Comprehensive Endocrine System: Hormones, Glands, and Regulation
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
What is the primary function of the endocrine system?
Regulates long-term processes such as growth, development, and reproduction.
What type of messengers does the endocrine system use?
Chemical messengers to relay information and instructions between cells.
Which gland produces melatonin?
Pineal Gland.
What hormones are produced by the hypothalamus?
ADH (antidiuretic hormone), OXT (oxytocin), and regulatory hormones.
What is the function of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
Regulates calcium levels in the blood.
Which hormones are released by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland?
ACTH, TSH, GH, PRL, FSH, LH, and MSH.
What hormones are released by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland?
Oxytocin (OXT) and antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
What is the role of the adrenal medulla?
Produces epinephrine and norepinephrine.
What hormones do the adrenal cortex produce?
Cortisol, corticosterone, aldosterone, androgens.
What is the function of insulin?
Regulates blood glucose levels.
What are the two main classes of hormones?
Amino acid derivatives and peptide hormones.
What are steroid hormones derived from?
Cholesterol.
How do free hormones behave in the bloodstream?
Remain functional for less than 1 hour before being broken down or absorbed.
What is the significance of bound hormones?
They remain in circulation longer because they are attached to transport proteins.
What is a hormone receptor?
A protein molecule to which a particular hormone binds strongly.
What are the first and second messengers in hormone action?
First messenger binds to the receptor; second messenger mediates the effect inside the cell.
What is cyclic-AMP (cAMP)?
A derivative of ATP that acts as a second messenger in hormone action.

What is the process of amplification in hormone action?
The binding of a small number of hormone molecules leads to thousands of second messengers in the cell.
What is down-regulation in hormone sensitivity?
A decrease in the number of hormone receptors due to high hormone levels.
What is up-regulation in hormone sensitivity?
An increase in the number of hormone receptors due to low hormone levels.
What is the role of G proteins in hormone action?
They link the first messenger to the second messenger and activate intracellular responses.
What is the role of eicosanoids?
They coordinate cellular activities and can have secondary roles as hormones.
What are glycoproteins?
Proteins that are more than 200 amino acids long and have carbohydrate side chains.
What hormones are secreted by the pancreas?
Insulin and glucagon.
What is the function of thymosins?
Regulate immune cell development in the thymus.
What is the primary function of the kidneys in the endocrine system?
Secrete erythropoietin (EPO) and calcitriol.
What hormones do the ovaries produce?
Estrogens, progesterone, and inhibin.
What hormones do the testes produce?
Androgens, especially testosterone, and inhibin.
What is a hormone?
A chemical messenger produced by glands that regulates various functions in the body.
What role do protein receptors play in hormone action?
They bind to hormones and initiate a cellular response.
What happens when a G protein is activated?
It can increase or decrease the levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in the cell.
What is the function of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in cells?
cAMP acts as a second messenger that transmits signals from hormones to target cells, affecting metabolic activity.
How can G protein activation affect cAMP levels?
It can either enhance the production of cAMP or promote its breakdown.
What are some examples of first messengers?
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, calcitonin, parathyroid hormone, ADH, ACTH, FSH, LH, TSH.
What is the role of calcium ions (Ca2+) in hormone signaling?
Ca2+ can act as a second messenger, facilitating various cellular responses.
What is the difference between simple and complex endocrine reflexes?
Simple reflexes involve one hormone, while complex reflexes involve multiple hormones and intermediary steps.
What triggers endocrine reflexes?
They can be triggered by humoral, hormonal, or neural stimuli.
What is the hypophyseal portal system?
A system of blood vessels that connects the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary, allowing regulatory hormones to reach their target cells.
