4.1 Fundamentals of Programming
1/42
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What two things are data types defined by?
The values they can take.
The operations that can be performed on them.
Is -44 an integer?
Yes. An integer is a whole number, positive or negative, including zero.
Which data type can only be true or false?
Boolean.
What is a user-defined data type?
A data type derived from existing data types in order to create a customised data structure.
What is meant by assignment?
Giving a constant or variable a value.
What is meant by iteration?
Repeating an instruction.
What is meant by a subroutine?
A named block of code containing a set of instructions designed to perfom a frequently used operation.
In which type of iteration is the number of repetitions required not known before the loop starts?
Indefinite iteration.
What visible feature of program code signifies nesting?
Identation.
Using integer division, what is 14 DIV 3?
4
Using the modulo operation, what is 30 MOD 4?
2
What is 1 XOR 1?
0
Name two advantages of using constants over hard-coded values.
Constants can be given identifier names, making code easier for a human to understand.
When updating a value, constants only need updating at one position in code.
What is meant by concatenation?
Joining two or more strings together to form a new, longer string.
What is a seed value used for?
Generating random numbers.
What name is given to the code which is run to handle an exception?
Catch block.
What name is given to a type of subroutine which always returns a value?
Function.
What are parameters used for?
Passing data between subroutines in programs.
What name is given to the actual value passed by a parameter?
Argument.
What type of variable can be accessed from any part of a program?
Global.
Name three items stored in a stack frame.
Return addresses
Parameters
Local variables
What is meant by a recursive subroutine?
A subroutine which is defined in terms of itself.
What is meant by a base case?
The terminating situation in recursion that does not use recursion to produce a result.
What error will occur if a recursive subroutine never meets its base case?
Stack overflow.
What scope is a variable that can be accessed from all parts of a program said to have?
Global.
List the four types of basic structure used in the structured approach to program design and construction.
Assignment
Sequence
Selection
Iteration
What do rectangles represent in hierarchy charts?
Procedures
How is data stored in procedural programs?
By constants and variables.
What name is given to containers for data and instructions in object-oriented programming?
Objects.
In object-oriented programming, what specifies the properties and methods that objects have?
Classes.
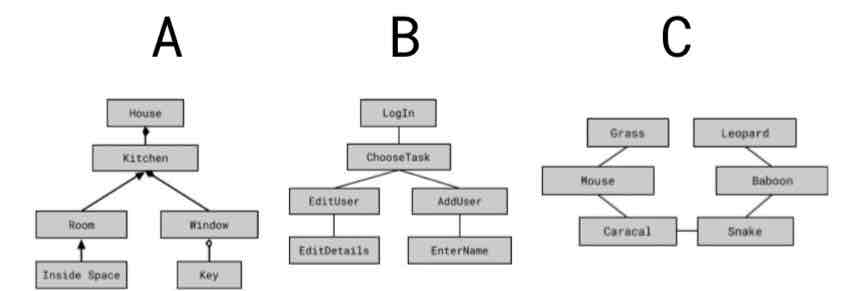
Which of the following is an example of a hierarchy chart?
B.
In OOP, what name is given to the process of combining methods and procedures in an object?
Encapsulation.
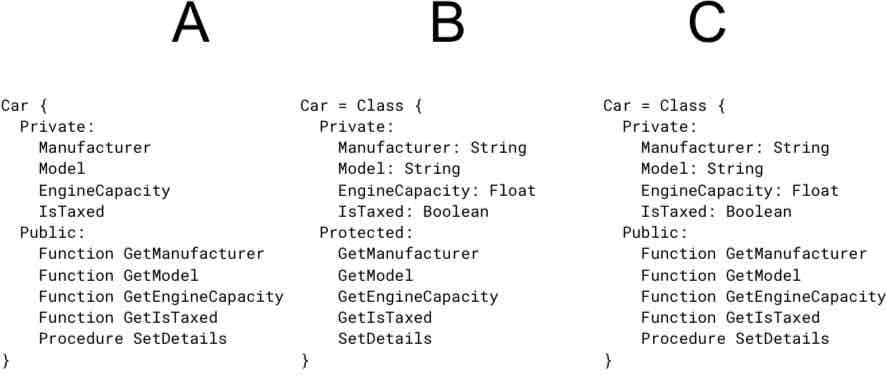
Which class definition is correct?
C.
In OOP, what is said to occur when objects are processed differently depending on their class?
Polymorphism.

Which class definition shows inheritance?
C.
In OOP, what type of method has the same name as a method in an inherited class but different implementation?
An overridden method.
Name the stronger of the two kinds of association.
Composition.
In OOP, what is the purpose of inheritance?
Inheritance allows one class to share the properties and methods of another class.
What type of association exists between a class and a student: aggregation or composition?
Aggregation. If the class is destroyed, the student still exists.
In class diagrams which feature properties and methods, what symbol represents a private property?
A minus sign (-).
Name three object-oriented design principles.
Encapsulate what varies.
Favour composition over inheritance.
Program to interfaces, not implementation.
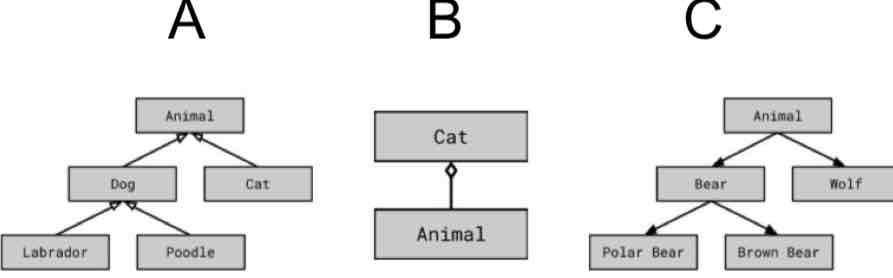
What is an inheritance diagram?
A.
In class diagrams which type of line represents aggregation?
A line with a hollow diamond cap.