AP BIO Unit 4:Cell membrane
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
Surface area
total amount of area of the outer surface
2
New cards
volume
total amount of space a object occupies
3
New cards
Surface area: Volume
determines surface area relativeness to volume ( less surface area relative to volume= decrease rate of diffusion)
4
New cards
Diffusion
net movement of molecules moving from high to low concentration, stops when both regions have equal concentration (random motion still continues), as distance increases rate of diffusion decreases.
5
New cards
solutes
dissolved substances
6
New cards
solvents
water
7
New cards
molarity
concentration of a solute in a solution (mol/L)
8
New cards
permeable
membrane allows water or solutes to diffuse freely
9
New cards
impermeable
membrane blocks diffusion entirely
10
New cards
Relationship between water and solute concentration
solute concentration increases the water concentration decreases.
11
New cards
osmosis
movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane in response to a difference in solute concentration
12
New cards
osmotic pressure
tendency of water to move from one solution to another through osmosis ( higher the solution concentration, higher osmotic pressure)
13
New cards
hydrostatic pressure
pressure that gravity exerts on the solution (=osmotic pressure)
14
New cards
toncity
strength of water pulled from one solution to another
15
New cards
hypertonic
higher solute concentration
16
New cards
hypotonic
lower solute concentration
17
New cards
isotonic
equal solute concentration
18
New cards
Contracticle vacuoles
organelles that take up excess water from inside the cell then expel it outside
19
New cards
water potential
measure of all factors that influence the movement of water
20
New cards
water potential formula
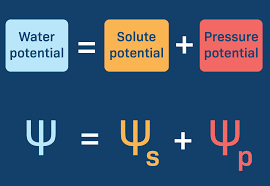
21
New cards
pressure potential
effect pressure on movement of water
22
New cards
solute potential
effect solutes of a solution on movement of water
23
New cards
formula of solute potential

24
New cards
Which molecules CANNOT cross the membrane on their own?
polar, charged, and large molecules
25
New cards
Which molecules CAN cross the membrane on their own?
nonpolar, uncharged, and small molecules
26
New cards
Contentration gradient
the way molecules are distributed (high/low concentration)
27
New cards
Passive transport
molecules move across the membrane through diffusion
28
New cards
Simple diffusion
molecules directly diffuse through the cell membrane
29
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
diffusion across a membrane through a transport protein
30
New cards
channel protein
provides an opening between the inside and outside of the cell, gated ( open by signal), allows molecules in based on shape and charge
31
New cards
Carrier protein
binds and transports specific molecules in the membrane, on both sides, changes shape based on molecule for transport
32
New cards
aquaporin
channels that allow water to enter/exit the cell through facilitated diffusion
33
New cards
phospholipids
found in cell membrane, most are made up of glycerical backbone attached to a phosphate group and two fatty acids, amiphatic
34
New cards
micelle
sphereical structure packed with bulky head and a single fatty acid tail
35
New cards
lipid bilayer
structure formed of two layers of lipids, hydrophillic heads outside to interact with water while hydrophobic tails are sandwiched in between, isolated from contact with water.
36
New cards
Liposomes
formed when phospholipids are at a neutral ph , cell like (inner and outer space) , outer = polar (interacts with water) protects inner, self-healing
37
New cards
Cell membranes are
dynamic (allows them to perform functions) and fluid ( longer fatty acid tail = less fluid)
38
New cards
Relationship between carbon bonds and cell membrane stability
More carbon bonds = more stability
39
New cards
Cholesterol
major component of animal cell membrane (30%), amiphatic , can insert into lipid bilayer, maintains homeostasis
40
New cards
Relationship between temperature and membrane fluidity
higher temperature=higher fluidity (fluid is not always uniform)
41
New cards
Lipid rafts
specific types of lipids assembled into defined patches
42
New cards
Lipid flip-flop
spontaneous transfer of a lipid between layers of a bilayer, requires hydrophilic groups to pass hydrophobic interior, causes exchange of layer components (differences in layer composition)
43
New cards
proteins
are embedded into the cell membrane, used for many different functions (speed up chemical reactions , anchors, and maintains shape)
44
New cards
transport protein
moving ions or other molecules across the membrane
45
New cards
receptor protein
allows cell to receive signals from the environment
46
New cards
Integral membrane protein
permanently with the cell membrane, cannot be separated
47
New cards
peripheral membrane protein
temporarily binds with lipid bilayer or with integral membrane proteins through weak noncovalent reactions
48
New cards
transmembrane protein
integral, span entire lipid bilayer, composed of 3 regions (2 hydrophilic[outer one is a receptor while the inner one posses the message inside] , 1 hydrophobic [holds protein to membrane]),