Anatomy- Lymphatic System
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
lymphatic system is the nexus btwn …
cardiovascular, immune, and digestive systems
primary functions
1) help maintain fluid balance
2) immune function
3) dietary fat absorption and transport
components of the lymphatic system
1) clear fluid
2) lymphatic vessels
3) lymphoid tissue
lymphoid tissue composition
1) cells
reticular cells
T and B lymphocytes
macrophages
2) gels
3) fibers (reticular)
lymphoid tissue serves as:
stations for lymphocytes
can activate and multiply
surveillance point for lymphocytes and macrophages
primary lymphoid organs
where B and T cells mature
B cells: red bone marrow
T cells: thymus
where do lymphocytes travel after maturation
secondary lymphoid organs
s[leen
lymph nodes
tonsils
under normal conditions, which riving force is slightly greater?
filtration
what do lymphatic capillaries do with extra fluid from filtration/reabsorption?
it absorbs, and eventually send it back into systemic circulation to maintain fluid balance
where are lymphatic found in relation to blood vessels
lymphatic capillaries weave btwn tissues and blood capillaries in the LOOSE connective tissues of the body
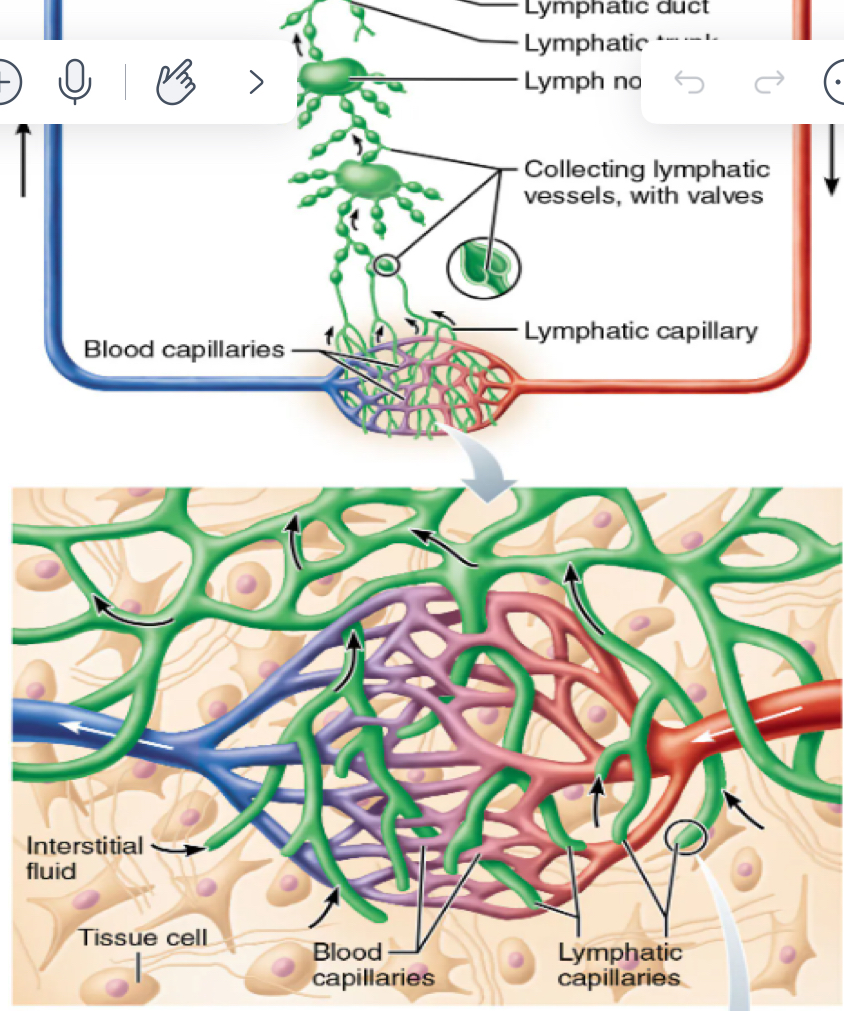
permeability of capillaries
flap like mINI VALVES that open when interstitial pressure > lymphatic capillary pressure
down pressure gradient
anchored to connective tissue by collagen fibers and prevent collapse
promote on eway flow; prevents draining into interstitium
why does inflammation make lymphatic capillaries more permeable
in response to inflammatory cytokines lymphatic capillaries develop openings to allow the uptake of cells
transport pathogens to lymph nodes for removal
downside?→ cancer takes advantage of process/travels through lymph
larger lymphatic vessels
lymphatic capillaries→ collecting lymphatic vessels→ lymphatic trunks→ lymphatic ducts
composition of lymphatic vessels
