Bin Packing and Data Clustering
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
what is bin packing?
fitting items effectively into a container
2
New cards
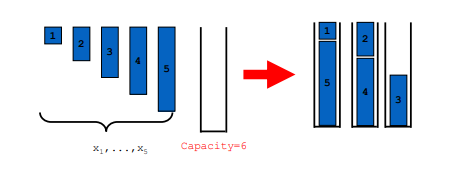
what is the bin packing problem?
a combinatorial problem
a number of items n of size x1…xn need to be put into the smalles number of bins of capacity c
a number of items n of size x1…xn need to be put into the smalles number of bins of capacity c
3
New cards
what are bin packing algorithms?
algorithms that solve the bin packing problem
4
New cards
what are the applications of bin packing algorithms?
filling recycle bins
tape compilations
tv advertisement time
tape compilations
tv advertisement time
5
New cards
what is an example of a bin packing algorithm?
first-fit decreasing algorithm
many other algorithms exist
many other algorithms exist
6
New cards
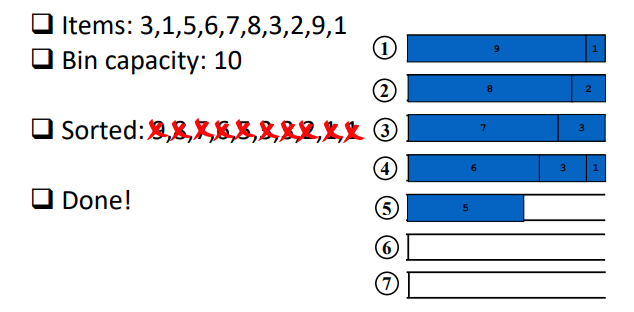
what is the first-fit decreasing algorithm?
1. n empty bin are created and numbered 1..n
2. items to be packed are sorted in descending order
3. starting from largest item, pack item into the first bin it fits into
4. any empty bins at the end are discarded/ignored
7
New cards
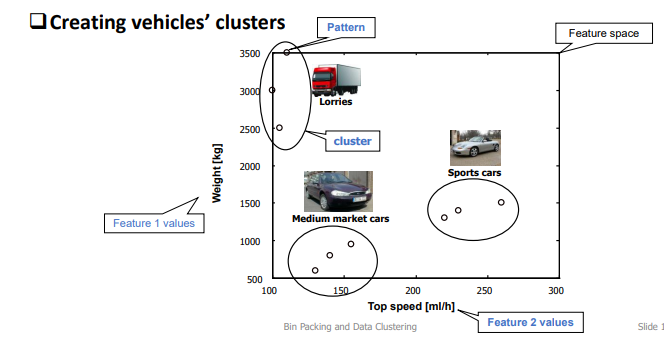
what is data clustering?
the process of arranging objects (as data points) into a number of sets \[k\] according to a metric \[e.g., *distance]*
8
New cards
what is a pattern?
physical objects
9
New cards
what is a cluster?
a set/ category of objects
10
New cards
what is a feature?
an attribute of an object
objects with similar features are grouped together
data can be grouped based on 1 feature or multiple (eg. group by age vs. group by age and weight)
objects with similar features are grouped together
data can be grouped based on 1 feature or multiple (eg. group by age vs. group by age and weight)
11
New cards
how do objects relate in data clustering?
* each set ideally shares a common trait (eg. similarity or proximity for some defined distance measure)
* each set is called a cluster/ group
* each set is mutually exclusive (item cannot be in multiple clusters)
* objects in 1 cluster are dissimilar to the objects in other clusters
* each set is called a cluster/ group
* each set is mutually exclusive (item cannot be in multiple clusters)
* objects in 1 cluster are dissimilar to the objects in other clusters
12
New cards
given a set of data, what do we already know about it?
the features of each object in the data set - features represented using a feature vector
13
New cards
what is a feature vector?
