AP PSYCH UNIT 1.1 - 1.3
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Nature vs. Nurture
Debate about whether genetics (nature) or environment (nurture) plays a bigger role in shaping behavior and mental processes.
Correlation vs. Causation
Correlation: Two things happen together.
Causation: One thing makes the other happen.
Rule: Correlation does NOT mean causation!
Intelligence: Environment vs. Biology
Intelligence is shaped by both biology (genes) and the environment (life experiences).
Both nature and nurture influence how smart someone is.
Natural Selection
The idea that traits that help survival are more likely to be passed down to future generations.
Evolutionary Perspective
This perspective explains behavior through natural selection — traits that helped our ancestors survive and reproduce were passed down.
Example: Fear of danger (like snakes) helped early humans stay alive.
Case Study
A detailed, in-depth study of one person/group
Identical Twin Studies
Research comparing identical twins to see how many traits come from genes (nature) versus environment (nurture).
Correlational studies
Research that looks at how two things are related, but it can’t prove that one causes the other.
CNS (Central Nervous System)
Sympathetic N.S (Nervous System)
Parasympathetic N.S
Somatic N.S
Autonomic N.S
CNS (Central Nervous System): Made up of the brain and spinal cord; it processes information and controls behavior and body functions.
Sympathetic N.S: Part of the autonomic system that activates the body’s “fight-or-flight” response by increasing energy and alertness.
Parasympathetic N.S: Part of the autonomic system that calms the body, conserving energy and returning it to a “rest-and-digest” state.
Somatic N: Controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles and transmits sensory information to the central nervous system.
Autonomic N.S: Controls involuntary body functions like heartbeat, breathing, and digestion; includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
Oxytocin
Melatonin
Oxytocin: A hormone linked to bonding, trust, and social connection; often called the “love hormone.”
Melatonin: a hormone that regulates sleep and wake cycles; higher levels make you feel sleepy.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
A disease in which the immune system attacks the myelin sheath of neurons, disrupting communication between the brain and body and causing symptoms like muscle weakness and coordination problems.
Mode
The value that appears most frequently in a set of data.

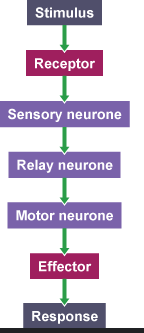
Reflex Arc → Chain
The simple path a signal takes to create an automatic response.
Resting State
When a neuron is not firing, the inside of the neuron is negatively charged (-) and the outside is positively charged (+).
Acetylcholine (ACh)
A neurotransmitter that enables muscle movement, learning, and memory.
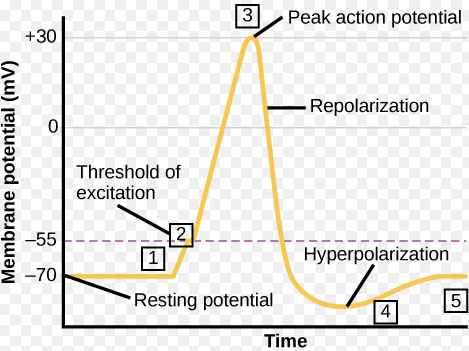
Stages of Neural Firing
1.) Resting State: Neuron is inactive; inside negative, outside positive.
2.) Depolarization: Sodium enters, making the inside more positive.
3.) Action Potential: Neuron fires; electrical impulse travels down the axon.
4.) Repolarization: Potassium leaves, restoring negative inside.
5.) Return to Resting State: Ion balance restored; neuron ready to fire again.
Major Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine (ACh): Muscle movement, learning, memory (excitatory)
Dopamine: Reward, motivation, movement (excite or inhibit)
Serotonin: Mood, sleep, appetite (mostly inhibitory)
Norepinephrine: Alertness, arousal, stress response (excitatory)
GABA: Major inhibitory neurotransmitter; calms nervous activity
Glutamate: Major excitatory neurotransmitter; memory and learning
Endorphins: Pain relief, pleasure (inhibitory/excitatory)
Oxytocin: Bonding, trust, social connectio
Reuptake Inhibitors
Drugs that block the reabsorption of neurotransmitters, leaving more available in the synapse to increase signaling.
