Amino Acids
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the structure and characteristics of the the 20 standard amino acids.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Glycine
Smallest side chain; only amino acid with no chiral carbon; most flexible amino acid in a protein chain.

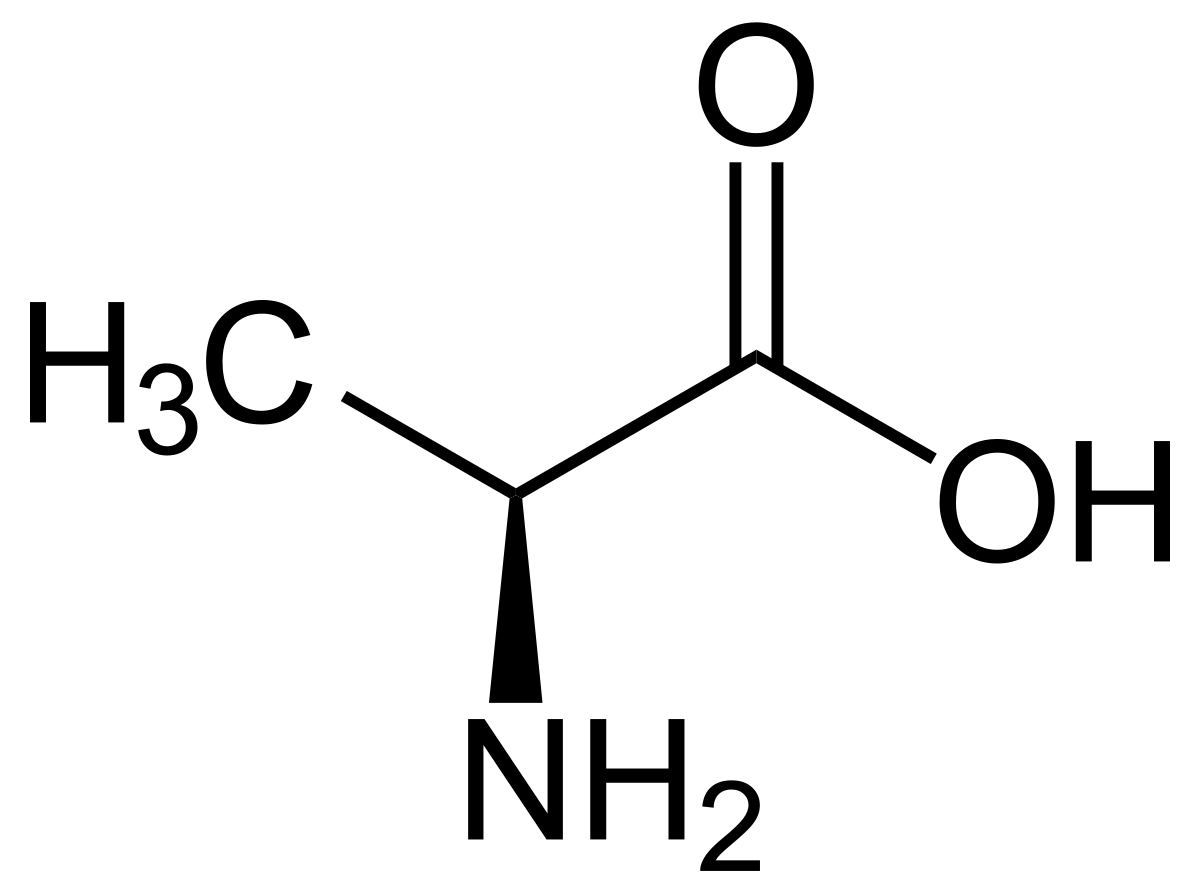
Alanine
Small side chain, non-polar (aliphatic).