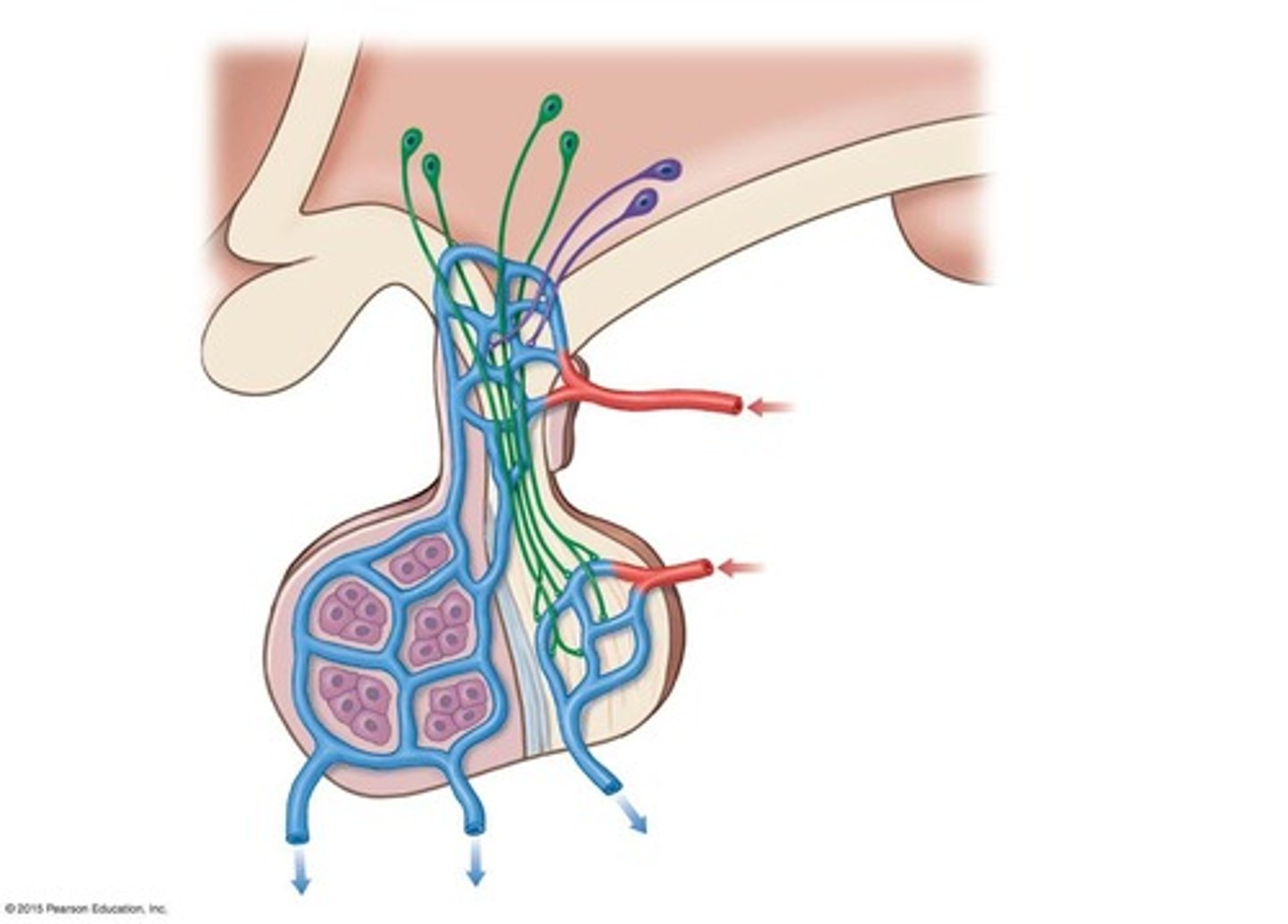
What hormones are released by the posterior pituitary gland?
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OXT).
What is the function of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland?
It releases hormones that regulate other endocrine glands and support various organs.
How do steroid hormones exert their effects?
They diffuse through the plasma membrane and bind to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus, altering gene expression.
What is the significance of the sellar diaphragm?
It isolates the pituitary gland from the cranial cavity and helps maintain its position.
What is the role of calmodulin in hormone signaling?
Calmodulin binds to calcium ions and activates various enzymes within the cell.
How do thyroid hormones affect cellular activity?
They bind to receptors in the nucleus and mitochondria, activating genes and increasing ATP production.
What is the primary function of G proteins in hormone signaling?
They serve as molecular switches that relay signals from receptors to effector proteins.
What is the effect of increased cAMP levels in a cell?
It can activate enzymes or open ion channels, enhancing metabolic activity.
What is the role of the hypothalamus in endocrine control?
It regulates the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland and other endocrine organs.
