China-History
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Loess:
A type of soil, this soil is mainly found in northern china, the soil is yellowish and is made from wind deposit over the years. The soil is important for wheat, millet, and dry crops. (NOT RICE)
Oracle Bones:
Animal bones or turtle Shells that were used in the Shang Dynasty and were used for divination (predicting future harvests), important because they show the earliest known examples of chinese writing.
Sui Wendi:
Founded the Sui dynasty, he restored China from chaos and re-centralized China’s strong government. The Sui dynasty laid foundation for Tang Dynasty. Sui reestablished the Civil Service examination system, laws, taxes, and currency. And the last Sui emperor is chocked to death at the age of 12.
Dynastic Cycle:
Dynasty is founded by a powerful leader
Period of great power and prosperity (restores peace, restores glory to country, build roads, irrigation systems, improves everyday life of people in the dynasty)
Period of Decline (Higher taxes, social service decline, natural disaster)
Period of rebellion, dynasty is overthrown.
Mandate of Heaven:
The belief that rulers were chosen by heaven and could lose their right to rule if they governed poorly, leading to rebellion and dynastic change.
Tang Taizong:
He was a strong ruler who strengthen and centralized the government. He expanded civil service exams and promoted confucianism in the government. He was very testable and listened to advisors and expanded lots of Chinese territory. (Tang dynasty introduced land reform)
Tributary state:
A state that recognized China as superior and paid tribute (gifts such as silver and silk) in exchange for protection, trade rights, and political legitimacy.
Korea: The biggest the tributary state]
Vietnam: paid tribute but remained politically independent
Tibet: Tibet was sometimes a tributary state of China, depending on the dynasty and historical period.
Wu Zhao:
She was a ruler during the Tang dynasty who started as a concubine and made her way up in political power after TangTaizong died. She stengthed the civil service exams, and bureaucracy.
Land Reform:
Government policies that redistributed land so more farmers could own or farm land, rather than it being controlled by a few wealthy landowners.
Grand Canal:
Waterway made by the Sui dynasty that connected northern and southern China, mainly linking the yellow river and Yangtze River. Allowed rice from the south to be exported to the north capitals.(half of the workers died when building it.)
Yellow River (Huang He) is mainly called what:
Its called “China’s Sorrow” because it looks like poopy brown from the soil Loess in the river
Gentry:
Small elite group of people that gained mainly political power through the civil service exams.
-They were NOT nobles
-They were upper-milddle class that had money so they could by tutors and resources to well on the CSES.
Civil service exams:
A merit based testing system that selected government officials based on confucian knowledge and helped create an educated ruling class in China. (CSES was founded in the Sui dynasty)
Footbinding:
Disgusting cultural practice in China where young girls feet were tightly bounded in and broken down to meet a certain standard. Footbinding showed power, daintiness, wealth, and also reinforced women being more dependent on men as they could barely move. (Women wore lotus shoes which made there feet footbinded and the shoes were shaped like lotuses)
Gun Powder/Mechanical clock/Block Printing/Movable type:
Gun Powder: Changed warfare and was used mainly during the Tang and Song dynasties
Mechanical Clock: Helped measure time and was founded in the Song dynasty
Block Printing: Made books cheaper and was invented in the Tang dynasty
Movable type: Process where characters are provided and carved into blocks so people could reuse them, this effiecinized writing and was invented and used in the Song dynasty
Confucius:
Founded confucianism and lived during the Zhou dynasty, he taught respect elders, education is important, a good ruler is a moral and fair. He also taught the five core relationships…
Ruler → Subject
Father → Son
Husband → Wife
Older brother → younger brother
friend → friend
Landscape painting:
Nature paintings that reflected Confucian and Daoist ideas, they had 1-2 colors max and were made through ink and brush. Prominent and mainly used during the Tang and Song dynasties.
Pagoda:
Multi Storied temple with upturned roofs, they were Buddhist religious structures and were mainly built in the Tang Dynasty.
Porcelain:
high quality ceramic developed in China that became a valuable trade good. (Used in Tang mainly)
Li Bo:
Lived during the Tang dynasty, he was the greatest poet of Tang, his poetry reflects nature friendship, wine, the moon, and the golden age of the Tang dynasty.
yurt:
a round portable tent made of felt and wood, used by nomadic mongols. They were easy to assemble and protected mongols from harsh weather. The yurts were kept warm using dried horse manure.
Chingiss Khan:
First mongol leader who united all Steppe Civilization. He created the largest land empire in history, he promoted religious tolerance, built a powerful cavalry army, he set up his descendants to conquer China. Ghengis was born with a blood clot in his hand aswell. His tribes rival tribe were the Tartars. (His dad was killed and his mom taught him about the arrow thingy)
Pax Mongolica:
A time of peace and stability when merchants traveled safely along the silk roads. The pax increased trade, communication, cultural exchange, and the Black Death.
