BIO1320 Class
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Hale's Second Semester Biology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Reductionism
reduction of complex systems to simpler components
Emergent Properties
emerge from the arrangement and interaction of parts within a system
blind men and the elephant prinicple
Systems Biology
constructs models for dynamic behaviour of biological systems
Predator - Prey Model
Unity and Diversity of Life
the concept that living organisms are modified descendants of common ancestors
accumulation of heritable changes contribute to differences in species
lots of supporting evidence
~evolution~
Taxonomy
the branch of biology that names and classifies into groups of increasing breadth
Carolus Linnaeus
Natural Selection
is a process in which individuals with favourable inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce
Descent with Modification
refers to the view that all organisms are related through descent from an ancestor that lived in the past
proposition that natural selection could cause ancestral species to give rise to two or more descendent species
Lyell’s Principle of Uniformitarianism
states that the mechanisms of change are constant over time
The Geologists
James Hulton
Charles Lyell
proposed changes in Earth’s surface can result from slow continuous actions still operating today
Catastrophism
speculation that each boundary between strata represents a catastrophic event
George Cuvier
Evolutionary Trees
are hypotheses about relationships among different groups
homologies form nested patterns in evolutionary trees
can be made using different types of data (anatomical or DNA sequence)
Biogeography
the study of the geographic distribution of species providing evidence of evolution
tracking/understanding Pangaea and continental movement to predict when and where different groups evolved
Endemic Species
species not found anywhere else in the world
Microevolution
is a change in allele frequencies of genes in a population over time
Mechanisms of Microevolution
Natural Selection
Genetic Drift
Gene Flow
Genetic Drift
describes the fluctuation of allele frequencies due to RANDOM CHANCE
small populations are most susceptible
tends to REDUCE genetic variation
two main types
Founder Effect
Bottleneck Effect
Founder Effect
occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population
smaller founder population often very different from parent population
the smaller founders LOSE genetic diversity
harmful genotypes may occur more frequently
Bottleneck Effect
a sudden reduction in population size due to a change in environment
volcano/flood/carrying capacity reached
the resulting gene pool may not contain the variation it once had
population with reduced diversity is vulnerable to further genetic drift
Gene Flow
consists of movement of alleles among populations
exchange of alleles between populations
keeps different populations very similar - won’t become individual species
Measures of Gene Variation
two primary measures:
gene variability (average heterozygosity)
nucleotide variability
Average Heterozygosity
measure of the average percent of loci that are heterozygous in population
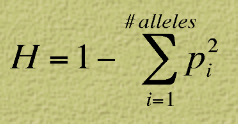
Heterozygosity
the state of having different alleles at a particular gene locus - measure of genetic variation within a POPULATION
Nucleotide Variability
is measured by comparing DNA sequences of pairs of individuals
rarely results in phenotypic variation
Gene Pool
consists of all the alleles for all loci in a population
Fixation
when all individuals in a population are homozygous for the SAME
Mendelian Population
a theoretical model of infinite size (no sampling error) consisting of:
completely random mating
No migration (in or out)
No mutation
No natural selection
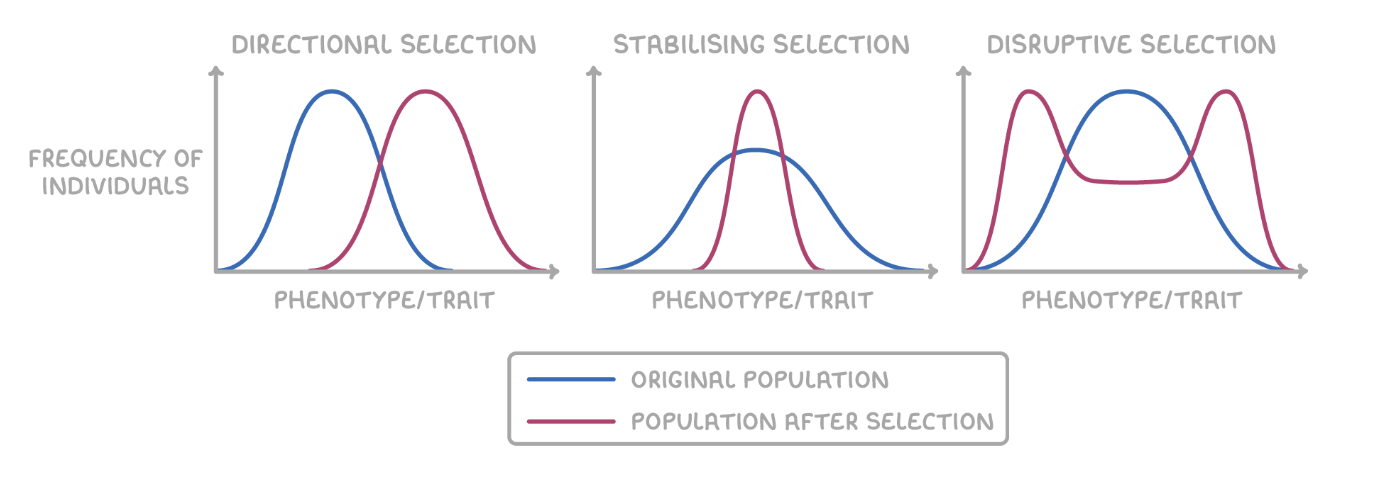
Modes of Selection
Directional Selection
favourable individuals at one end of the phenotypic range
Disruptive Selection
favours individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
Stabilizing Selection
favours intermediate variants and acts against extreme phenotypes
Sexual Selection
natural selections for mating success
can result in SEXUAL DIMORPHISM (marked differences between the sexes in secondary sexual characteristics
Intrasexual Selection
a direct competition among individuals (males) for mates
Intersexual Selection
aka mate choice
when individuals (female) are choosy in mate selection
