Chapter 12 - Saturated Hydrocarbons
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
hydrocarbon
a compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms
hydrocarbon derivative
a compound that contains carbon and hydrogen and one or more additional elements (like O, N, F)
saturated hydrocarbon
a hydrocarbon in which all carbon-carbon bonds are single bonds
unsaturated hydrocarbon
hydrocarbon with one or more carbon-carbon multiple bonds (double bonds, triple bonds, or both)
organic chemistry
the study of hydrocarbons and their derivatives
inorganic chemistry
the study of all substances other than hydrocarbons and their derivatives
alkane
a saturated hydrocarbon in which the carbon atom arrangement is acyclic
acyclic
straight chain or branched
methane
ethane
propane
what are the three simplest alkanes?
4
how many bonds will each carbon atom have?
expanded structural formula
a two dimensional structural representation that depicts the bonding of all atoms in a molecule
condensed structural formula
the structural arrangement of different groupings
skeletal structural formula
an arrangement of all bonded carbon atoms without showing the attached hydrogen atoms
isomers
compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements
continuous-chain alkane
an alkane in which all carbon atoms are connected in a continuous nonbranching chain
branched-chain alkane
an alkane in which one or more branches of carbon atoms are attached to a continuous chain of carbon atoms
constitutional isomers
isomers that differ in the connectivity of atoms, that is, in the order in which atoms are attached to each other within molecules
conformation
the specific three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an organic molecule at a given instant that results from rotations about carbon-carbon single bonds
substituent
an atom or group of atoms attached to a chain (or ring) of carbon atoms
alkyl group
the group of atoms that would be obtained by removing a hydrogen atom from an alkane
line-angle structural formula
a structural representation in which a line represents a carbon-carbon bond and a carbon atom is understood to be present at every point where two lines meet and at the ends of lines
primary carbon atom
a carbon atom in an organic molecule that is directly bonded to one other carbon atom
secondary carbon atom
a carbon atom in an organic molecule that is directly bonded to two other carbon atoms
tertiary carbon atom
a carbon atom in an organic molecule that is directly bonded to three other carbon atoms
quaternary carbon atoms
a carbon atom in an organic molecule that is directly bonded to four other carbon atoms
cycloalkane
a saturated hydrocarbon in which carbon atoms connected to one another in a cyclic (ring) arrangement are present
stereoisomers
isomers that have the same molecular and structural formulas but different orientations of atoms in space
cis-trans isomers
isomers that have the same molecular and structural formulas but different orientations of atoms in space because of restricted rotation about bonds
trans-
a prefix that means "across from"
cis-
a prefix that means "on the same side"
combustion reaction
chemical reaction between a substance and oxygen (usually from air) that proceeds with the evolution of heat and light (usually as a flame)
halogenation reaction
a chemical reaction between a substance and a halogen in which one or more halogen atoms are incorporated into molecules of the substance
substitution reaction
a chemical reaction in which part of a small reacting molecule replaces an atom or a group of atoms on a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative
halogenated alkane
an alkane derivative in which one or more halogen atoms are present
halogenated cycloalkane
a cycloalkane derivative in which one or more halogen atoms are present
1. methane
2. ethane
3. propane
4. butane
5. pentane
6. hexane
7. heptane
8. octane
9. nonane
10. decane
what are the first ten continuous-chain alkanes?
1. methyl
2. ethyl
3. propyl
4. butyl
5. pentyl
6. hexyl
what are the first six continuous-chain alkyl groups?
identify the longest continuous carbon chain
what is the first rule for identifying IUPAC nomenclature for alkanes?
number the carbon atoms
what is the second rule for identifying IUPAC nomenclature for alkanes?
alphabetical order
what takes precedence over the numbering of substituents?
2
carbon atoms classified as secondary are bonded to _________ H atoms
0
carbon atoms classified as quaternary are bonded to _________ H atoms
3
carbon atoms classified as primary are bonded to __________ H atoms
1
carbon atoms classified as tertiary are bonded to _________ H atom
solubility
density
boiling point
what are the physical properties of alkanes and cycloalkanes?
combustion
halogenation
what are the chemical properties of alkanes and cycloalkanes?
insoluble in water
soluble in nonpolar solvents
what is the solubility of alkanes and cycloalkanes?
less dense than water
what is the density of alkanes and cycloalkanes?
increase as carbon-chain length increases
decrease with increase in degree of branching
what is the boiling point of alkanes and cycloalkanes?
all are flammable
combustion products are CO2 and H2O
what is the combustion of alkanes and cycloalkanes?
hydrogen atoms are replaced with halogen atoms
requires the presence of heat or light
what is halogenation of alkanes and cycloalkanes?
