2.1.2. parasympathetic nervous system - anticholinergic agents
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
JLDT
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
atropine
or hyoscyamine
Atropa belladona (deadly nightshade)
Datura stramonium (jimson-weed/sacred Datura thorn apple)
prototype of muscarinic antagonists
beautiful lade in italian
cosmetically used to cause dilation of the pupils, according to some references
belladona
rapid phase t1/2= 2h, slow phase=13h
50% excreted unchanged
effects decline across body rapidly except eyes (persist 72 hours)
2 phase elimination of atropine
Reversible inverse agonism or antagonism
MOA of anticholinergic agents
opposite of DUMBBELSS and CNS ACh effects (+cycloplegia)
cycloplegia — loss of eye’s ability to focus due to paralysis of ciliary muscle
low dose: bradycardia → blockage of presynaptic AChR (provides feedback inhibition)
presynapse releases NT, postsynapse receives NT
ACh (NT) comes from the presynaptic nerve. When this nerve releases ACh but instead of going to the postsynaptic nerve, it binds with the presynaptic AChR where it came from, cholinergic transmission decreases → lowers/inhibit ACh release (negative feedback)
if AntiACh binds with presynaptic AChR, cholinergic transmission increases → DUMBBELS
thus, first effect of anti ach at low dose is cholinergic in nature (unique instance)
cholinergics | anticholinergics | |
D | Diarrhea | Constipation |
U | Urination | Urinary Retention |
M | Miosis | Mydriasis |
B | Bradycardia | Tachycardia |
B | Bronchospasm | Bronchodilation |
E | Emesis | Antiemetic |
L | Lacrimation (increased secretions) | Dry mouth |
L | Lethargy | |
S | Salivation | Decreased secretions |
S | Smooth muscle contraction | Smooth muscle relaxation |
effect if anticholinergic agents
Umeclidinium |
Ipratropium |
Tiotropium |
Glycopyrronium |
Glycopyrrolate |
quaternary amines
Atropine |
Biperiden |
Cyclopentolate |
Darifenacin |
Solifenacin |
Dicycloverine |
Homatropine |
Oxybutin |
Scopalamine / Hyoscine N-butylbromide |
Tropicamide |
tertiary amines
MOA | Non-selective muscarinic ACh receptor antagonist |
SOURCE | Atropa belladonna, Datura stramonium |
— indication
Symptomatic Bradycardia — 1st line tx (esp for resuscitation), IM/IV
important in critical care when hr is too low or when px is experiencing persistent bradyarrhythmia. instead of immediately giving cpr, atropine is given at a maximum dose of 3mg (1mg x 3) to resuscitate patient
effect: tachycardia (fast HR)
Class IIC anti-arrhythmic (M2 AChR antagonist) → vagolytic effect (improved conduction in SA node) → ↑ heart rate
vagus nerve — nerve associated with parasympathetic NS which causes bradycardia to the heart.
SA node — natural pacemaker
Anesthesia adjuvant — prevent bronchoconstriction, reduce salivation and respiratory secretion = good for airway management during surgery
M3 → ↓secretion → improve efficacy of topical anesthetics (prevent anesthetic from being diluted from secretions) + laryngoscopy imaging
laryngoscopy — use of small camera to examine larynx.
you can decrease dose of anesthesia
Neuronal M2 autoreceptor → release ACh → ACh binds to M3 in lungs → bronchoconstriction
M1 in brainstem chemoreceptor trigger zone (vomiting center) → reduce nausea, anti-emesis
Ophthalmologic — corneal abrasions, eye exam, strabismus and amblyopia
eye exam: M3 (in iris smooth muscle) → mydriasis (dilation of pupil) makes it easier to examine eye
corneal abrasions, strabismus and ambyopia: M3 (in ciliary) → cycloplegia / loss focus to specific images (opposite of accomodation) → pain relied, encourage use of amblyopic eye
2nd line for strabismus (cross eye) & amblyopia (lazy eye) — due to weak muscles in the eye
atropine
MOA | Non-selective muscarinic ACh receptor antagonism |
SOURCE | Hyoscyamus niger |
BRAND | Buscopan (Hyoscine N-Butylbromide) |
— indication
Reduce GI motility — M1 in brainstem chemoreceptor trigger zone → reduce motion sickness
tx for motion sickness — can be given as transdermal patch due to adequate lipophilicity
genitourinary spasms (dysmenorrhea, gallbladder spasms), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Sialorrhea/Hypersalivation
dysmenorrhea — pag masyadong contracted yung muscles, brain interprets it as pain → buscopan allows pain relief