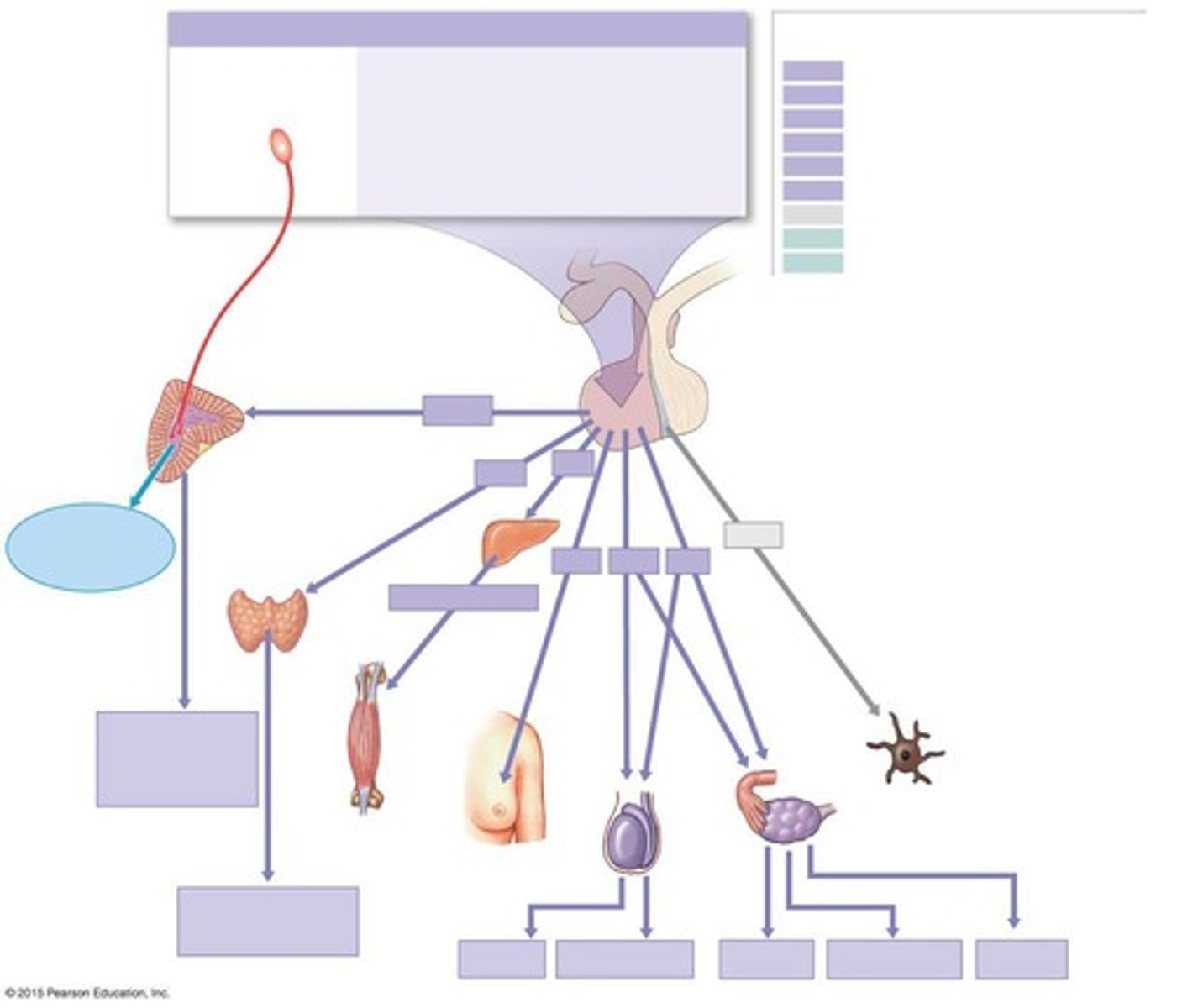
What are neuroendocrine reflexes?
Pathways that include both neural and endocrine components, integrating nervous system signals with hormonal responses.
What is the function of the median eminence?
It is the site where hypothalamic neurons release regulatory hormones into the hypophyseal portal system.
What is the relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland?
The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland's hormone release through regulatory hormones and neural signals.