1. expanded
2. condensed
3. abbreviation
4. skeletal
5. line-angle
what are the five ways to draw/write compounds?
b.
how many carbon atoms are present in the compound:
2,2,4-trimethylpentane
a. nine
b. eight
c. five
d. seven
c.
for the pair of compounds, select a correct characterization from the response list:
chlorocyclobutane and
1,2-dichlorocyclopropane
a. constitutional isomers
b. have the same number of carbon atoms but are not constitutional isomers
c. one but not the other exists in cis-trans forms
d. both exist in cis-trans forms
b.
which of the following statements concerning organic compounds is correct?
a. organic compounds are always soluble in water
b. organic compounds always contain the element carbon
c. organic compounds cannot be found in nature; they must be synthesized in a laboratory
d. organic compounds are found only in non-living systems
c.
the distinction between a saturated hydrocarbon and an unsaturated hydrocarbon relates to
a. number of carbon atoms present
b. boiling points
c. the number of multiple bonds present in the molecule
d. volatility
b.
what is the correct molecular formula for
2,2-dimethylbutane?
a. C8H18
b. C6H14
c. C8H16
d. C6H12
a.
select the correct number of constitutional isomers that exist for dichlorocyclopentane
a. three
b. five
c. four
d. two
a.
the four hydrogen atoms bonded to the central carbon atom in methane lie at the corners or apexes of a _______________
a. tetrahedron
b. rectangle
c. square
d. parallelogram
d.
determine the appropriate characterization of the two organic compounds:
pentane and 2,2-dimethylpropane
a. not constitutional isomers but have the same number of carbon atoms
b. only one compound exists in a cis-trans form
c. both compounds exist in cis-trans forms
d. constitutional isomers
a.
select the correct number of constitutional isomers that exist for a five-carbon alkane
a. three
b. two
c. five
d. four
d.
which of the following statements concerning saturated hydrocarbons is incorrect?
a. every carbon atom present has four bonds
b. no correct response
c. all bonds present are single bonds
d. every carbon atom present must be bonded to at least two hydrogen atoms
a.
determine the appropriate characterization of the two organic compounds:
cyclohexane and methylcyclopentane
a. constitutional isomers
b. not constitutional isomers but have the same number of carbon atoms
c. only one compound exists in a cis-trans form
d. both compounds exist in cis-trans forms
c.
how many hydrogen atoms are present in the alkane 2,5-dimethyloctane?
a. 24
b. 18
c. 22
d. 20
b.
in which of the following alkanes are 13 covalent bonds present?
a. CH3-CH-CH3
|
CH3
b. more than one correct response
c. CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3
d. CH3-CH2-CH3
d.
which could not be the molecular formula for an alkane molcule?
a. C24H50
b. CH4
c. C4H10
d. C5H14
a.
which of the following compounds is a constitutional isomer of
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 ?
a. 2-methylbutane
b. 2-methylpentane
c. 2,2-dimethylbutane
d. no correct response
c.
when the molecular formulas for cyclic and noncyclic alkanes with the same number of carbon atoms are compared, it is always found that the cycloalkane has
a. four less hydrogen atoms
b. two more hydrogen atoms
c. two less hydrogen atoms
d. the same number of hydrogen atoms
c.
which statement concerning the boiling points of specific alkanes is correct?
a. butane has a higher boiling point than cyclobutane
b. hexane has a higher boiling point than heptane
c. pentane has a higher boiling point than 2-methylpentane
d. more than one correct response
d.
which statement concerning cycloalkanes is correct?
a. each exists in two or more isomeric forms
b. more than one correct response
c. molecular formula always fits the general formula C(n)H(2n+2)
d. all are hydrocarbons
d.
for which of the following halogenated cycloalkanes is cis-trans isomerism possible?
