Nitrogen Cycle
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Matter
Elements or molecules which are also nutrients necessary for life on earth
biogeochemical cycle
cycling of matter through a Earth's systems; follows movement of matter between all 4 spheres
Assimilation
Incorporating nonliving matter into tissues of a living things; all cycles incorporate (H+G -> B)
Dissimilation
organic form back to an inorganic form through decomposition

Sink
Reservoir where matter cycles into ex. Tree can be a carbon sink because carbon is stored in the tree in carbohydrate molecules.
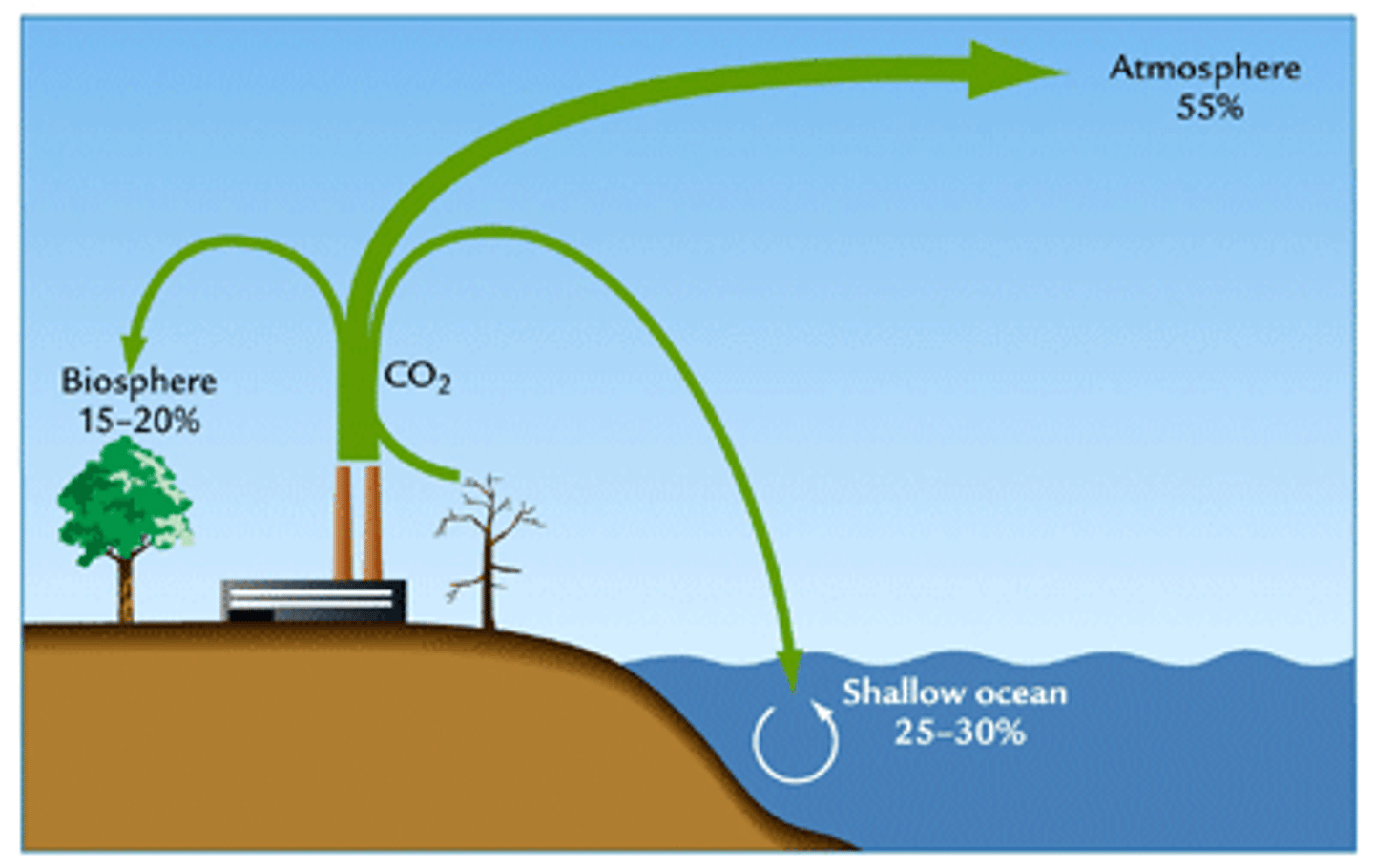
source
A source is the sink the matter is cycling out of, so the same reservoir can be both a source and sink at different phases of the cycle.
Nitrogen gas (N2)
Inert/Stable
78 % of earths atmosphere
when in atmosphere cant be absorbed by multicellular organisms
must be separated by ex. lightning to combine with hydrogen and oxygen to provide compounds for organisms to use

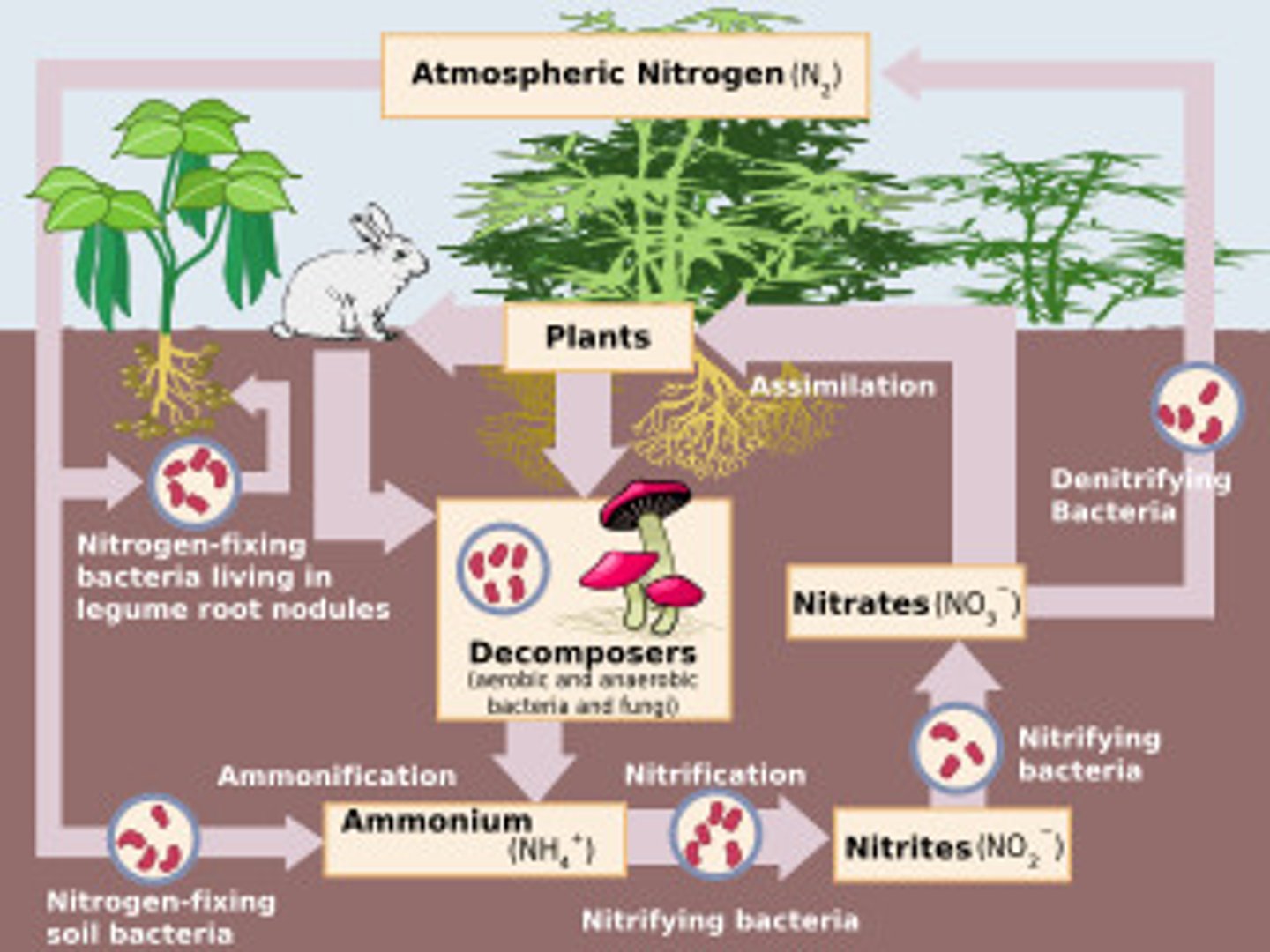
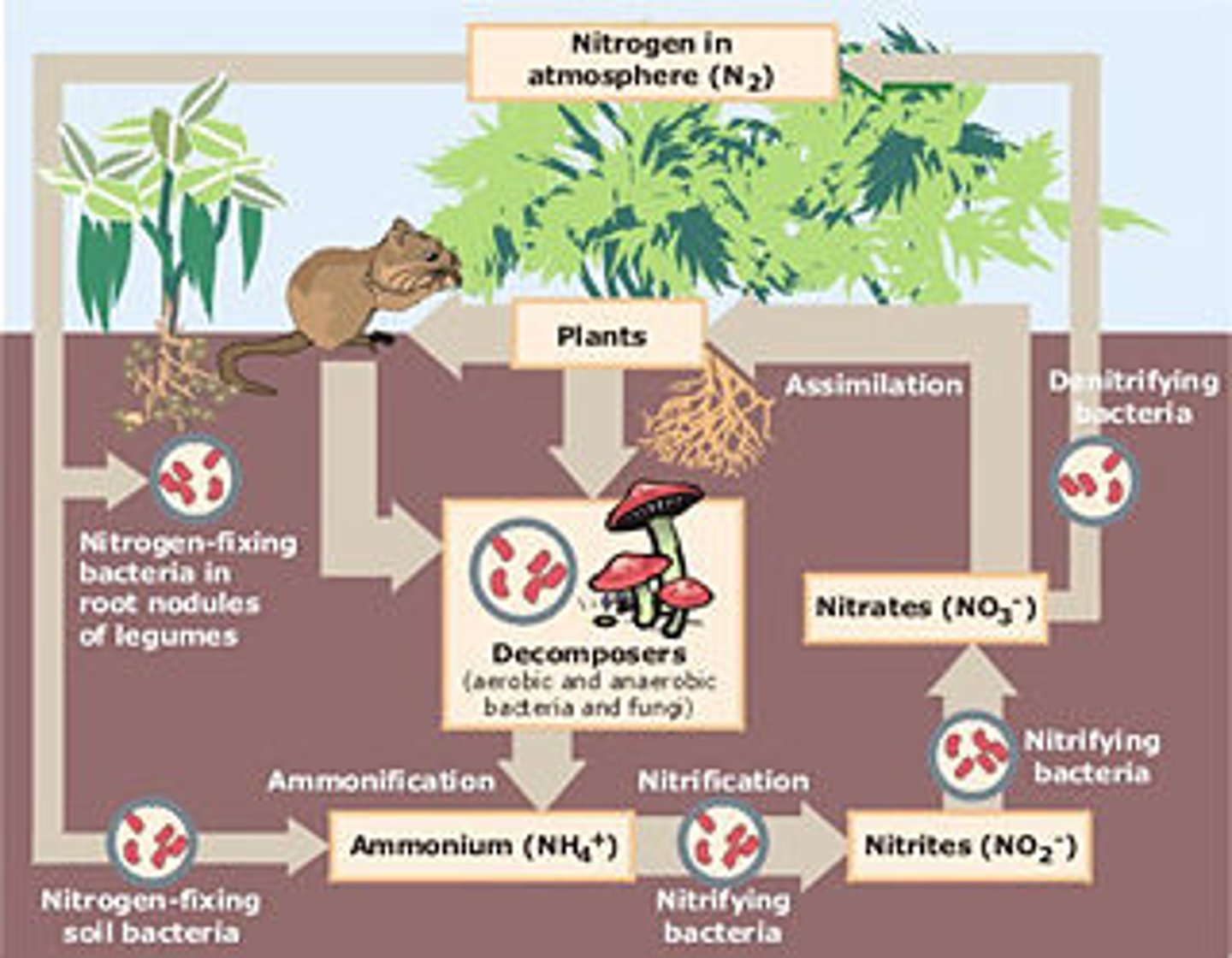
nitrogen fixation
gaseous (gas form of) nitrogen to ammonia in soil and water, naturally carried out by lightning/ N. fixing bacteria in soil and water
