Social Determinants of Health in the Population
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What is population health research concerned with?
Investigation of differences in health status (e.g. demographic groups - age, race/ethnicity, gender; geographically defined populations - HIV/AIDS not in Africa)
What does population health research examine?
Interrelationships between the distribution of social, economic, demographic, cultural, political, and other valued societal resources and health at the community level
What is population health research aimed at improving?
Health of the entire population rather than individuals
What term can be defined as the absence of disparities or avoidable differences among socioeconomic and demographic groups or geographic areas in health status and health outcomes such as disease, disability, or mortality?
Healthy equity
Health Equity
The absence of disparities or avoidable differences among socioeconomic and demographic groups or geographic areas in health status and health outcomes such as disease, disability, or mortality (e.g. leveling the playing the field)
What term can be defined as the inequalities that are deemed to be unfair, unjust, avoidable, or unnecessary?
Health inequities
Health Inequities
The inequalities that are deemed to be unfair, unjust, avoidable, or unnecessary
What can health inequities be reduced or remedied through?
Policy action
What do health inequities lead to?
Health disparities
4 Types of Health Disparities
1. Racial/ethnic disparities (e.g. osteoporosis in white women)
2. Socioeconomic status
3. Lack of access to healthcare
4. Decreased quality of healthcare
Examples of Health Disparities
Diabetes among Latinos
Stroke among African Americans
Cancer in minority groups
HIV among African Americans and Latinos
Environmental inequities among low-income communities
Are health inequities avoidable; yes or no?
Yes
What model describes well documented, chronically high levels of stress faced by members of stigmatized minority groups?
Minority stress model
Minority Stress Model
Describes well documented, chronically high levels of stress faced by members of stigmatized minority groups
According to the Minority Stress Model, what may the chronically high levels of stress faced by members of stigmatized minority groups be caused by?
Poor social support
Low socioeconomic status
Interpersonal prejudice and discrimination
6 Social Determinants of Health
1. Economic stability (e.g. socioeconomic status - housing)
2. Neighborhood and physical environment
3. Education
4. Food
5. Community and social context
6. Health care system
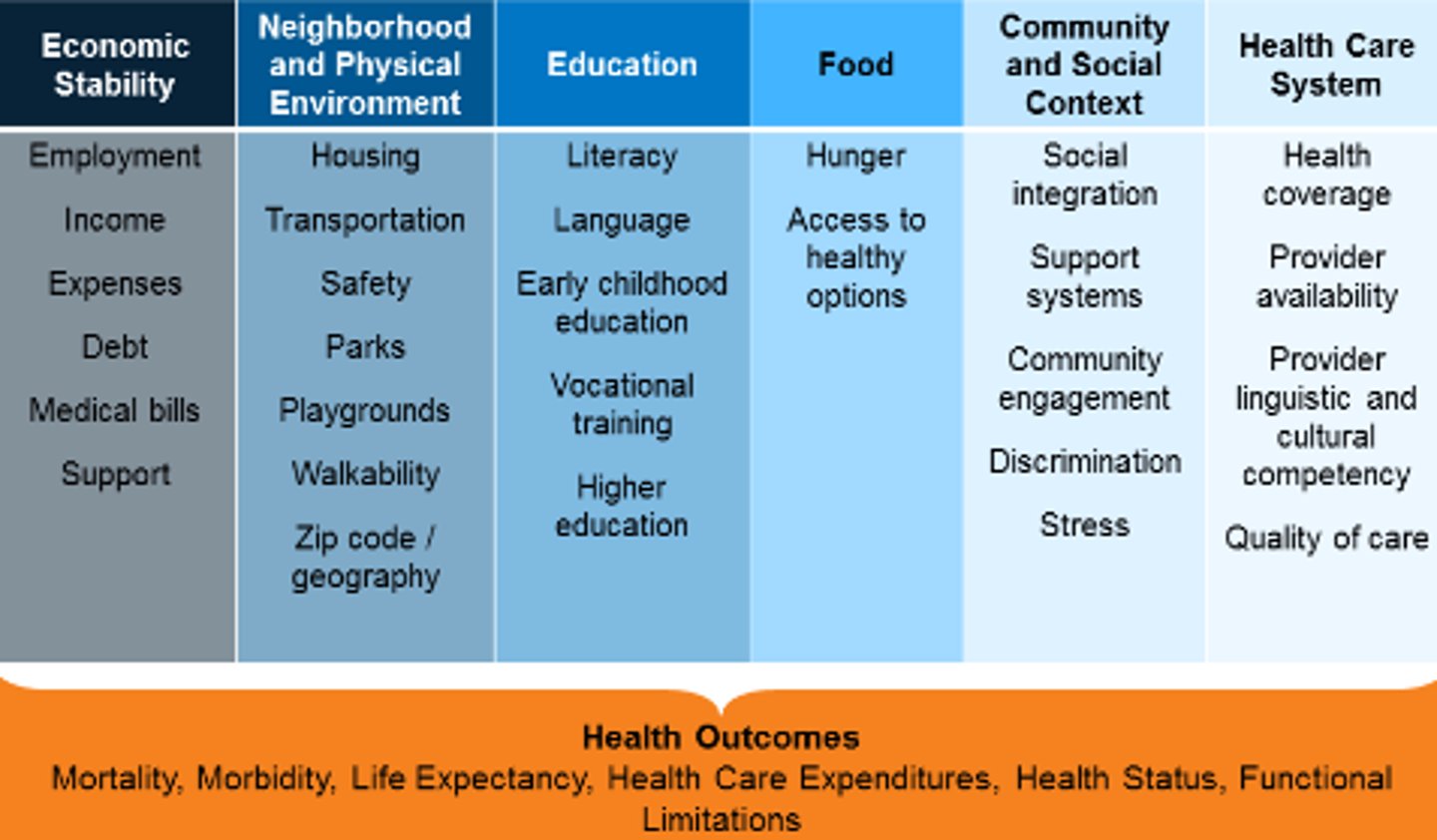
Which social determinant of health includes the following: employment, incomes, expenses, debt, medical bills, support; economic stability, neighborhood and physical environment, education, food, community and social context, or health care system?
Economic stability
2 Types of Employment
1. Stable (e.g. healthcare workers)
2. Unstable (e.g. service workers)
Is consumerism economy-driven or recession proof?
Economy-driven
Is healthcare economy-drive or recession proof?
Recession proof
What is the type of employment an individual has linked to?
Education level
Age
Race/ethnicity
Gender
What can the type of employment affect?
Health outcomes
What does the U.S. Census Bureau use to determine who is in poverty?
Set of dollar value thresholds that vary by family size and composition
Although defined in several ways, what is poverty particularly determined by?
Socioeconomic status