same three layers as veins
externa
media
intima
thinner and have more valves (due to low pressure)
lymph transport
lacks a pump
mvmt is slow, but facilitated by:
rhythmic smooth muscle contraction
arterial pulsations
skeletal muscle contractions
function of lymph nodes
1) filter lymph
macrophages remove pathogens and debris
2) immune system activation
antigen presentation
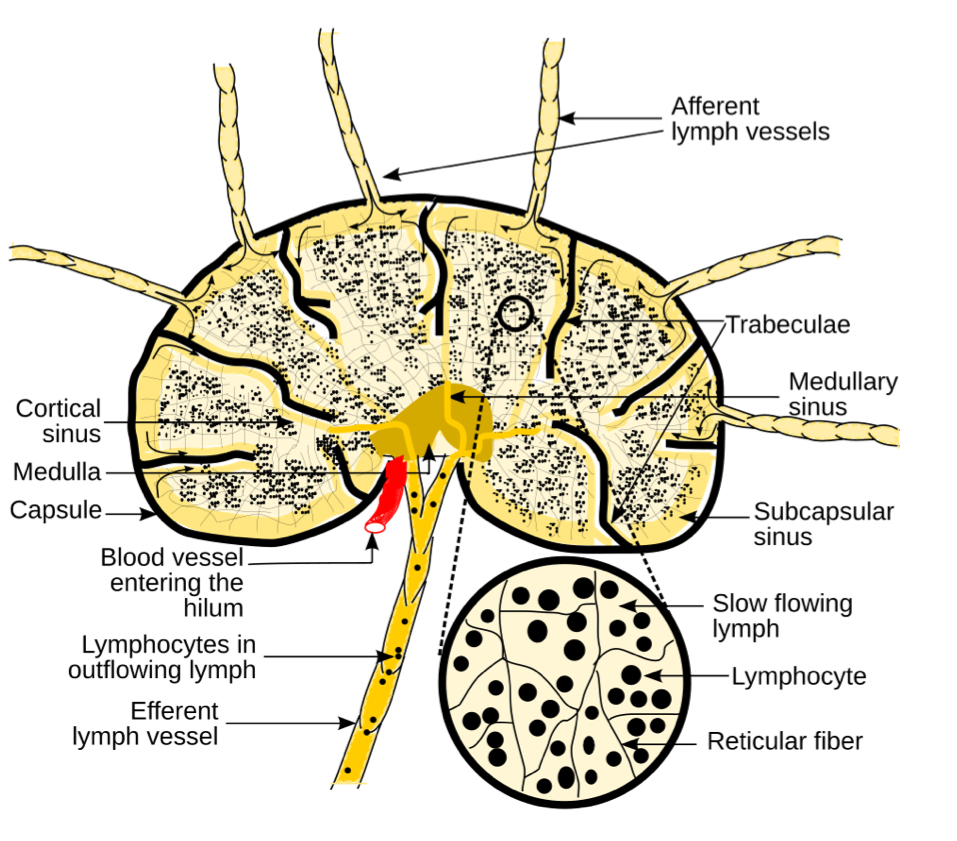
lymph node structure
>2.5cm in length
outer dense fibrous capsule
trabeculae divide node into compartment
internal reticular mesh
lymphatic capillaries spanned by reticular fibers
MACROPHAGES: phagocytosis
T and B LYMPHOCYTES: interacting with APCs and will proliferate if stimulated
lymph enters through AFFERENT vessels, is filtered and leaves vis EFFERENT vessels
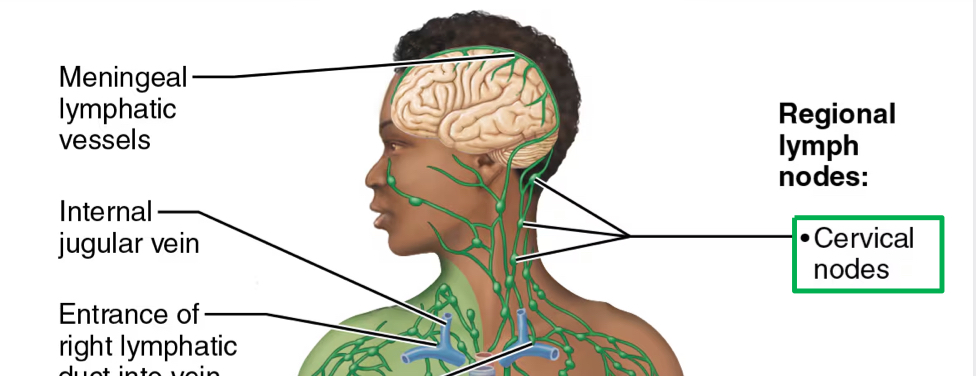
cercvical nodes
ear/nose/throat/eyes
all potential routes of infection
inguinal nodes
genitourinary tract
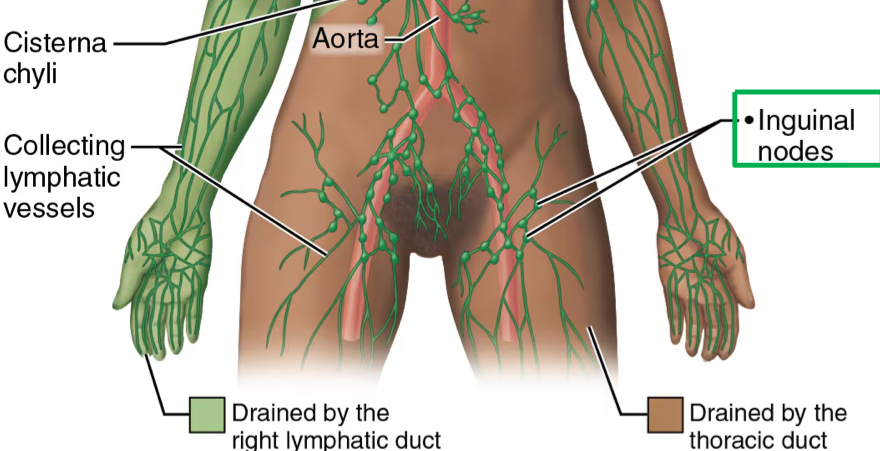