in a feature vector there is an object x, and the \[ \] shows the values of its features e.g., first 1 has 2 features, 2nd x has d features. compare the feature vectors of objects to cluster the date
![in a feature vector there is an object x, and the \[ \] shows the values of its features e.g., first 1 has 2 features, 2nd x has d features. compare the feature vectors of objects to cluster the date](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/62d3cf1c042d4cf7b5d9c0f958872456.jpeg)
14
New cards
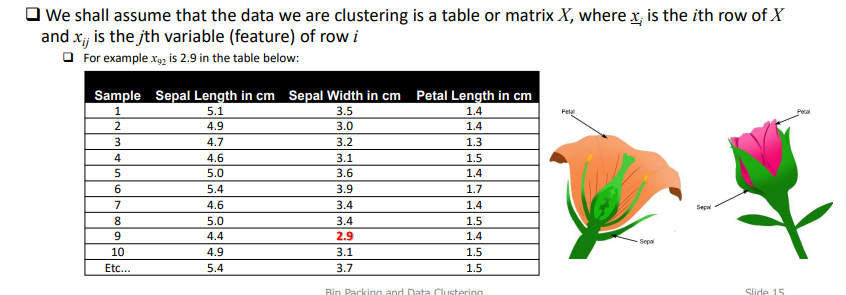
what type of data can we use for clustering?
data in a table/matrix X, where xi is the ith row of the table and xij is the jth variable (feature) of row i
15
New cards
how do we interpret data in a matrix to be used for clustering?
* columns = features = objects with similar features grouped together. (header shows the actual feature, the y axis shows that object’s value in a certain feature)
* rows = the objects
rows need to be clustered together based on how similar the values of their feature are
* rows = the objects
rows need to be clustered together based on how similar the values of their feature are
16
New cards
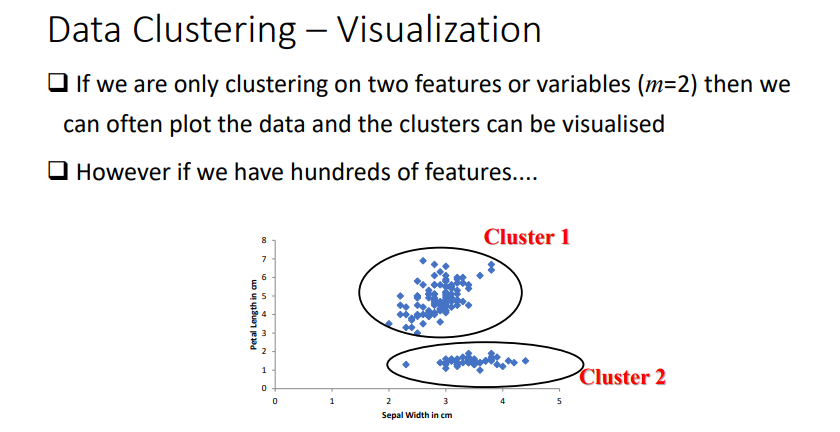
how can data clustering be visualised?
is using 2 features we can plot data as a graph
cannot do this with hundreds of features
cannot do this with hundreds of features
17
New cards
why do we need to clustering?
it is a data analysis technique which helps us understand how objects are related
* less complex to model
* clustering is used as a pre-processing tool
* can give us insight into an object’s unknown properties
* less complex to model
* clustering is used as a pre-processing tool
* can give us insight into an object’s unknown properties
18
New cards
what are the applications of data clustering?
retail - identify households via: household income, household size, distance from urban area
\
sports science - identify players via: points per game, assists per game, steals per game
\
health science - health companies cluster via: household size, number of doctor visits, average household age
\
sports science - identify players via: points per game, assists per game, steals per game
\
health science - health companies cluster via: household size, number of doctor visits, average household age
19
New cards
when implementing clustering after data has been collected, what do we need to consider?
* cluster representation
\
* @@data similarity@@ - how can we determine if one data object is similar to another data object - eg. using distance or a different metric
* @@cluster worth@@ - how to evaluate our cluster results and know if they are good or not
* @@clustering method@@ - what clustering method do we use
* @@number of clusters@@ - do we need to define the number of clusters to make ourselves (kmeans = yes vs. hierachal = no)
\
* @@data similarity@@ - how can we determine if one data object is similar to another data object - eg. using distance or a different metric
* @@cluster worth@@ - how to evaluate our cluster results and know if they are good or not
* @@clustering method@@ - what clustering method do we use
* @@number of clusters@@ - do we need to define the number of clusters to make ourselves (kmeans = yes vs. hierachal = no)
20
New cards
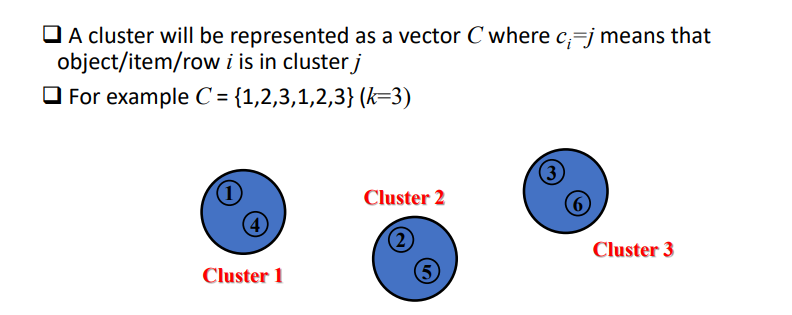
how are clusters represented?
