Ap Hug: Unit 1 Vocab
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Human Environment Interaction
Relationship between the natural world and humans is at the heart of human geography.
Exmpl: pollution and deforestation
Land Use
How land is used, modified and organized by people.
Exmpl: agriculture, housing, industries
Distance Decay
The interaction between two places decline as the distance between the two places increases.
Exmpl: weakening of a radio signal as it travels across space away from a radio tower.
Sense of Place
Factors that contribute to the uniqueness of a location.
Exmpl: Rome, Italy might be describes differently by a local than by an outsider.
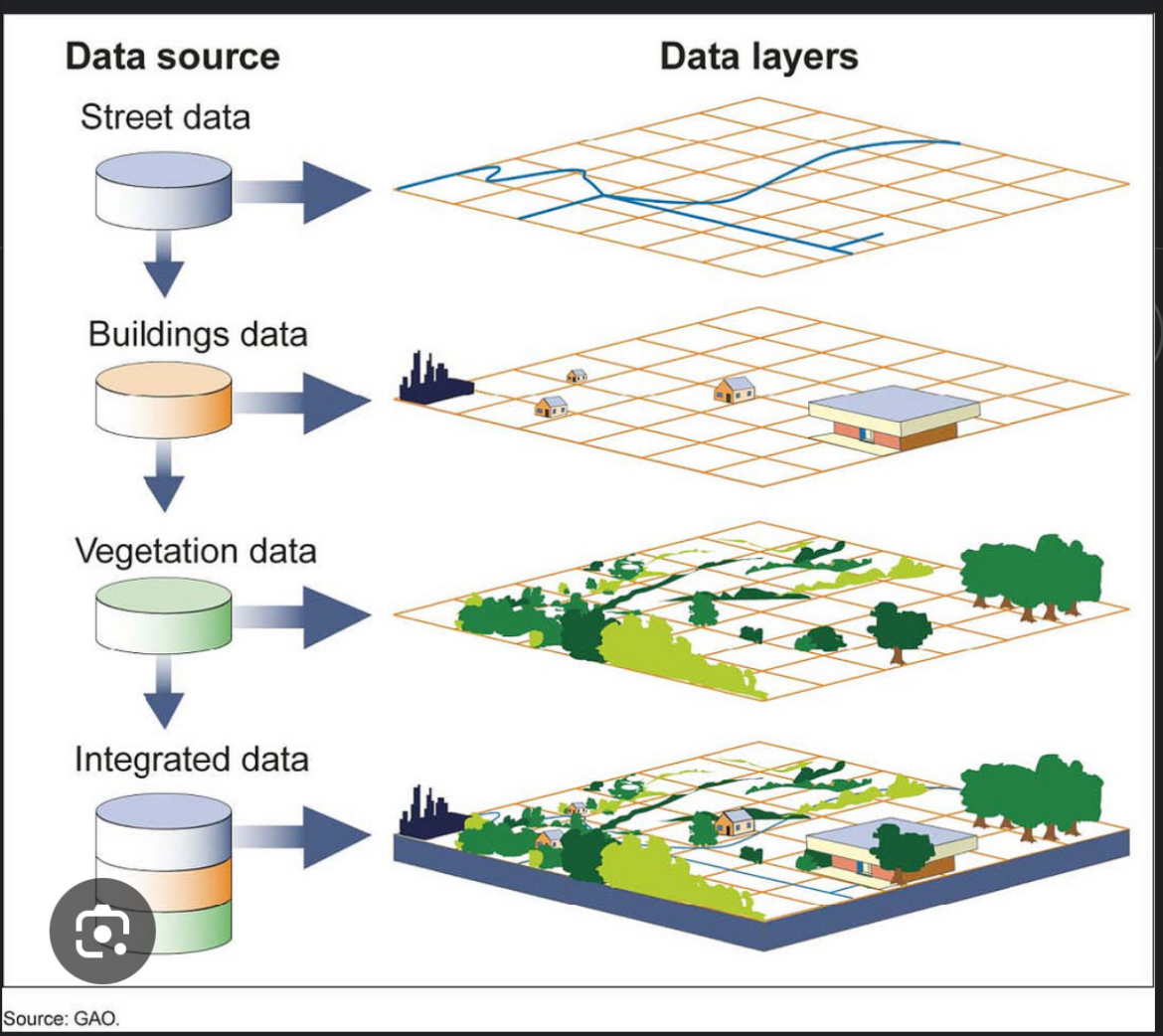
Geographic information system (GIS)
Computer systems/ software that stores analyzes and displays info from multiple digital maps or data sets.