other clinically important groups of lymph nodes
axillary nodes
epitrochanter nodes
supraclavicular nodes
popliteal nodes
lymphadenopathy
when “bad sample’ is detected, there is INCREASED blood flow and PROLIFERATION OF LYMPHOCYTES within lymph nodes involved
can be detected with palpation
what is the most concerning sign of malignancy
supraclavicular lymphadenepathy
lymph nodes of head and neck
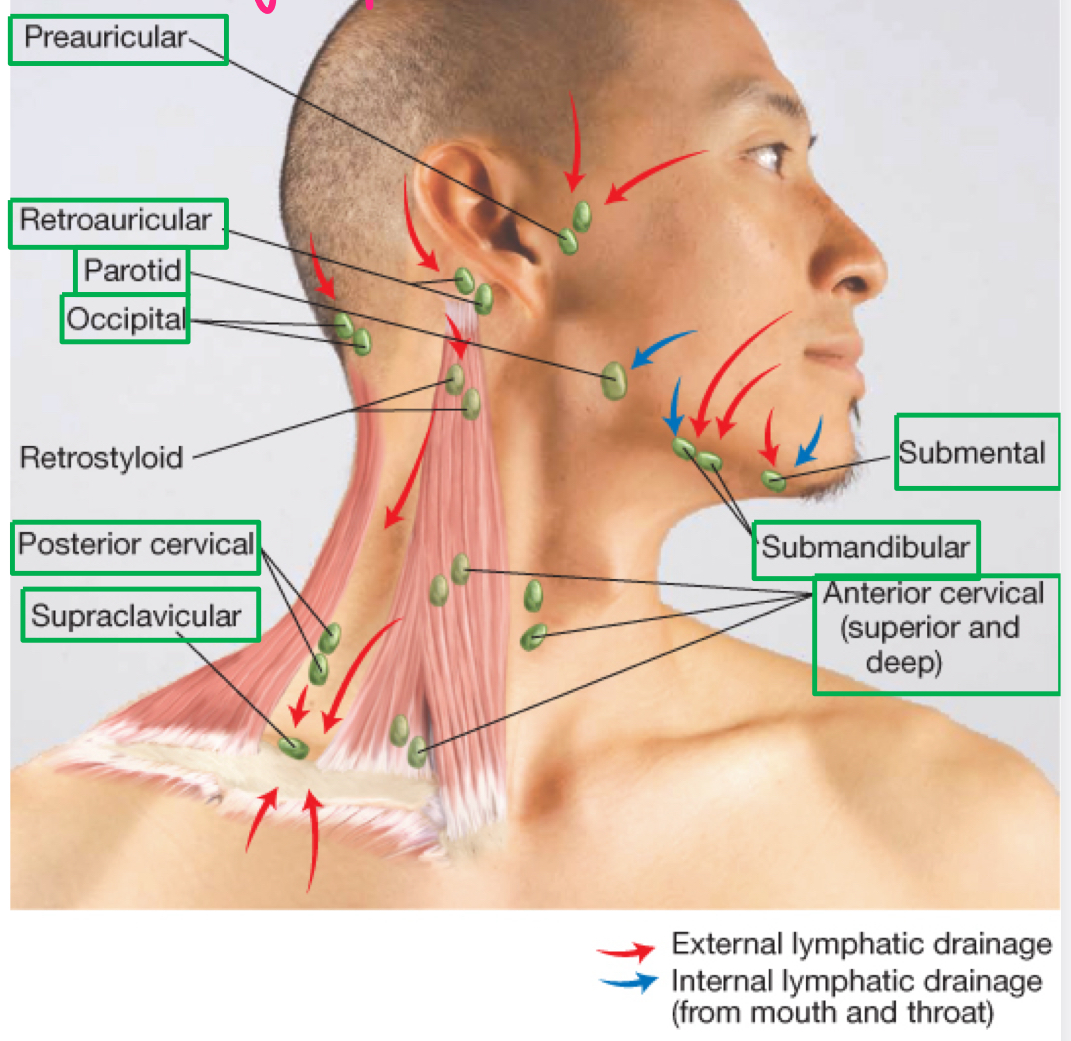
where do all lymphatics drain toward?
subclavian veins
lymphatic trunks
the largest lymphatic vessels drain into lymphatic trunks
R and L JUGULAR trunks (head and neck)
R and L SUBCLAVIAN trunks (upper extremities)
R and L bronchomediastinal trunks (thorax)
INTESTINAL trunk (abdomen)
R and L LUMBAR trunks (lower extremities)
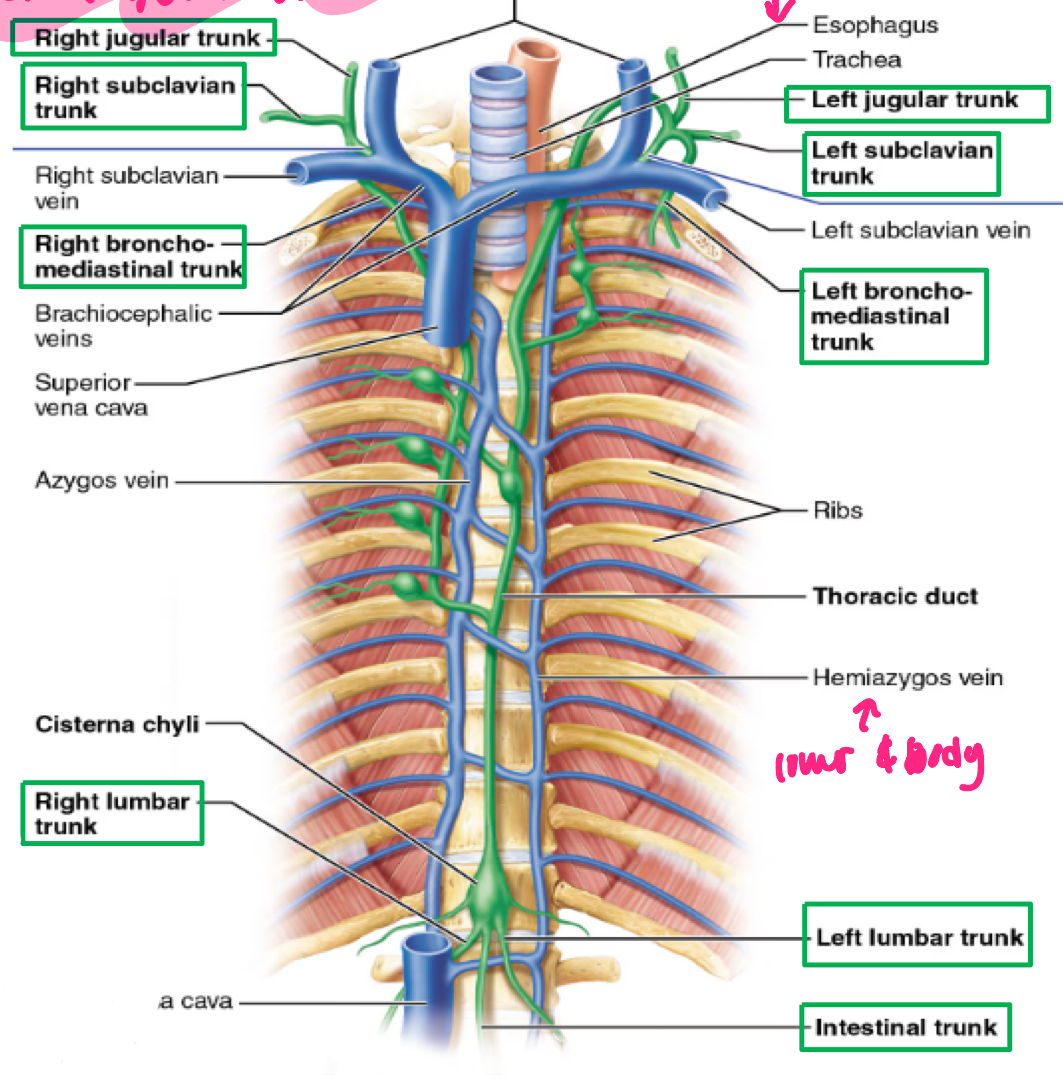
lymphatic ducts
lymphatic trunks lead to two lymphatic ducts that drain into subclavian veins
R LYMPHATIC DUCT → R subclavian
THORACIC DUCT→ L subclavian