a. 1,1-dichlorocyclobutane
b. 1-bromo-1-chlorocyclobutane
c. more than one correct response
d. 1-bromo-2-chlorocyclobutane
b.
what is the correct molecular formula for 2,3,4-trimethylpentane?
a. C8H16
b. C8H18
c. C6H12
d. C6H14
b.
in which of the following pairs of compounds are the two members constitutional isomers?
a. hexane and 3-methylhexane
b. 3-methylnonane and 3,4-dimethyloctane
c. 2,4-dimethylhexane and 2,4-dimethylheptane
d. ethane and propane
b.
what is the correct molecular formula for 3-ethylhexane?
a. C6H14
b. C8H18
c. C8H16
d. C6H12
c.
what is the common name for the halogenated hydrocarbon whose IUPAC name is 2-bromopropane?
a. sec-propyl bromise
b. ethyl bromide
c. isopropyl bromide
d. propyl bromide
b.
determine the appropriate characterization of the two organic compounds:
butane and cyclobutane
a. both compounds exist in cis-trans forms
b. not constitutional isomers, but have the same number of carbon atoms
c. constitutional isomers
d. only one compound exists in a cis-trans form
d.
select the correct number of constitutional isomers that exist for a four-carbon cycloalkane
a. three
b. five
c. four
d. two
b.
for the organic compound shown using a skeletal structural, determine the number of hydrogen atoms present in the compound
a. 6 hydrogen atoms
b. 8 hydrogen atoms
c. 9 hydrogen atoms
d. 7 hydrogen atoms
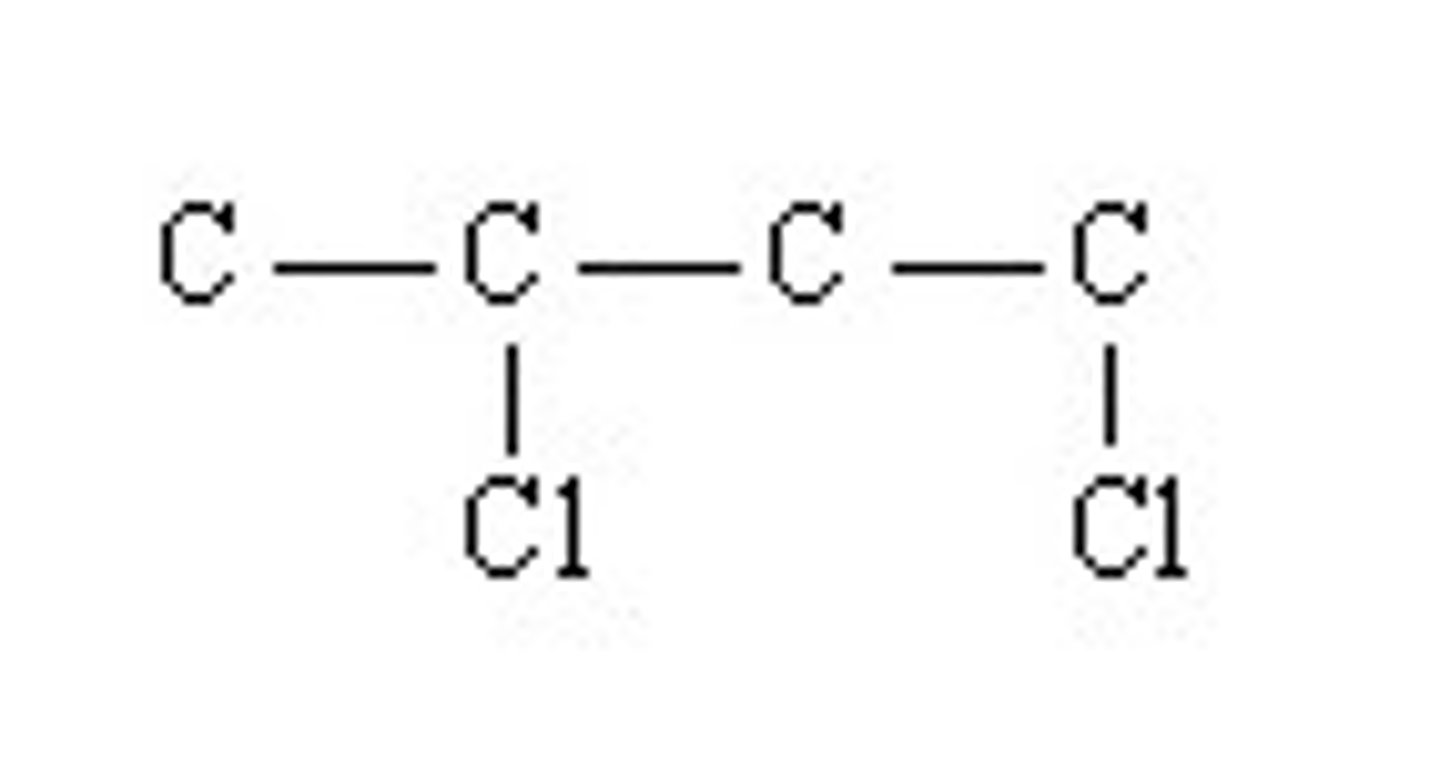
a.