Experiment
A research method where variables are manipulated to determine cause-and-effect relationships.
MRI of a Rat’s Brain after a Stimulant?
You would see increased brain activity in certain areas, shown as brighter regions on the scan, because stimulants excite neurons and boost signaling.
Endorphins
Neurotransmitters that relieve pain and boost pleasure; the body’s natural “feel-good” chemicals.
Double-Blind Design
A research method where neither the participants nor the experimenters know who is in the control or experimental group, reducing bias.
Placebo
An inactive substance or treatment given to a control group to test the effect of expectations in an experiment.
Reuptake
The process where neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the sending neuron after transmitting a signal, taking place at the synapse.
Antidepressants block what?
The reuptake of neurotransmitters.
Depolarization happens where?
In the axon of a neuron, when sodium enters and the inside becomes more positive.
Major depressive disorder is linked to which neurotransmitter?
Serotonin (low levels are associated with depression).
Action Potential
A brief electrical charge that travels down the axon, allowing the neuron to send a signal.
All-or-None Response
A neuron either fires completely or not at all; there is no partial action potential.
What is the master gland?
The pituitary gland; it controls other endocrine glands and regulates growth and hormones.
Seizures → ?
Abnormal electrical activity in the brain, which can cause convulsions or loss of consciousness.
Agonist
A chemical that mimics or increases the effect of a neurotransmitter.
Myelin Sheath
A fatty layer around the axon that speeds up neural impulses and protects the neuron.
Which drugs stimulate?
Caffeine, cocaine, meth, ecstasy — they increase neural activity, energy, and alertness.
Indicator of addiction?
Craving, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms show that the body or brain is dependent on a substance.
Near-Death Experience
A personal experience reported by someone close to death, often including out-of-body sensations, bright lights, or feelings of peace.
Synapse function
The gap between neurons where neurotransmitters are released to send messages to the next neuron.
Psychoactive Drugs
Chemicals that alter perception, mood, or behavior by affecting the brain’s neurotransmitters.
Adrenal Glands
Glands above the kidneys that release hormones like adrenaline and cortisol to help the body respond to stress
Barbiturates
Depressant drugs that slow down the central nervous system, reducing anxiety and inducing sleep.
Methamphetamine (Meth)
A powerful stimulant that increases neural activity, energy, and euphoria but is highly addictive.
Generalization
The tendency to respond similarly to stimuli that are alike or resemble the original conditioned stimulus.
LSD
A hallucinogen that alters perception, thoughts, and feelings, often causing vivid sensory experiences.
Motor neurons = ? Interneurons = ?
Motor neurons: Carry messages from the brain/spinal cord to muscles to produce movement.
Interneurons: Connects sensory and motor neurons within the brain and spinal cord.
Chemical messengers of the endocrine system?
Hormones
Epigenetics
The study of how environment and experience can change gene expression without altering DNA.
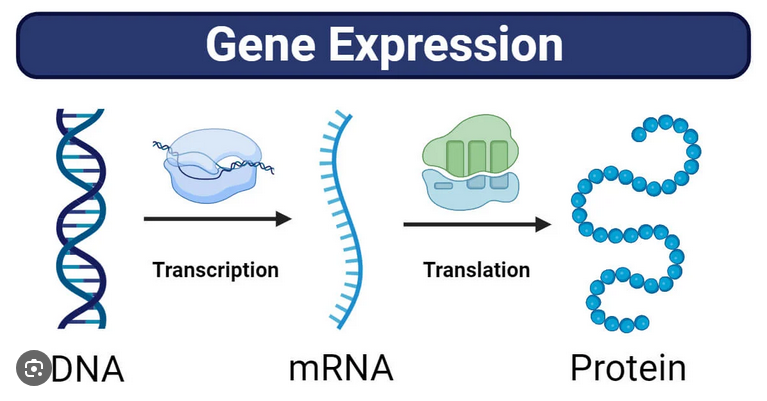
Genome
The complete set of an organism’s genes or genetic material.