CISTERNA CHYLI: enlarged sac that begins the thoracic duct (meeting point of lumbar and intestinal)
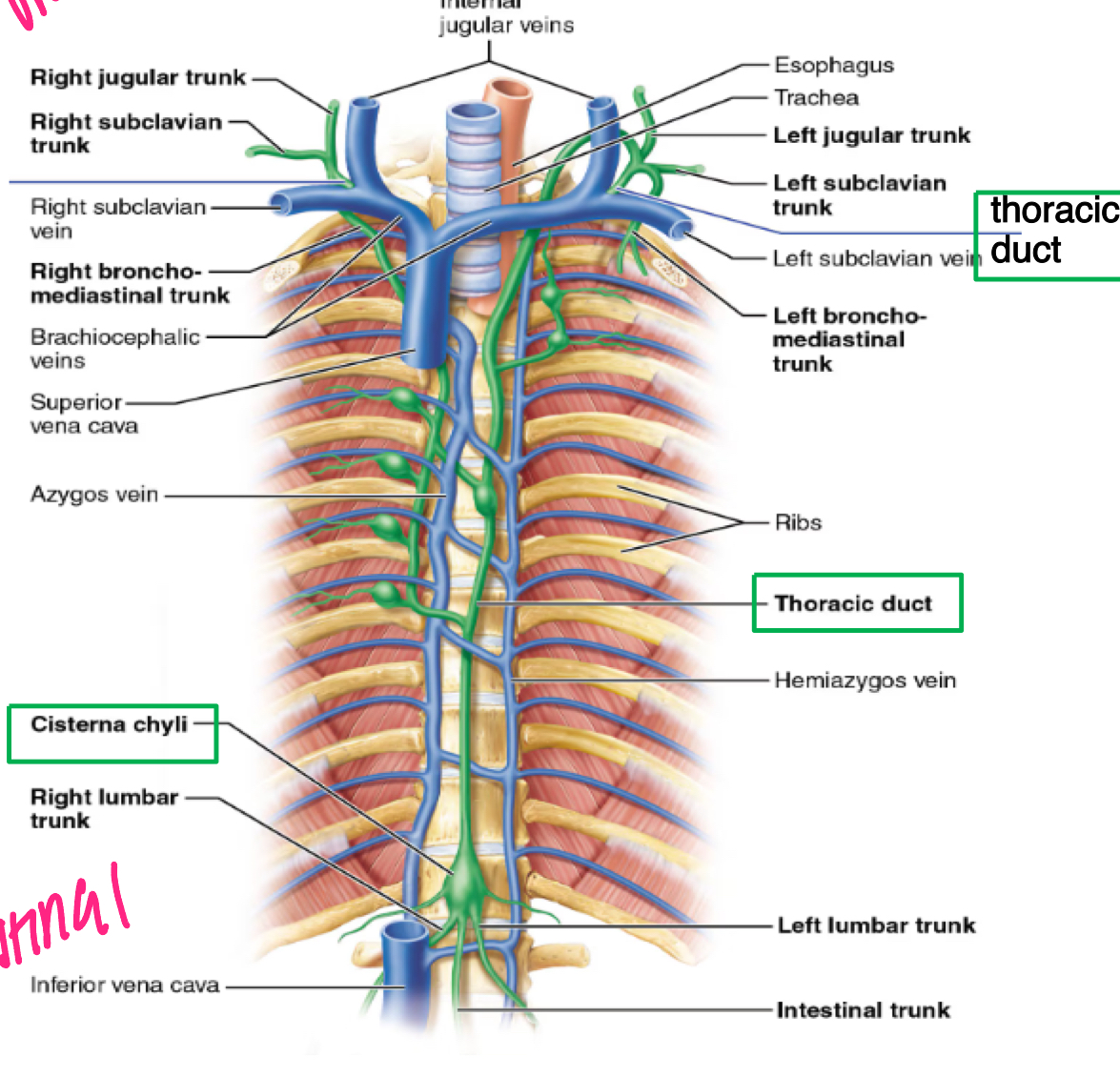
right lymphatic duct
empties at junction of RIGHT INTERNAL JUGULAR and TIGHT SUBCLAVIAN VEINS
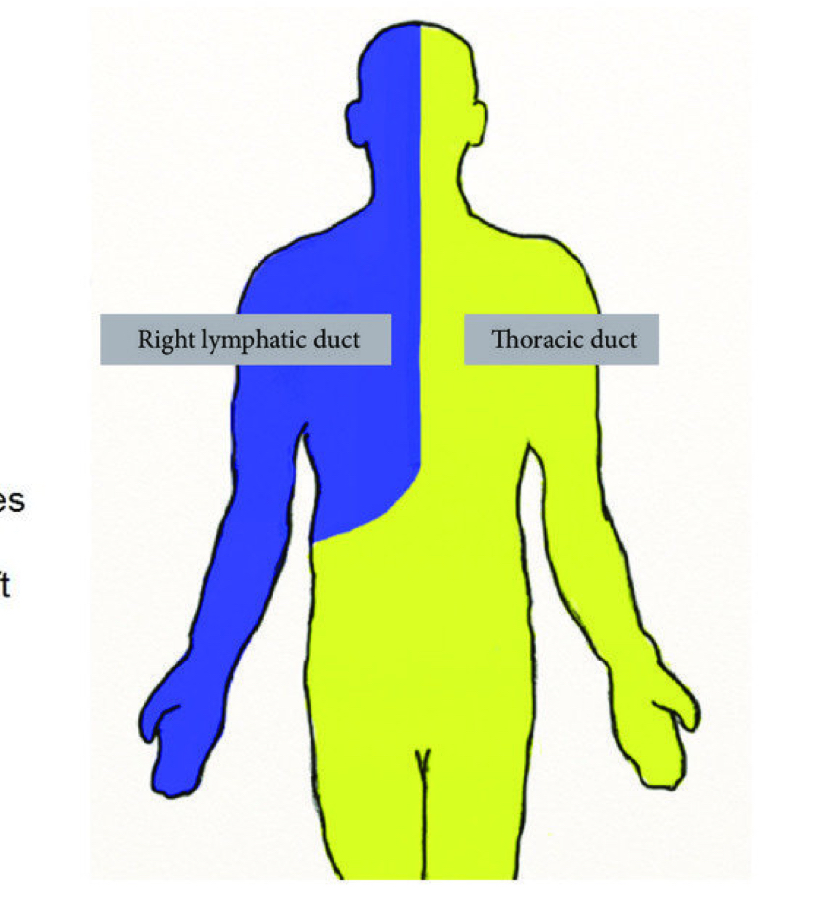
thoracic duct
empties into junction of LEFT INTERNAL JUGULAR and LEFT SUBCLAVIAN VEINS
lymphedema
localized damage to or compression of the lymphatic system can IMPAIR the body’s ABILITY TO REABSORB FLUID in the INTERSTITIAL SPACE
common causes of lymphedema
1) surgery (removal)
2) radiation therapy
3) trauma
4) cancer
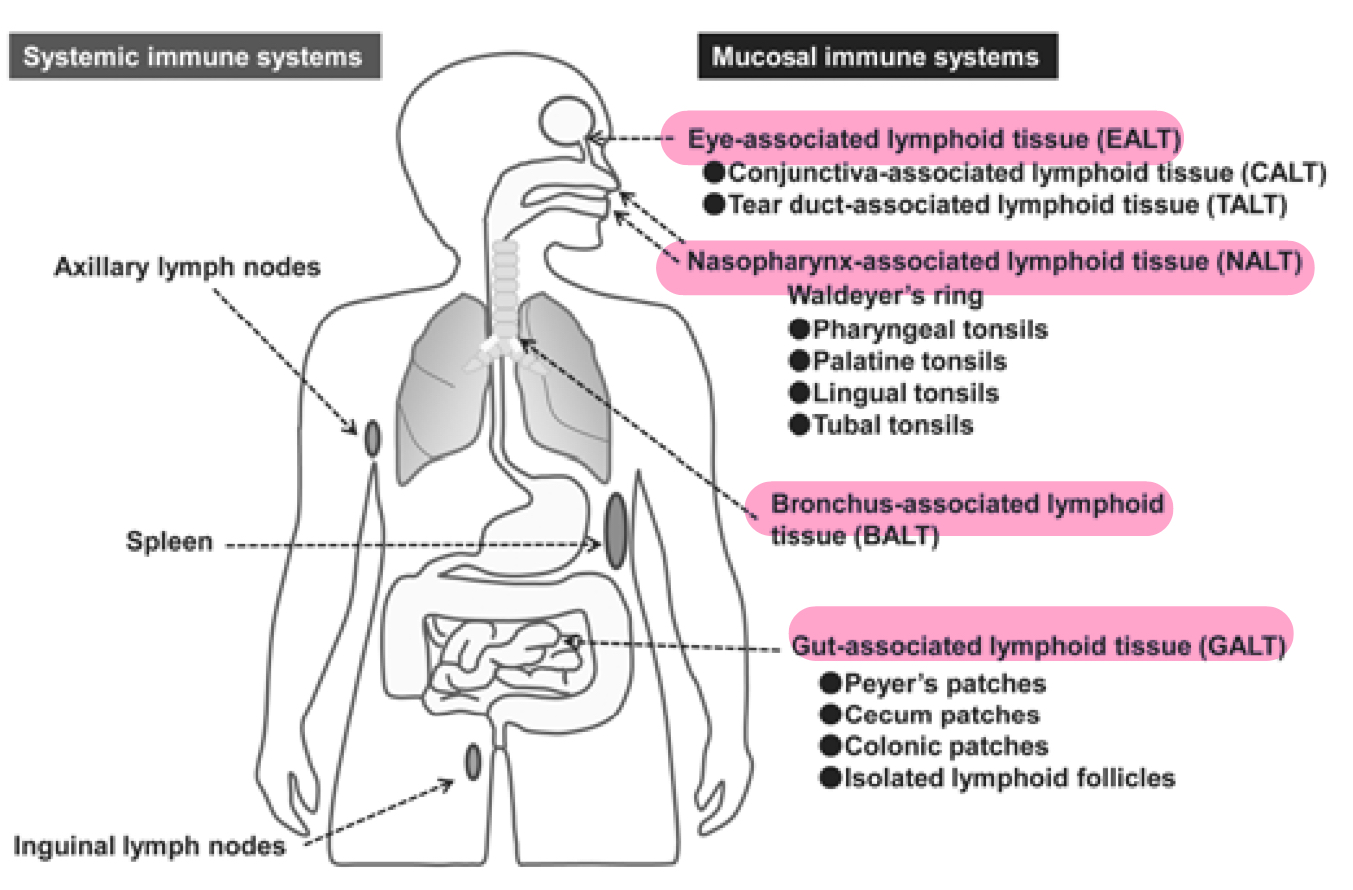
other lymphoid tissues
MALT
tonsils
peyers patches
appendix
spleen
thymus
mucosa- associated lymphoid tissues (MALT)
lymph tissues strategically located in the MUCOUS MEMBRANES of the body
areas of frequent pathogen entry
how does MALT differ from lymph nodes?
1) location (mucosa)
2) first-lune defense (vs systemic)
3) not fully encapsulated
