Skin, hair and nails, Vitals
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Skin
Heaviest single organ of the body
Accounting for ~16% of body weight
Functions:
Secretion
- Ex: Sebum
Heat regulation
Absorption
Protection
From radiation, microorganisms, the elements, of the organs
Excretion
Sweat allows our bodies to rid itself of waste
Sensation
Nerve endings that contain stimuli
Three Layers of Skin:
Epidermis - no vessels
Dermis - big layer, BV, nerves, sweat glands and hair follicles. Provide nutrients
Subcutaneous tissues: adipose tissue, provides storage and insulations
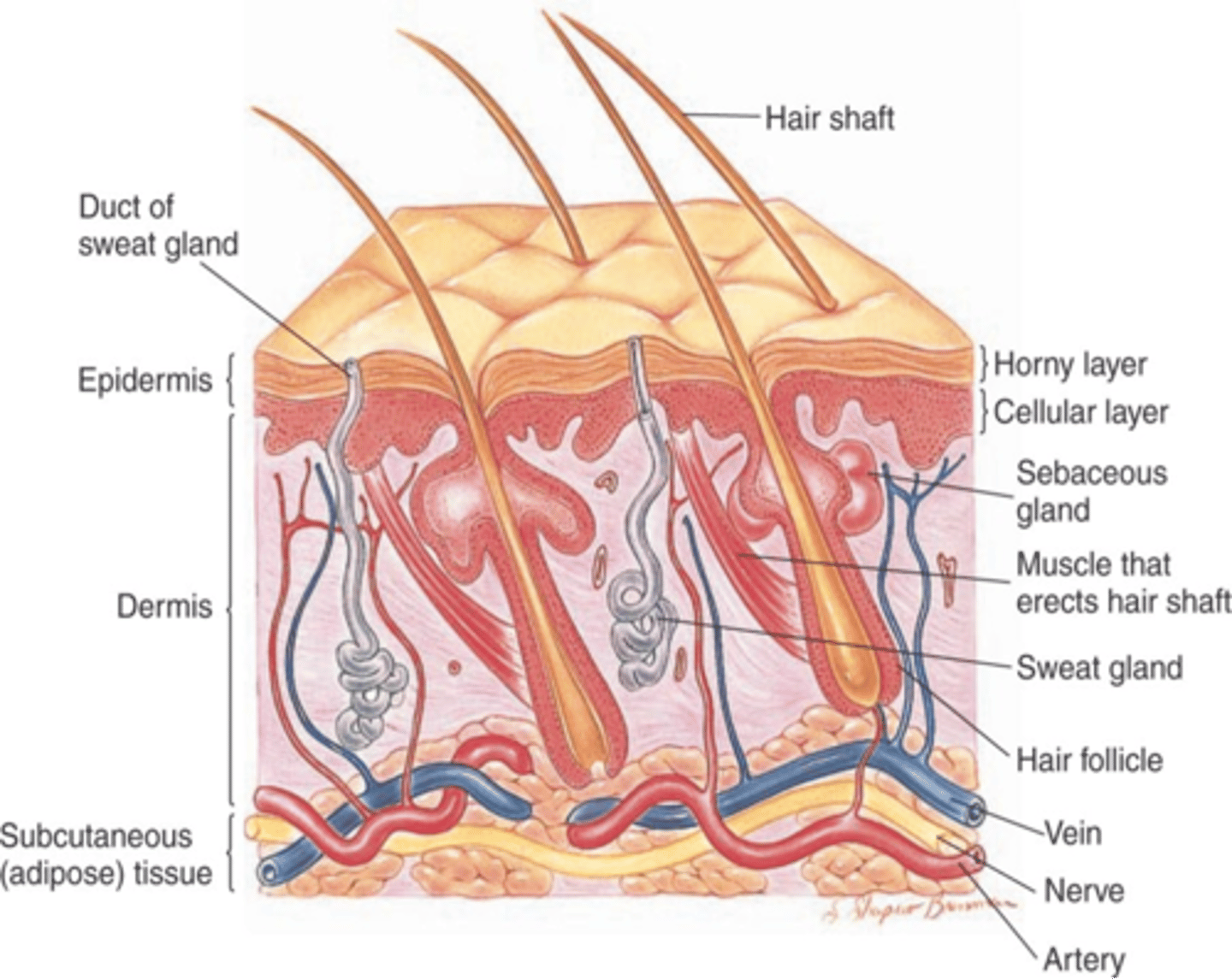
Sebaceous Glands:
oil glands secrete sebum and come out of hair follicles, spare palms and soles.
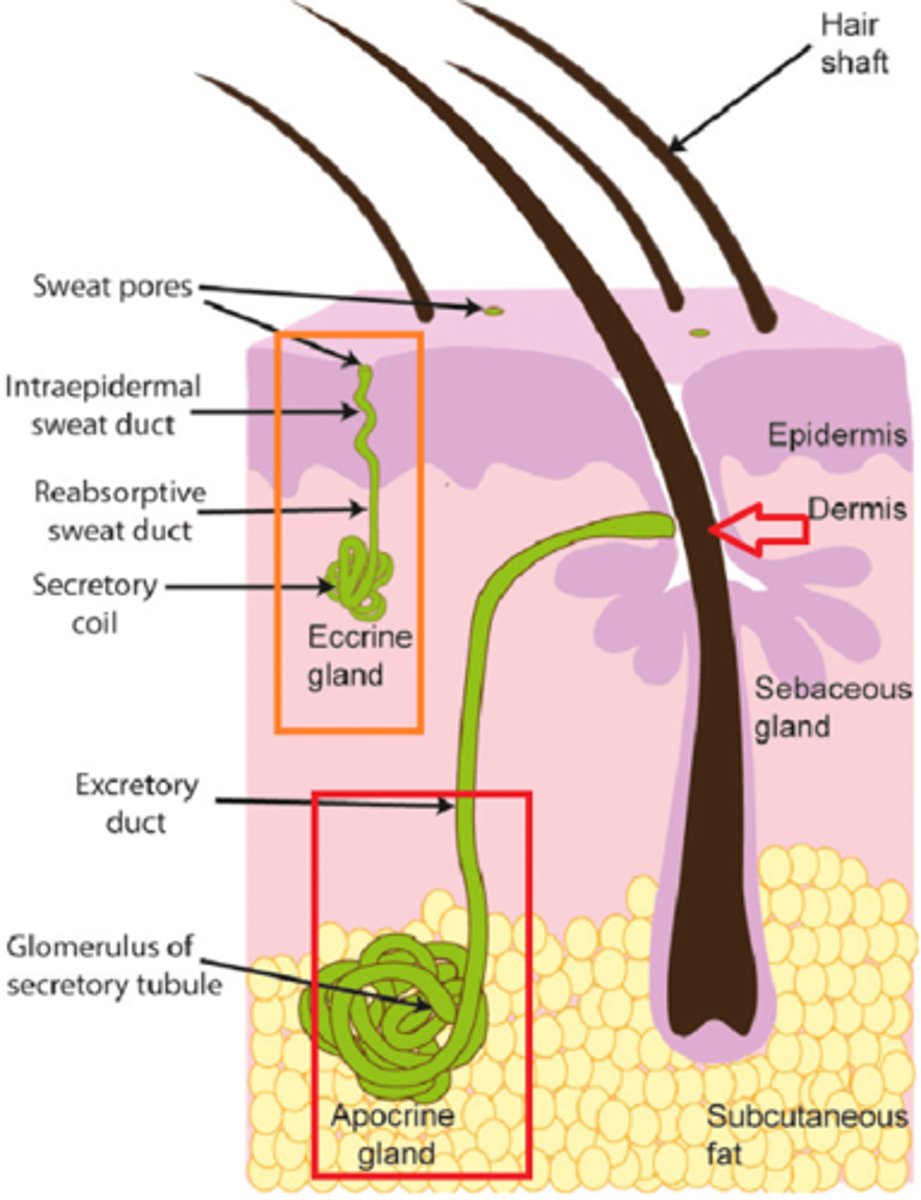
Sweat glands
1. Apocrine (lives deeper and secrete into hair follicle area, can be in genital and airmpit area and
2. eccrine (secrete directly onto the surface)
Melanin
Brownish pigmentation of the skin
Genetically determined
Increases with exposure to the sun
Carotene
Golden yellow pigment
Exists in the subcutaneous fat and in heavily keratinized areas
Oxyhemoglobin
Bright red pigmentation
Predominant in the arteries and capillaries
Deoxyhemoglobin
Darker and somewhat bluish pigment
Ex: cyanosis
OPQRST in derm
onset: new? What is the setting/location
provocation/palliative: what makes it better or worse?
quality: is the pain dull, burning or aching?
radiation: Where is it spreading? viral rashes tend to spread
severity: itching severity, 1-10 scale, nocturnal awakenings?
time: have you had it before, seasonally?
Common Derm Complaints
Skin lesions/rash/moles
Dry skin
Itching
Erythema (redness) to the skin
Bruising
Hair loss
Changes in nails
Personal Medical History: Derm
Recent travel? Outdoors a lot/recently?
Severe sunburns as a child?
Previous skin problems and treatments/biopsies?
Recent hospitalizations or surgeries?
Allergic skin reactions prior?
Recent viral or bacterial illness?
Are you pregnant? Are your menstrual periods regular?
Do you see a dermatologist?
Personal and Social History: Derm
Do you sunbathe/tan?
Do you perform skin self-examination once a month?
Exposed to chemicals or irritants that may harm the skin?
Long periods in one position? Important to know for elderly, can develop ulcers
Exposure to extreme temperatures?
Body piercings/tattoos?
Anything new? Changed?
- Ex: scents, lotions, detergents, creams
Smoking and/or drinking alcohol?
Stress in your life?
Family History
Exposure to sick contacts or rash?
Family history of skin conditions
Skin cancers? Melanoma is the worst to have
History of keloids?
Skin Exam: Prepare/set up
Adequate lighting
Examination equipment
- Ex: ruler
Change into a gown
- Maintain privacy with a drape
- Take off shoes/socks
Wash and warm your hands
Examine the patient while seated
- always tell the patient to get on exam table, not bed
Approach to the Skin Exam
Head-to-toe approach, full body exam
Hair/scalp
- Inspect
- Palpate
Skin/Nails
- Inspect, then palpate
- Face and neck
- Arms and Hands (including nails) and webbed areas
- Trunk and groin
- Legs and feet (including nails) and webbed areas
Skin Mobility and Turgor
Skin inspection
Color
Skin Type
Integrity
Hair distribution
Lesions:
- Types: Primary vs. Secondary vs. Vascular Lesions
- Note:Location, distribution, pattern/configuration, shape, size, color, number, ABCDE
Skin Type - Fitzpatrick Scale
Type I and II more likely to get skin cancer

Skin Exam - Palpation
Temperature and Moisture - use the back of hands to examine and check from head to feet
Texture and thickness
Mobility and turgor - mobility is how much the skin moves, turgor is the ability to come back to normal, pulling up skin then letting go.
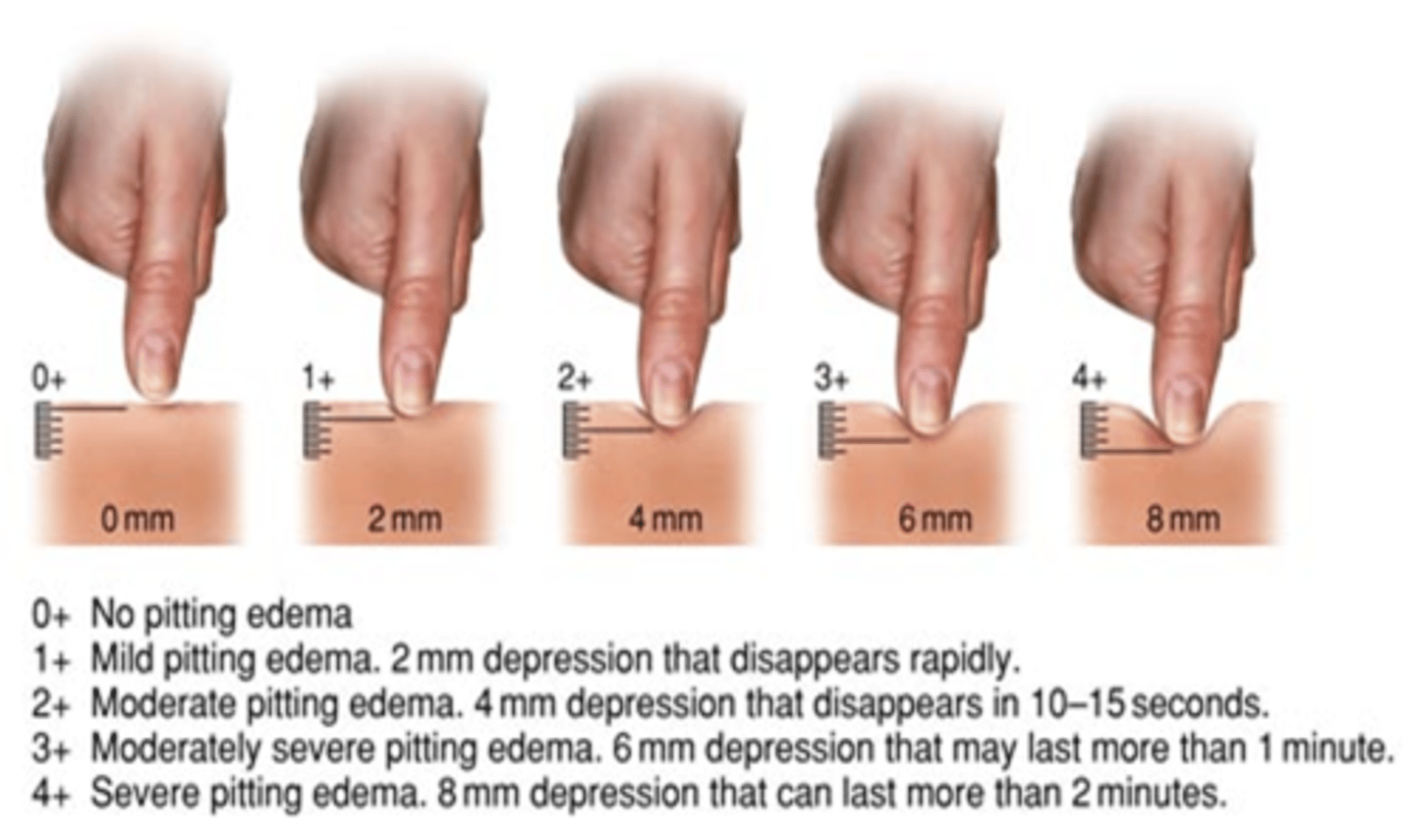
Swelling (Edema) and pitting edema (in legs push in and let go, how long does the indent go.
Skin Lesions
Primary Lesions: develop on previosly nl skin
- Ex: Macule, patch, papule, plaque, nodule, pustule, vesicle, bulla, wheal, etc.
Secondary Lesions: primary lesions that have changed, i.e starts with hive then you itch and now have escoriasion
- Ex: Erosion, scar, ulcer, fissure, etc.
