BIO 120 contd.
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Plants do not have ____, so spindles tend to be broader at poles. (“acentrsomal“ spindles)
centrosomes
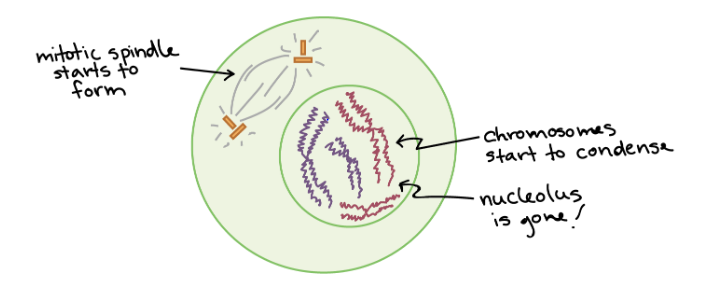
This is the ______ stage of mitosis.
early prophase
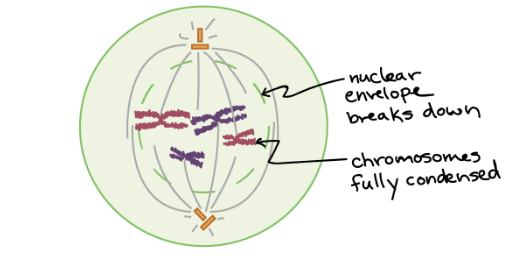
This is the ________ stage of mitosis
late prophase (prometaphase)
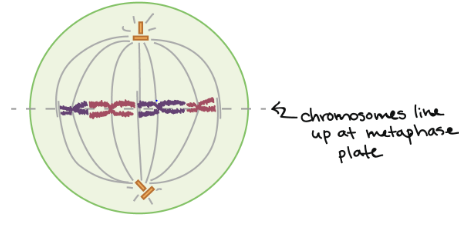
This is the _______ stage of mitosis.
metaphase
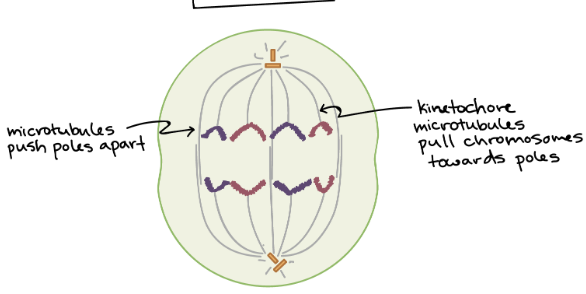
This is the _________ stage of mitosis.
anaphase
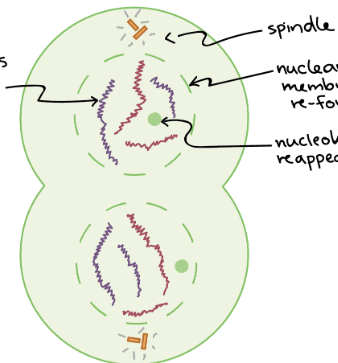
This is the ________stage of mitosis
telophase
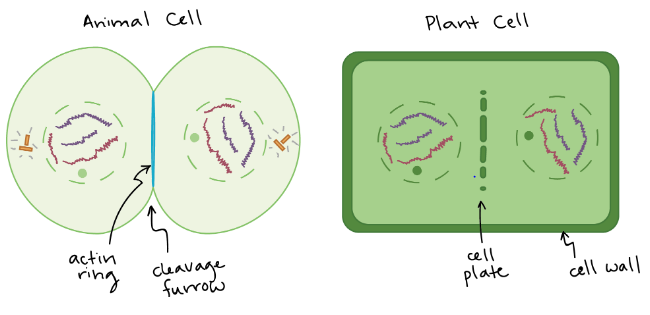
This is the _______ stage of mitosis. It usually overlaps with the telophase.
cytokinesis
PASS ME A TACO CHEF, stands for what?