4) do NOT filter lymph
goal of MALT
first line defense to identify and respond to a patogen before it gets into lymphatic circulation
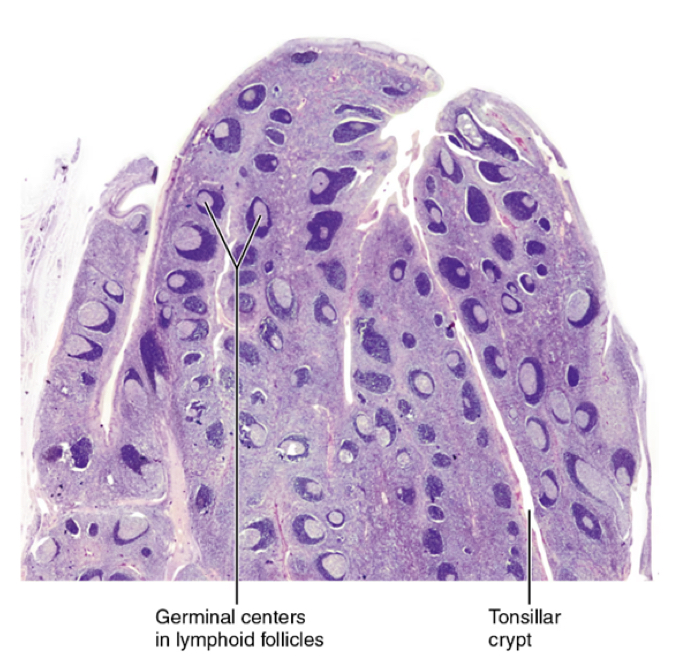
tonsils
ring of lymphoid tissue around the entrance of the pharynx
look like localized swellings of mucosa
remove ingested/inhaled pathogens
PALATINE TONSILS are the largest and most often infected
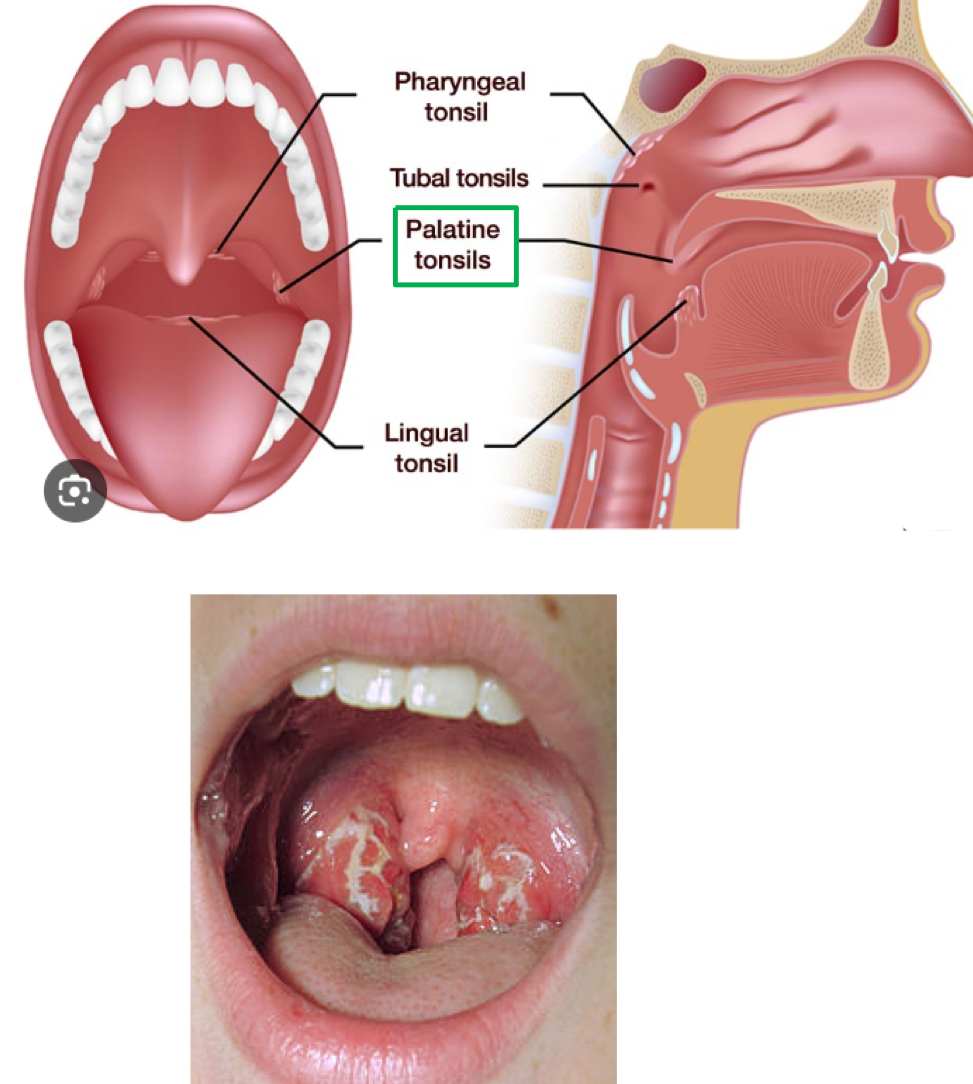
tonsillar anatomy
CRYPTS: trap pathogens and facilitate their interaction with macrophages and lymphocytes
GERMINAL CENTERS: site of proliferation of of T and B lymphocytes in response to pathogen recognition
peyer’s patches
large clusters of lymphoid tissue located in the wall of the ileum
facilitate the interaction of T and B cells with antigens
PATHOGEN DESTRUCTION
IMMUNE TOLERANCE
food allergies
inflammatory bowel disease
intussusception
bowel obstruction that can occur when the intestines fold in on themselves in the telescope- like fashion