Exmpl: computer analyzes population density, land use patterns, and transportation networks.
Thematic Map: Isoline
Use lines that connect points of equal value to depict variations in the data across space.
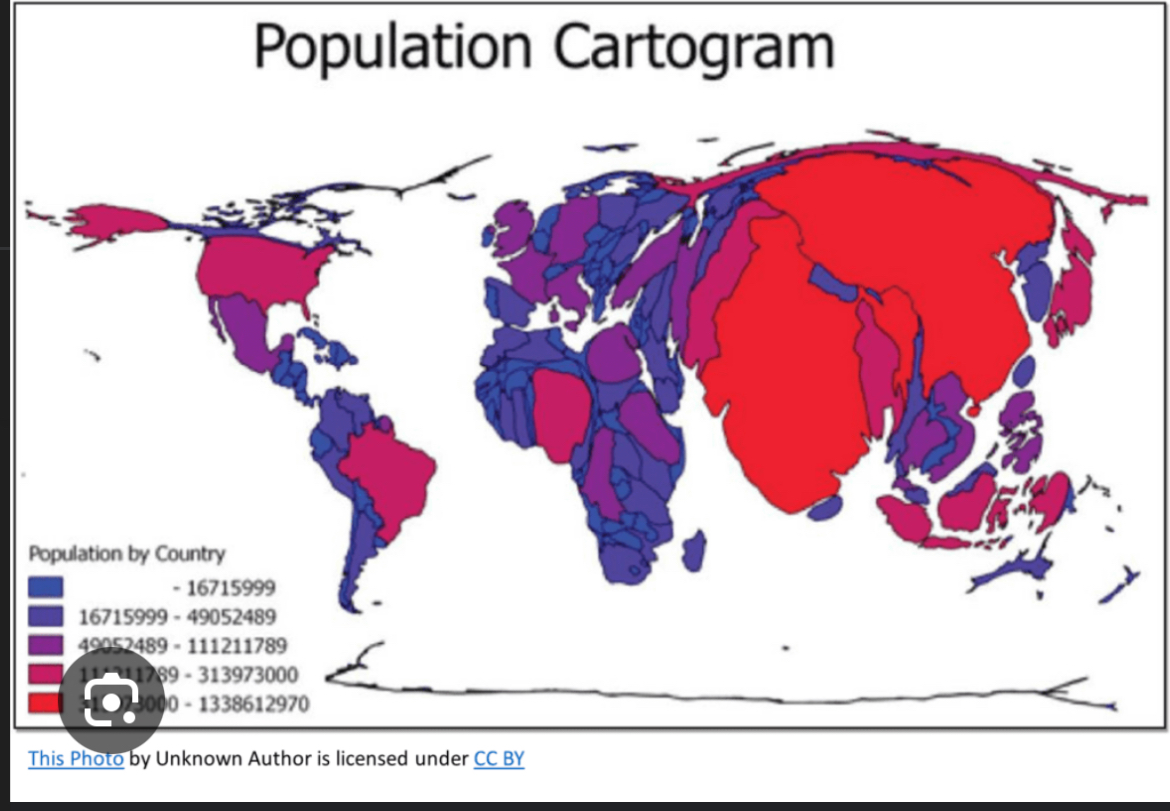
Thematic map: cartogram
Changes size of Countries according to the data being presented.