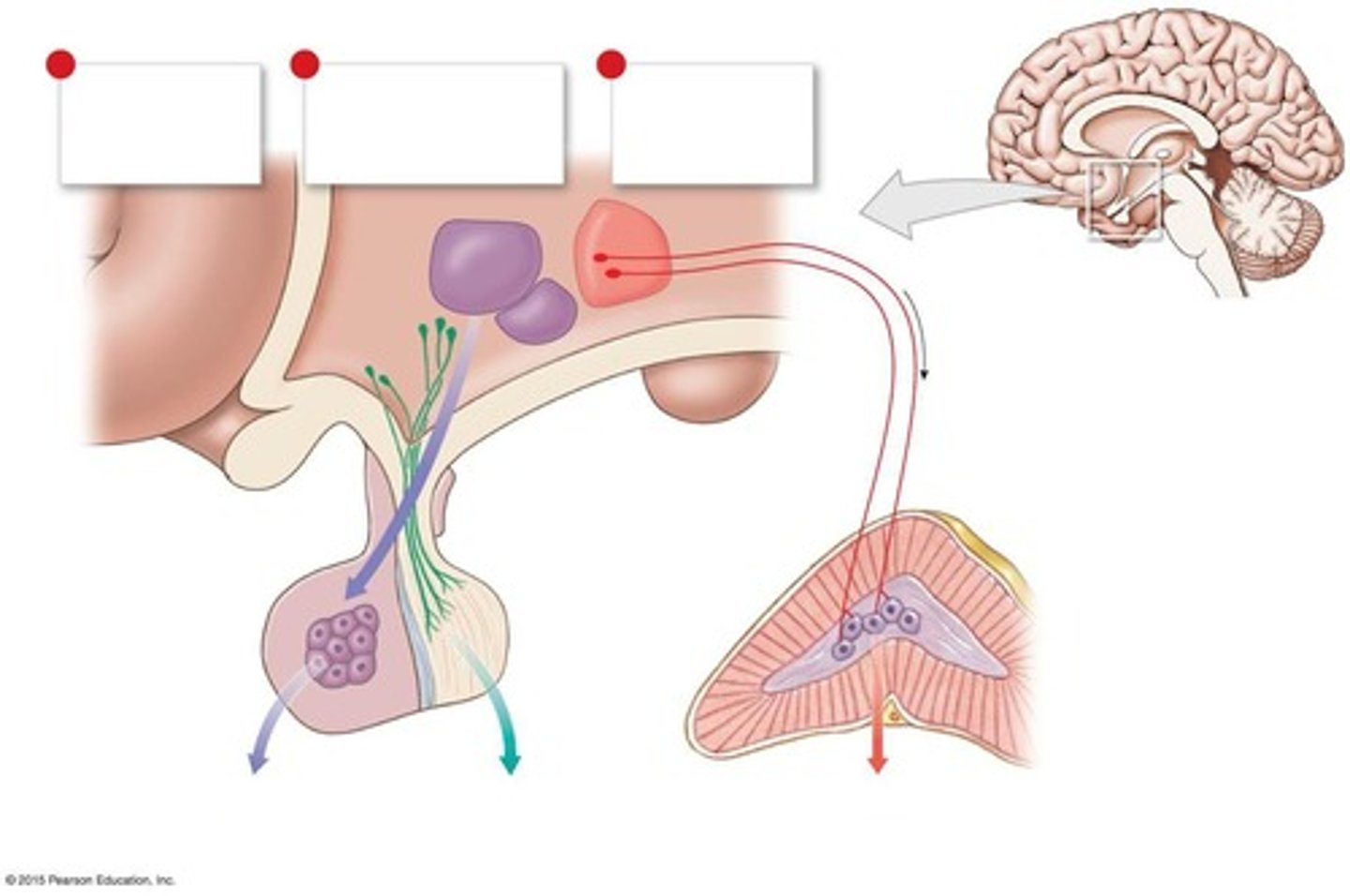
What is the primary function of the anterior pituitary hormones?
To stimulate other endocrine glands or support the function of target organs.
What is the effect of decreased cAMP levels in a cell?
It can inhibit cellular activity and reduce the activation of enzymes.
What is the role of PDE in cAMP signaling?
Phosphodiesterase (PDE) breaks down cAMP, decreasing its levels and effects in the cell.
How do hormones alter DNA transcription?
Hormones bind to intracellular receptors, activating specific genes in the nucleus.
What is the significance of the infundibulum?
It connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland, facilitating hormone transport.
What are the two classes of hypothalamic regulatory hormones?
Releasing hormones (RH) and inhibiting hormones (IH).
What is the function of releasing hormones (RH)?
They stimulate synthesis and secretion of one or more hormones at the anterior lobe.
What do inhibiting hormones (IH) do?
They prevent synthesis and secretion of hormones from the anterior lobe.
How is the rate of secretion of hypothalamic hormones controlled?
By negative feedback.
What is the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland also called?
Neurohypophysis.
Which hormones are manufactured by the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei?
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OXT).
What is the role of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)?
It activates key enzymes in thyroid hormone production.
What happens in the absence of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)?
Thyroid follicles become inactive, and neither synthesis nor secretion occurs.
What are thyroid-binding globulins (TBGs)?
Plasma proteins that bind about 75% of T4 and 70% of T3 entering the bloodstream.
What is thyroglobulin?
A globular protein synthesized by follicle cells and secreted into the colloid of thyroid follicles.
What are the two main thyroid hormones?
Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
What is the difference between T4 and T3?
T4 contains four iodide ions, while T3 contains three iodide ions.
What is the primary function of thyroid hormones?