(Root Nodule) Rhizobium bacteria
in small root nodules (legumes) which can fix nitrogen and produce ammonia
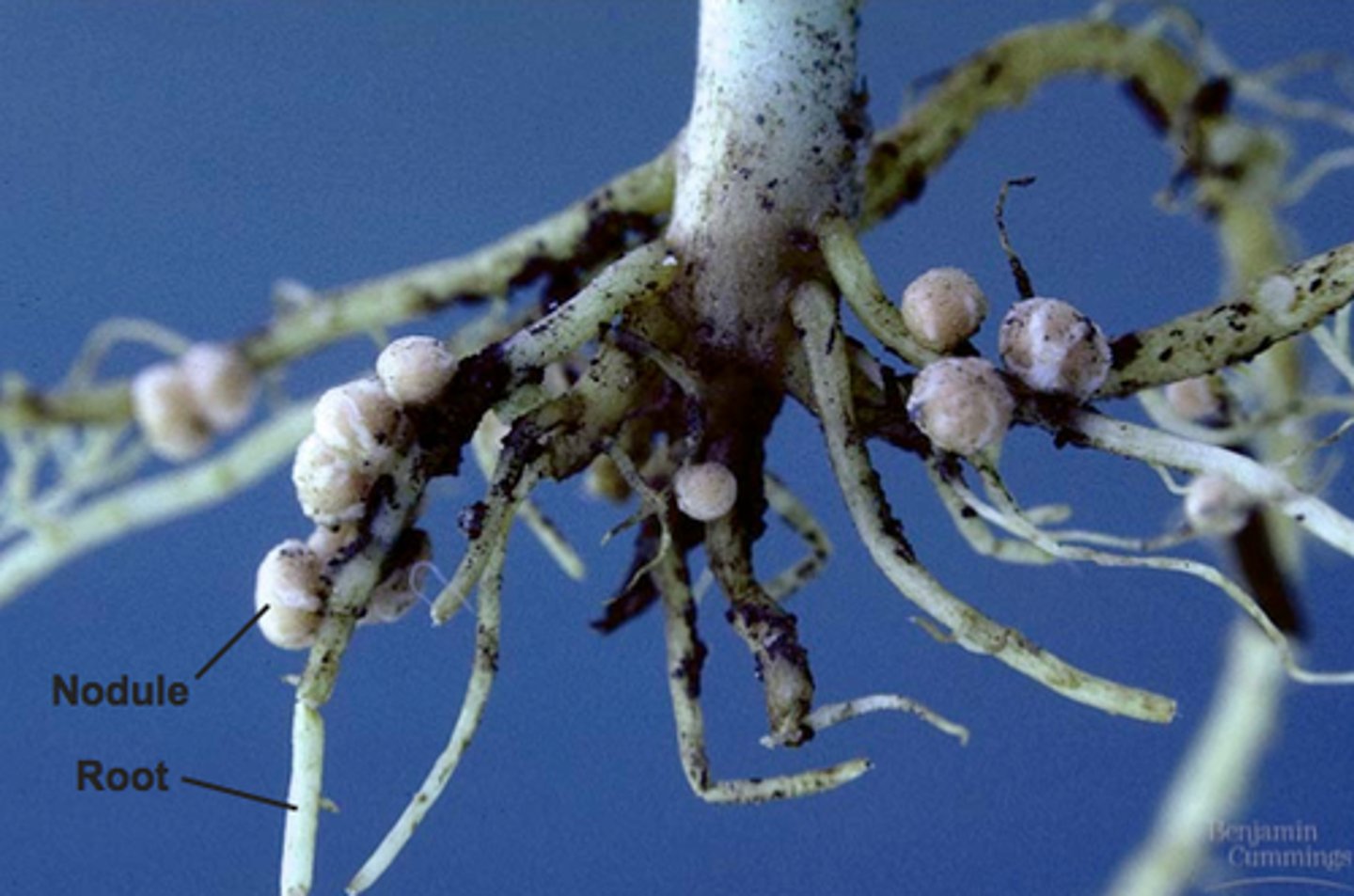

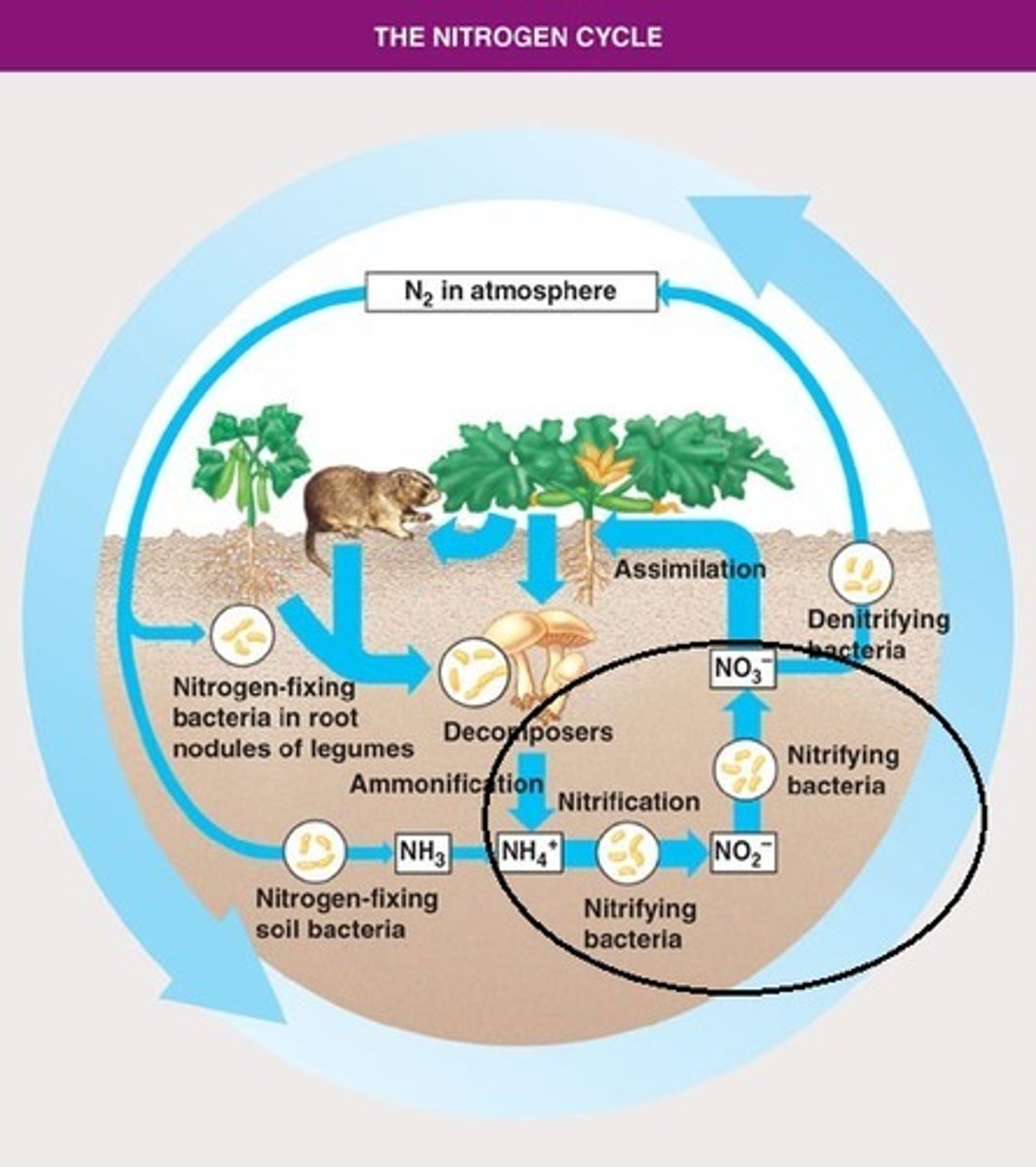
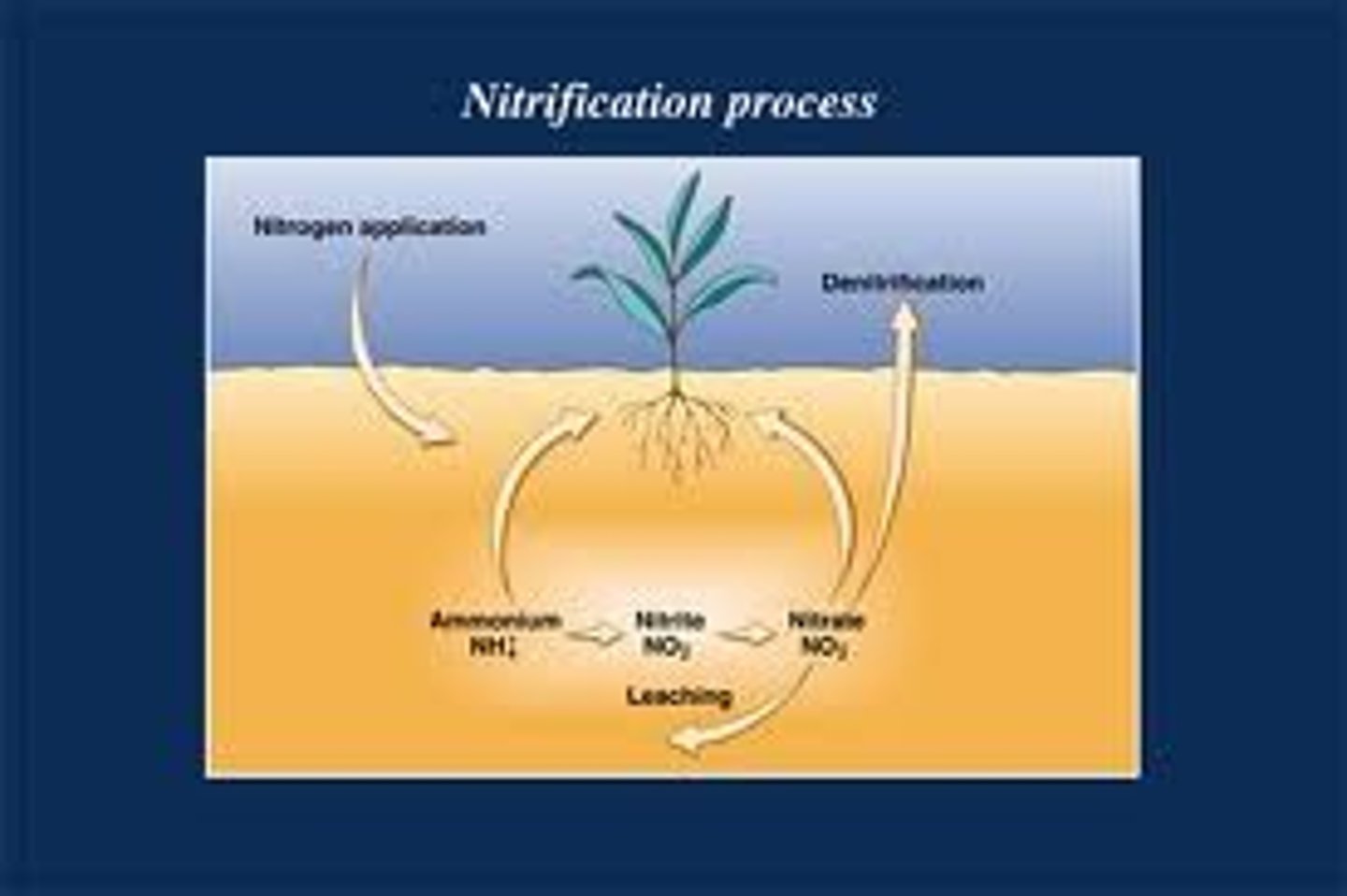
Nitrification
ammonia in soil is converted to nitrite ions (toxic to plants), then converted to nitrate which are easy to take by plants
Runoff (part of water cycle AND biogeochemical cycle)
Runoff moves nitrate and other nitrogen compound to the hydrosphere through weathering and erosion

assimilation plants and animals