choose the correct reactants that produce the products, CO2 and H2O, during the process of complete combustion
a. more than one correct response
b. 2,3,3,4,4-pentamethylheptane
c. sodium hydroxide
d. methane
a. inorganic
b. inorganic
c. organic
d. organic
indicate whether each of the following compounds is an organic or inorganic compound
a. H2SO4
b. Na2CO3
c. CH3N
d. C6H12
a. does meet
b. does not meet
c. does not meet
d. does meet
indicate whether each of the structures meets or does not meet the "bonding requirement" for carbon atoms
a. four single bonds
b. three single bonds and a double bond
c. two double bonds and two single bonds
d. two double bonds
a. 6 carbon
b. 14 hydrogen
c. 22 bonds
using the general formula or an alkane, derive the specific alkane
a. number of carbon atoms present when 14 hydrogen atoms present
b. number of hydrogen atoms present when 6 carbon atoms present
c. total number of covalent bonds in a molecule with 16 hydrogen atoms
a. 12 hydrogen
b. 2
determine the following for the five carbon alkane whose skeletal formula is:
C--C--C--C--C
a. how many hydrogen atoms are present?
b. how many CH3 groups are present?
a. same
b. different
c. different
d. same
indicate whether the following would be expected to be the same or different for two alkane isomers:
a. number of carbon atoms present in the molecule
b. the shape of the molecule
c. the density of the molecule
d. the molecular formula of the molecule
a. 8 hydrogen
b. 3 carbon
c. 12 hydrogen
d. 10 bonds
using the general formula for a cycloalkane, derive the following for the specific alkanes:
a. number of hydrogen atoms present when 4 carbon atoms are present
b. number of carbon atoms present when 6 hydrogen atoms present
c. number of hydrogen atoms present when there are a total of 18 atoms present in the molecule
d. number of covalent bonds are present when 8 hydrogen atoms are present
a. ethane
b. cyclohexane
c. butane
d. pentane
which member in each set of alkanes has the higher boiling point?
a. methane and ethane
b. cyclohexane and hexane
c. butane and methylpropane
d. pentane and 2,2-dimethylpropane
a. C3H8 + 5O2 --> 3CO2 + 4H2O + heat
b. 2C6H14 + 19O2 --> 12CO2 + 14H2O + heat
c. 2C5H10 + 15O2 --> 10CO2 + 10H2O + heat
write the formulas of the products from the complete combustion of the following alkanes or cycloalkanes
a. C3H8
b. 2-methylpentane
c. cyclopentane
a. no, trichloromethane
b. no, dichloromethane
c. no, chloromethane
indicate whether or not the following halogenated alkane chemical formulas are paired with the correct name
a. CH3Cl3 --> chloromethane
b. CH3Cl2 --> carbontetrachloride
c. CH3Cl --> methylene chloride
b. 2,2-dimethylpentane
what is the IUPAC name of the compound shown?
(CH3)3-C-CH2-CH2-CH3
a. 1,1,1-trimethylbutane
b. 2,2-dimethylpentane
c. 2-dimethylpentane
d. heptane
d. C8H18
what is the correct molecular formula for 3-ethylhexane?
a. C6H12
b. C6H14
c. C8H16
d. C8H18