They affect most cells in the body and are essential for normal development of the skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems in children.
How do thyroid hormones enter target cells?
By a transport system.
Where do thyroid hormones bind within target cells?
To receptors in the cytoplasm, on the surfaces of mitochondria, and in the nucleus.
What is the role of the hypothalamus in endocrine regulation?
It produces releasing and inhibiting hormones that regulate the anterior pituitary gland.
What is the feedback control mechanism in endocrine secretion?
Control occurs by negative feedback, where the secretion of hormones is regulated based on the levels of other hormones.
What is the function of growth hormone (GH)?
It stimulates growth of skeletal muscle, cartilage, and many other tissues.
What does the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland secrete?
Hormones such as ACTH, TSH, GH, PRL, FSH, and LH.
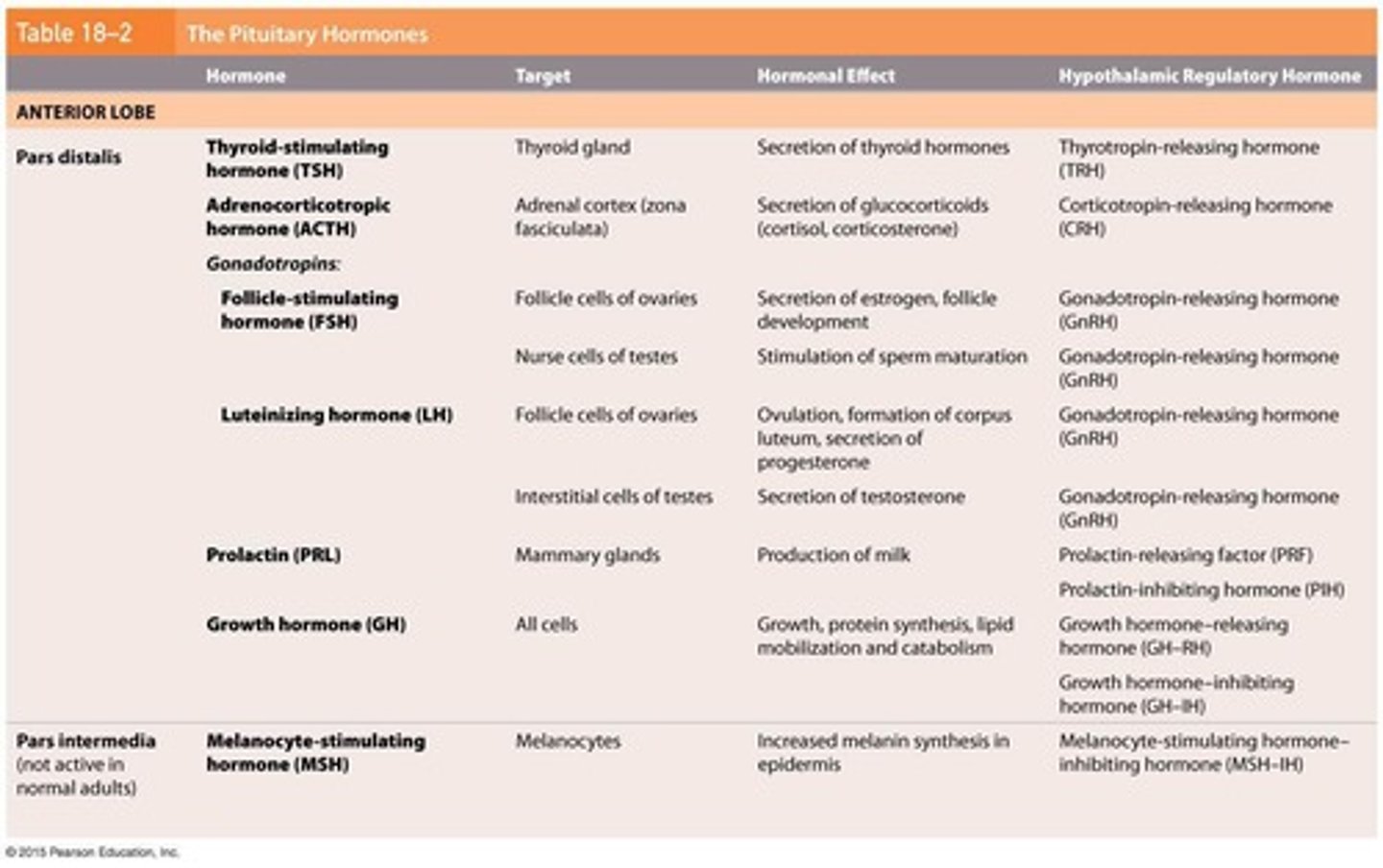
What is the role of prolactin (PRL)?