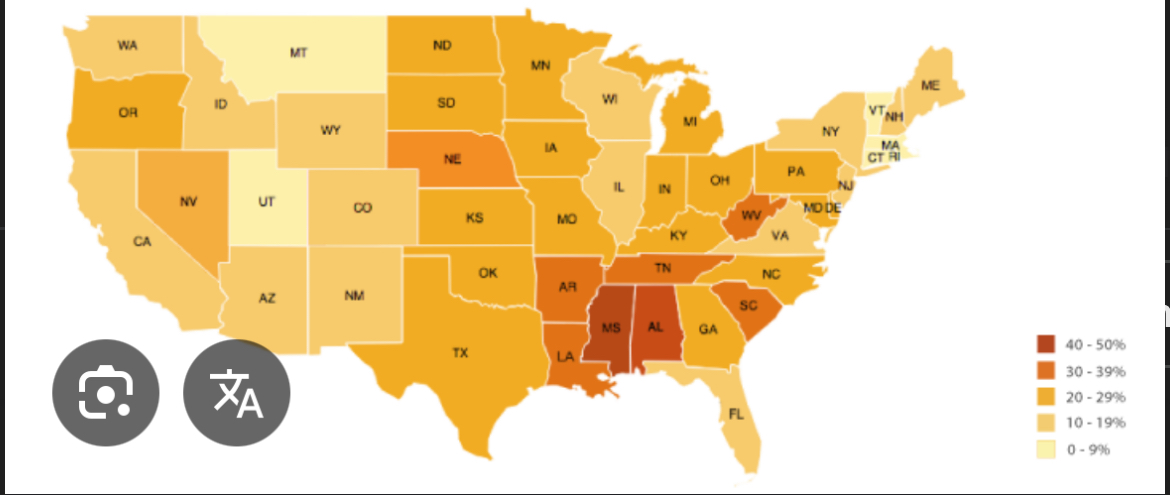
Thematic map: choropleth
Use variations of colors, shades of one color/patterns to show distribution of spatial data.
Reference Maps
A map that provides spatial information, showing where things are located on a earths surface
exmpl: physical and political
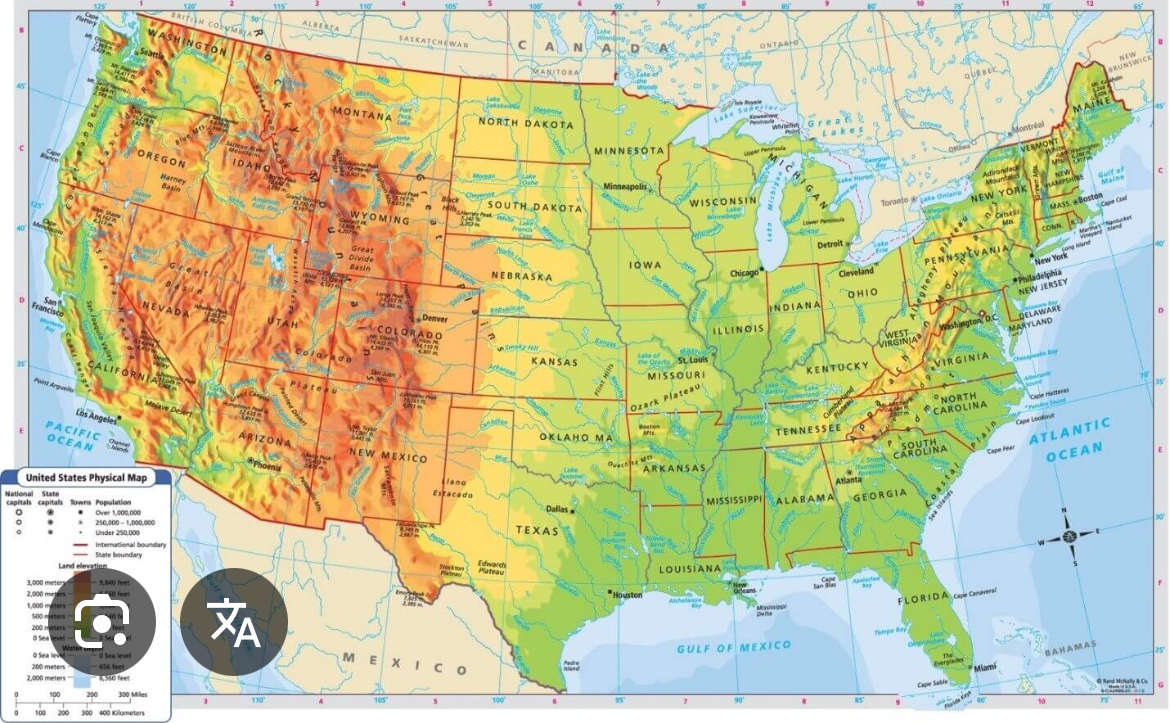
Reference map: physical
Physical map show natural features: mountains, rivers, and desserts.
