Delirium
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is delirium?
Disorder of attention of cognition defined by its acute onset and fluctuating course of symptoms, inattention, impaired level of consciousness, and disturbance of cognition
Key features in diagnosis (4)
fluctuations
inattention
impaired consciousness
cognitive disturbances
Supportive features of diagnosis
sleep disturbances
perceptual disturbances (hallucinations)
psychomotor disturbances (hypo/hyper activity)
inappropriate behaviour
emotional lability
How is delirium diagnosed?
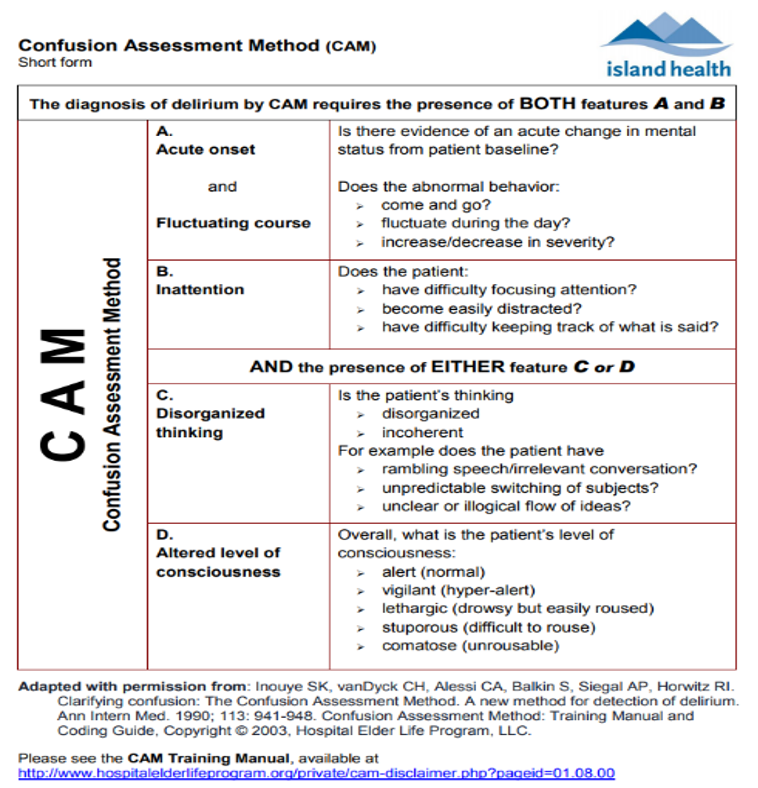
Diagnostic tool: CAM (confusion assessment method)
FAM CAM - family CAM, identifies delirium from collateral history
What are the 2 major forms of presentation?
Hyperactive:
increased arousing, agitation, hallucination, sleep disturbances, aggressive
treatment→ antipsychotics/benzodiazepines
Hypoactive:
confusion, lethargy, hypoactivity
greater risk of being missed
worse prognosis
4AT scoring

CAM assessment
Leading risk factors (8)
dementia
functional impairment
sensory impairment
alcohol abuse
comorbidity burden
poly pharmacy (especially psychoactive drugs)
physical restraints
electrolyte disturbance
Key reasons for hospitalised patients (5)
constipation
pain
acute illness
medications
change of environment
Pathophysiology
multiple biological factors interacting → disruption on neuronal networks→ acute cognitive dysfunction
interference with cellular metabolism/neurotransmission→ cholinergic deficiency/ dopamine excess
inflammatory changes → neuroinflammation and microglial over activation → neurotics response and neuronal injury
permanent damage to neurons + cerebrovascular disease + head trauma
Does delirium lead to dementia?
can lead to dementia
may bring unrecognised cognitive impairments to attention
commonly coexist, bidirectional relationship
Formal cognitive screening tests
short portable mental status questionnaire
Montreall cognitive assessment
mini-Cog
CAM, 4As
How is an EEG used for delirium? (4)
•Differentiate functional/psychiatric disorders from organic
•Spot non convulsive epileptic episodes
•Deteriorating dementias
•Creutztfeldt-Jakob
How is an MRI/CT head used for delirium? (4)
•Acute neurological findings
•Hx or signs of fall with head trauma
•Suspected encephalitis
•Decreased level of consciousness and no other etiology
How can a lumbar puncture be used in delirium?
suspected meningitis, encephalitis or subarachnoid haemorrhage. Persistent delirium
What is the Hospital Elder Life Programme? (HELP) (5)
non pharmacological treatment
reorientation, mobility, therapeutic activities
reduction of psychoactives, sleep hygiene
hydration and nutrition
providing hearing/visual aids
interdisciplinary team
What pharmacological treatment is used in delirium?
Only use if high risk of self/harm others, or interrupting life sustaining treatment
rapid tranquillisation with lorazepam 0.5mg or midazolam 1mg IM → reassess every 15 mins
if important psychotic symptoms, lease with geriatrician or mental health advice on antipsychotics
Treatment for persistent hyperactive delirium >24h
Antipsychotics (1 week or less)
1st line quetiapine 25mg
2nd line olanzapine 2.5mg
3rd line risperidone 250mcg
Check QTc before starting