Plants-plants absorb nitrate ions through the roots and use these ions to make nitrogen containing organic molecules such as DNA amino acids and proteins
Animals- obtain their nitrogen by eating plants or plant eating animals to build proteins in the body
Ammonification
converting organic nitrogen rich compounds into simpler nitrogen inorganic compounds carried out by ammonifying bacteria (decomposition) (B -->G+h)
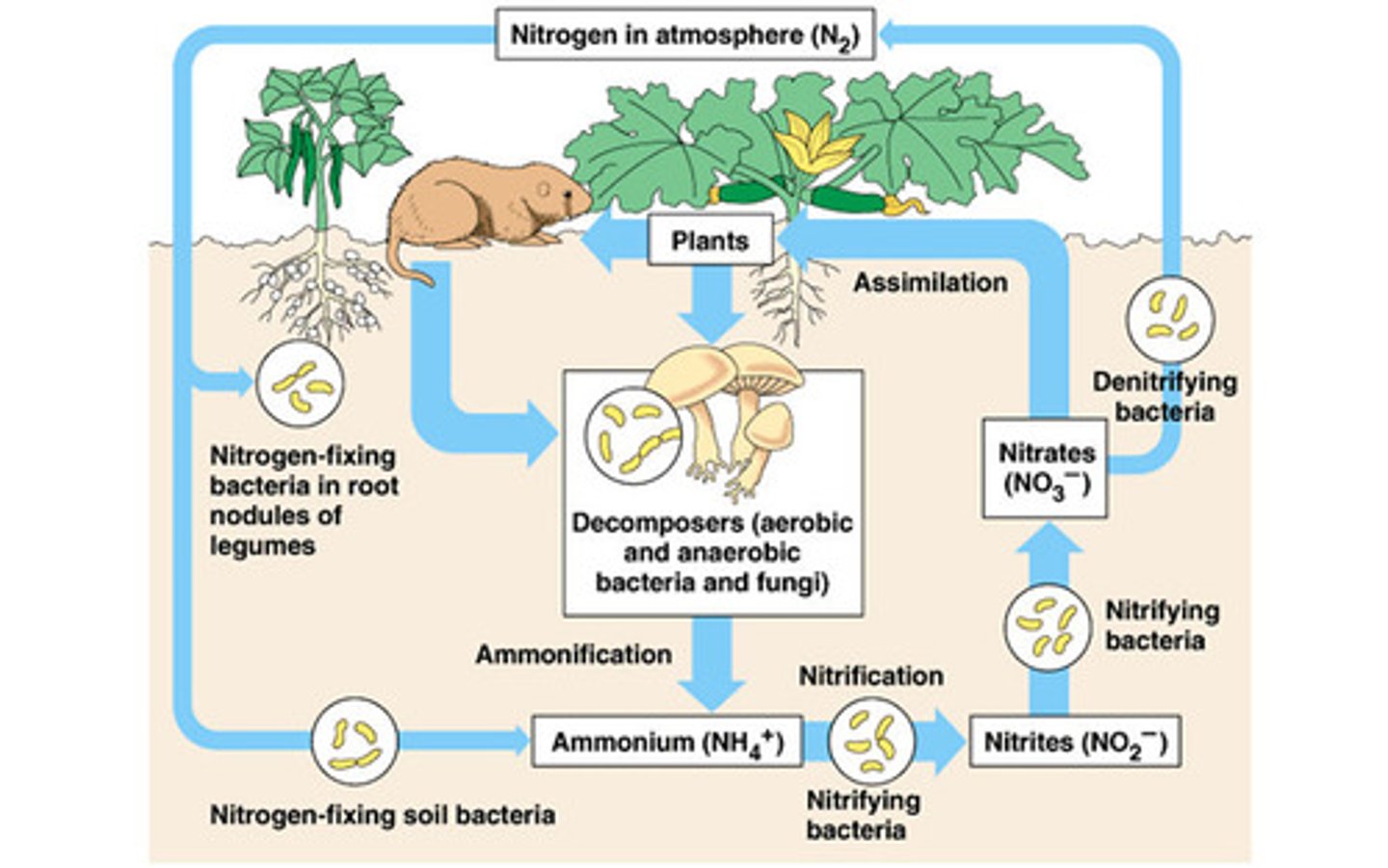
Denitrification
ammonia is converted back into inert nitrogen gas carried out by denitrified bacteria which can be returned into the atmosphere (G+H --> A)