more of a performance than competition
Speciation
the origin of new species is at the focal point of evolutionary theory
evolution explains how new species originate and how they evolve
Biological Species Concept
states a species is a group whose members have the potential to interbreed in NATURE and produce Viable and Fertile offspring
based on potential to interbreed rather than physical similarity
Allopatric Speciation
gene flow is interrupted when a population is divided into Geographically Isolated Subpopulations
definition of barrier depends on the ability of a population to disperse
separate populations may evolve independently through mutations, natural selection and genetic drift
reproductive isolation may arise as a result of genetic divergence
Sympatric Speciation
when speciation take place in a geographically overlapping populations
can occur if gene flow is reduced by factors including:
polyploidy
sexual selection
habitat differentiation
Polyploidy
the presence of extra chromosome sets due to ACCIDENTS during cell division
two main subtypes:
Autopolyploid
Allopolyploid
Autopolyploidy
when an individual has more than 2 chromosome sets derived from A SINGLE SPECIES
tetraploids
Allopolyploidy
a species with multiple sets of chromosomes derived from DIFFERENT SPECIES
Habitat Differentiation
the appearance of new ecological niches within the same geographical range
Hybrid Zones
a region in which members of a different species mate and produce hybrids
between species with incomplete reproductive barriers
3 potential outcomes
reinforcement
fusion
stability
Reinforcement Hybrid Zone
when hybrids are less fit than parent species
reinforces reproductive barriers
Fusion Hybrid Zone
if hybrids are a fit as parents
substantial enough gene flow between species to fuse into a single species
Stability Hybrid Zone
continued/steady production of hybrids
extensive gene flow outside the hybrid zone can overwhelm selection for increased reproductive isolation inside hybrid zone
Phylogeny
the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species
Systematics
the discipline that classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships
uses:
phenotypic data
fossils
molecular data
genetic data
Homoplasies
analogous structures or molecular sequences that evolve independently
Molecular Systematics
uses DNA and other molecular data to determine evolutionary relationships
Cladistics
the process that groups organisms by common descent
Monophyletic Clade
signifies that is consists of the ancestor and ALL its descendants
Paraphyletic Clade
consists of ancestor but NOT ALL of its descendants
Polyphyletic Clade
grouping includes distantly related species but not their most recent common ancestor
avoided at all costs
Maximum Parsimony
assumes the shortest number of events is the best way to build the evolutionary tree/pathway
Maximum Likelihood
states that the rules of how DNA changes reflects the most likely evolutionary pathway
DNA Barcodes
species can be identified using their CYTOCHOME OXIDASE (COI) gene sequence as barcode
used to compare molecules to infer relatedness
Key Factors of Genetic Evolution
rRNA code changes very SLOWLY making it useful for branch-point investigation
mtDNA evolve rapidly making it useful to explore recent evolution
Orthologous Genes
same gene in different species as a result of divergent speciation
99% of human genes are orthologous with mice
Paralogous Genes
two copies of a gene in one species
creates a larger genome
Molecular Clock
uses constant rates of evolution in some genes to estimate the absolute time of evolutionary change
Taxis
in a heterogenous environment bacteria may exhibit the ability to move toward or away from a stimuli
Phototaxis, Chemotaxis, Geotaxis
Genetic Recombination in Prokaryotes
combining DNA from two sources
3 methods:
transformation
transduction
conjugation
Genetic Recombination: Transformation
the passive/random take up and incorporation of DNA from surroundings
Genetic Recombination: Transduction
movement of genes between bacteria via BACTERIOPHAGE
Genetic Recombination: Conjugation
the process where genetic material is transferred between prokaryotes directly via the SEX PILUS
requires F-Factor
Conjugation in 3 Steps
a donor cell (cell containing F-Factor) attaches to a recipient
donor pulls recipient closer
donor donates DNA
the F-Factor is transferable via conjugation
Metabolic Cooperation
intraspecies cooperation to allow individuals to use resources more easily
