APUSH Unit 1 Key Terms
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms

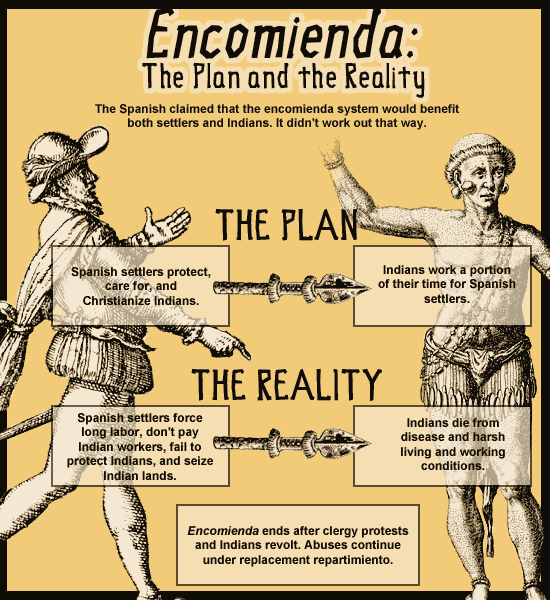
Encomienda System
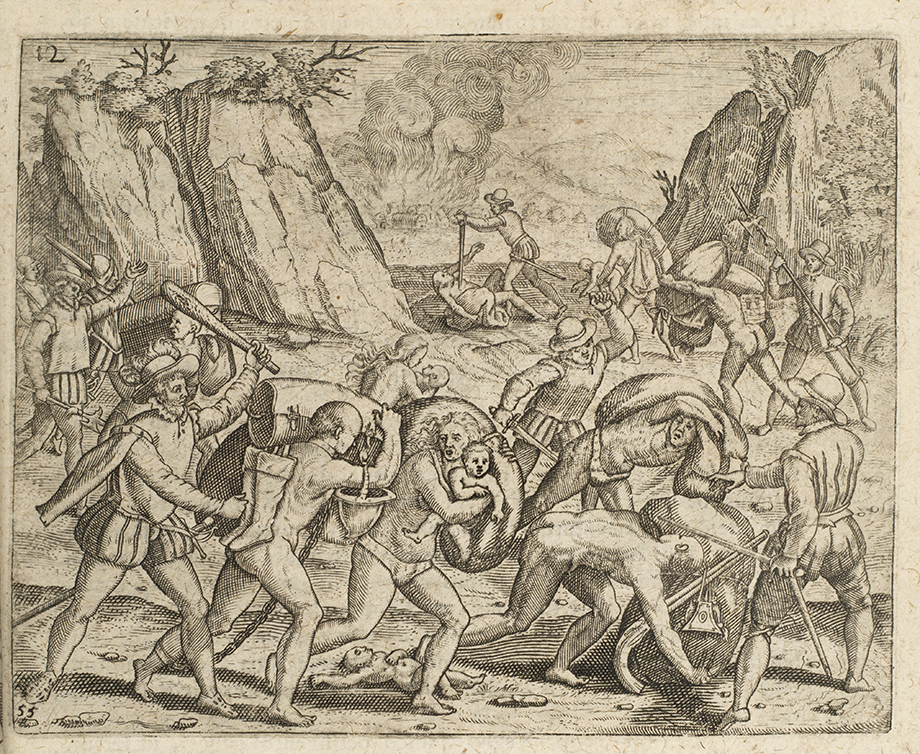
Was a labor system instituted by the Spanish Crown in the American colonies. In this system a Spanish encomendero was granted a number of native laborers who would pay tributes to him in exchange for his protection.

Asiento System
A key trade agreement established in the 18th century between Spain and private companies to import enslaved Africans to the Spanish colonies in the Americas for labor.
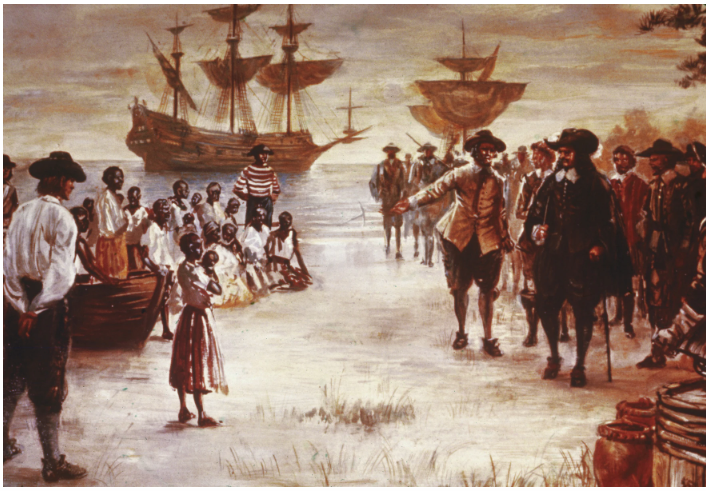


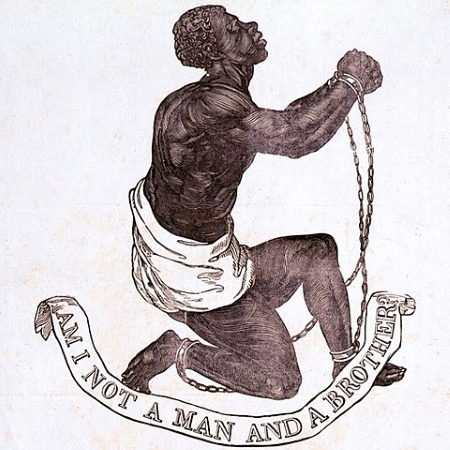
Slavery
A System where one person is owned by another. Treated as property, and deprived of most rights and freedoms.


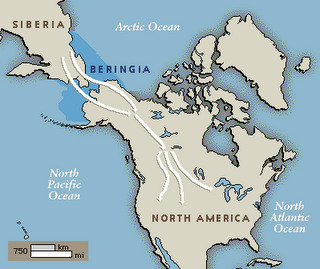
Land Bridge
A natural formed land connection between two large land masses, often appearing during periods of lower sea levels.
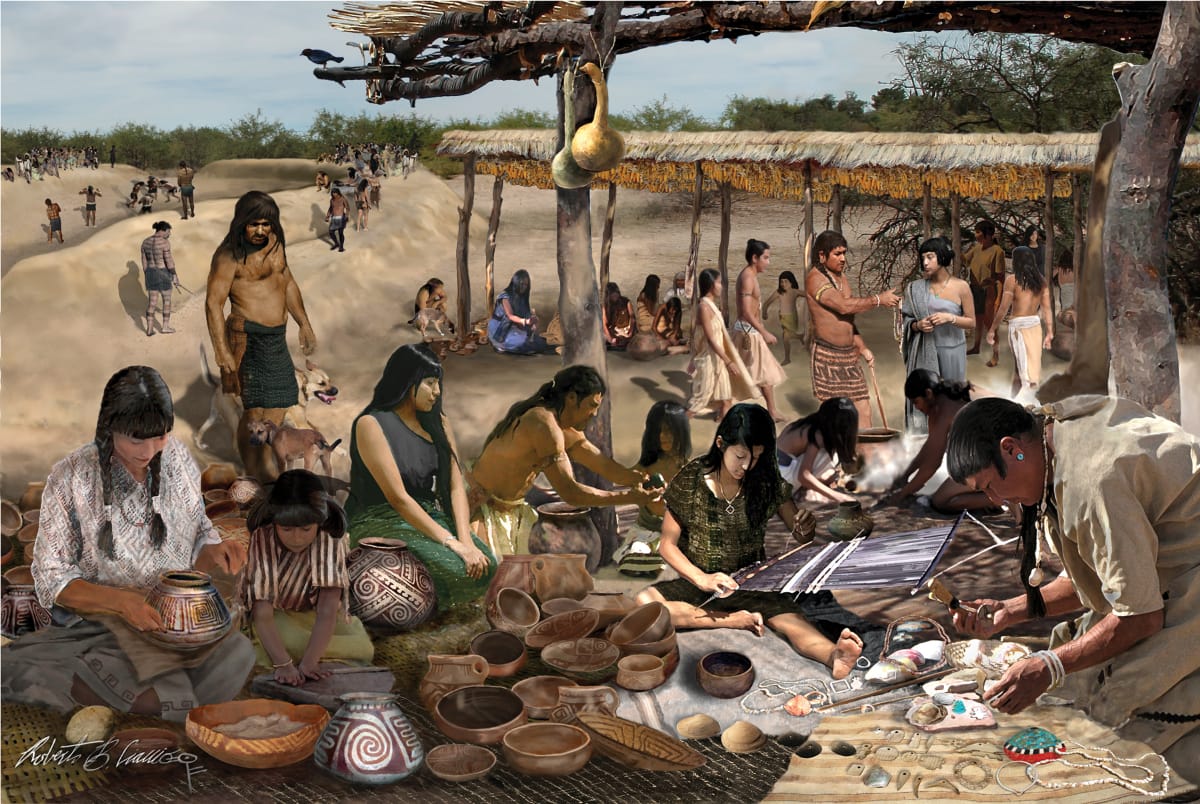

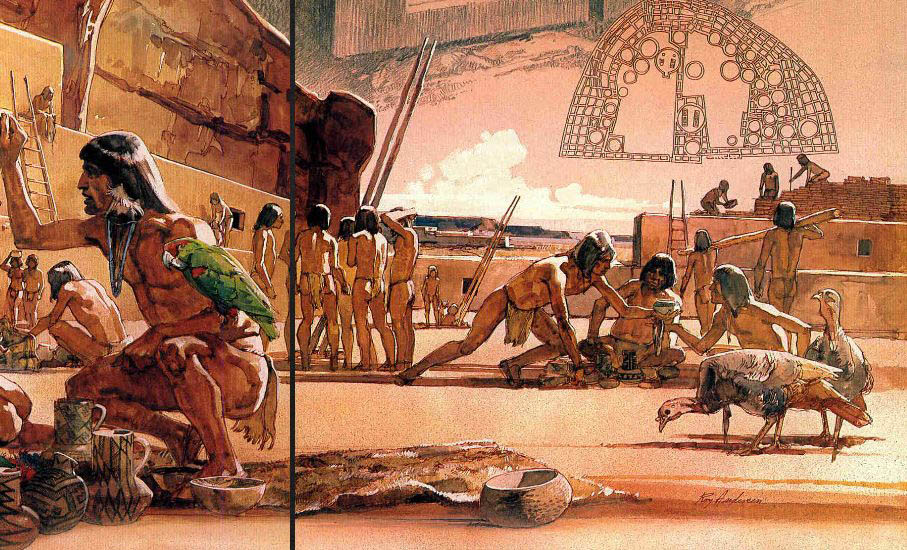
Hohokam
A prehistoric Native American culture that lived from 200 A.D. to 1450 A.D. and flourished in the southwestern United States, known for their elaborate irrigation systems, permanent settlements and confederations.

