Anatomy Lab 3 Skull
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
1. Support: a hard framework that supports the weight of the body
2. Movement: used as levers for muscles for human locomotion and movement
3. Protection: The skull protects the brain, vertebrae surround the spinal cord, and the rib cage protects the organs of the thorax
4. Mineral Storage: calcium and phosphate, released into the bloodstream
5. Blood cell formation and energy storage: red and yellow marrow
6. Energy metabolism: osteoblasts secrete osteocalcin (hormone) that stimulates pancreatic secretions that reduce blood sugar levels; makes cells store less fat and secrete a hormone to increase insulin sensitivity of cells
What are the six functions of bones/skeletal system?
Yellow: site of fat storage, with little or no role in blood cell formation
Red: makes blood cells
Difference between yellow and red marrow
classified by shape: long, short, flat, or irregular
By what characteristics are bones classified? List and describe the four classifications of bones. Give examples of each
longer than they are wide with two distinct ends; most limbs, even fingers and toes
Long bone
cube-shaped, sesamoid bones (seed-shaped) forms within a tendon; alter the direction of pull in a tendon/reduce and modify pressure in tendons; ex. patella
Short bone
thin, flattened, curved; ex. cranial bones of the skull, sternum, scapula
Flat bones
irregular shapes that do not fit into the previous categories; ex. vertebrae and hip bones
Irregular bones
- compact bone: dense outer layer that looks smooth and solid; external layer
- Spongy bone (trabecular bone): honeycomb trabeculae; the network of open spaces between the trabeculae are filled with red or yellow bone marrow
Differences between compact and spongy bone
- By canaliculi which are extensions of osteocytes that touch each other and form gap junctions; nutrients form capillaries cross at gap junctions and into osteocytes, then, the nutrients run between osteocytes to distribute the nutrients
- How do the mature bone cells connect to each other? What is the purpose of this formation?
Osteocytes:
keep bone matrix healthy; occupy lacunae; canaliculi; run through the matrix connecting neighboring lacunae to one other and to capillaries in central canals
-What are the mature bone cells called and what do they do? What do their bodies occupy? And what do those bodies' legs occupy? What is the function of this?
Osteon/Haversian system
What system makes up compact bone
Lamellae:
- Concentric (complete rings within osteon),
-Interstitial (incomplete lamellae that were cut by bone remodeling),
- circumferential (extends around the entire circumference of diaphysis, resist twisting of entire bone)
What are the tubes and rings called that make up the Osteon system? Give examples
have blood vessels that supply nutrients to bone cells of the osteon and nerve fibers;
What are the osteonic/central canals? What do they do
Osteonic canal/Haversian/Central Canal
Perforating/Volkmann's canals
What are the canals in the Osteon system
has blood vessels that supply nutrients to bone cells of the osteon and nerve fibers;
Osteonic canal/ Haversian canal
lie at right angles to central canals and connect blood and nerve supply of the periosteum to the central canals and marrow cavity
Perforating/Volkmann's canals
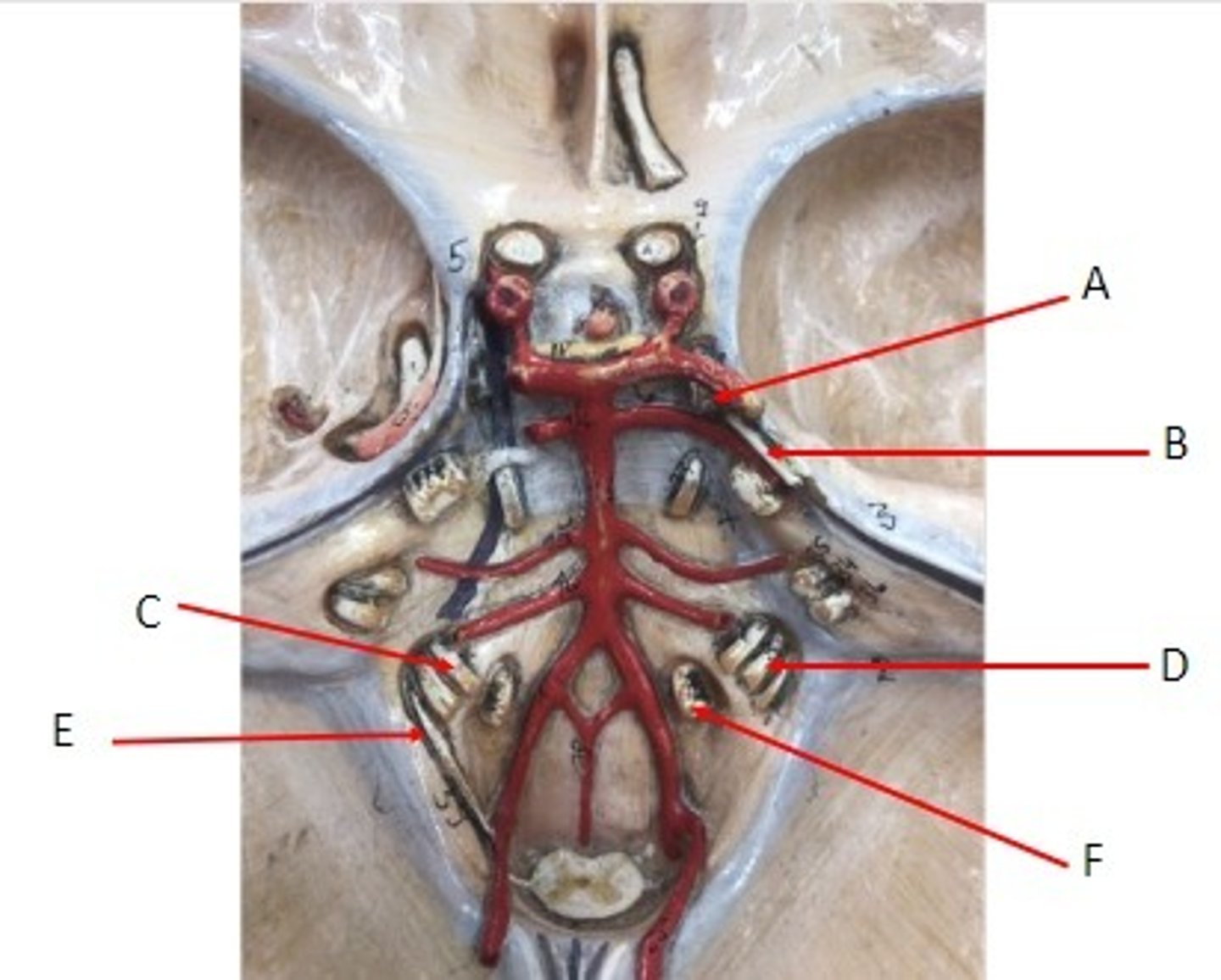
A: Osteon/Haversian system
B: Central canal/Haversian/Osteonic canal
C: Concentric lamella
D: Interstitial lamella
E: Osteocyte
F: Lacuna
G: Canaliculus
Identify the structures.
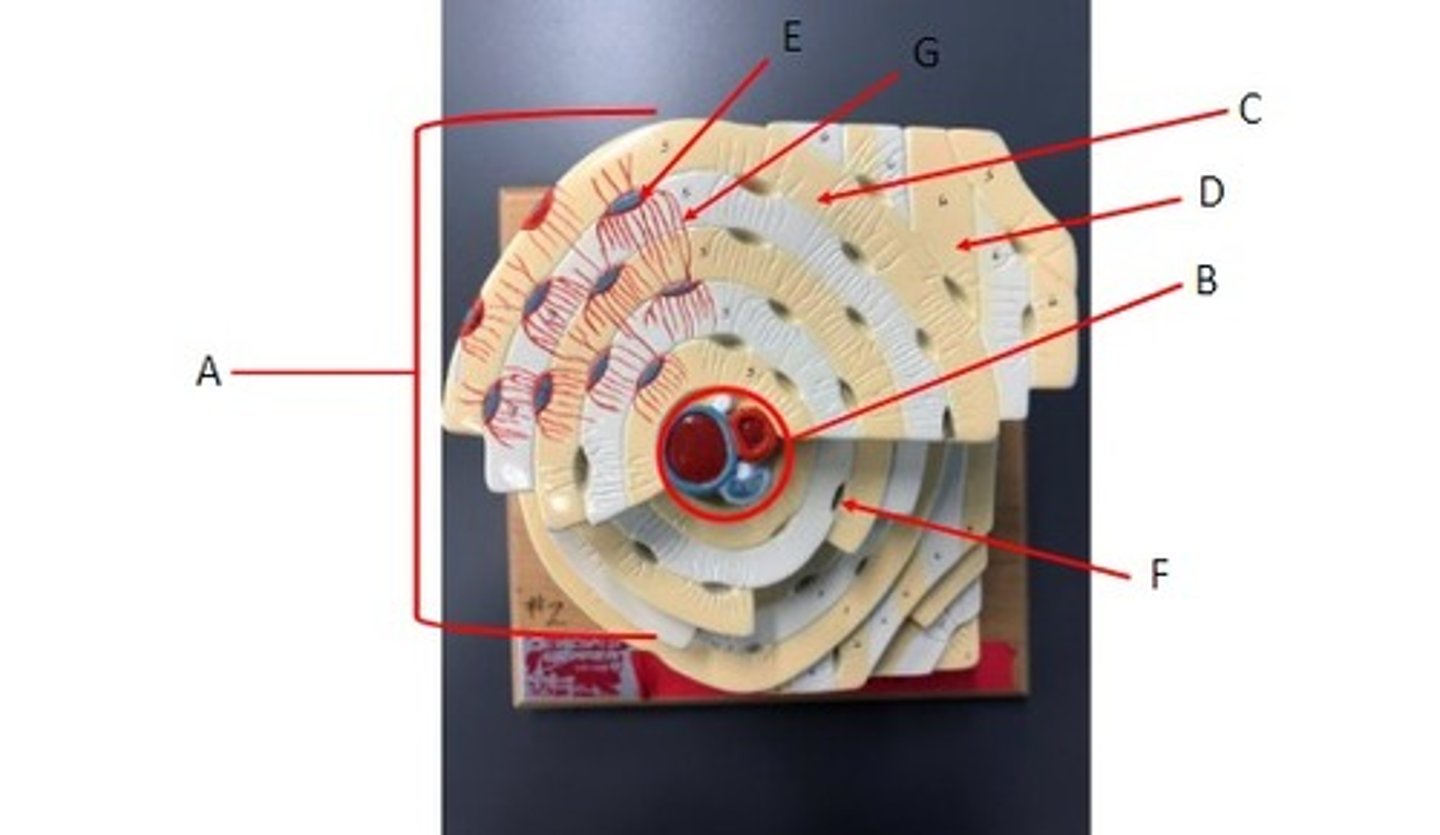
A: Osteocyte
B: Lacuna
C: Canaliculi
Identify the structures.
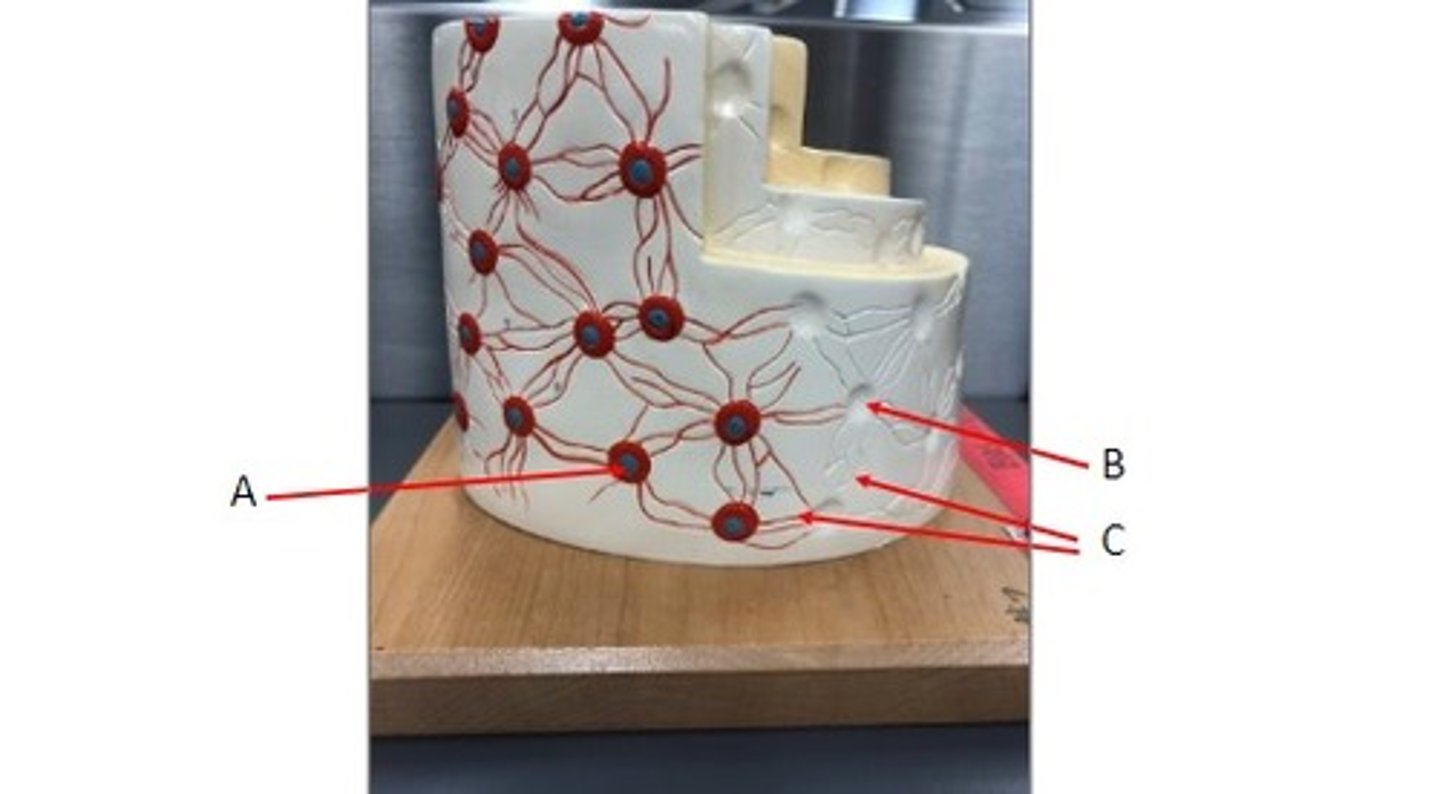
A: Outer circumferential lamellae
B: Inner Circumferential lamellae
Identify the structures.
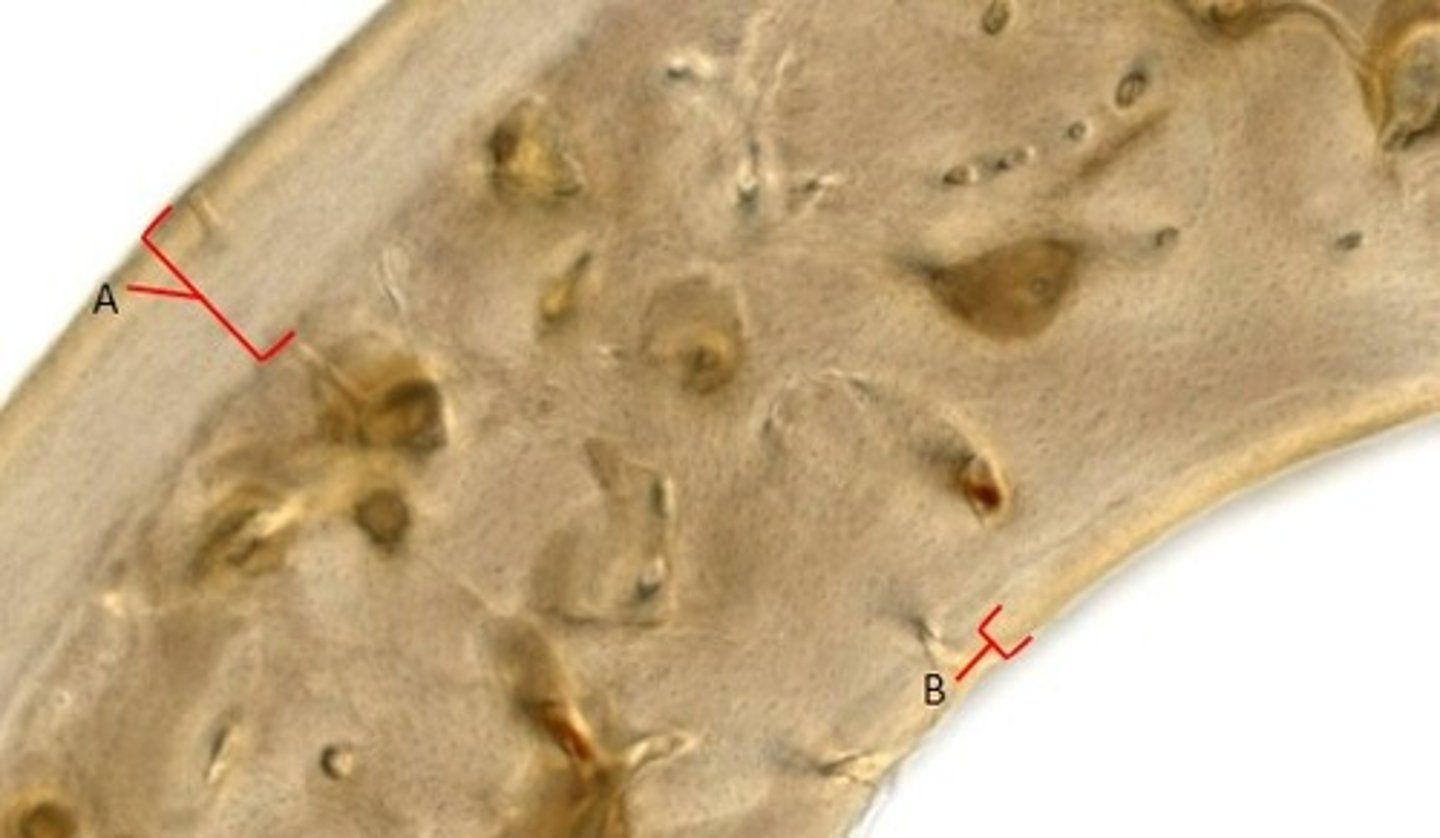
Perforating/Volkmann's canal
Identify the structures.
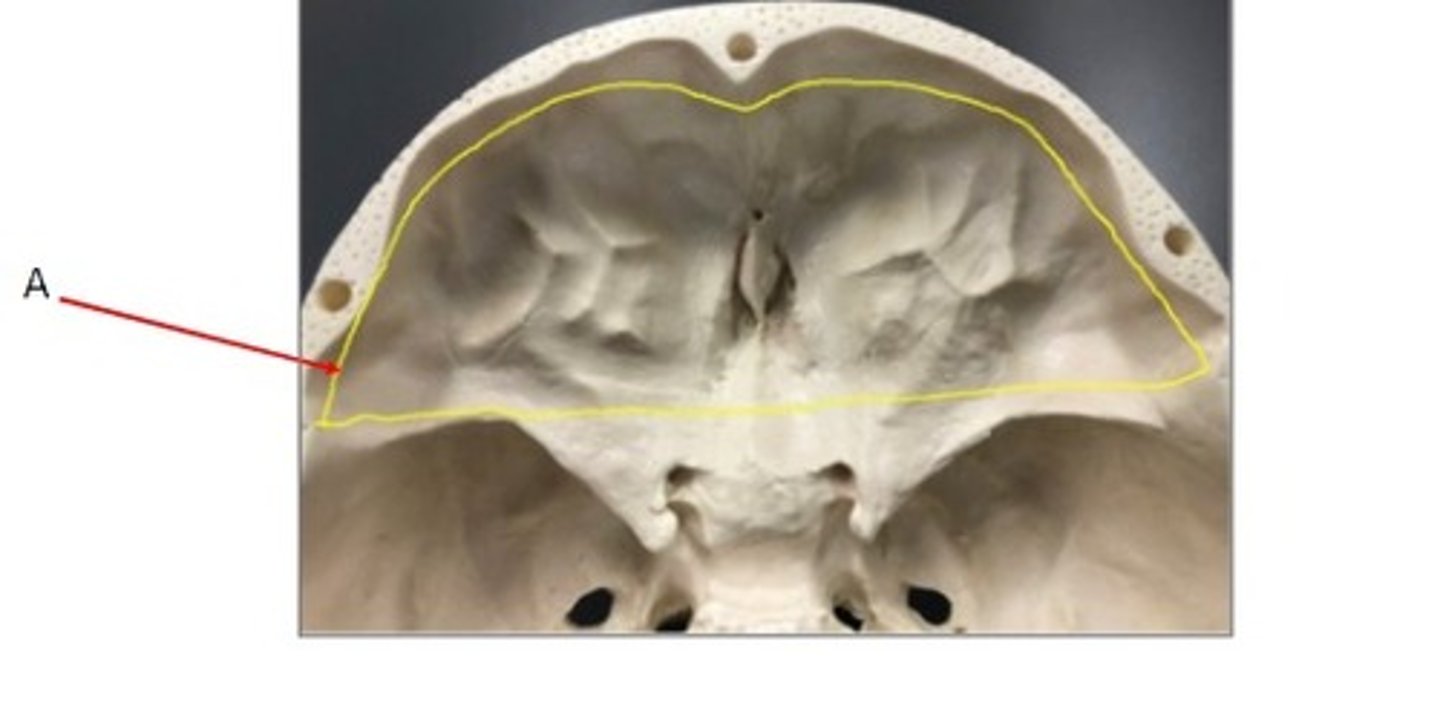
- Canial bone
- Frontal bone
- A: Supraorbital notch/foramen
- B: Zygomatic process
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
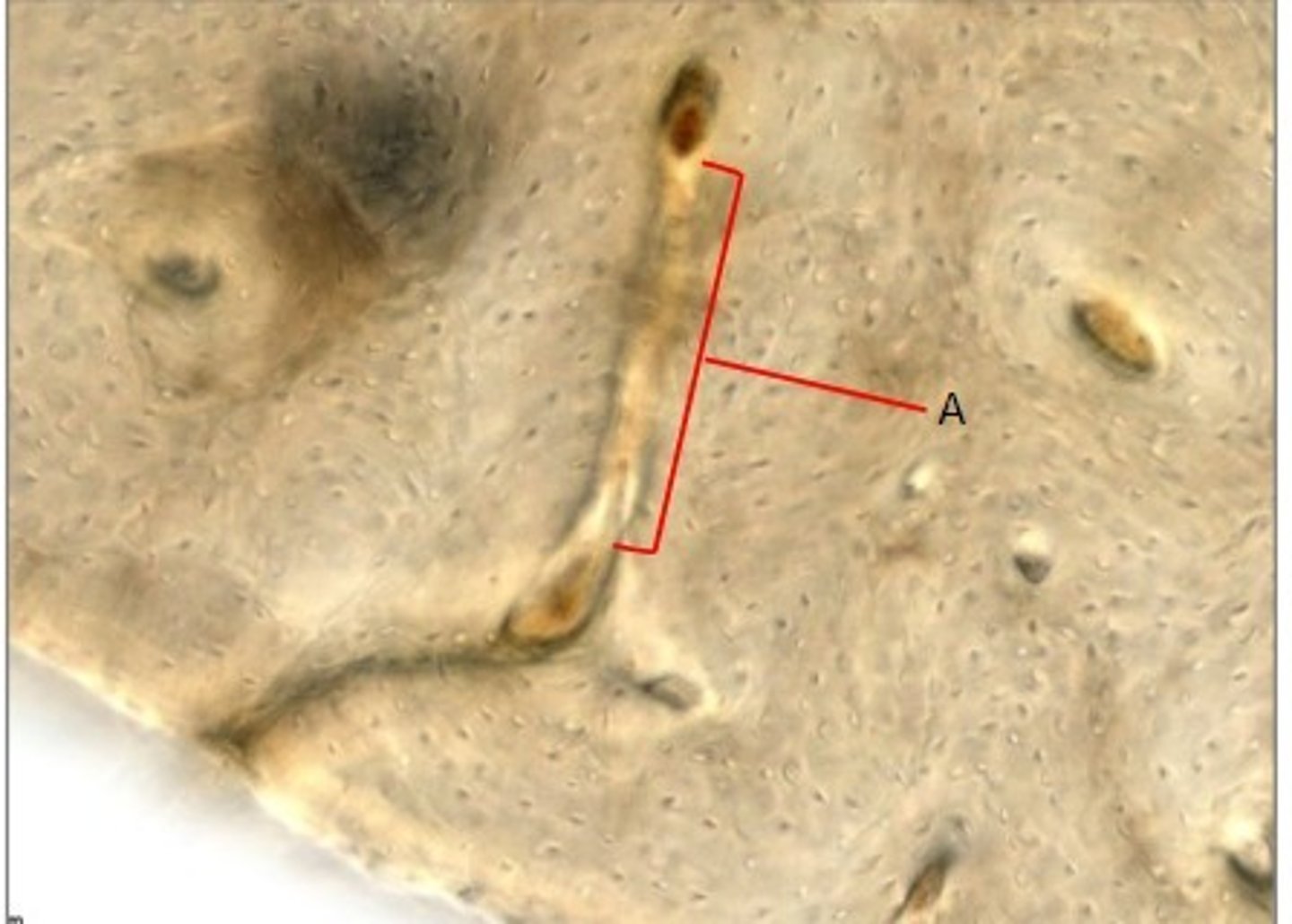
- Canial bone
- Frontal bone
- A: Anterior Cranial Fossa
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
Frontal bone
What bone is this?
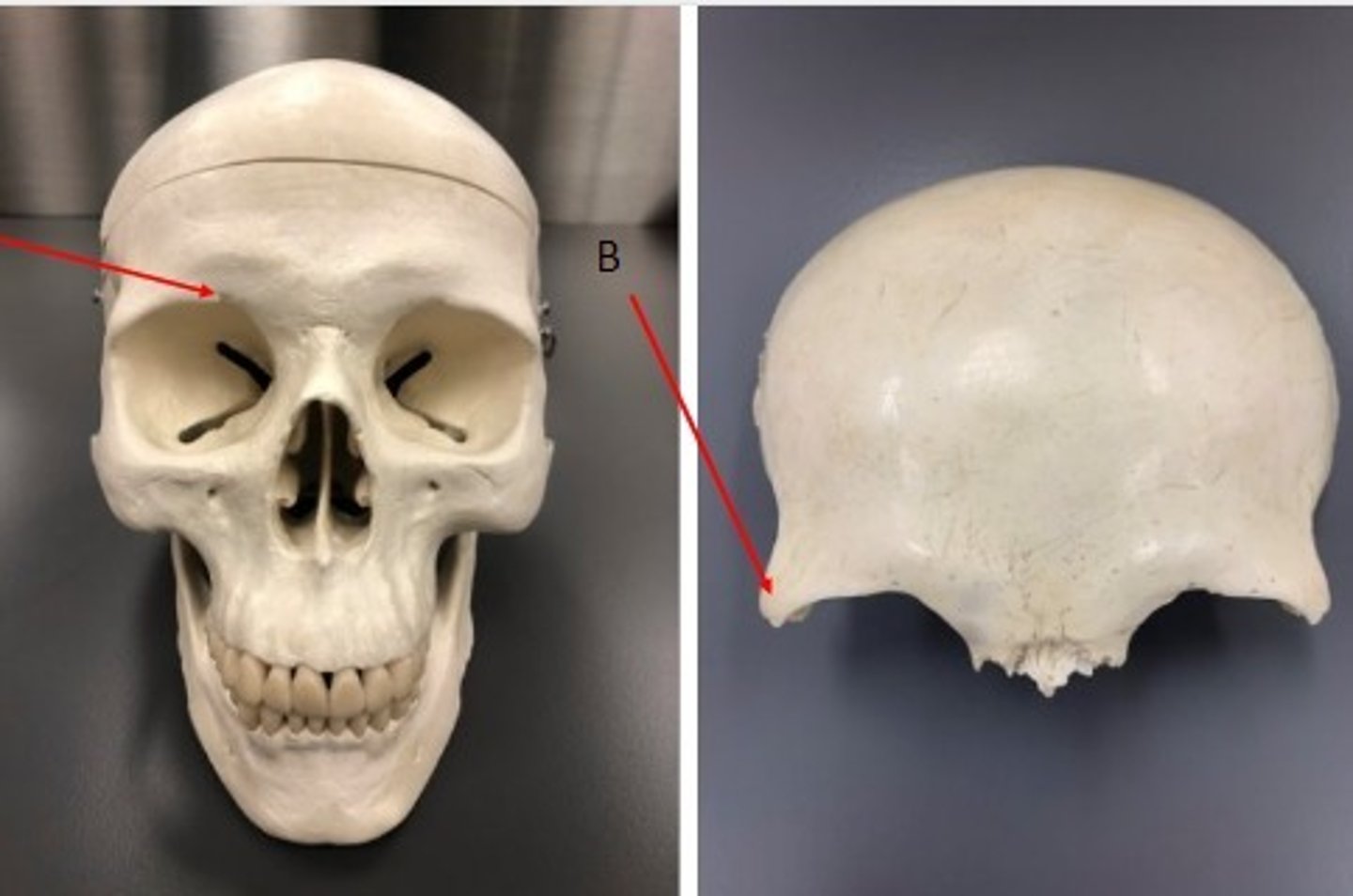
- Cranial Bones
- Frontal Bone
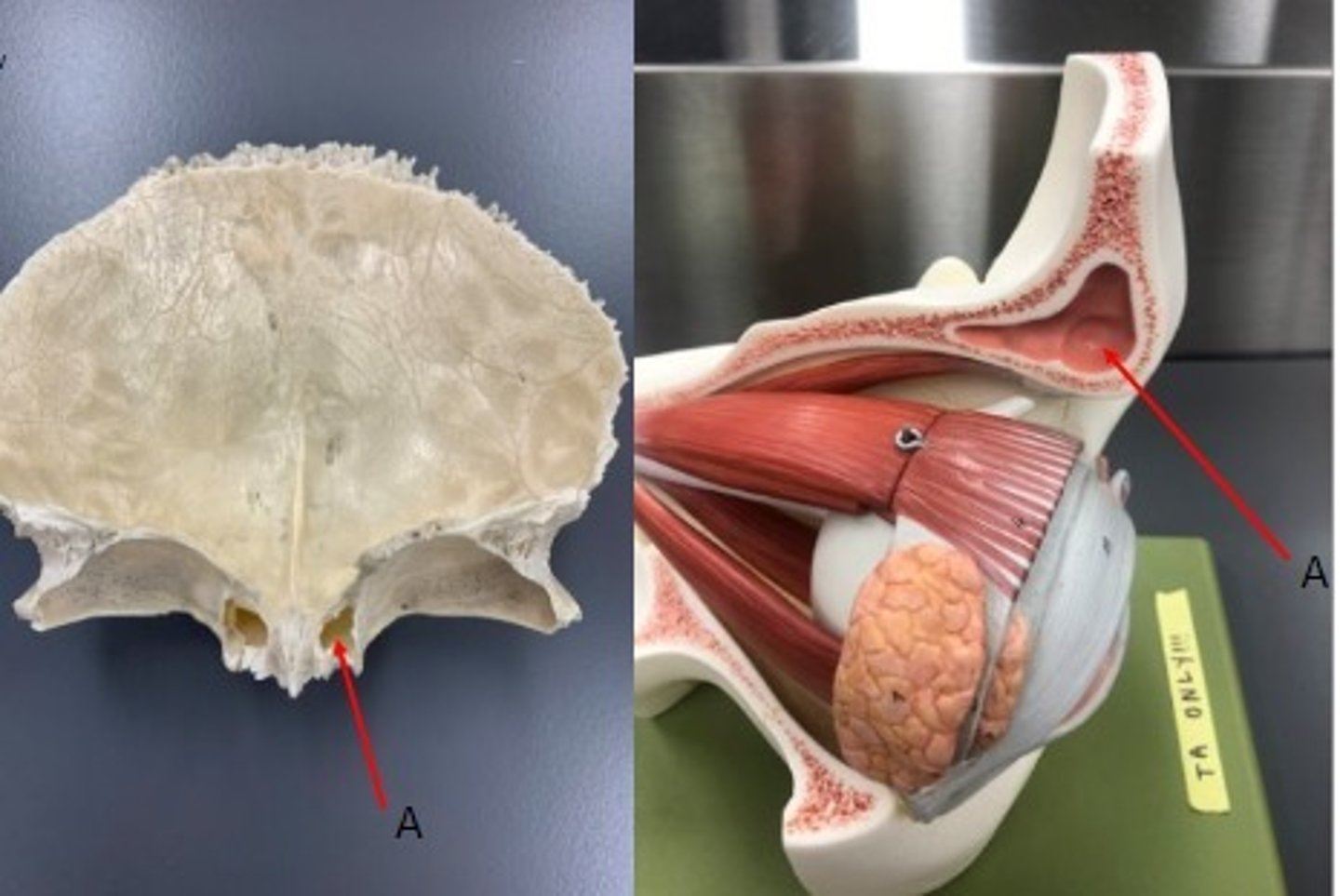
- A: Frontal sinus
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structure.