It stimulates mammary glands.
What is the significance of negative feedback in hormonal regulation?
It helps maintain homeostasis by regulating hormone levels based on physiological needs.
What is the primary target organ for antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
The kidneys.
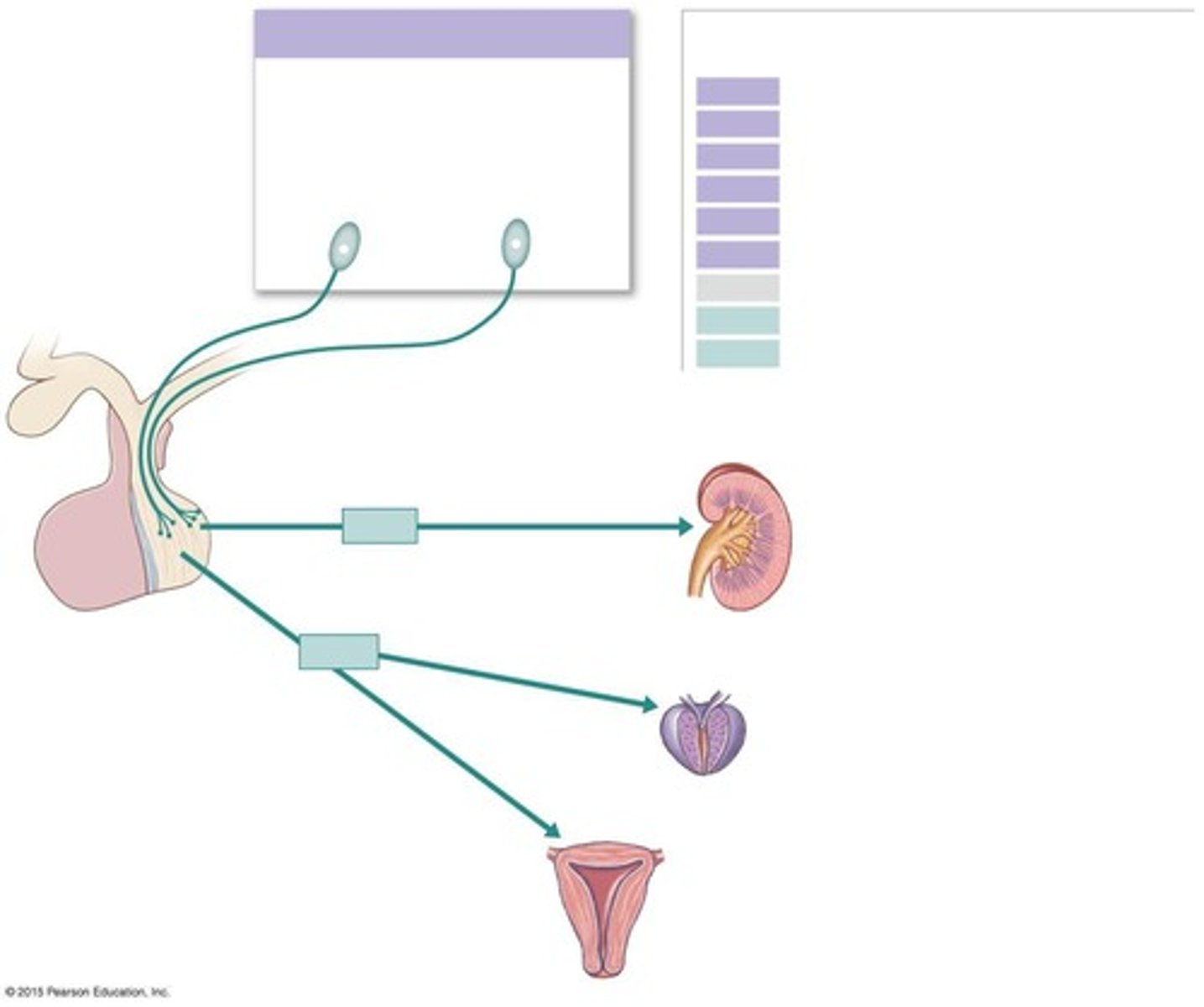
What physiological processes does oxytocin (OXT) influence?
It influences uterine smooth muscle contraction and milk ejection from mammary glands.