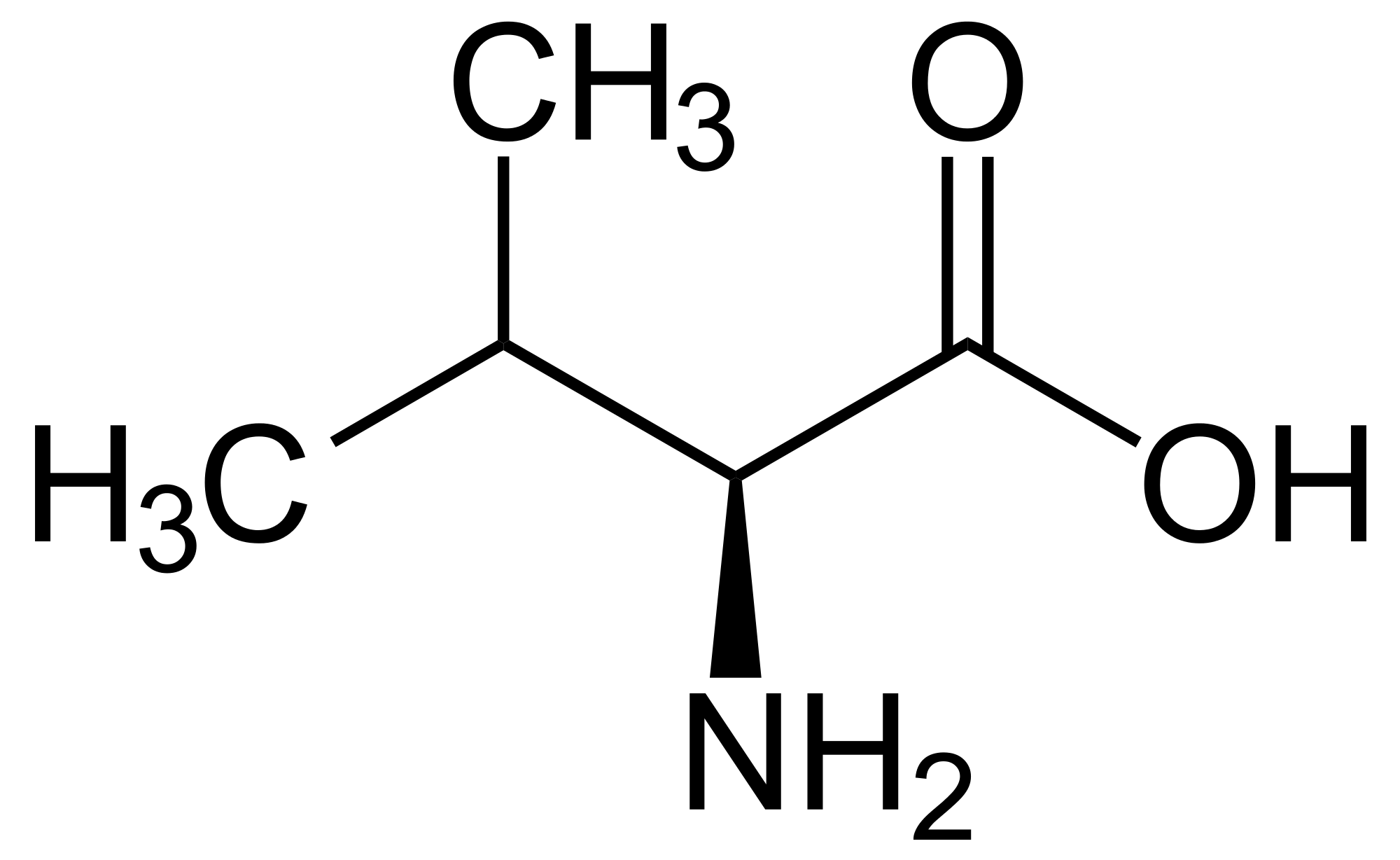
Isoleucine
Branched amino acid with a tertiary carbon atom in the side chain & this a.a. has more than one chiral C, non-polar (aliphatic).
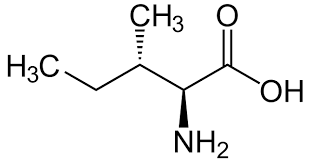
Leucine
Branched amino acid with a tertiary carbon atom in the side chain, non-polar (aliphatic).

Valine
Branched amino acid with a tertiary carbon atom in the side chain, non-polar (aliphatic).