most often occurs in the ileum
associated with viral infections
inflammation from infection→ pulling in on other areas of bowels
most seen in kids
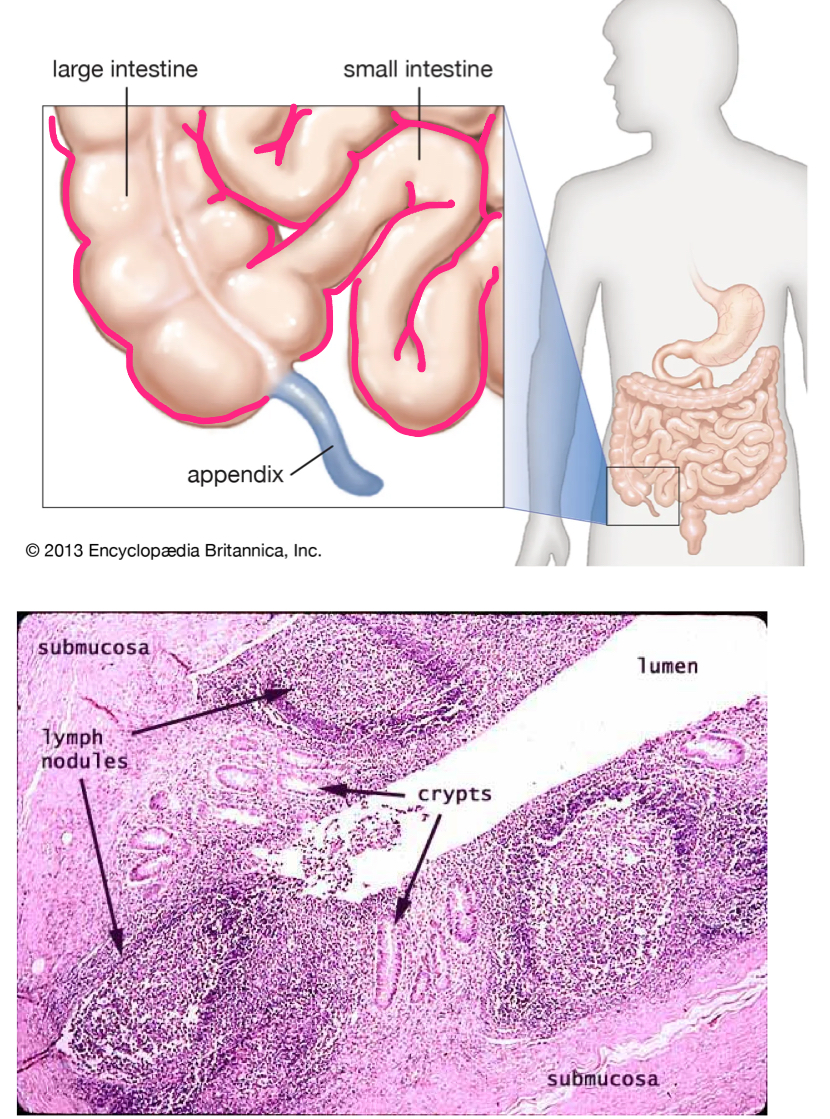
appendix
tubular offshoot of the proximal large intestine with a HIGH CONCENTRATION OF LYMPHOID TISSUE
immune function like peyer’s patches (crypts and memory lymphocytes)
may have a role in repopulating normal flora after intestinal infections
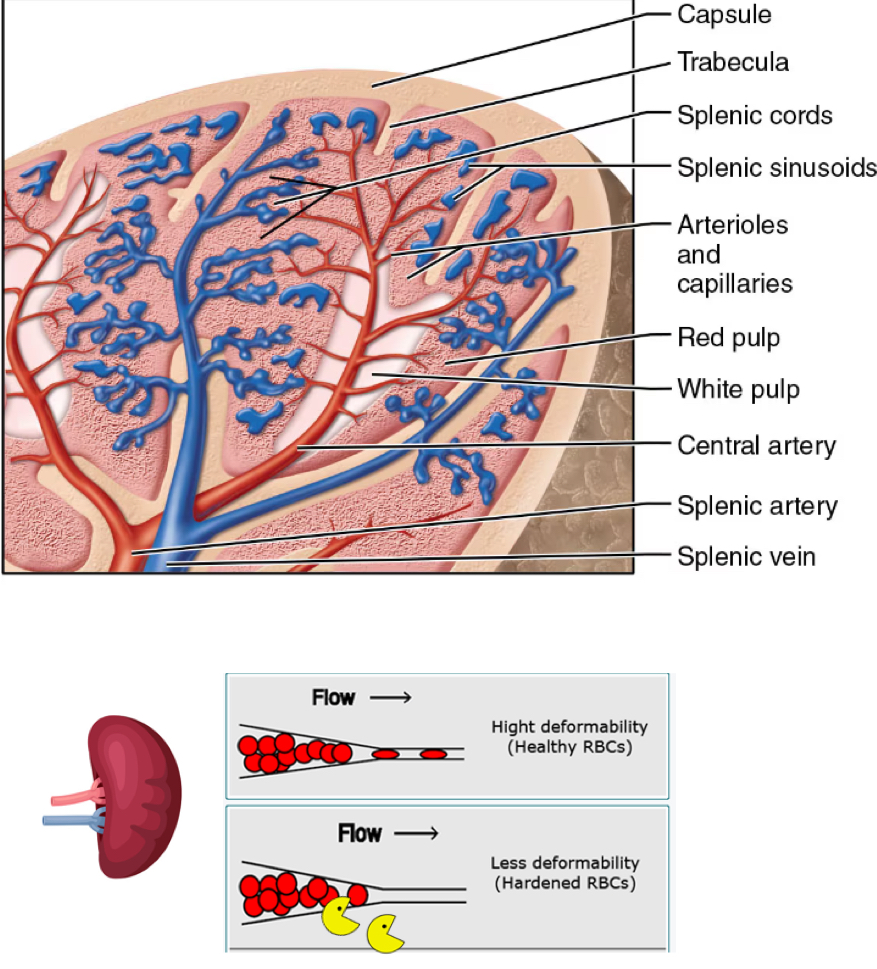
the spleen
“big lymph node”
left upper quadrant beneath diaphragm and posterior to the stomach
highly vascular
fed by splenic artery
drains into portal circulation via splenic vein
splenic histology
vessels branch into:
red pulp
“red blood cell graveyard”
sinusoidal capillaries trap old RBCs
reticular fibers the macrophages engulf and RECYCLE IRON and BILIRUBIN (from heme)
store some platelets
white pulp:
lymphocytes suspended in reticular fibers
filters blood
house many B cells
sea of red pulp
lots of blood
