OB Lecture Exam 2 & Terminology
1/129
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ch. 5 (violence against women), ch. 13 (A&P of pregnancy), ch. 14 (nursing care of the family during pregnancy), ch. 15 (maternal nutrition), ch. 26 (assessment of HR pregnancy), ch. 27 (hypertensive disorders), ch. 28 (hemorrhagic disorders), ch. 29 (endocrine & metabolic disorders)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
ch. 13 (uterus during pregnancy) - alters size, shape, and position; Hegar sign indicates softening of the lower uterine segment by 6 weeks
uterine growth
ch. 13 - increased blood flow & contractility lead to Braxton Hicks contractions; fetal-related changes include ballottement & __________
quickening (first movements perceived by the pregnant woman)
ch. 13 (cervix during pregnancy) - the cervix remains firm and closed; __________ develops from increased vascularization
Goodell sign (softening of the cervix during early pregnancy)
ch. 13 (ovaries during pregnancy) - ovarian ovulation ceases; __________ produces hormones that support amenorrhea in early pregnancy
corpus luteum
ch. 13 (vagina during pregnancy) - __________ appears; hormonal changes increase leukorrhea and lower vaginal pH
Chadwick sign (blue discoloration of vaginal and pelvic mucosa)
ch. 13 (vulva during pregnancy) - __________ pelvic blood flow and uterine pressure cause vulvar edema and varicosities
increased
ch. 13 - __________ from plasma volume increase leads to physiologic anemia; Hgb <11 g/dL or <10.5 g/dL is diagnostic
hemodilution
ch. 13 - pregnancy increases O₂ consumption and thoracic expansion, while respiratory rate stays unchanged
structural and pulmonary changes
ch. 13 - include nausea (from hCG), reflux, constipation, pica, gum bleeding, increased salivation, slower digestion, and higher gallstone risk
pregnancy GI effects
ch. 13 - pregnancy increases kidney size, GFR, and urine flow time; bladder irritation and urine glucose/protein spillage may occur
renal adaptation and function
ch. 13 - pregnancy skin changes include hyperpigmentation (chloasma, linea nigra), stretch marks, and abdominal itching
skin changes
ch. 13 - pregnancy affects the musculoskeletal system with lordosis, joint laxity, widened symphysis pubis, waddling gait, leg cramps, and fall risk
effects of pregnancy on musculoskeletal
ch. 13 - pregnancy may cause headaches, carpal tunnel, corneal changes, and increased thyroid, prolactin, and insulin levels
neurologic and endocrine systems
ch. 13 - stimulates enlargement of breasts and uterus; relaxes pelvic ligament and joints
estrogen
ch. 13 - suppresses FSH & LH; facilitates implantation and decreases uterine contractility
progesterone
ch. 13 - stimulates corpus to secrete estrogen and progesterone until placenta is mature enough to do so
human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
ch. 13 - stimulates fetal growth by regulating available glucose and stimulates breast development
human placental lactogen (hPL)
ch. 13 - water-soluble protein secreted by corpus luteum; causes relaxations of symphysis; softens ligaments and cervix
relaxin
ch. 13 - secreted by anterior pituitary; prepares for lactation
prolactin
ch. 13 - produced by posterior pituitary; stimulates uterine contractions
oxytocin
ch. 13 - subjective signs (e.g., nausea, fatigue, missed period) felt by the woman
presumptive pregnancy
ch. 13 - objective signs (e.g., positive pregnancy test, uterine changes) observed by the examiner
probable pregnancy
ch. 13 - definitive signs (e.g., fetal heartbeat, ultrasound, fetal movement felt by provider)
positive pregnancy
ch. 14 - is calculated from the first day of the last menstrual period using Nägele’s Rule—subtract 3 months, add 7 days, and adjust the year
estimated date of birth (EDB)
ch. 14 - was is the EDB when the patient says the first day of her last menstrual period was december 21, 2024?
september 28, 2025
ch. 14 - what is the gravida & parity of a woman who had 3 pregnancies and normal deliveries, but the third was a twin birth?
G3; P3
ch. 14 - what does GTPAL stand for?
G - gravida
T - term
P - preterm
A - abortion
L - living
ch. 14 - J. D. is 8 weeks pregnant and is at her first prenatal visit. she has two children aged 9 delivered at 38 weeks and 4 delivered at 36 weeks. what is the GTPAL?
