Human A&P Nervous System
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What does the nervous system control?
Every thought, action, and emotion.
How do nervous system cells communicate?
Using electrical and chemical signals.
What are the 3 main functions of the nervous system?
Sensory input
Integration
Motor output
What is sensory input?
Receptors monitor changes inside and outside the body.
What is integration?
Processing and interpreting sensory input.
What is motor output?
Activating effectors (muscles/glands) for a response.
What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
CNS (brain + spinal cord)
PNS (nerves + ganglia)
What is the CNS?
Brain = integration center
Spinal cord = sends info to/from body
What is the PNS?
Spinal nerves, cranial nerves, ganglia
What are the PNS subdivisions?
Sensory (afferent): to CNS
Motor (efferent): from CNS
What are the sensory divisions?
Somatic: from skin, muscles, joints
Visceral: from organs (thorax/abdomen)
What are the motor divisions?
Somatic: to skeletal muscles (voluntary)
Autonomic (ANS): to organs (involuntary)
What are the two parts of the ANS?
Sympathetic: "Fight or Flight"
Parasympathetic: "Rest and Digest"
What are neuroglia (glial cells)?
Support cells for neurons
. CNS glial cells (4 types)?
Astrocytes: blood-brain barrier
Microglia: immune defense
Ependymal: CSF production
Oligodendrocytes: myelinate CNS axons
PNS glial cells (2 types)?
Schwann cells: myelinate PNS axons
Satellite cells: regulate around ganglia
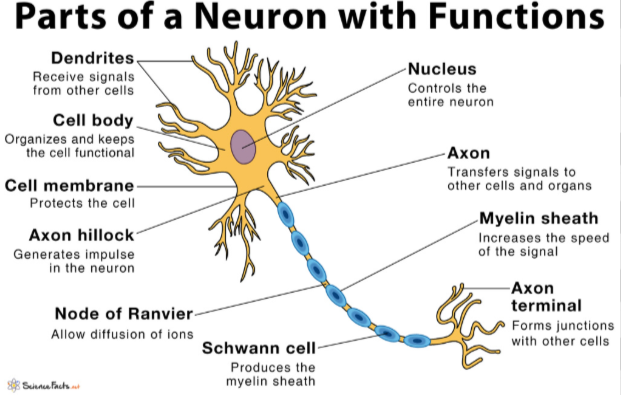
What are the parts of a neuron?
Cell body (soma)
Dendrites (receive signals)
Axon (sends signals)
Axon hillock (start of axon)
Axon terminals (release neurotransmitters)
What is myelin?
Insulating layer that increases signal speed
Who makes myelin?
CNS: Oligodendrocytes
PNS: Schwann cells
What is anterograde transport?
Moves materials from soma → axon terminal
What is retrograde transport?
Moves materials from axon terminal → soma
Multipolar
1 axon, many dendrites (motor neurons)
Bipolar:
1 axon, 1 dendrite (special senses)
Unipolar:
1 process (sensory neurons)
Types of neurons by function:
Sensory: to CNS
Interneurons: connect neurons
Motor: from CNS to effectors
What is a nerve?
Bundle of axons in the PNS
Nerve structure layers:
Endoneurium (around each fiber)
Perineurium (around fascicles)
Epineurium (around whole nerve)
What is resting membrane potential?
Electrical charge difference across the neuron membrane
What are ion channels?
Leakage channels: always open
Gated channels: open/close in response to signals