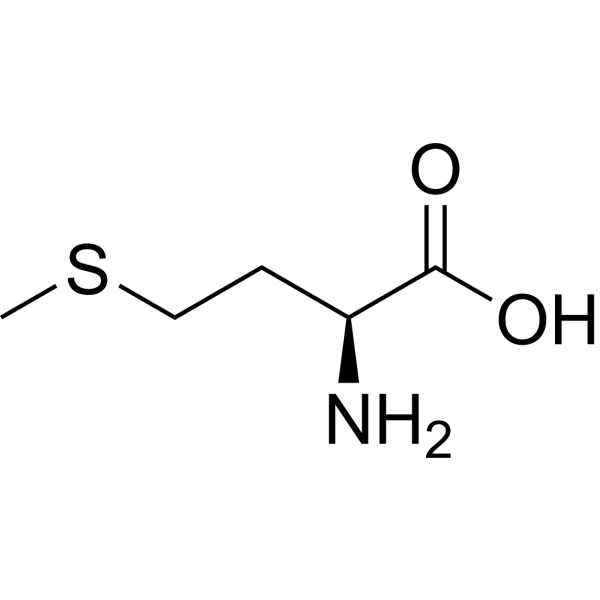
Methionine
Sulfur is non-polar, roughly the size of a CH2 group; sulfide/thioether functional group; non-polar (aliphatic).
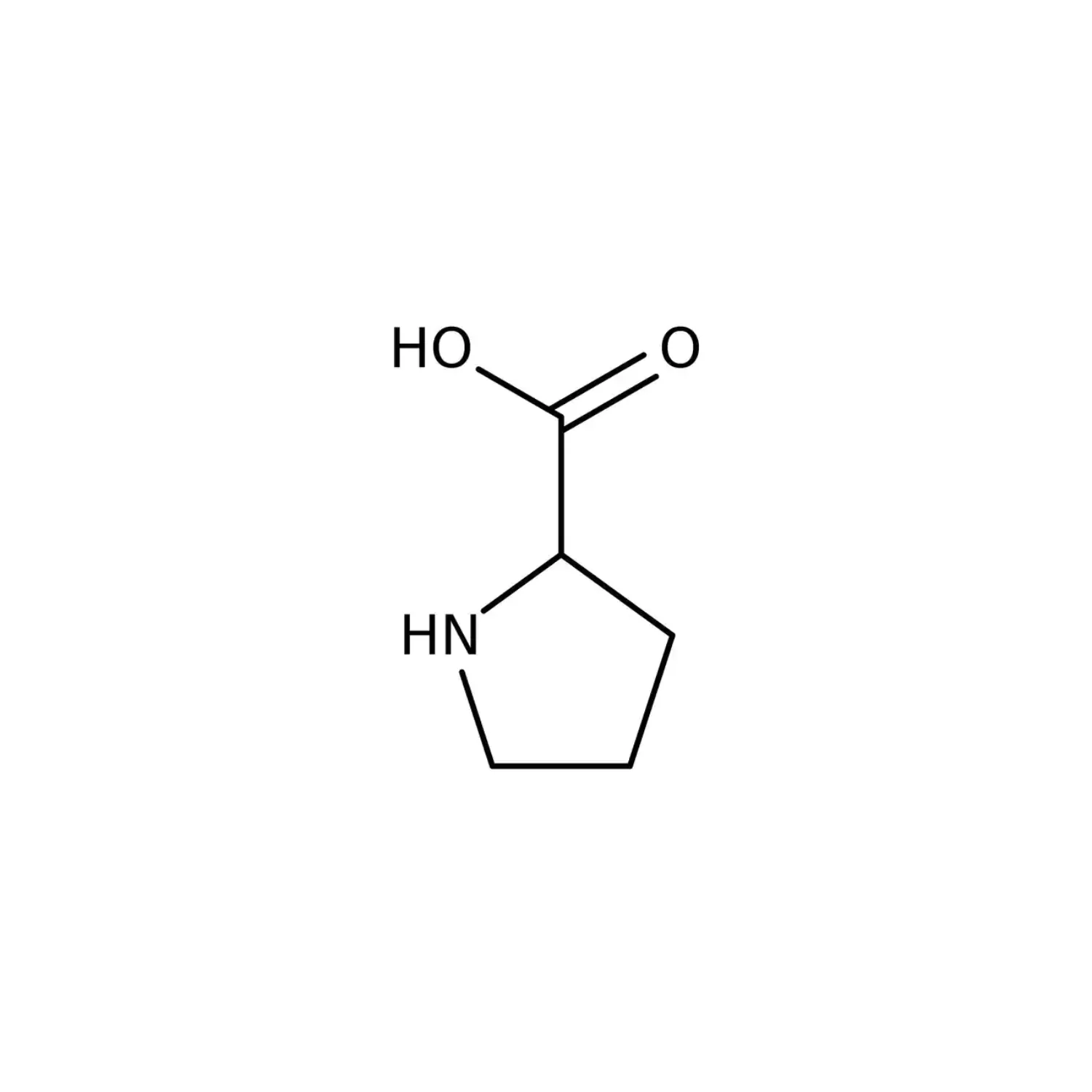
Proline
Forms a ring with the amino acid N; least flexible amino acid in protein; non-polar, cyclic, aliphatic.