Vascular lesions: BV that is comprimised: could be dt truama or congenital
- Reddish-blue lesions
Primary lesions: Macule
A flat, non-palpable lesion measuring < 1 cm.
- Ex: freckles, flat moles
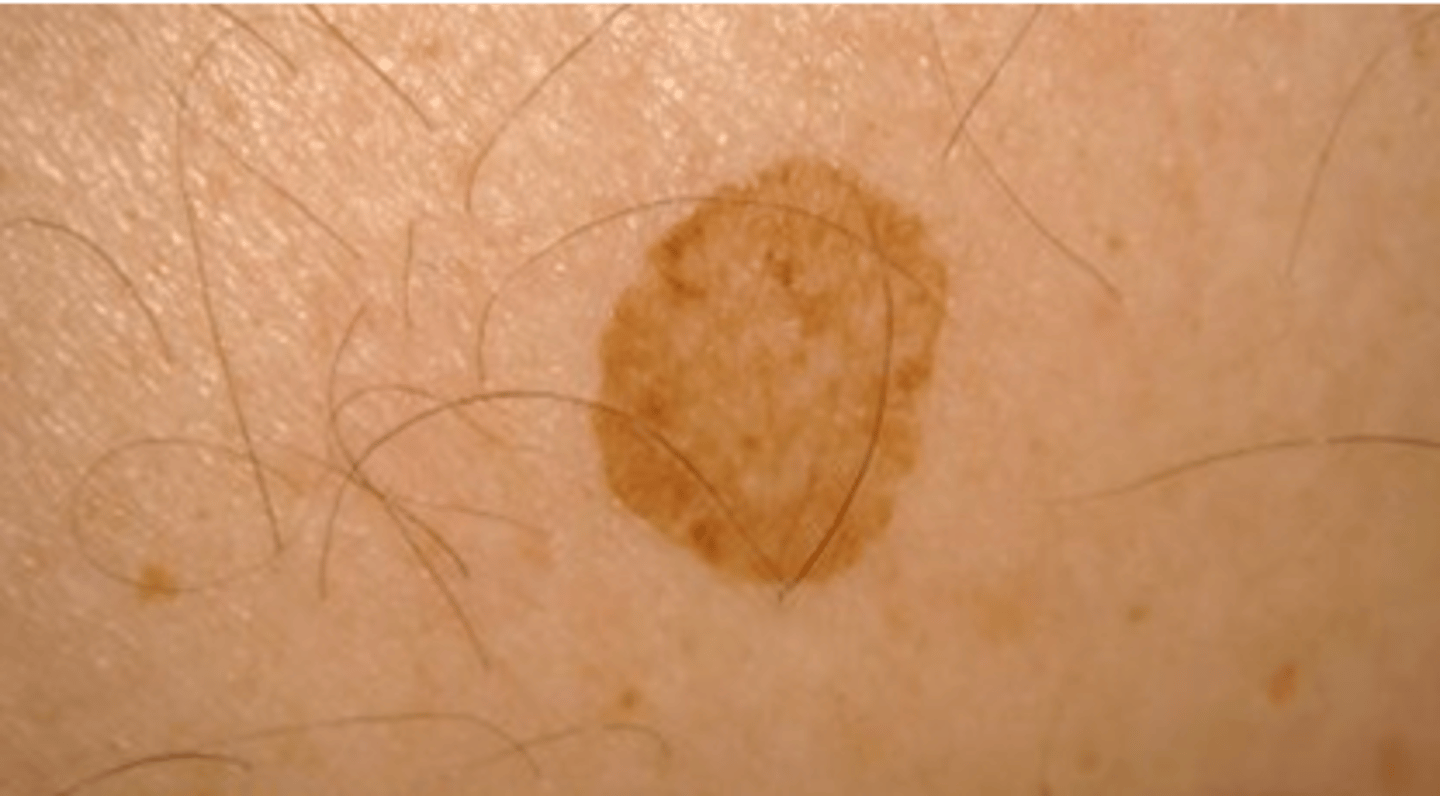
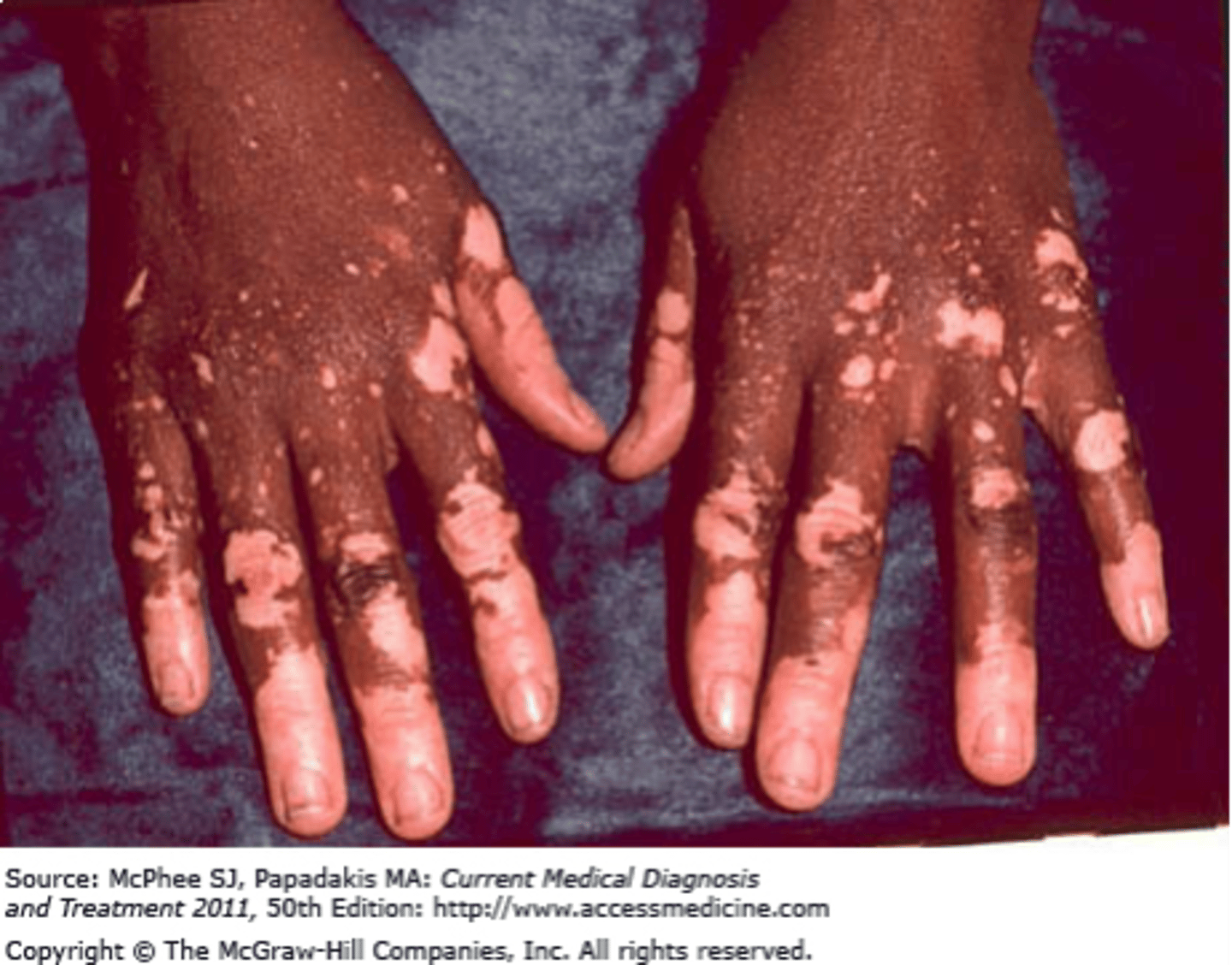
Primary lesion: Patch
Same as a macule, but > 1 cm
- Ex: Vitiligo
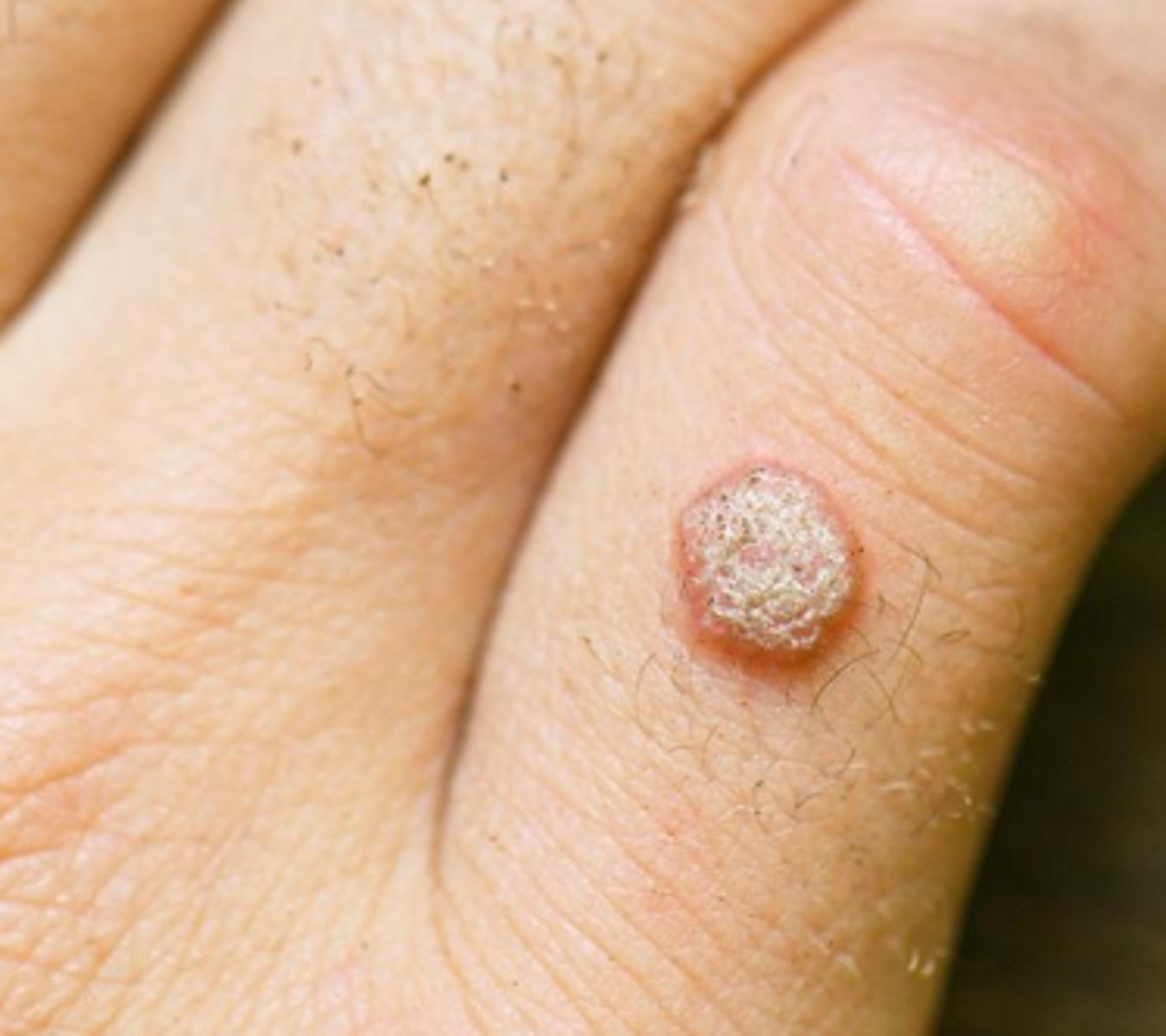
Primary Lesion: Papule
•A solid, elevated, palpable lesion measuring < 1 cm
- Ex: Elevated nevus, wart, insect bite, acne
primary lesions: nodule
•Solid, firm, rounded elevation of the skin, usually > 1 cm
•Typically extends into deep skin layers
- Ex: Cyst, tumor, lipoma
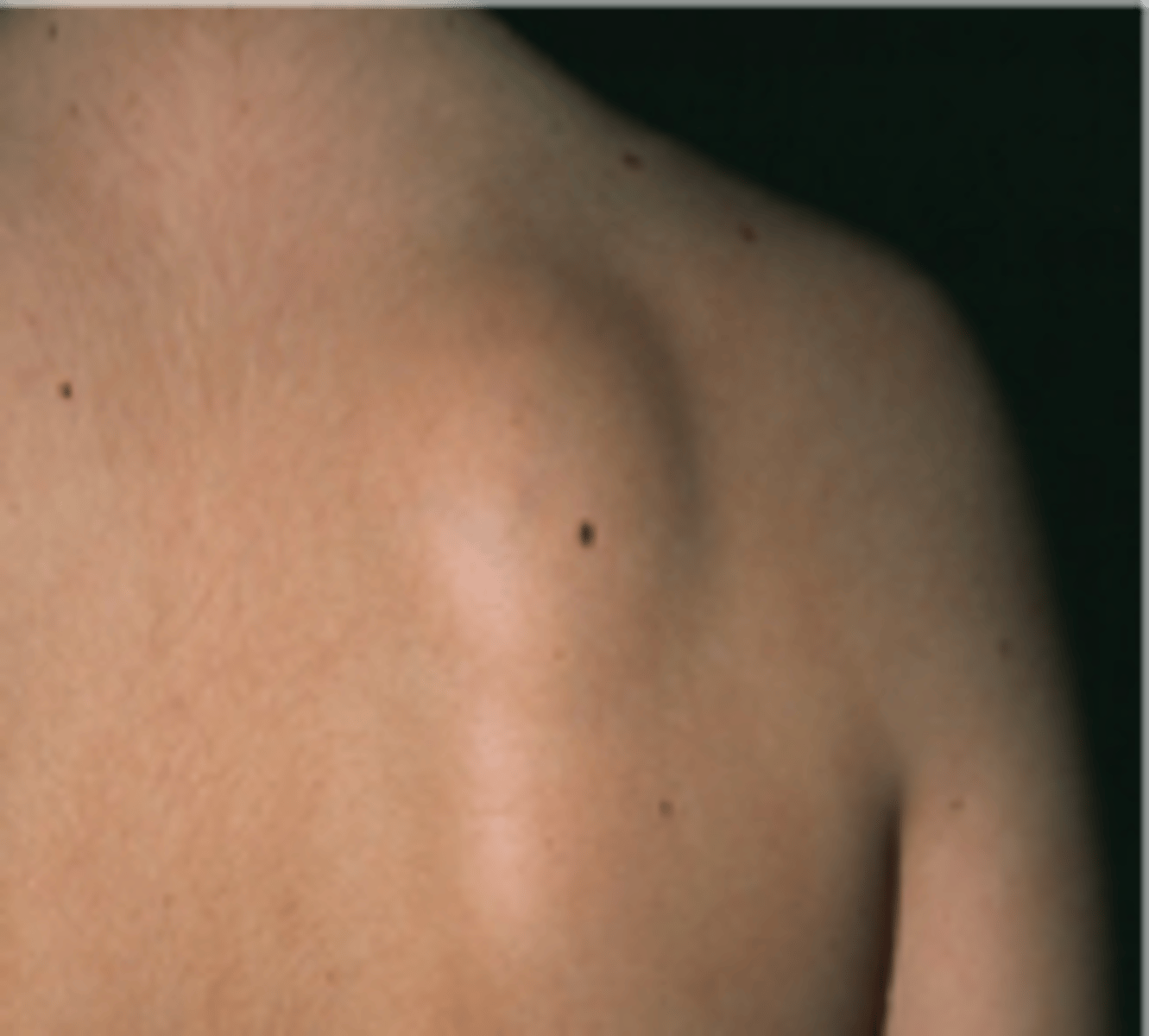
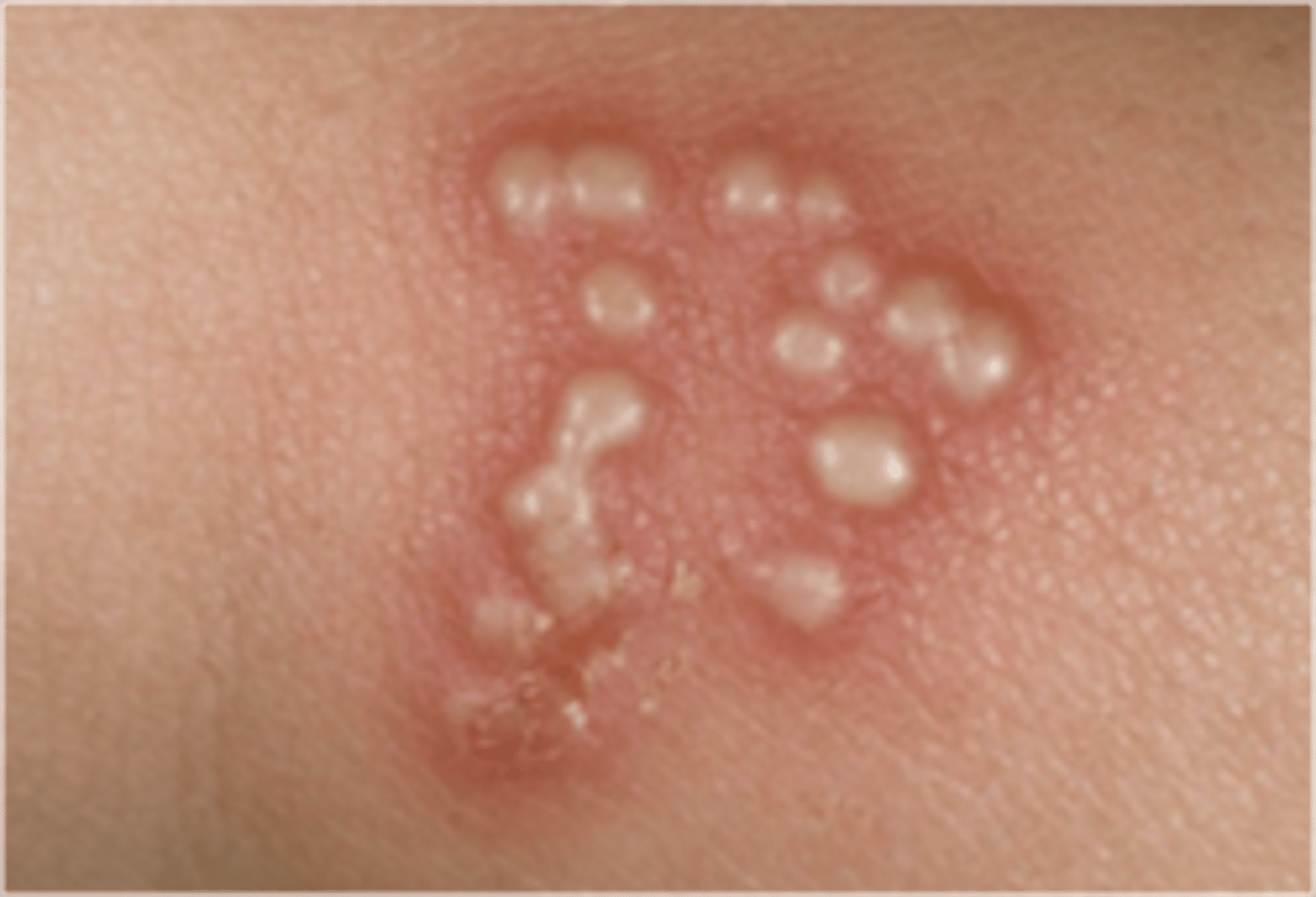