G - 3
T - 1
P - 1
A - 0
L - 2
ch. 14 - every 4 weeks until 28 weeks, every 2 weeks until 36 weeks, then weekly until birth
prenatal visits
ch. 14 - includes interview, full health and OB history, physical exam, lab tests, and education on pregnancy care, and nutrition
initial PNC visit
ch. 14 - include interview, vital signs, weight, urinalysis, physical exam, fundal height, fetal assessment, and ongoing teaching
PNC follow-up visits
ch. 14 - assessment includes asking direct questions, gaining the client’s trust, and interviewing the client away from their partner
intimate partner violence (IPV)
ch. 14 - follow ABCDES (alone, belief, confidentiality, documentation, education, safety) interventions
intimate partner violence (IPV)
ch. 14 - include CBC, blood type and Rh with antibody screen, urinalysis with culture, rubella titer, and STI panel (syphilis, HIV, hep B)
labs at PNC initial visit
ch. 14 - repeat CBC, syphilis, HIV, and hep B labs; screen for gestational diabetes, chromosomal abnormalities, and NTDs
28 week visit labs
ch. 14 - test for group B streptococcus and administer recommended immunizations including Tdap, hep B, and influenza
35-37 week visit labs & immunizations
ch. 14 - key topics such as nutrition, prenatal vitamins, and personal hygiene
self-management during pregnancy
