in class sayings chapter 7
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
process of bone elongation
epiphyseal plate, new cartlige
1) proliferation
2)hypertrophy (large cells)
3)calcification
4)ossification (osteoid collagen)
5)spongy bone
5) compact bone (in diaphysis)
where is the parathyroid hormone located?
parathyroid
where is calcitonin located
thyroid
where is the growth hormone located
pituitary
thyroid hormone
T3/T4
what does 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D
vitamin D concentrations are high in sarcoidosis and other granulomatous diseases, some malignancies, primary hyperparathyroidism, and physiologic hyperparathyroidism.
how does bone calcium and blood calcium work together
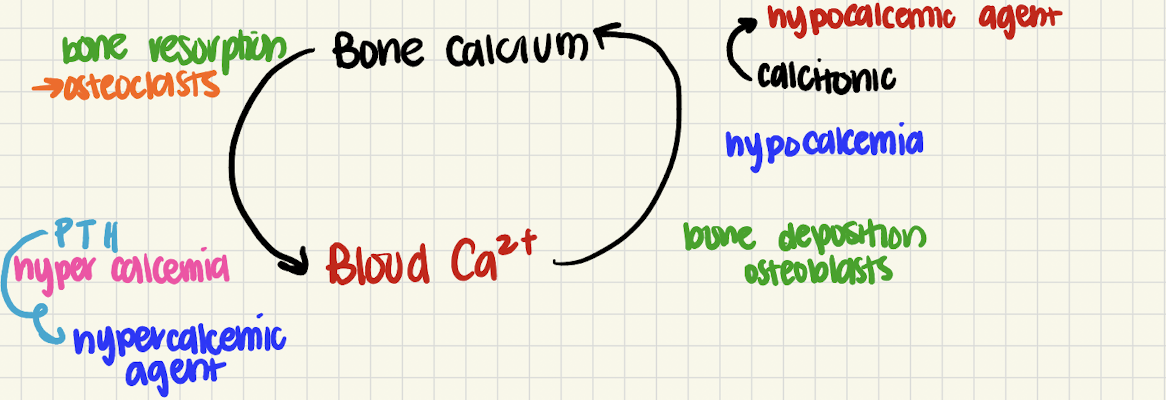
what happens when bone calcium goes to blood calcium
bone resorption (osteoclasts)
what happens when blood calcium goes to bone calcium
bone deposition (osteoblasts)
what is PTH
hypercalcemic agent, hypercalcemia
what osmosis process is thyroid
hypo
what osmosis process is PTH
hyper
what is gigantism
excess growth hormone
what creates dwarfism
deficency in growth hormone
what is excess growth hormone in an adult called
acromegaly
what is somatomedins
inhibit the release of growth hormones by acting directly on anterior pituitary
where does somatophrin go
liver
what are somatomedins
insulin like growth factors (IGF-1-2)
what is the next step in putuitary transport from somatomendins
epiphyseal plate, bone elongation, increase in height
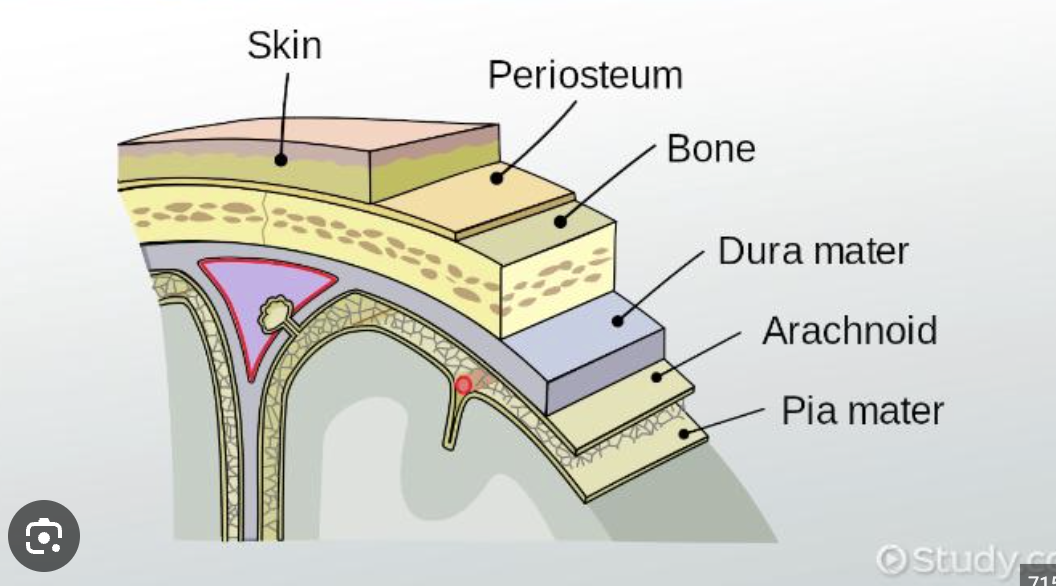
periosteum
outer surface diaphysis
glistening white and double layered