Ansazi
The Ancestral Pueblo people that inhabited the southwestern United States who lived in the 4 counters. Their culture was centered around Maize-based farming and fell into decline by 1300 A.D. the term Ansazi translates to “ancient enemy”.


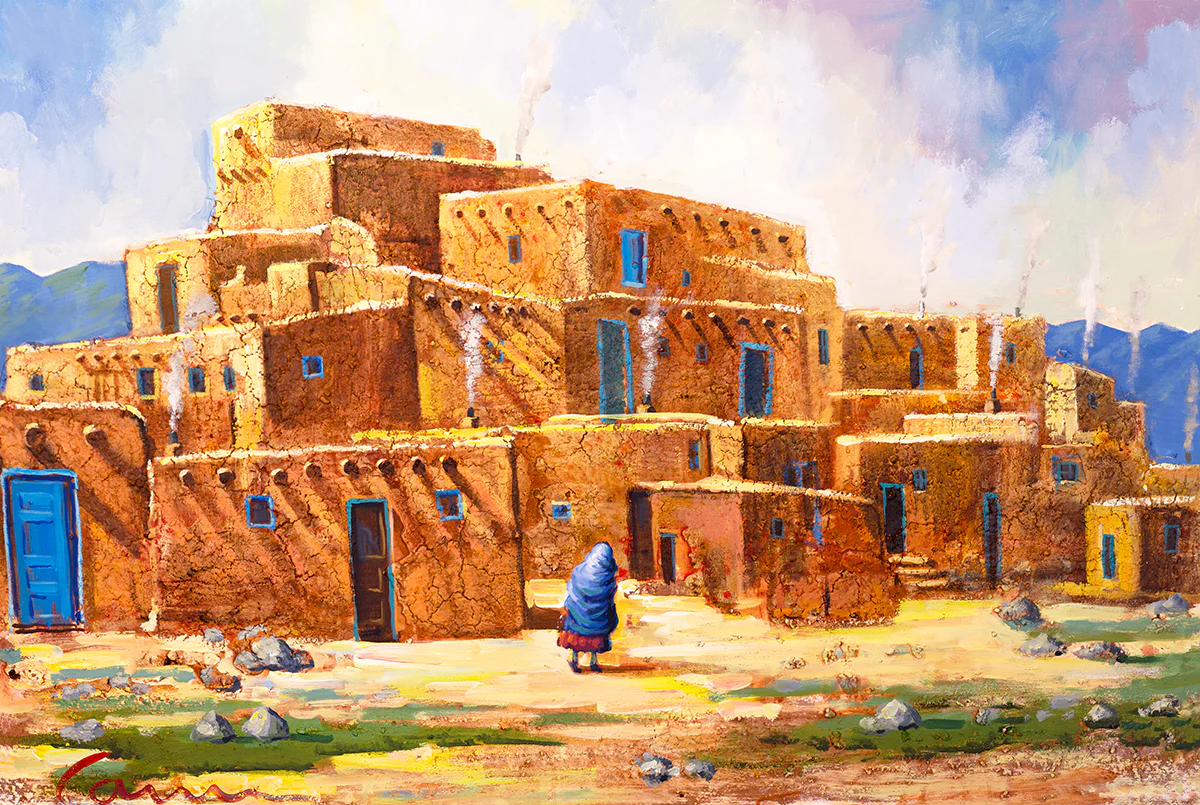
Pueblos
Refers to Native American tribes of the Southwestern United States (New Mexico & Arizona) and the settlements they built. They were a sedentary community.
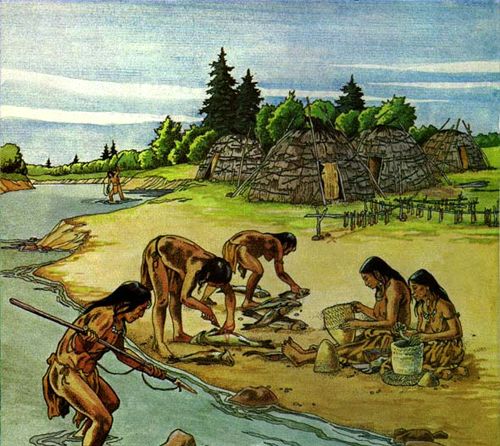


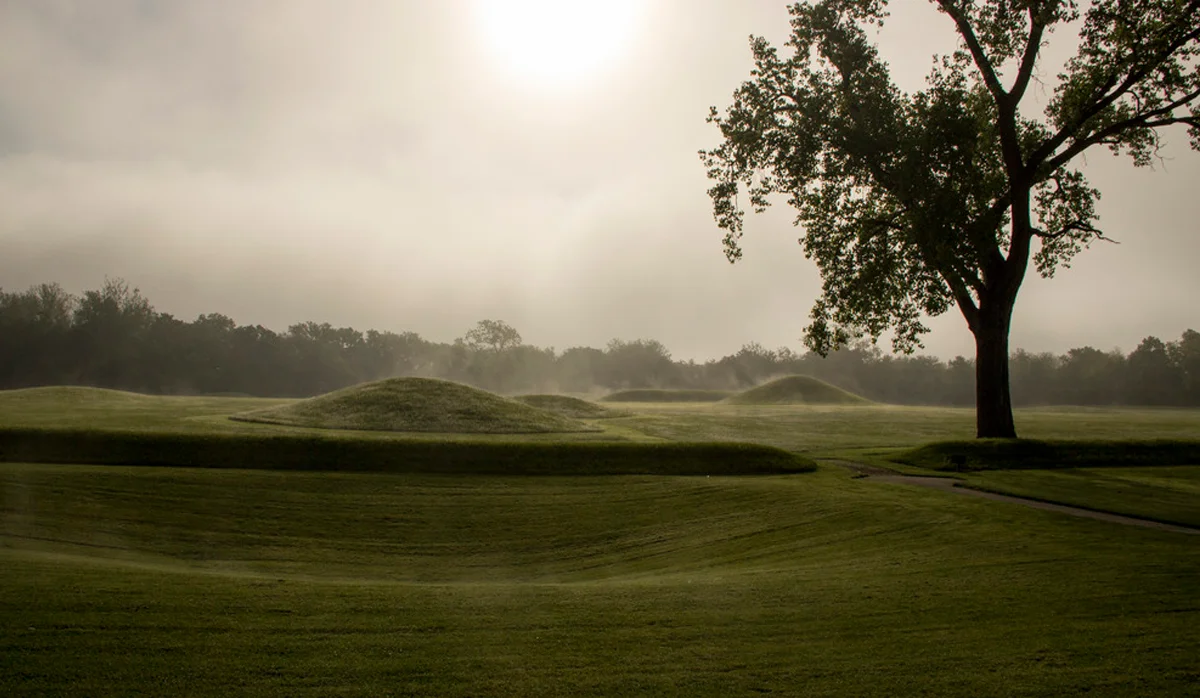
Woodland Mound Builders
A broad group of pre-Colombian North American Cultures particularly during the woodland period between 1000 BCE to 1600 CE. They built mounds for burial and ceremonial purposes.