hyoscine / scopalamine
MOA | Non-selective muscarinic ACh receptor antagonism |
|---|
— indication
Reduce GI motility
tx irritable bowel syndrome, copious respiratory secretions caused by COPDs
dicycloverine / dicyclomine
MOA | Slightly selective antagonist at M3 but no kinetic selectivity (does not bind longer) |
|---|
— kinetic selectivity: drugs stay longer on M3 receptors vs other receptors
— indication
M3R: ↓ secretions — improved efficacy of topical anesthetics + laryngoscopy imaging
low affinity for cardiac M2 → less vagolytic than atropine → tachycardia
Anesthesia adjuvant (IM/IV) — prevent bradycardia, bronchoconstriction, ↓ salivation and secretion
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Inhalation but not used in PH)
Sialorrhea (PO)
Hyperhidrosis (PO, topical)
glycopyronium / glycopyrrolate
MOA | M3 AChR-selective antagonist with kinetic selectivity (long acting) |
|---|
— indication
Umeclidinium — inhaler for asthma and COPD
M3 in lungs → long bronchodilation
Tiotropium, Umeclidinium
MOA | M1, M2, M3 ACh receptor antagonist (short acting) |
|---|
— indication
COPD, Sialorrhea
M3 in lungs → bronchodilation
Neuronal M2 → release ACh → ACh to m3 in lungs → transient bronchoconstriction
ipratropium
MOA | Slight preference for blocking m3 over m1/m2 (darifenacin more selective) |
|---|
— indication
overactive bladder → lead to urinary retention
— CYP
Darifenacin - 2D6 inhibitor;
Solifenacin - 3A4 substrate
solifenacin, darifenacin
MOA | Muscarinic ach blocker (prefer m1/m3/m4) |
|---|
— indication
Hyperhidrosis and overactive bladder (alternative, not available in pnf)
M3 in bladder → ↓ bladder tone, sphincter contraction → less urination
oxybutynin
MOA | Non selective muscarinic ach receptor antagonism |
|---|
— indication
eyes — 2nd line for strabismus (crossed eye) and amblyopia (lazy eye), corneal abrasions, eye exams
m3 in iris smooth muscle → mydriasis
m3 in ciliary muscle → cycloplegia → pain relief, encourage use of amblyopic eye
tropicamide, cyclopentolate, homatropine
MOA | Non selective CNS M1-5 ach receptor antagonist |
|---|
— indication
tremors in parkinsons, dystonias, and pseudoparkinsonism from antipsychotics (ineffective for akathisia)
block DA blockade → ↑ DA release
biperiden
Cholinergic rebound: nausea, diaphoresis (Sweating), hypotension, dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue
upregulation
cognitive impairment: AEC scale
high score = increased risk of cognitive impairment
atropine = 3
hyoscine hydrobromide = 3
hyoscine n-butylbromide = 1
solifenacin = 1
darifenasin, dicycloverine. ipratropium, tiotropium (inhalational) = 0
caution with elderly due to being more at risk of cognitive impairment
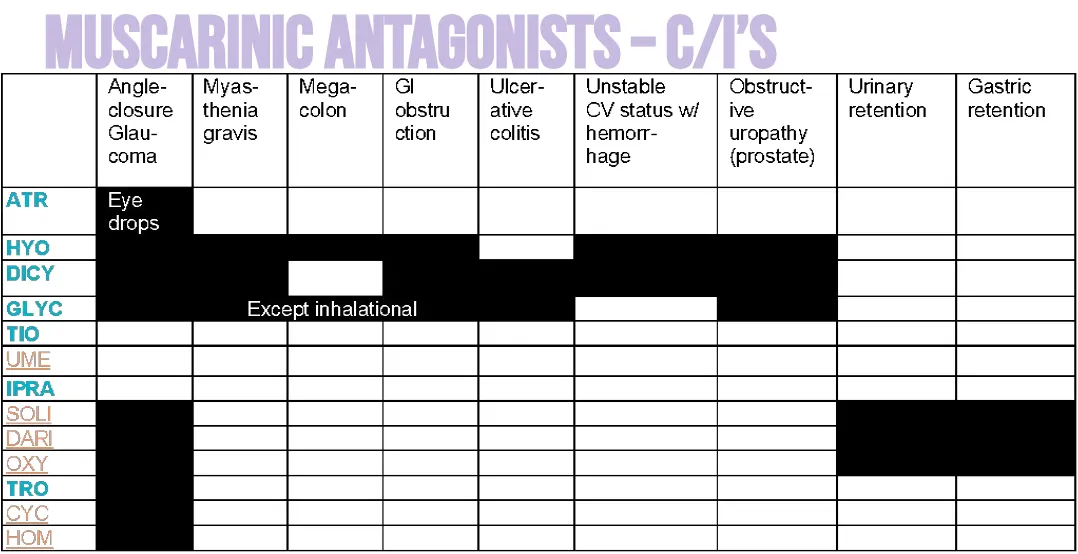
side effects of anticholinergics
additive — anticholinergics, CNS depressants, tachycardics
physiologic antagonism — drugs with opposite physiologic effects
K salts (oral) — strong anti-ACh may enhance ulcerogenic effect of K salts
Nitroglycerin — Anti-ACh decrease dissolution of sublingual tablets
Thiazide diuretics — Anti-ACh may increase their concentration
Topiramate — Anti-ACh increase its hyperthermia risk
interactions of anticholinergic agents
— Onabotulinumtoxin A, Abobotilunumtoxin A, Incobotulinumtoxin A, Prabotulinumtoxin A
— MOA
Zn endopeptidase from Clostridium botulinum
Cleaves certain proteins to stop vesicular fusion and Ca-induced release of ACh from presynaptic neuron in neuromuscular junction → paralysis
— Indication
glabellar lines (from lines), forehead lines, lateral canthar lines (crow’s feet)
cervical dystonia
focal tardive dystonia
severe axillary hyperhidrosis
refractory conditions (overactive bladder, localized tics, anal fissures, migraine, sialorrhea)
— Side effects
injection site swelling/bruising, headache, flu-like sx, hoarseness, UTI, urinary retention, dry mouth
BLACK BOX WARNING: muscle weakness further from injection site
botulinum toxin type A
— historical
hexamethonium — 1st line drug for hypertension (ion channel blocker)
— Rarely used competitive nicotinic ganglionic blockers
Trimethaphan — hypertensive emergencies due to dissecting aortic aneurysm, pulmonary edema
mecamylamine — moderately severe to severe htn
ganglionic blockers