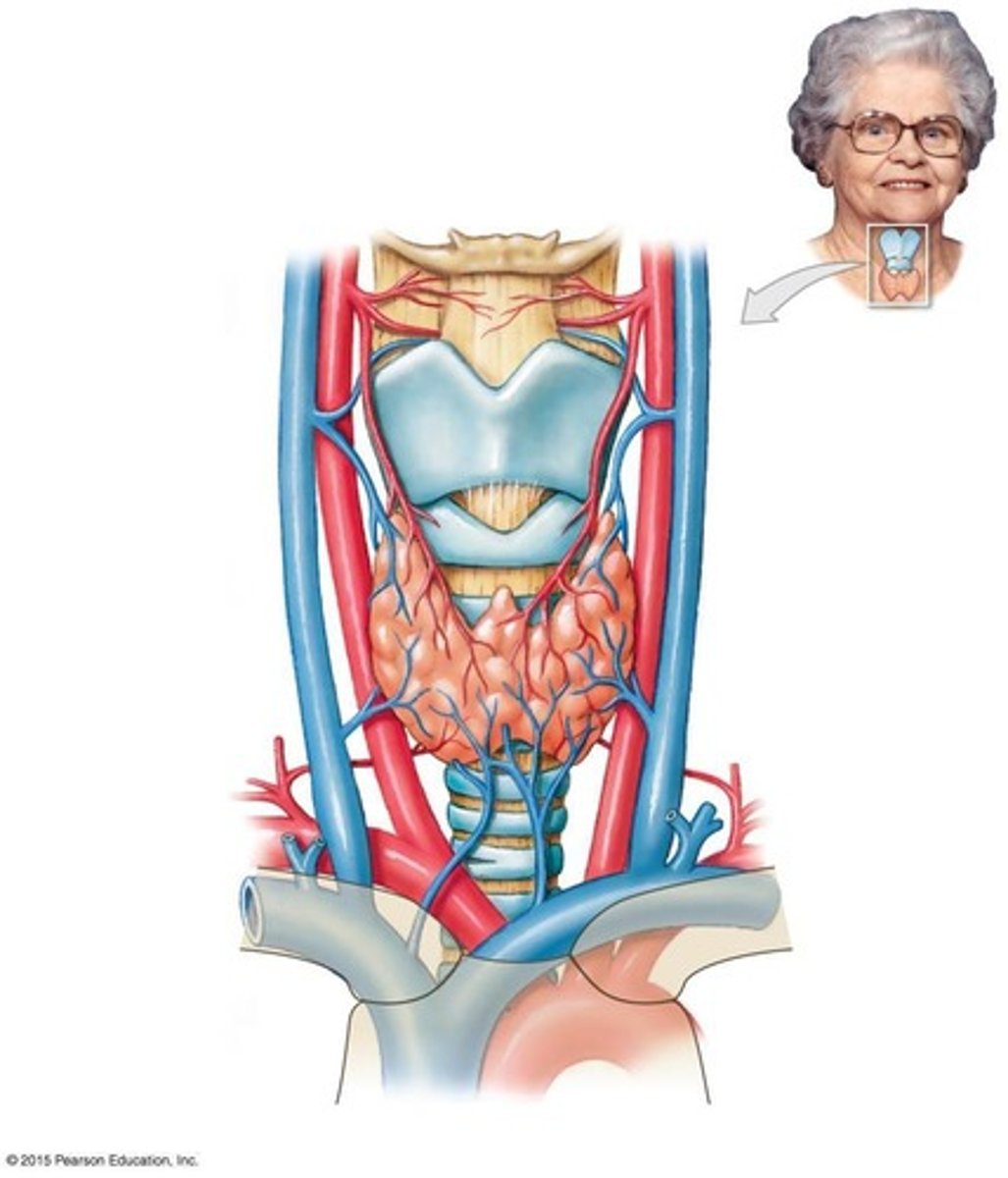
What is the anatomical location of the thyroid gland?
It lies inferior to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx.
What is the structure of thyroid follicles?
Hollow spheres lined by cuboidal epithelium, containing viscous colloid.