Primary Lesion: Vesicle
Small circumscribed elevation of the epidermis containing clear fluid, < 1 cm in diameter
- Ex: herpes simplex, herpes zoster, allergic contact dermatitis
Primary Lesion: Bulla
A circumscribed elevation of the epidermis containing clear fluid >1 cm in diameter
- Ex: 2nd degree burn
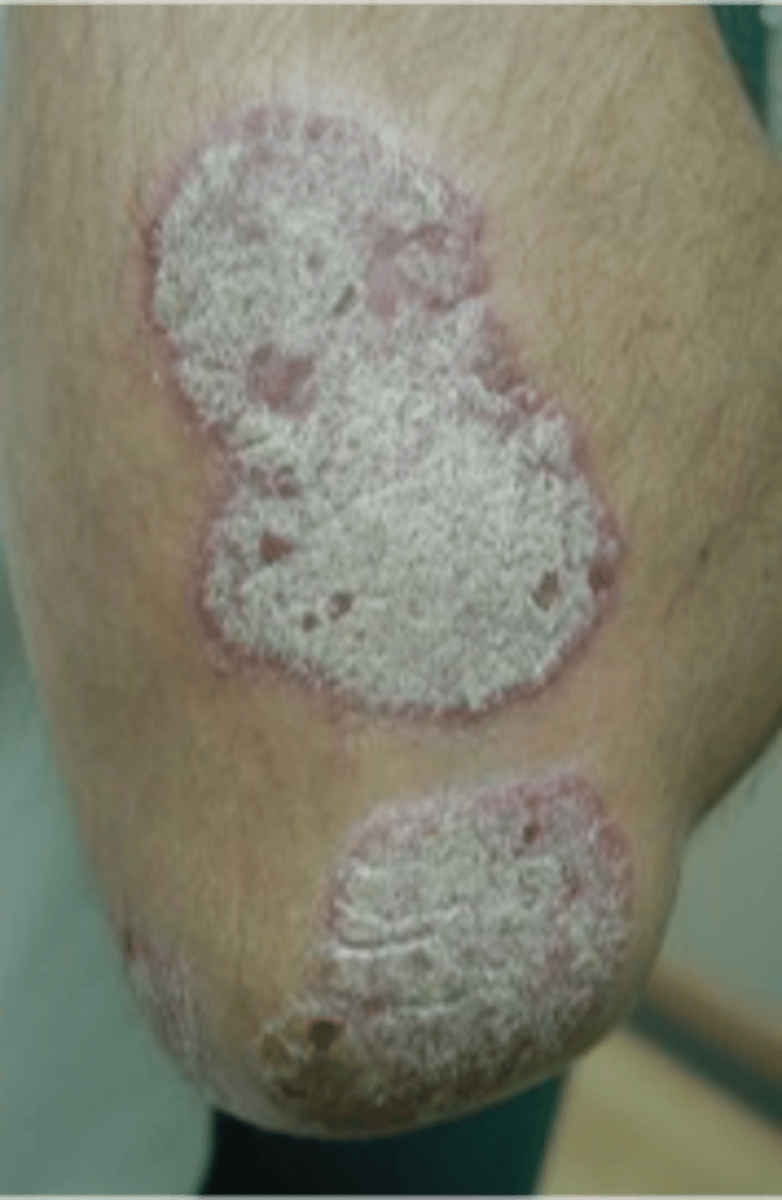
Primary Lesion: Plaque
A solid flat elevated lesion, usually >1 cm
- Ex: Psoriasis
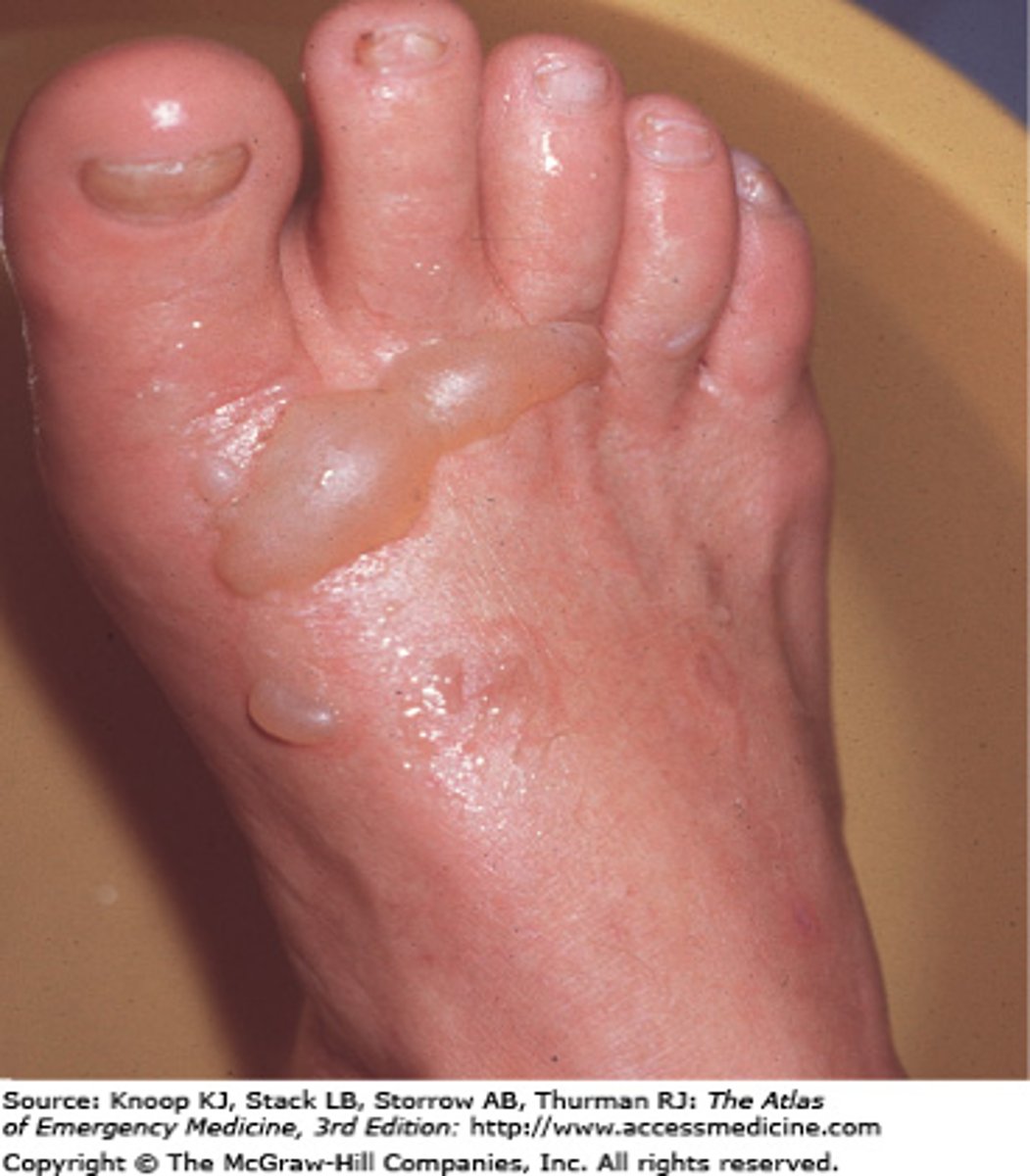
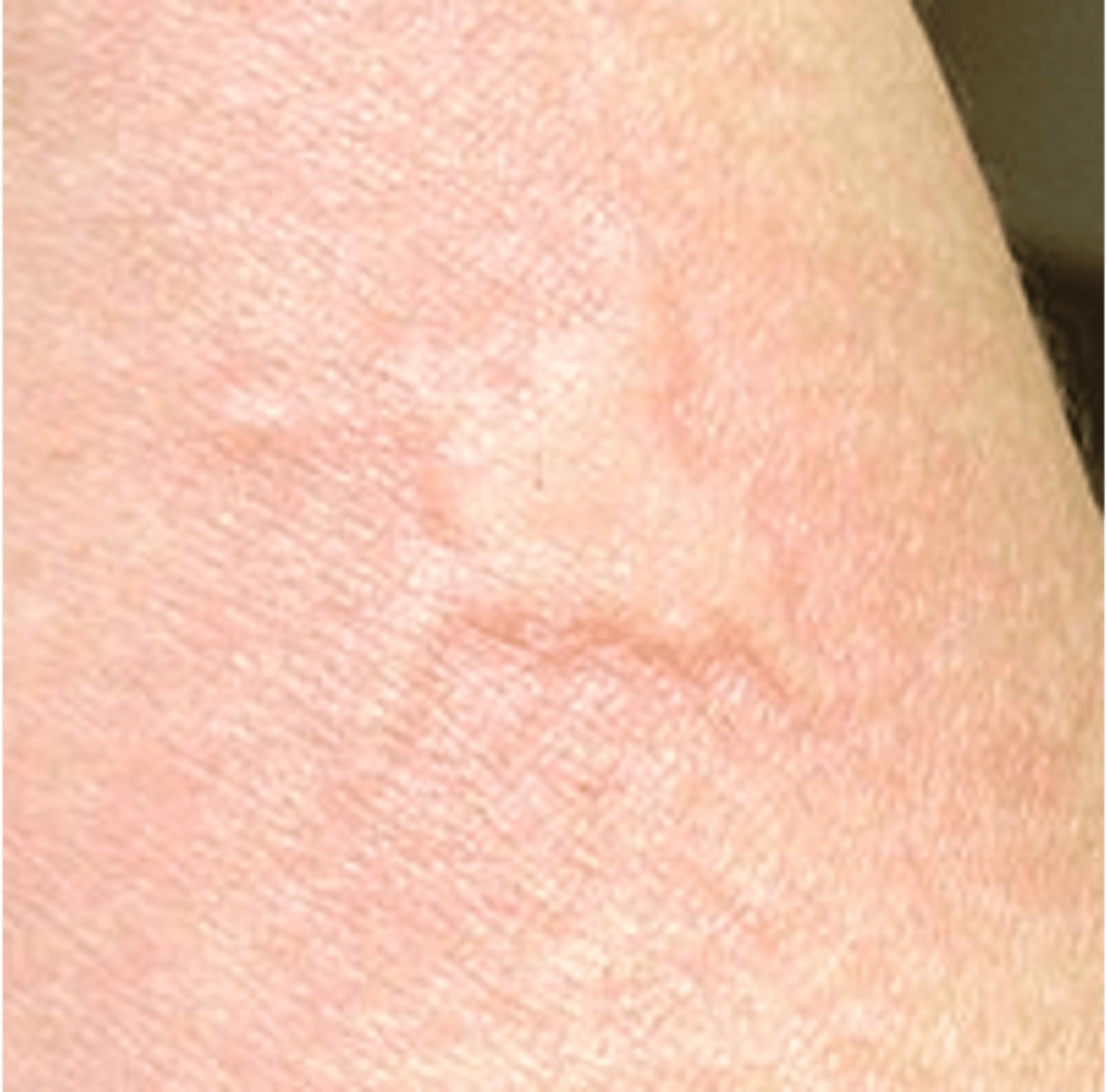
Primary Lesion: Wheal
A circumscribed, raised lesion consisting of dermal edema
- Ex: hives, mosquito bite
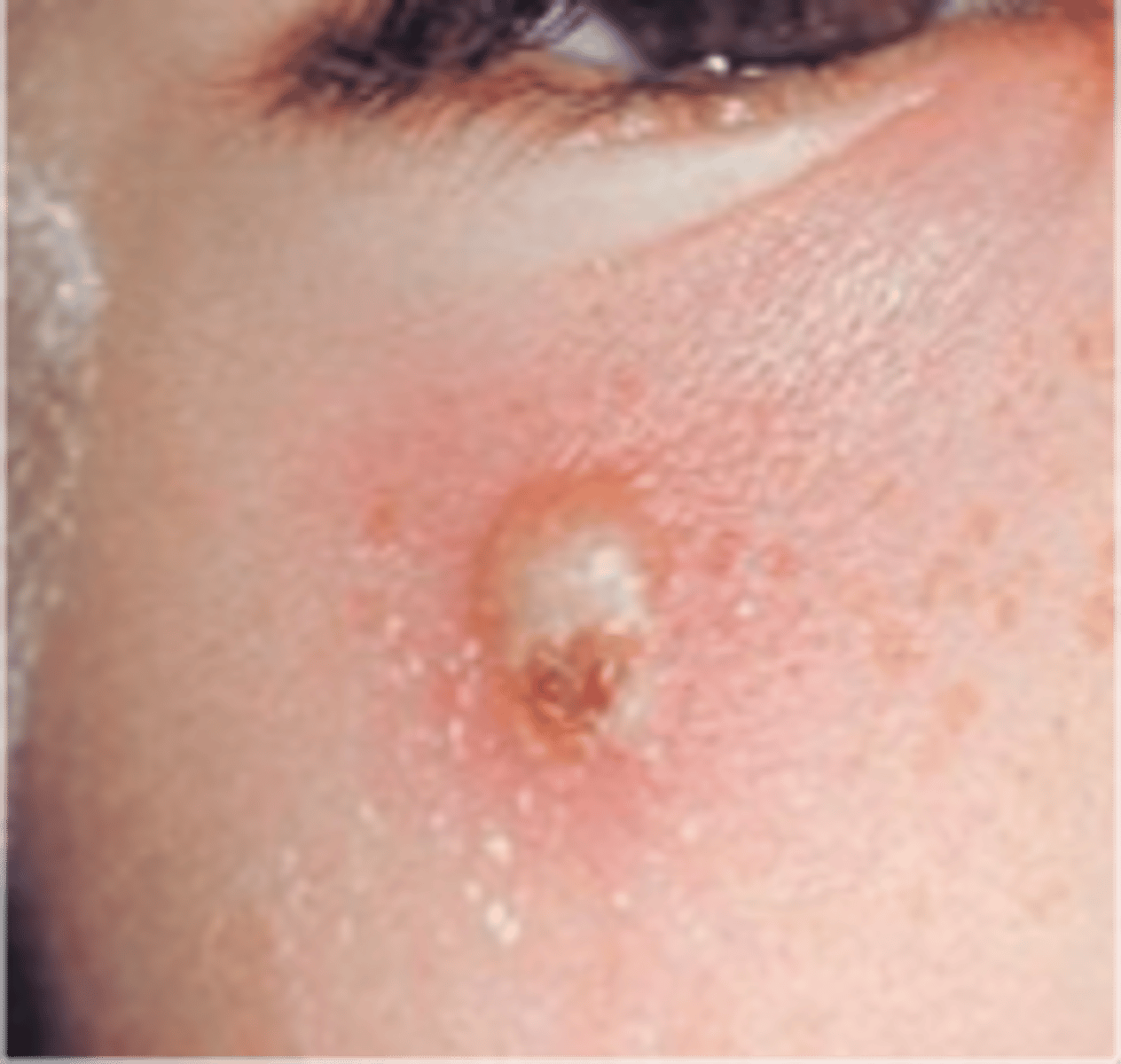
Primary Lesion: Pustule
Small palpable collection of pus