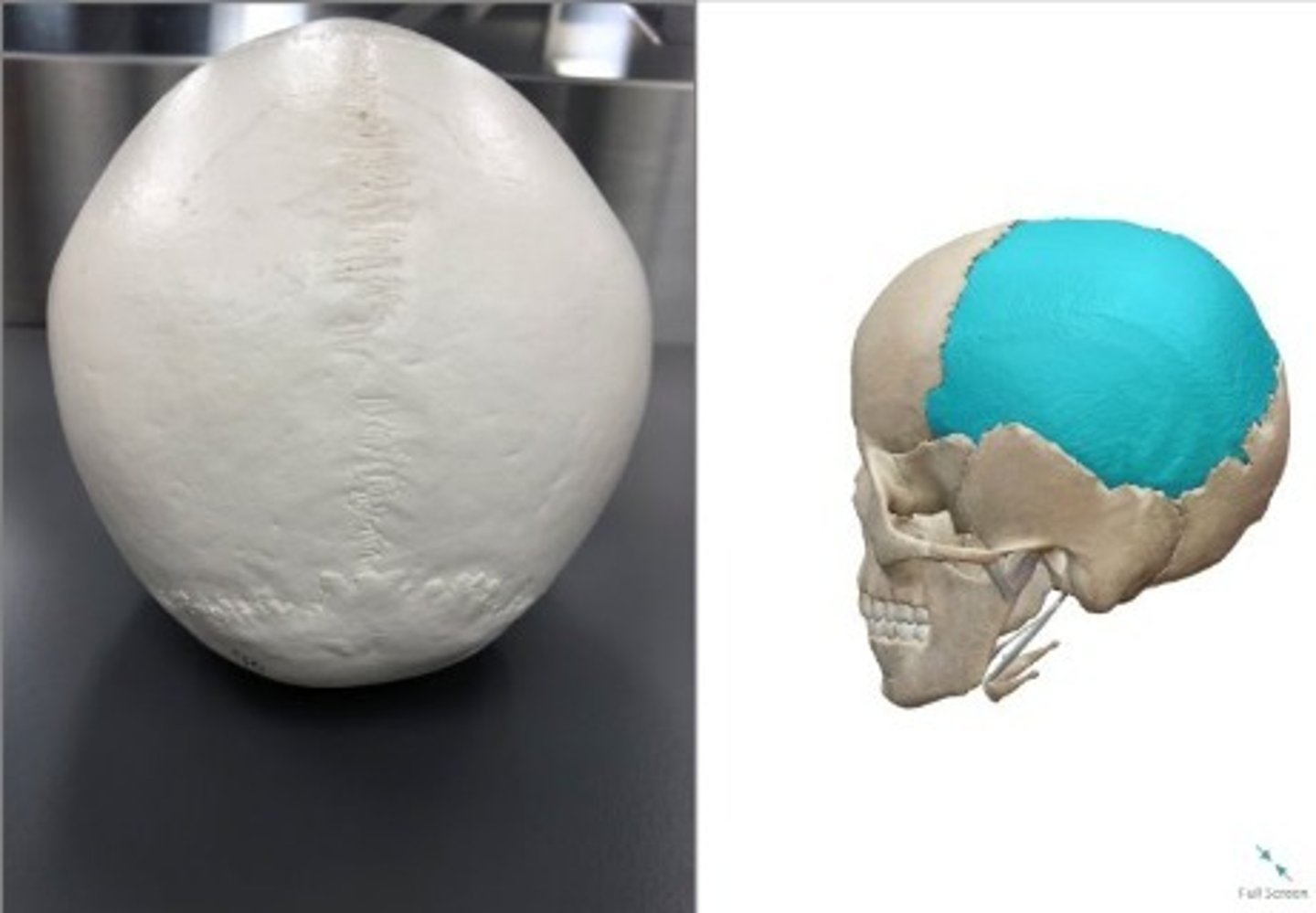
- Cranial Bones
- Parietal bone
What category of bone is this? What bone is this?
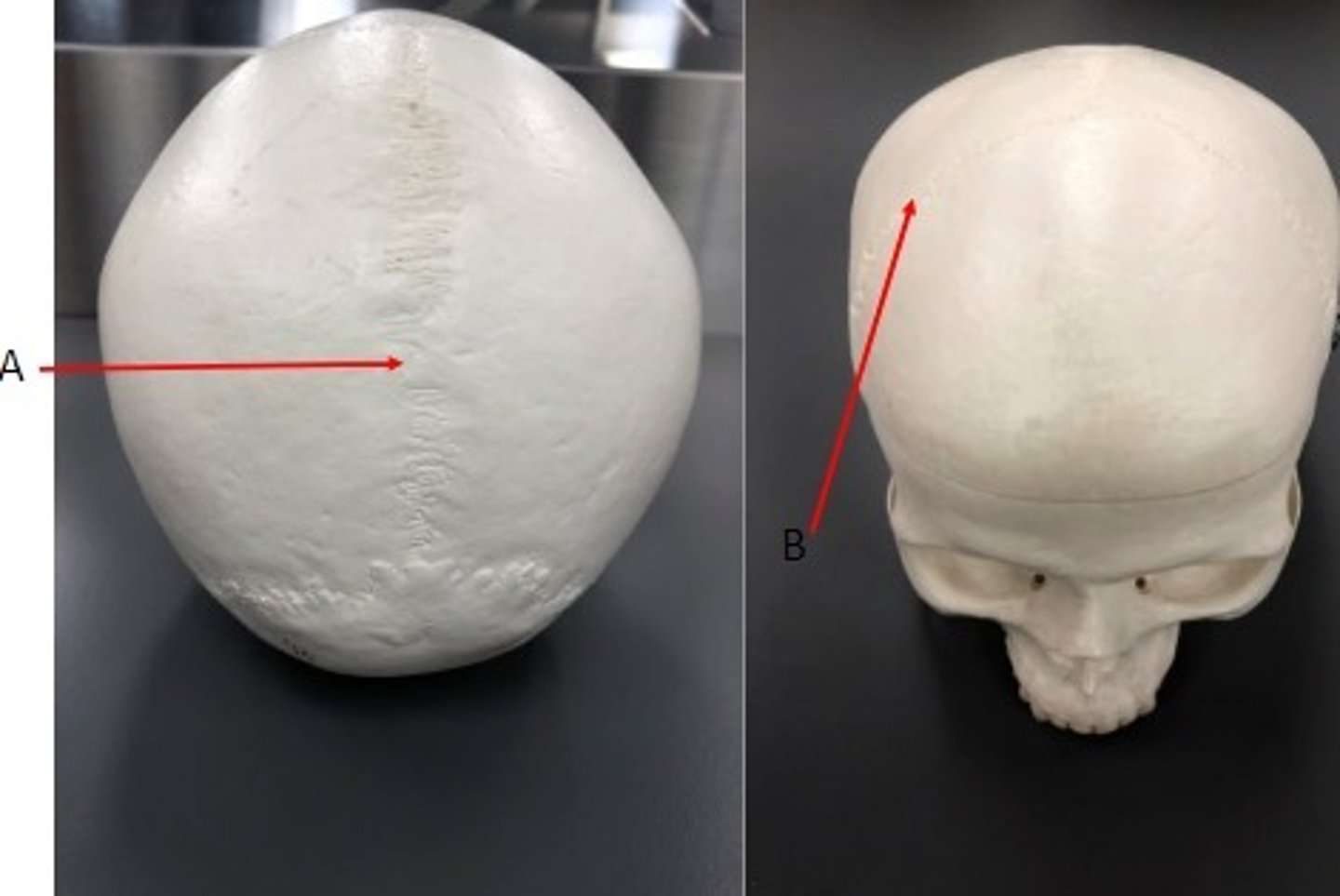
A: Sagittal suture
B: Coronal suture
Label the structures.
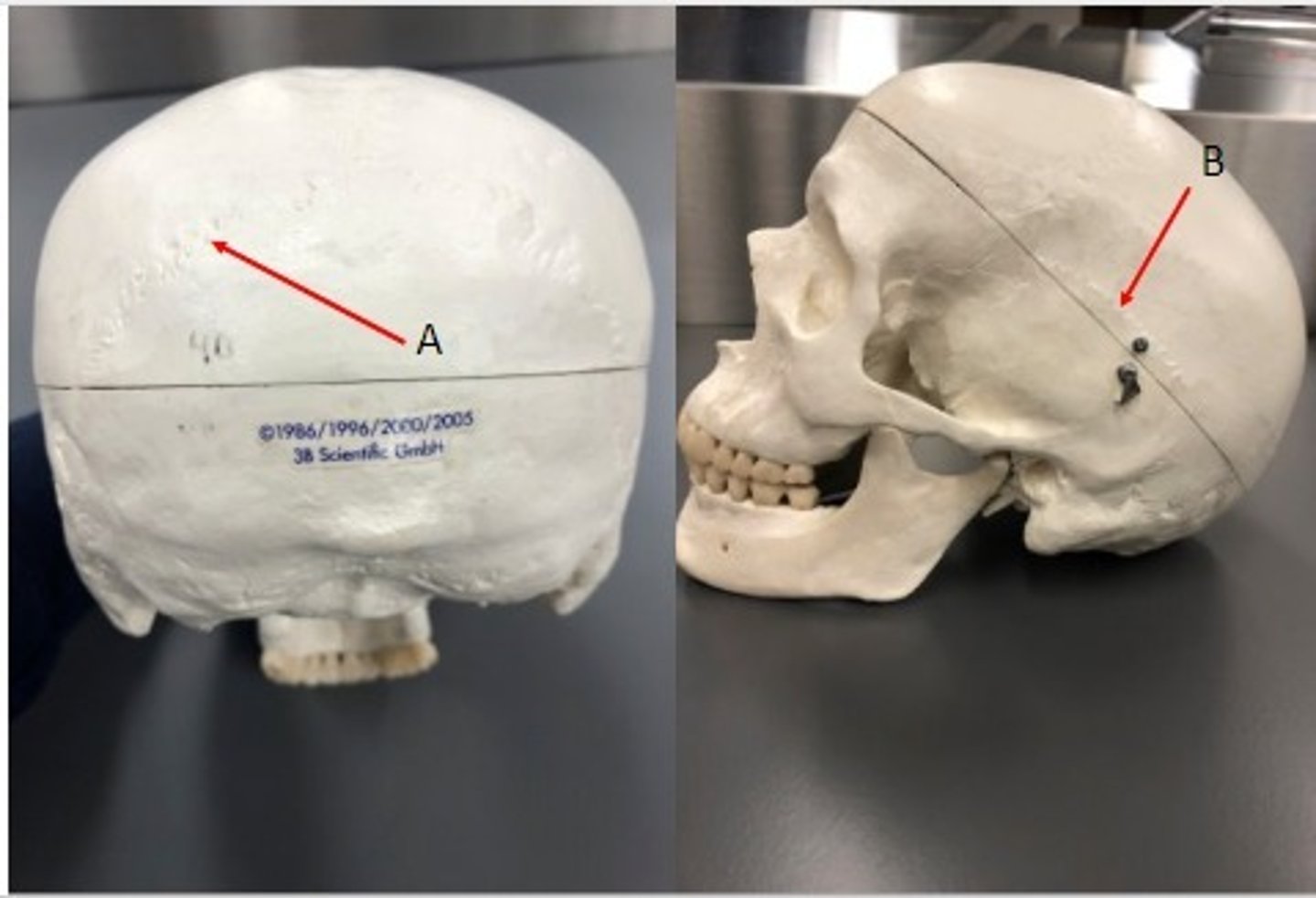
A: Lambdoid suture
B: Squamous suture
Label the structures.
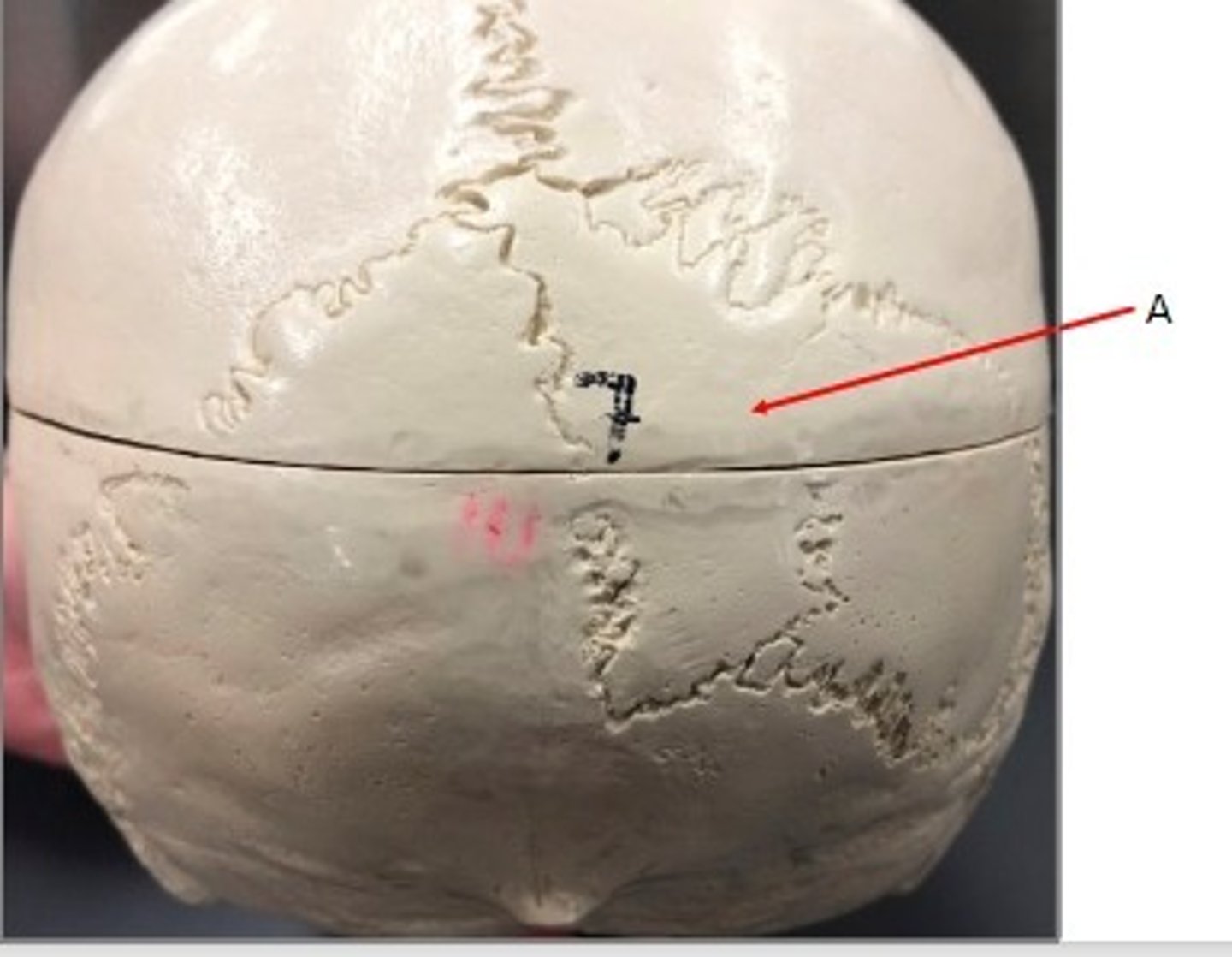
Wormian/Sutural bones
Label the structure

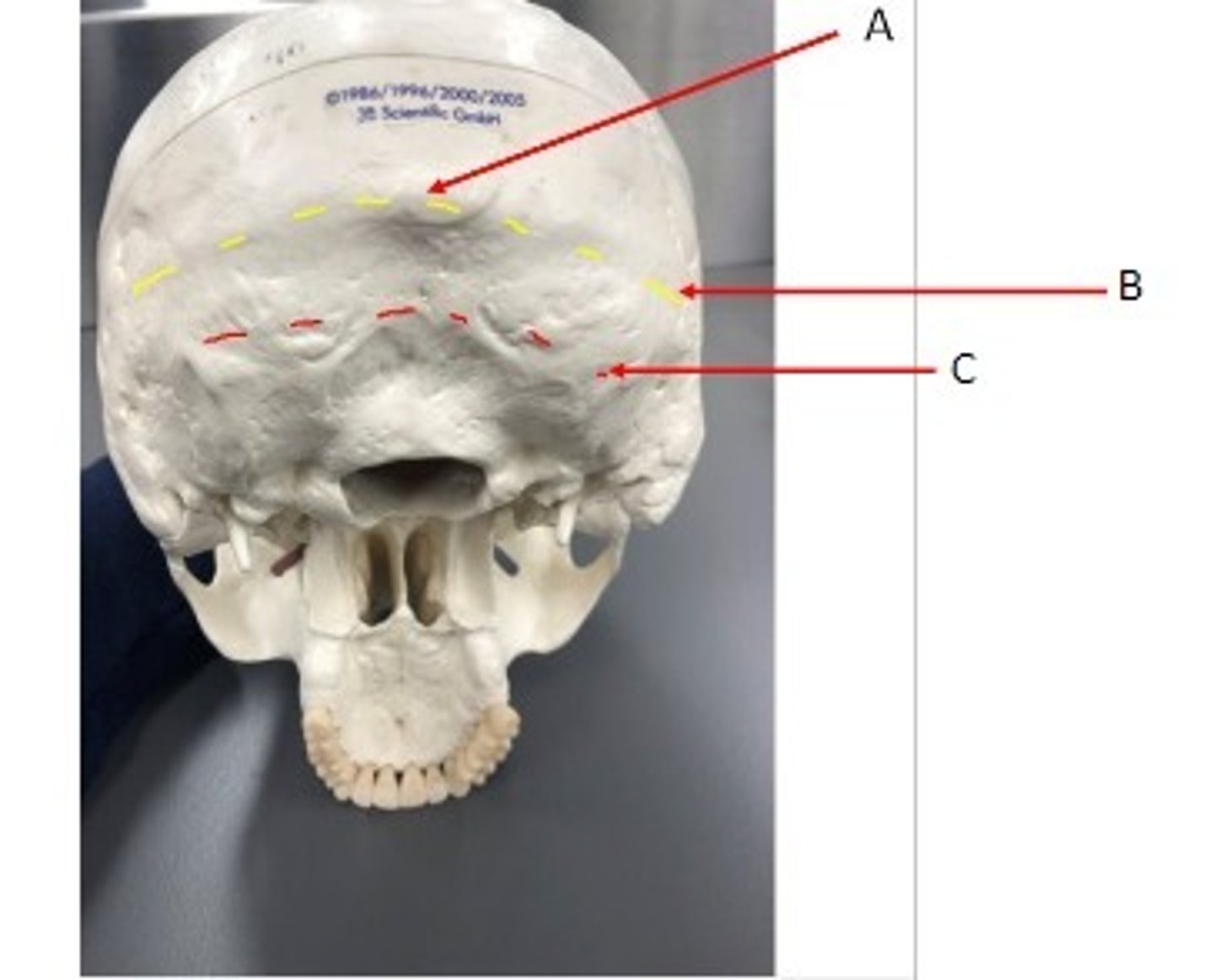
- Cranial bone
- Occipital bone
What category of bone is it? What bone is it?
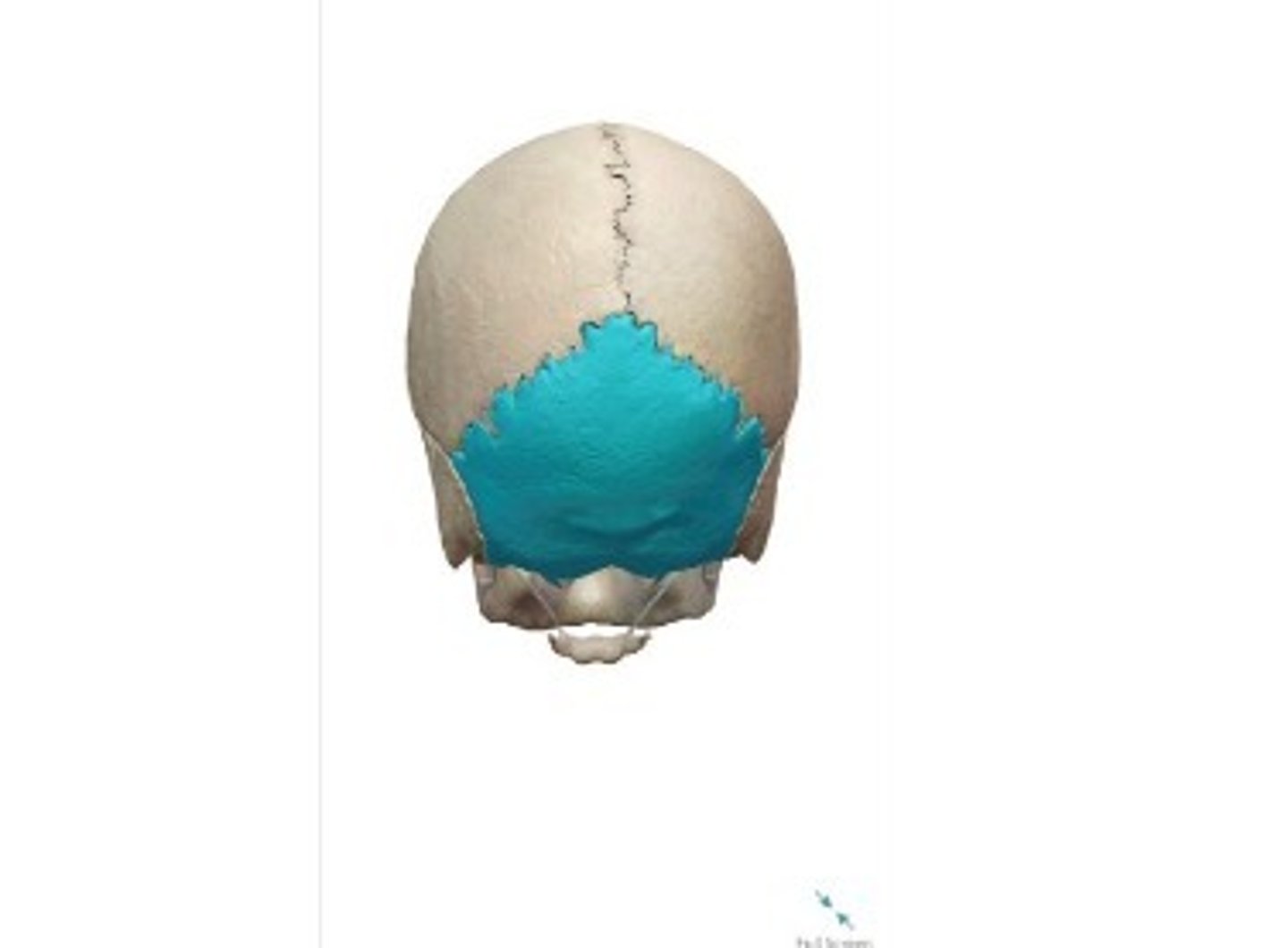
- Cranial bone
- Occipital bone
- A: External occipital protuberance
- B: Superior nuchal line
- C: Inferior nuchal line
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
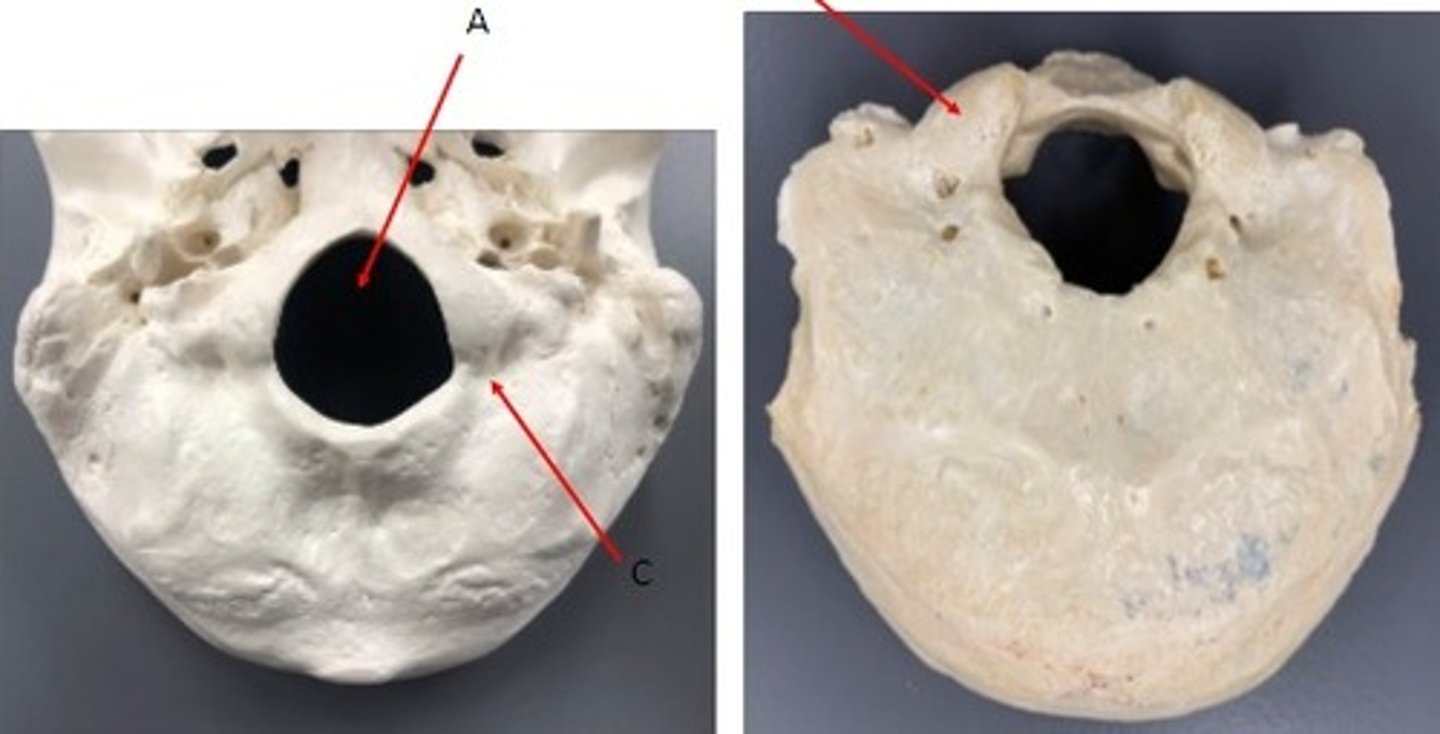
- Cranial Cone
- Occipital bone
- A: Foramen magnum
- B: Occipital condyle
- C: Condylar/Condyloid fossa
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
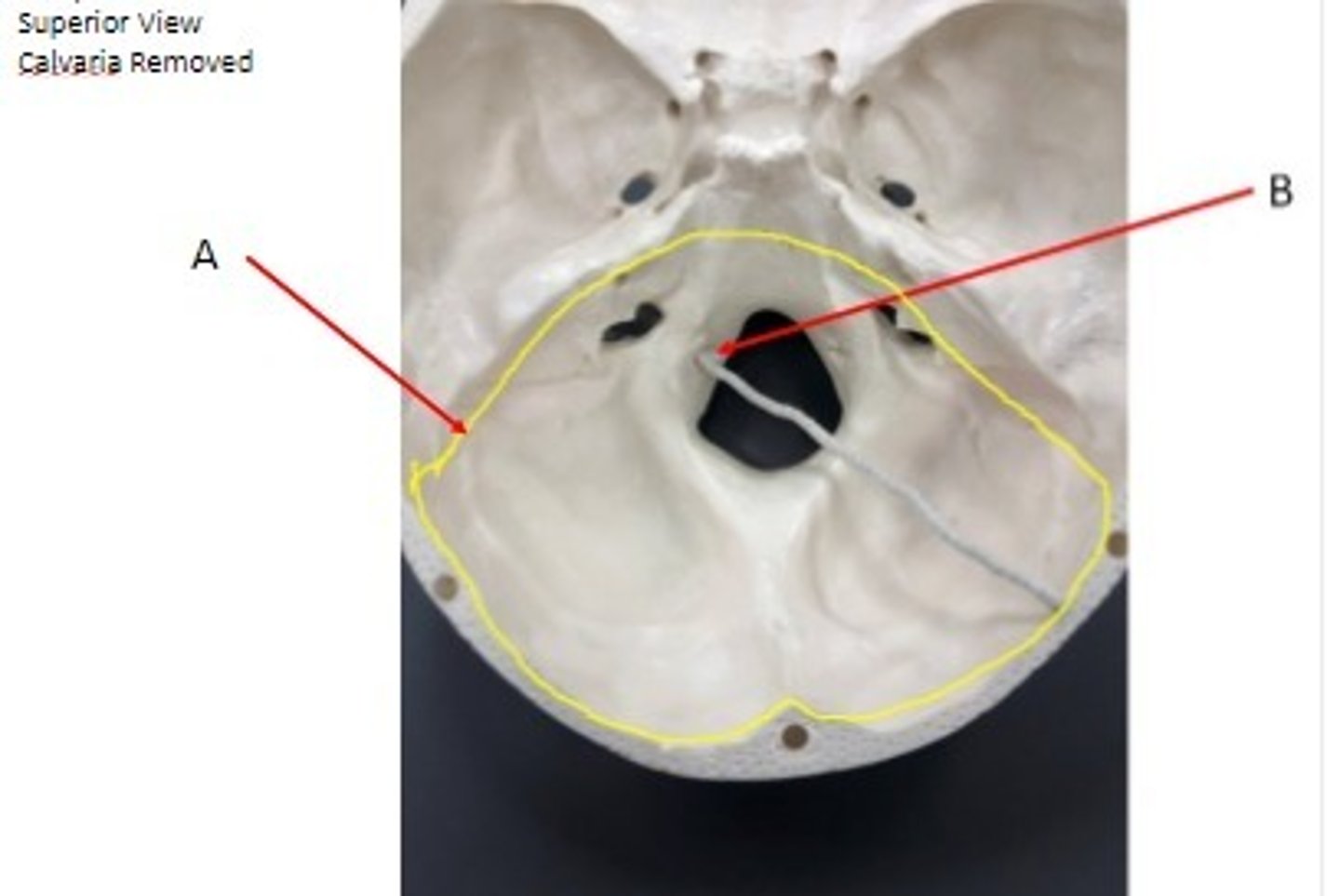
- Cranial bone
- Occipital bone
- A: Posterior cranial fossa
- B: Hypoglossal canal
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
- Cranial bones
- Temporal bone
What category of bone is it? What bone is it?