Absolute distance
The precise/exact distance something is from something else.
Exmpl: my house from the school is 2.2 miles.
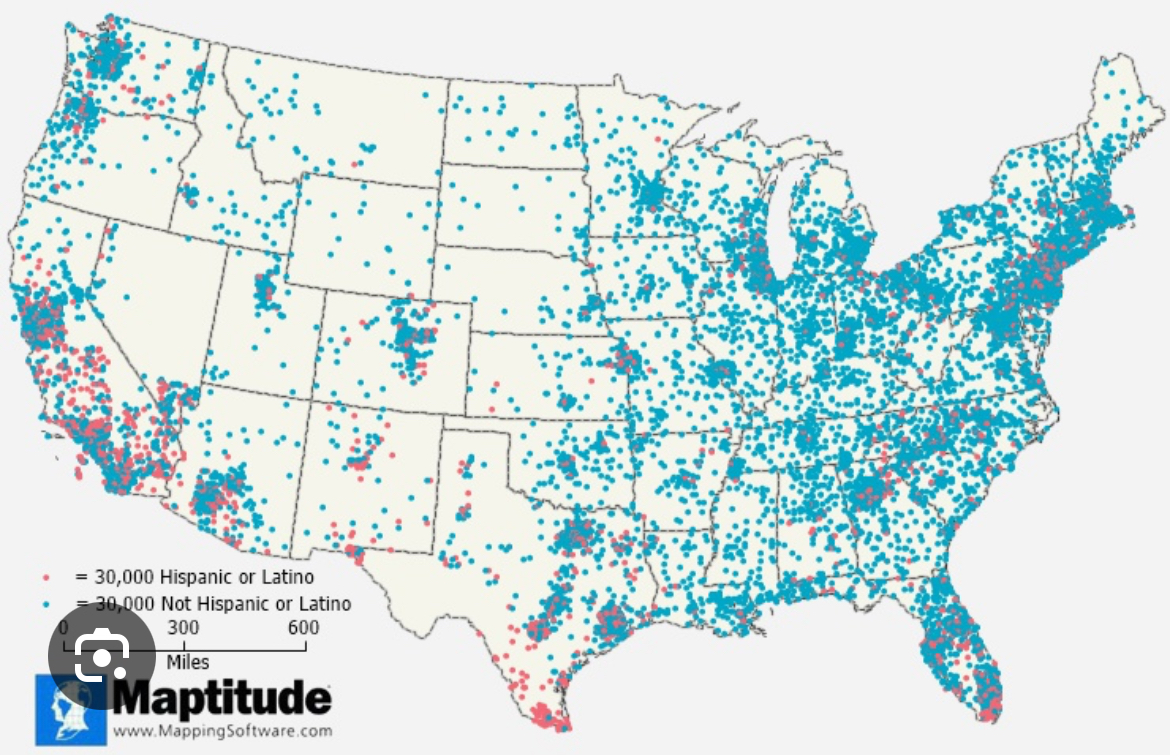
Thematic map: dot density
Uses dots to show the specific location and distribution of something across a map.