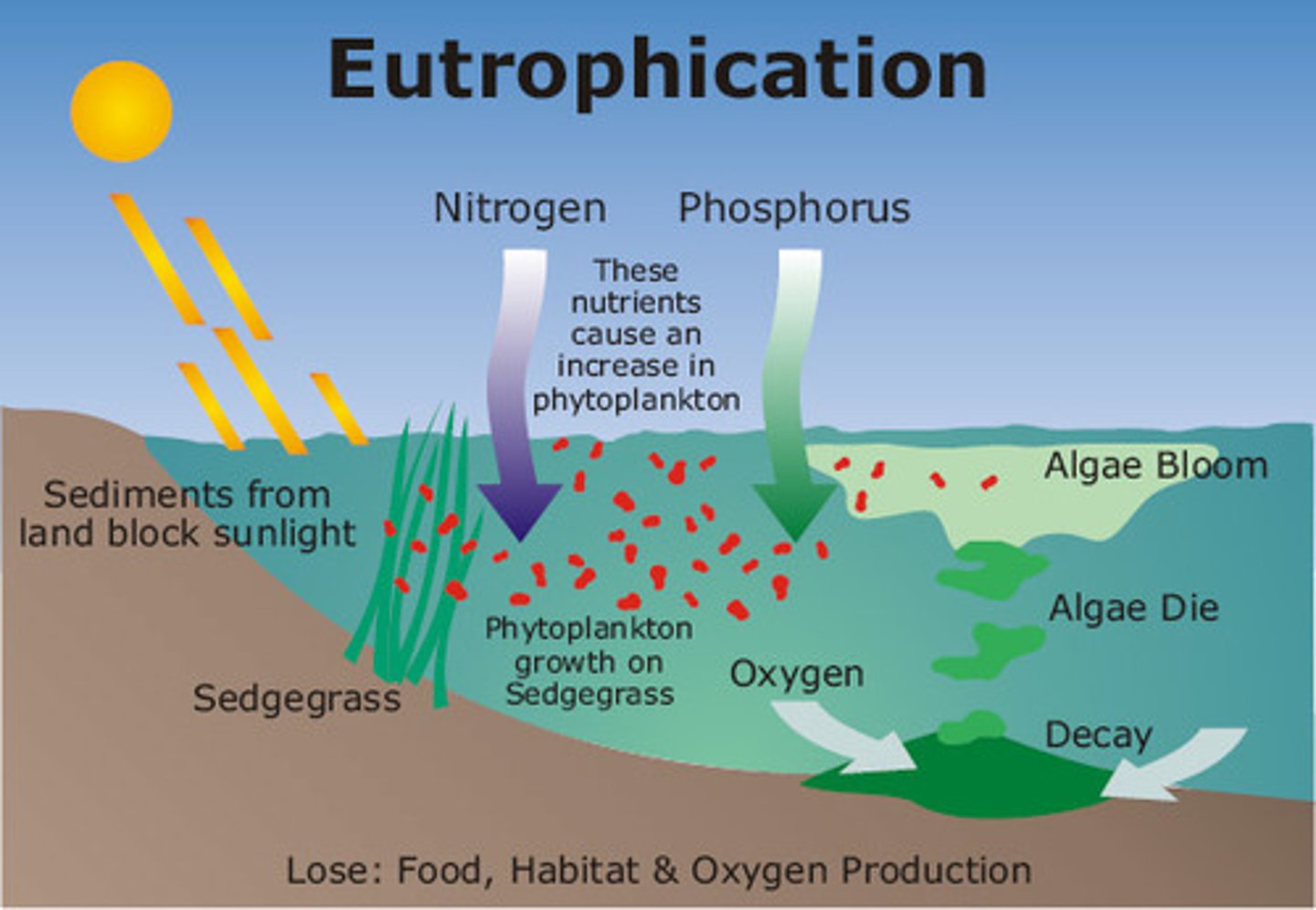
algal bloom
excessive growth of algae in bodies of water because of high levels of nutrients, usually from fertilizer in runoff

Role of Bacteria in Nitrogen Cycle
convert nitrogen into a form that can be assimilated
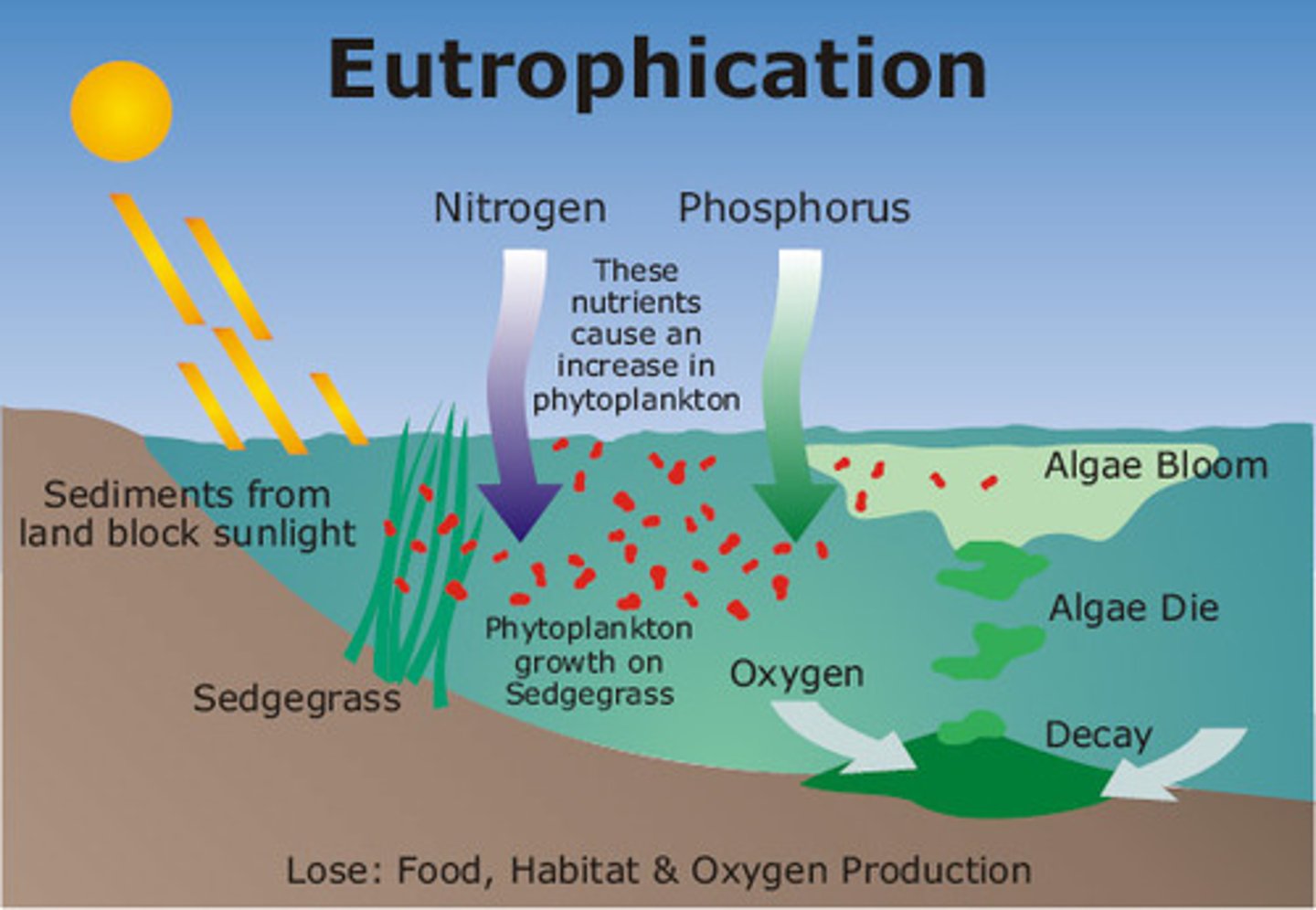
Eutrophication
Excess nutrients cause algae bloom, which forms a thick blanket over ocean plants, causes water to warm up, blocks the sun meaning plants and algae die , leads to decomposition which uses oxygen finally leading to anoxic water or a dead zone.