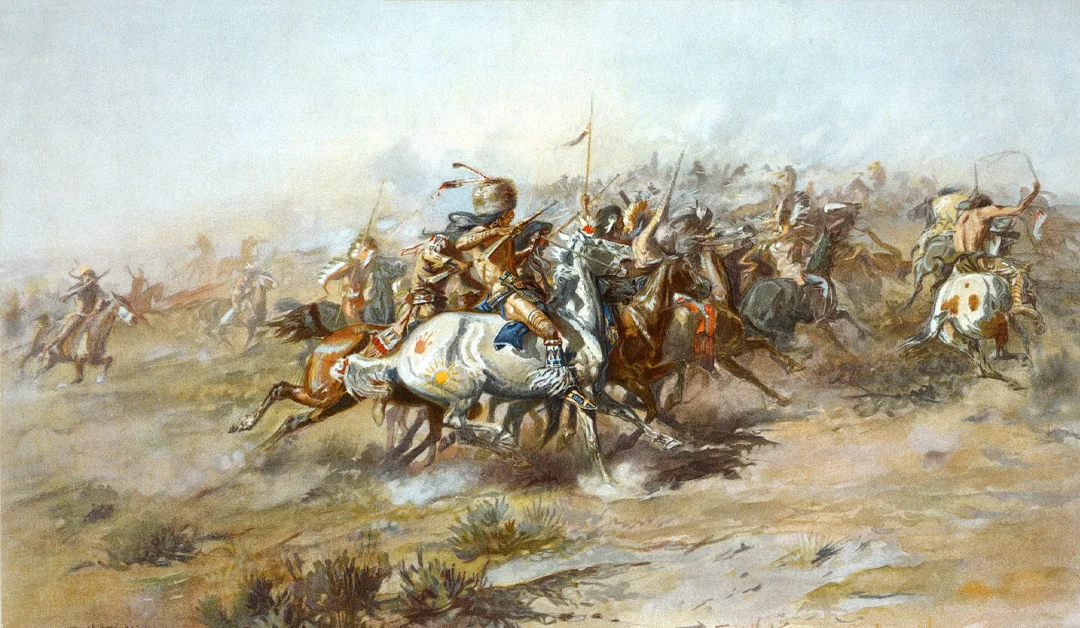
Lakota
A Native American group that, along with the western and eastern Dakota tribes, make up the Great Sioux Nation.
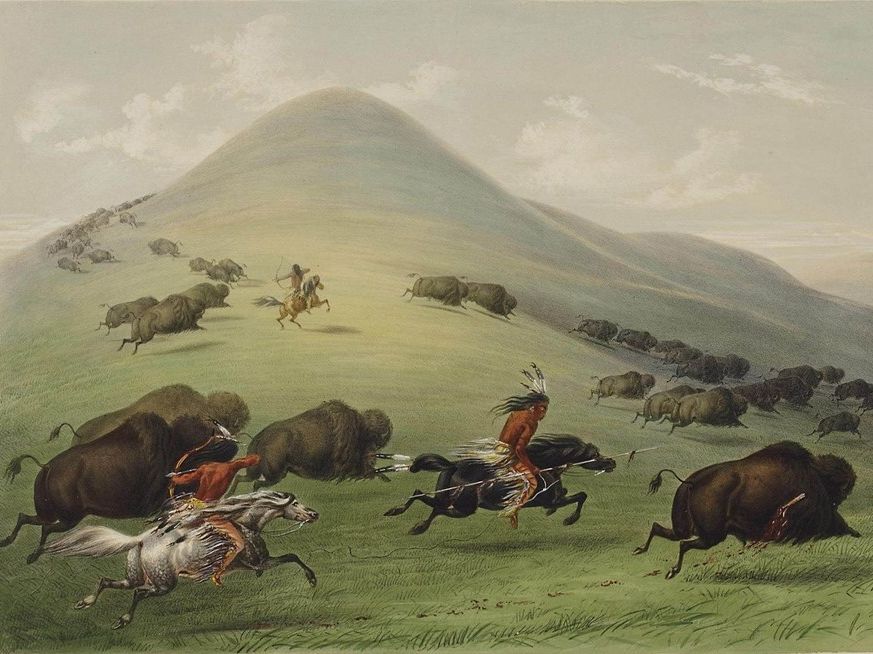


Sioux
A prominent Native American tribe primarily known for their involvement in the Great Sioux War in 1876 and their resistance to westward expansion.


Mayas
An ancient Mezo American civilization known for its advanced knowledge in mathematics, astronomy and calendar systems. Inhabited Southeast Mexico, Guatemala and Belize. Established themselves on the Yucatán Peninsula
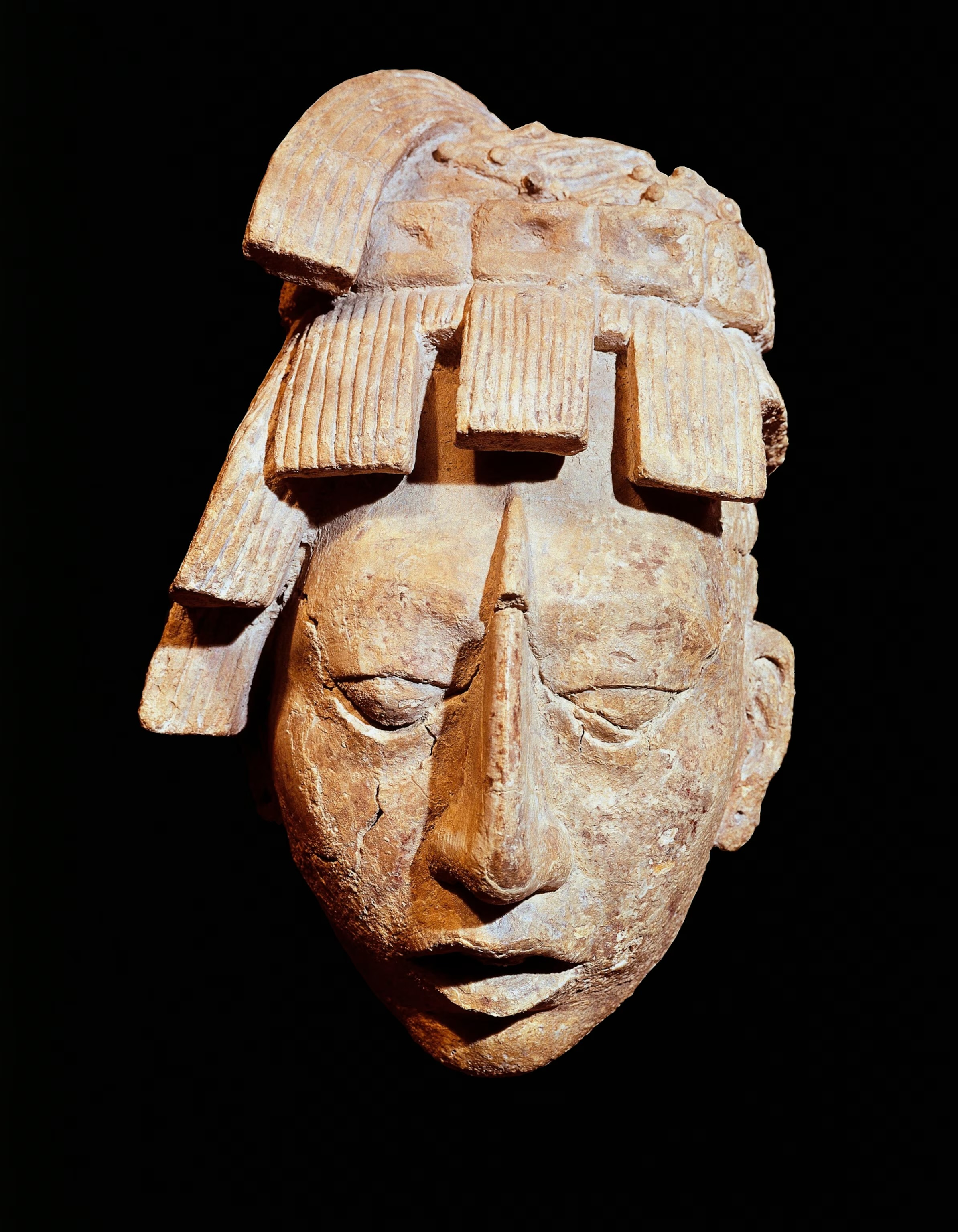


