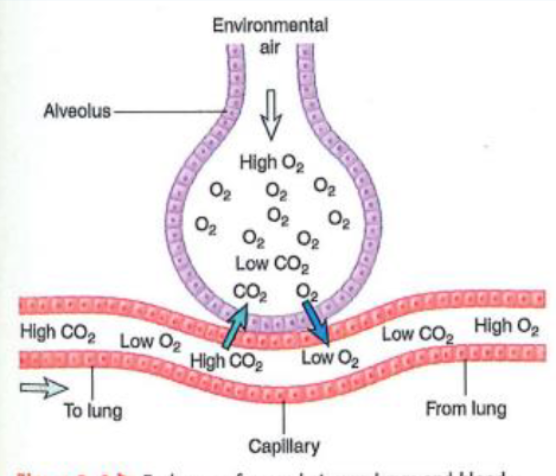
The surface area of lungs is large and allows for rapid uptake and release of certain molecules
For particulate matter (smaller particles), they move deeper into the respiratory system. They move through alveolar cells and are carried to other organs and can also carry absorbed materials
What are chemicals that can be exposed through vaping?
Nicotine
Formaldehyde and flavoring diacetyl (both cause lung damage)
Ultrafine particles
Heavy metals including lead
Cancer causing chemicals
When chemicals are absorbed into the skin, the amount absorbed depends on what factors?
Whether the skin is damaged (cuts, abrasions, etc.)
Thickness of the outer layer (stratum corneum) of the skin
Skin temperature (absorption increases with temperature)
Physical and chemical properties of the chemical
Concentration of chemical on skin
Amount of time the chemical on skin
Location - hair follicles, sweat ducts, sebaceous glands
How are chemicals absorbed through the GI tract?
Through the small intestine as it has a large surface area to facilitate nutrient absorption. Chemicals can also be absorbed into the body through the small intestine
How does the FDA handle dietary supplement products?
FDA is not authorized to review dietary supplement products for safety and effectiveness before they are marketed. However, the FDA is responsible for taking action against adulterated or misbranded dietary supplement products AFTER they reach the market. (bruh)
What are the four parts of the environmental risk assessment?
How much chemical is present?
How are people exposed and how much?
How toxic is it?
What is the likelihood of an adverse effect?
Which act regulated many airborne contaminants?
The Clean Air Act
What is one category of regulated contaminants and what does it include?
Criteria Air Pollutants":
Particulate matter
Lead
Ground-level ozone
Carbon monoxide
Sulfur dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide
How small are particulate matters?
Less than 10 microns in diameter
Why are particulate matters the greatest risk?
Because they can cause…
Premature death in people who have heart or lung disease
Nonfatal heart attacks
Irregular heartbeat
Aggravated asthma
Reduced lung function
Increased respiratory symptoms (airway irritation, coughing, or difficulty breathing)
Who are most susceptible to the effects of particle pollution exposure?
Children, older adults, and people with heart or lung diseases
How does lead affect children ages 0-6 years old?
Reduced IQ, learning problems, and behavioral problems
How does lead affect pregnancies?
Lead can be stored in the bones with calcium and during pregnancy, lead can be released with calcium from the mother’s bones and expose the fetus or breastfeeding infant to lead
How does lead affect fetuses and infants?
Preterm birth or low birthweight
Damage to baby’s brain, kidneys, nervous system
Increased leaning and behavioral problems
Reduced IQ
What are the health effects of breathing ozone?
Chest pain
Coughing
Throat irritation
Airway inflammation
Reduced lung function
Damage to lung tissues
Can worsen bronchitis, emphysema, and asthma
How can elevated CO levels affect people?
Reduced oxygen to heart and angina (chest pain), affects people who have a reduced ability to get oxygenated blood to the heart
How does sulfur dioxide affect people?
Can make breathing difficult, sensitive individuals include children and those with asthma
How does nitrogen dioxide affect people?
Irritate respiratory airways, aggravate respiratory diseases (particularly asthma), longer exposures may contribute to the development of asthma and increase risk of respiratory infections, and sensitive individuals include children, elderly, and those with asthma