- Ex: Acne, impetigo
Primary lesions: Comedone
The plugged opening of a sebaceous gland at pore/follicle
- Ex: Acne
- White (closed)
- Black (open)
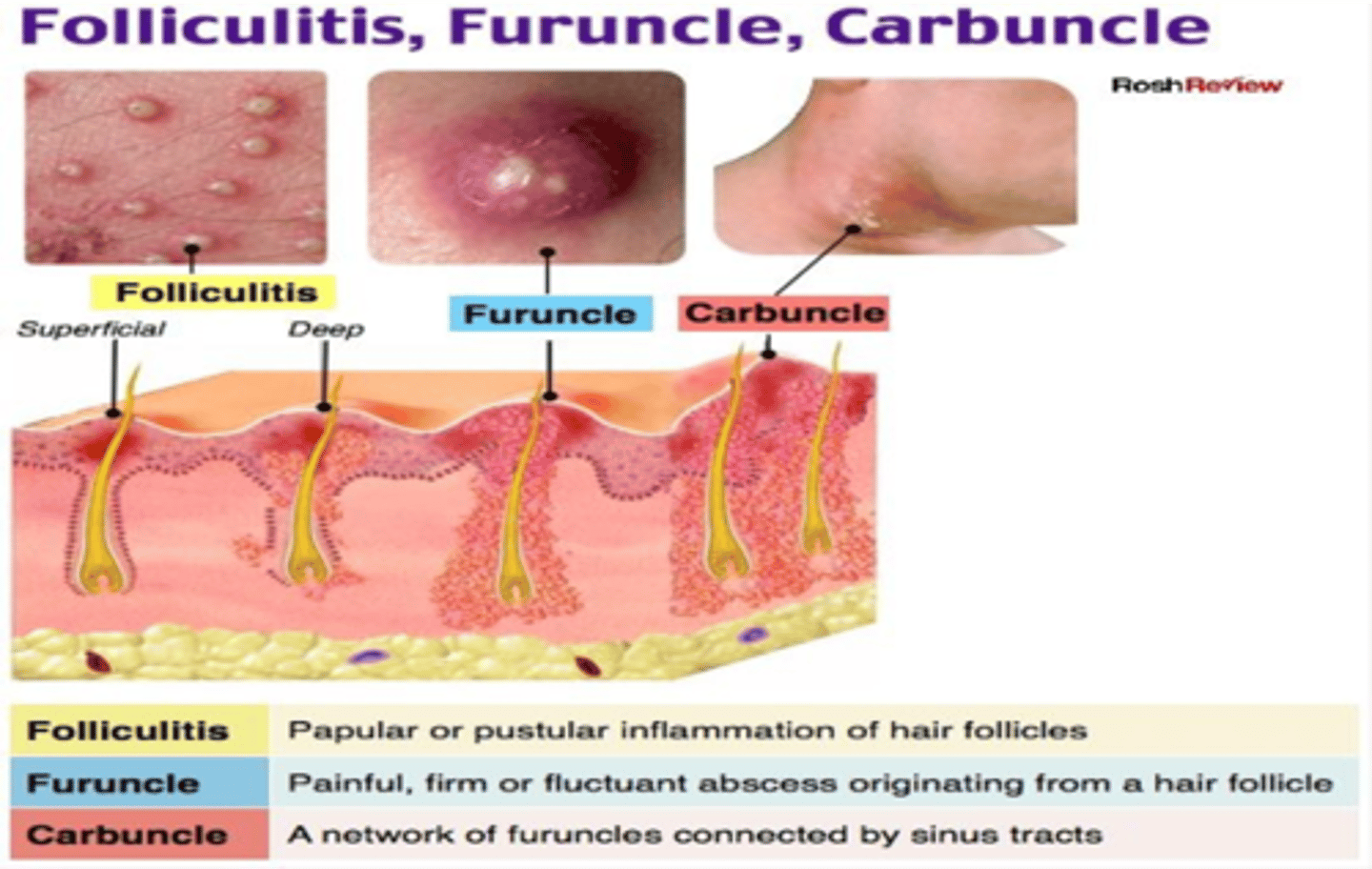
Primary Lesion: Furuncle and carbuncle
Furuncle: Skin abscesses at the hair follicle and surrounding tissues
Carbuncle: ØMultiple furuncles form a carbuncle
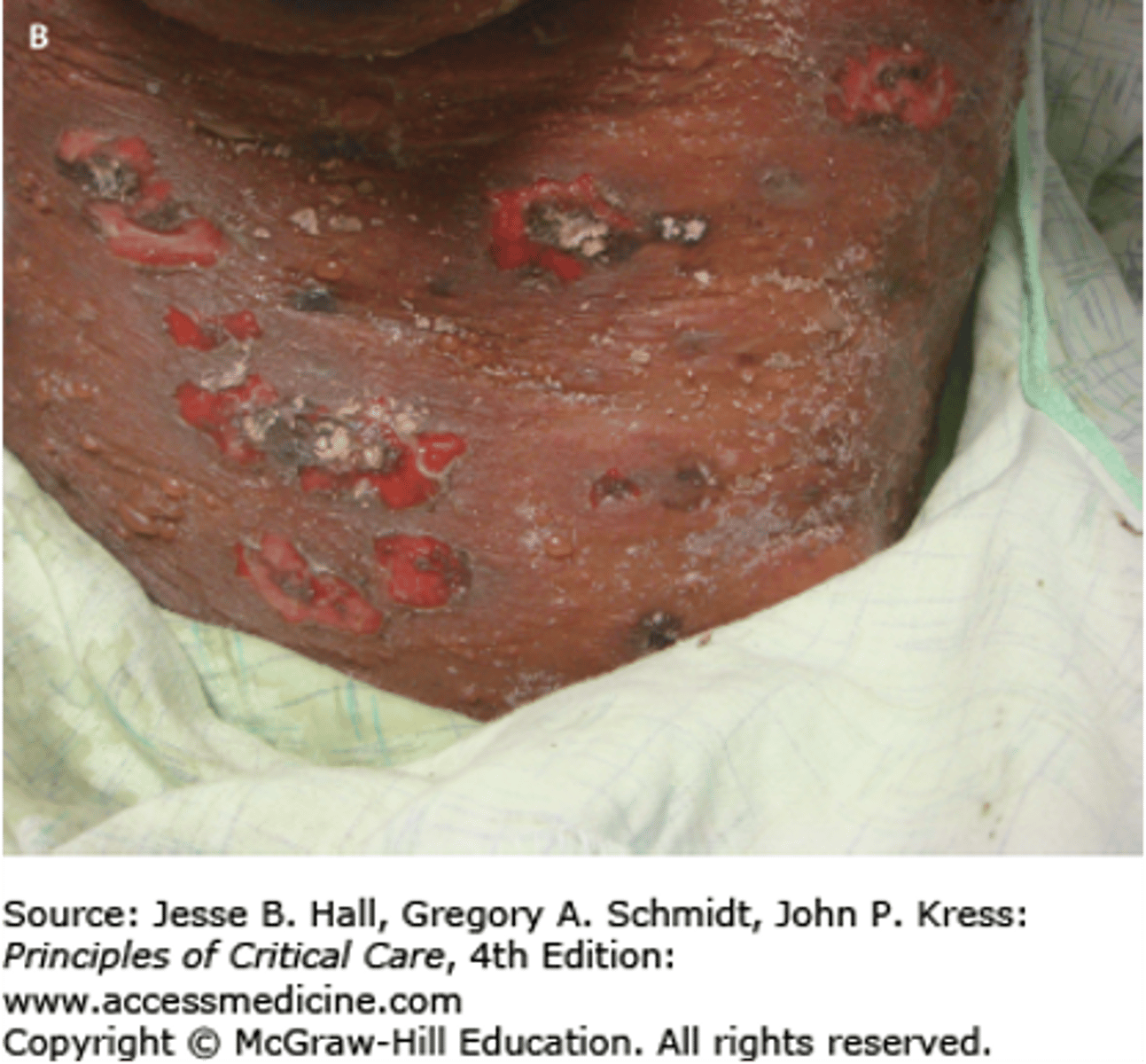
Secondary Lesions: Erosion
Loss of the superficial epidermis, the surface is moist but does not bleed
- Ex: Rupture of a vesicle in chicken pox
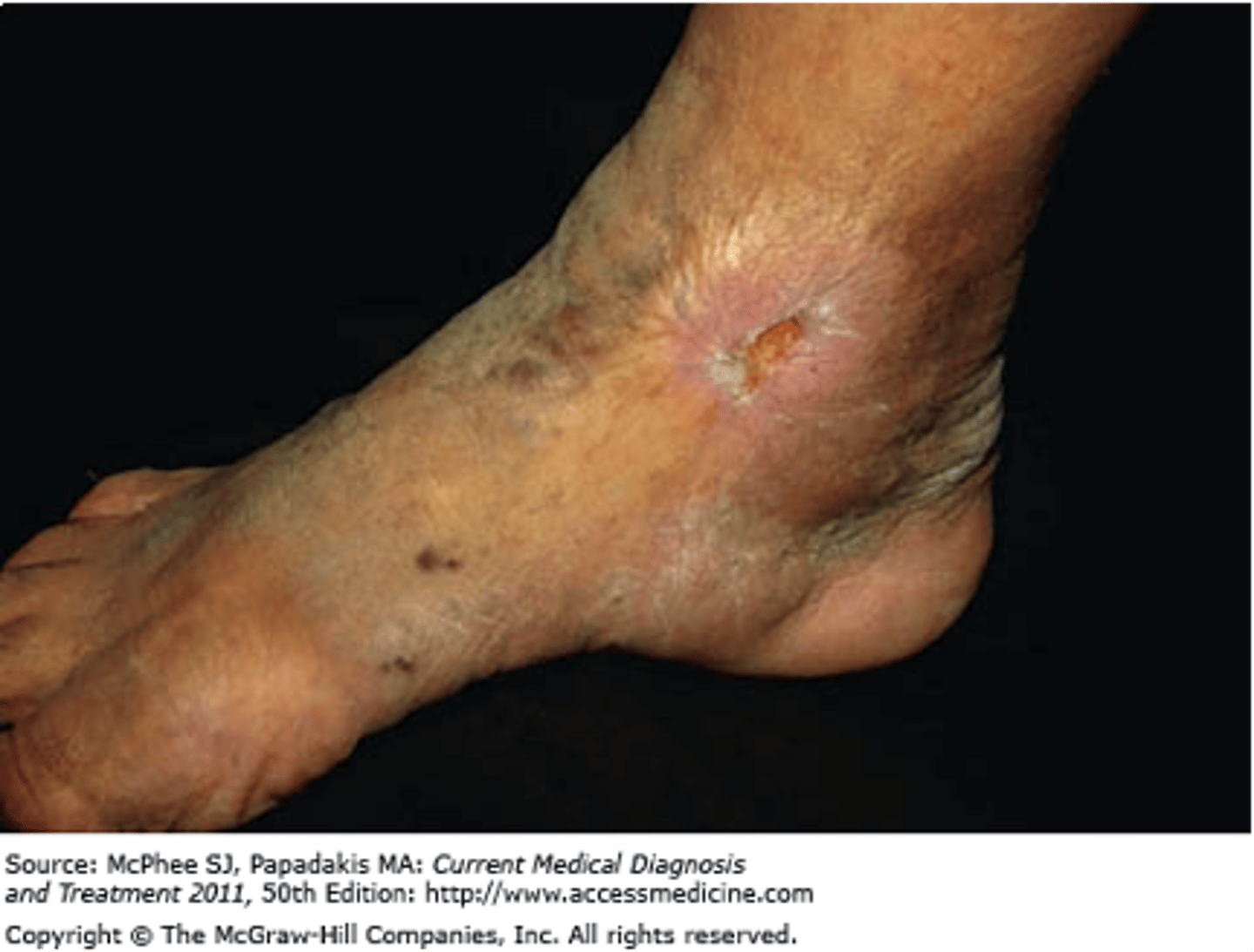
Secondary lesion: Ulcer
Full-thickness loss of the epidermis with damage to the dermis
Important, especially in bed-bound patients.
