Principles of Chemistry I: Ionic and Covalent Bonding
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Ionic Bonding
Formation of cations and anions through electron transfer.
Cation
Positively charged ion formed by losing electrons.
Anion
Negatively charged ion formed by gaining electrons.
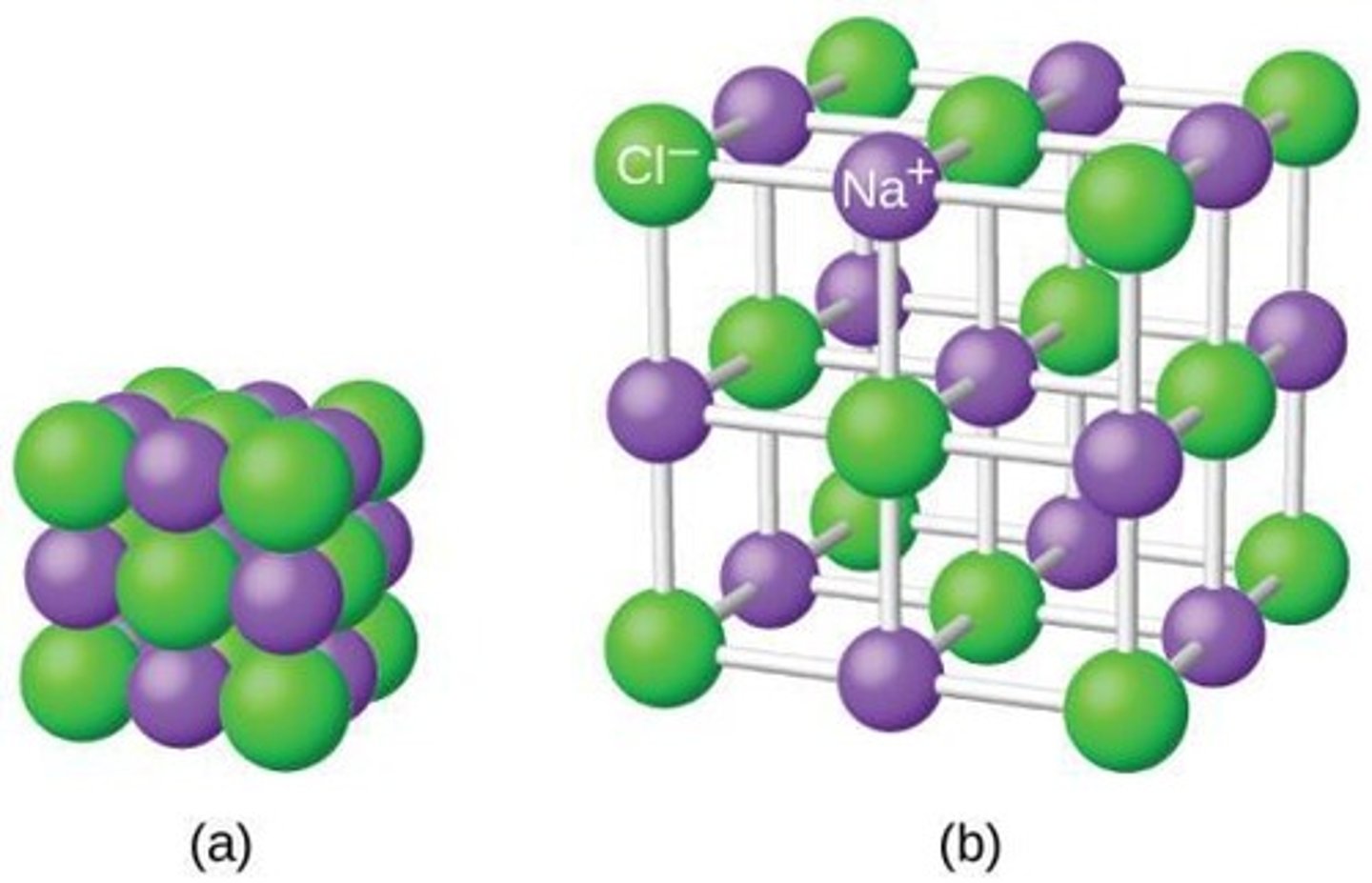
Ionic Compound
Compound formed from ionic bonds between ions.
Example of NaCl
Sodium gives one electron to chlorine.
Example of CaCl2
Calcium gives two electrons to two chlorines.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
High melting points, solid, conductive when molten.
Electronegativity
Atom's tendency to attract electrons in bonds.
Covalent Bonding
Atoms share electrons to form molecular compounds.
Pure Covalent Bond
Equal sharing of electrons between identical atoms.