What can poverty lead to?
Increase in chronic diseases and early death
Which social determinant of health includes the following: housing, transportation, safety, parks, playgrounds, walkability, zip code/geography; economic stability, neighborhood and physical environment, education, food, community and social context, or health care system?
Neighborhood and physical environment
Quality of Housing
The physical condition of a person's home as well as the quality of the social and physical environment in which the home is located (e.g. air quality, home safety, space per individual, presence of mold, asbestos, or lead)
What 3 environment conditions affect health and contribute to health disparities in the quality of housing?
1. Water quality
2. Air quality
3. Air temperature
What challenges does housing instability cause?
Paying rent
Overcrowding
Moving frequently
Staying with relatives
Spending the bulk of income on housing
What can housing instability negatively affect?
Physical health (making it harder to access healthcare)
True or False: Housing instability can impact some populations more than others including members of marginalized communities.
True
How may people with housing instability be victimized?
Witness violence or property crimes in their community
Hear about crime and violence from other residents
What can violence lead to?
Premature death
Non-fatal injuries
Which social determinant of health includes the following: literacy, language, early childhood education, vocational training, higher education; economic stability, neighborhood and physical environment, education, food, community and social context, or health care system?
Education
Components of Literacy
Oral literacy (e.g. listening and speaking skills)
Print literacy (e.g. writing and reading skills)
Numeracy (e.g. ability to understand and work with numbers)
Cultural and conceptual knowledge
Language
Method of human communication, either spoken or written, consisting of the use of words in a structured and conventional way
What does early childhood, particularly the first 5 years of life, impact?
Long-term social, cognitive, emotional, and physical development
What does a healthy development in early childhood help prepare children for?
Educational experiences of kindergarten and beyond
What environmental and social factors can early childhood development and education opportunities be affected by?
Early life stress
Socioeconomic status
Relationships with parents and caregivers
Access to early education programs
What is a standard requirement for most jobs and for higher education opportunities?
A high school diploma
What is the dropping out of high school linked to?
Negative health impacts (e.g. limited employment prospects, low wages, poverty)
What factors may a student’s ability to graduate from high school be affected by?
Personal (e.g. family)
Institutional (e.g. school, community)
Higher Education
Any type of education after high school (e.g. 12th grade) including 2-year college (e.g. community college), certificate programs, 4-year college (e.g. bachelor programs), graduate programs, and professional programs
What are 3 barriers to accessing a higher education?
1. Gender
2. Age
3. Race/ethnicity
Which social determinant of health includes the following: hunger, access to healthy options; economic stability, neighborhood and physical environment, education, food, community and social context, or health care system?
Food
What factors is food security based on?
Income
Employment
Race/ethnicity
Disability
What does access to healthy foods support?