Incas
A Pre-Colombian civilization located on the Andes/Pacific coast, that emerged and flourished in South America, specifically Peru Bolivia and Chile, prior to the Spanish Conquest.
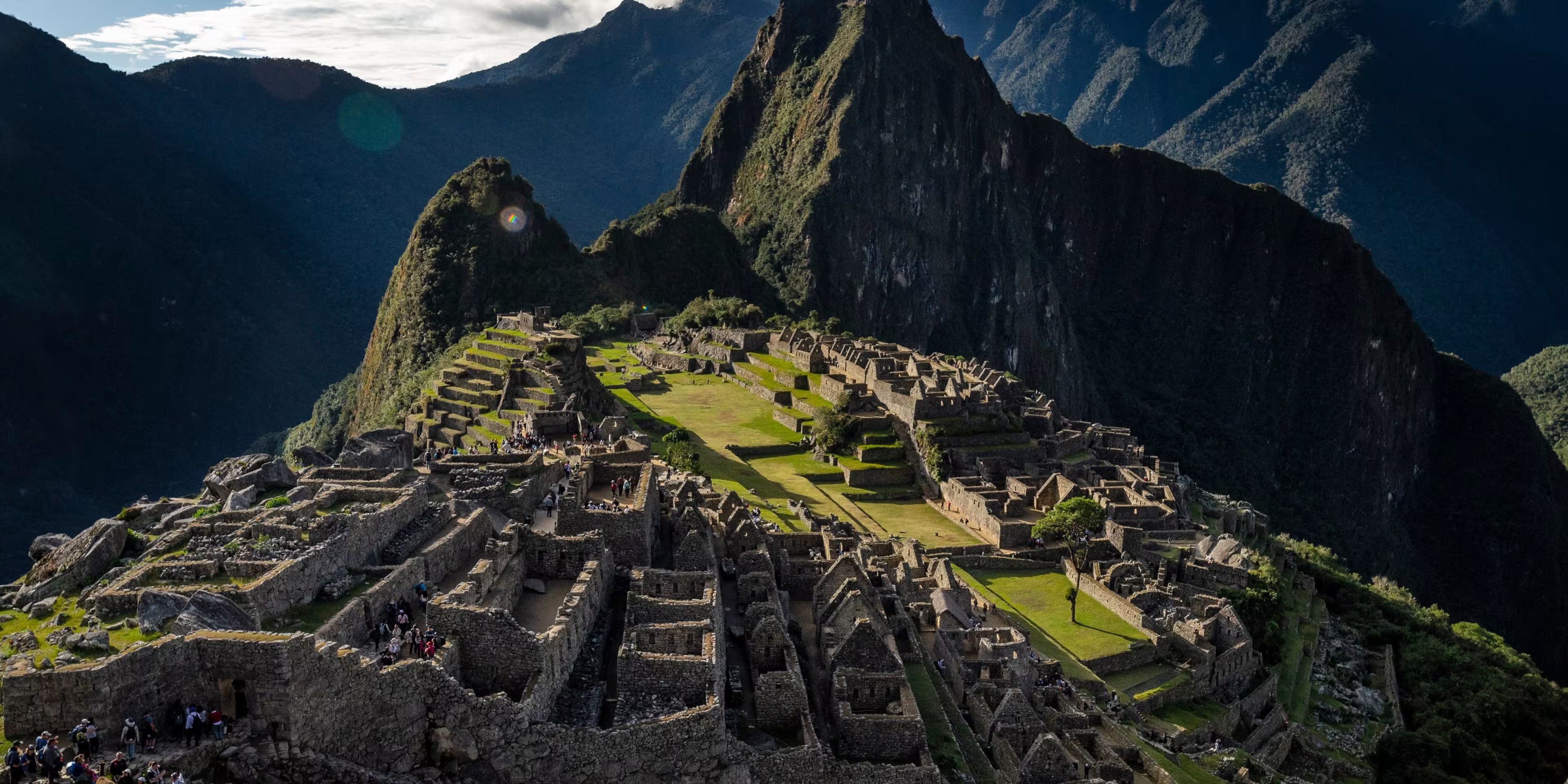
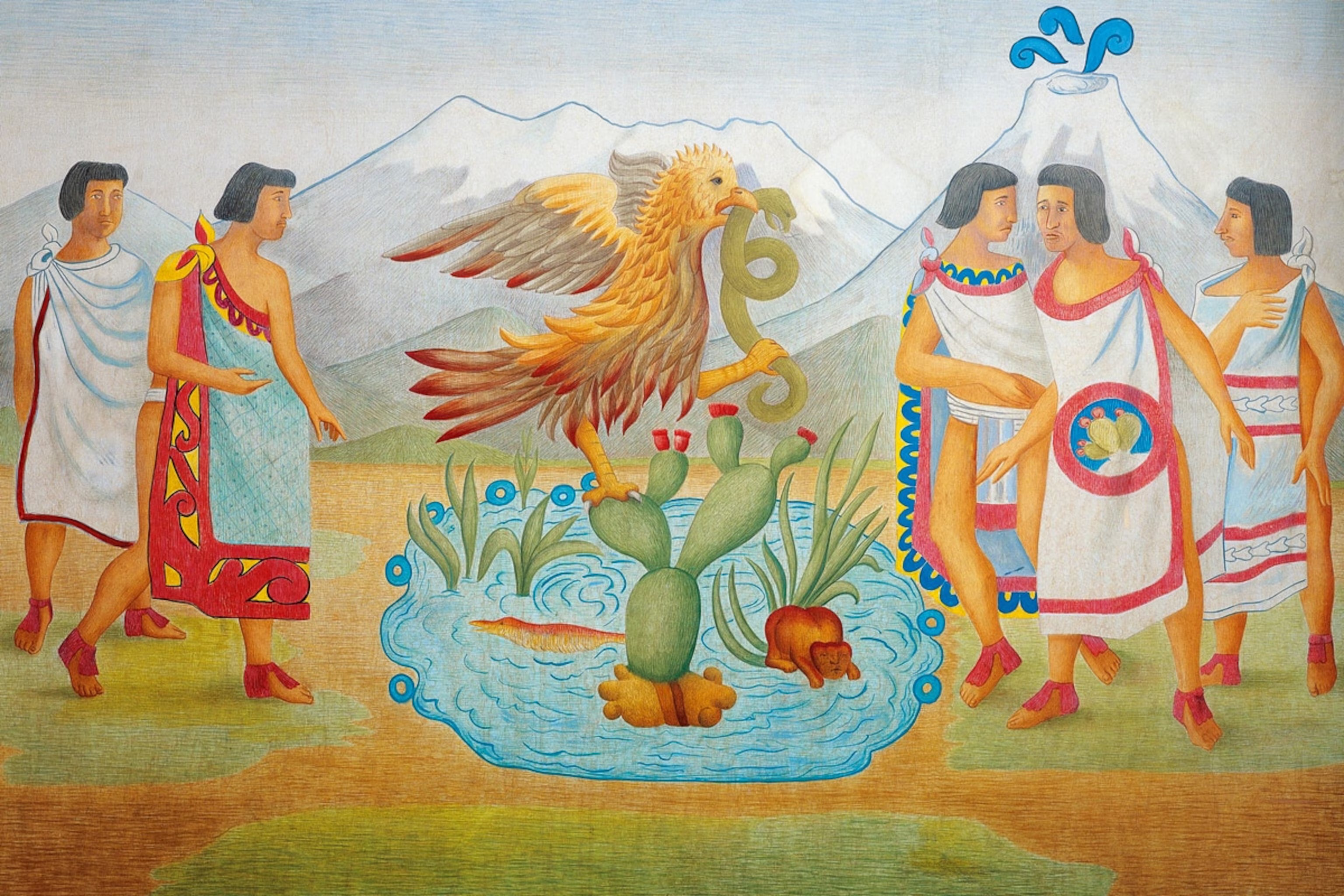


Aztecs
A powerful Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in Central Mexico from the 13th to 16th centuries.


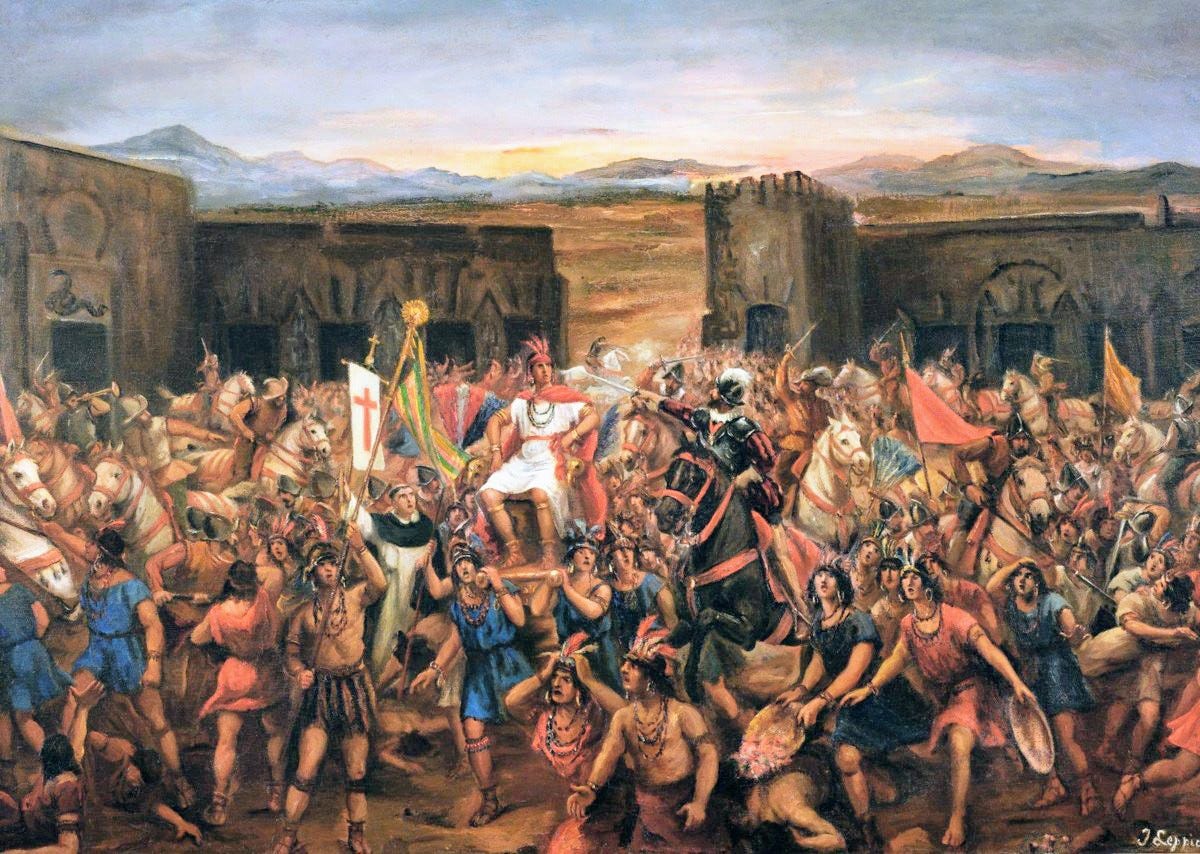
Conquistadors
Spanish soldiers and explorers who led military expeditions in the Americas and captured land for Spain
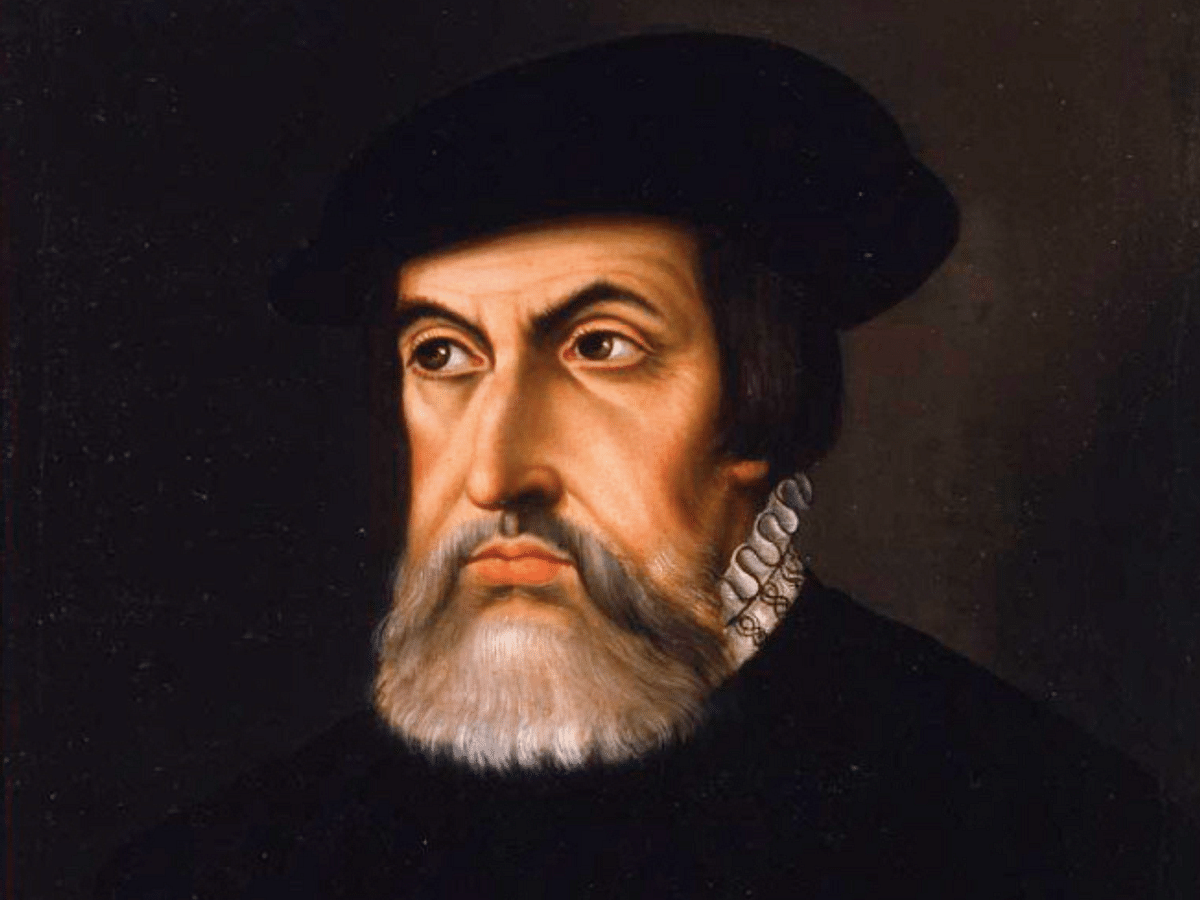