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
cytokinesis
mention the two membrane protein locations
integral membrane proteins
peripheral proteins
_____ proteins sit on the surface of the membrane and form non-covalent bonds with lipids and membrane proteins
peripheral
Transmembrane or __________ proteins contain hydrophobic domains that cross the bilayer
integral membrane
mention four major functions of membrane proteins
signal transduction
enzymes
transporters
cell recognition/surface attachment
Stretches of non-polar amino acids indicate ______________ proteins (that is, even though they also have polar ends, there is a stretch of non-polar ones)
the polar
transmembrane
the polar charged amino acids are _________ while the non-polar charged amino-acids are ___
hydrophilic (can mix with water)
hydrophobic (water resistance, can only dissolve in oil-based substances)
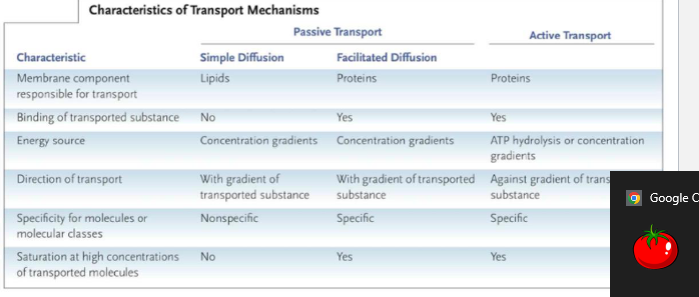
mention three ways of movement across membranes and the amount of energy required
passive transport - no energy required
active transport - energy required
exo/endocytosis
In ____________ transport, transport from high to low concentration is driven by increase in entropy.
while in _________ transport, transport against the concentration gradient (low to high con.) requires ________
passive transport
active, energy
passive transport consists of _____ and _____
diffusion
facilitated diffusion
H20, indole, glycerol are all ____________ molecules
glucose, sucrose are _________ molecules
O2, CO2, N2 are _________ molecules
Cl-, K+, Na+ are ______ molecules
small uncharged polar
large uncharged polar
non-polar
ions (also polar)
The difference between osmosis and diffusion is that in diffusion, _____ move from high to low conc.
But in osmosis, _______ move from high to low conc.
solutes
solvents
For osmosis to work, the _______ cannot pass through the membrane, only the solvent.
solute
todo : know difference between hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic
The difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion is that in facilitated diffusion, solutes move through with the aid of __________
membrane proteins
mention the three kinds of proteins involved in facilitated diffusion
channel proteins
carrier proteins
gated channel proteins
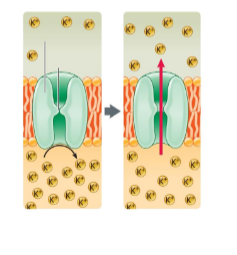
These are ________ proteins
gated channel proteins
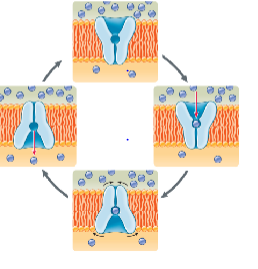
These are _____ proteins
carrier
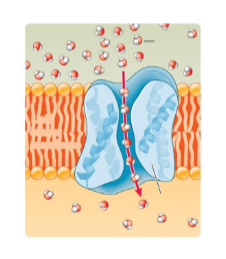
These are _____ proteins
channel
osmosis is a kind of diffusion, under ____ transport.
passive
mention the two types of active transport
primary
secondary
primary transport is a kind of active transport that uses ____
secondary transport uses ____
ATP
electrochemical gradients
active transport uses energy because it moves against the concentration gradient. that is, it moves from _____ conc. to ______ conc.
low concentration to high concentration
1 ̊ active transport is ______. An example is the sodium-potassium pump.
Inside an animal cell, the ion concentrations are high in ____ but low in _____.
Outside the cell, the concentrations are reversed, so it is high in _____ and low in _____
primary transport
high in potassium, low in sodium
******
high in sodium, low in potassium
2° active transport is ____. It does not use ATP but instead _________ or electrochemical for energy.
Energy released from the ion as it moves with its concentration is used to drive movement of a solute ____ its concentration gradient.
secondary transport
ion gradients
against (low to high)
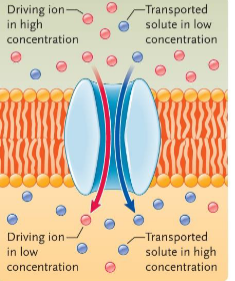
the transported solute moves in the same direction as the gradient of the driving ion. this is called _____ or cotransport
symport
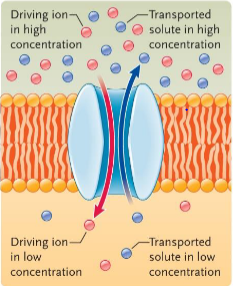
the transported solute moves in the direction opposite from the gradient of the driving ion. this is called ____ or exchange diffusion
antiport
mention the two types of exo/endocytosis
exocytosis
endocytosis
mention the three types of endocytosis
receptor-medicated (e.g LDL cholesterol)
bulk-phase or pinocytosis (pino means to drink)
phagocytosis (phago means to eat)
learn.