Forms of nitrogen in different sinks
Biosphere: DNA, Proteins, amino acids
Geosphere: Fixed Nitrogen, ammonia
Atmosphere: Nitrogen Gas
Hydrosphere: Fixed Nitrogen, ammonia
Mitigation of Human Impacts on Nitrogen Cycle
1. Rotation of crops
How have humans influenced nitrogen in the following spheres?
ATM (atmosphere)
GEO (geosphere)
HYDRO (hydrosphere)
BIO (biosphere)
ATM: Burning fossil fuels --> acid rain in atmosphere
GEO: Fertilizer In soil
HYDRO: anoxic water
BIO: deforestation
nitrogen fixing
because atmospheric N cannot be used directly by plants, it must first be converted into ammonia by bacteria.

anoxic water
Water without oxygen
deforestation
The removal of trees faster than forests can replace themselves.

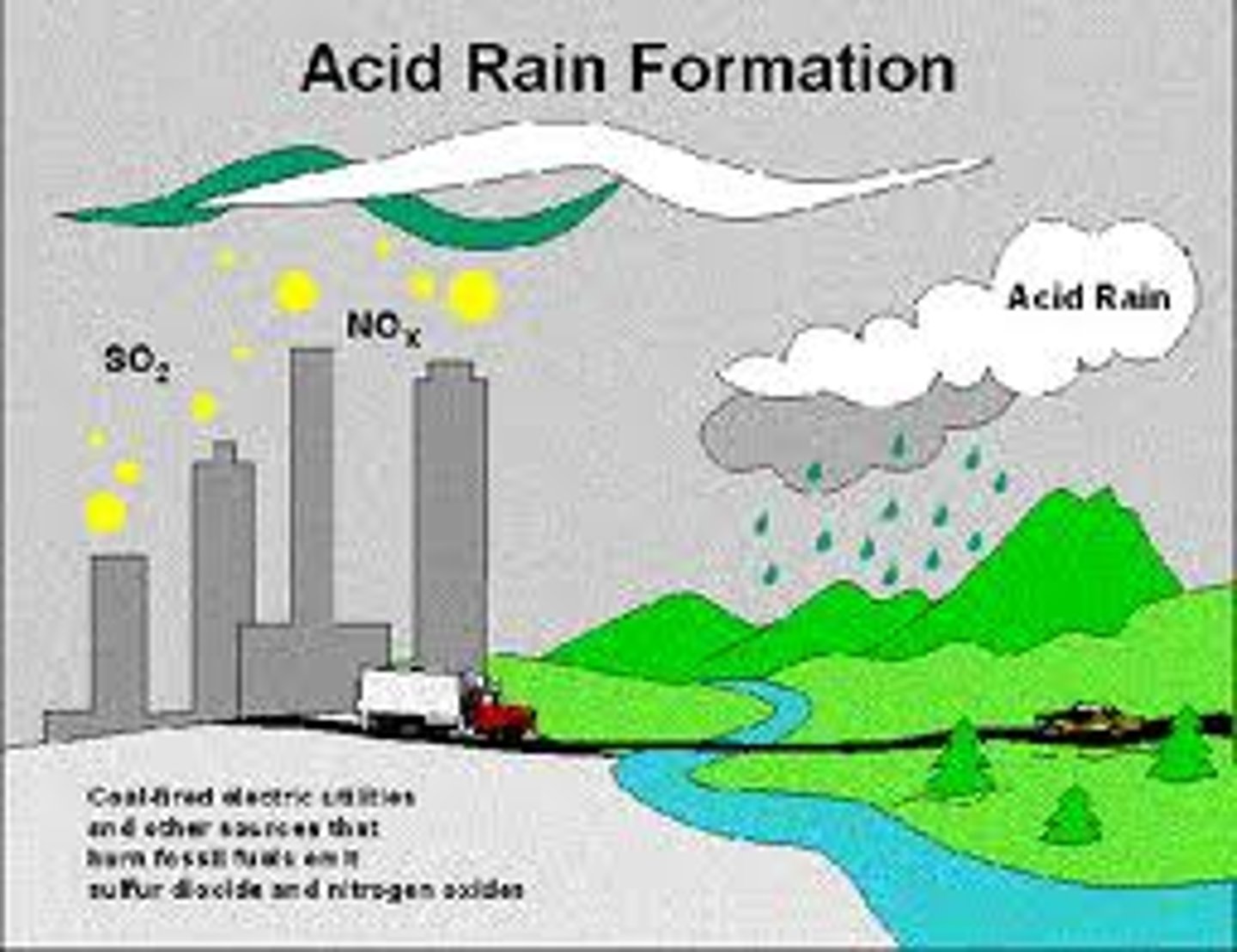
acid rain