May bleed and scar
- Ex: venous stasis ulcers, syphilitic chancre
Secondary Lesion: Crust
Dried exudate overlying and impaired epidermis
- Ex: Impetigo
Secondary Lesion: Scale
Accumulation of loose fragments exfoliated epidermis
- Ex: Dandruff or psoriasis
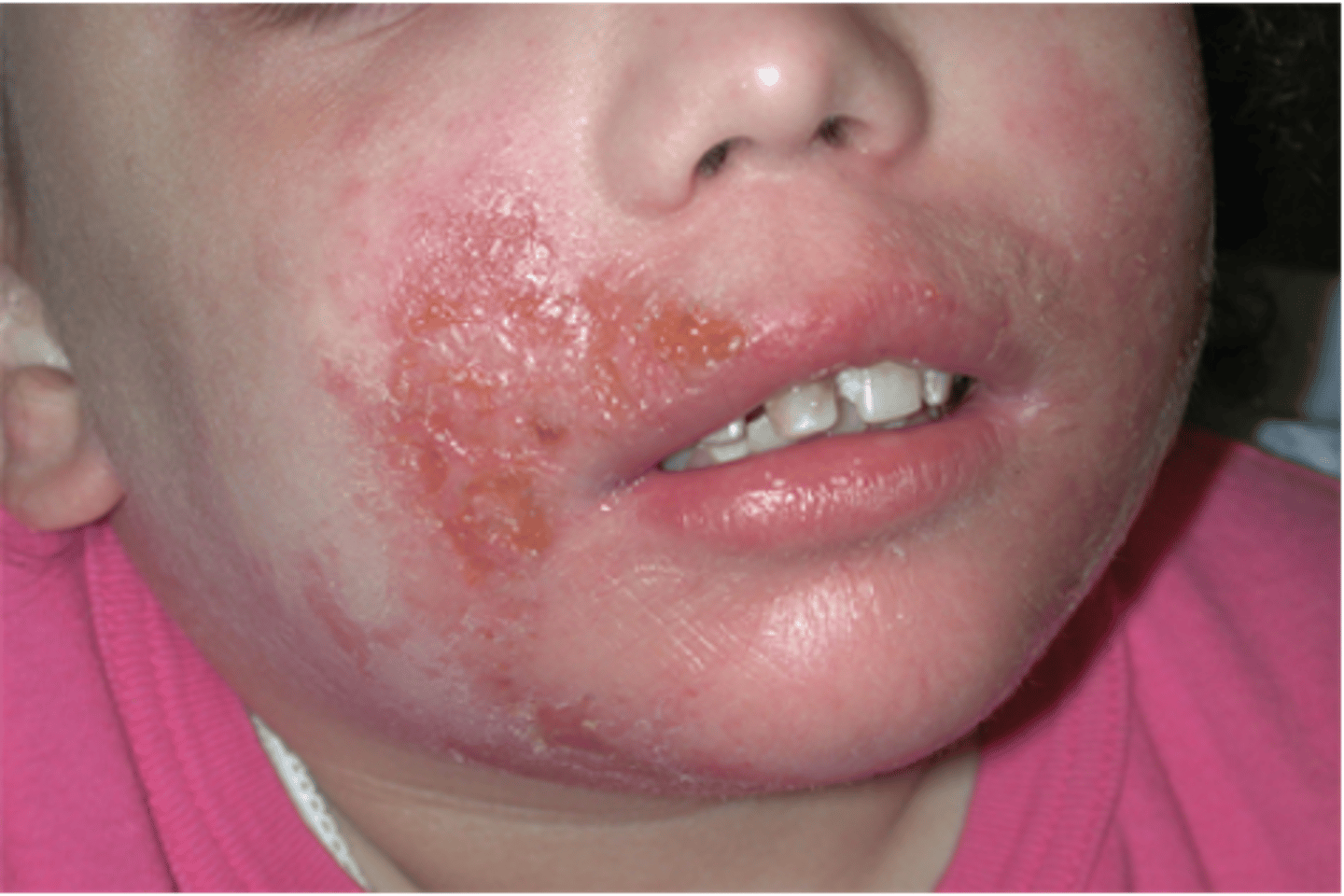
Secondary lesion: Lichenification
Thickening and roughening of the skin with increased visibility of the normal skin furrows
- Ex: atopic dermatitis
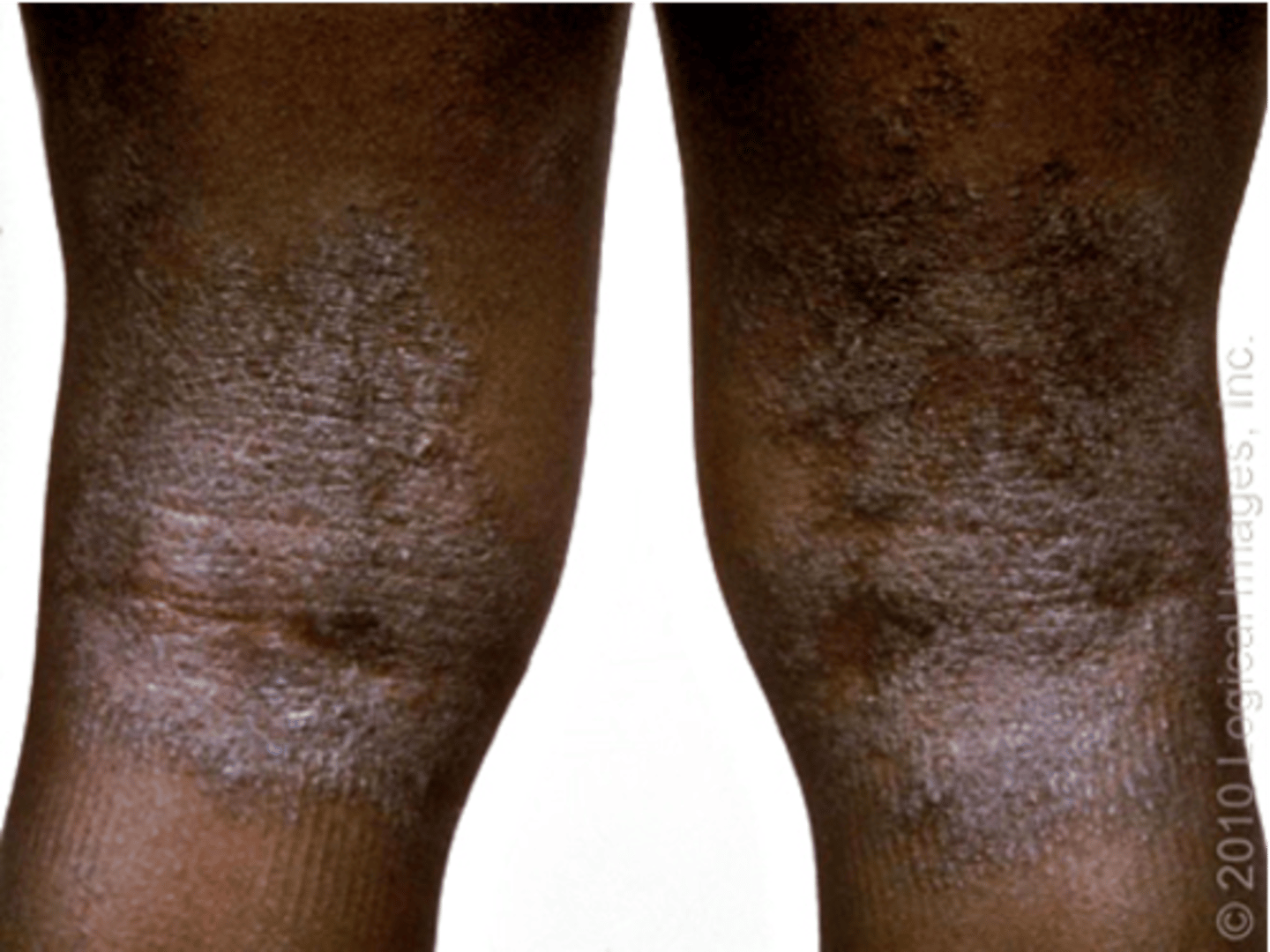
Secondary Lesion: Atrophy
Thinning of the skin with the loss of the normal skin furrows
- Skin looks shinier and more translucent
- Seen in aging
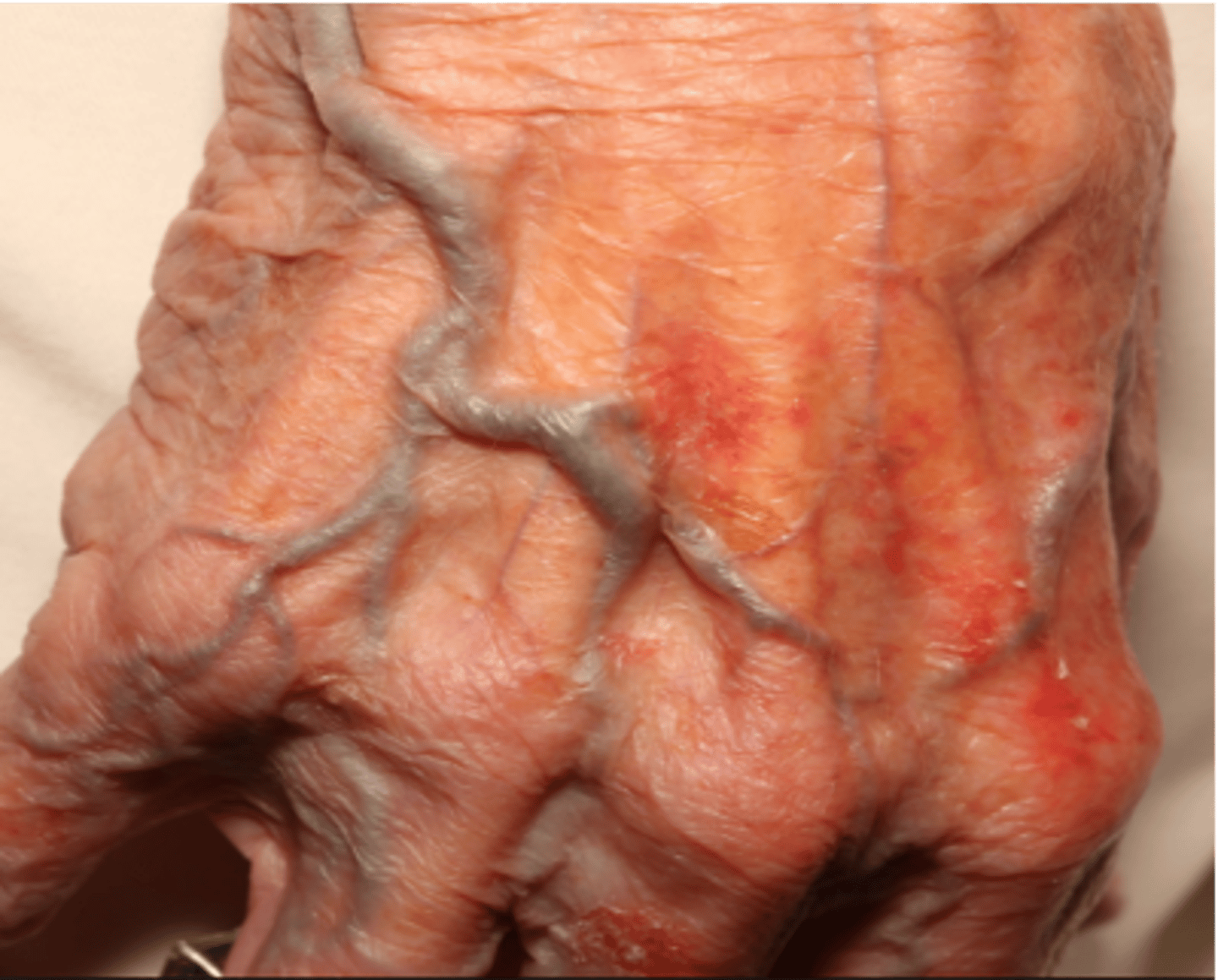
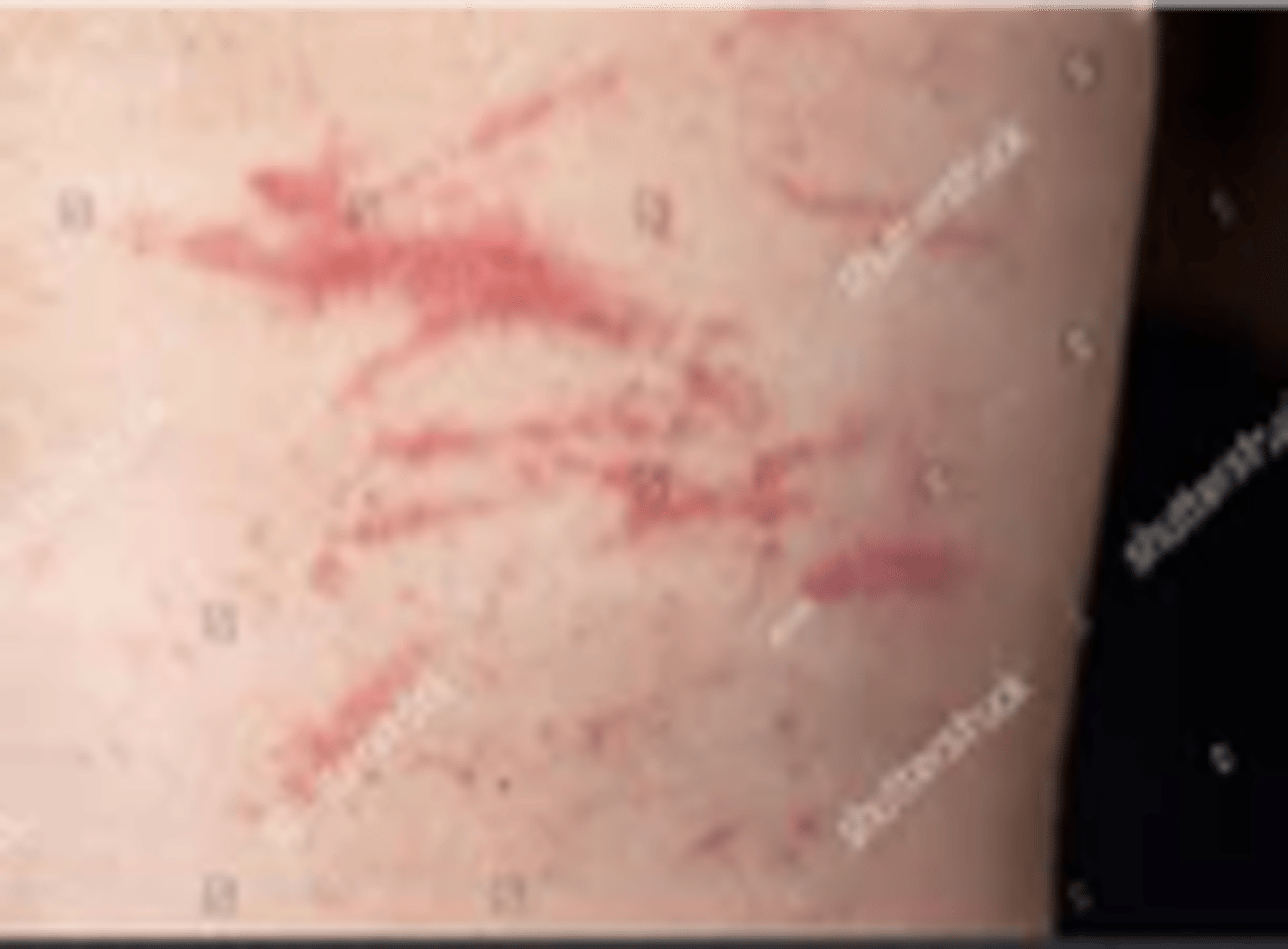
Secondary Lesion: Excoriation
An abrasion or scratch mark.
