SE 4351 Requirements Engineering (MODELS)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What does the Why-What-How model consist of?
Enterprise Requirements (WHY?)
the reason why the system is to be created
(System) Functional Requirements (WHAT?)
a description of what system is to do
(System) Non-Functional Requirements (HOW?)
constraints on how the system is to be constructed & function
In the WRSPM Model what is Domain Properties?
Things in the environment (application domain) that are true regardless of the proposed system.
phenomena/things not observable by machine (eh)
q
In the WRSPM Model what is Requirements
Things in the application domain that we wish to be made true through the proposed system.
In the WRSPM Model what is Specification
A description of the behaviors that the program must have in order to meet the requirements.
phenomena/shared things
domain-controlled (ev)
machine-controlled (sv)
Enterprise Model: Four worlds of RE?
System Worlds (FRs, NFRs)
Subject Worlds (problem domain accountants, bankers, loan mgrs)
User Worlds (tellers, clients, mgrs)
Developer Worlds (analysist, specifers, designers, mgrs)
Four worlds of RE for Information Systems?
Subject System
Information Systems
Development Systems
Usage Systems
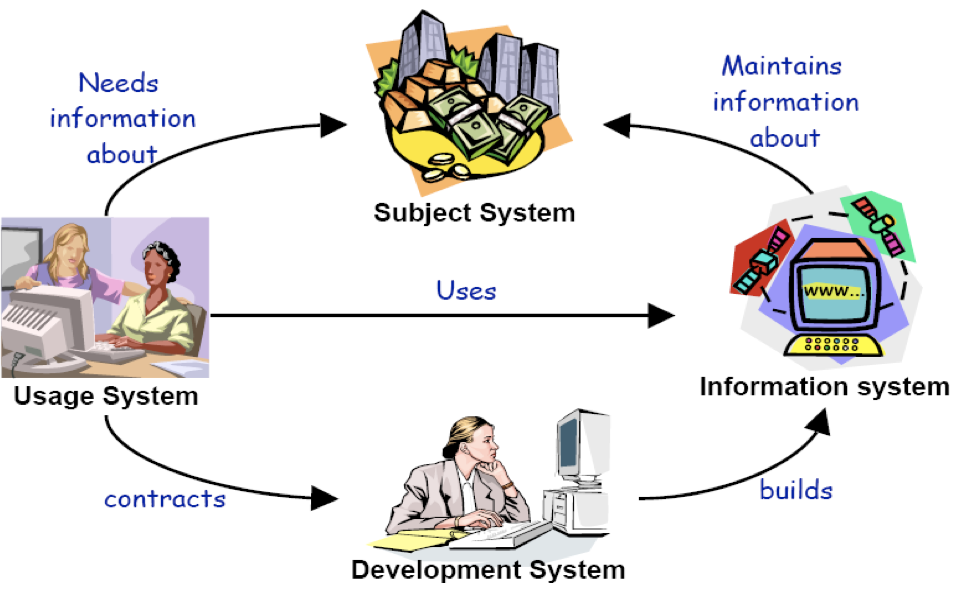
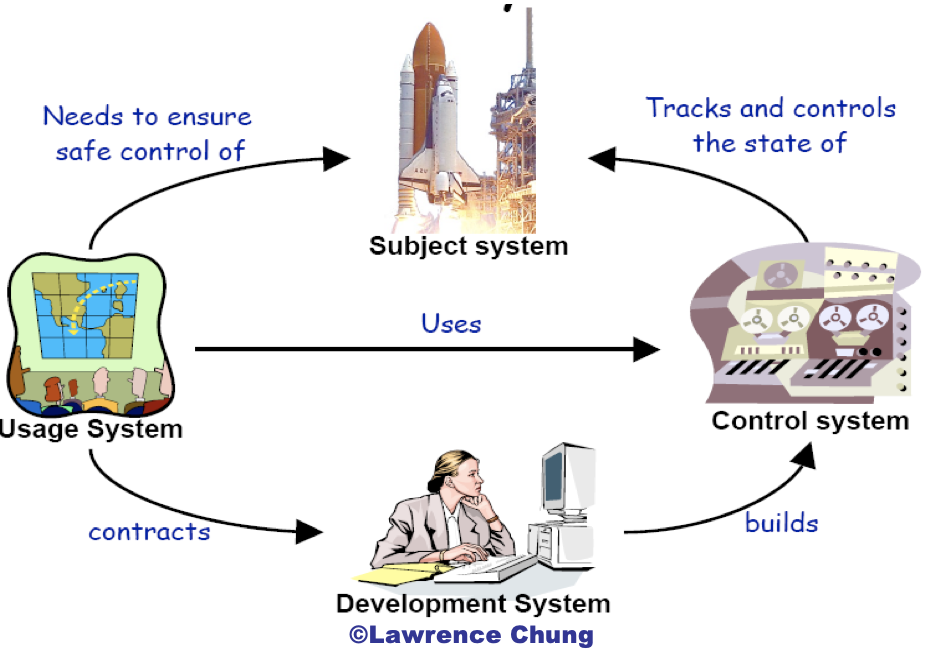
Four worlds of RE for Control Systems?