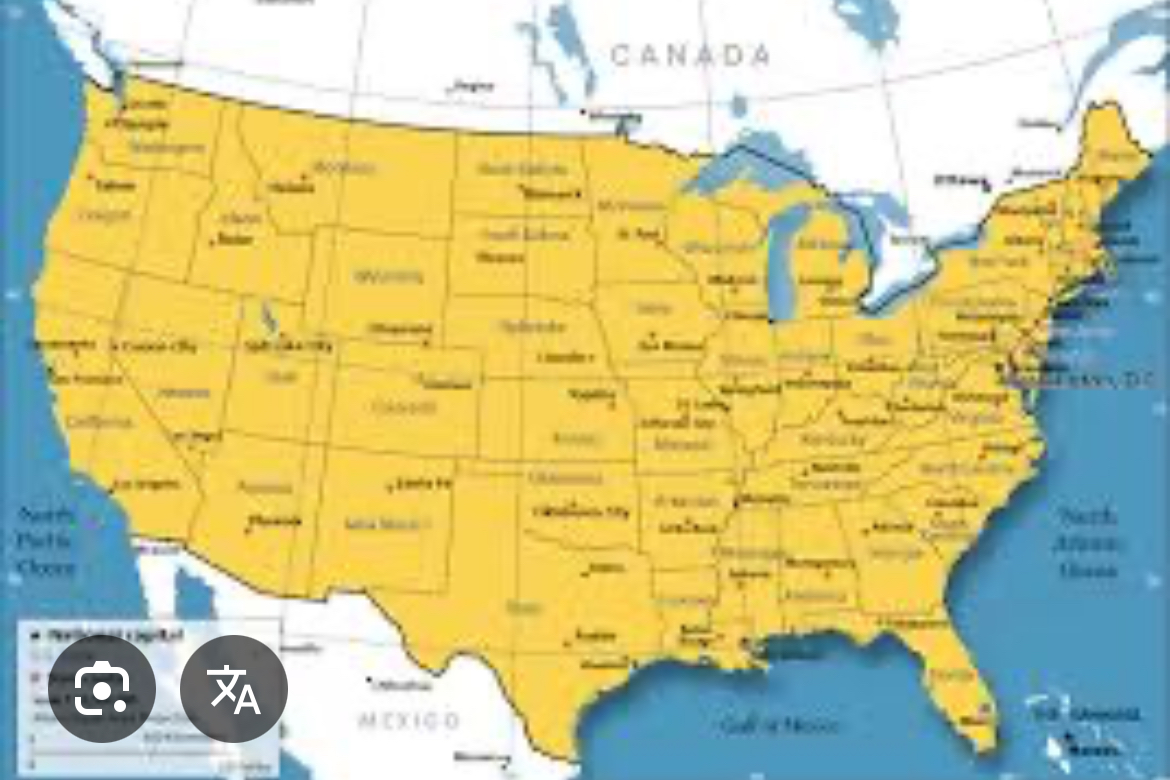
Reference map: political
Show and label human created boundaries, countries, states, cities, and capital.
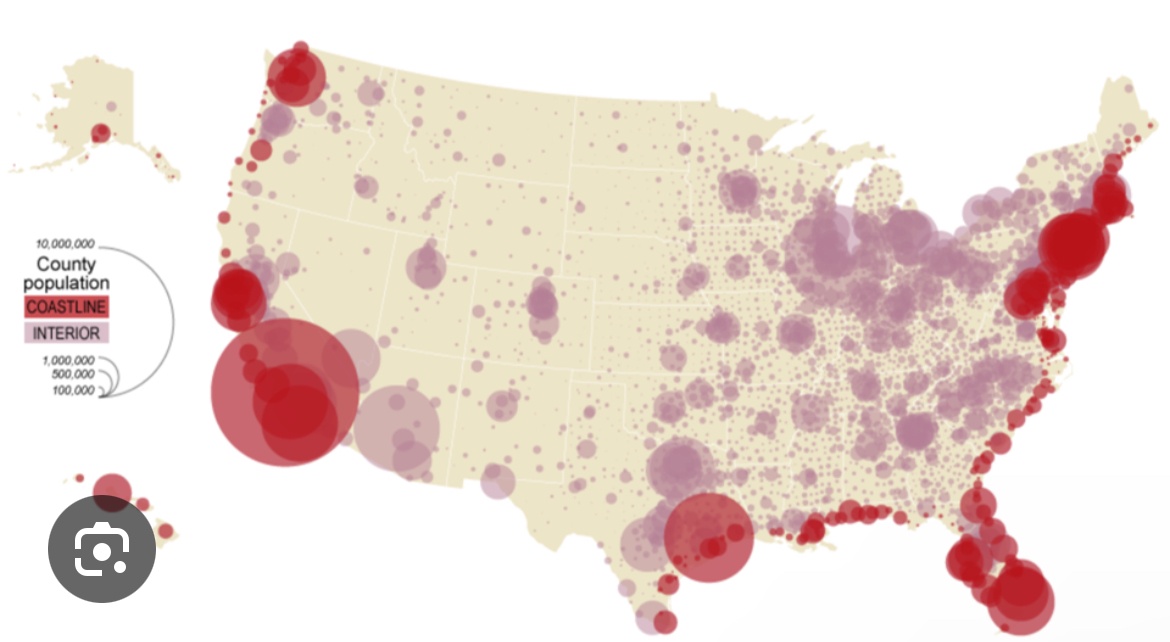
Thematic map: graduated/proportional symbol
Displays symbols that changes in size according to the value of the variable/data.