Kublai Khan:
Ghengis’s grando, he conquered Southern Asia and moved the capital to Beijing. He practiced religious tolerance, and became settled and no long nomadic. He kept Mongols > Chinese in the government.
Silk Road:
Main direction east-west traded paper, porcelain, and silk. Spanded from China to middle and east.
Yuan Dynasty:
Kigali Khan → Bejing
-Valued mongols over Chinese, increased trade routes, military, and cultural exchange, it fell due to discrimination of Chinese, heavy taxes, natural disasters and rebellion which led to the loss of the Mandate of Heaven.
Marco Polo:
Venician merchant who traveled from Venice → China due to the Pax Mogolica - He lived in China for 17 years and was in Kublai Khans court, he was later captured by a rival state back in Europe called Genoa in a naval war. In prison he shared with other prisoners about the amazing China and how they burnt coal and used paper.
Zhu YuanZhang:
Founded the ming dynasty, he was a peasant who was the face of the Yuan rebellion, he restored Chinese rule over Mongol rule.
Ming Dynasty:
Dynasty that rebuilt Chinese traditions, had a strong emperor and rebuilt the Great Wall of China. Early in the dynasty they sponsored Zheng He’s voyages and flaunted wealth, but later they became very isolated.
The Water Magin:
A famous Chinese novel written during the Yuan Dynasty, but the book was set in the Song dynasty, tells a story of 108 rebels who were good people who became rebels because of the corrupt Chinese governments, they band together to fight injustice. This book criticizes government rulers, and has sympathy for the common people.
Zheng He:
A Chinese-Muslim admiral and explorer during the Ming dynasty, he traveled through Ithe Indian Ocean, Southeast Asia, India, the Middle East, and east Africa. He was the symbol of chinas wealth and naval power.
Geography:
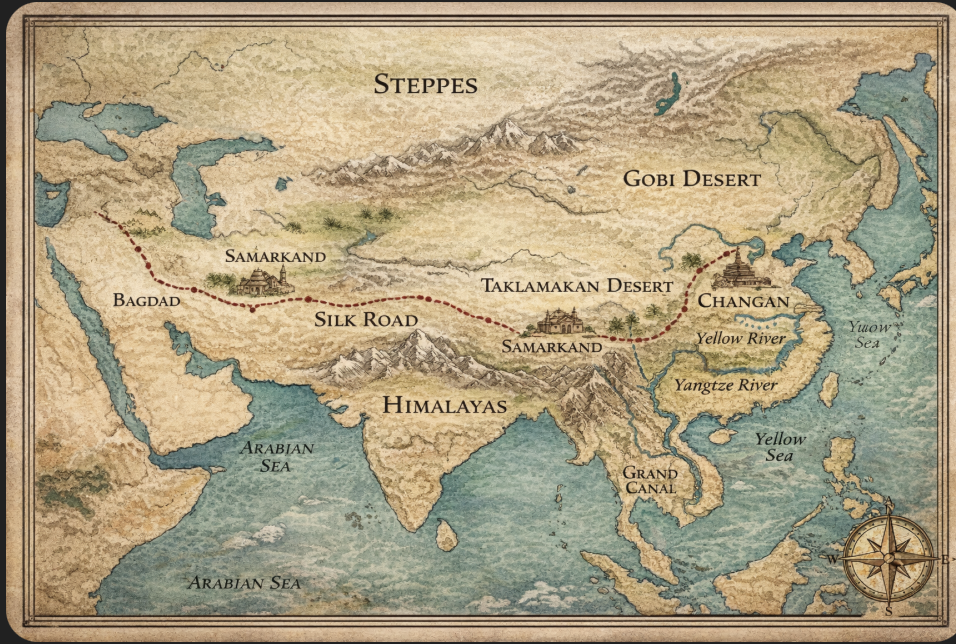
Chinese Philosophies:
Legalism: Believes people need strict laws and harsh punishments to maintain in order
Daoism: teaches living in harmony with nature and following the Dao (the way)
Buddhism: Focusing on ending suffering through self discipline, meditation, and enlightenment.
The laughing buddha symbols:
Joy, Good luck, satisfaction, generosity, protection.
Status of Merchants:
Merchant status was low due to traditional chinese society under confucianism valued scholar and farmers more than people who made money through trade.
When was tea introduced?
Tang dynasty
Karakorum:
was the “capital” for the mongols before they took control of china. It was basically just a bunch of yurts.