occurs in biofilms
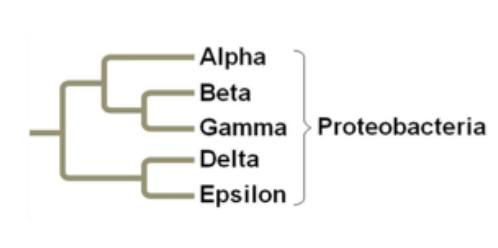
Proteobacteria
the largest group of Gram Negative bacteria
examples:
E. Coli
Salmonella
Campylobacter
Firmicutes
largest group of Gram Positive bacteria
examples:
bacillus + clostridium
staphylococcus
streptococcus
lactobacillus
Extremophiles
archaea that live in extreme environments
Extreme Halophiles
live in high saline environment
Extreme Thermophiles
thrive in very hot environments
Methanogens
archaea that live in swamps. and marshes and PRODUCE METHANE as waste
strict anaerobes
Exotoxins
are secreted and cause disease even if prokaryote is not present
Endotoxins
are released only when bacteria die and their cell walls break down
common in gram negative bacteria
Protists
unicellular eukaryotes
exhibit more structural and functional diversity then any other group of eukaryotes
nutritionally diverse
photoautotrophs
heterotrophs
mixotrophs
some reproduce asexually others sexually or via meiosis/fertilization
Supergroups
eukaryotes can be divided into 4 supergroups including protists
Excavata
SAR
Archaelplastidia
Unikonta
Supergroup: Excavata
some have a groove on one side of the cell body
includes parasites, many predatory and photosynthetic species
examples:
Diplomonads
Euglenozoans
Excavata - Diplomonads
have modified mitochondria (MITOSOMES)
anaerobic biochemical pathways
2 equal sized nuclei and multiple flagella
often parasites → Giardia
Excavata - Euglenozoans
spiral or crystalline rod inside their flagella
some are mixotrophic
Supergroup: SAR
diverse monophyletic group
named for 3 major clades
STRAMENOPILES
ALVEOLATES
RHIZARIANS
a controversial group due to lack of evidence
examples:
Diatoms
Dinoflagellates
Ciliates
Apicomplexans
Brown Algae
SAR - Diatoms
unicellular algae
unique 2-part, glass-like wall of silicon dioxide
major component of phytoplankton
highly diverse
SAR - Dinoflagellates
2 flagella and reinforced by cellulose plate
abundant component of phytoplankton
cause toxic red-tides
SAR - Ciliates
large and varied group of protists
use cilia to move and feed
have large MACRONUCLEI and small MICRONUCLEI
exchange haploid micronuclei via conjugation
SAR - Apicomplexans
parasites
spread via SPOROZOITES
one end = the APEX
contains a complex of organelles specialized for penetrating host cells/tissues
have sexual and asexual stages that require two or more host species for completion
SAR - Brown Algae
largest and most complex algae
multicellular
mostly marine
have plant-like structures:
rootlike → HOLDFAST
stemlike → STIPE
leaflike → BLADES
includes some species of ‘seaweed’
Supergroup: Archaeplastidia
a monophyletic group
descended from protists that engulfed cyanobacterium
examples:
Red Algae
Green Algae
Land Plants
Archaeplastidia - Red Algae
reddish due to PHYCOERYTHRIN accessory pigment that masks chlorophyll
usually multicellular → largest seaweeds
most abundant large algae. in tropical coastal waters
Archaeplastidia - Green Algae
aka - CHLOROPHYTES and CHAROPHYTES
named for grass-green chloroplasts
ancestor of plants
paraphyletic group
most are freshwater some marine
Chlorophytes can live as symbionts in lichens, in high visible light and UV light environments
Supergroup: Unikonta
extremely diverse - including aminals, fungi and some protists
2 main clades
AMEOBOZOANS
OPISTHOKONTS
root of eukaryotic tree (unclear timline)
example = Slime Molds
Slime Molds
resembles fungi due to convergent evolution
2 lineages
Plasmodial Slime Molds
Cellular Slime Molds
Plasmodial Slime Molds
brightly pigmented (usually yellow or orange)
PLASMODIUM = a mass formed during lifecycle
not multicellular
undivided by membranes
contains many diploid nuclei
extends pseudopodia
Cellular Slime Molds
form multicellular aggregates
cells separated by their membranes
cells feed individually but can aggregate to form a fruiting body
Traits of Charophytes and Land Plants
rings of cellulose
structure of flagellated sperm
formation of cell plate during cell division
shared genes for nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Derived Traits of Land Plants
Alteration of Generations
Multicellular Dependent Embryos
Walled Spores
Multicellular Gametangia
Apical Meristems
also:
the Cuticle
Mycorrhizae Relationships
Gametangia
organs responsible for producing gametes
Female Gametangia = ARCHEGONIA
Male Gametangia = ANTHERIDIA
Leaf Categories
1 - Microphylls = single vein
2. -Megaphylls = highly branched vascular system