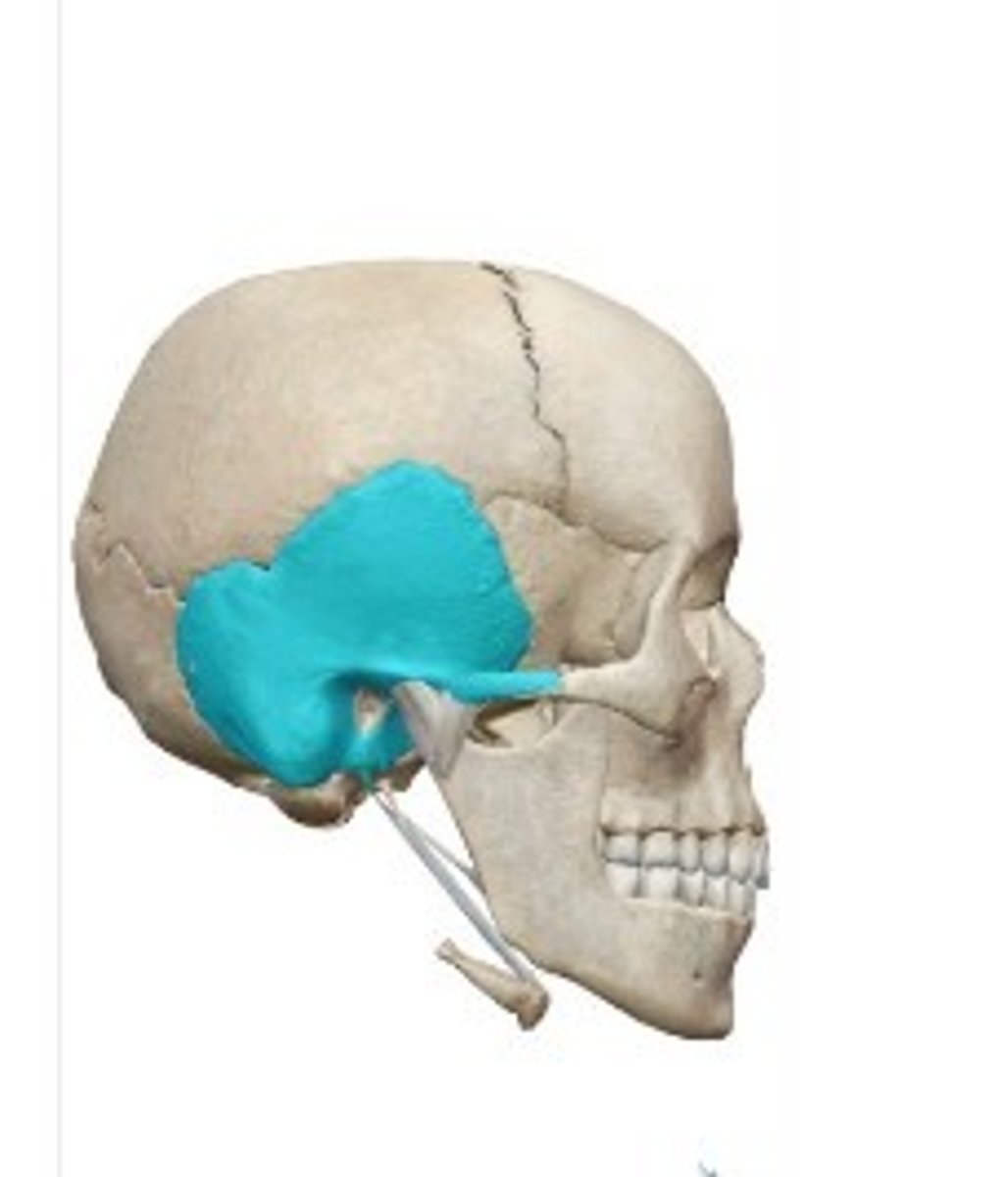
- Cranial bones
- Temporal bone
- A: Zygomatic arch- squamous region
- B: Mandibular fossa- squamous region
- C: Styloid process- tympanic region
- D: External auditory canal- tympanic region
- E: Mastoid process- mastoid region
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? What region is it? Label the structures.
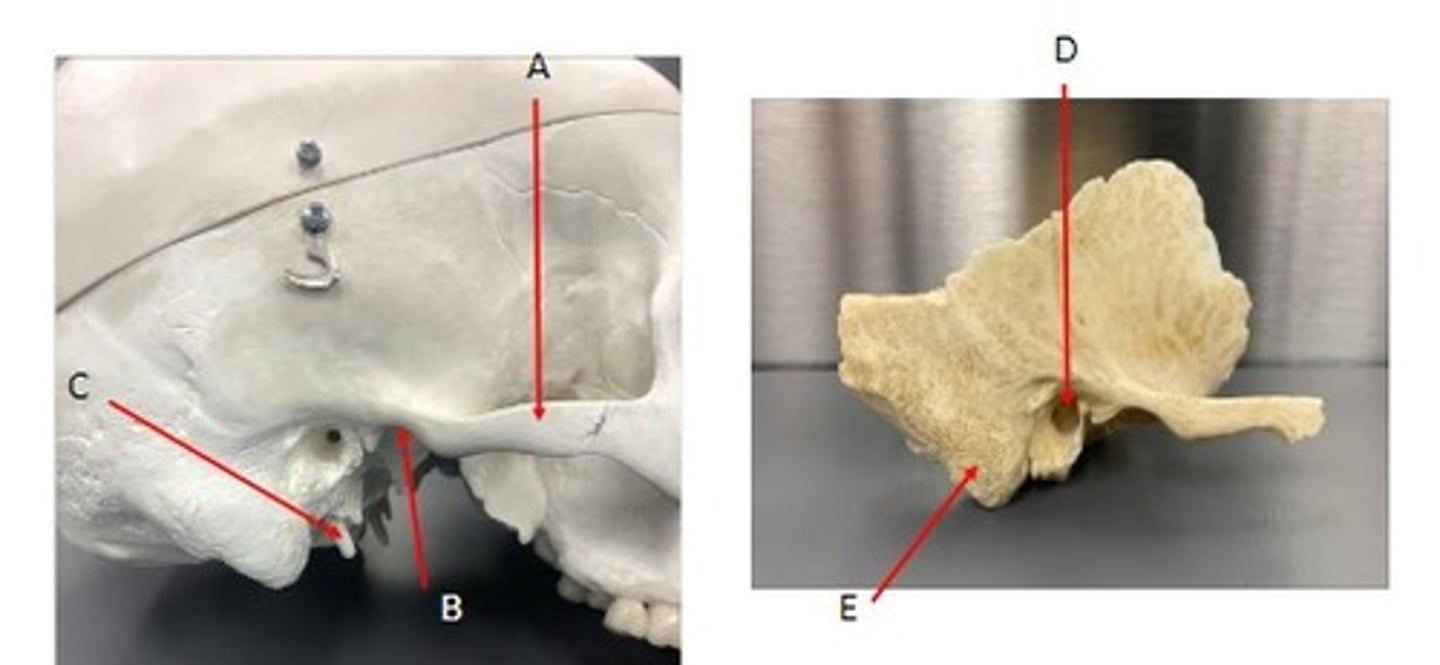
- Cranial bones
- Temporal bone
- A: Stylomastoid foramen- mastoid region
- B: Mastoid foramen- mastoid region
- C: middle cranial fossa
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
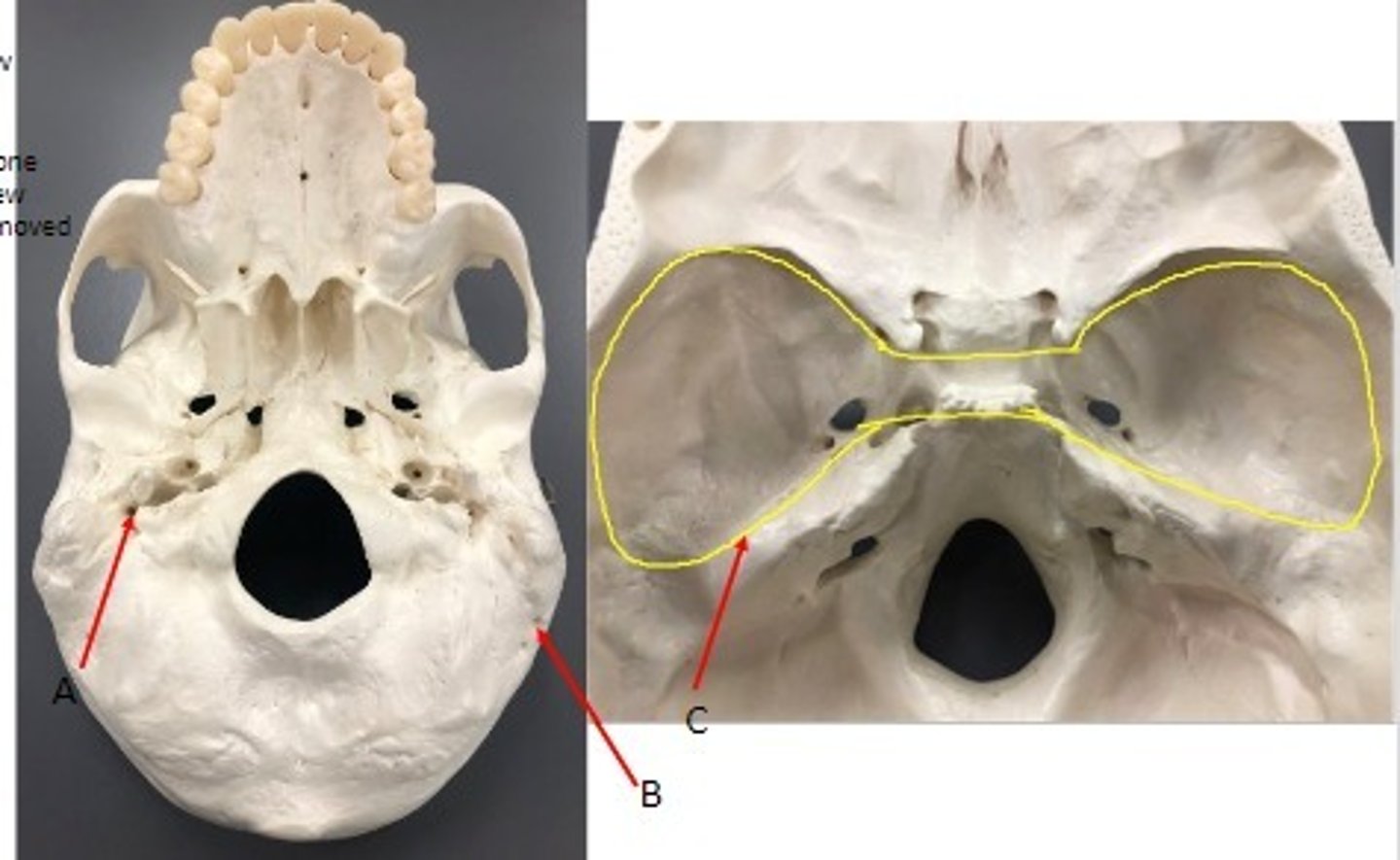
- Cranial bones
- Temporal bone
- A: Jugular foramen- petrous region → (anterior- temporal bone, posterior- occipital bone)
- B: Internal Auditory Canal- petrous region
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
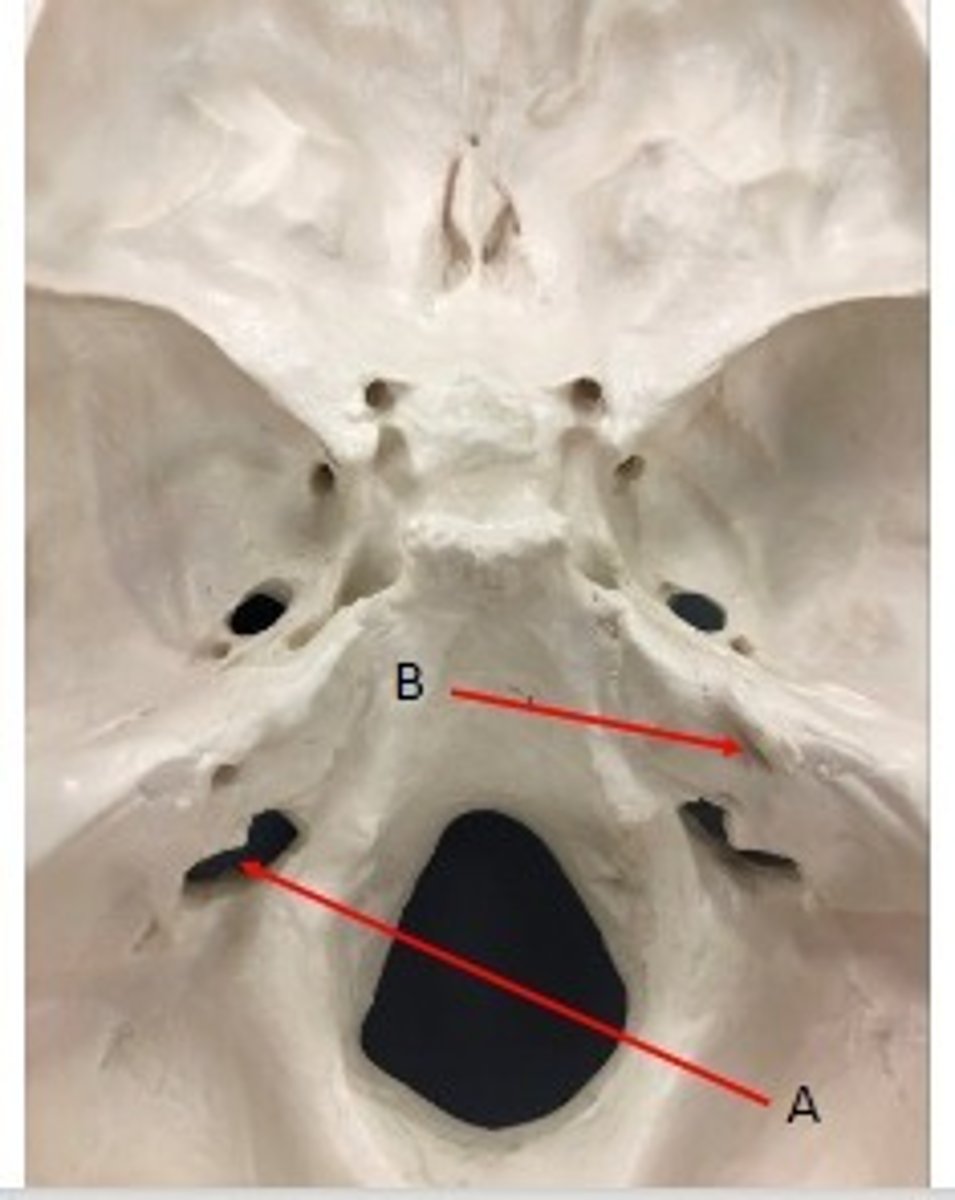
- Cranial Bones
- Temporal bones
- A: Carotid canal- petrous region
- B: Foramen lacerum- petrous region
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
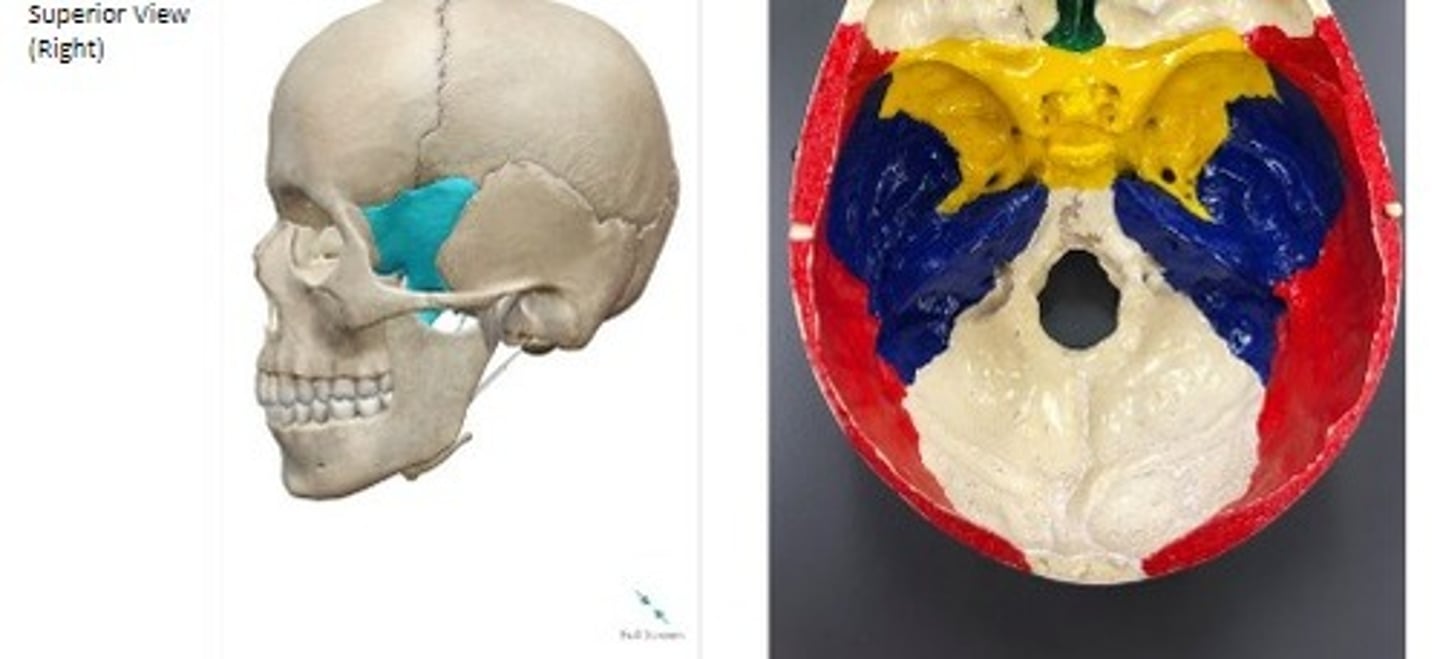
- Cranial bones
- Sphenoid bone
What category of bone is it? What bone is it?
- Cranial bones
- Sphenoid bone
- A: Jugum sphenoidale
- B: Tuberculum sellae
- C: Hypophyseal fossa
- D: Dorsum sellae
- E: Foramen ovale
- F: Foramen spinosum
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
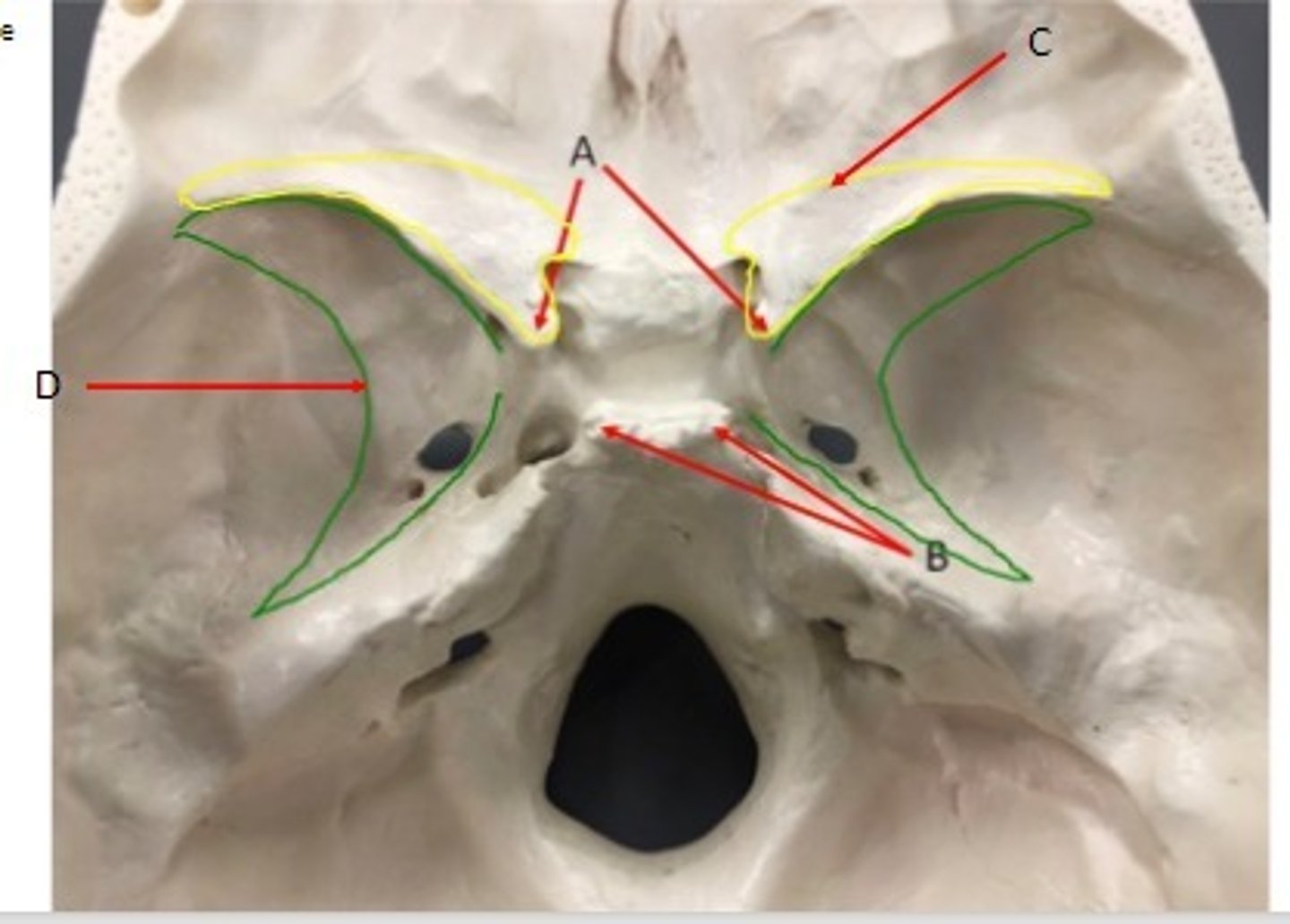
- Cranial Bones
- Sphenoid bone
- A: Anterior clinoid process
- B: Posterior clinoid process