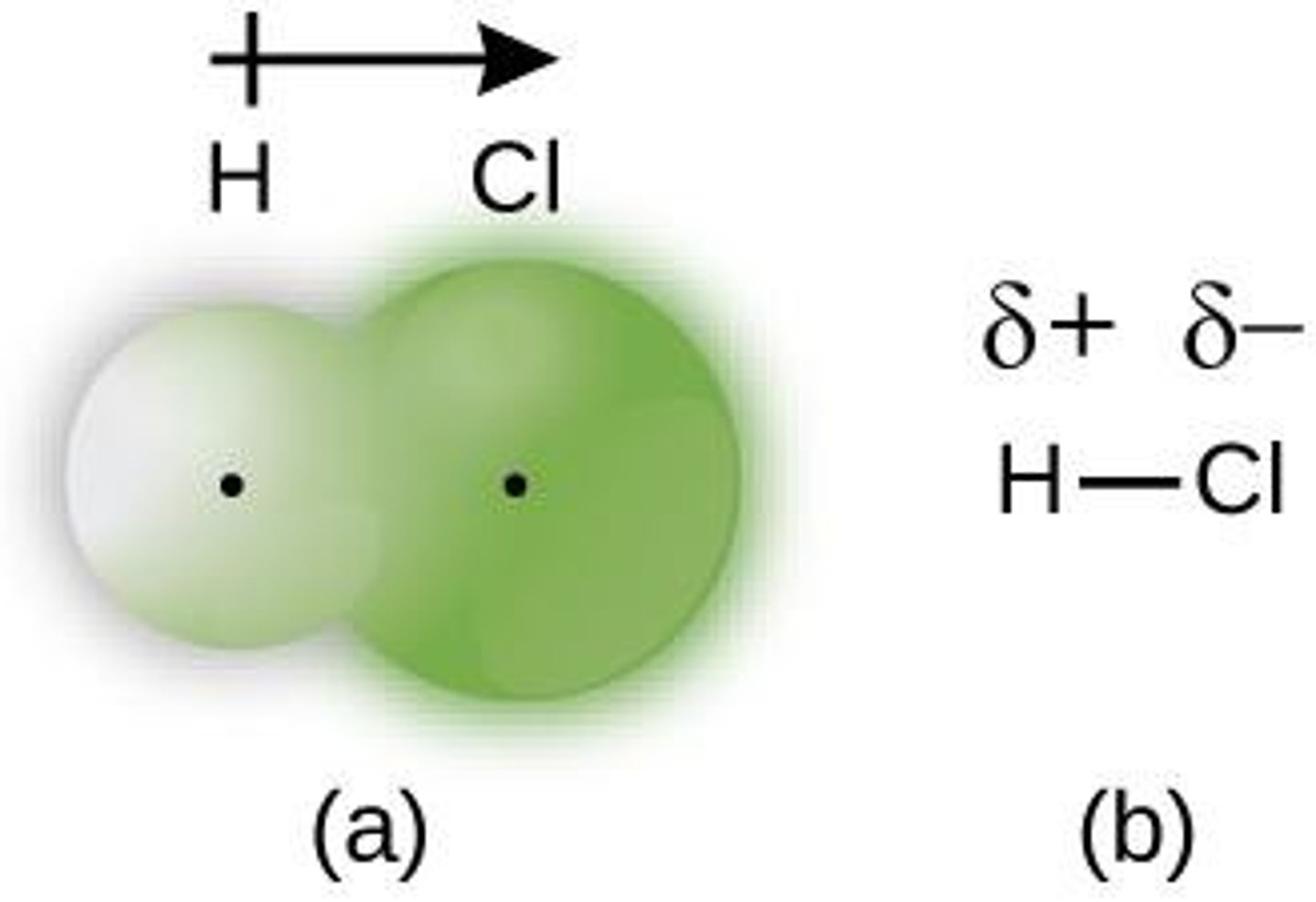
Polar Covalent Bond
Unequal sharing of electrons between different atoms.
Electron Affinity (EA)
Energy released when an atom gains an electron.
Water (H₂O)
Essential molecule with two hydrogen and one oxygen.
Methane (CH₄)
Natural gas component with one carbon and four hydrogens.
Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)
Simple sugar vital for cellular energy.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂)
Gas with one sulfur and two oxygen atoms.
Lewis Symbols
Representation of valence electrons around an atom.