yes?
yes
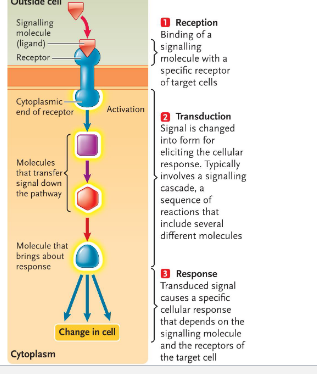
show the process for signal transduction
reception (signal) → transduction → response
_____ is an enzyme that phosphorylates other proteins things using ATP
kinase
learn
yes?
yes
_________ is a common procedure used to separate organelles and other sub-cellular particles based on their sedimentation rate. e.g low speeds for big dense stuff and high speeds for small, light stuff
differential centrifugation
outline the process for differential centrifugation
spin → pour out supernatant → spin supernatant faster
collect pellet after each step
(supernatant are the lighter materials floating above the the pellet)
when centrifuging whole cells, first we homogenize the cells (break it down).
then we do a slow spin to get the big stuff like ____
then we gather up what is floating at the top (supernatant) and spin it faster to get smaller fragments like _______ and _____
gather up supernatant and spin even faster to get smaller stuff like _____, _____ and ____
nuclei
mitochondria, chloroplasts
ribosomes, proteins, nucleic acids
we discussed two main research methods, differential centrifugation and _____ which won the Noble Prize in chemistry 2008
green fluorescent protein (GFP)
green fluorescent protein (GFP) is good for visualizing subcellular structures such as organelles and membranes
also good for:_
visualizing whole cell behaviour
whole-organ growth and physiology
molecular scale processes
true or false?
true
mention four things the nucleus consists of.
a nucleus is an _____ (an organ ish found in the cell)
organelle
nuclear pore complex
nuclear envelope
chromatin
nucleolus
nuceloplasm
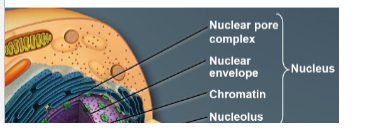
the double membrane surrounding the nucleus is the _______
DNA + associated proteins in the nucleus are stored in the _____
the site of the ribosomal subunit assembly is at the _____
these determine what goes in and and out of the nucleus ____
the “cytoplasm“ of the nucleus _____
nuclear envelope
chromatin
nucleolus
nuclear pore complex
nucleoplasm
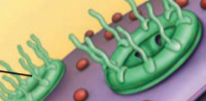
the green hairy looking things are the ______ found in the nucleus
nuclear pore complex
prokaryotic cells are _____ (they lack a nucleus).
protists cells are ____ (have more than one nucleus) e.g _____
anucleate
multinucleate, amoeba
some cells lose their nucleus as the mature, e.g ____________ cells (hint : mammalian and blood)
mammalian blood cells
mention the 7 parts of the endomembrane system and membrane trafficking
nuclear envelope
Golgi
lysosomes
vacuoles
plasma membrane
nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
the nuclear envelope is an extension of the ______. This is mainly due to _________ after anaphase
endoplasmic reticulum
cell division
the ____________ system is responsible for metabolic activities like breakdown, storage, synthesis
vesicles carry stuff from compartment to compartment. The vesicle contents are released, then the vesicle membrane gets incorporated into target membrane and the vesicle membrane proteins gets incorporated into _____
target membrane
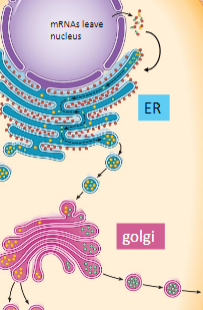
outline the process of how vesicles move
ER → Golgi → Plasma membrane
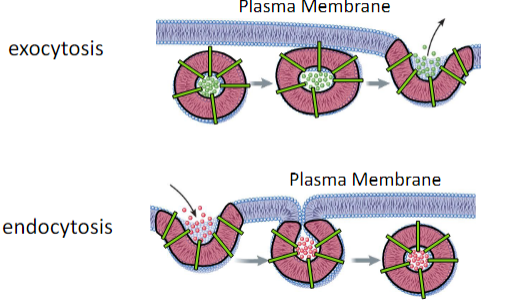
facilitated diffusion involves the help of _____
membrane proteins
carrier proteins
channel proteins
gated channel proteins
endocytosis has three types, it involves the use of vesicles.