spleen= reservoir for about 20% of blood volume under normal conditions
what happens to the spleen in times of stress
it can contract and release blood into the circulation when acted upon by he sympathetic nervous system
muscles in the capsule contract to squeeze blood out
clinical relevance: spleen
thin capsule + reservoir = potential for injury and HEMORRHAGE
spleen can become enlarged in states of damaged/abnormal cells, or increased B cell proliferation
mono
splenectomy leaves individuals immunocompromised
loss of filtering mechanism adn B lymphocytes
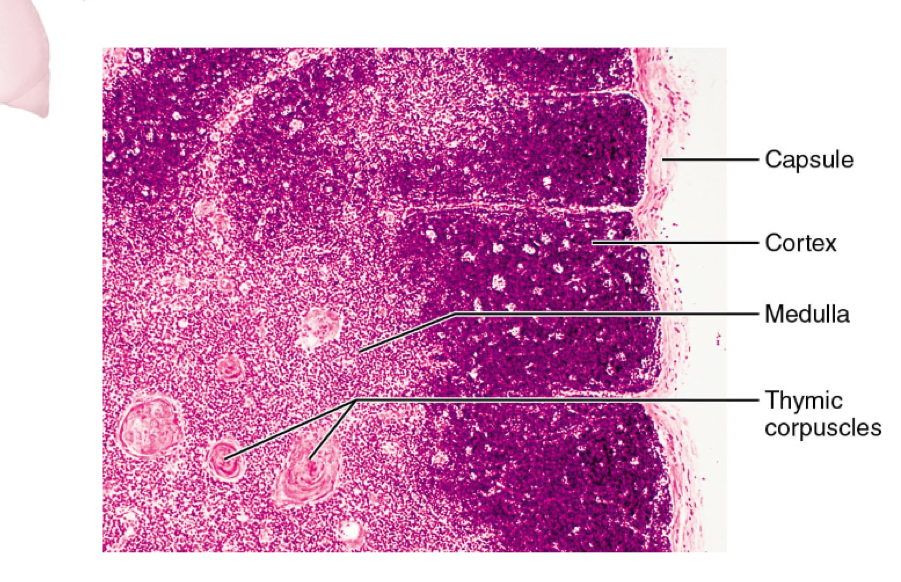
thymus
located in mediastinum, deep to sternum
site of T cell development
largest as infant and dimities with age
maturation site for T lymphocytes
components of thymus
cortex: site of POSITIVE selection
can you identify the MHC 1 complex of self cells?
medulla: site of NEGATIVE selection
will you not act against self-antigens
corpuscles: site of T cell dstruction