May be linear or rounded.
Secondary Lesion: Scar
Replacement of destroyed tissue with a more fibrous tissue
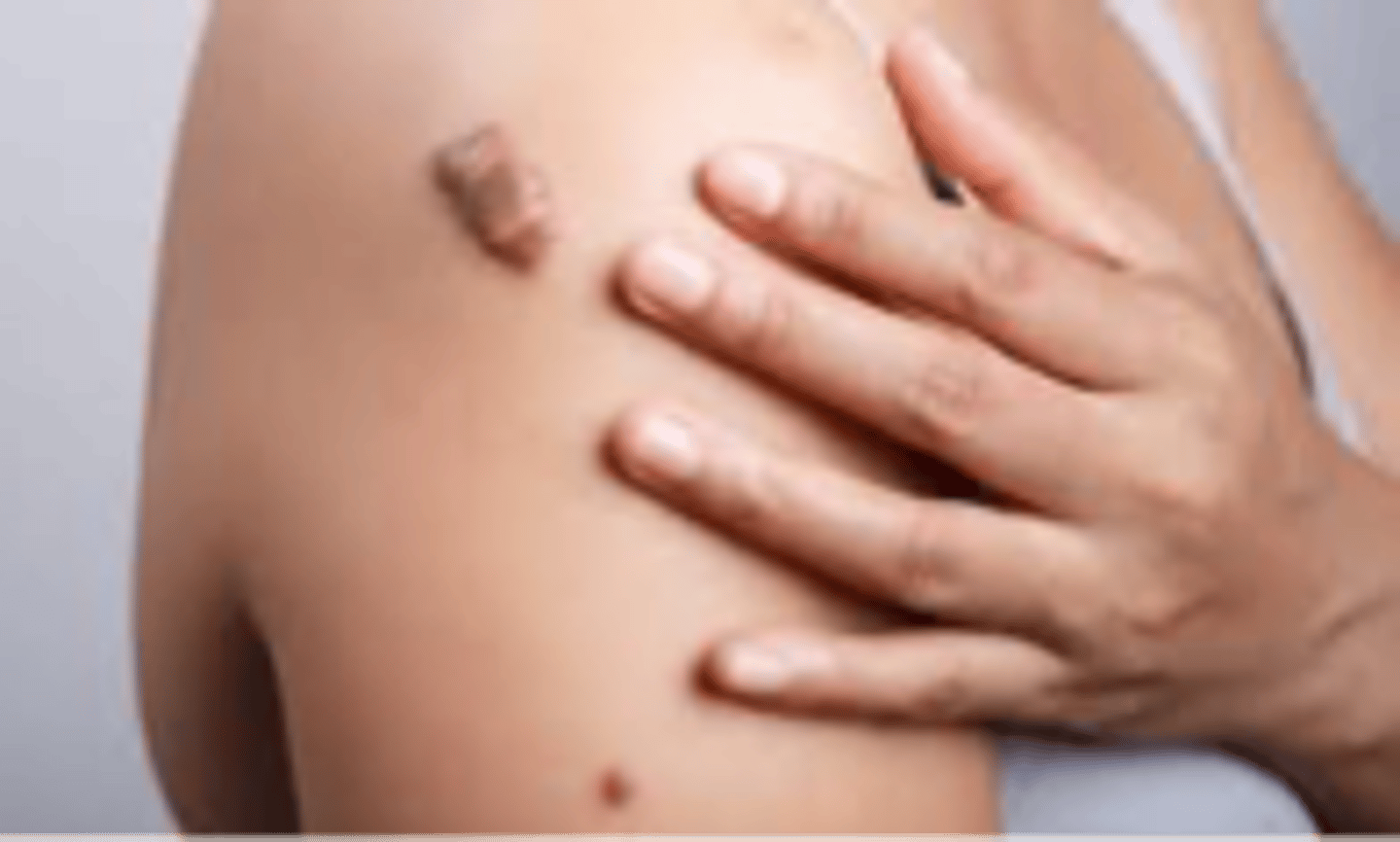
Secondary Lesion: Keloid
Firm, hypertrophic mass of scar tissue that extends beyond the area of injury
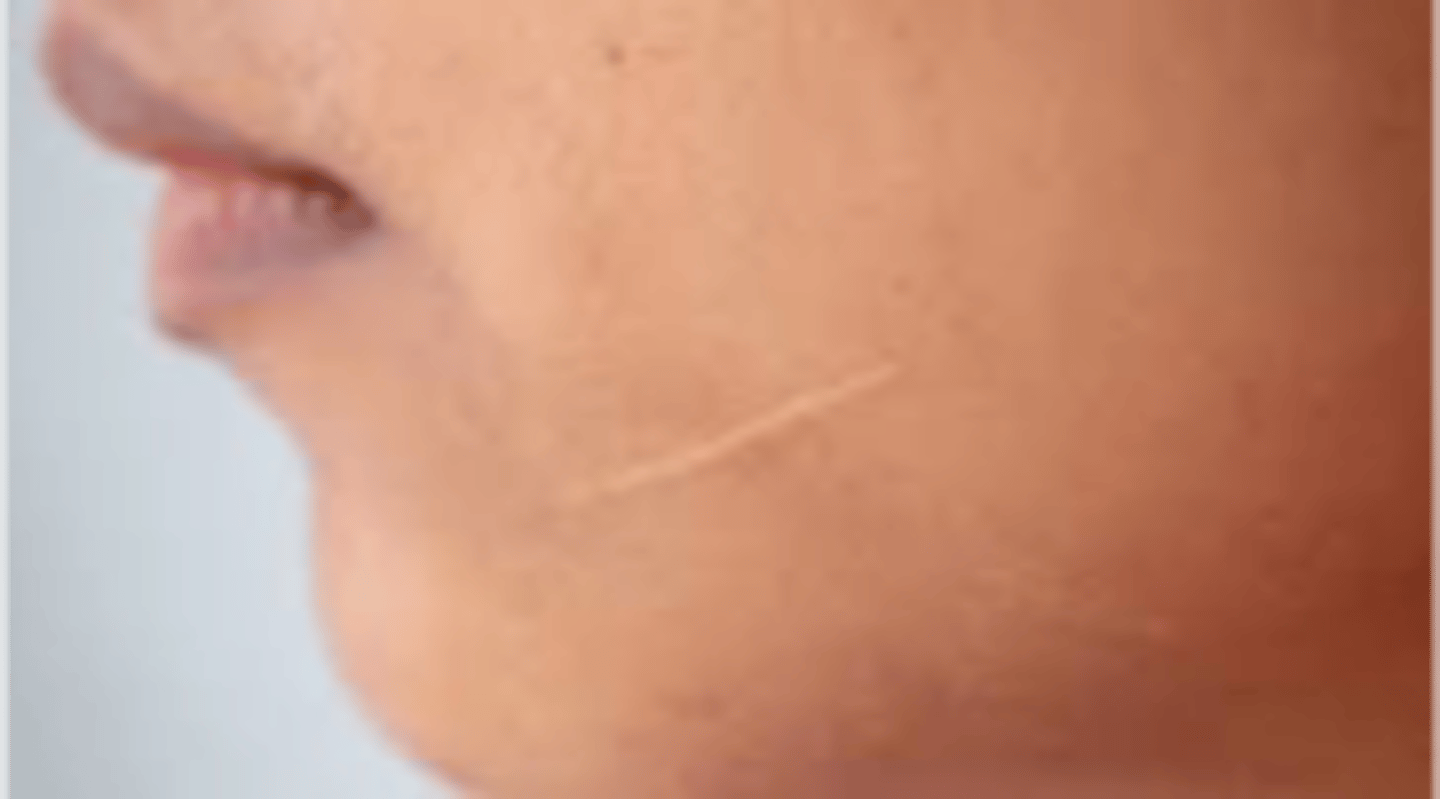
Secondary Lesion: Fissure
A linear crack in the skin
- Ex: Angular cheilitis
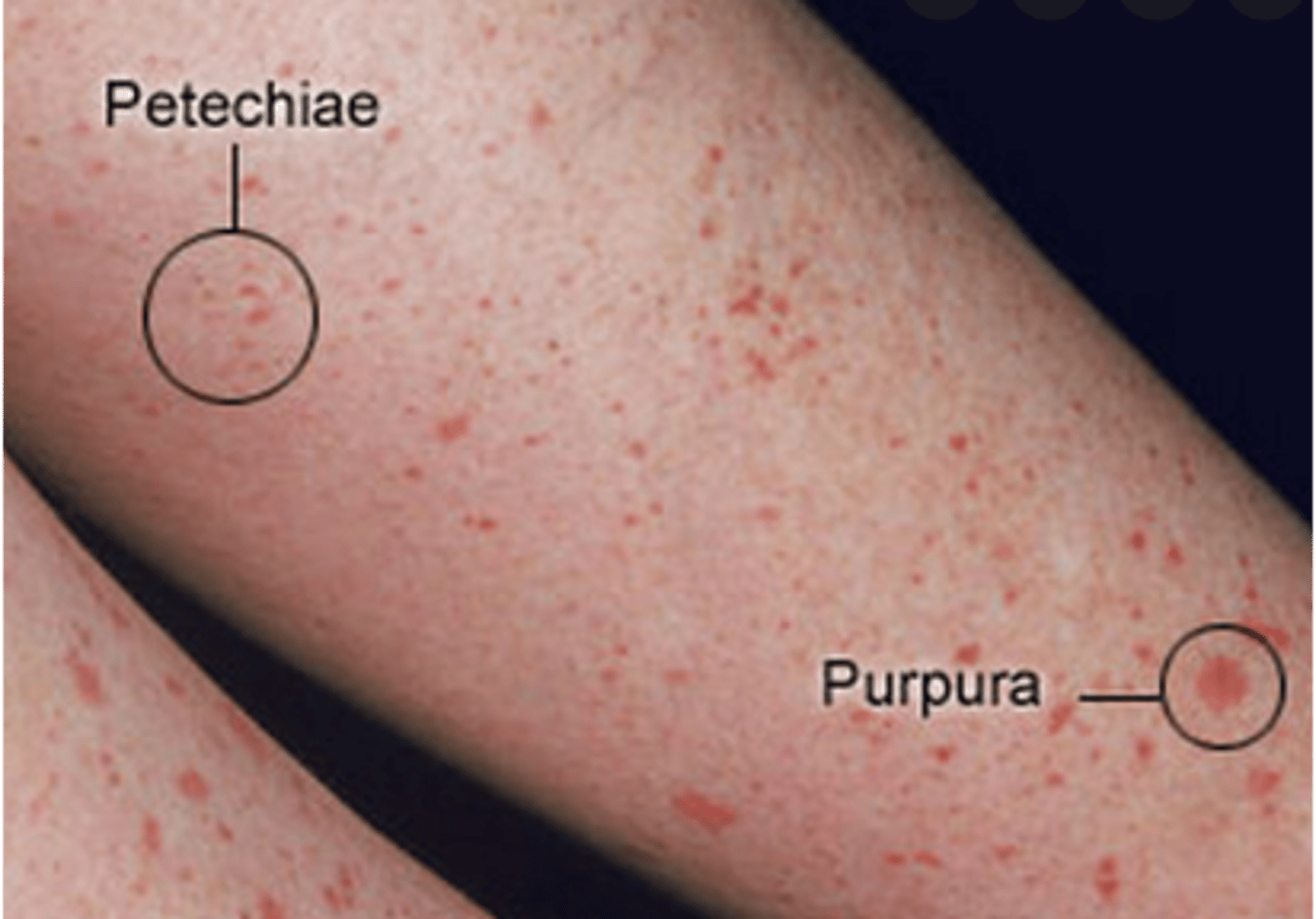
Vascular lesions: Petechiae and Purpura
Petechiae: Reddish-purple macules <4 mm
Purpura: Reddish-purple macules, 4 mm - 10mm
Vascular lesions: Ecchymosis
Purple or blue macules caused by trauma, fade over time, >10mm
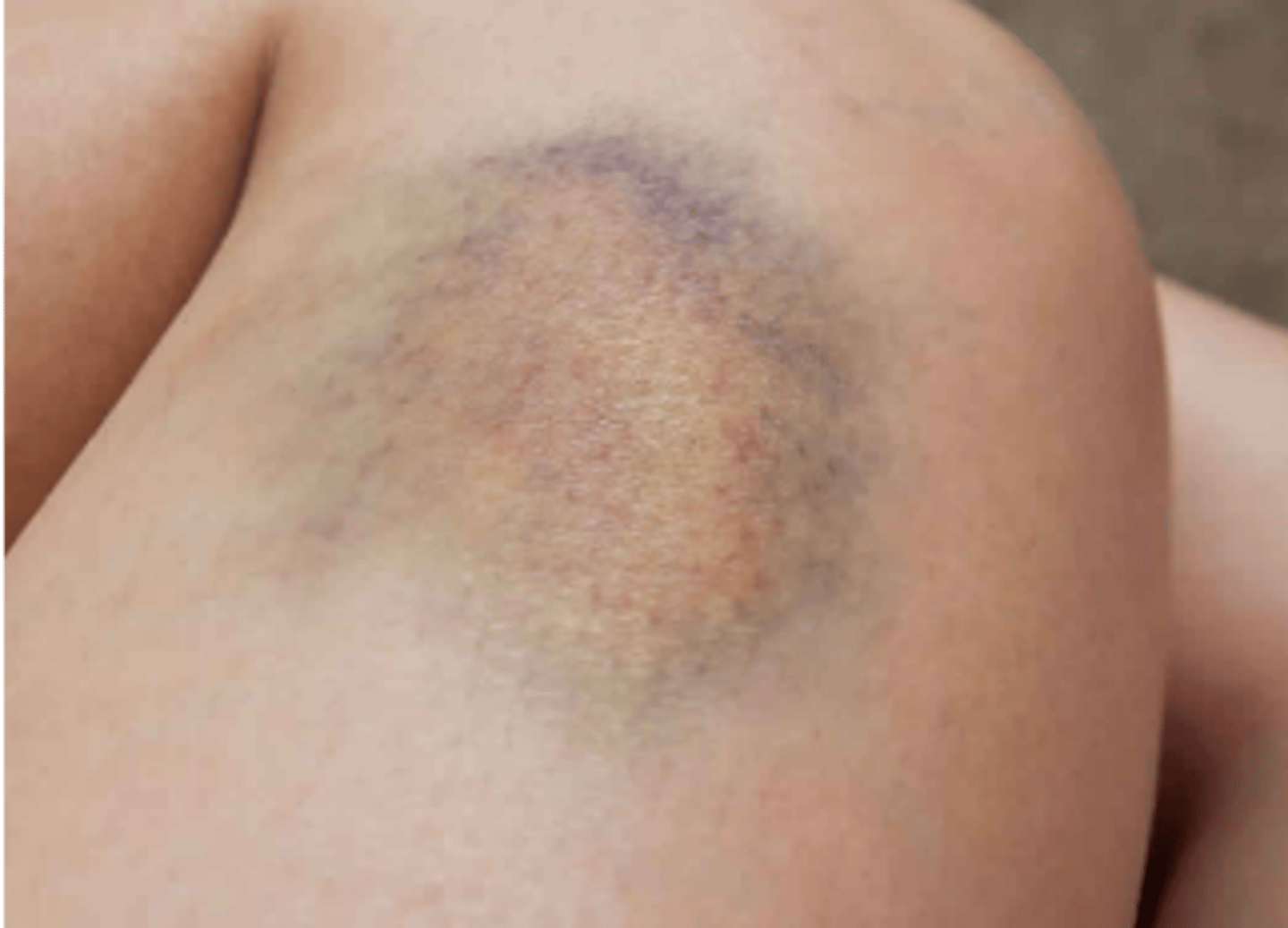
Vascular Lesions: Hematoma
Localized collection of blood creating an elevated ecchymosis.