Rain containing acids that form in the atmosphere when industrial gas emissions (especially sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides) combine with water.
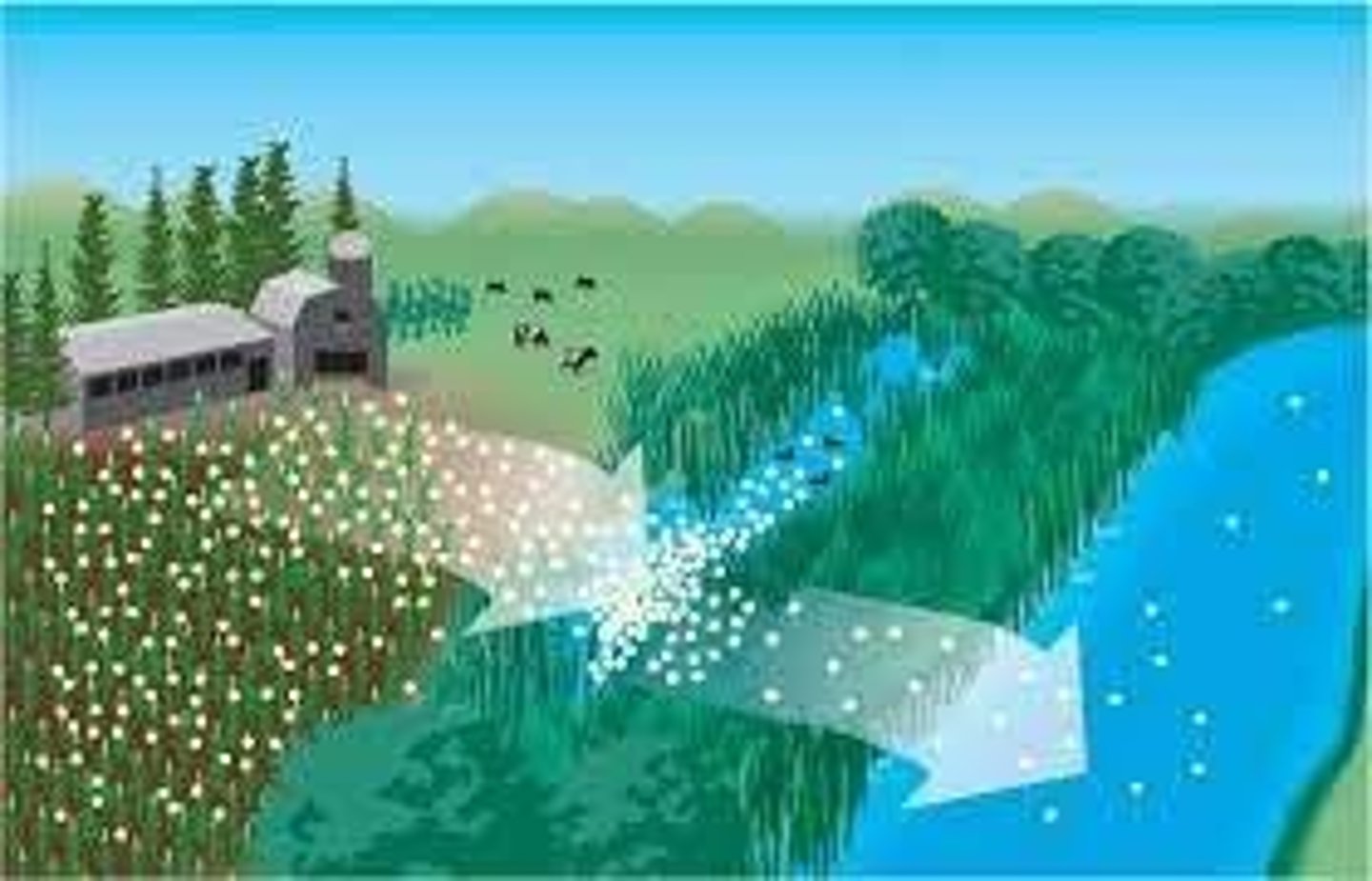
fertilizer runoff
overapplied fertilizer can run off into local water bodies, infiltrate into aquifers and evaporate into air. nitrates and phosphates can cause health problems
Watershed protection fertilizer pollution
a means of protecting a lake, river, or stream by managing the water that drains into it from people's grass & gardens, and from businesses such as farms and golf courses
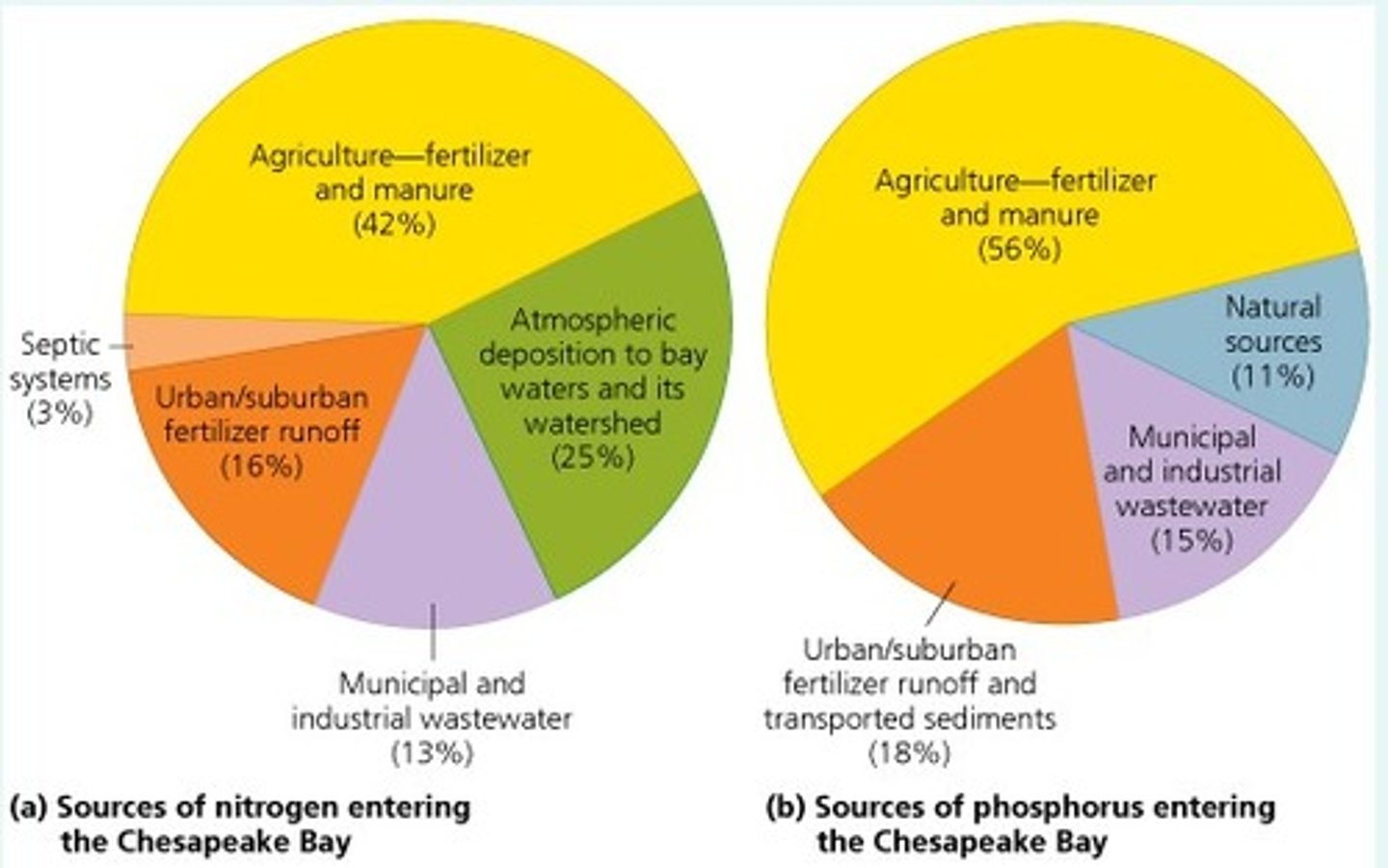
urbanization
Burning of fossil fuels is seen with cars, which can produce greenhouse gases, and lead to acid rain that kills plant life.
It's an increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban areas (large cities).

