4.4.3 - Electrolysis
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Electrolysis
A way of breaking down a substance using electricity
What happens when an ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water?
The ions are able to move within the solution and can conduct electricity
Electrolyte
The substance being broken down by electrolysis
Diagram for electrolysis of sodium chloride
Where do positive ions go when an electric current is passed through an electrolyte?
Negative electrode (cathode)
Where do negative ions go when an electric current is passed through an electrolyte?
Positive electrode (anode)
What happens at the electrodes?
Ions are discharged to produce elements
What material are electrodes made from and why?
Platinum or graphite as they are inert and can conduct electricity
Half equations for the electrolysis of zinc chloride
2H+ + 2e- --> H2
2Cl- --> Cl2 + 2e- OR 2Cl- - 2e- --> Cl2
Is the metal or non-metal in a molten ionic compound produced at the cathode and why?
Metal as they form positive ions
Is the metal or non-metal in a molten ionic compound produced at the anode and why?
Non-metals as they form negative ions
When can metals be extracted using electrolysis?
When they are in molten compounds
When is electrolysis used to extract metals?
When the metal is too reactive to be extracted by reduction with carbon or if the metal reacts with carbon
Why is electrolysis expensive?
Lots of energy is required to melt compounds and produce the current
Aluminium extraction steps
1) Cryolite added to aluminium oxide to lower the melting point
2) The mixture is melted
3) Electrolysis is carried out on the molten mixture
What is the element used as the positive electrode (anode)?
Carbon
Why must the anode be replaced regularly?
The oxygen produced there reacts with the carbon in the anode to form CO2
When is hydrogen produced by electrolysis?
If the metal is more reactive than hydrogen (in an aqueous solution)
Where is hydrogen produced?
Cathode
When is oxygen produced by electrolysis?
If halide (halogen) ions aren't present in an aqueous solution
Where is oxygen produced?
Anode
Why can oxygen and hydrogen be produced by electrolysis?
Some water molecules break down into positive hydrogen ions (H+) and negative hydroxide ions (OH-) which are discharged
OILRIG
Oxidation is loss, reduction is gain (of electrons)
Aqueous solution: Copper sulphate
What are the positive and negative ions in the solution?
Positive: Cu2+, H+
Negative: SO42-, OH-
Aqueous solution: Copper sulphate
What elements are formed at the positive and negative electrodes?
Positive: Oxygen
Negative: Copper
Aqueous solution: Copper sulphate
Word equation
Copper sulphate solution --> Oxygen + Copper + Sulphuric acid
Aqueous solution: Copper sulphate
Half equation at positive and negative electrodes
Positive: 4OH- --> O2 + 2H2O + 4e-
Negative: Cu2+ + 2e- --> Cu
Aqueous solution: Copper II chloride
What are the positive and negative ions in the solution?
Pos: Cu2+, H+
Neg: Cl-, OH-
Aqueous solution: Copper II chloride
What elements are formed at the positive and negative electrodes?
Pos: Chlorine (gas)
Neg: Copper
Aqueous solution: Copper II chloride
Word equation
Copper chloride solution --> Copper + Chlorine + Water
Aqueous solution: Copper II chloride
Half equation at positive and negative electrodes
Pos: 2Cl- --> Cl2 + 2e-
Neg: Cu2+ + 2e- --> Cu
Is copper oxidised or reduced during the electrolysis of Copper II chloride and why?