ch. 14 - high-mercury fish (shark, swordfish, king mackerel), raw/smoked seafood, and unpasteurized dairy (soft cheeses)
foods to avoid during pregnancy
table 14.3 - what are the most common breast changes during pregnancy?
breasts feel heavy and full and areola darkening
table 14.3 - what are the most common skin discomforts during pregnancy?
pigmentation changes, acne, oily skin, spider nevi, and pruritus
table 14.3 - what are the most common musculoskeletal discomforts during pregnancy?
round ligament pain, joint pain, backache, pelvic pressure, and leg cramps
table 14.3 - what are the most common GI discomforts during pregnancy?
nausea and vomiting, ptyalism, gingivitis and gum bleeding, heartburn, constipation, and flatulence with bloating and belching
ch. 14 - is generally safe unless contraindicated; desire may fluctuate, positions may need adjusting, and open communication is key
intimacy during pregnancy
table 14.4 - what are five signs of potential complications in the first trimester of pregnancy?
severe vomiting, fever and chills, burning with urination, abdominal cramping, and vaginal bleeding
table 14.4 - what are five signs of potential complications in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy?
sudden fluid discharge from the vagina before 37 weeks, decreased fetal movement, severe backache, visual disturbances, and swelling of the face and fingers
ch. 14 - uterus becomes an abdominal organ; by 16 weeks, fundus is midway between symphysis pubis and umbilicus
13-16 weeks
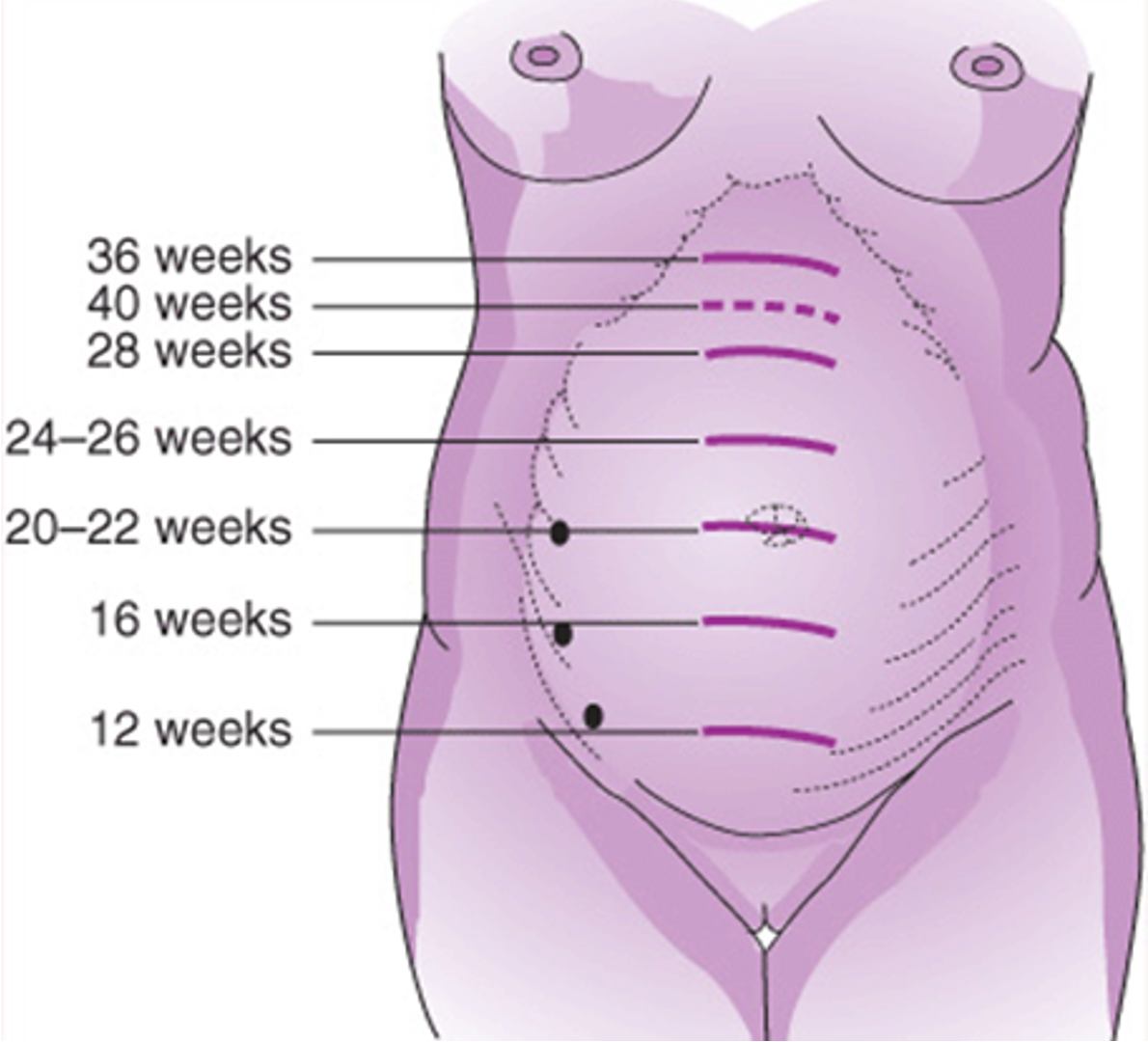
ch. 14 - fundus reaches the umbilicus
20-22 weeks
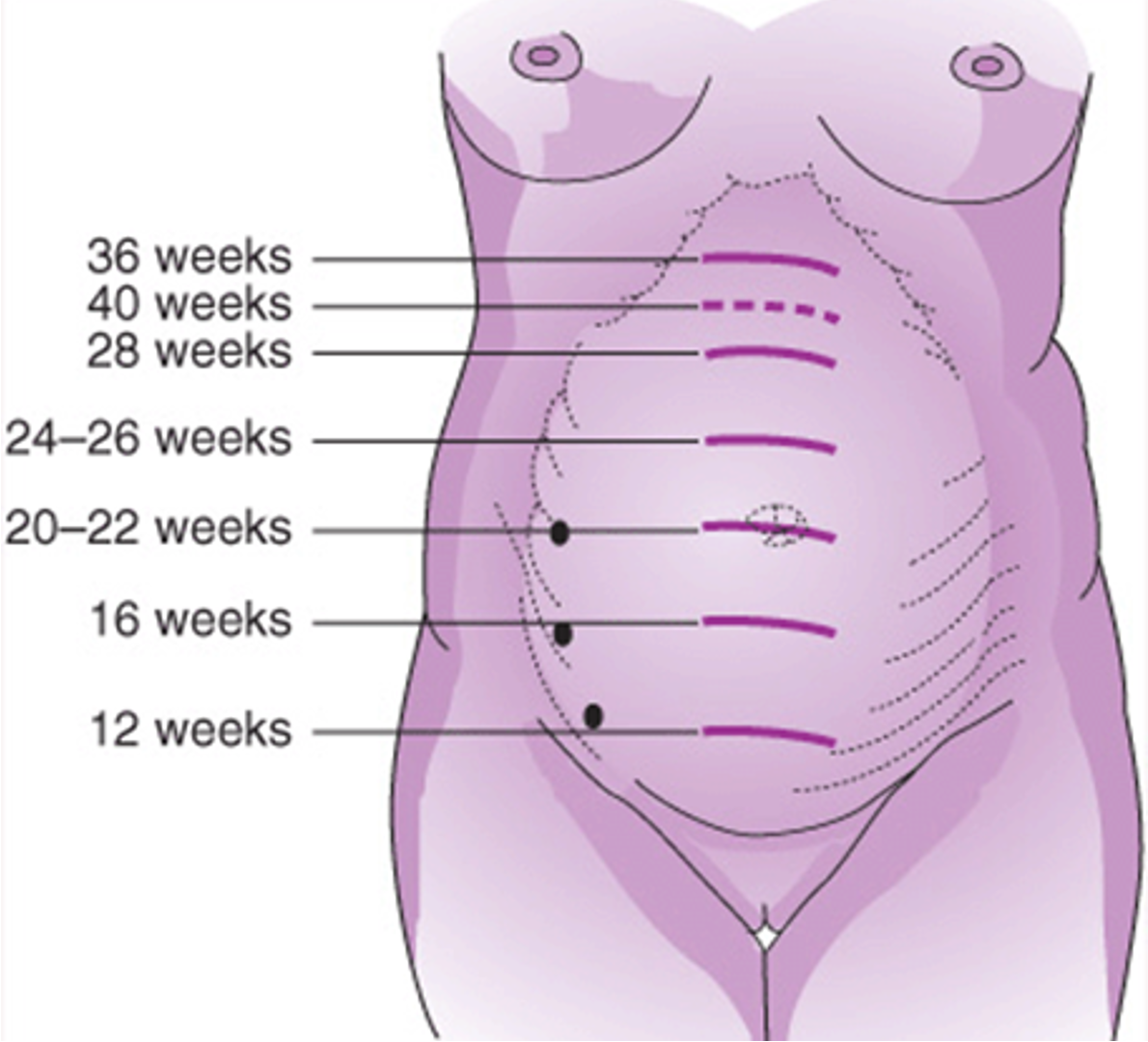
ch. 14 - fundus rises from midway between umbilicus and xiphoid (26–28 weeks) to xiphoid process (36 weeks)
26-36 weeks
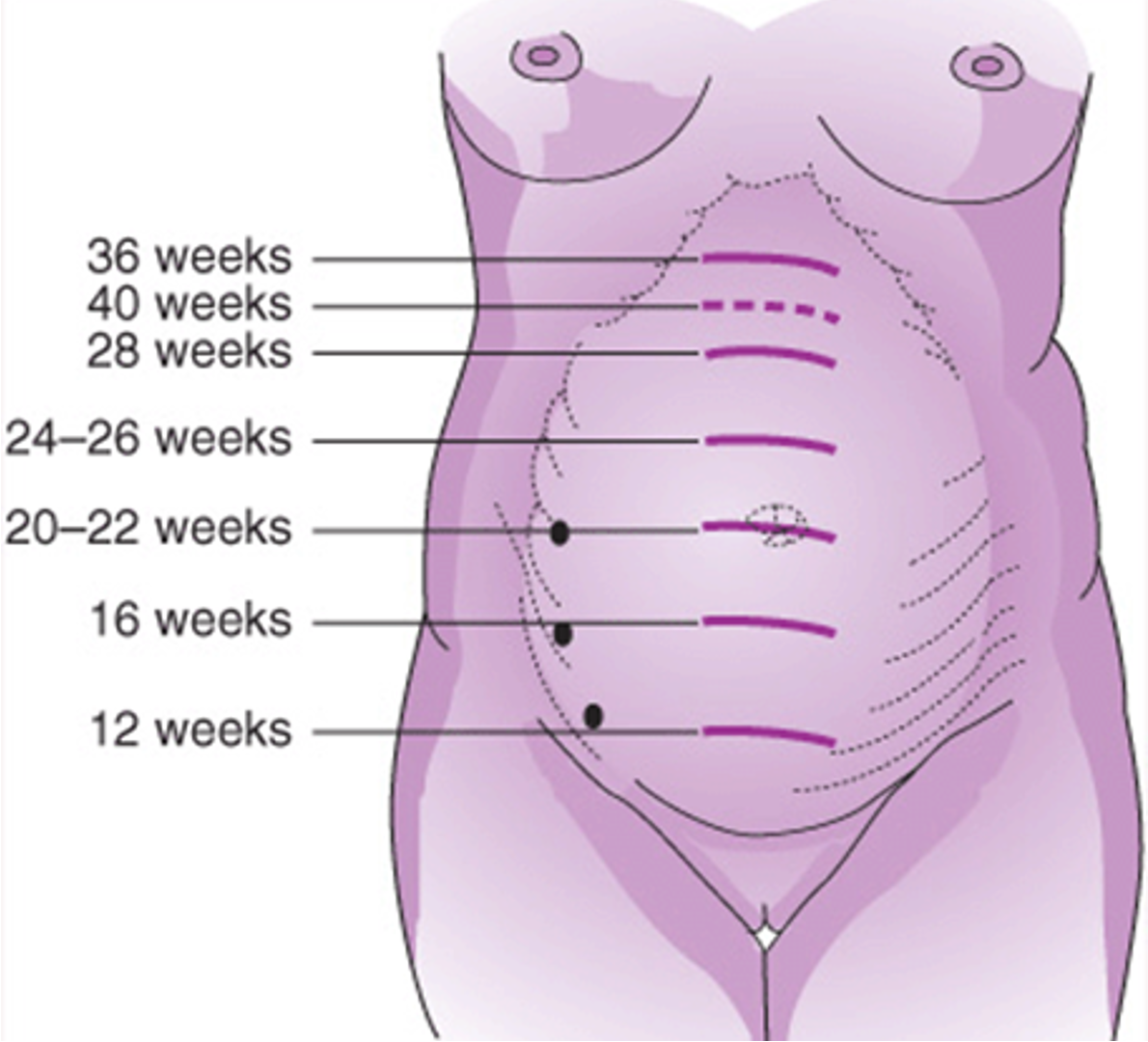
ch. 14 - fundal height ≈ gestational age in cm (±2 cm); 38–40 weeks: fundus may drop (lightening)
28-32 weeks
ch. 15 - based on prepregnancy BMI—25–35 lbs for normal weight, 28–40 lbs underweight, 15–25 lbs overweight, and 11–20 lbs obese
recommended gain
ch. 15 - 2–4 lbs in the first trimester, then ~1 lb/week; excessive gain may signal fluid retention or preeclampsia
weight gain pattern
ch. 15 - inadequate or excessive gain increases risk of preterm birth, small for gestational age, or complications like gestational diabetes and HTN
risks of poor gain
ch. 15 - focus on nutrient-dense foods, avoid empty calories, stay active, and do not diet—weight quality matters more than quantity
healthy habits
table 15.3 - calcium needs during pregnancy and lactation are 1000–1300 mg daily. what are sources of calcium?
milk, cheese, yogurt, sardines, and dark leafy greens
ch. 15 - may need supplements for calcium, iron, B12, and vitamin D
vegan pregnancies
ch. 15 - raw fish, unpasteurized dairy, and deli meats unless reheated to prevent foodborne illness
avoid
ch. 15 - good hygiene, wash produce, and cook foods thoroughly
practice
quiz 2 prep - as the clinic nurse, what instructions would you give to a group of pregnant women in preventing constipation? select all that apply.
a) perform regular exercises such as walking
b) take stool softeners as needed
c) increase green leafy veggies
d) consume 8-10 glasses of water daily
e) have 20 mL olive oil once a week
a. perform regular exercises such as walking
c. increase green leafy veggies
d. consume 8-10 glasses of water daily
rationale: pregnant women should prevent constipation by exercising regularly, eating high-fiber foods like leafy greens, and drinking plenty of water. stool softeners are not routinely recommended without a provider’s order. olive oil is not a standard or evidence-based remedy for constipation in pregnancy.
quiz 2 prep - a pregnant client visits the clinic for her first prenatal visit. her obstetric history includes 2 live births at term, 1 stillborn at term, and 1 miscarriage at 6 weeks. what is her GTPAL?