Tolerance
When the body needs more of a drug to achieve the same effect due to repeated use.
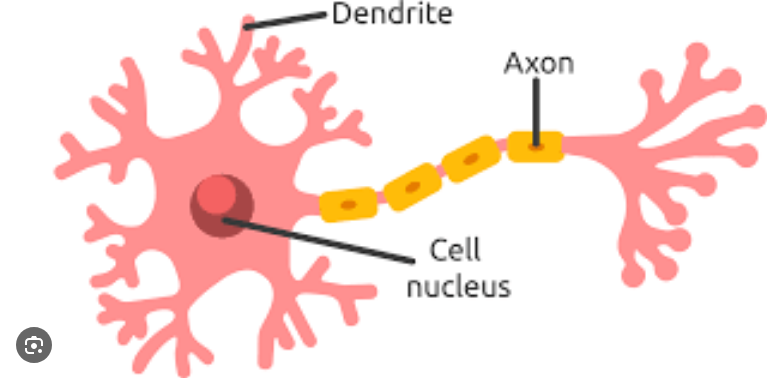
Dendrites
Branch-like structures of a neuron that receive messages from other neurons.
Migraines – why? Neurotransmitter?
Caused by changes in brain activity and blood flow; linked to low serotonin levels.
Heroin
A depressant and opioid that relieves pain and produces euphoria, but is highly addictive.
Antagonist
A chemical that blocks or reduces the effect of a neurotransmitter.
Amphetamines
Stimulant drugs that increase neural activity, energy, and alertness; can be addictive.
Function of glial cells?
Support and protect neurons, provide nutrients, and remove waste.
Cocaine – what does it do?
Stimulant that increases neural activity, alertness, and euphoria by blocking dopamine reuptake.
Ecstasy
A stimulant and hallucinogen that increases energy, pleasure, and emotional closeness by boosting serotonin and dopamine.
Threshold
The minimum level of stimulation needed for a neuron to fire an action potential.
Sensory Neuron
nerve cells that transmit sensory information from the body's periphery (skin, muscles, organs) to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
Strong vs. Weak Correlation Coefficients
Strong correlation: Close to +1 or -1 (variables closely related)
Weak correlation: Close to 0 (variables barely related
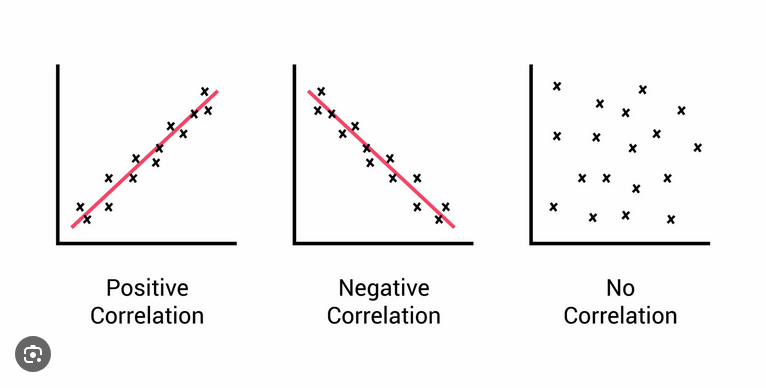
Inferential Statistics
Methods used to draw conclusions or make predictions about a population based on sample data.
Random Assignment
A procedure that assigns participants to experimental or control groups by chance to reduce bias.
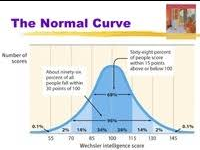
Normal Curve
A bell-shaped curve representing the distribution of data; most scores cluster around the mean, with fewer at the extremes.
Example of data: Height, IQ, or test scores.
Independent Variable
The variable that is manipulated or changed by the experimenter to see its effect.