Herman Cortes
Was a Conquistador and a key figure in European expansion that conquered the Aztec empire and claimed Mexico for the Spanish in the 16th Century.
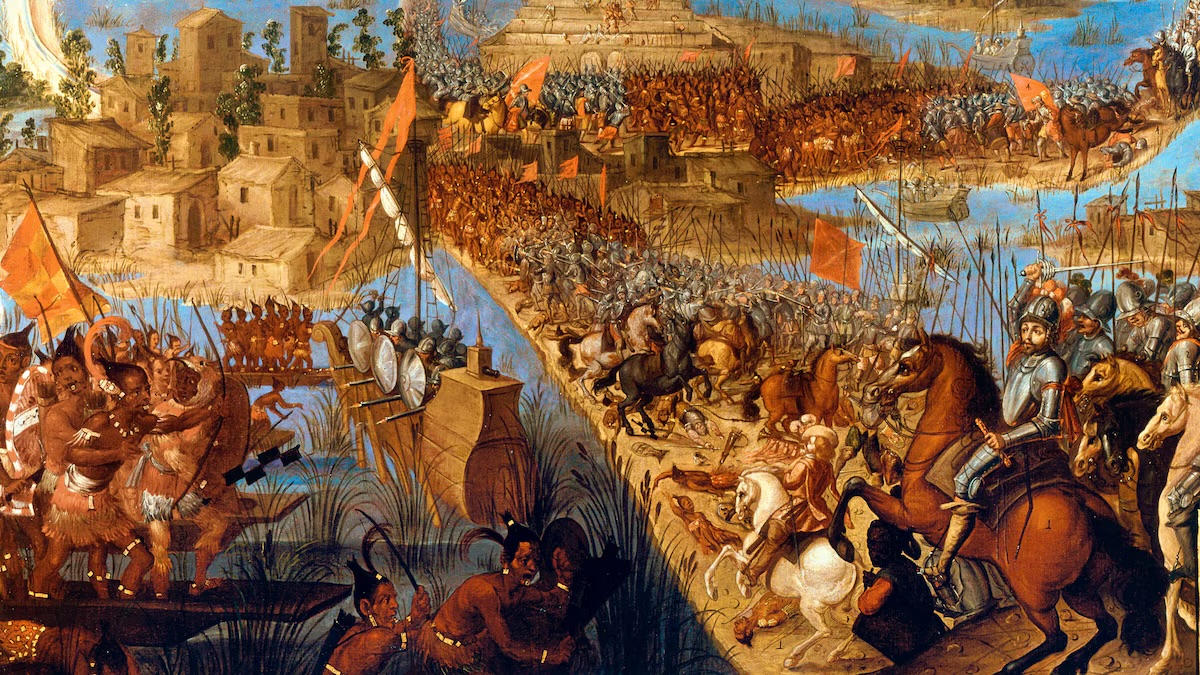
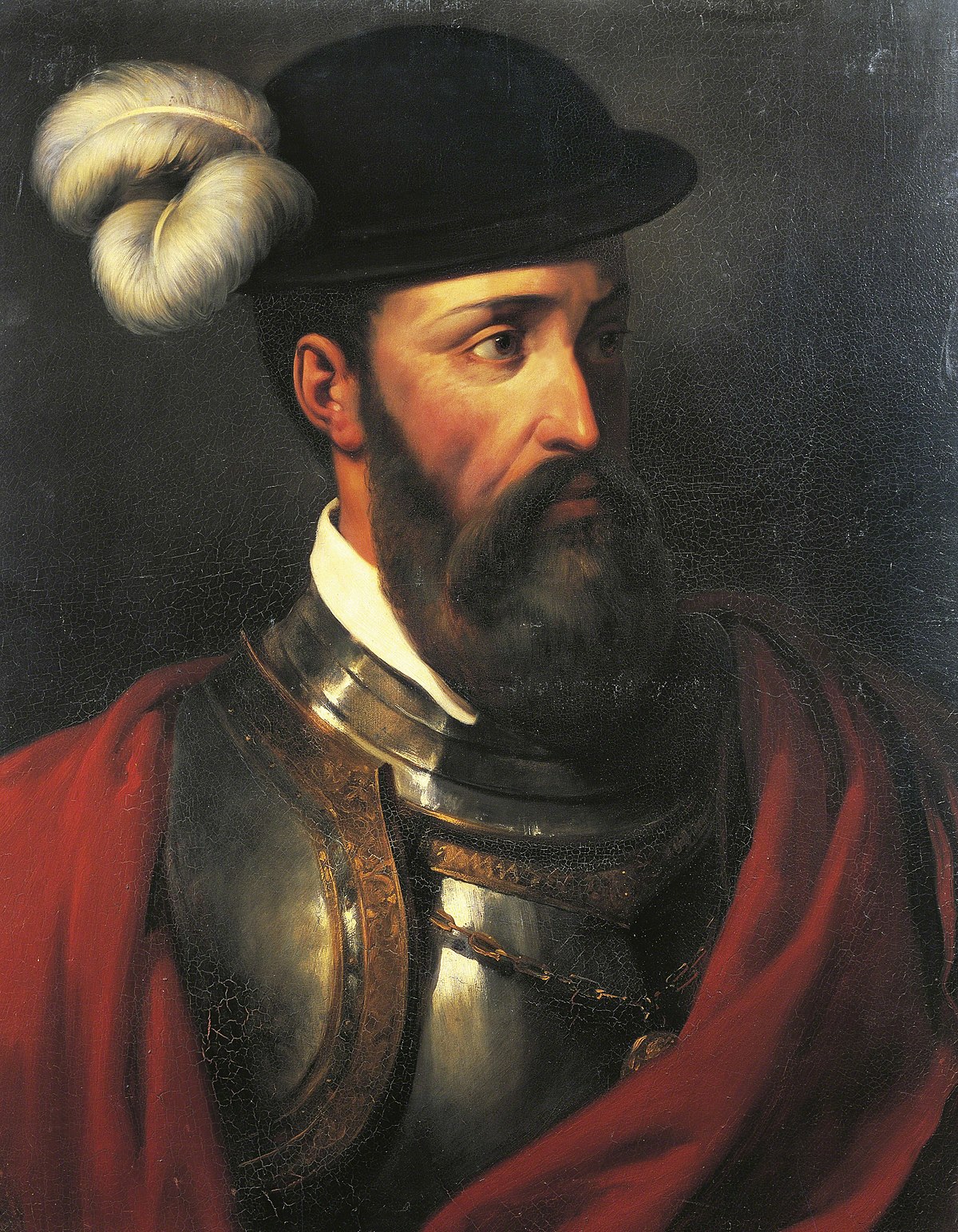


Francisco Pizarro
Was a Spanish conquistador who led the conquest of the Inca empire in the 16th century. His conquest led to Spanish rule in Peru and the fall of the Inca people.
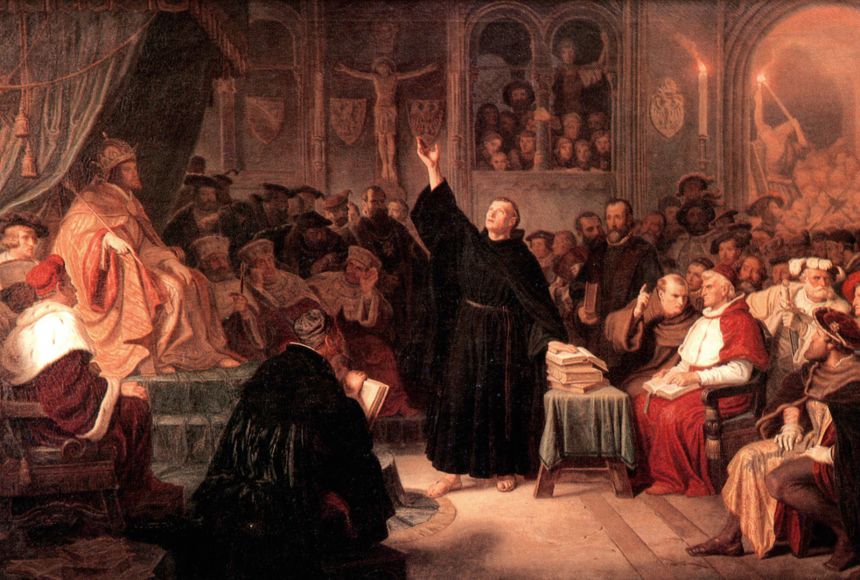