Map projections
The process of a cartographer(map maker) showing the curved surface of the earth on a flat map.
exmpl: Mercator, Robinson, and Goode projections.
Robinson map projections
Map that aims to balance distortion of shape, size, distance, and direction rather than focusing on accuracy in one specific area when representing the earth on a flat surface.
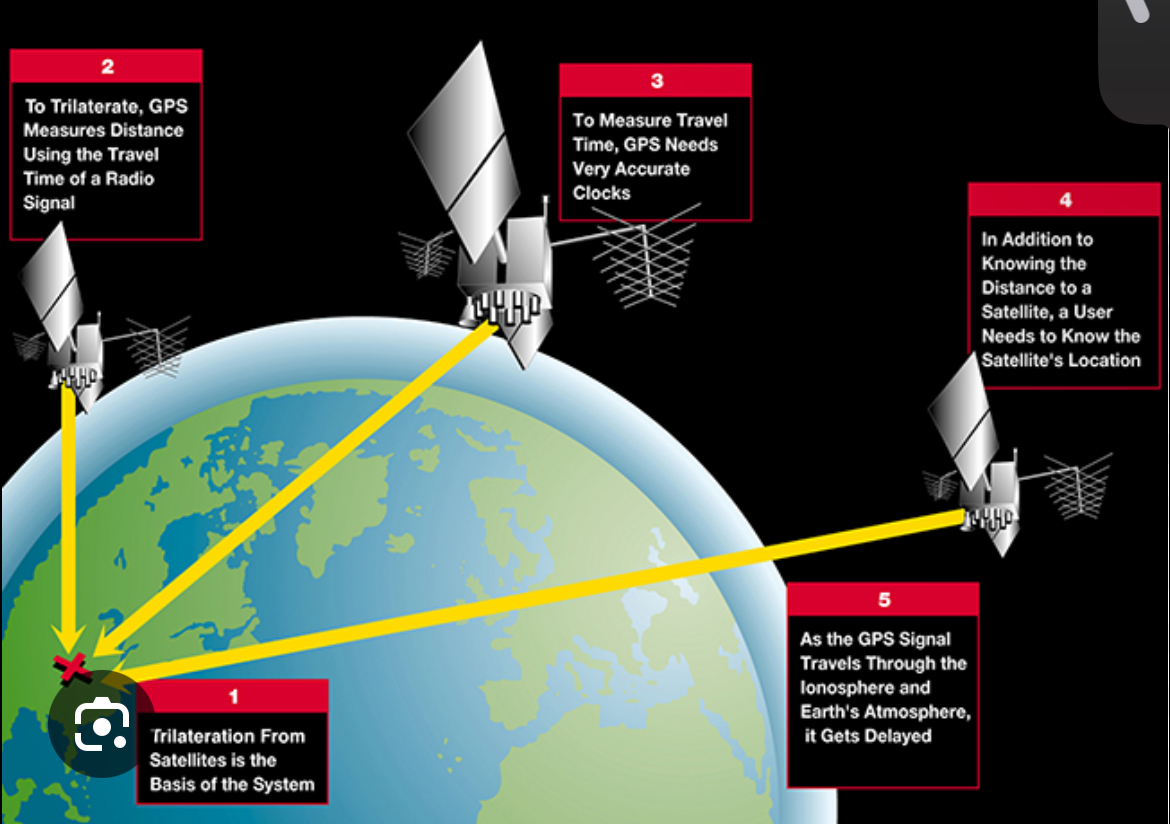
Satellite navigation system
Enable precise location determination by using satellites orbiting earth to calculate a receiver’s position.