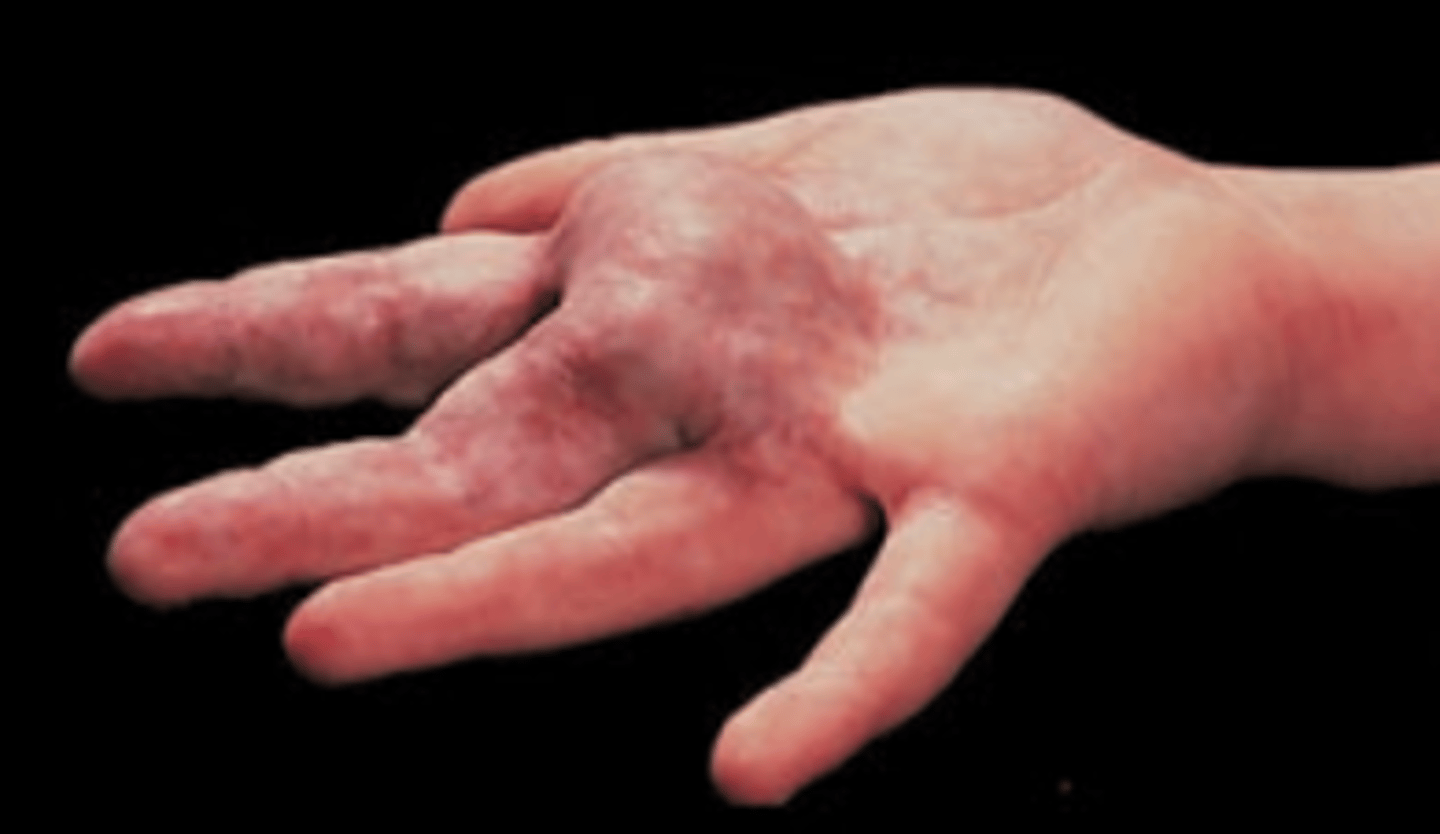
Vascular lesions: Telangiectasia
Fine, irregular blood vessels
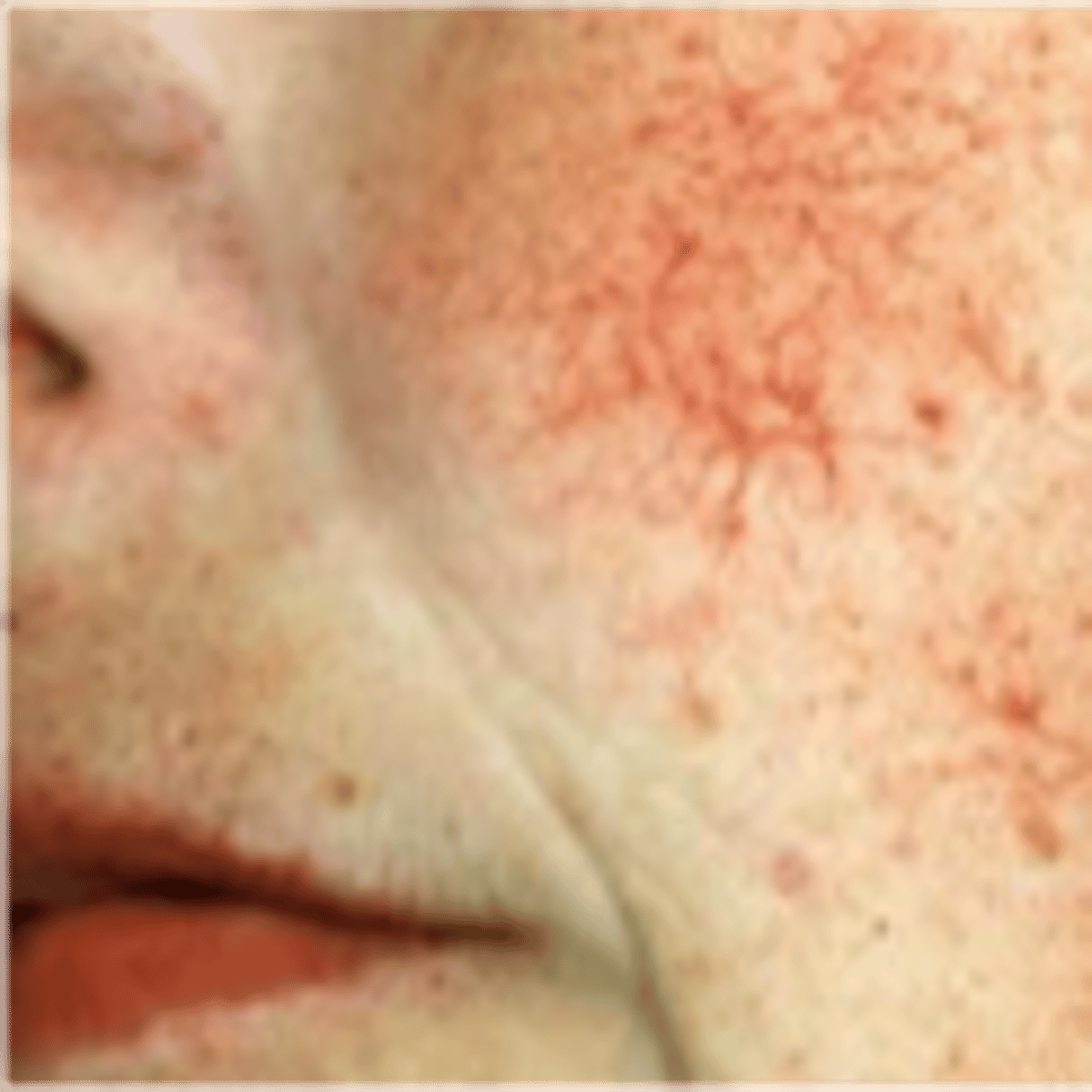
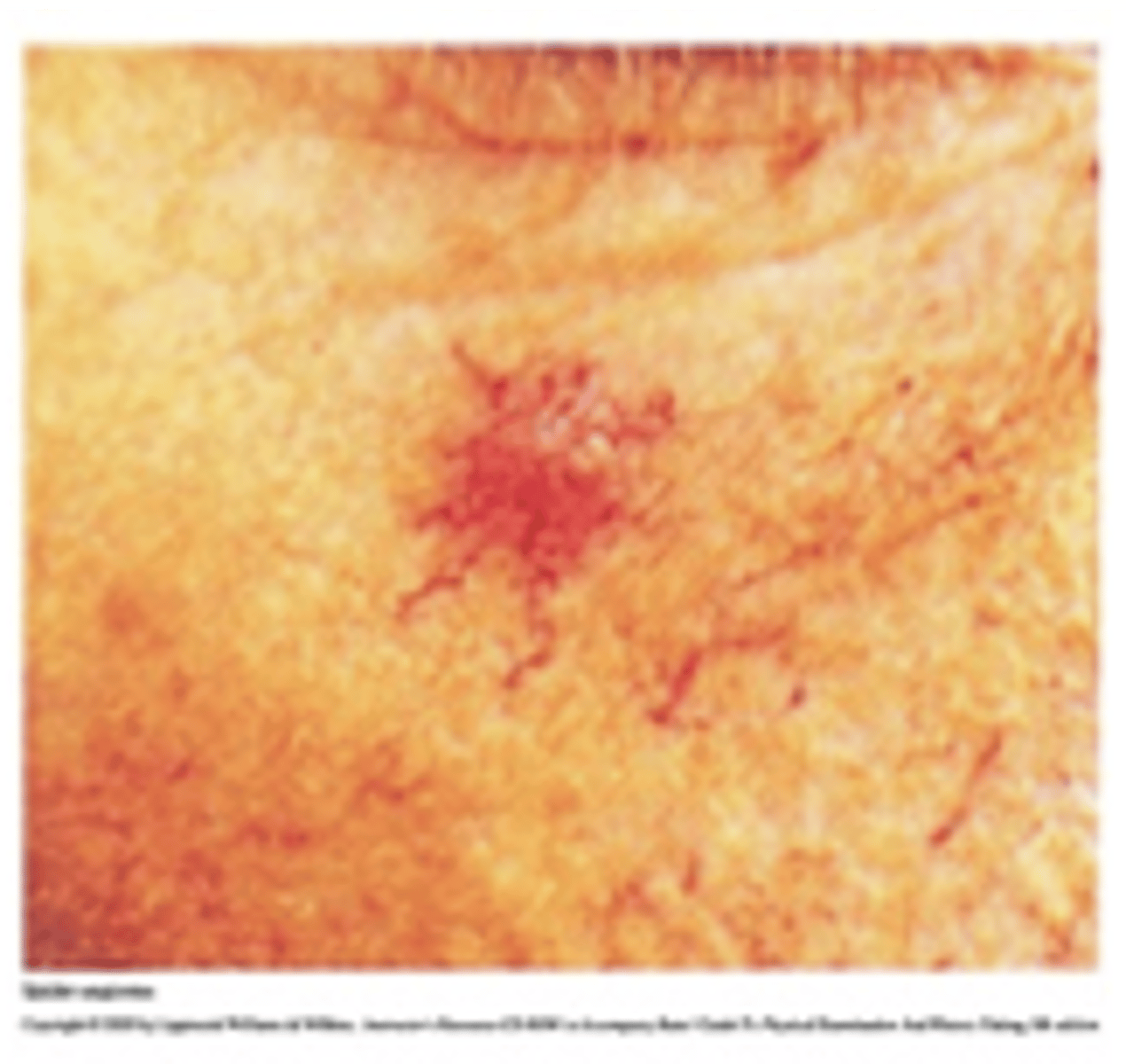
Vascular lesions: Spider angioma
Central red macule with radiating spider-like arms
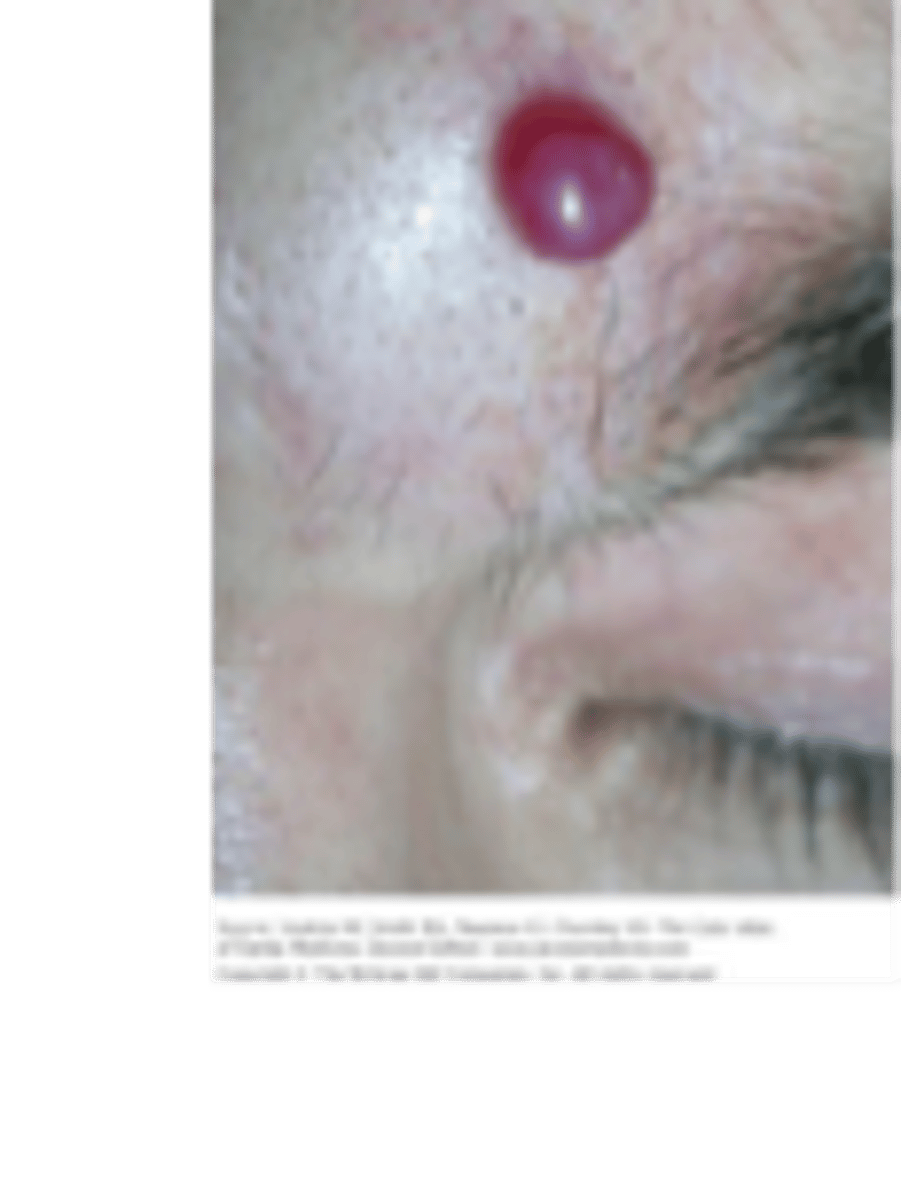
Vascular lesions: cherry angioma
small red papule
Descriptions Should Include
Size
Number
Distribution
Configuration
Texture
Color
Blanchable? - when you take your finger and push on lesions and turns white , if you push down and color does not change then damaged bv present