index 0 is in cluster 1, since there are two 1s in the set C that means there are 2 items in cluster 1, eg. index 1 is in cluster 2
21
New cards
what is data similarity?
the distance between the various data points from the data. different metrics can be used to measure similarity e.g., distance, and different methods are used to measure the different metrics.
22
New cards
how does data similarity affect clustering?
* rows are compared to each other
* clustering methods use the measure data similarity to place similar rows into the same cluster
* a better distance function means better cluster algorithm performance
* clustering methods use the measure data similarity to place similar rows into the same cluster
* a better distance function means better cluster algorithm performance
23
New cards
what methods are there to measure data similarity?
* **Euclidean distance** - used by k means method
* correlations
* pearson
* spearman
* kenda
* manhattan distance
\
choose simplest one for given data
* correlations
* pearson
* spearman
* kenda
* manhattan distance
\
choose simplest one for given data
24
New cards
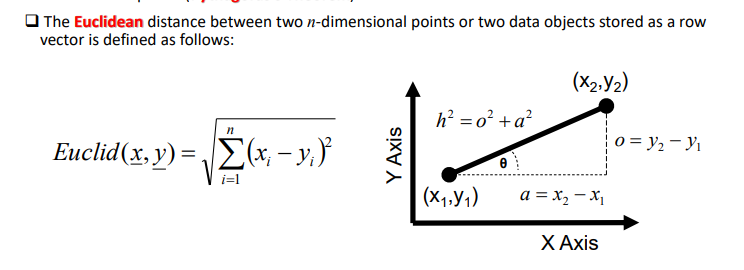
what is Euclidean distance
the shortest distance between 2 points
* 2D - length of the right angle constructed between the 2 points aka Pythagoras's theorem. needed if we have a graph or don’t directly have th exact distances
* 2D - length of the right angle constructed between the 2 points aka Pythagoras's theorem. needed if we have a graph or don’t directly have th exact distances
25
New cards
what is cluster worth?
used to evaluate the goodness of clustering algorithm results - how good the actual clusters created were
* different ways to judge the worth of a clustering arrangement so need to choose the right worth metric for success. each metric has different methods to measure it
* different ways to judge the worth of a clustering arrangement so need to choose the right worth metric for success. each metric has different methods to measure it
26
New cards
what type of metrics can be used to measure cluster worth?
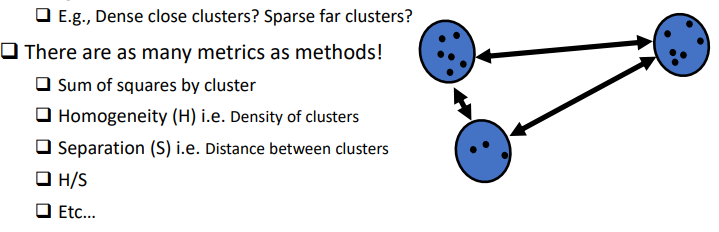
27
New cards
what is the sum of squares by cluster metric?
for one cluster, calculate each elements distance from the cluster’s centre, square each distance and sum them
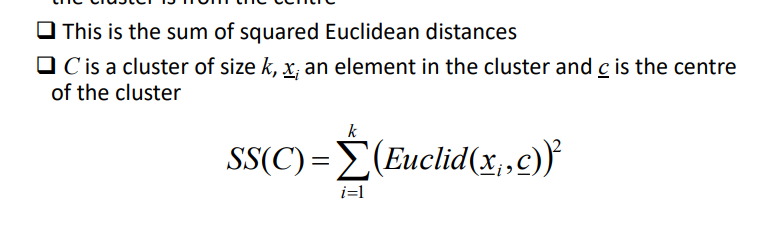
28
New cards
what is the impact of the number of clusters on a clustering method?