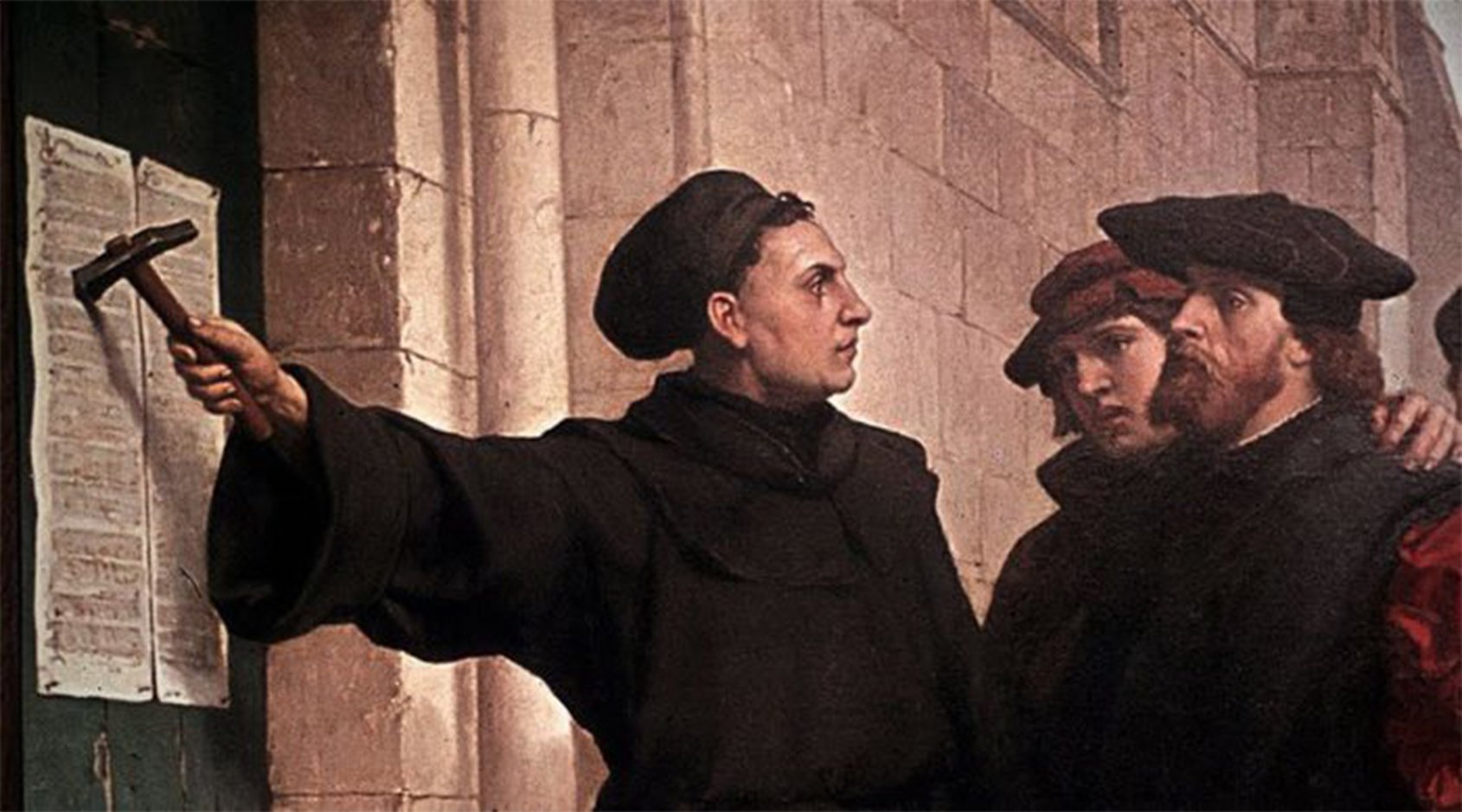
Protestant Reformation
A 16th century religious movement that challenged the authority of the Roman Catholic Church and led to an establishment of various Protestant reformations. Fueled by dissatisfaction with the Church’s practices and a call for a return to biblical Christianity.
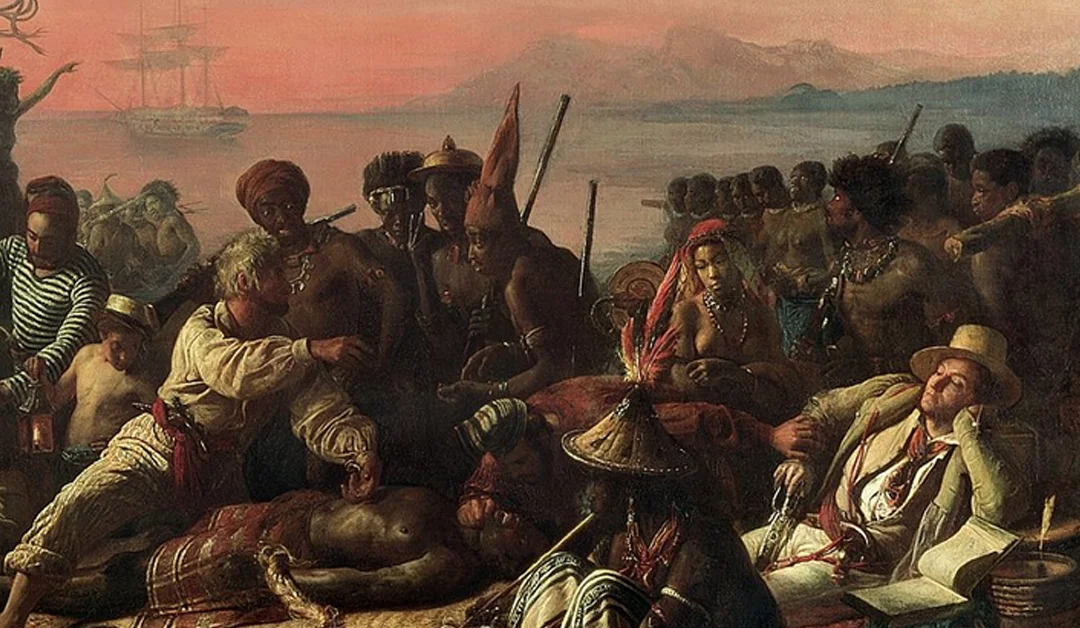


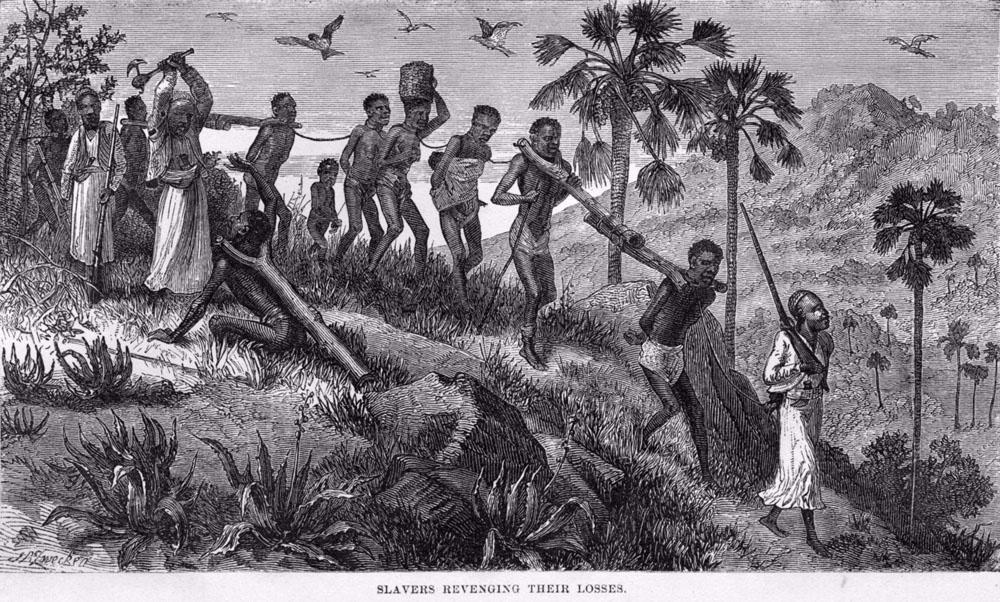
Slave Trade
The Forced transportation of millions of Africans from the 16th to 19th century where they were enslaved and exploited for labor.
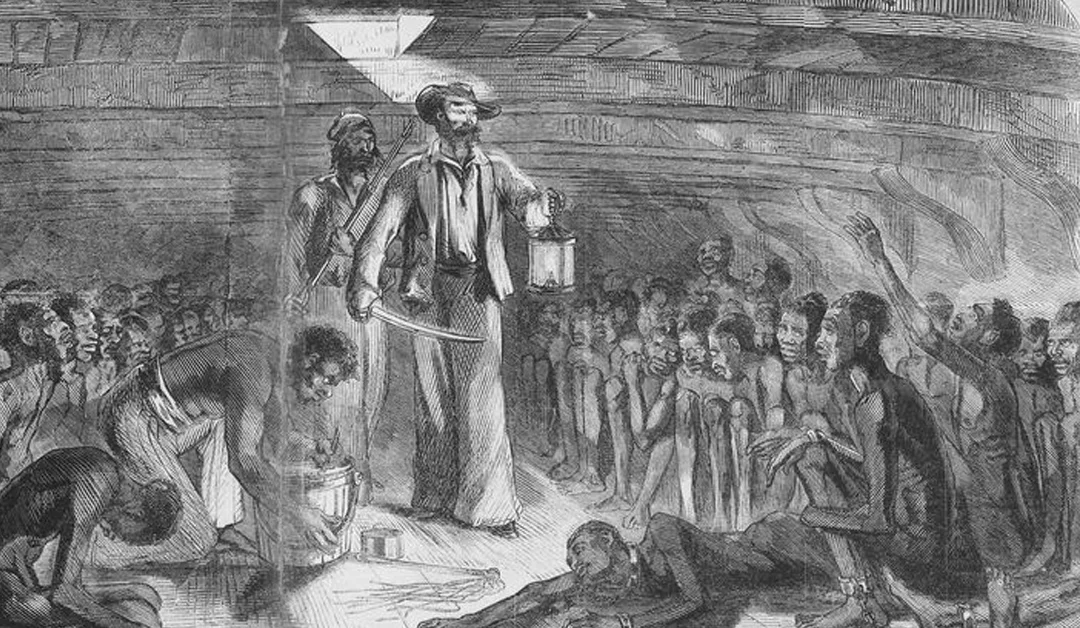