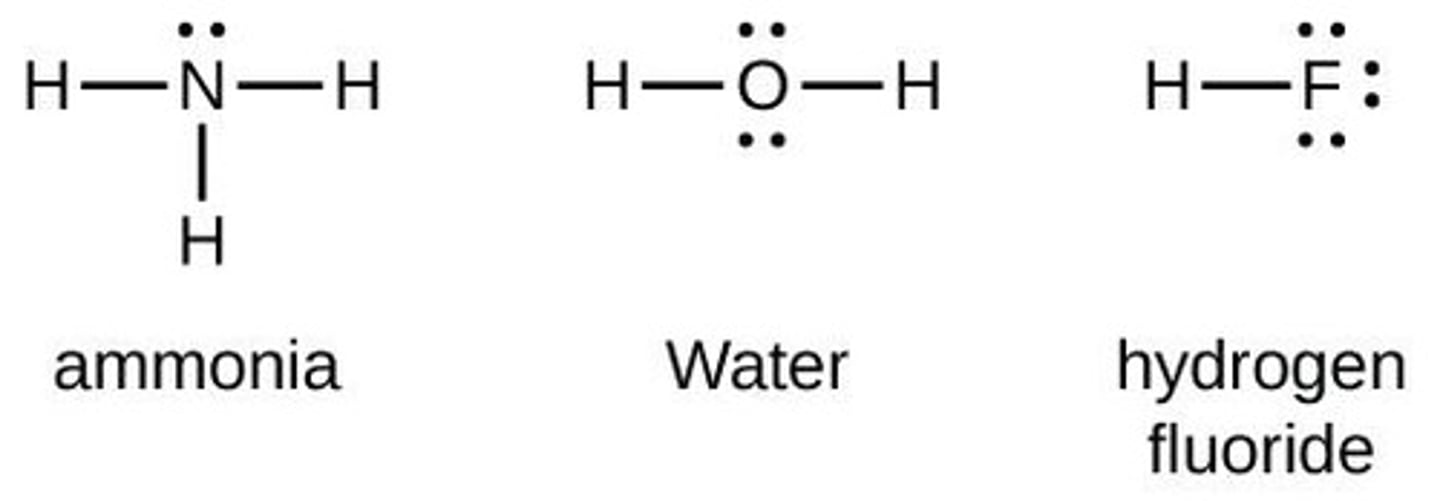
Lewis Structures
Diagrams showing bonding and lone pairs in molecules.
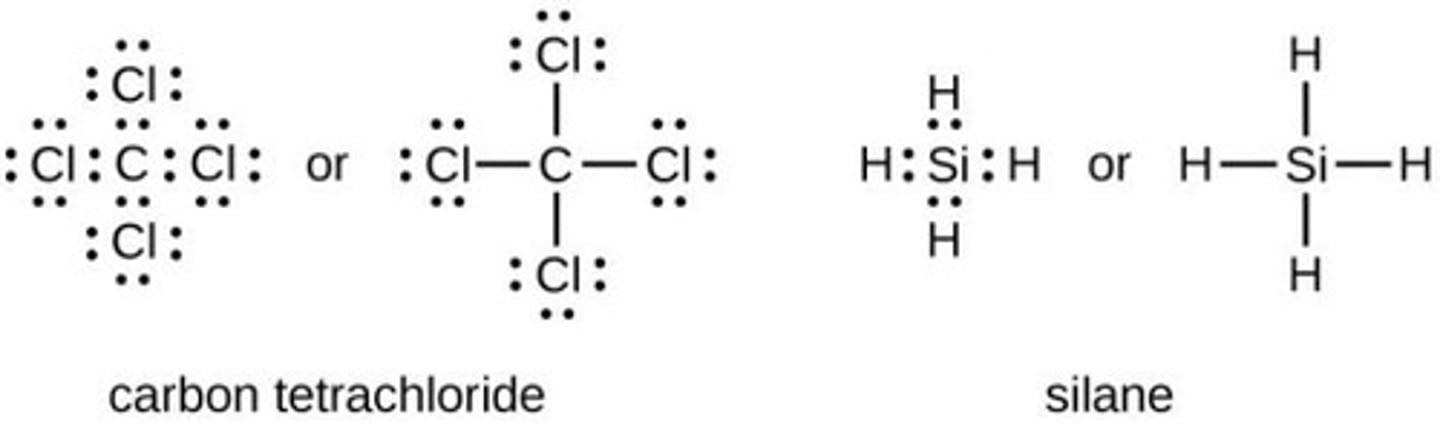
Lone Pairs
Non-bonding pairs of electrons in Lewis structures.
Bonding Pairs
Shared electron pairs represented by dashes.
Balancing Charges
Ensuring overall ionic compound neutrality.
Monatomic Ion
Ion formed from a single atom.
Polyatomic Ion
Ion composed of multiple atoms.
Conductivity of Ionic Compounds
Conductive when molten, nonconductive in solid state.