* Some applications need the number of clusters a solution creates specified and some applications do not eg. hierarchal clustering will cluster into a tree format and not K number of clusters, K-means groups into K clusters
* Determining the number of clusters is very difficult
* Need a method to find the number clusters and their contents
* Determining the number of clusters is very difficult
* Need a method to find the number clusters and their contents
29
New cards
what is a clustering method/ algorithms?
sequence of events that carries out the data clustering
30
New cards
what are the different types of clustering algorithms?
* Centroid-based clustering
* K-Means
* Hierarchical clustering - categorise data into a tree
* Density-based clustering - determine if dense or sparse items
* Distribution-based clustering
* Optimisation / Search AI
* Hill Climbing and Simulated Annealing
* K-Means
* Hierarchical clustering - categorise data into a tree
* Density-based clustering - determine if dense or sparse items
* Distribution-based clustering
* Optimisation / Search AI
* Hill Climbing and Simulated Annealing
31
New cards
what is K-means clustering?
1. requires the number of clusters K to be defined and maintains each cluster’s means - **centre** points
2. judges the worth of a clustering arrangement based on the square of how far each item in the cluster is from the centre
32
New cards
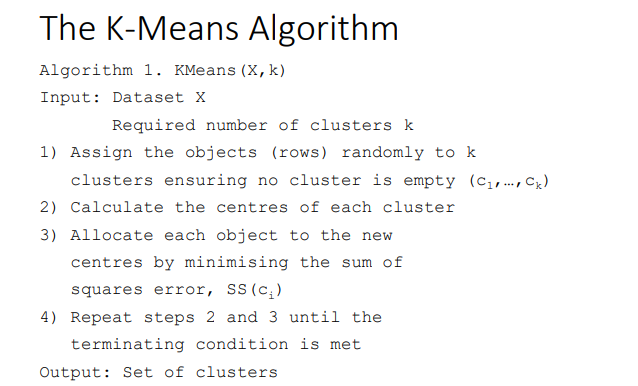
how does the k-means algorithm work?
1. create k amount of ***centres (means)*** and place them in random locations on the matrix. each centre will form a cluster a cluster
2. for each data point/ object/ row, assign it to the closest centre. (for each row, calc the distance between object and each centre and pick centre with shortest distance)
3. for each cluster, calculate the mean of all the data points in that cluster (not including the centre). the centre positions become the means
4. the algorithm terminates when the centres (means) do not change or a fixed number of iterations have been reached
33
New cards
what is the pseudocode for the k-means algorithm?
34
New cards
how can we evaluate the clustering method we used?
obtain insight into how the cluster method performed based on
* cluster worth
* expert knowledge
* run method many times and compare the clustering arrangements
this can helps us see if we selected right method, select correct metric for cluster worth, ensure results are consistent
* cluster worth
* expert knowledge
* run method many times and compare the clustering arrangements
this can helps us see if we selected right method, select correct metric for cluster worth, ensure results are consistent
35
New cards
what metrics can we use to compare 2 clustering arrangements?
Kappa metric
36
New cards
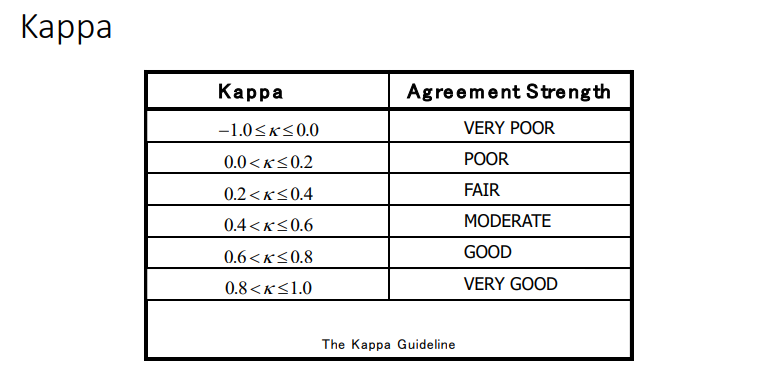
what can we determine about clustering arrangements based on the kappa score?
if the clustering arrangements have a high kappa score, then the clustering arrangements are similar.
\
if the method produces 2 or more similar clustering arrangements then the method itself is consistent
\
if the method produces 2 or more similar clustering arrangements then the method itself is consistent