Nation-State
A political entity where a a state corresponds with the boundaries of a nation, which is a group of people united by factors like a shared culture, language or beliefs.
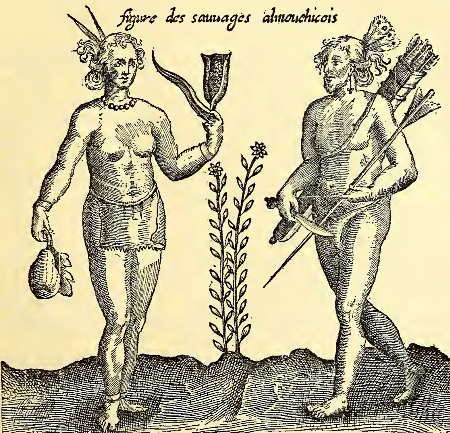

Algonquian
An American Indian group in the Northeast, prominent along the Atlantic coast who spoke the Algonquian language, and were headed in eastern Canada and the Great Lakes region.
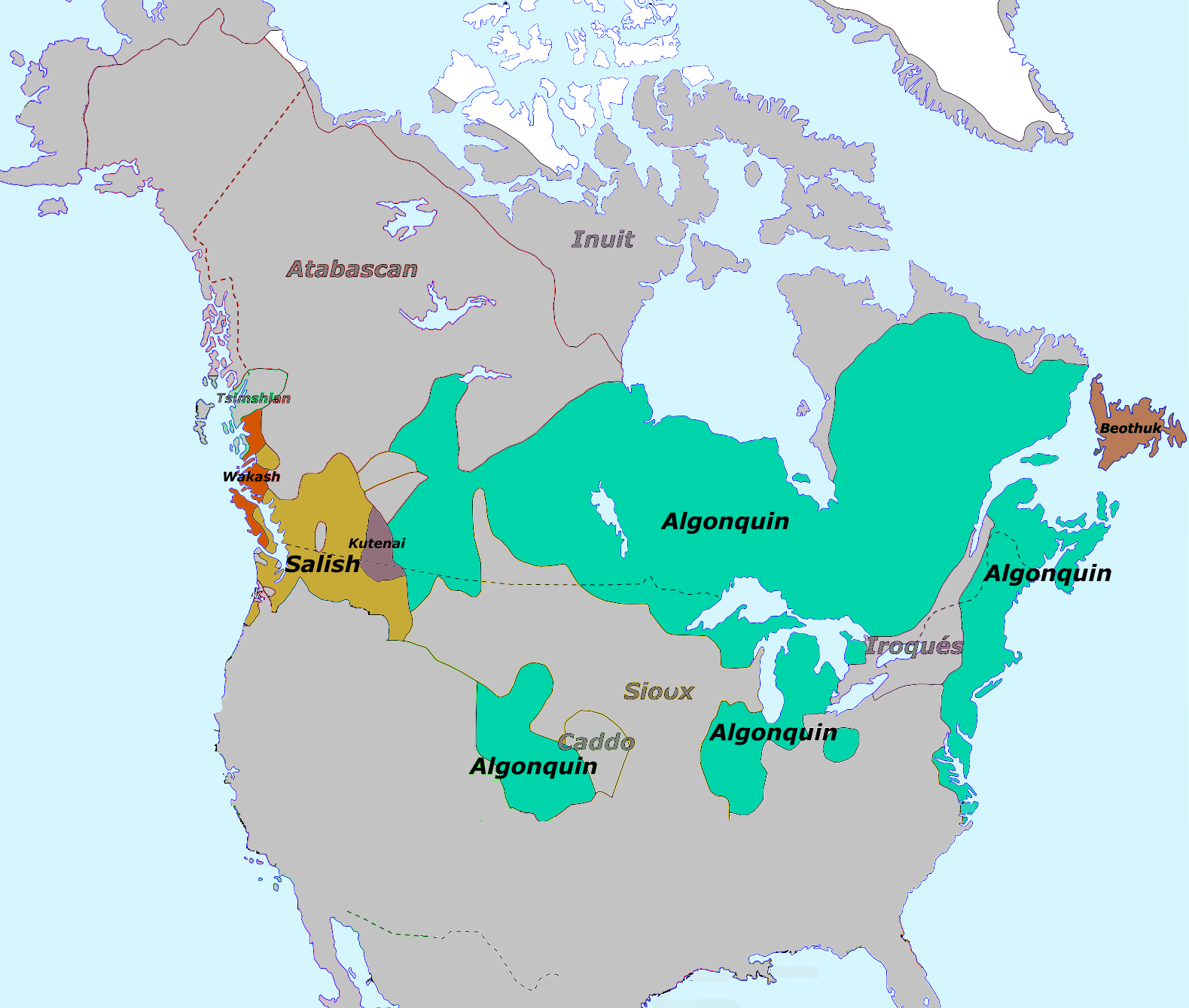

Iroquois Confederation
A powerful alliance of six Native American nations comprised of the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca and Tuscarora. With the goals of maintaining peace, forming military alliances and fending off any foreign threats.