Subject Systems
Control Systems
Development Systems
Usage Systems
The WRSPM Model should contain…
Requirements: Nothing but information about the environment.
The 4 Variable Model: NAT(m, c)
describes nature without making any assumptions about the system;
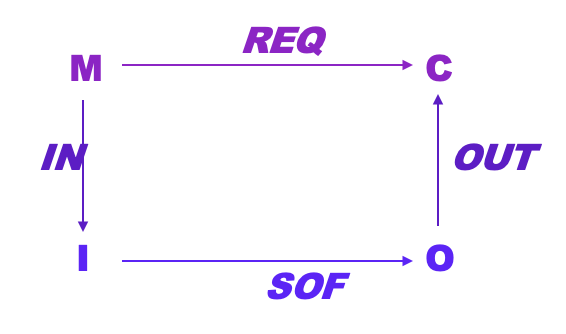
The 4 Variable Model: REQ(m, c)
describes the desired system behavior;
The 4 Variable Model: IN(m, i)
monitored real-world values to their corresponding internal representation;
The 4 Variable Model: OUT(o, c)
relates the software-generated outputs to external system-controlled values;
The 4 Variable Model: SOF(i, o)
relates program inputs to program outputs.
What is a Reference Model?
WRSPM (World, Requirements, Specification, Program, Machine)
Security means…
Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability
In the Reference Model what is “eh”
Not observable by the machine (Domain Properties)
In the Reference Model what is “ev”
Domain-Controlled (Specification)
In the Reference Model what is “sv”
Machine-Controlled (Specification)
In the Reference Model what is “sh”
Not observable by domain/program (Program)
Match 4-Var with Event Type: m (monitor)
ev
Match 4-Var with Event Type: i (input)/ o (output)
sh
Match 4-Var with Event Type: c (control)
sv
Can sh in one system be turned into sv in another system?
Yes sh (not observable) in one system can be transformed in another system if specifications change to observed and controlled.