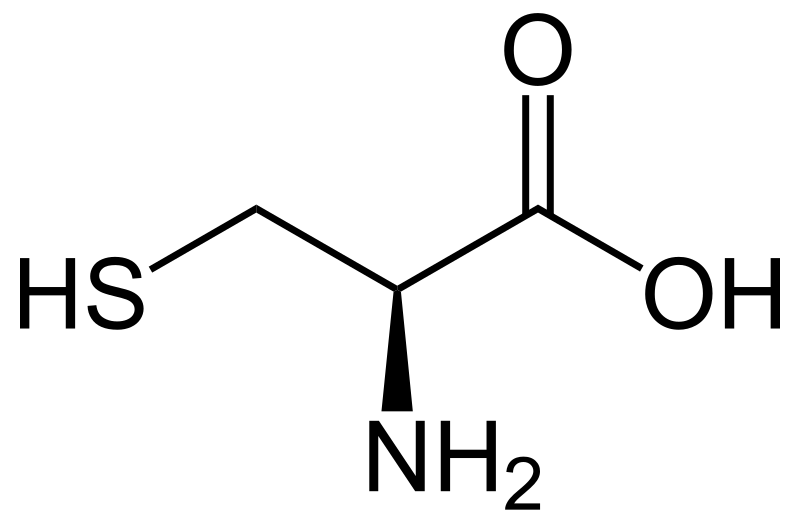
Cysteine
S-H bond (thiol group) has polarity; pKa ~8 for thiol H; S often makes disulfide bonds with other C side chains; polar, uncharged.
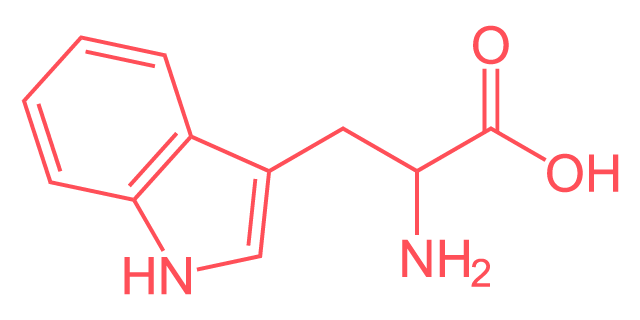
Tryptophan
Largest amino acid; mostly non-polar; fused rings are aromatic; non-polar and aromatic.
Phenylalanine
Has an aromatic ring group on the side chain; non-polar and aromatic.
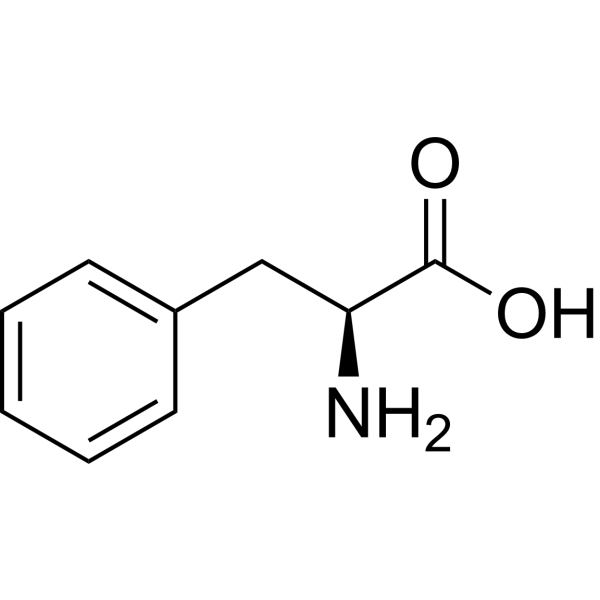
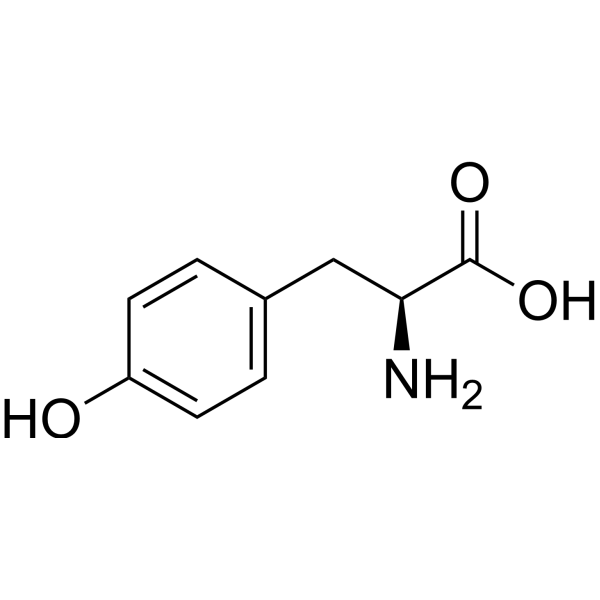
Tyrosine
Aromatic group is non-polar & can make hydrophobic interactions; hydroxyl group H can make H-bonding interactions; H on the hydroxyl has a pKa of 10.1 & can be deprotonated; side chain is a phenol group; aromatic and polar, uncharged.