Electronegativity Difference
Increased difference leads to more ionic character.
Practice Problems
Exercises to predict bond types and electronegativity.
Octet Rule
Atoms form bonds to achieve eight valence electrons.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
Double Bond
Two pairs of electrons shared between atoms.
Triple Bond
Three pairs of electrons shared between atoms.
Lewis Structure
Diagram showing electron arrangement in molecules.
Skeleton Structure
Initial arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Electron Deficient Molecules
Central atom has fewer electrons than needed.
Hypervalent Molecules
Atoms with more than eight valence electrons.
Odd-Electron Molecules
Molecules with an unpaired electron.
Free Radicals
Molecules containing an odd number of electrons.
Formal Charge
Hypothetical charge from electron redistribution.
Formal Charge Formula
Valence Electrons - Lone Pairs - 1/2 Bonding Electrons.
Resonance
Multiple Lewis structures represent a molecule's electrons.
Resonance Hybrid
Actual electron distribution averaged from resonance forms.
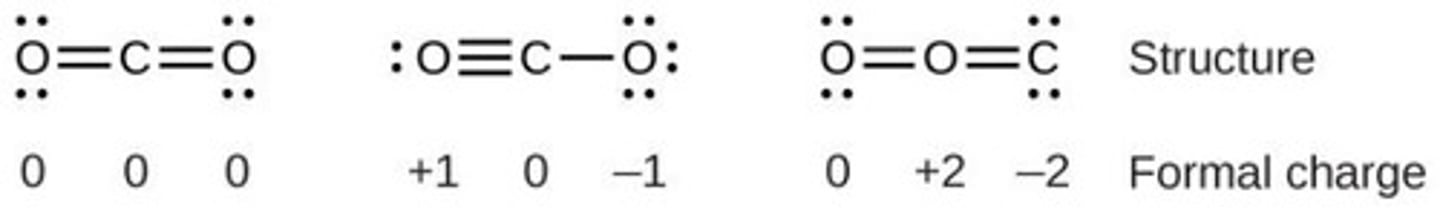
Bond Strength
Energy required to break a bond.
Bond Energy
Energy needed to break one mole of bonds.
Enthalpy (H)
Measurement of energy in thermodynamic systems.
Endothermic Process
Chemical process that absorbs heat.
Bond Length
Distance between two bonded nuclei.
Bond Dissociation Energy
Standard enthalpy change for breaking a bond.
Strength and Number of Bonds
More bonds increase bond strength.
Bond Length and Strength Relationship
Stronger bonds have shorter lengths.
Example of Bond Energy
CH4 bond energy is 415 kJ/mol.
Molecular Structure
Arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Charge Distribution Preference
Prefer structures with minimal formal charges.
Least Electronegative Element
Typically placed at the center of structures.
Enthalpy Change (ΔH)
Energy change during a chemical reaction.
Exothermic Reaction
ΔH negative; heat produced, stronger product bonds.
Endothermic Reaction
ΔH positive; heat absorbed, weaker product bonds.
Lattice Energy (ΔHlattice)
Energy to separate one mole of ionic solid.
Born-Haber Cycle
Series of steps for ionic solid formation.
Ionization Energy (IE)
Energy needed to remove an electron from an atom.
Enthalpy of Sublimation (ΔHs)
Energy required to convert solid to gas.
Bond Dissociation Energy (D)
Energy required to break a bond in a molecule.
VSEPR Theory
Predicts molecular structure based on electron pair repulsion.
Bond Angle
Angle between two bonds at a common atom.
Bond Distance
Distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms.
Ångstrom (Å)
Unit of length; 1 Å = 10⁻¹⁰ m.
Picometer (pm)
Unit of length; 1 pm = 10⁻¹² m.
Electron Density
Regions of high electron concentration around atoms.
Lone Pair
Pair of valence electrons not involved in bonding.
Molecular Polarity
Distribution of electrical charge across a molecule.
Dipole Moment (µ)
Vector representing charge separation in a molecule.
Nonpolar Molecule
Molecule without a net dipole moment.
Bond Moment
Vector quantity representing bond dipole.
Partial Charge (δ+ or δ-)
Charge distribution in polar covalent bonds.
Electric Field Alignment
Polar molecules align in an electric field.
Like Dissolves Like
Polar dissolves polar; nonpolar dissolves nonpolar.
Trigonal Planar Geometry
Three regions of electron density around a central atom.
Tetrahedral Geometry
Four regions of electron density around a central atom.
Trigonal Bipyramidal Geometry
Five regions of electron density around a central atom.
Octahedral Geometry
Six regions of electron density around a central atom.