- C: Lesser wings
- D: Greater wings
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
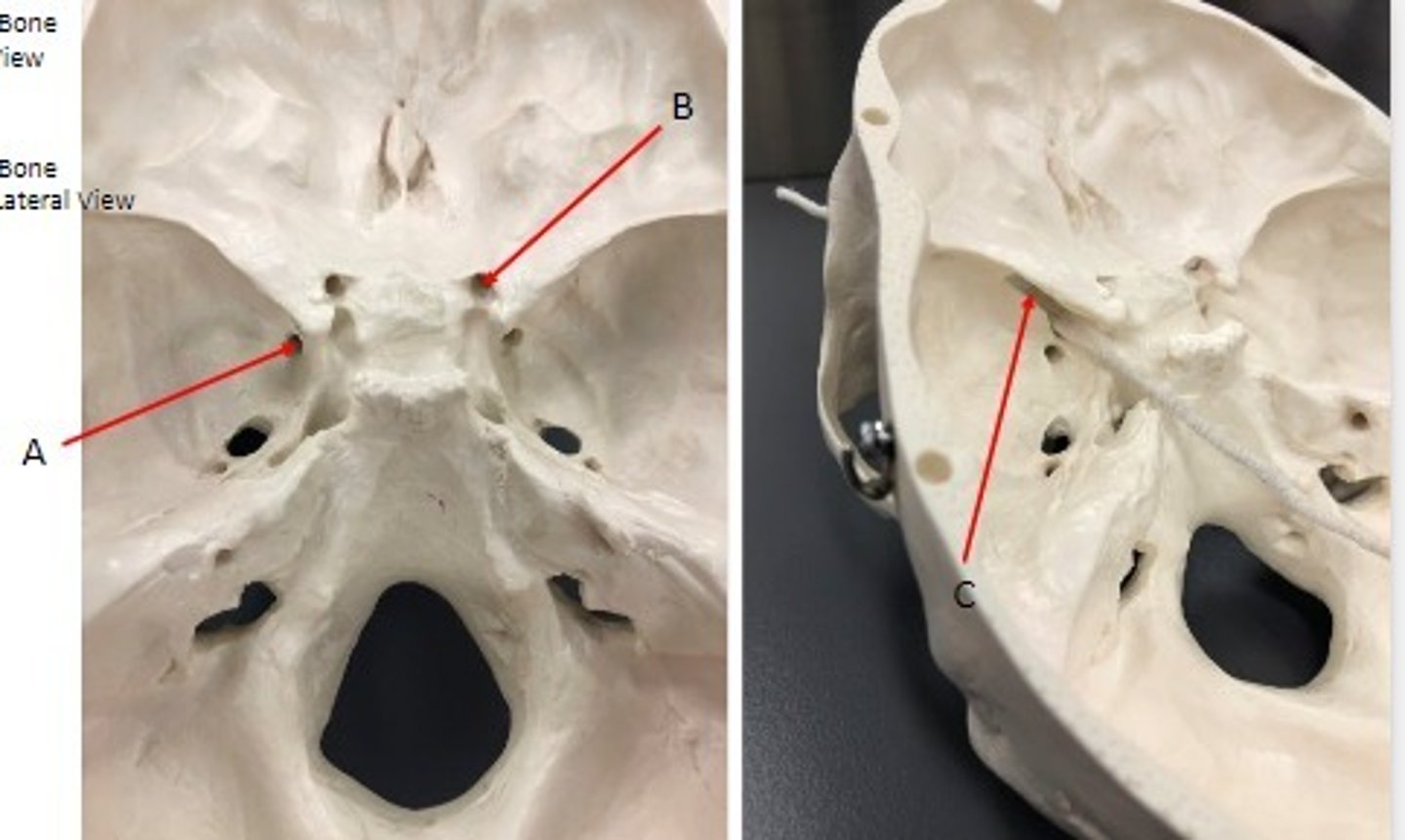
- Cranial bones
- Sphenoid bone
- A: Lateral pterygoid plate
- B: Medial pterygoid plate
- C: foramen ovale
- D: foramen spinosum
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
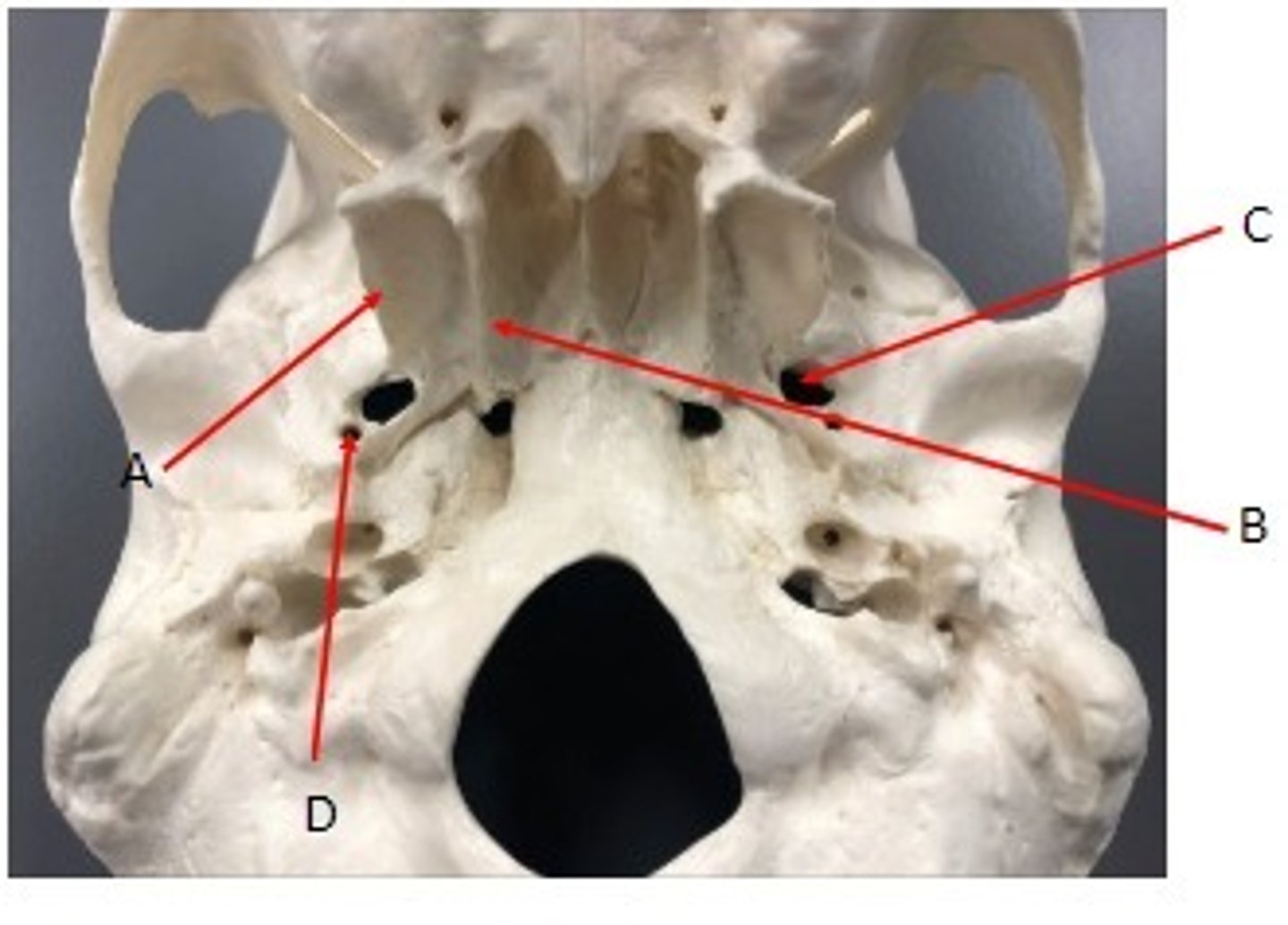
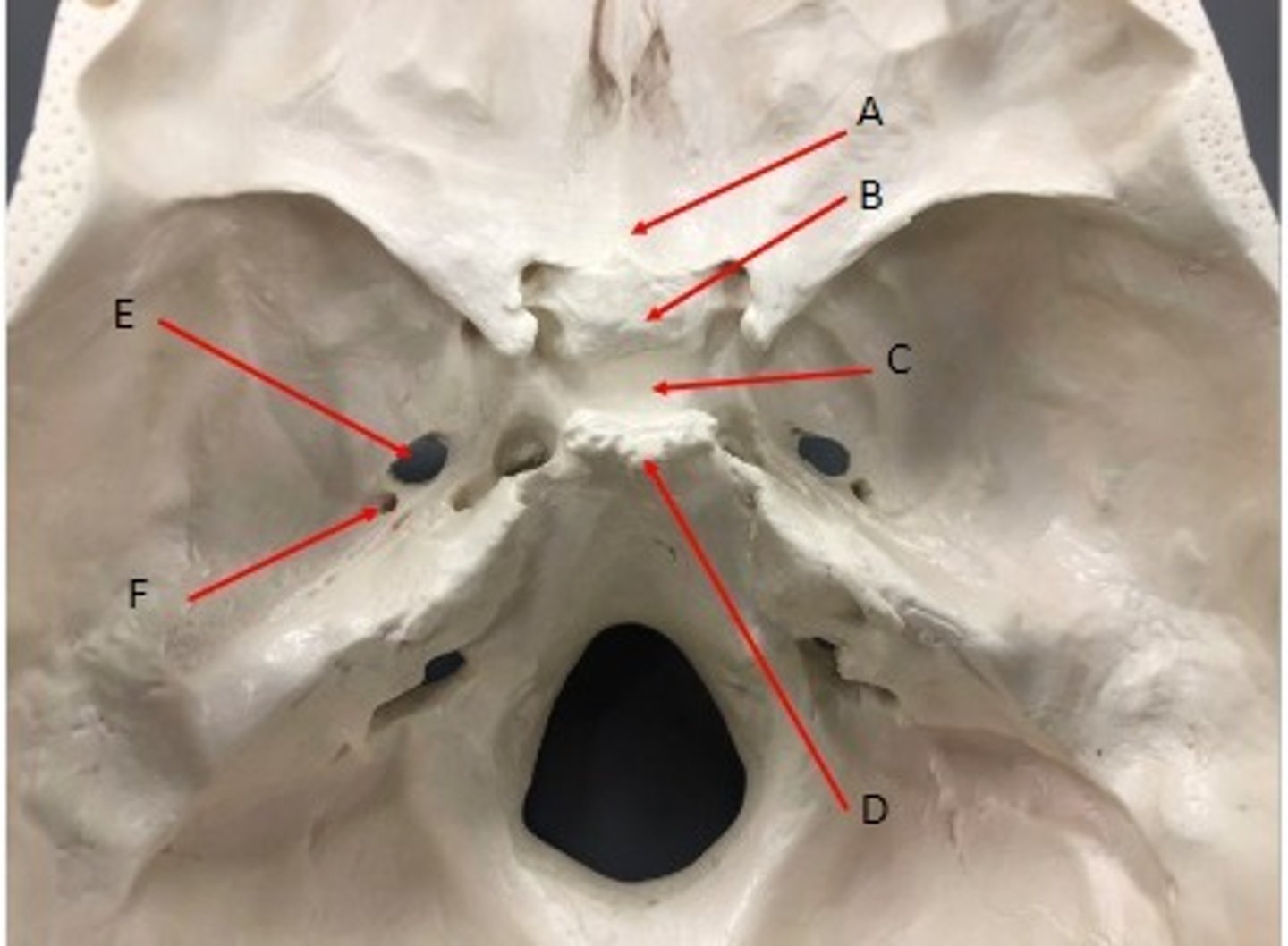
- Cranial bones
- Sphenoid bone
- A: Foramen rotundum
- B: optic canal
- C: superior orbital fissure
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
- Cranial bones
- Sphenoid bone
- A: Sphenoid sinus
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
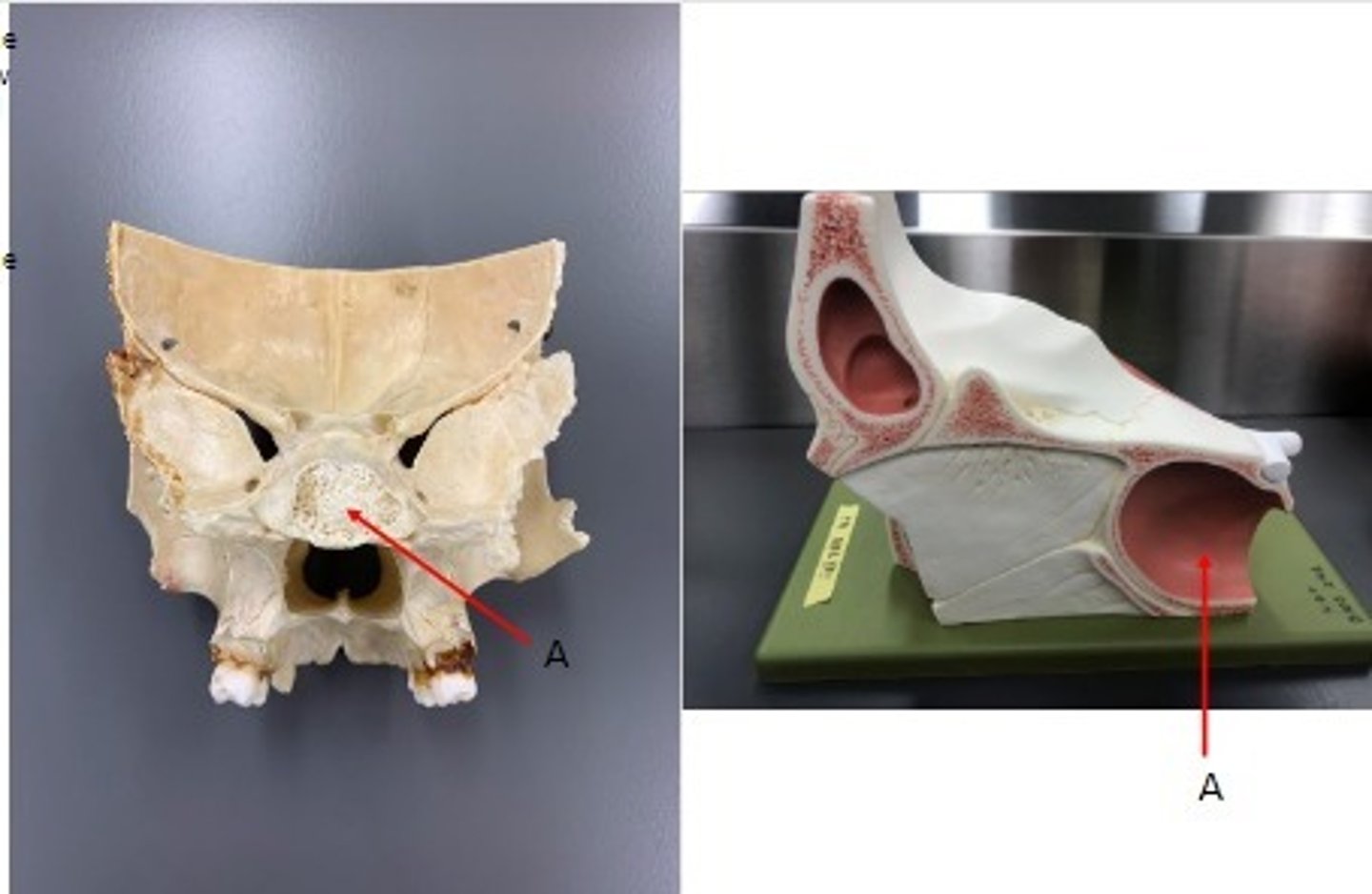
- Cranial bones
- Ethmoid bone
What category of bone is it? What bone is it?
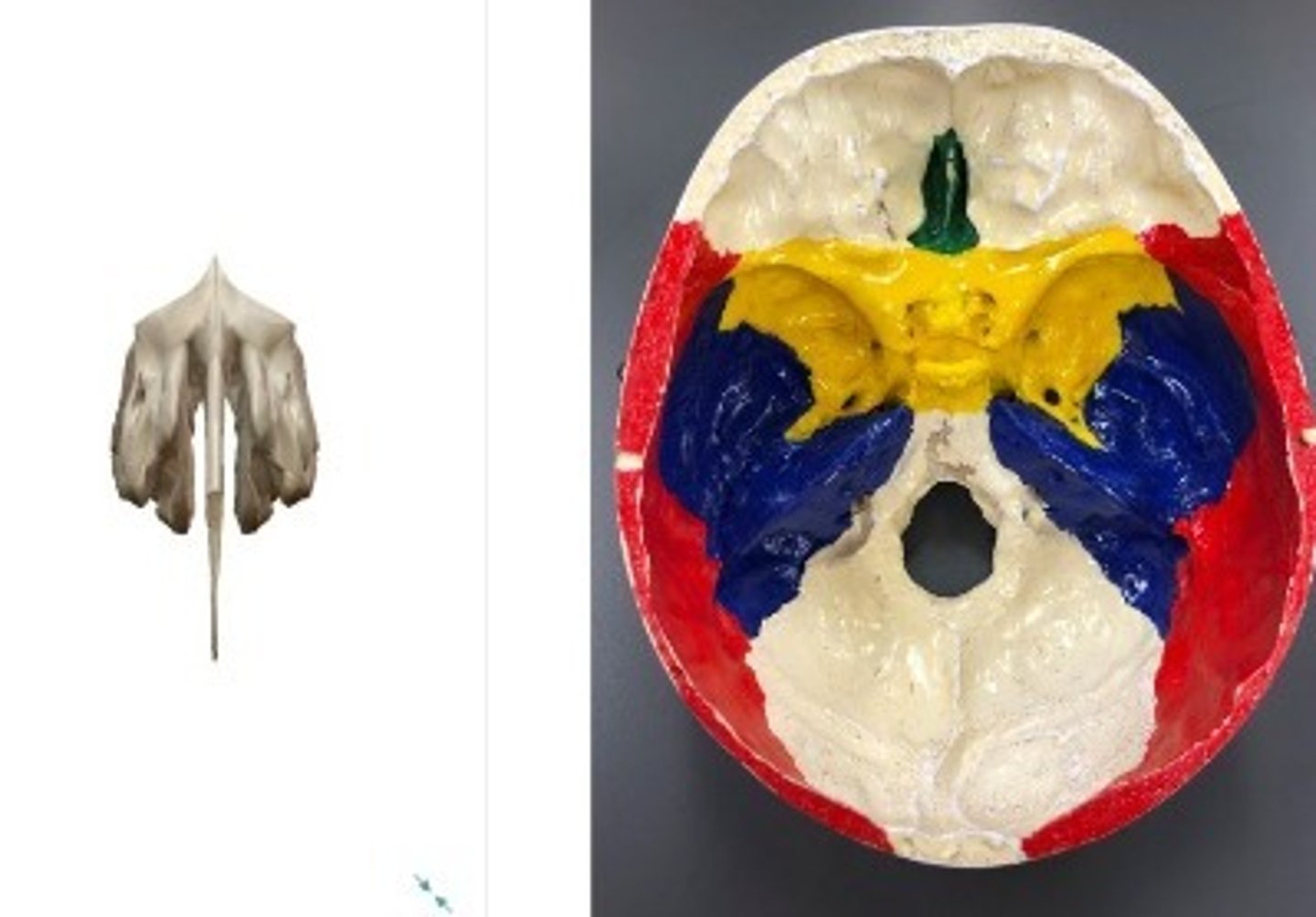
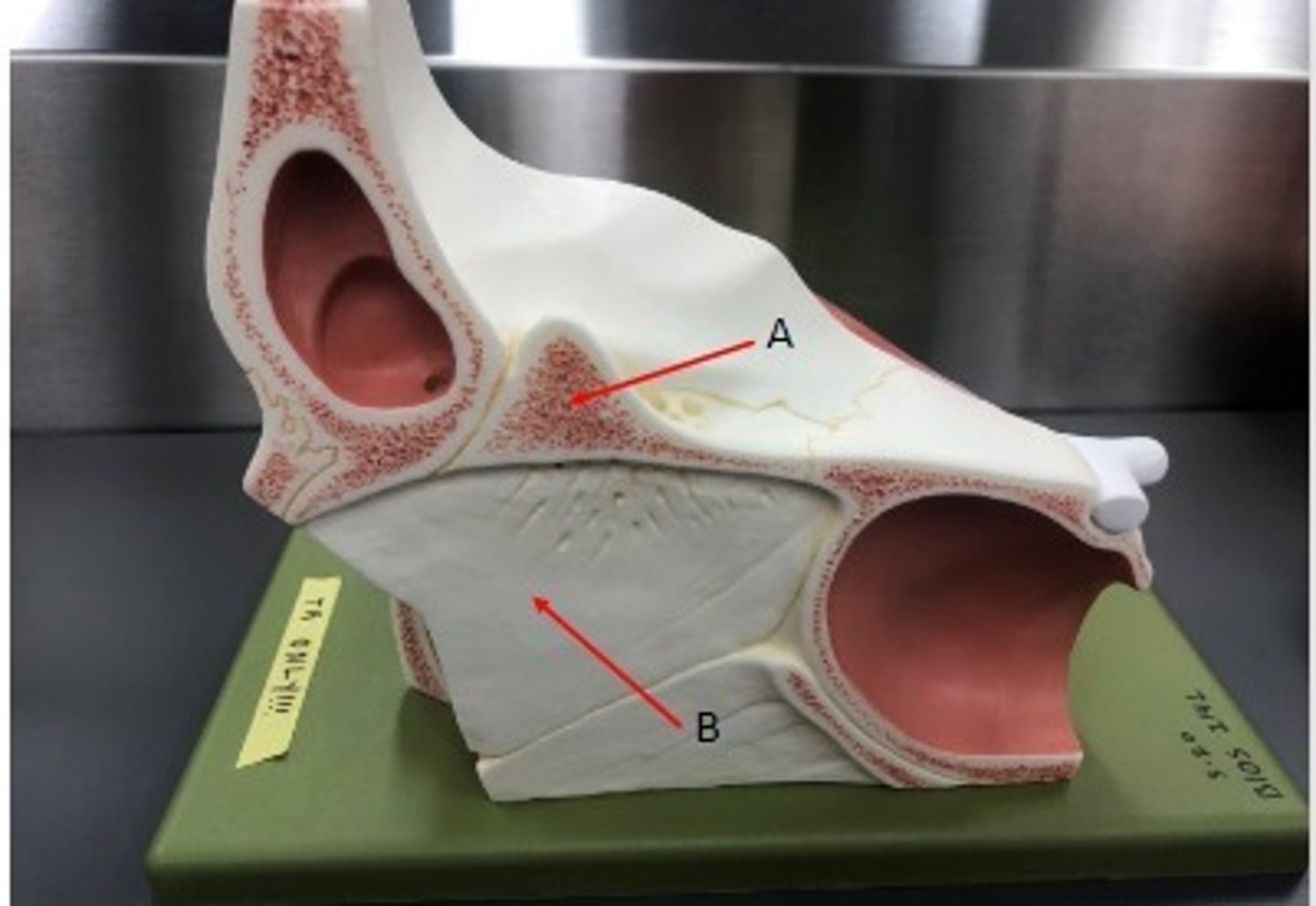
- Cranial bones
- Ethmoid bone
- A: Cribriform plate
- B: Crista galli
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
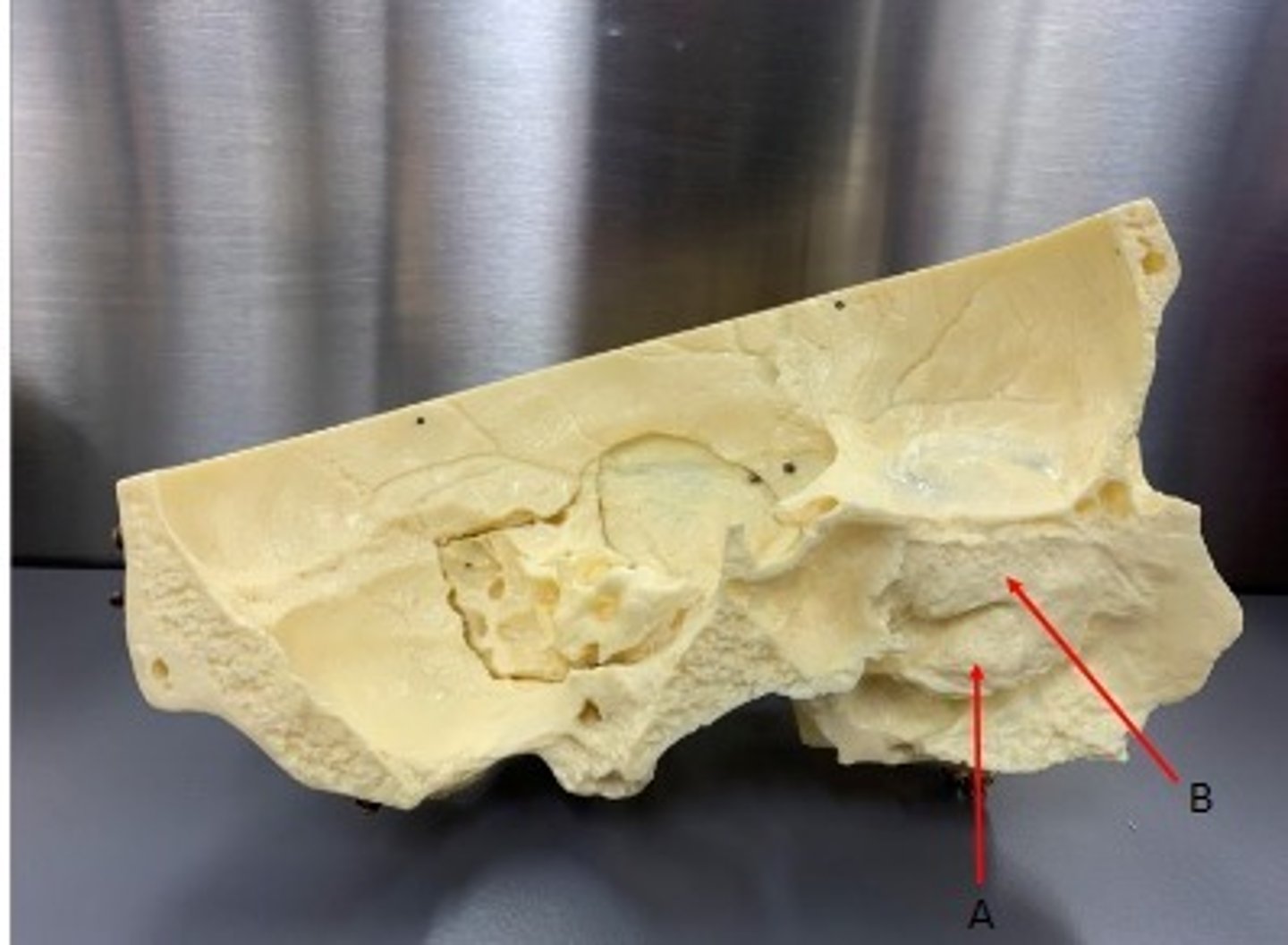
- Cranial bones
- Ethmoid bone
- A: Middle nasal concha
- B: Perpendicular plate
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
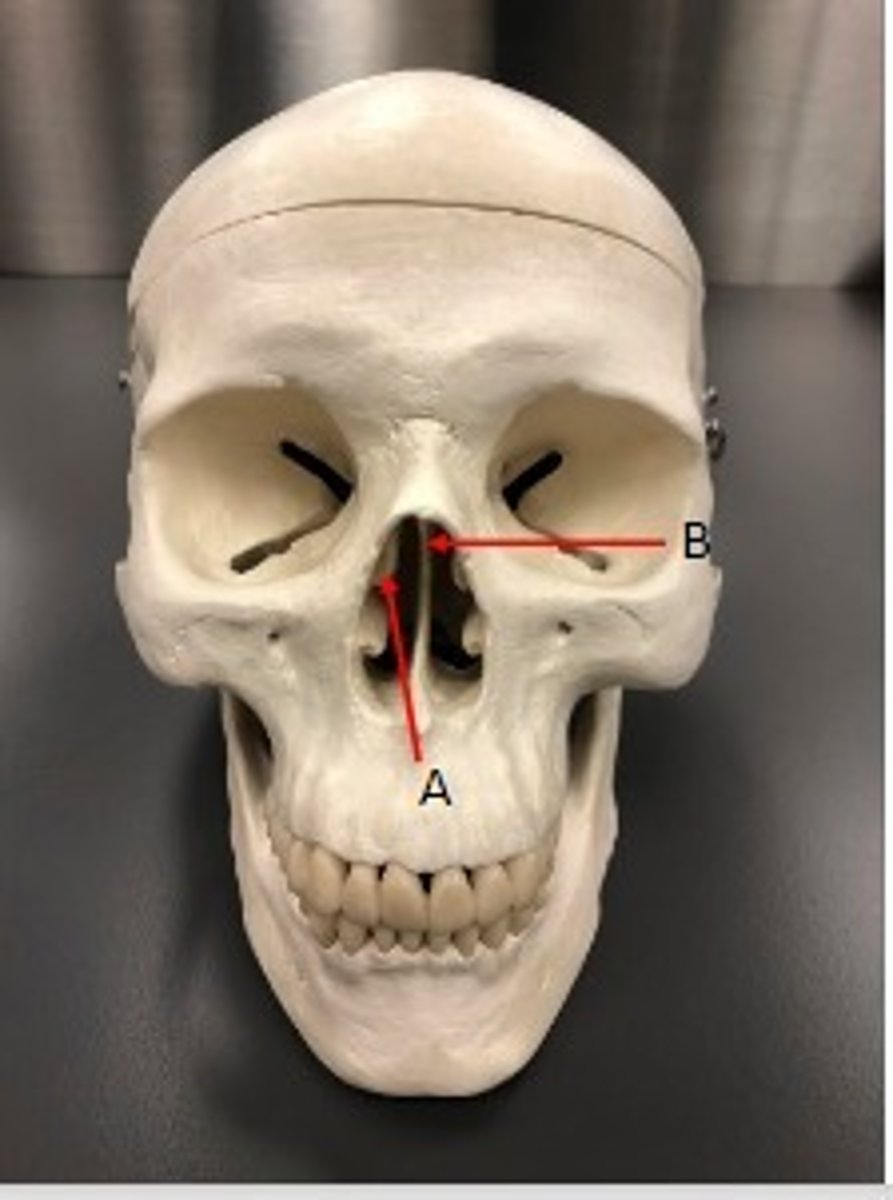
- Cranial bones
- Ethmoid bone
- A: Middle Nasal concha
- B: Superior nasal concha
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
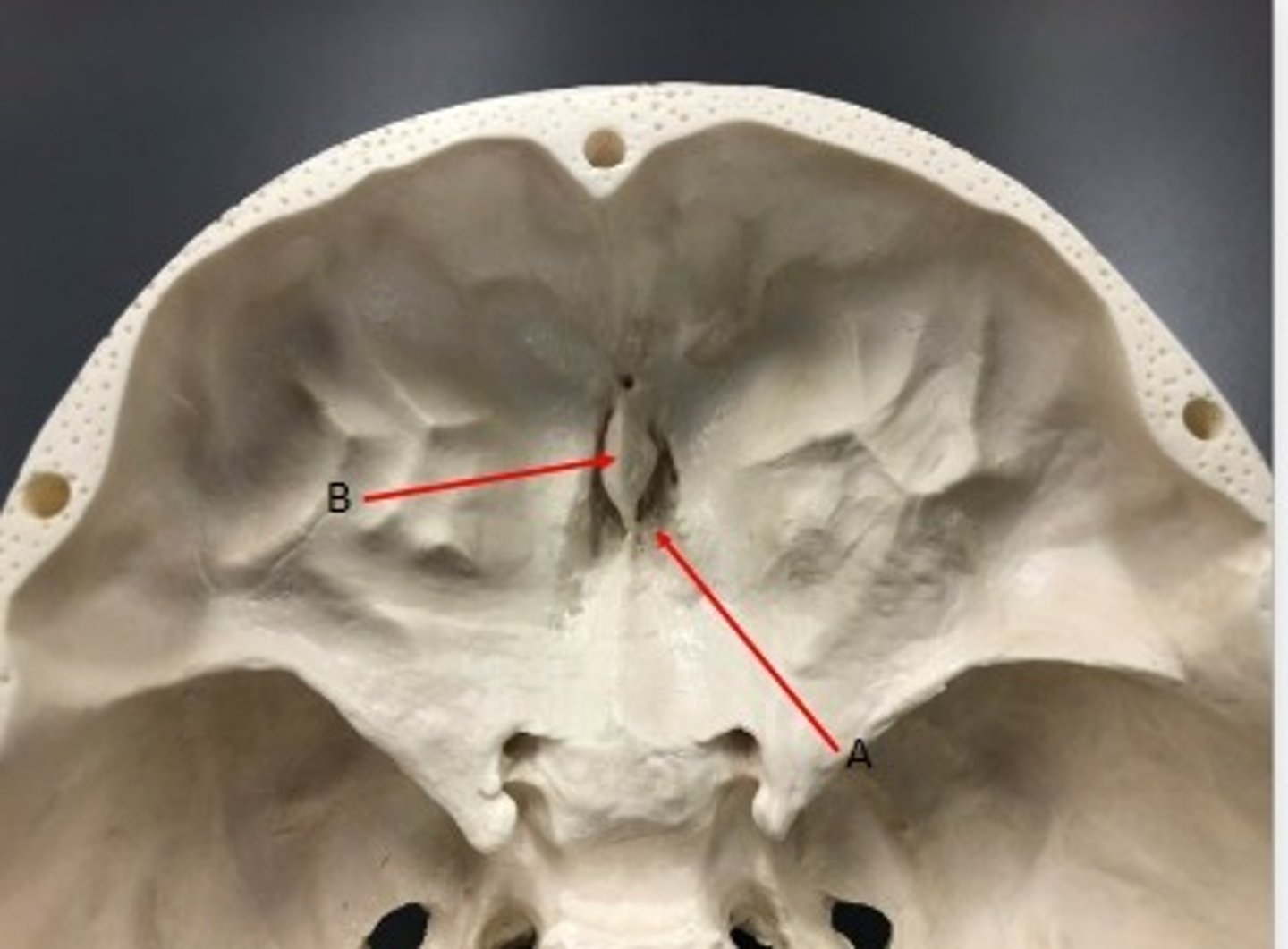
- Cranial bones
- Ethmoid bone
- A: Crista galli
- B: Perpendicular plate
What category of bone is it? What bone is it? Label the structures.