EX: Elevator is initially eh but when sensor is used to detect people waiting it then becomes sv
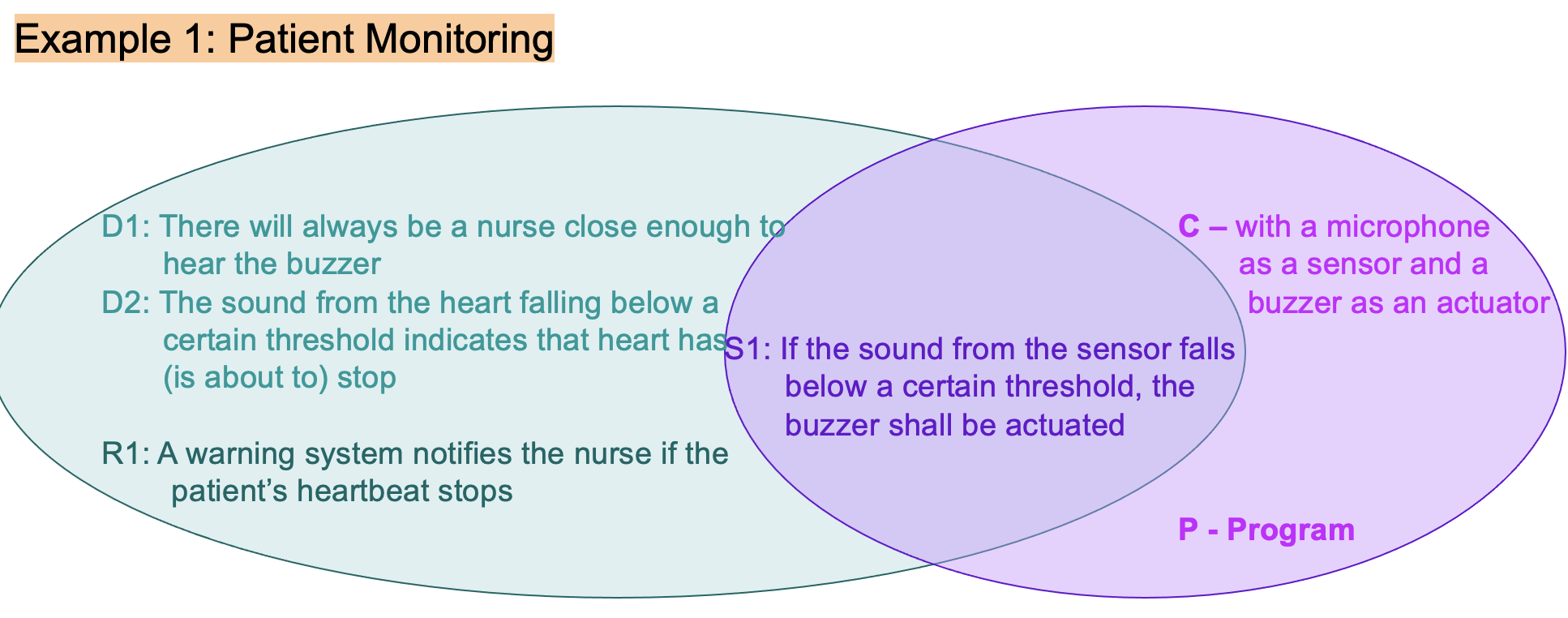
What are two major issues in patient monitoring example?
False alarm notifications
Assumptions that healthcare staff is nearby to hear the buzzer.
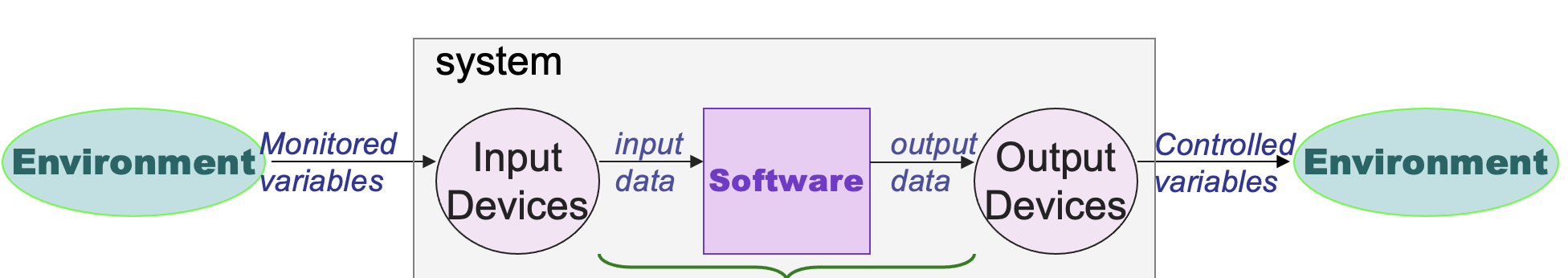
RE are only concerned with 2 out of 4 variables what are they?
Monitored & Controlled Variables
In the WRSPM model what does each element need?
It needs a unique identifiers (“FR1”, “NFR1”)