Toponym
The name of a place on earth.
Theory of environmental determinism
Human cultures, societies, and development are primarily shaped by the physical environment, including climate, geography, and resources
Formal region
An area defined by a specific characteristic, such as language, climate, or economic activity, where that characteristic is consistently present throughout the area.
Functional Region
An area defined by the interaction and connections between its parts, centered around a central point or node.
Perceptual/vernacular region
Geographic area defined by people’s perceptions, feelings, and attitudes, rather than formal boundaries or scientific criteria.
Contagious diffusion
The rapid spread of an idea or innovation, like a cultural trend, through a local population, often through direct contact between individuals, similar to the spread of a contagious disease.
Stimulus diffusion
Type of cultural diffusion where an idea or innovation is intoduced but is adapted and modified in its new environment, rather than spreading in it’s original form.
Hierarchical diffusion
The spread of ideas, innovations, or cultural traits from a larger, more influential cities or regions to smaller, less influential ones.
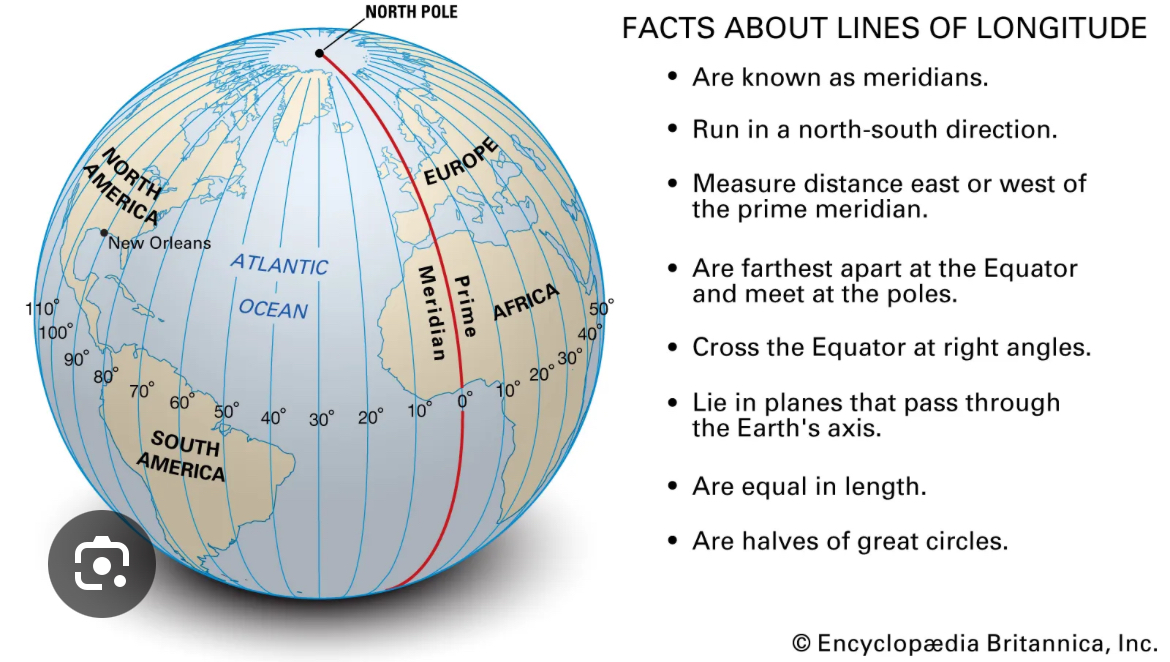
Meridian of longitude
An imaginary north-south line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole, connecting points with the same longitude.