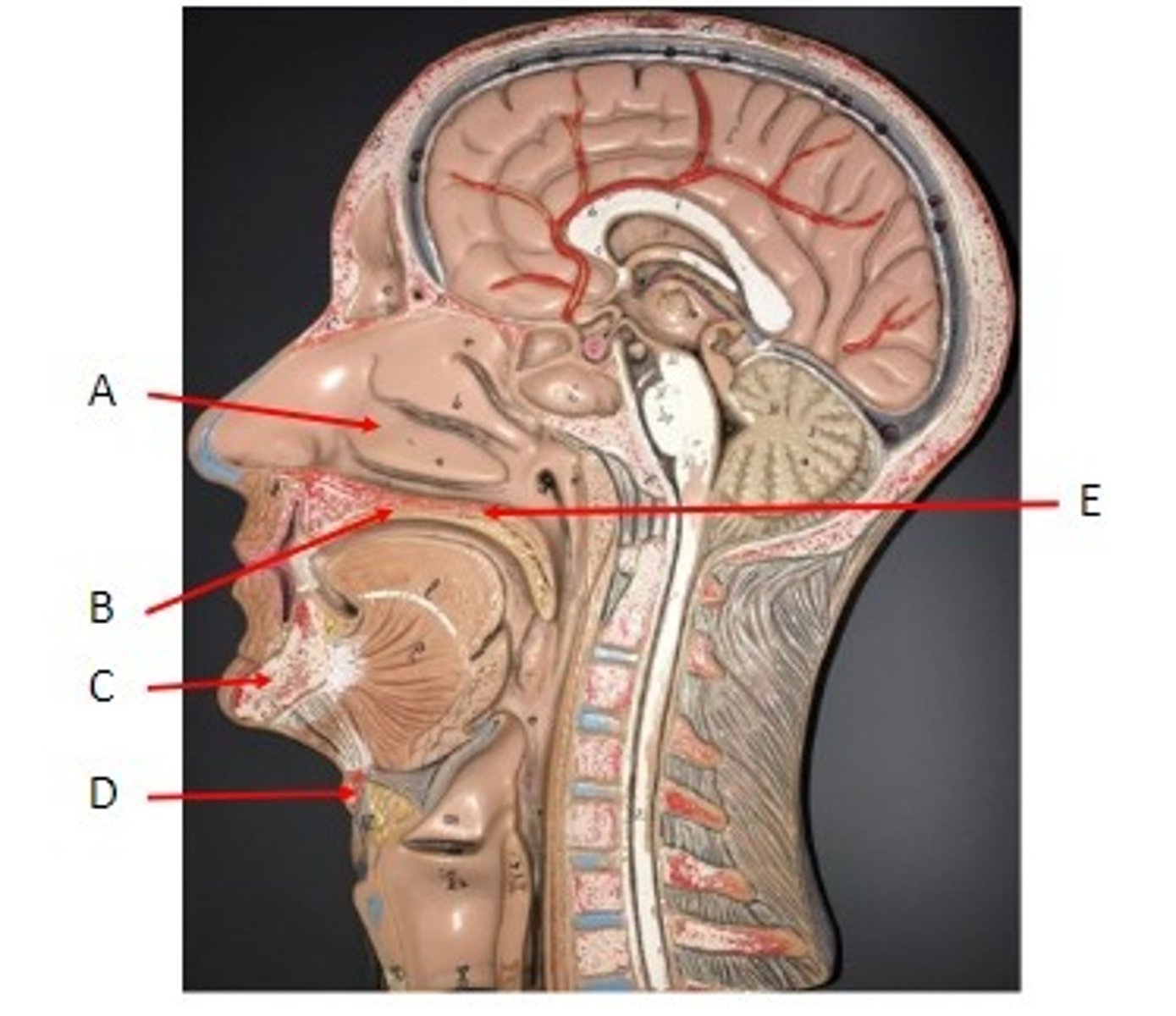
A. Inferior Nasal Concha
B. Palatine Process of the Maxilla
C. Mandible bone
D. Hyoid bone
E. Horizontal Plate of the Palatine Bone
Identify
A. Nasal Bone
B. Palatine Process of the Maxilla
C. Mandible Bone
D. Hyoid Bone
E. Inferior Nasal Concha
F. Horizontal Plate of the Palatine Bone
Identify
A. Inferior Nasal Concha
B. Palatine Process of the Maxilla
C. Horizontal Plate of the Palatine Bone
Identify
A. Lacrimal Bone
B. Infra-orbital Foramen of the Maxilla
C. Nasal Bone
D. Maxilla
E. Inferior Nasal Concha
Identify
A. Maxilla
B. Infra-orbital foramen of the maxillary bone
C. Nasal bone
D. Inferior Nasal Concha
E. Vomer bone
Identify
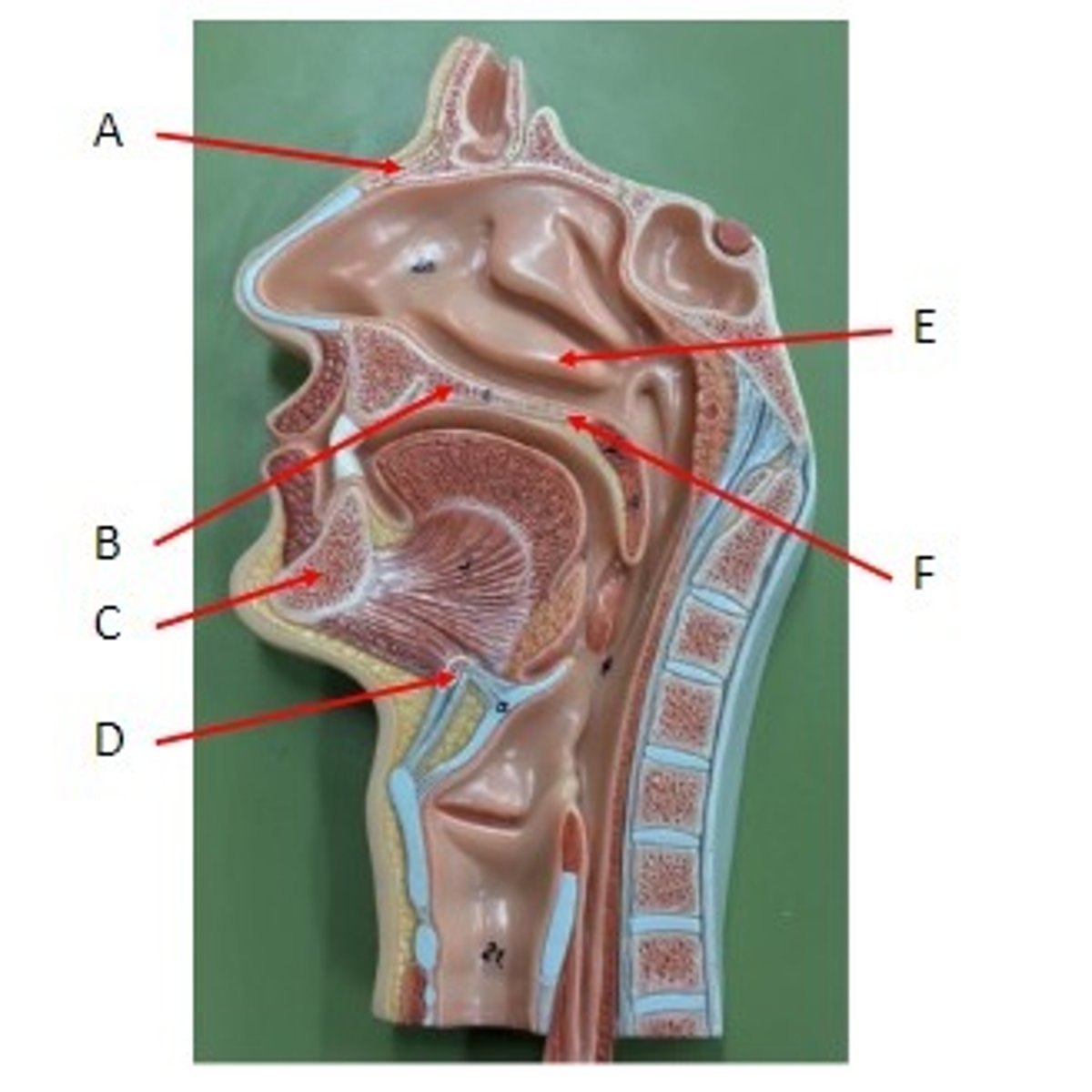
A. Nasal Bone
B. Vomer Bone
Identify
A. Greater Cornua of the Hyoid Bone
B. Lesser Cornua of the Hyoid Bone
Identify
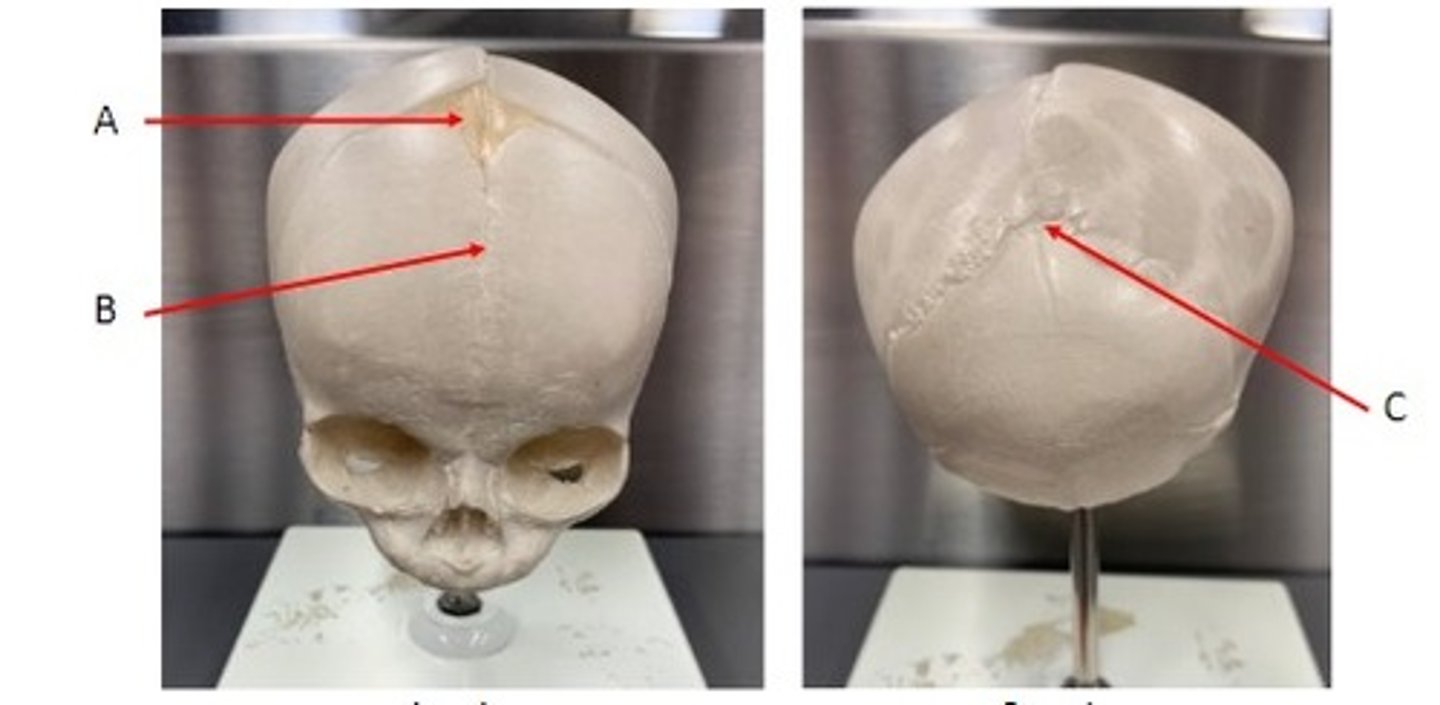
A. Frontal/Anterior Fontanelle of the Neonatal skull (unpaired)
B. Metopic/Frontal Suture (unpaired)
C. Occipital/Posterior Fontanelle of the Neonatal skull (unpaired)
Identify
A. Sphenoid/Anterolateral Fontanelle (paired)
B. Mastoid/Posterolateral Fontanelle (paired)
Identify
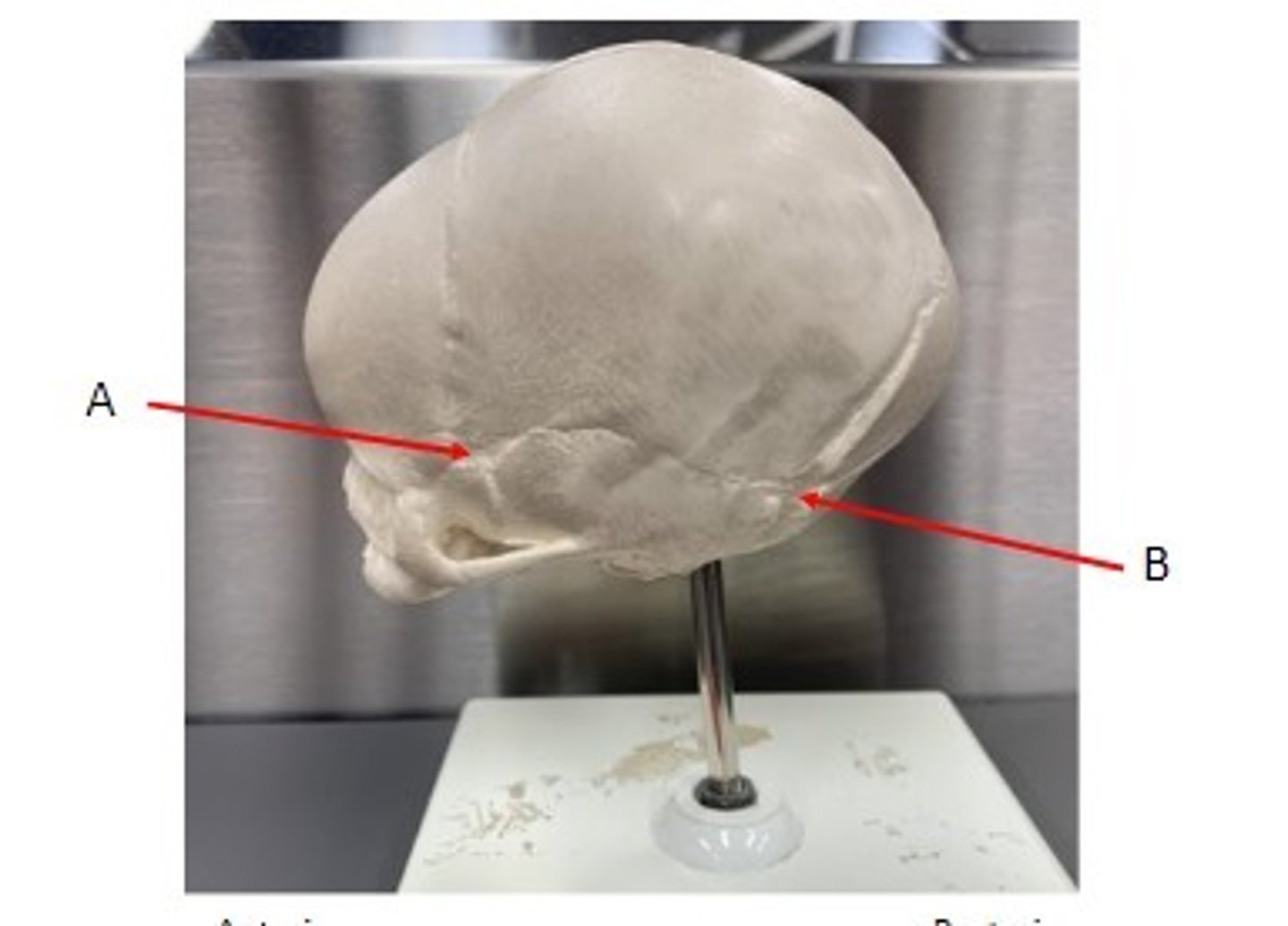
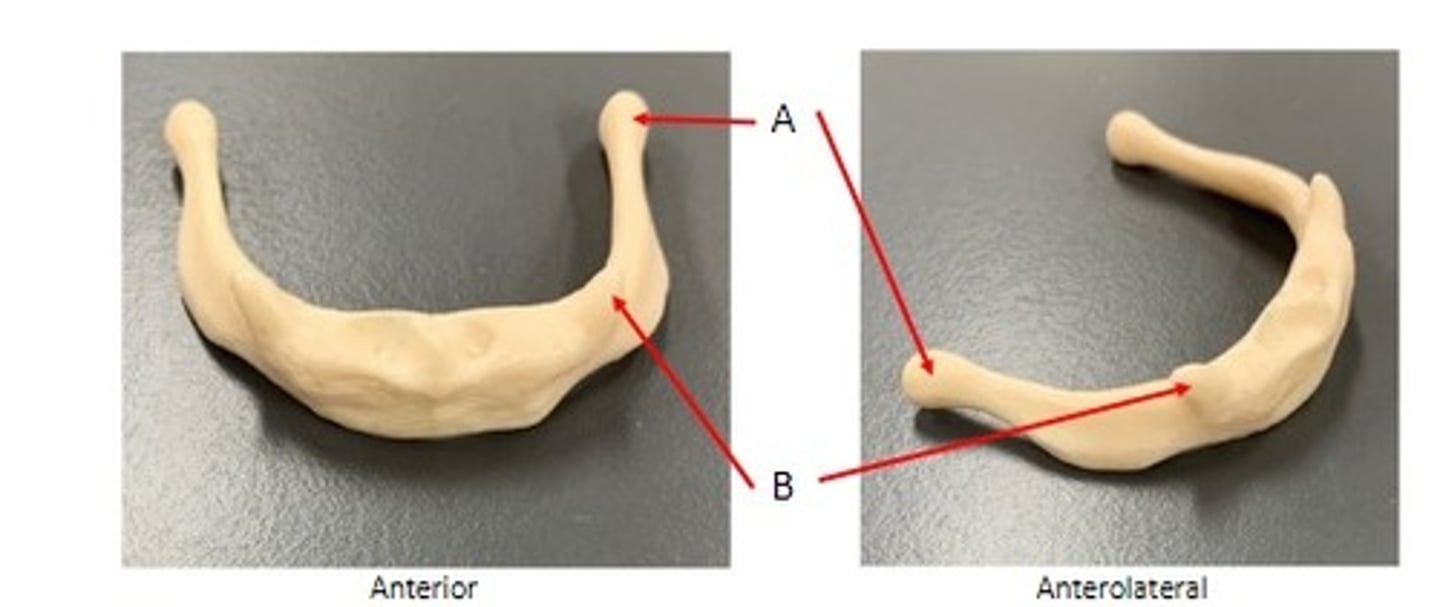
A. Condylar Process of the Neonatal mandible
B. Coronoid Process of the Neonatal mandible
C. Ramus of the Neonatal mandible
Identify
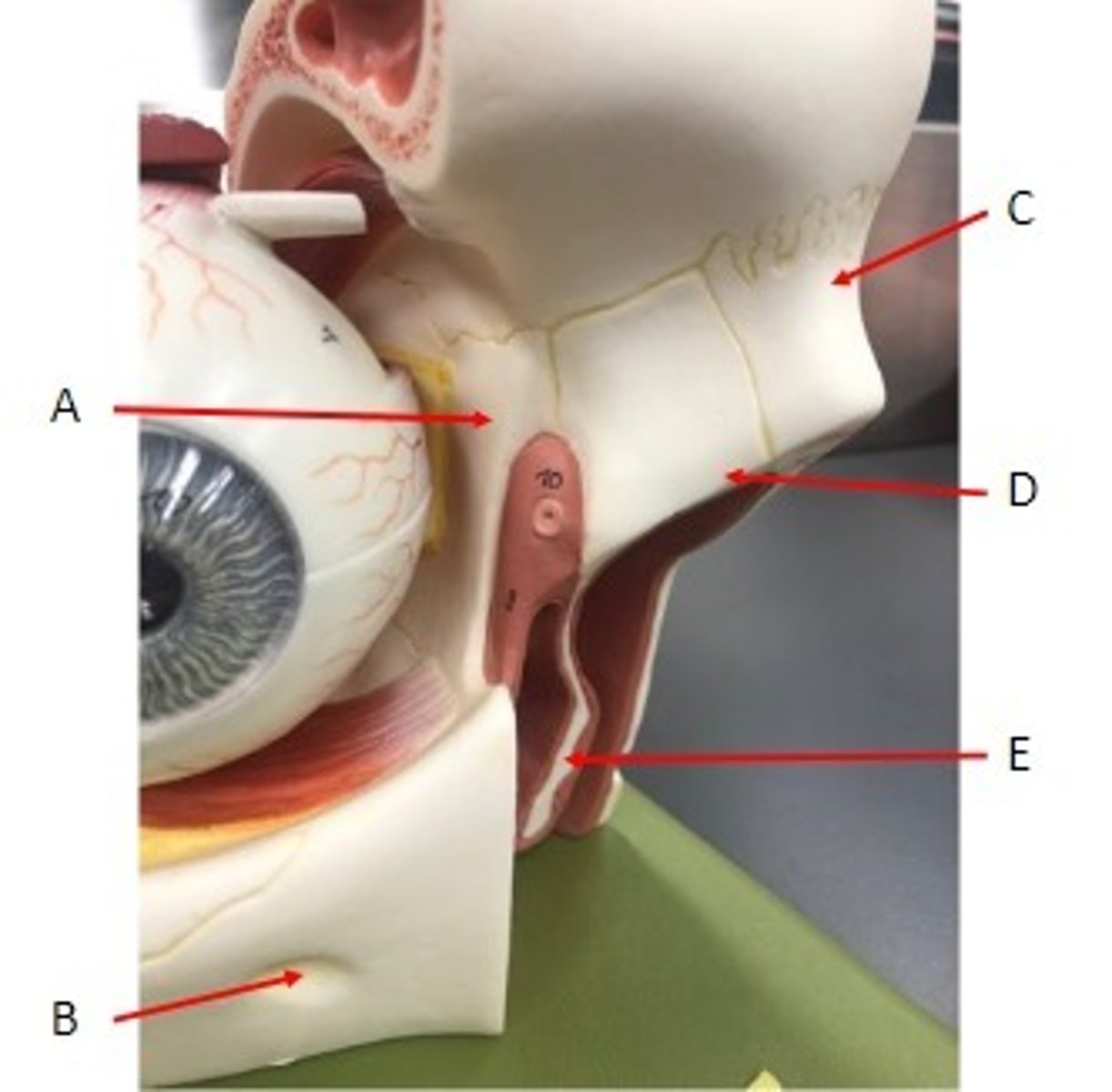
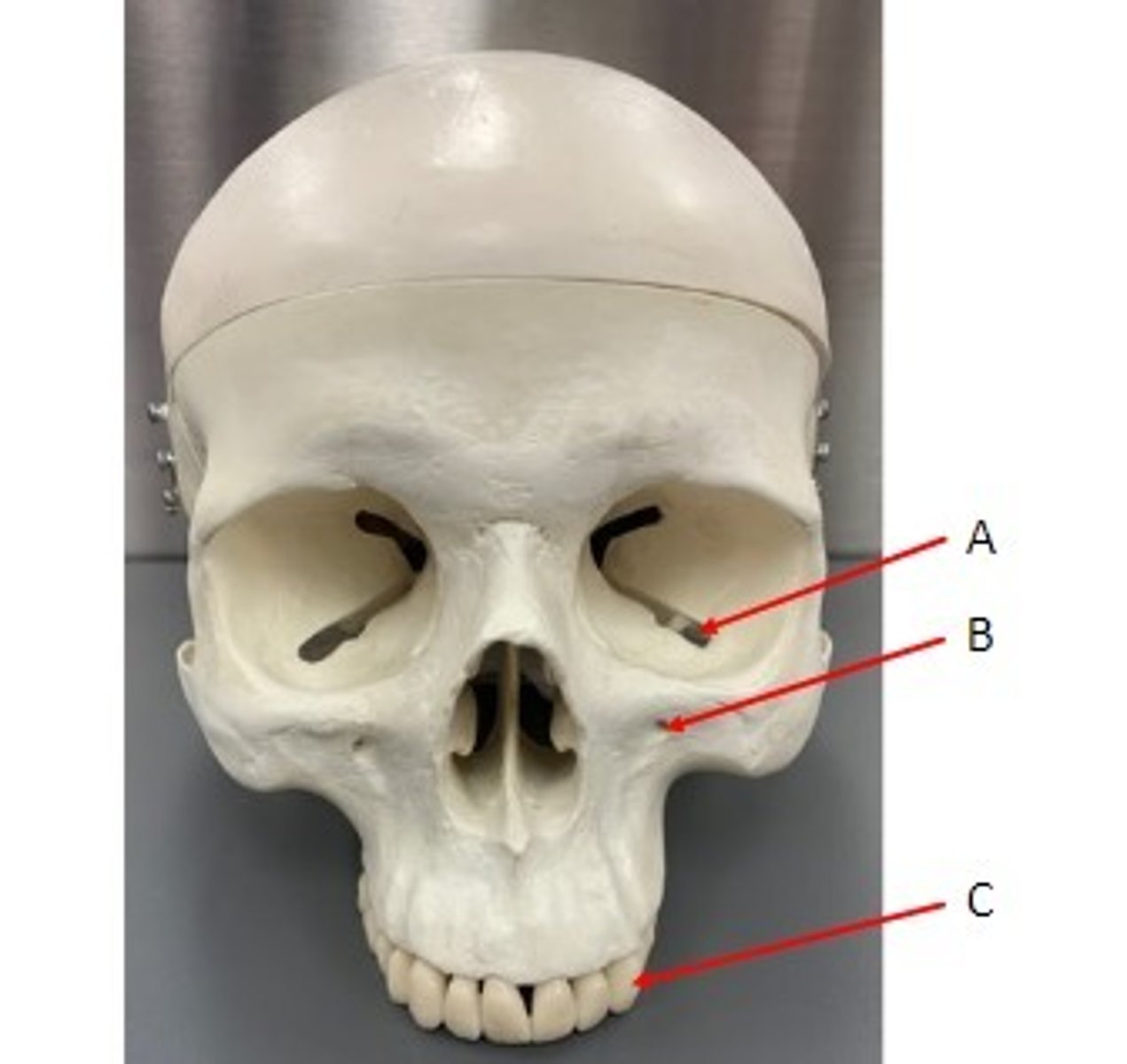