Reduced as it gains electrons
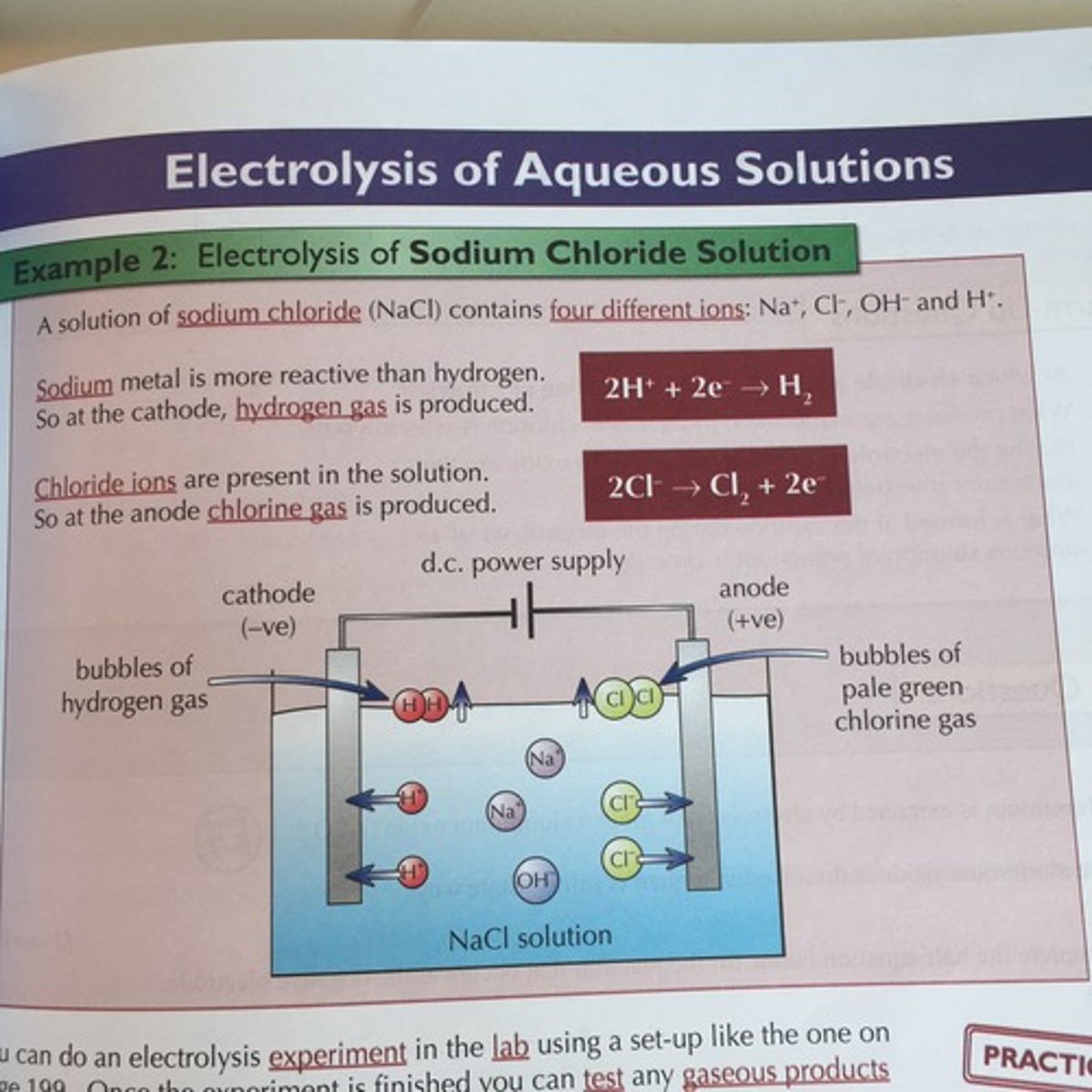
Aqueous solution: Sodium chloride
What are the positive and negative ions in the solution?
Pos: Na+, H+
Neg: Cl-, OH-
Aqueous solution: Sodium chloride
What elements are formed at the positive and negative electrodes?
Pos: Chlorine (gas)
Neg: Hydrogen
Aqueous solution: Sodium chloride
Word equation
Sodium chloride solution --> Hydrogen + Chlorine + Sodium hydroxide
Aqueous solution: Sodium chloride
Half equation at positive and negative electrodes
Pos: 2Cl- --> Cl2 + 2e-
Neg: 2H+ + 2e- --> H2
Is chlorine oxidised or reduced during the electrolysis of sodium chloride and why?
Oxidised as it loses electrons