phagocytosis (to eat)
pinocytosis (to drink)
receptor medicated
pinocytosis is how our cells absorb nutrients.
phagocytosis would be how our red blood cells kill bacteria
receptor medicated would be for absorbing specific substances, like cholesterol
mention the stages of interphase
G1 phase - cell is just growing
S (synthesis phase) - genetic material starts replicating, we get two centrosomes and the chromosomes duplicate into sister chromatids but are still the same amount prior.
G2 phase - cell grows even more, preparing for mitosis
G1 → S → G2
the plasma membrane is also called ______
cell membrane
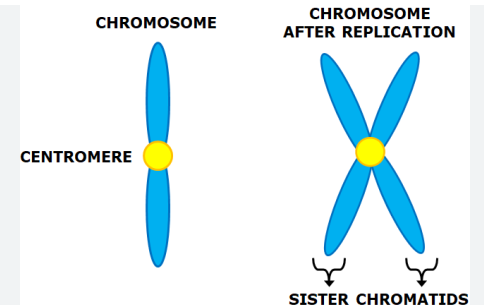
during the G2 stage, although the cell replicates its genetic material, it does not double the number of existing chromosomes, they just increase in size since they are copies joined to one.
these are called ______
sister chromatids
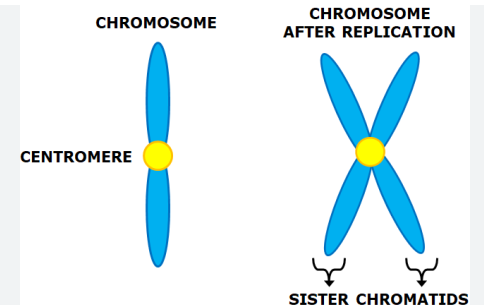
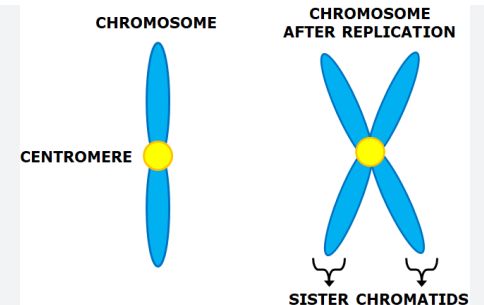
the middle of where the two sister chromatids are joined is called the ________
centromere
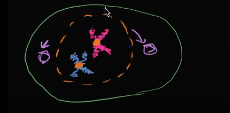
In the ______ stage of mitosis, the sister chromatids become more condensed, and the nuclear membrane starts to go away. The centrosomes also start separating to the sides
prophase
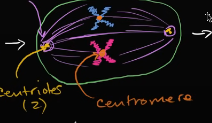
In the _____ stage of mitosis, the microtubules from the centrosomes latch onto the sister chromatids and line them on a plate.
also, each centrosome contains _____ centriole
metaphase
2 centrioles ( 1 centrosome = 2 centrioles)
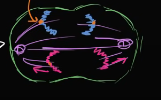
In the ____stage of mitosis , the microtubules pull the sister chromatids apart so they are double chromosomes (i.e 2 sister chromatids are now 4 chromosomes) and have one of each on either side
instead of the centromere holding the sister chromatids together, the microtubules now latch on to the kinetochore of each chromosome.
anaphase
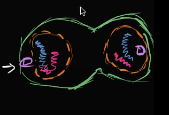
In the _____ of mitosis, the nuclear envelopes start to form around each pair of chromosomes
telophase
______ is really what divides the cells together after telophase, taking us back again to _____
cytokinesis
interphase
the endoplasmic reticulum has two parts : _____ and ______
ribosomes are found in the ________
smooth ER
rough ER
rough ER - ribosomes
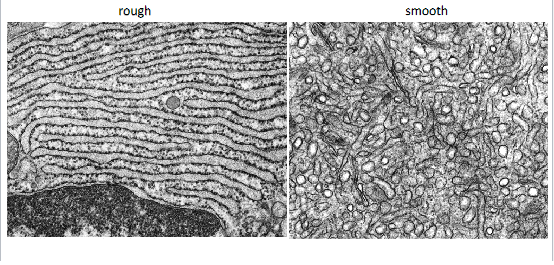
lipid synthesis and detoxification occurs in the __________ of the endoplasmic reticulum. This part also contains ____ cisternae
protein translation, folding and modification occurs in the ______ of the endoplasmic reticulum. Contains ___ cisternae
smooth ER - tubular cisternae
rough ER - flattened cisternae
after ribosomes in the rough ER translate mRNA to protein, they can either stay in the ___ of the rough ER or be packaged into vesicles and sent to the _____
lumen of the rough ER
golgi
_______ synthesizes lipids, phospholipids and steroids. Not abundant in most cells, only the ones that need to secrete those substances.