A. Inferior Orbital Fissure of the Maxillae
B. Infra-orbital Foramen of the Maxillae
C. Tooth that sits in the Alveolus of the Maxillae
Identify
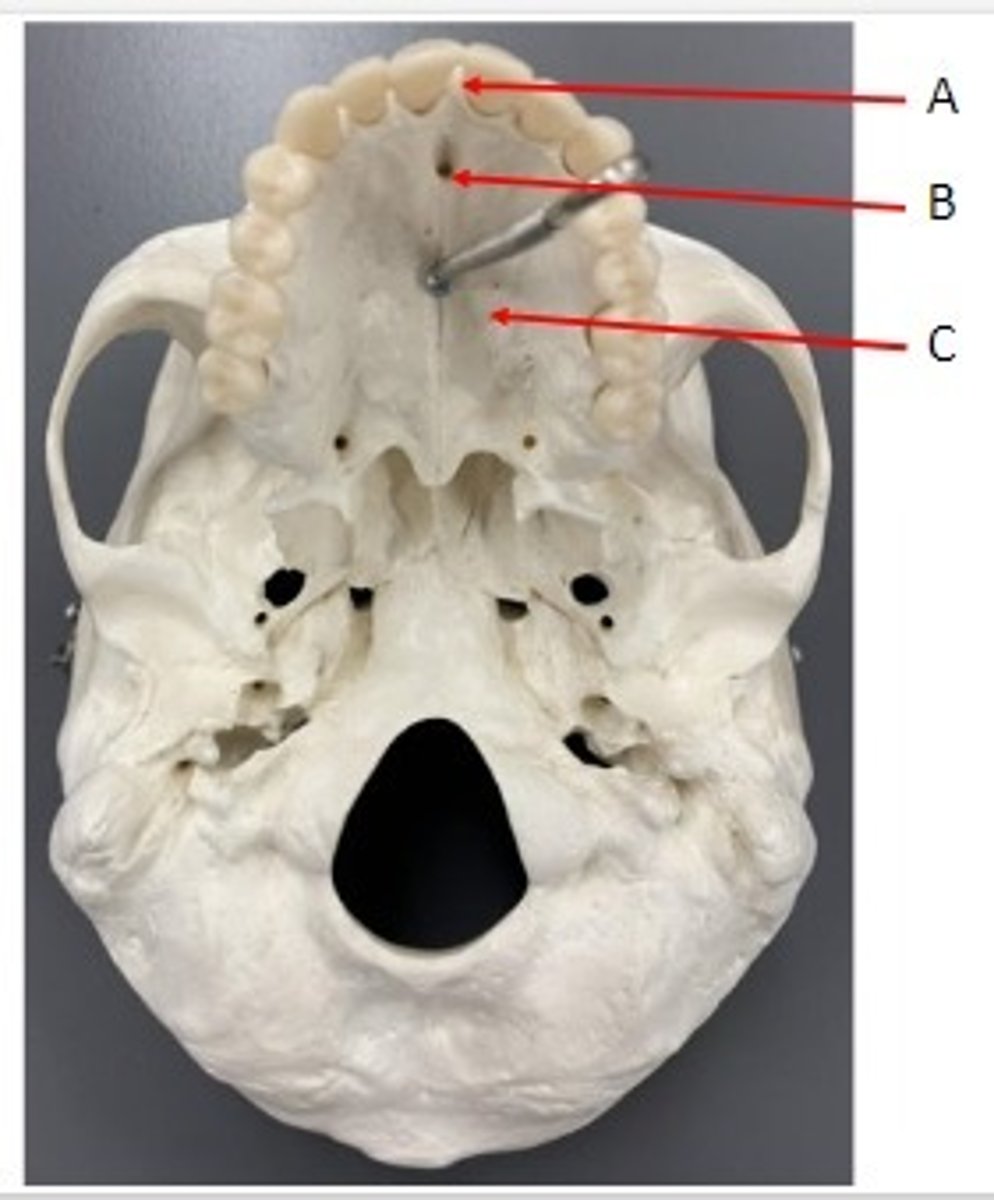
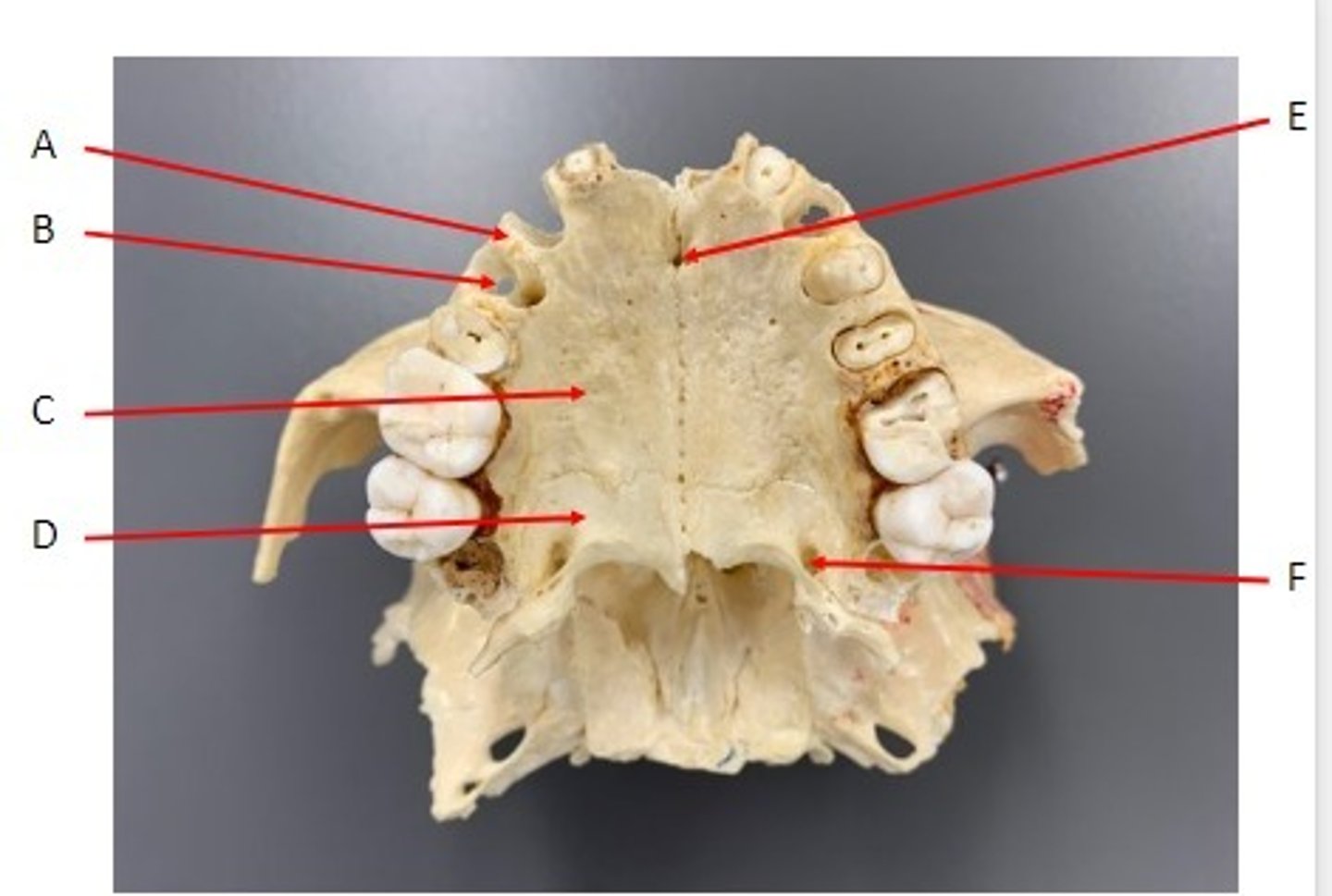
A. Alveolar Process of the Maxillae
B. Incisive Foramen of the Maxillae
C. Palatine Process of the Maxillae
Identify
A. Horizontal Plate of the Palatine bone
B. Greater Palatine Foramen of the Palatine bone
Identify
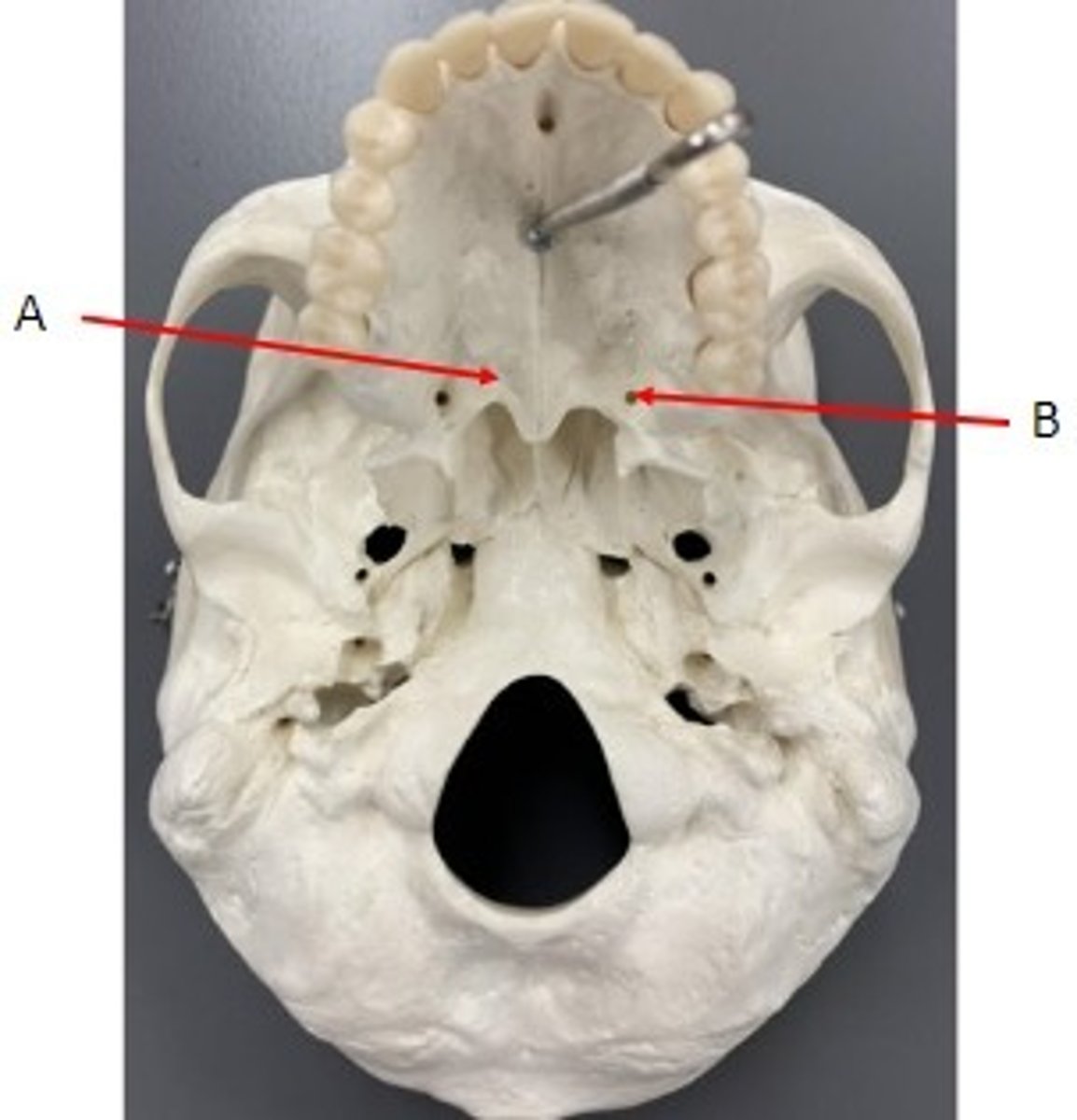
A. Horizontal Plate of the Palatine Bone
B. Perpendicular Plate of the Palatine Bone
Identify
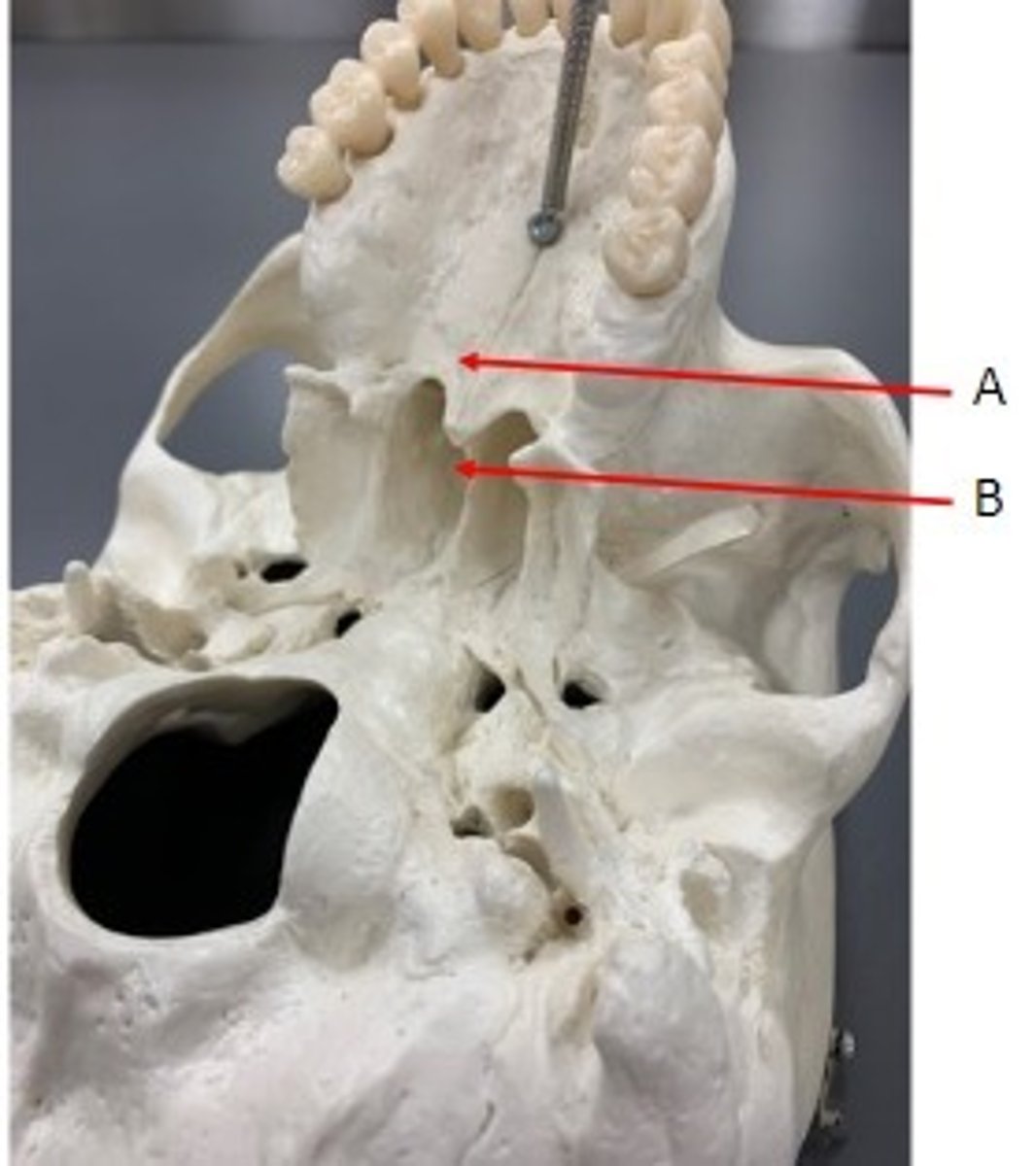
A. Zygomatic Arch of the Zygomatic Bone
B. Temporal Process of the Zygomatic Bone
Identify
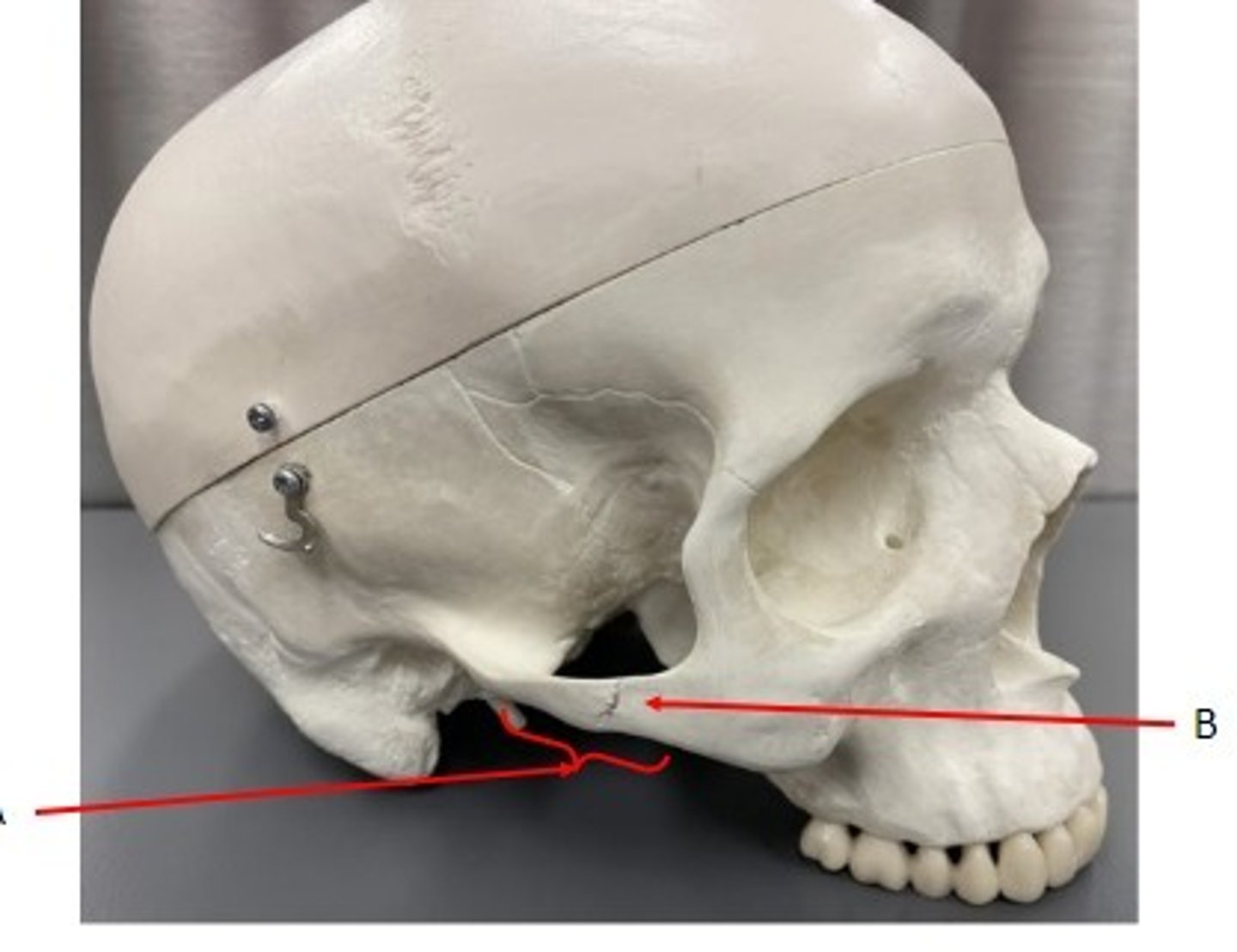
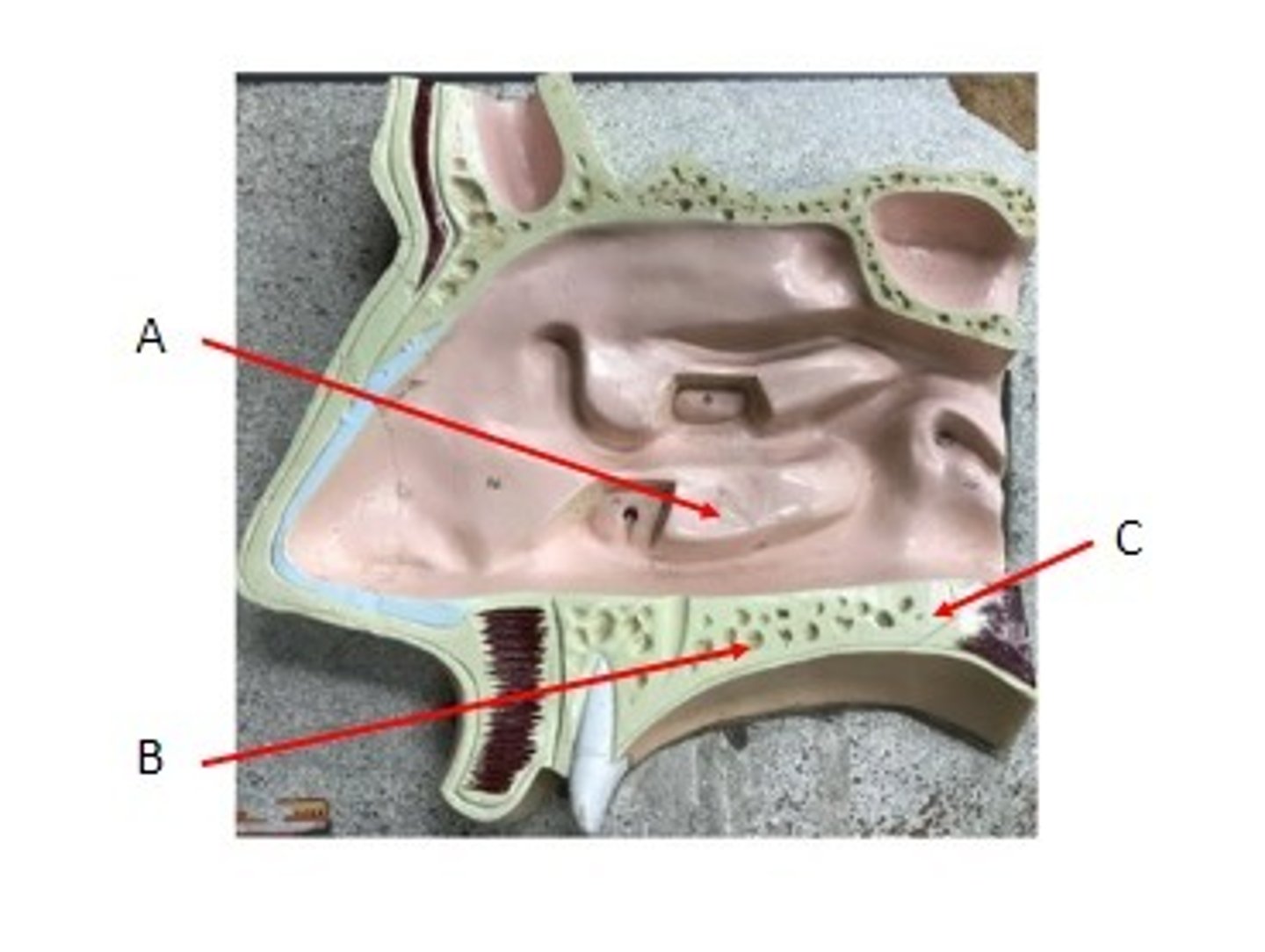
A. Nasolacrimal Canal of the Lacrimal Bone
Identify
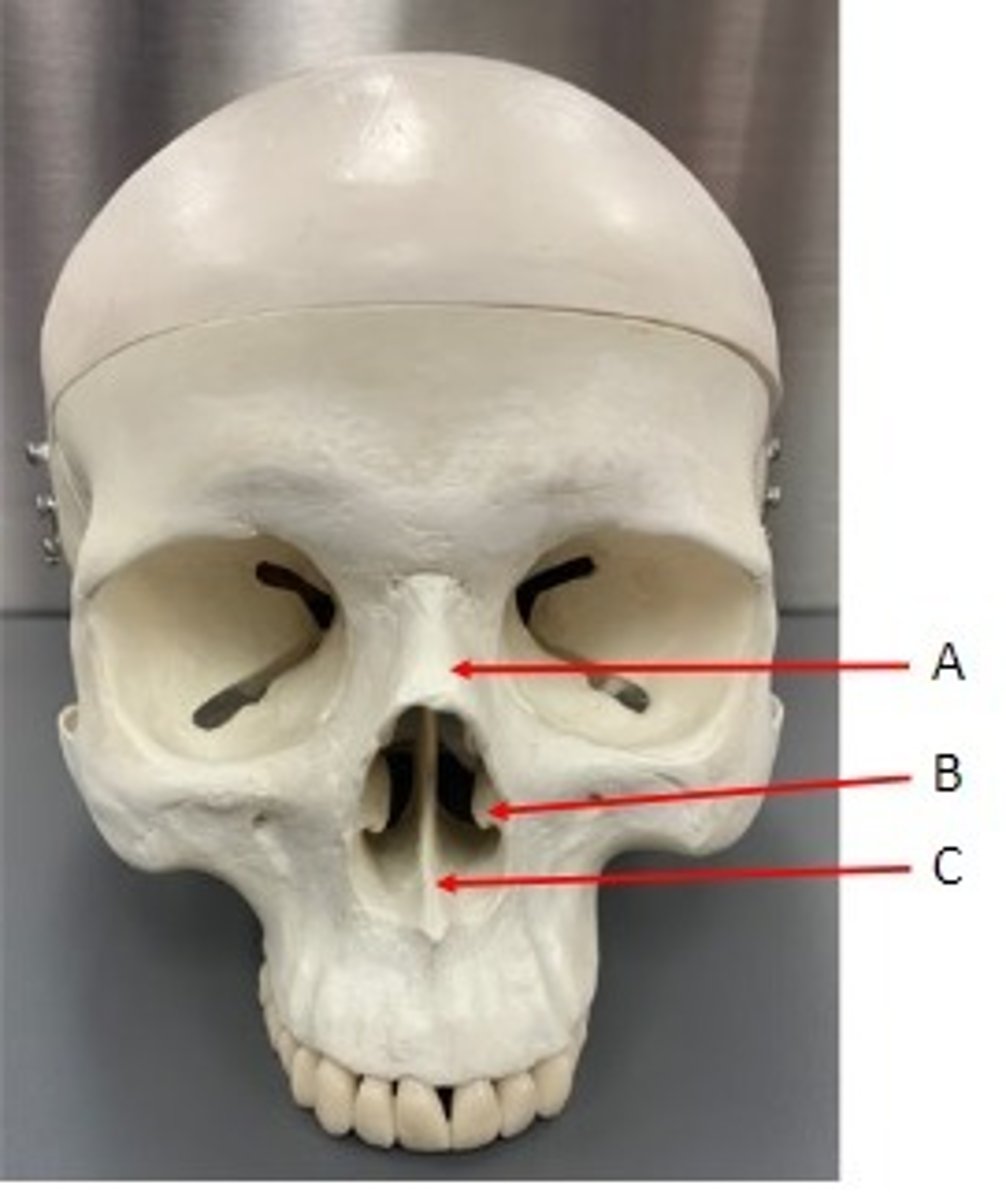
A. Nasal bone
B. Inferior Nasal Concha
C. Vomer bone
Identify
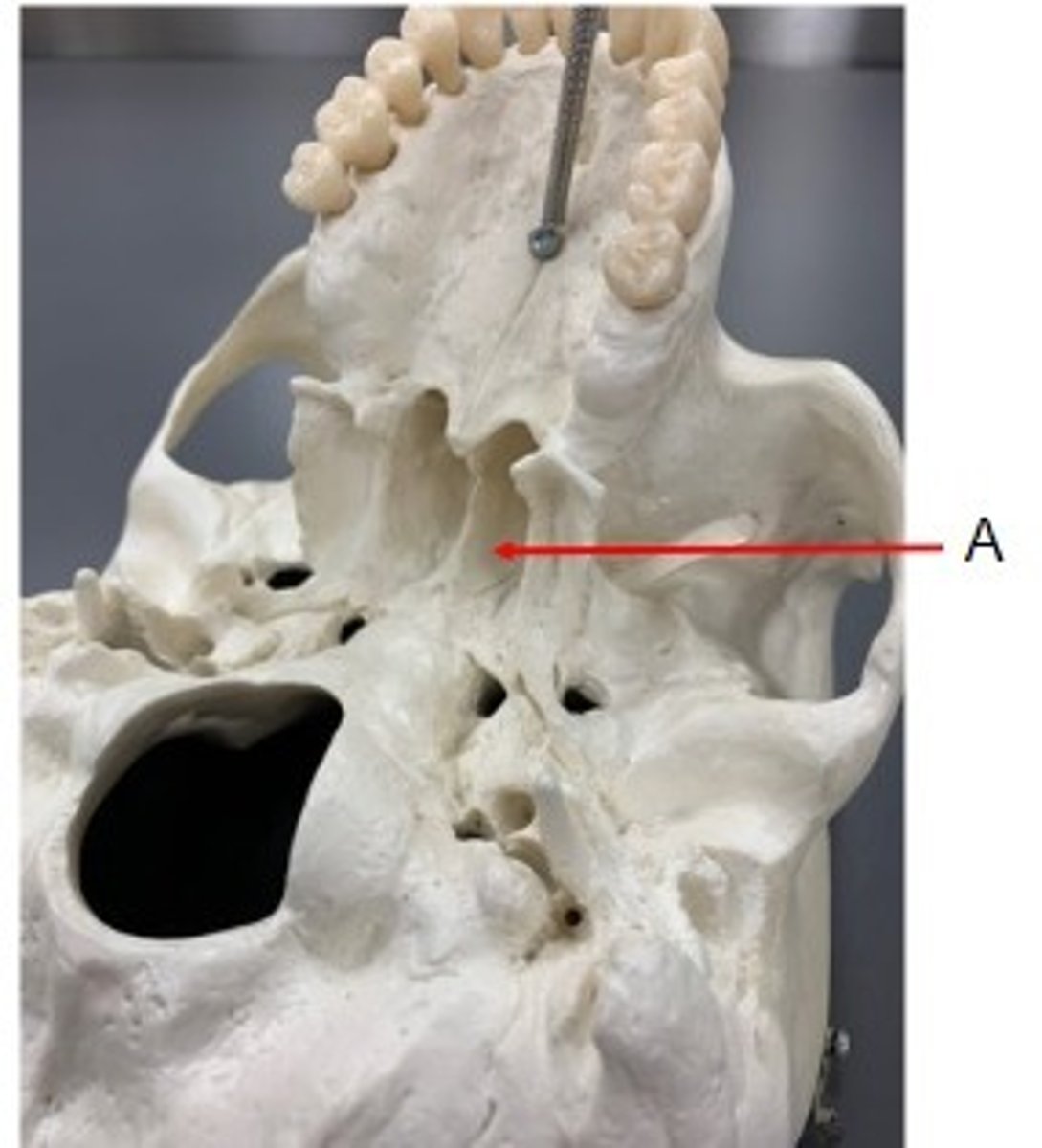
A. Vomer Bone
Identify
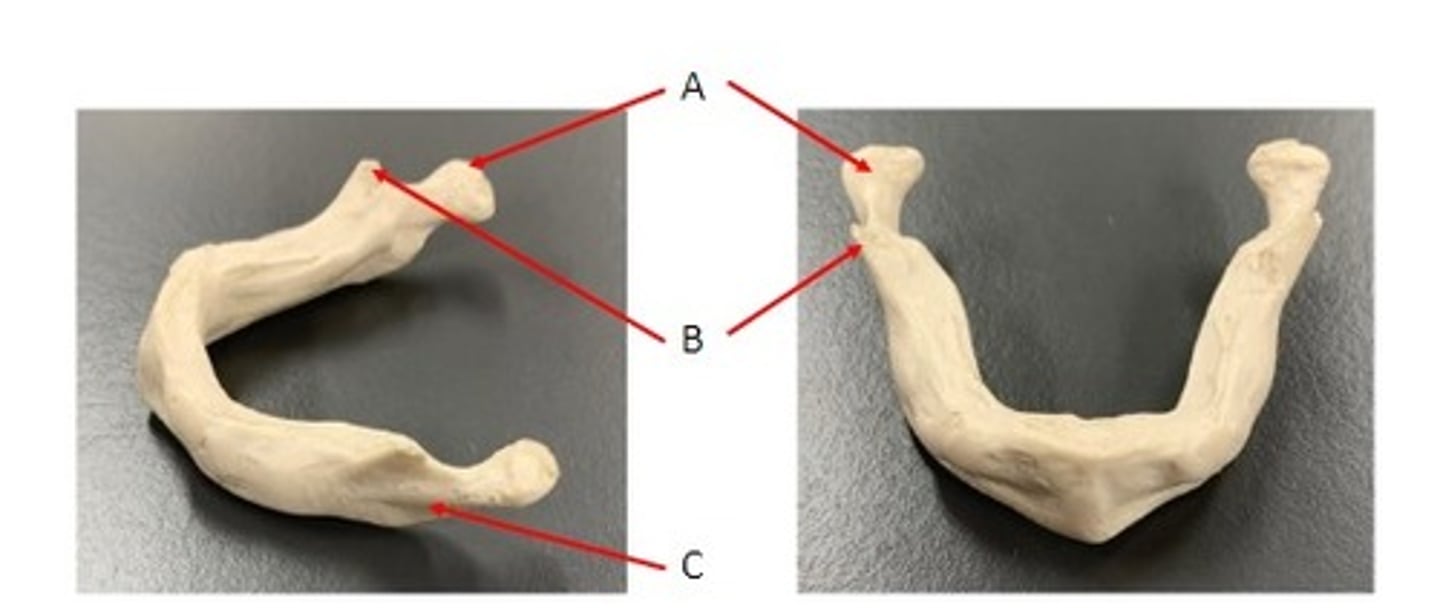
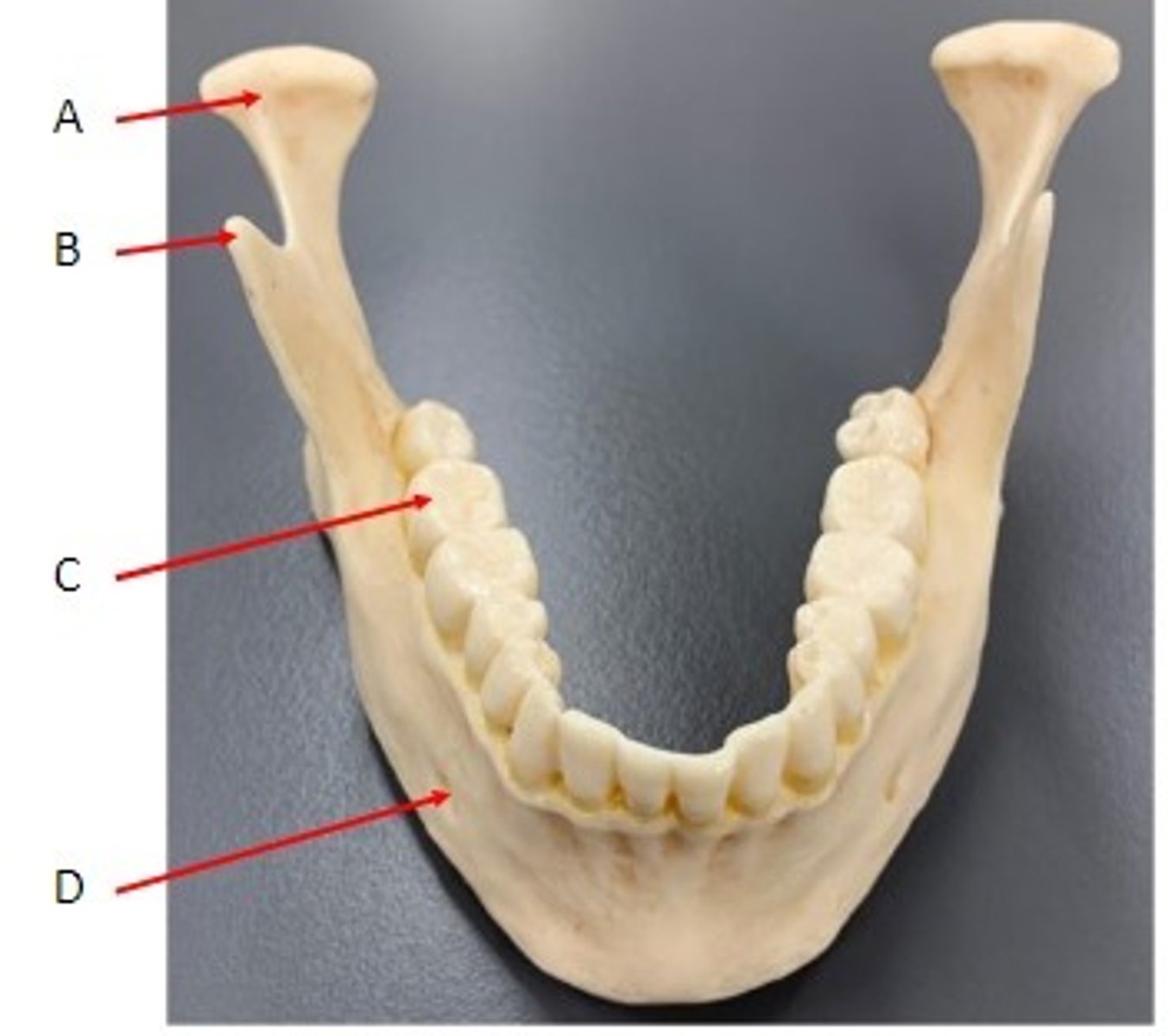
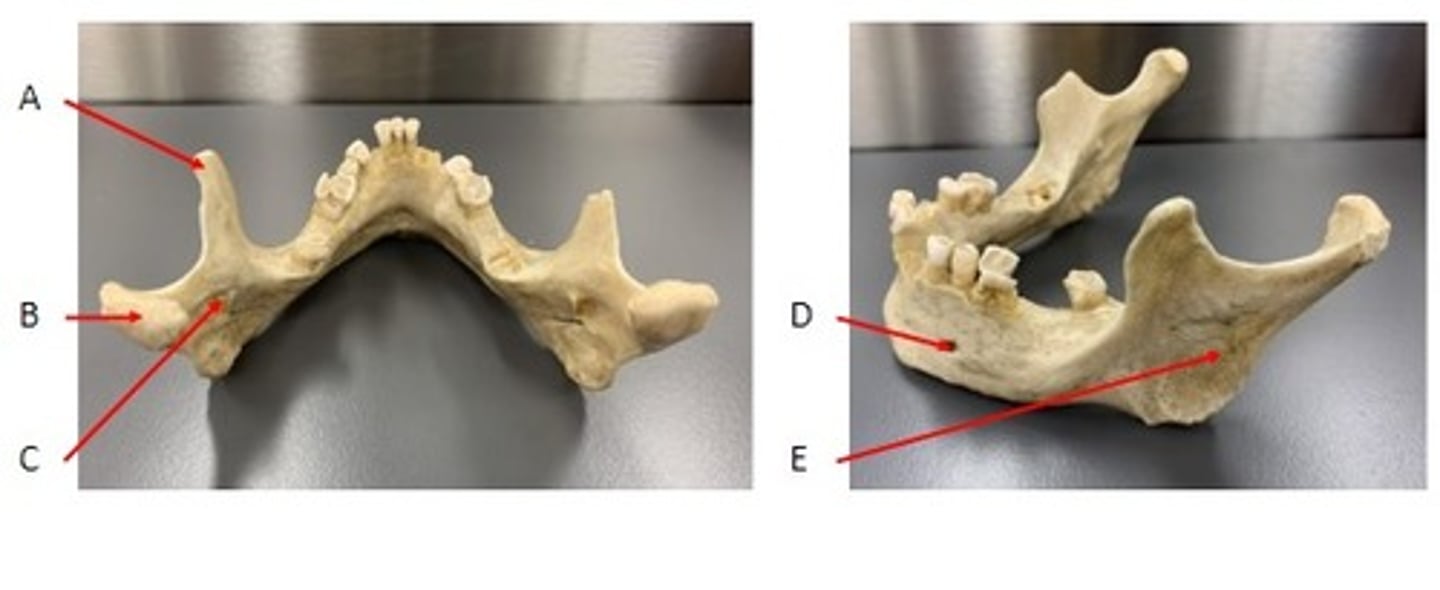
A. Condylar Process of the Mandible Bone
B. Coronoid Process of the Mandible Bone
C. Tooth (sits in alveolus) of the Mandible Bone
D. Mental Foramen of the Mandible Bone
Identify
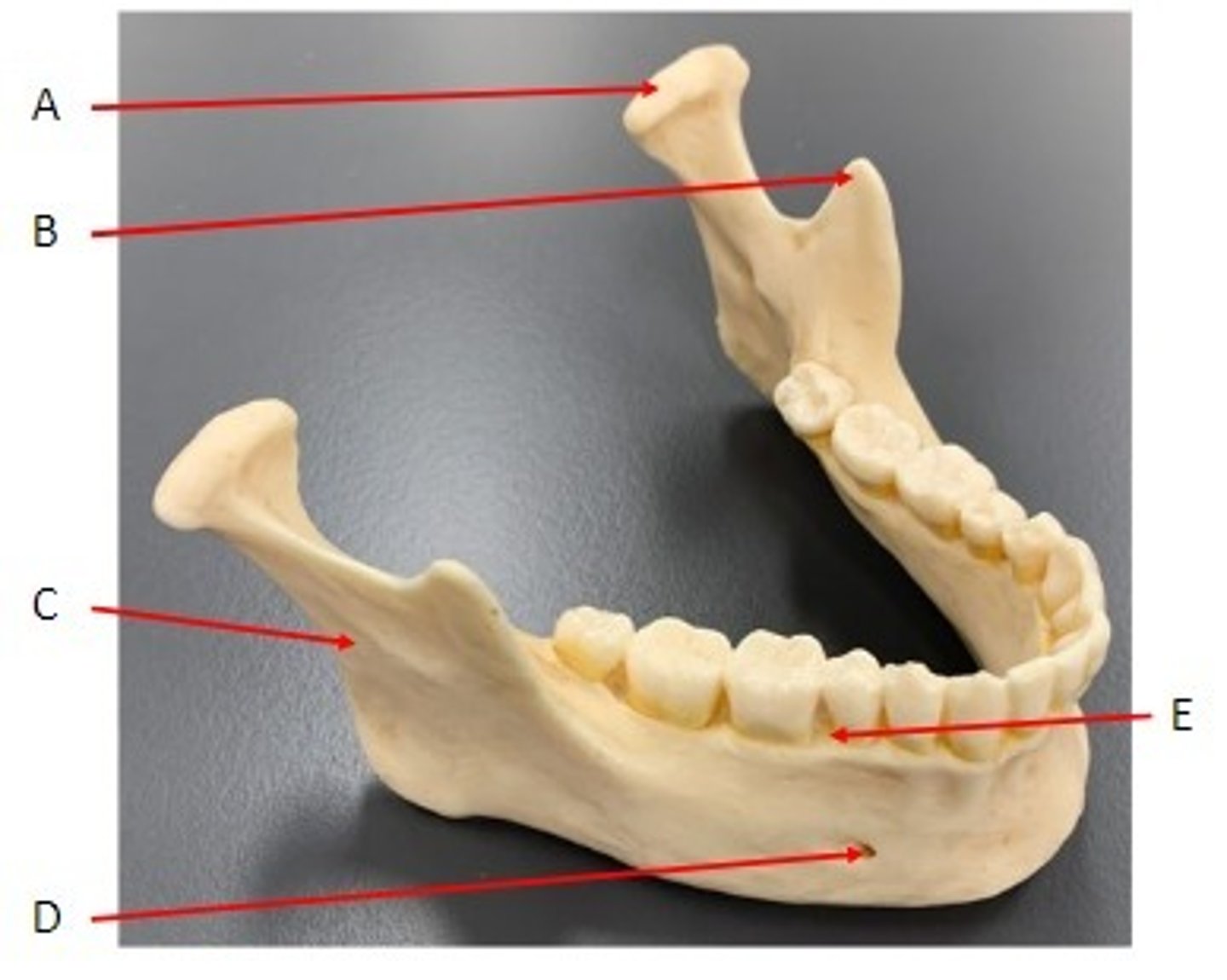
A. Condylar Process of the Mandible Bone
B. Coronoid Process of the Mandible Bone