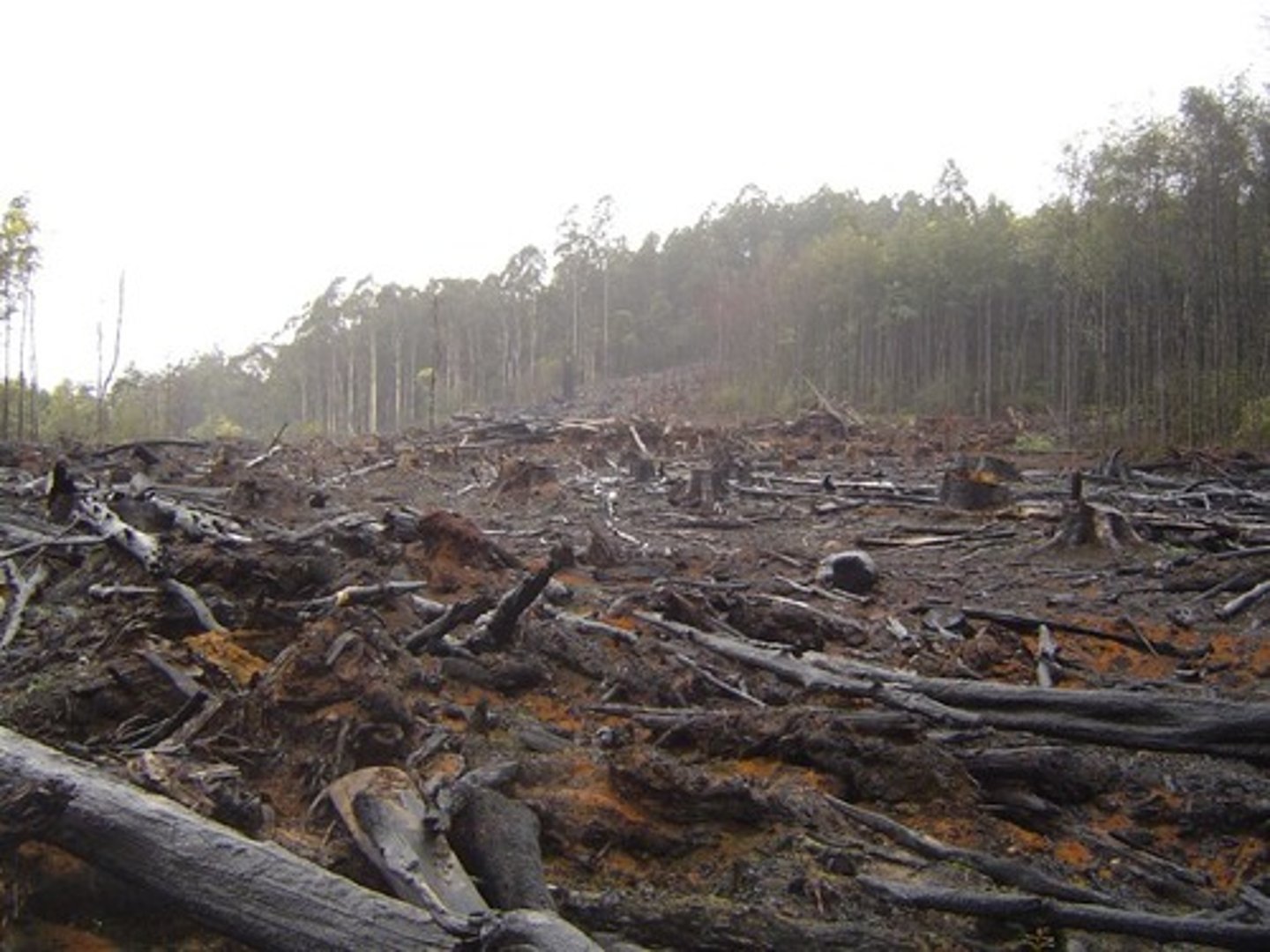
Impacts of Deforestation
1. Atmospheric CO2 increased - when trees are cut, they stop taking in CO2 AND release all of the CO2 they had stored in them previously
2. More soil erosion - no trees to protect the soil - soil infertility - desertification. Soil washes away in rainstorms and blows away in wind.
3. Landslides and mudslides - The roots of trees hold soil together when it's wet. With no trees, soil isn't stable so it is more vulnerable to landslides
4. Lack of biodiversity

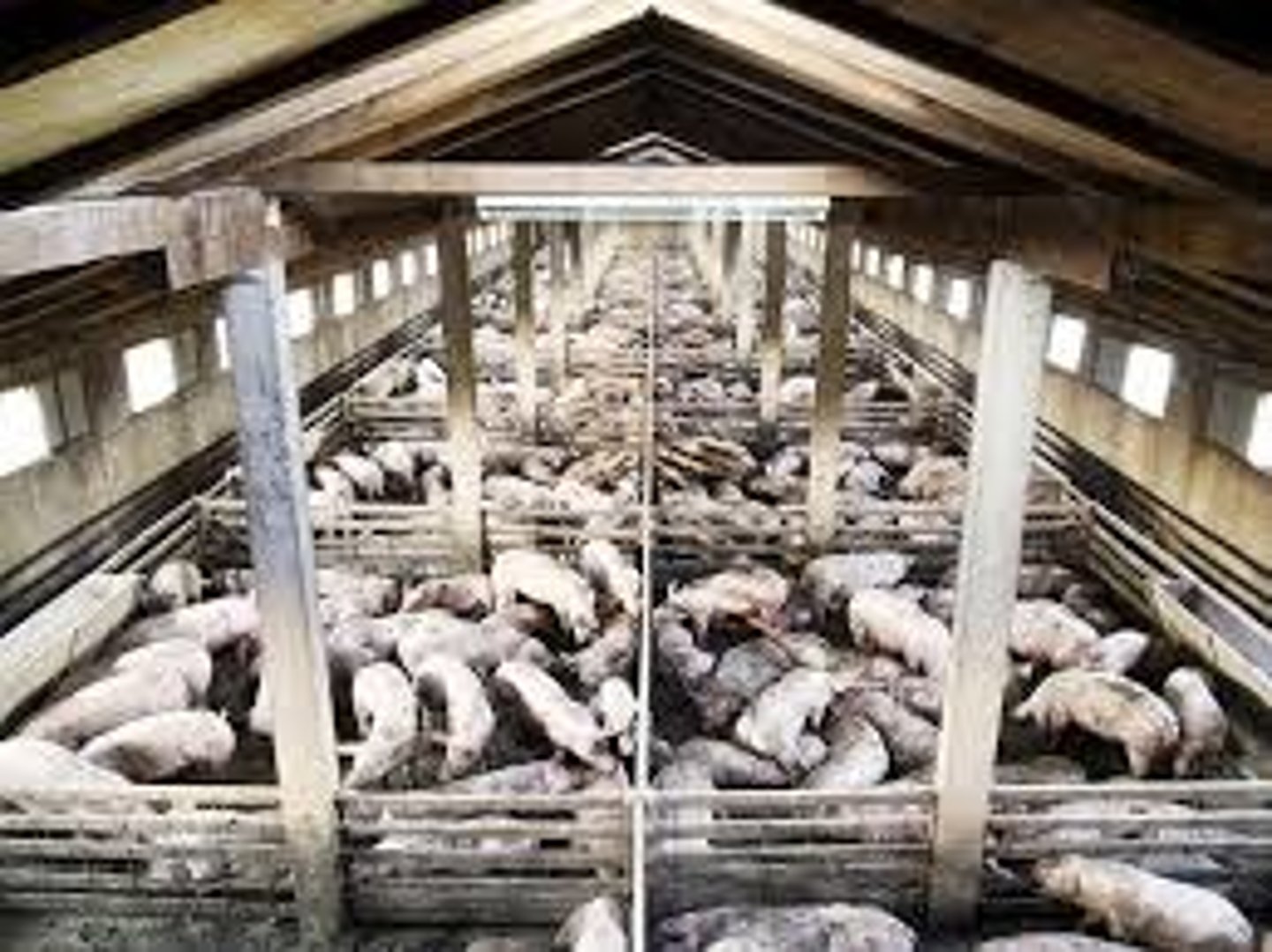
CAFOs
Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations for livestock. Animals live closely together on "factory farms," which produce so much animal feces they pollute soil and watersheds. Large amount of feces (poop) is spread on fields which carries in runoff, causing algal blooms and dead zones in lakes, rivers, oceans.

Haber Process
the manufacture of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen in factories, which is done at high pressure and high temperature with the aid of a catalyst. It can catch fire quickly, burn, or even explode.

legumes
plants of the bean and pea family, including peanuts, clover, & alfalfa grasses, with seeds that are rich in protein compared with other plant-based foods. Their roots help fix nitrogen in soil. They help make soil conditions better.

growing legumes
increase nitrogen fixation by bacteria. This picture shows white clover.