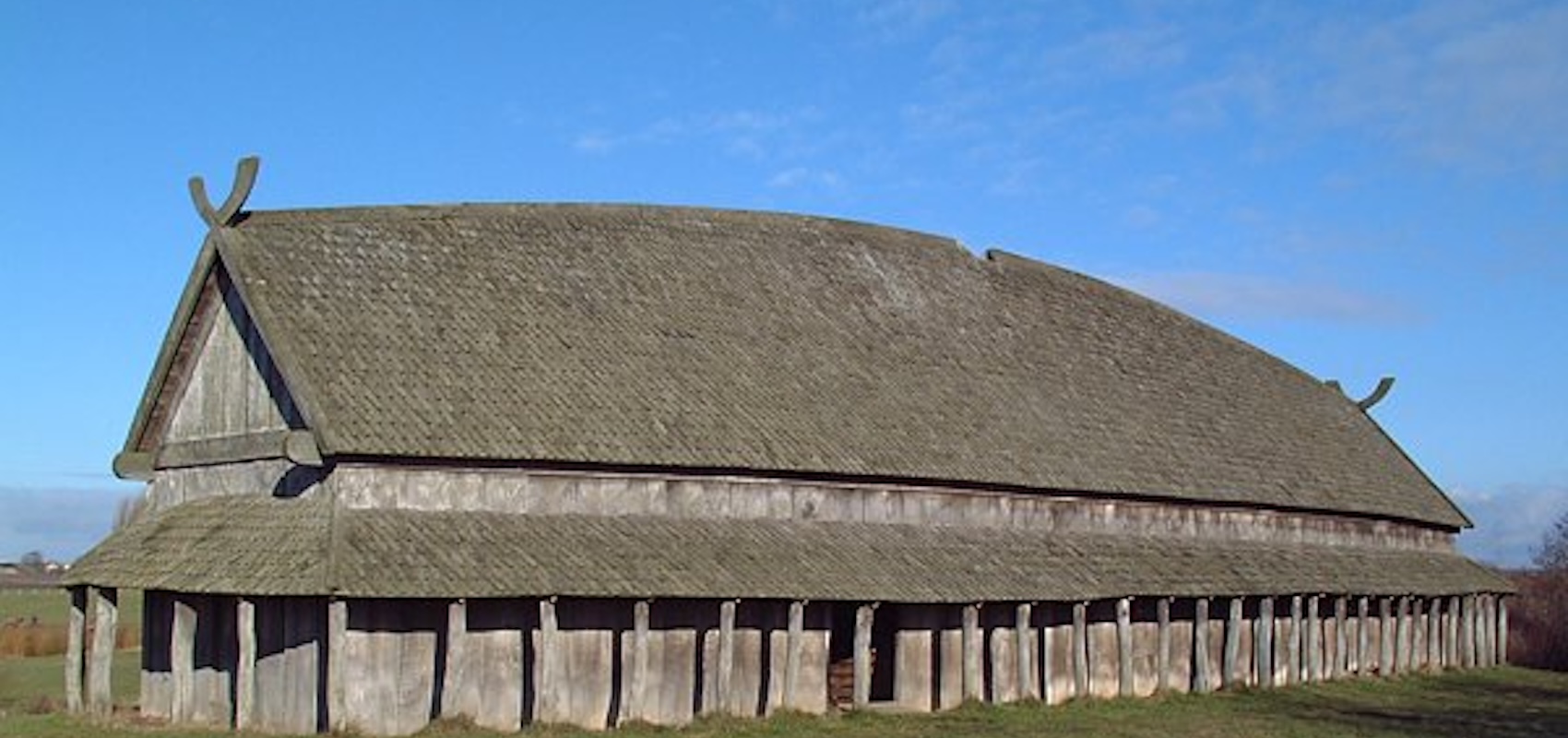
Longhouses
A type of Communal housing structure, prevalent among Native American Groups.
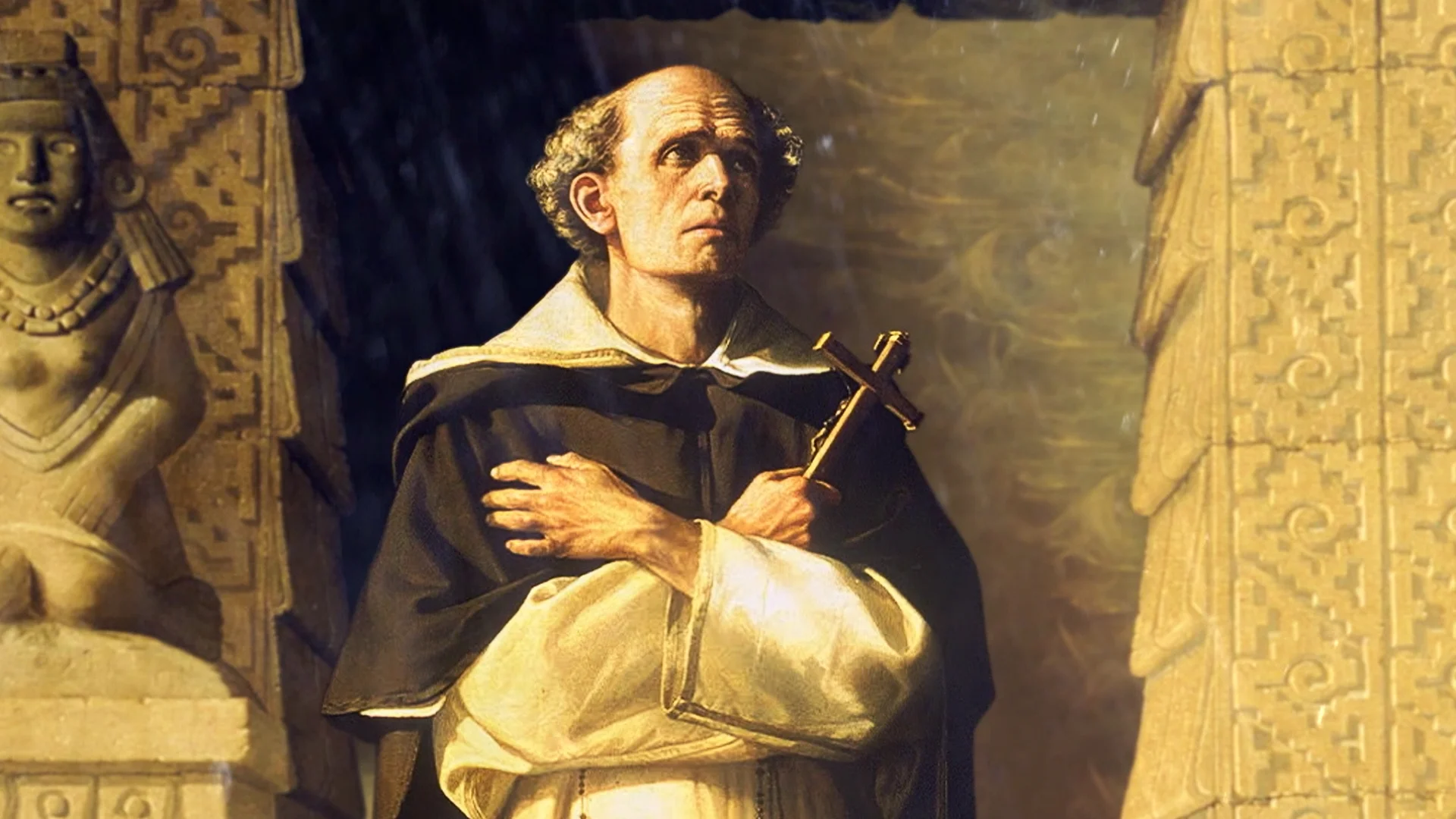


Bartolomé de las casas
A Spanish American Dominican Friar, known for his criticism of Spanish Colonial abuse and for his advocacy for rights and dignity of Native Americans.


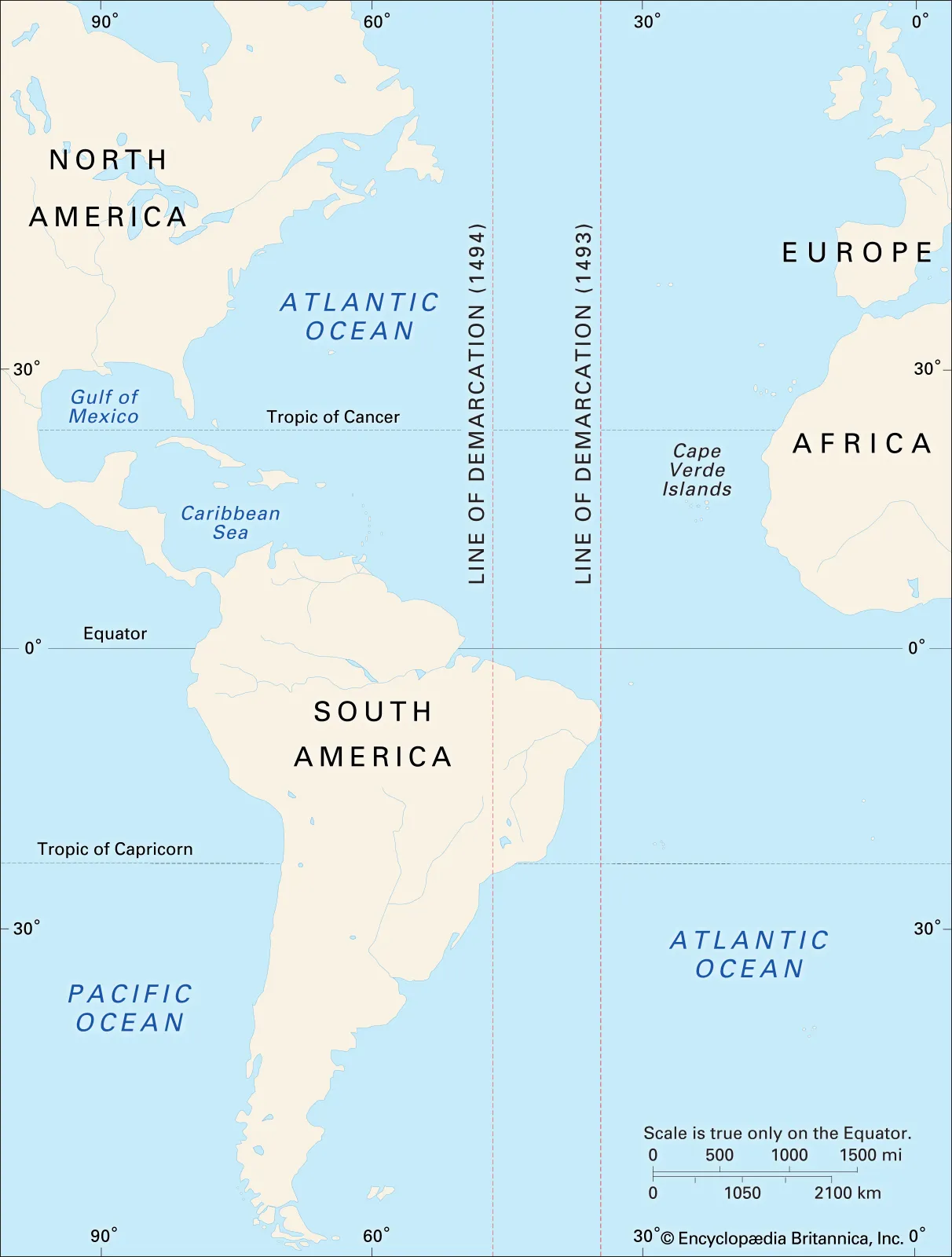
Treaty of Tirdesillas
An Agreement between Portugal and Spain that created an imaginary line in the Atlantic Ocean which divided newly discovered lands between them, in order to avoid conflict between nations. West of the line was Spains territory and east was Portugal’s

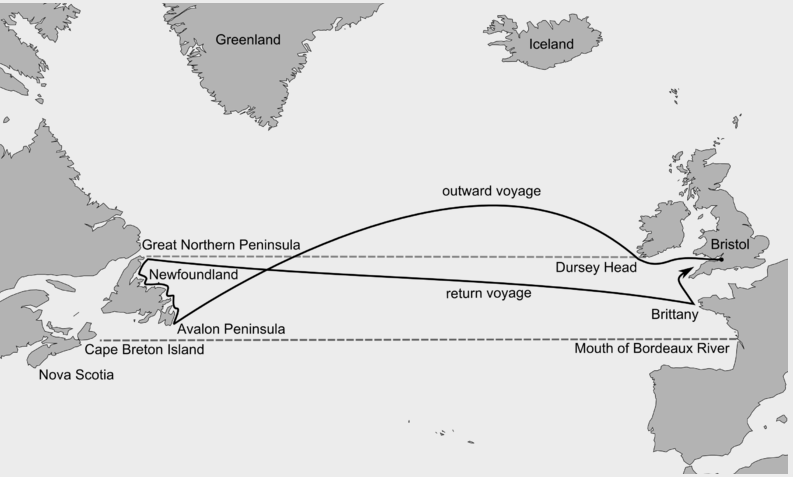
John Cabot
An Italian explorer known for his voyage to North America in 1497, who led an expedition to claim land for England. His voyage established a basis for future claims to land in North America.