C. Ramus of the Mandible Bone
D. Mental Foramen of the Mandible Bone
E. Alveolar Process of the Mandible Bone
Identify
A. Coronoid Process of the Mandible Bone
B. Condylar Process of the Mandible Bone
C. Mandibular Foramen of the Mandible Bone
Identify
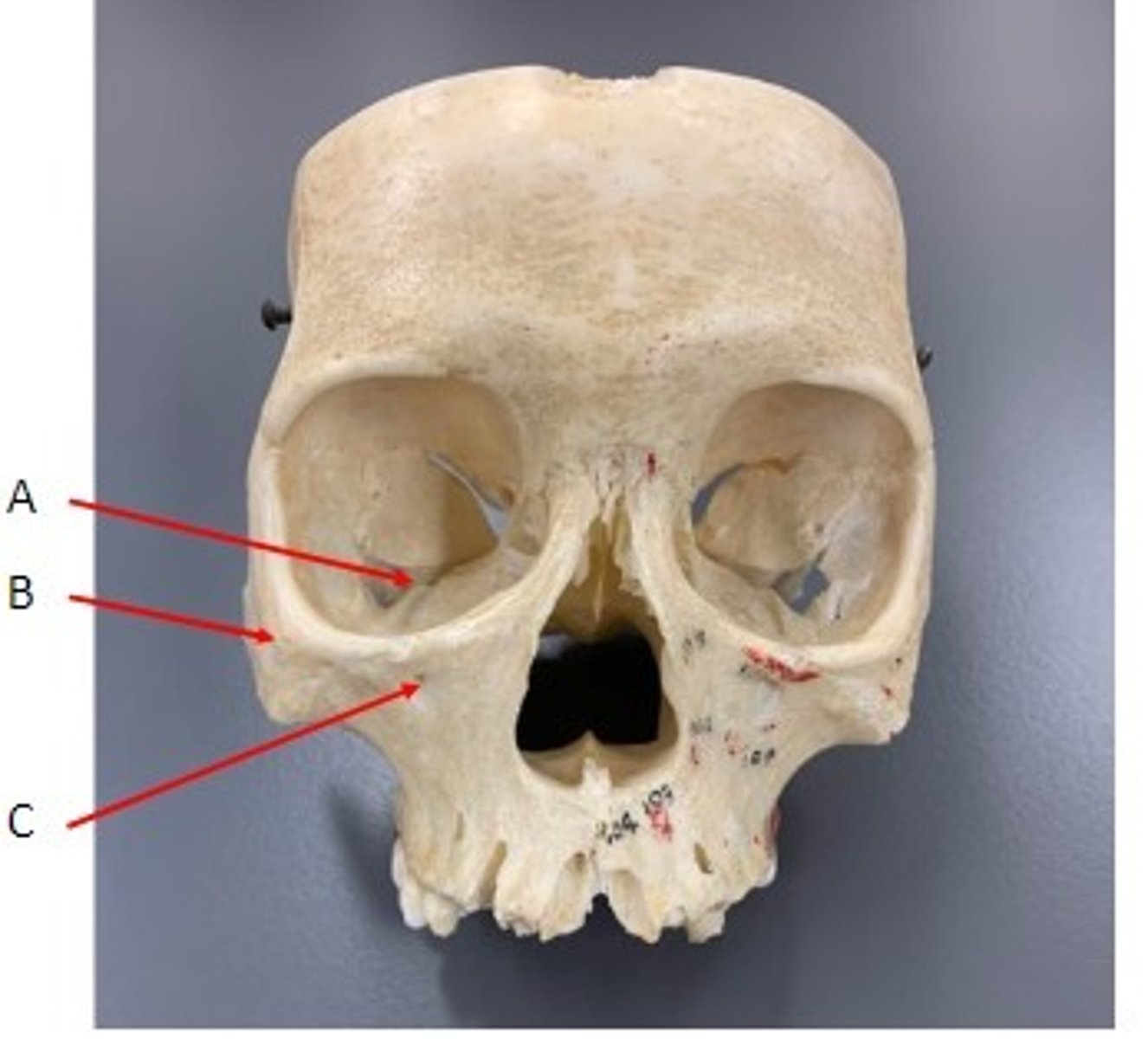
A. Inferior Orbital Fissure of the Maxilla
B. Zygomatic Bone
C. Infra-orbital foramen of the Maxilla
Identify
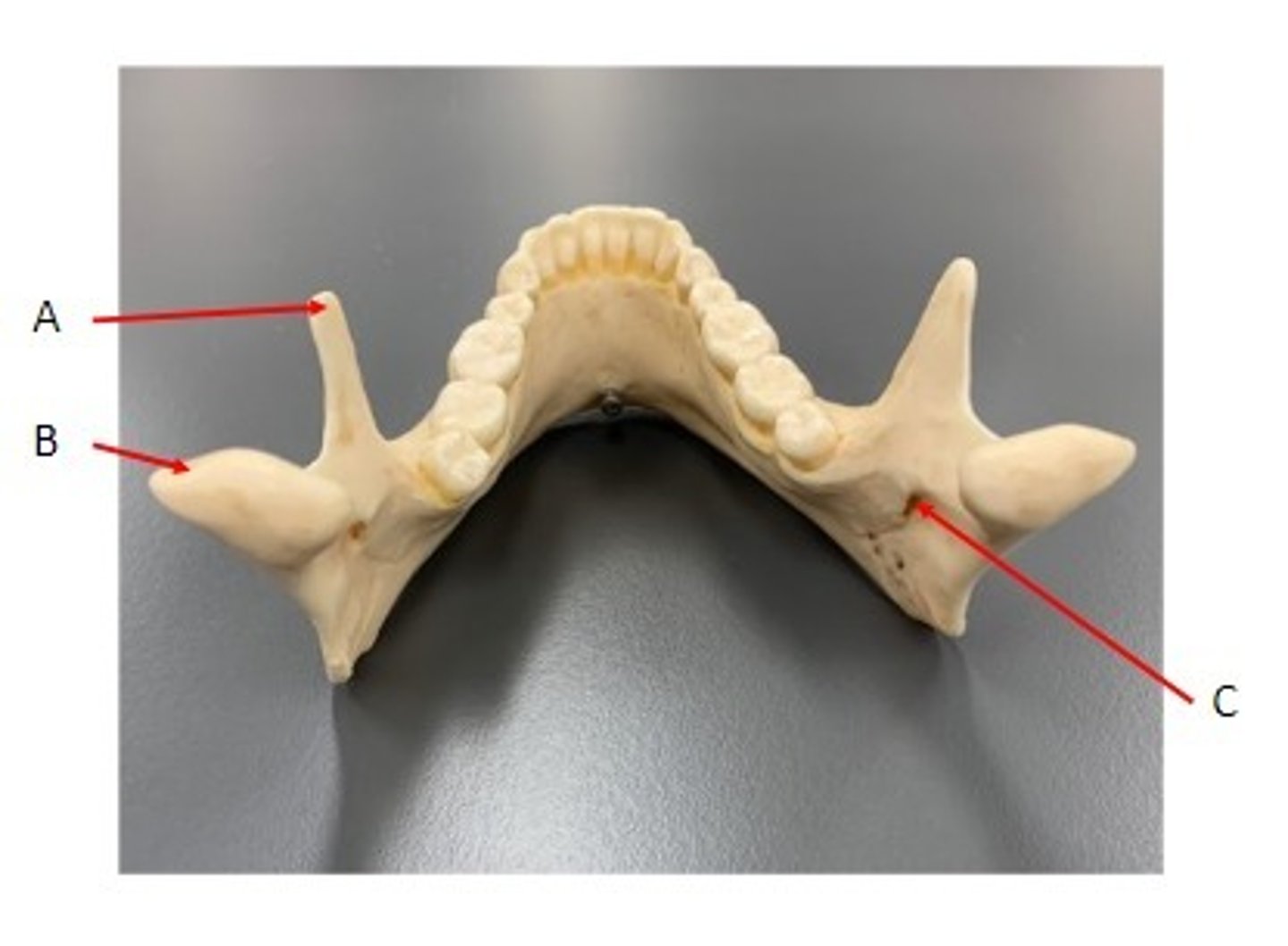
A. Alveolar Process of the Maxilla
B. Alveolus of the Maxilla
C. Palatine Process of the Maxilla
D. Horizontal Plate of the Palatine Bone
E. Incisive Foramen of the Maxilla
F. Greater Palatine Foramen of the Palatine Bone
Identify
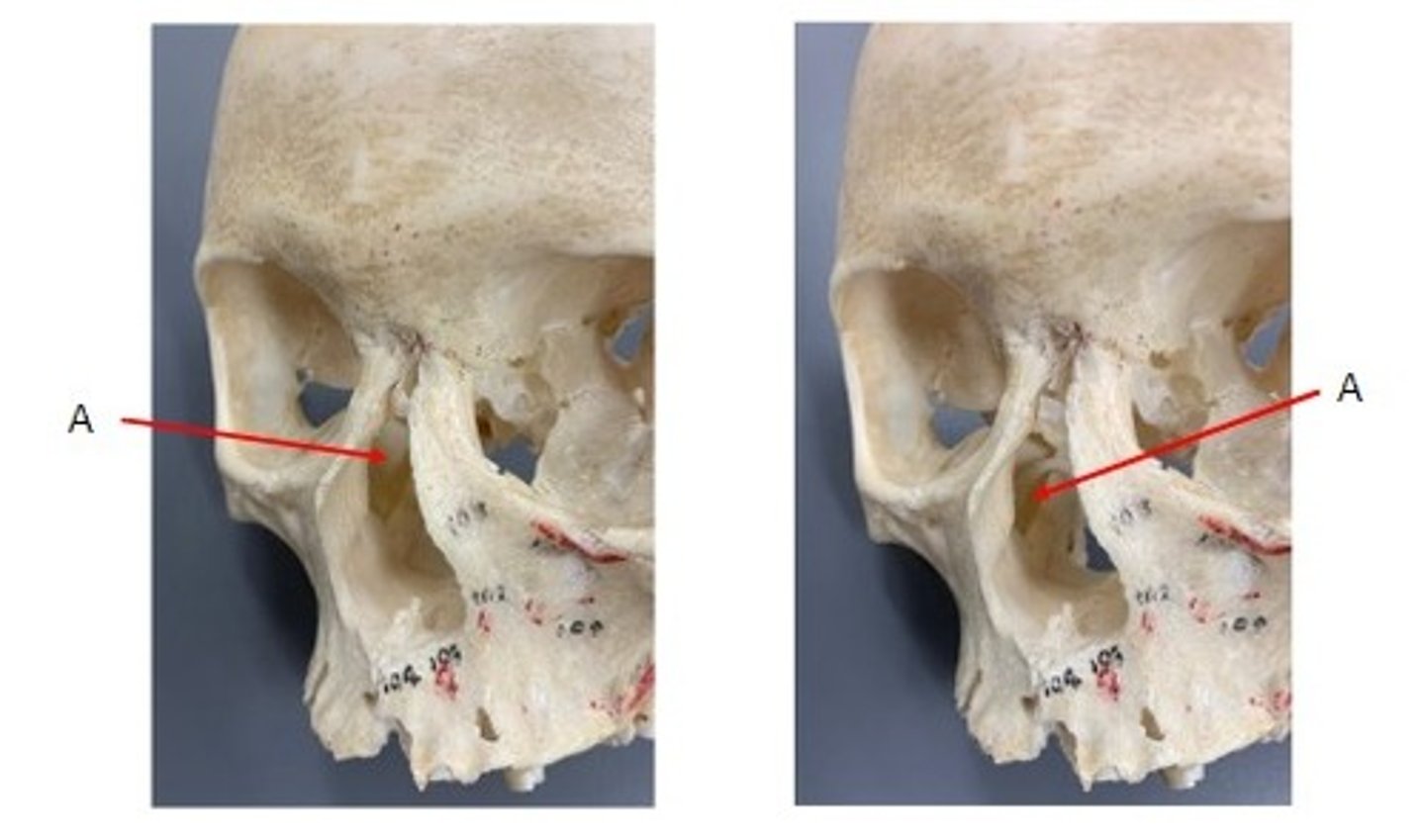
A. Maxillary Sinus of the Maxillae
Identify
A. Temporal Process of the Zygomatic Bone
B. Maxillary Sinus of the Maxillary Bone
Identify
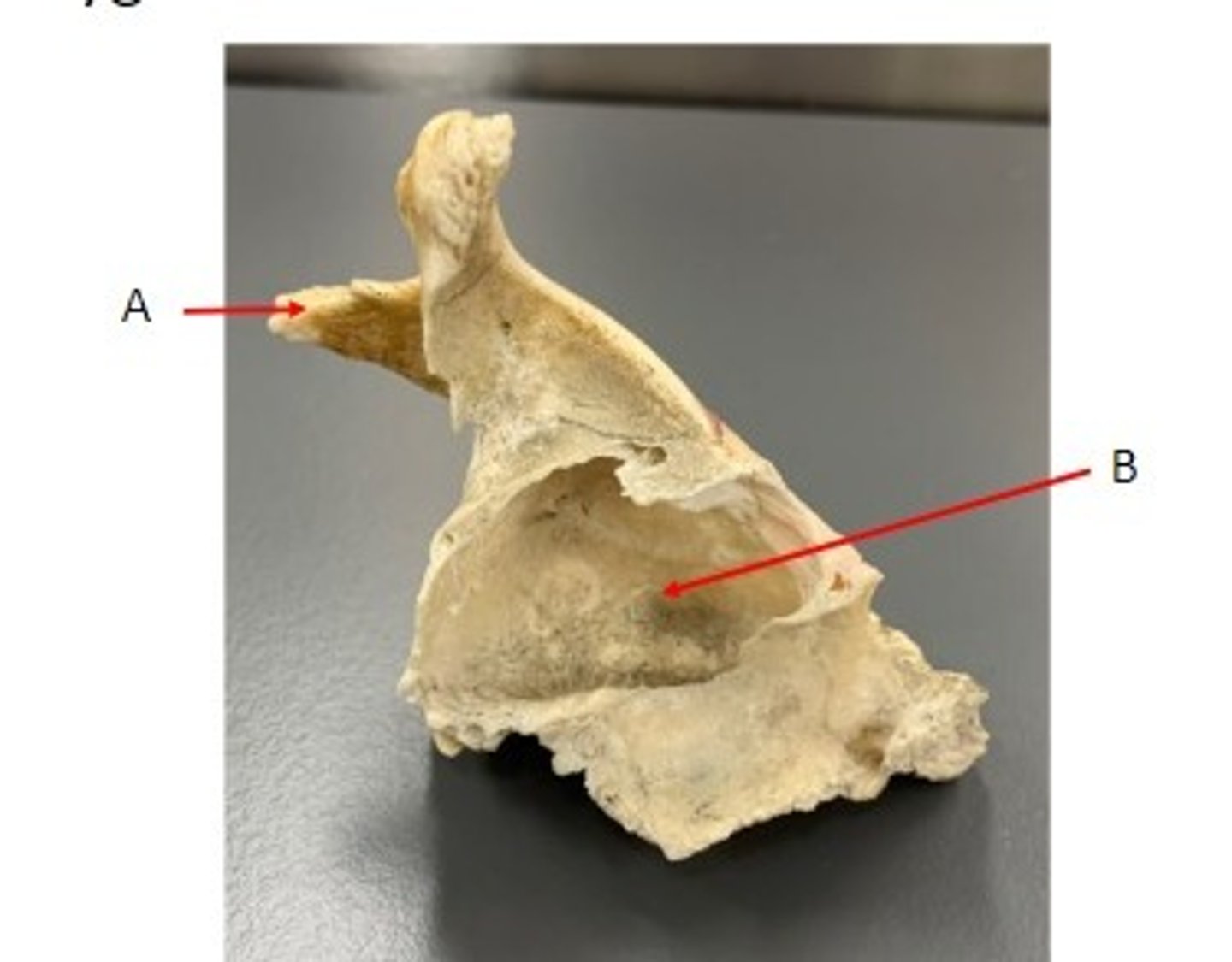
A. Temporal Process of the Zygomatic Bone
B. Infra-orbital Foramen of the Maxillary Bone
Identify
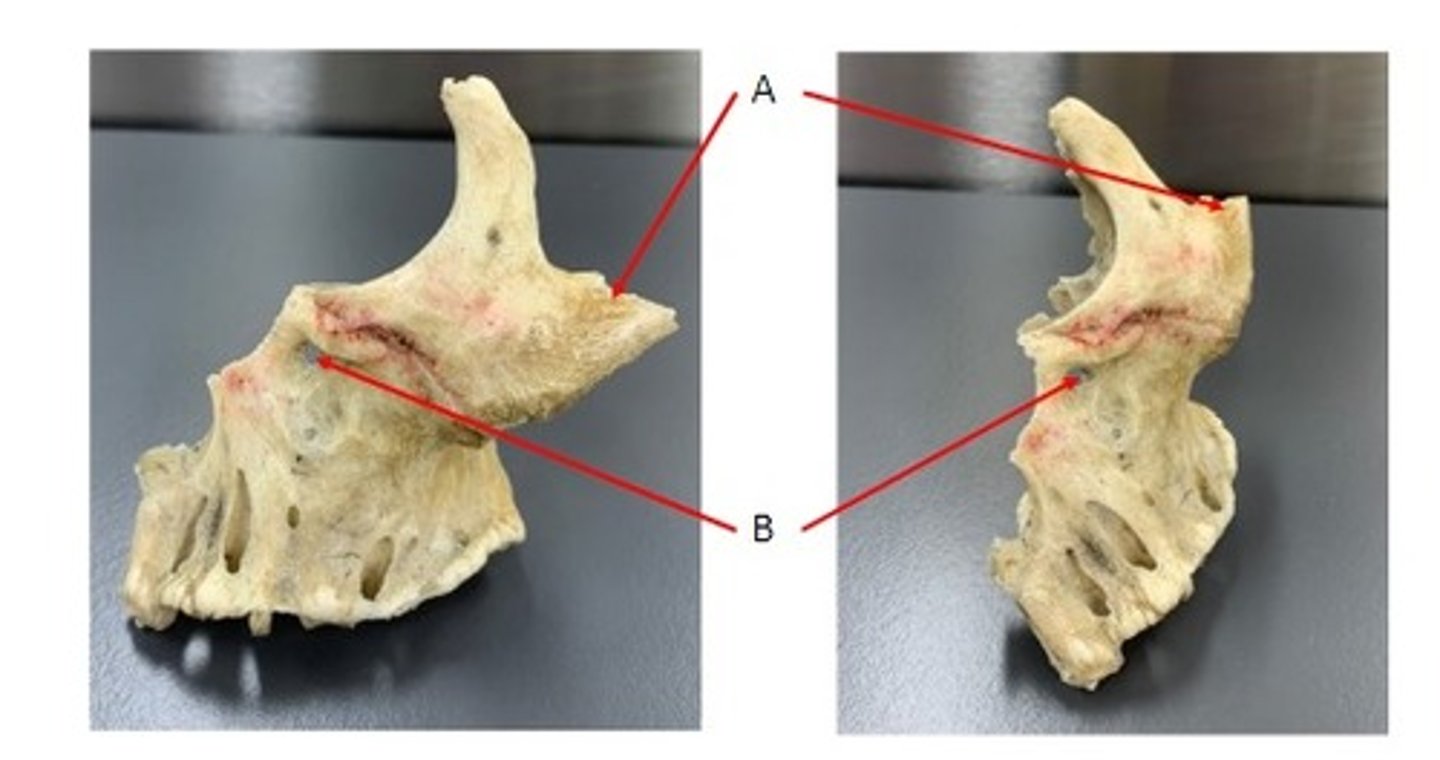
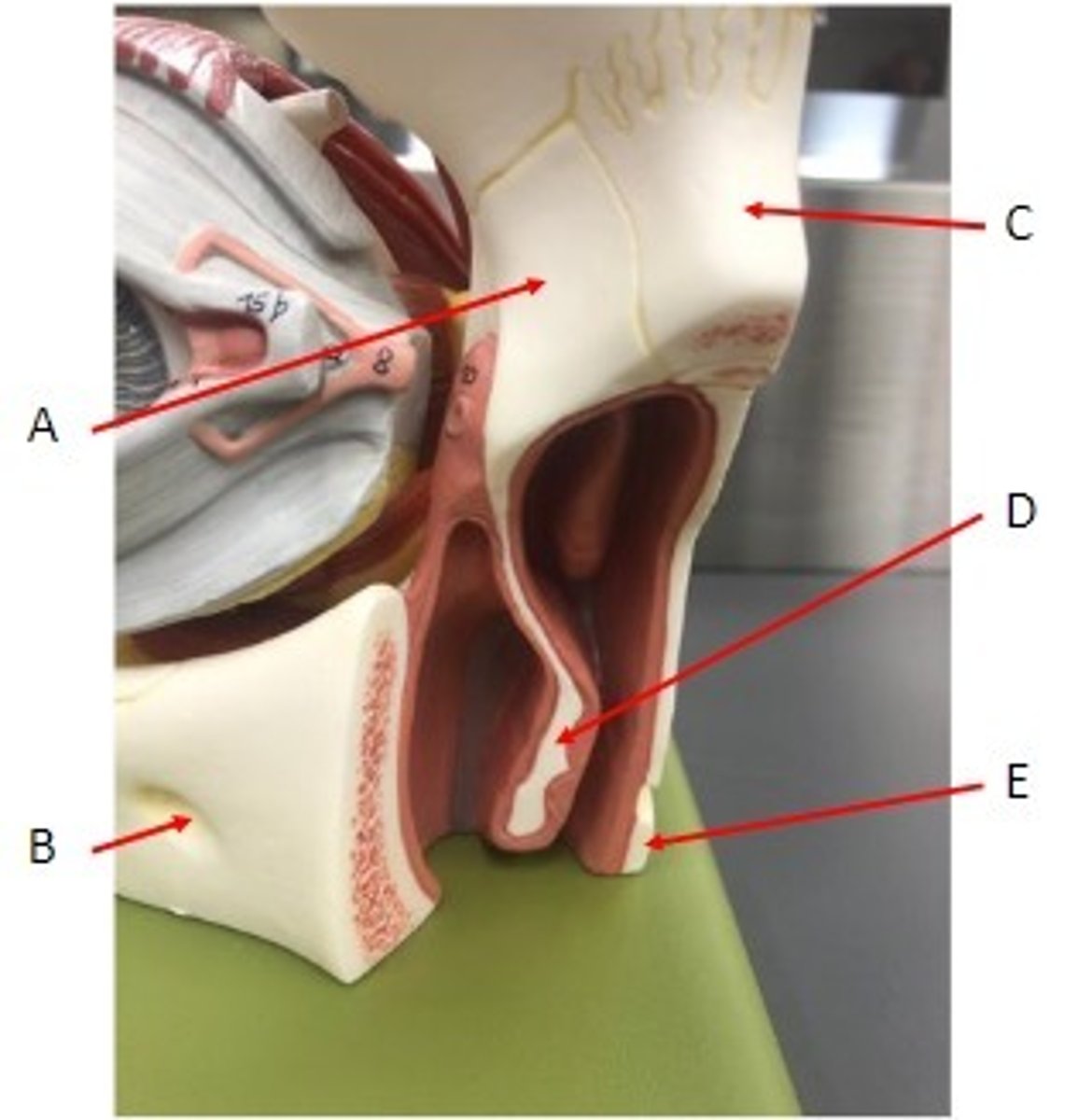
A. Middle Nasal Concha of the Ethmoid Bone
B. Inferior Nasal Concha
C. Palatine Process of the Maxillary Bone
Identify
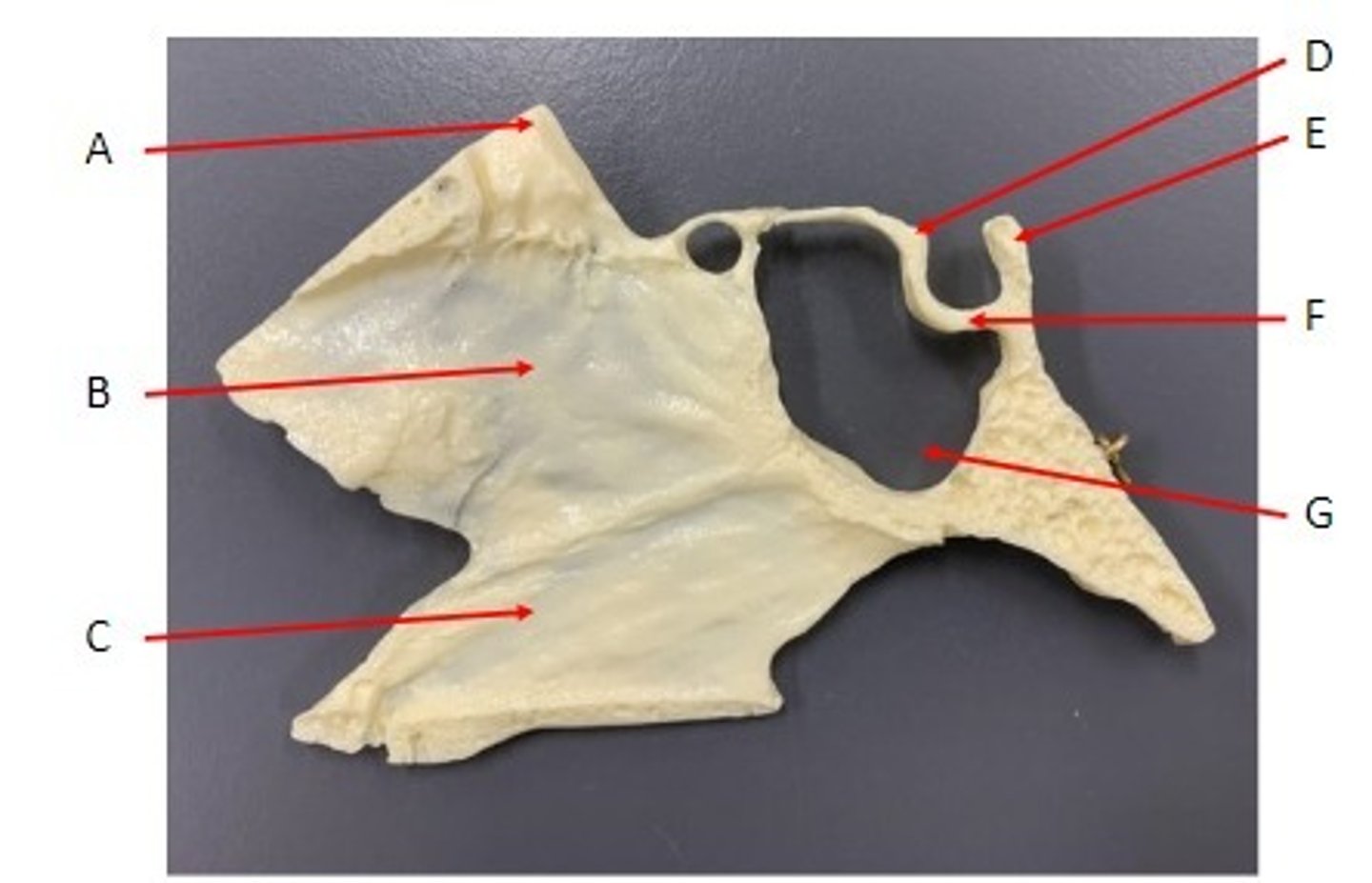
A. Crista Galli of the Ethmoid Bone
B. Perpendicular Plate of the Ethmoid Bone
C. Vomer Bone
D. Tuberculum Sallae of the Sella Turcica of the Sphenoid Bone
E. Dorsum Sallae of the Salla Turcica of the Sphenoid Bone