also present in cells that detoxify drugs and alcohol
smooth ER
________ receives vesicles containing protein from the ER and other locations and adds molecules to them preparing them to be delivered to different parts of the cell in vesicles.
like a post office of some kind
golgi bodies
lysosomes are not present in what organism? _____
plants
_______ are like the trash can of the cell. It is acidic like the stomach and hydrolyses or kills internal and external stuff.
internal stuff like old organelles and/or cells not working properly are hydrolyzed in a process called ________ (degrading of cells)
external stuff like bacteria and debris are engulfed by _____
lysosomes
autophagy
phagocytosis
________are present in animals, plants and fungi. Only plants and fungi would have a large central vacuole though, animals have multiple smaller ones
they are like specialized lysosomes
some of their functions
digest waste products
sometimes contain pigments
turgor pressure
storage of nutrients
maintain ion gradients
vacuoles
cell organelles can be organized into five parts
nucleus
endomembrane system
semi-autonomous organelles
cytoskeleton
extracellular matrices
what sets the endomembrane system apart, is that they send or receive _____. So even though semi-autonomous organelles are surrounded by membranes, they are not part of the system.
vesicles
mention the semi-autonomous organelles of a cell
mitochondria
chloroplasts
the two semi-autonomous organelles, mitochondria and chloroplasts use electrochemical reactions to make ___________. They have internal membranes with extensive folding to increase ____ of the energy-producing machine
energy
surface area
mitochondria and chloroplasts are referred to as semi-autonomous because they can almost operate entirely on their own.
they have their own:-
a) _________
b) _________
c) __________
d) ___________
genome, although most of them were lost or transferred to the host cell
replicate on their own (like cell division)
own ribosomes and make their own proteins, but most proteins still come from the host cell
have double membranes
they also have similar shapes and sizes as modern prokaryotes
there is a theory that semi-autonomous cells like the mitochondria and chloroplasts were once prokaryotic microbes like cyanobacteria once living independently but have now evolved to rely on the host cell and lost independence.
endosymbiotic theory
mitochondria is responsible for _________ in organisms while chloroplasts are responsible for ______
respiration
photosynthesis
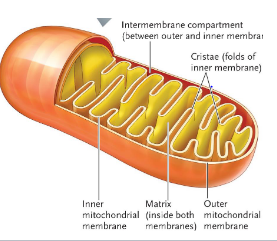
the ______ is the source of all cellular respiration which creates ATP. it has ____ membrane and the inner membrane has folds called ___
the ____ is the "cytoplasm” of the mictochondria
mitochondria
two membranes
cristae
matric
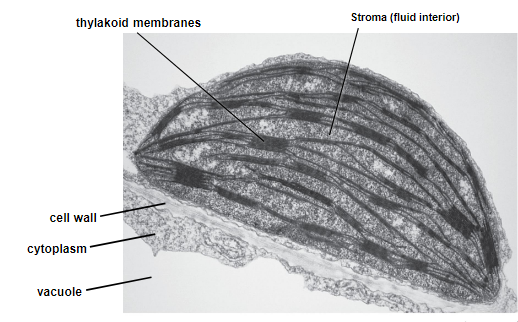
chloroplasts perform photosynthesis which generates _____.
The ______ is the “cytoplasm“. It has ___ membranes, two boundary membranes and one internal thylakoid membrane.
stacks of thylakoids are called _____. Photosynthetic reactions occur in the _________ and ________
sugars
stroma
three
grana
thylakoids and stroma
plastid types have roles in storage and pigmentation. They descended from chloroplasts.
Mention two and which one have pigments
chromoplasts - has pigments for organ colouration
leucoplasts - no pigments. e.g amyloplasts - starch storage and proteinoplast for protein storage