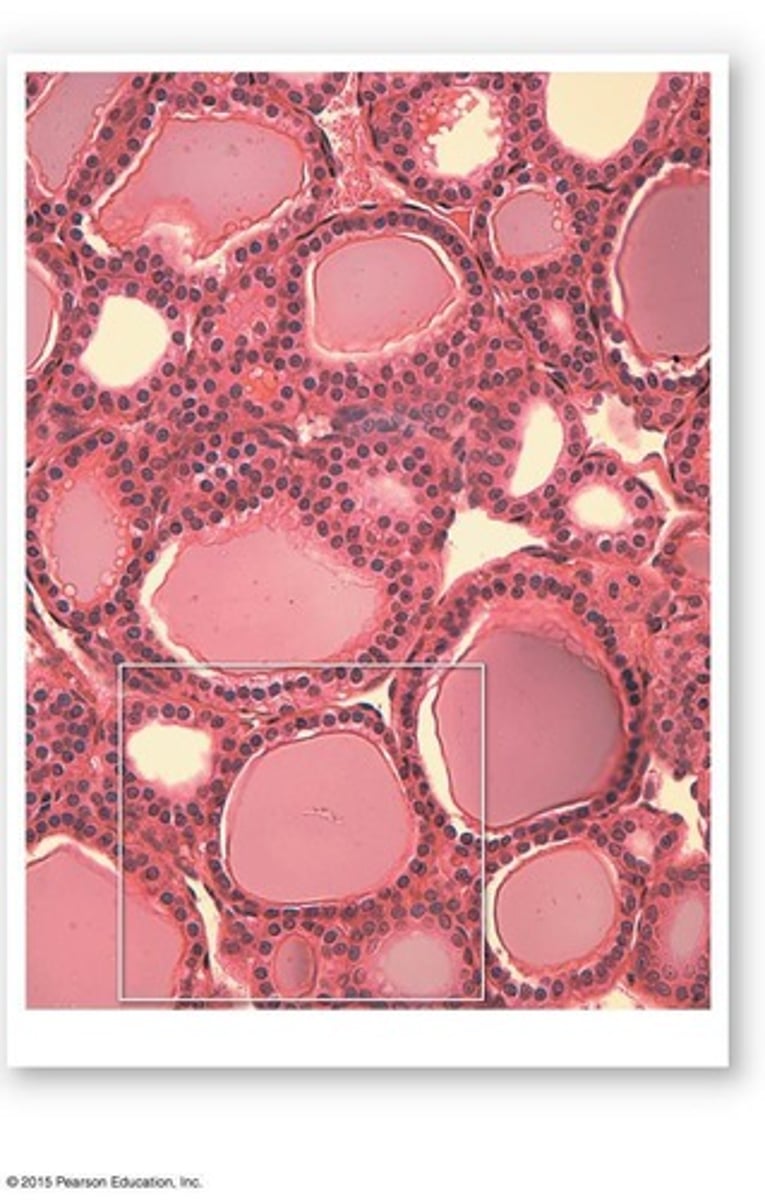
What is the role of capillaries surrounding thyroid follicles?
They deliver nutrients and regulatory hormones and accept secretory products and metabolic wastes.
What is the typical pattern of regulation for hypothalamic releasing hormones?
They stimulate the anterior pituitary gland, which in turn stimulates target endocrine organs.
What is the calorigenic effect of the thyroid gland?
It causes cells to consume more energy, resulting in increased heat generation and a strong, immediate, short-lived increase in the rate of cellular metabolism.
List one effect of thyroid hormones on peripheral tissues.
Elevates rates of oxygen consumption and energy consumption.
How do thyroid hormones affect heart rate?
They increase heart rate and force of contraction, generally resulting in a rise in blood pressure.
What is the role of C cells in the thyroid gland?
C cells, or parafollicular cells, produce calcitonin, which helps regulate calcium concentrations in body fluids.
What is the function of calcitonin?
It inhibits osteoclasts, slowing the rate of calcium release from bone, and stimulates calcium excretion by the kidneys.
Where are the parathyroid glands located?
Embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
What hormone is produced by the parathyroid glands?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), which responds to low concentrations of calcium.
What are the three main effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
Stimulates osteoclasts, enhances calcium reabsorption at kidneys, and stimulates formation of calcitriol.
What is the primary function of aldosterone?
Stimulates conservation of sodium ions and elimination of potassium ions.
What does the adrenal cortex produce?
It produces steroid hormones, including mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids.
What is the role of glucocorticoids?
They accelerate glucose synthesis and glycogen formation, and have anti-inflammatory effects.
What hormones are produced by the adrenal medulla?
Epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
How does epinephrine affect skeletal muscles?
It triggers mobilization of glycogen reserves and accelerates glucose breakdown to provide ATP.
What is the effect of norepinephrine on blood pressure?
It increases blood pressure by enhancing cardiac activity.
What stimulates the secretion of aldosterone?
A drop in blood sodium, blood volume, or blood pressure, and a rise in blood potassium concentration.
What is the primary target of calcitonin?
Bone and kidneys, where it regulates calcium levels.
What is the function of the zona glomerulosa?
It produces mineralocorticoids, primarily aldosterone.
What is the role of the zona fasciculata?
It produces glucocorticoids like cortisol, which regulate metabolism and stress response.