Healthy eating habits (e.g. caloric intake, availability of fresh and healthy foods)
What can the disruption of food intake or eating patterns occur as a result of?
Lack of money and other resources
What does the disruption of food intake or eating patterns not equal?
Hunger (but hunger is an outcome)
Which social determinant of health includes the following: social integration, support systems, community engagement, discrimination, stress; economic stability, neighborhood and physical environment, education, food, community and social context, or health care system?
Community and social context
Social Cohesion
The strength of relationships and the sense of solidarity among members of a community
What is one indicator of social cohesion?
Amount of social capital a community has (e.g. shared group resources such as a friend-of-a-friend's knowledge of a job opening)
Civic Participation
A wide range of formal and informal activities (e.g. voting, volunteering, participating in group activities, community gardening)
What does one-way civic participation improve? How?
Health by building social capital
Social Capital
Features of social organization such as networks, norms, and social trust that facilitate coordination and cooperation for mutual benefit
Discrimination
A socially structured action that is unfair or unjustified and harms individuals and groups
What can discrimination be attributed to?
Social interactions that occur to protect more powerful and privileged groups at the detriment of other groups
Do all stressful experiences negatively affect health and occur because of discrimination; yes or no?
No
Incarcerated Population
Number of inmates under the jurisdiction of state or federal prisons or held in local jails
State and federal prisons house inmates sentenced to more than how many years of incarceration?
One
Who are higher rates of incarceration often seen among?
Racial/ethnic minorities
People with lower levels of education
Which social determinant of health includes the following: health coverage, provider availability, provider linguistic and cultural competency, quality of care; economic stability, neighborhood and physical environment, education, food, community and social context, or health care system?
Health care system
Health Care Access
The timely use of personal health services to achieve the best possible health outcomes
True or False: Many people face barriers that prevent or limit access to needed health care services which may increase the risk of poor health outcomes and health disparities.
True
Primary Care Access
The provision of integrated, accessible health care services by clinicians who are accountable for addressing a large majority of personal health care needs, developing a sustained partnership with patients, and practicing in the context of family and community
What services do primary care providers offer?
Source of care
Early detection and treatment of disease
Chronic disease management
Preventive care
What are patients with a usual source of care more likely to receive?
Recommended preventive services (e.g. flu shots, blood pressure screenings, cancer screenings)
Health Literacy
The degree to which individuals have the capacity to obtain, process, and understand basic health information needed to make appropriate health decisions
What does health literacy encompass?
Being able to read and comprehend essential health-related materials (e.g. prescription bottles, appointment slips)
What may health literacy increase?
A person's capacity to take responsibility for their health and their family's health
Health Outcomes of the Social Determinants of Health
Mortality
Morbidity
Life expectancy
Health care expenditures
Health status
Functional limitations
What 5 social factors do the social determinants of health involve that strongly influence people’s ability to avoid risks and to minimize the consequences of disease once it occurs?
1. Knowledge
2. Money
3. Power
4. Prestige
5. Social connections
Through what intervening mechanisms are the inequities in health closely linked to the social inequities?
Health behaviors
Medical care
Working conditions
Environmental exposure
Personality
Early life conditions
What are ways to neutralize the social determinants of health?
Cultural humility
Lifestyle (e.g. sedentary vs active)
Illness/disability (e.g. locus of control)
Cultural Humility vs. Cultural Competence
Cultural humility is the ability to recognize one's limitations to avoid making assumptions about other cultures while cultural competence is the ability to work respectfully with people from diverse cultures while recognizing one's own cultural biases
What can the application of cultural humility to patient charting have a direct impact on?
Readmissions
Pain management ("drug seeking")
Surgical procedures
General health outcomes
Internal vs. External Locus of Control
Internal control is the belief that one's effort and decisions determine outcomes ("I am in control") whereas external control is the belief that luck, fate, and other people determine outcomes ("outcomes are beyond my control")
What did the initiative introduced by the Department of Health and Human Services in 1980 present?
A national strategy for increasing the span of healthy lives by reducing health disparities through the provision of access to preventive health services for all Americans
What type of impact did the initiative introduced by the Department of Health and Human Services have on the nation?
Geographic areas have become increasingly interested in population health monitoring and in providing background data needed to understand a population's health equity issues
What were the 2 main results of the Department of Health and Human Services initiative?
1. Improvements in access to healthcare (e.g. medications)
2. Higher life expectancies
What does trauma-informed care shift the focus from?
"What's wrong with you?" to "What happened to you?"
What does trauma-informed care seek to do?
Realize the impact of trauma and understand recovery paths
Recognize the signs and symptoms of trauma
Integrate knowledge about trauma into practices
Actively avoid re-traumatization