F. Hypophyseal Fossa of the Sella Turcica of the Sphenoid Bone
G. Sphenoidal Sinus of the Sphenoid Bone
Identify
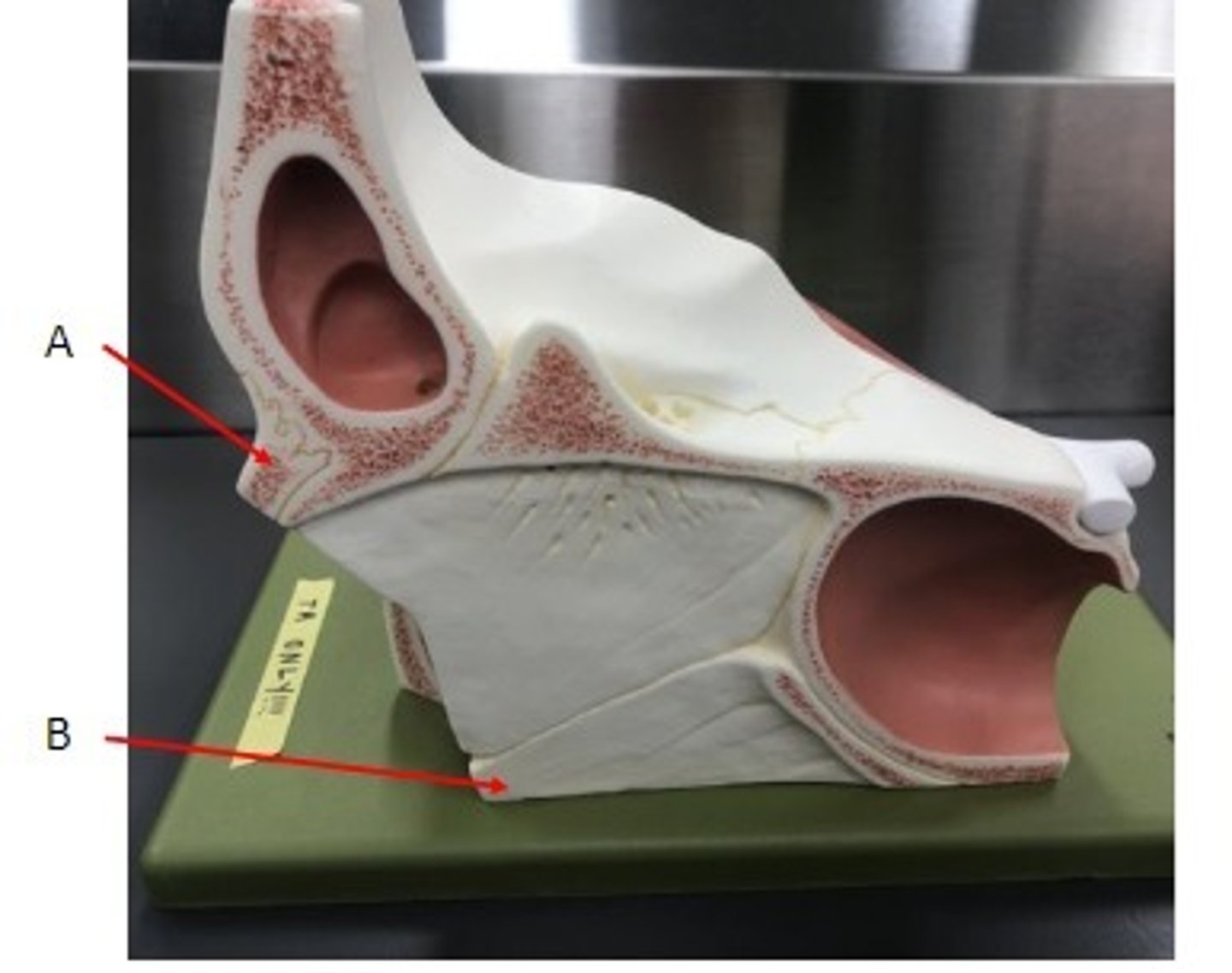
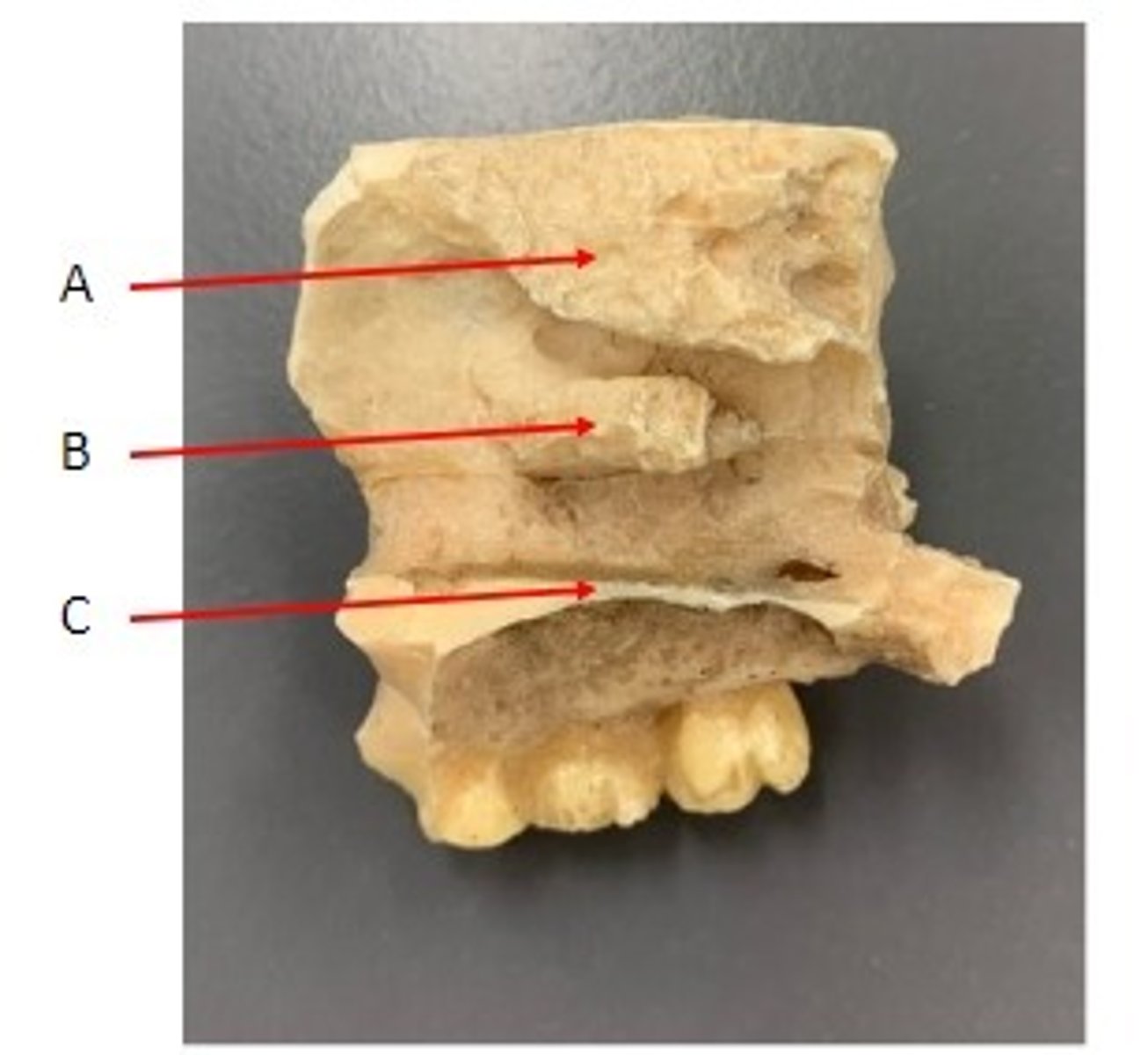
A. Superior Nasal Conchae of the Ethmoid Bone
B. Middle Nasal Conchae of the Ethmoid Bone
C. Inferior Nasal Conchae
Identify
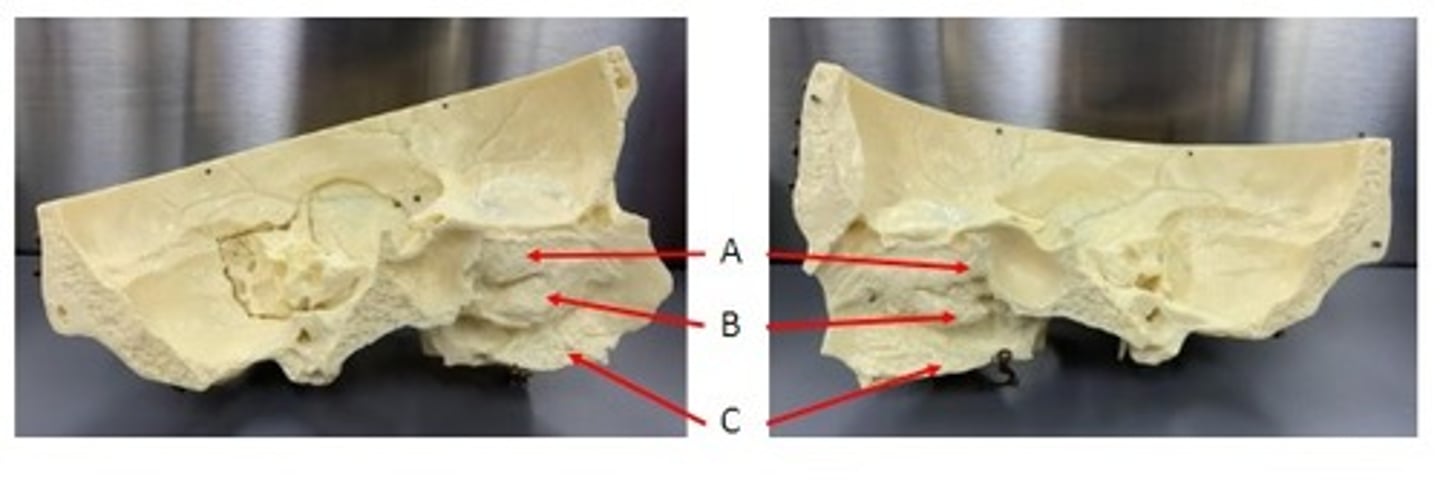
A. Condylar Process of the Mandible Bone
B. Coronoid Process of the Mandible Bone
C. Alveolus of the Mandible Bone
D. Mental Foramen of the Mandible Bone
Identify
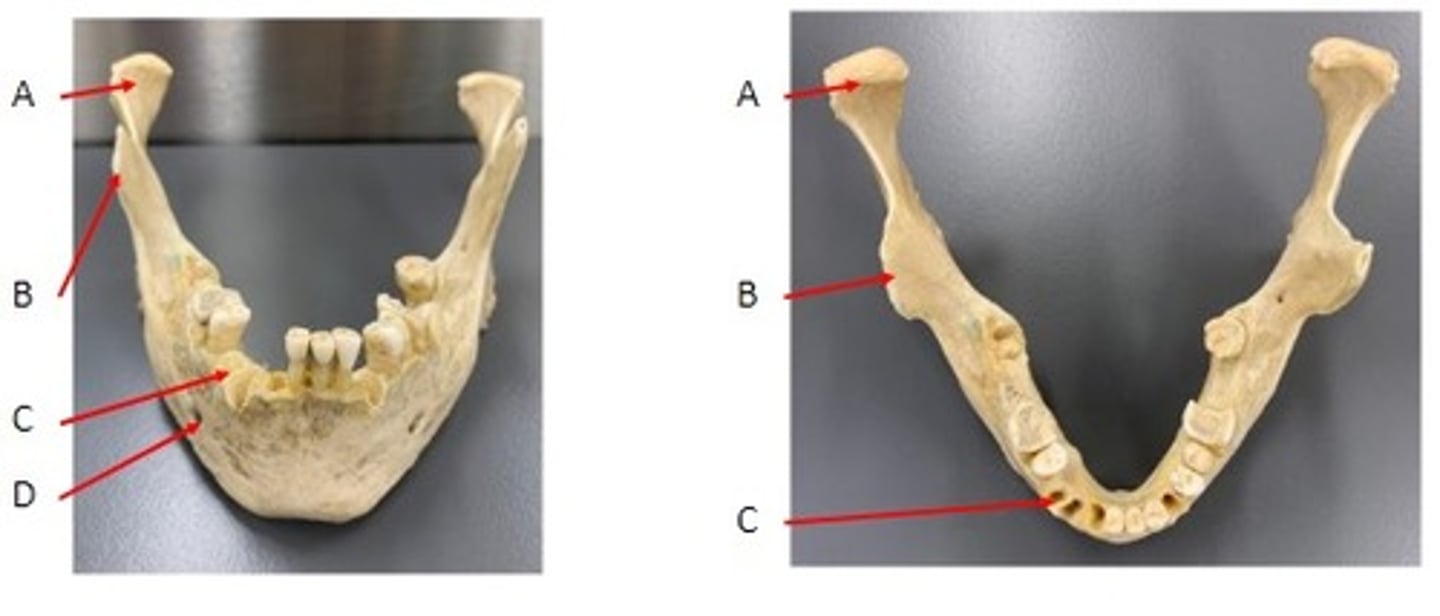
A. Coronoid Process of the Mandible Bone
B. Condylar Process of the Mandible Bone
C. Mandible Foramen of the Mandible Bone
D. Mental Foramen of the Mandible Bone
E. Ramus of the Mandible Bone
Identify
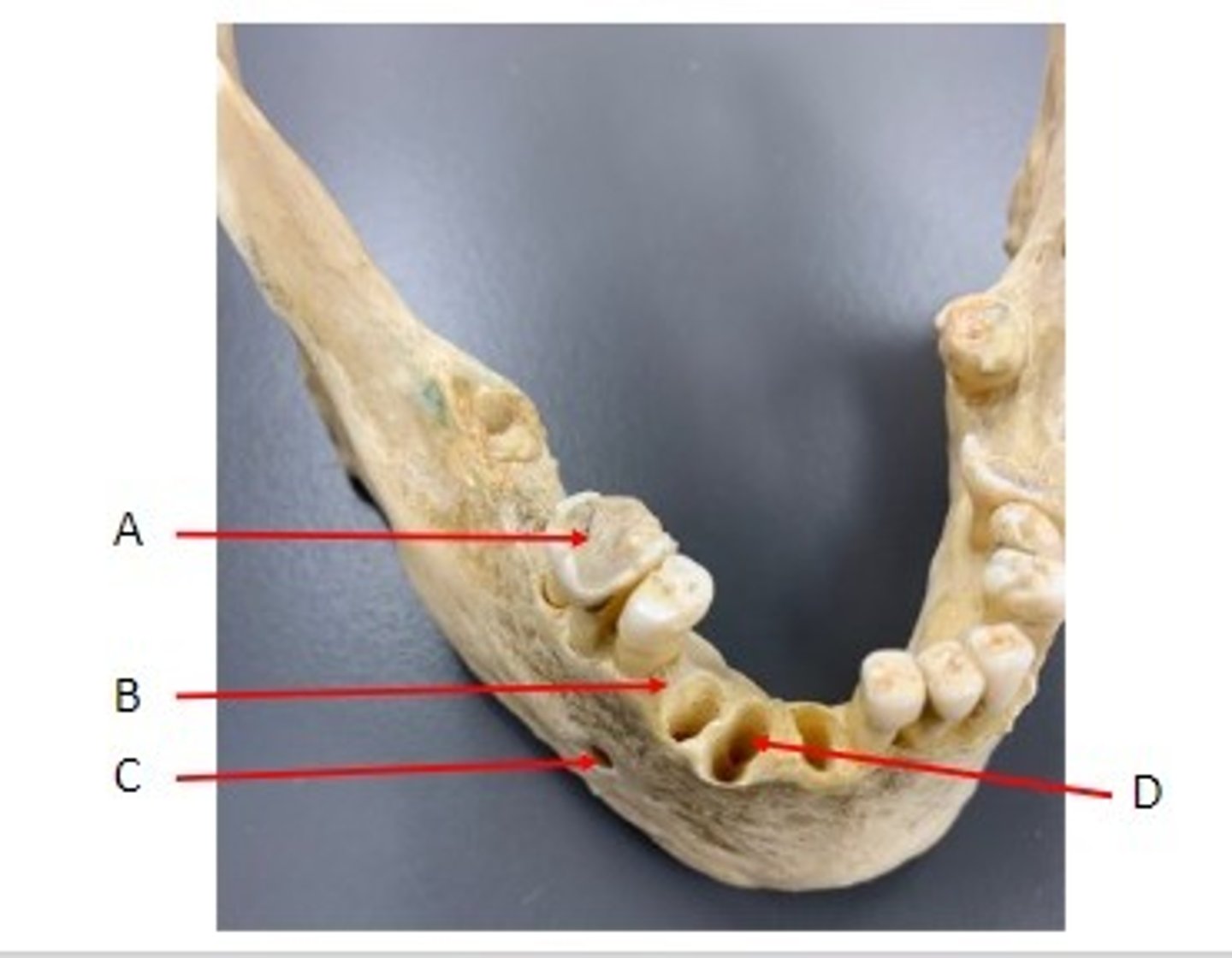
A. Tooth (Molar) of the Mandible Bone
B. Alveolar Process of the Mandible Bone
C. Mental Foramen of the Mandible Bone
D. Alveolus of the Mandible Bone
Identify
A: Olfactory Nerve CN I
B: Optic Nerve CN II
C: Trochlear Nerve CN IV
D: Trigeminal Nerve CN V
E: Abducens Nerve CN VI
F: Facial Nerve CN VII
G: Vestibulocochlear Nerve CN VIII
Identify the Nerves
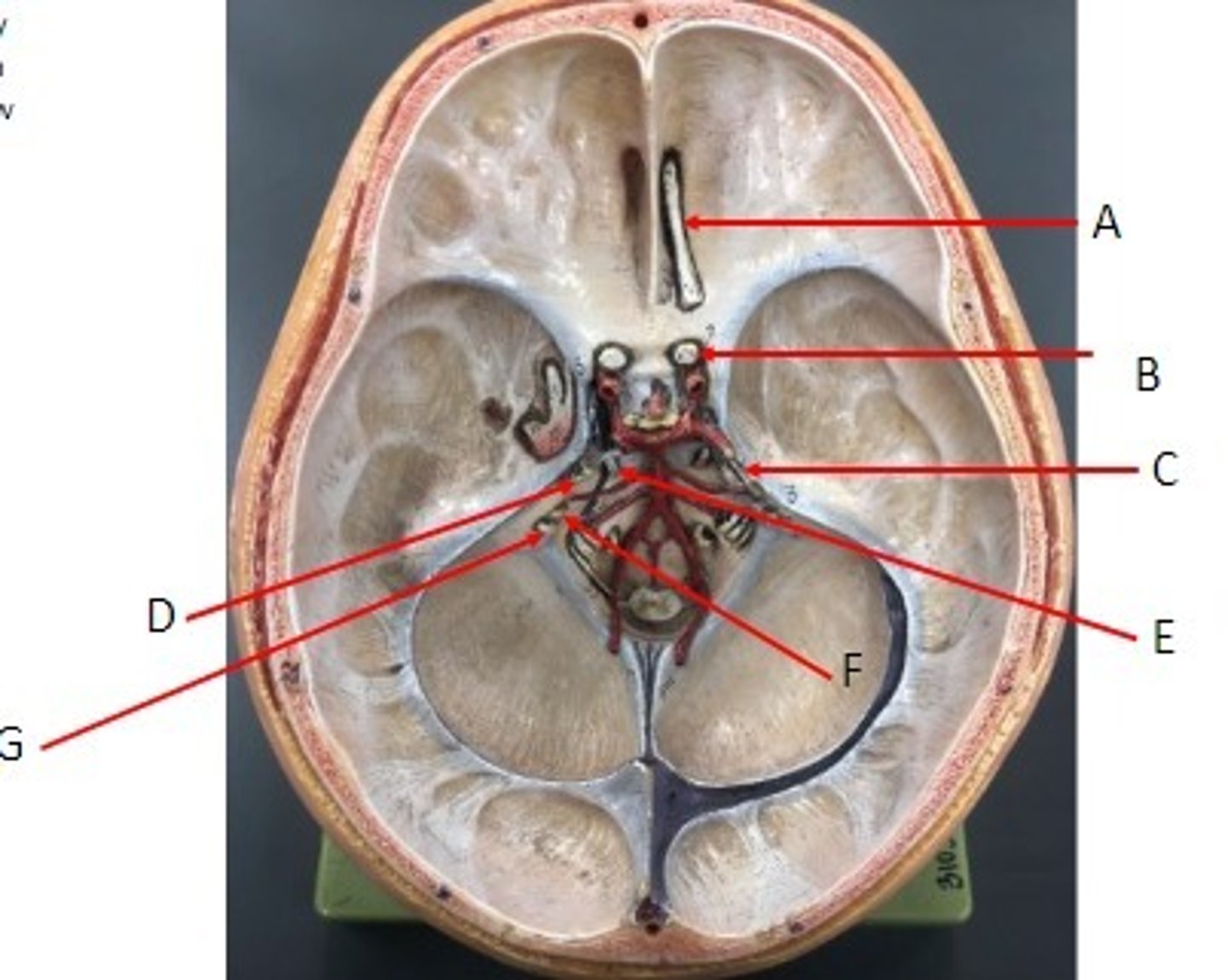
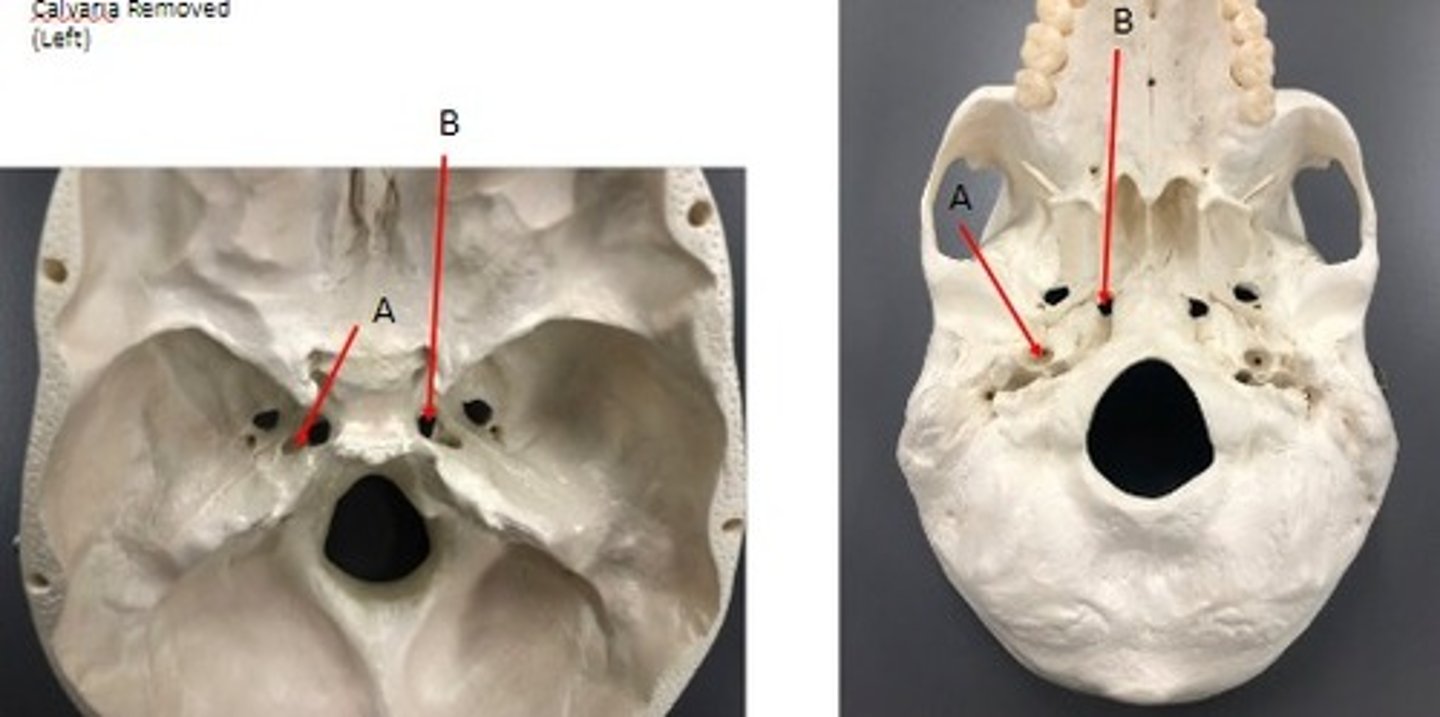
A: Oculomotor Nerve CN III
B: Trochlear Nerve CN IV
C: Glossopharyngeal Nerve CN IX
D: Vagus Nerve CN X
E. Accessory Nerve CN XI
F: Hypoglossal Nerve CN XII
Identify the Nerves