a) G4T3P1A1L2
b) G5T3P0A1L2
c) G5T3P1A1L3
d) G4T3P0A1L2
b) G5T3P0A1L2
rationale:
G (gravida) = 5 → 2 live + 1 stillborn + 1 miscarriage + 1 current
T (term) = 3 → all 3 babies were full-term
P (preterm) = 0 → no babies born between 20–36 weeks
A (abortion) = 1 → 1 miscarriage before 20 weeks
L (living) = 2 → only the 2 live births are living
quiz 2 prep - hormone produced by the placenta that relaxes smooth muscles during pregnancy
progesterone
gravida (G)
how many times a woman has been pregnant
nulligravida
a woman who has never been pregnant
primigravida
a woman who is pregnant for the first time
multigravida
a woman who has been pregnant more than once
parity (P)
how many pregnancies lasted 20 weeks or more
nullipara
a woman who has never carried a pregnancy to 20 weeks
primipara
a woman who has give birth once at 20 weeks or more
multipara
a woman who has give birth two or more times at 20 weeks or more
gestation
the time a baby grows in the womb—from conception to birth
antepartum
the time during pregnancy before labor begins
intrapartum
the period during labor and delivery
postpartum
the time after birth, usually the first 6 weeks
preterm
birth that occurs before 37 weeks of gestation
term
pregnancy between 37 and 42 weeks
post term
birth at or beyond 42 weeks
viability
ability of the fetus to survive outside the womb, usually at 24 weeks
stillbirth/stillborn
baby born without signs of life at or after 20 weeks
abortion/miscarriage
pregnancy loss before 20 weeks, either natural or induced
ch. 27 - SBP > 140 mm Hg or DBP > 90 mm Hg or both
HTN classification
ch. 27 - development of HTN after 20 weeks of pregnancy; woman was normotensive with no proteinuria
gestational HTN
ch. 27 - development of HTN and proteinuria after 20 weeks of pregnancy or in the early postpartum period
preeclampsia
ch. 27 - development of seizures or coma not attributable to other causes in a preeclamptic woman
eclampsia
ch. 27 - HTN in a pregnant woman present before pregnancy
chronic HTN
ch. 27 - chronic HTN in association with preeclampsia
superimposed preeclampsia
ch. 27 - starts with abnormal placental development, leading to poor perfusion and widespread endothelial dysfunction
preeclampsia
ch. 27 (preeclampsia) - causes vasospasm, increased BP, reduced organ perfusion, and plasma volume loss
placental ischemia
ch. 27 (preeclampsia) - kidney, liver, and brain are affected—resulting in proteinuria, __________, cerebral edema, and __________
elevated liver enzymes; seizures
ch. 27 (preeclampsia) - fluid shifts cause __________, edema, and serious complications like pulmonary edema or liver hemorrhage
hemoconcentration
ch. 27 - is identified by hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets, often without high BP or proteinuria
HELLP syndrome
ch. 27 - assess BP trends, proteinuria, reflexes, edema, and severe signs (headache, RUQ pain, vision changes)
preeclampsia
ch. 27 - includes stabilizing ABCs, giving magnesium, assessing fetus and uterus, and planning delivery
post-eclampsia care
table 27.2 in pptx - BP ≥ 140/90 after 20 weeks, with proteinuria ≥ 300 mg/24 hr or protein/creatinine > 0.3
preeclampsia diagnostic criteria
table 27.2 in pptx - may include mild thrombocytopenia, elevated liver enzymes, or renal changes (creatinine > 1.1 mg/dL)
preeclampsia
table 27.2 in pptx - BP ≥ 160/110, with new cerebral/visual changes, pulmonary edema, or RUQ pain
preeclampsia with severe features
table 27.2 in pptx - platelets < 100,000, liver enzymes ≥ 2× normal, or creatinine > 1.1 mg/dL
preeclampsia with severe features
box 27.3 - magnesium prevents seizures, not BP; explain route, side effects (flushing, sedation), and need for close monitoring
teaching care of the woman with preeclampsia receiving magnesium sulfate
box 27.3 - administer via pump; monitor vitals, DTRs, urine, FHR; report RR <12, urine <30 mL/hr, neuro changes, or abnormal labs
care of the woman with preeclampsia receiving magnesium sulfate
ch. 29 - increased insulin sensitivity lowers maternal blood glucose, raising hypoglycemia risk
metabolic changes associated with the first trimester of pregnancy
ch. 29 - placental hormones cause insulin resistance, increasing insulin needs up to 4x; needs drop after birth
metabolic changes associated with the second and third trimesters of pregnancy
ch. 29 - diabetes results from impaired insulin secretion or action, leading to hyperglycemia
DM cause