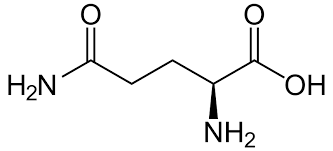
Glutamine
Amide group allows for H attached to N and carbonyl Oxy to make H-bonding interactions; more concentrated in blood and is considered a N carrier; polar, uncharged.
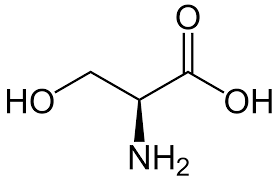
Serine
Side chain has an alcohol functional group; can be phosphorylated converting hydroxyl to a phosphate group (and a negative 2 charge at neutral pH); polar, uncharged.
Threonine
Side chain has an alcohol group, more than one chiral C and can be phosphorylated converting hydroxyl to a phosphate group (and a negative 2 charge at neutral pH); polar, uncharged.

Lysine
Side chain pKa is 10.5; If the N at the end of the side chain becomes acetylated, this amino acid becomes polar and uncharged; polar, charged, basic (positively charged).
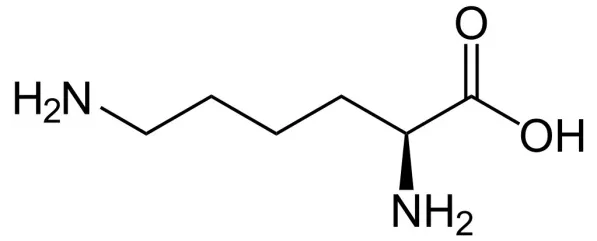
Asparagine
Amide group allows for H attached to N and carbonyl Oxy to make H-bonding interactions; one C shorter than Q; polar, uncharged.
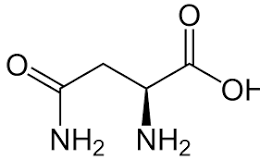
Arginine
Has a guanidine functional group and the side chain pKa is 12.5; Polar, charged, basic (positively charged).
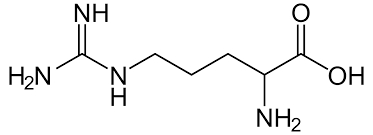
Glutamate (glutamic acid)
Has a carboxylic acid or carboxylate functional group & the side chain pKa is 4.3; Polar, charged, acidic (negatively charged).
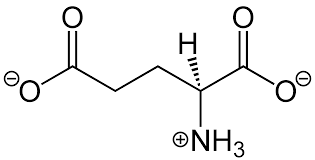
Aspartate (aspartic acid)
Has a carboxylic acid or carboxylate functional group; one C shorter than E & the side chain pKa is 3.7; Polar, charged, acidic (negatively charged).
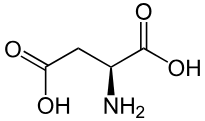
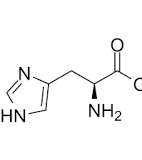
Histidine
Side chain pKa is 6; Only one N in the side chain is protonated; side chain group is called an imidazole ring; Polar, aromatic, charged, basic (positively charged).