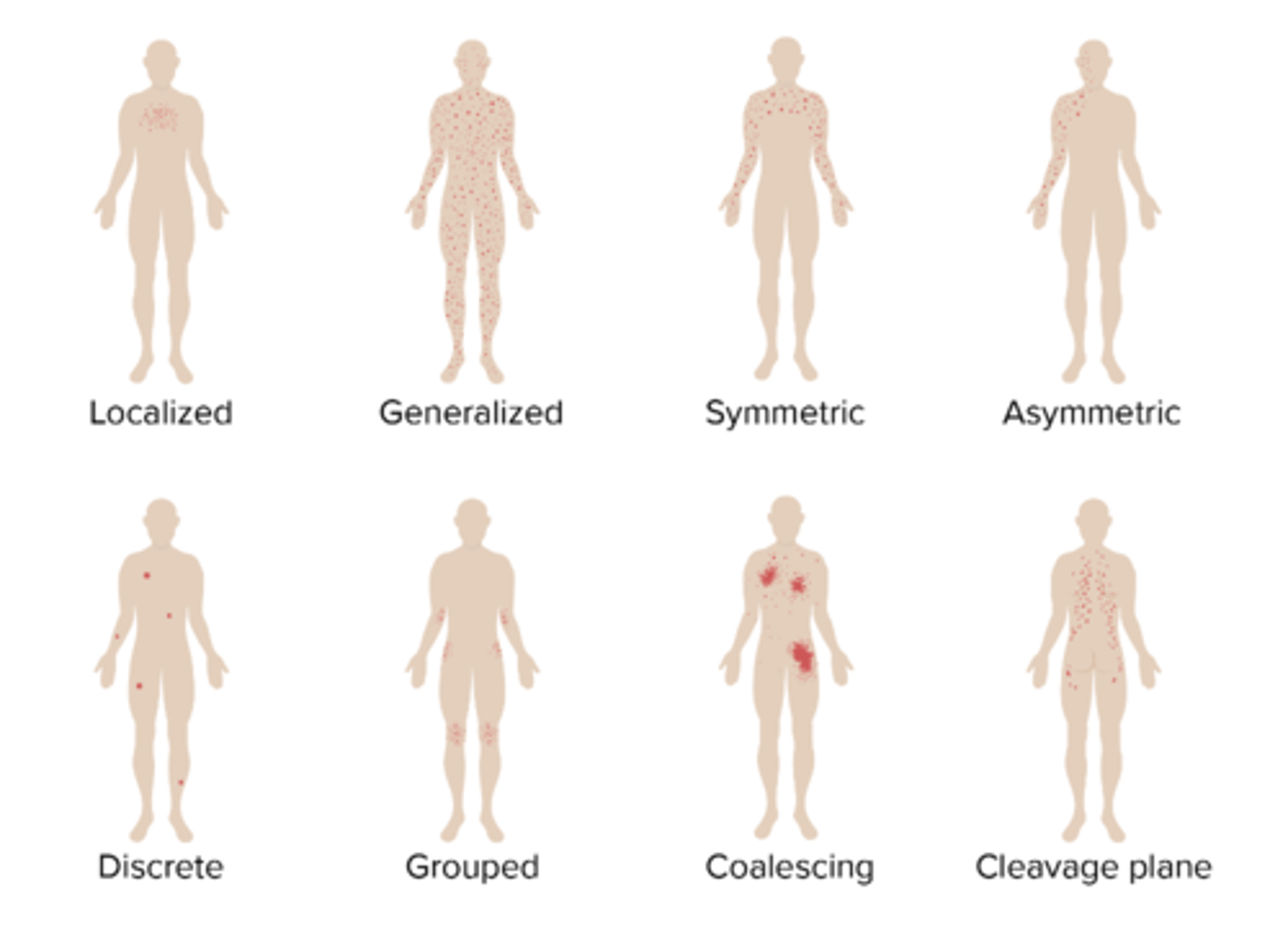
Distribution of Lesions
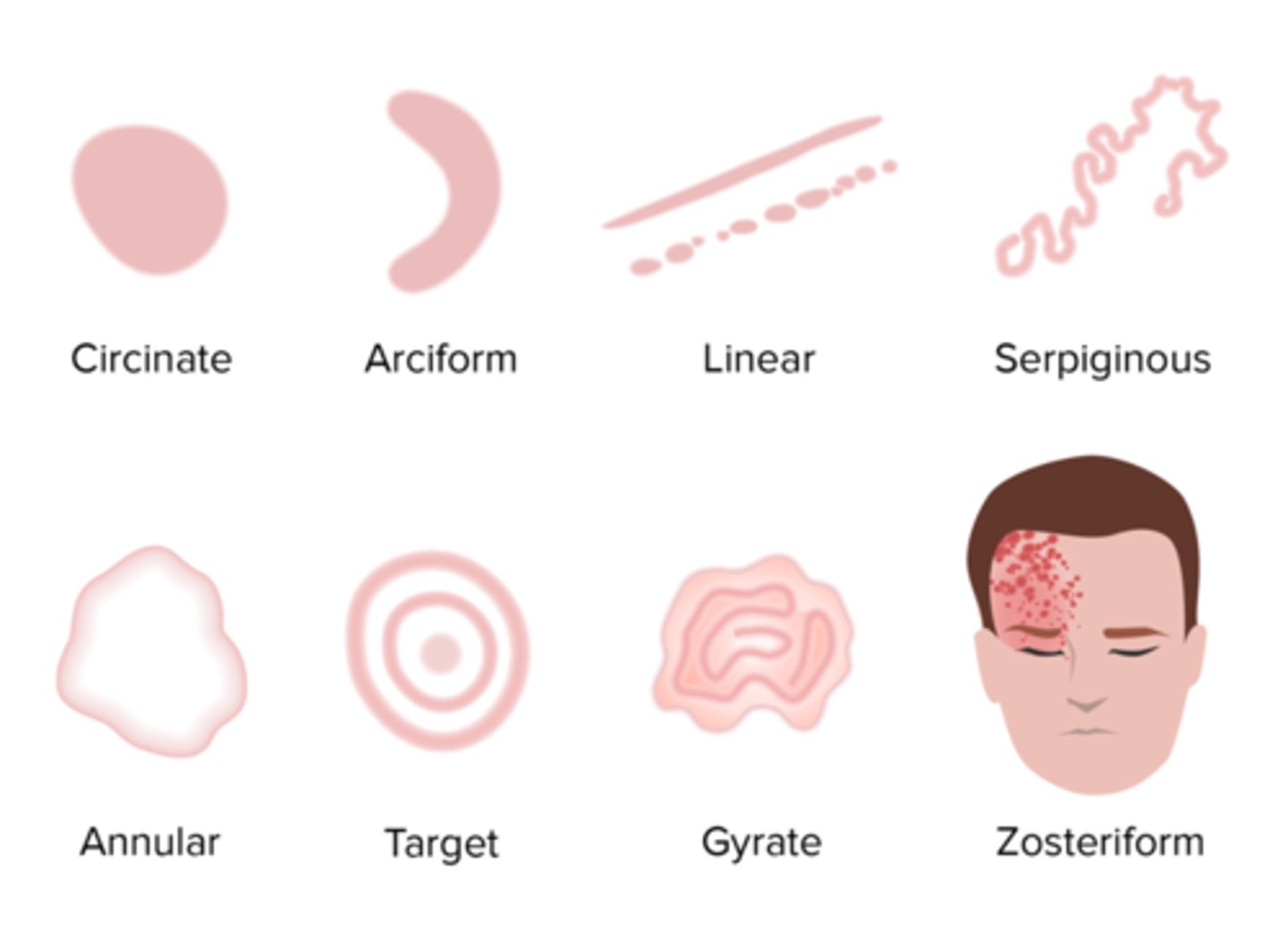
Configuration of Lesions
Geographic: resembles the outline of a map
Reticular: lesions with a "net-like" arrangement
Umbilicated: skin nodule with a central depression
Vegetative: the proliferation of papillomatous masses
Verruca: wart
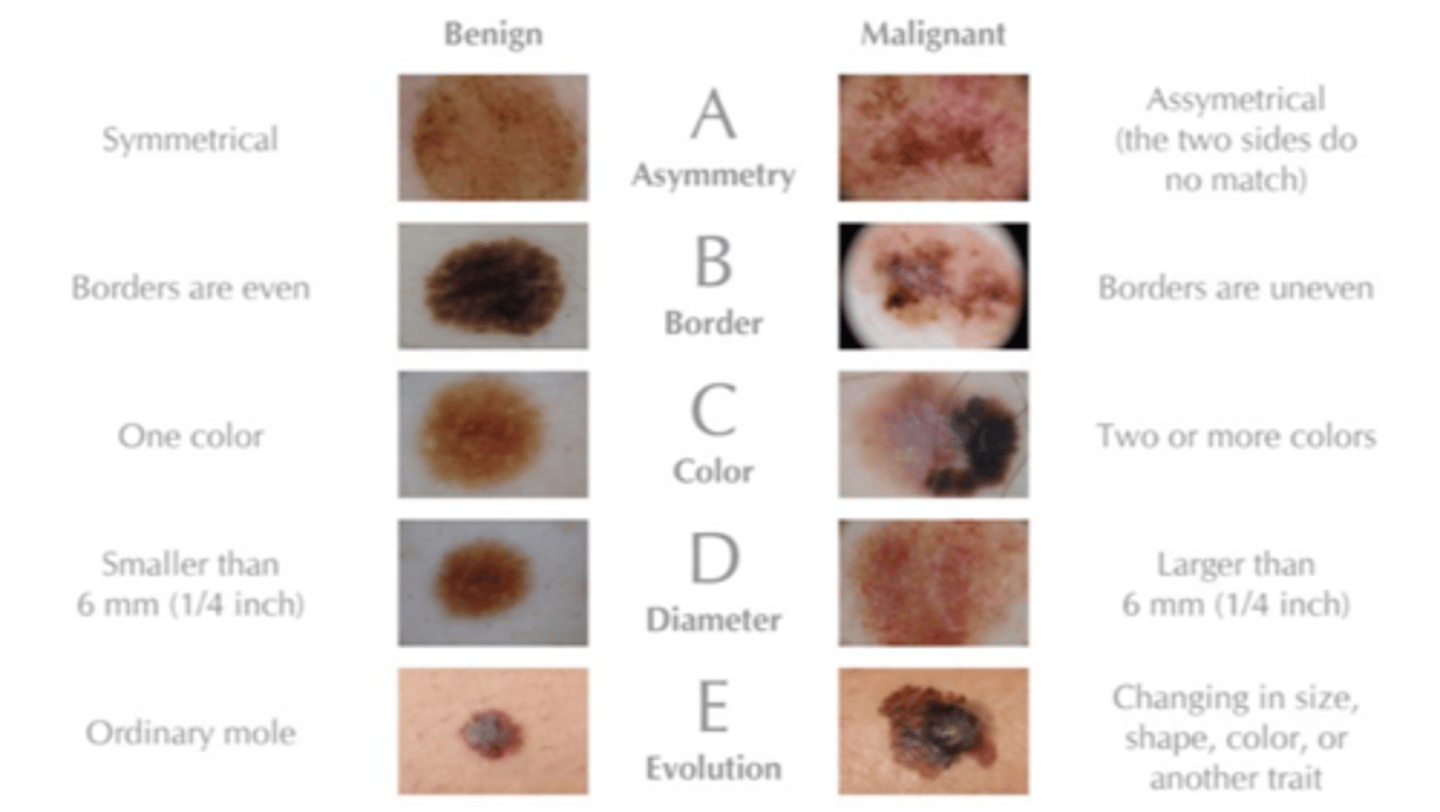
Nevi/Skin Lesion Evaluation
ABCDEFG's:
◦Asymmetry
◦Border irregularity
◦Color variation
◦Diameter > 6 mm, bigger than an eraser
◦Evolution/Elevation, changed overtime?
◦Family history of melanoma, Firm to Palpation
◦Growing progressively
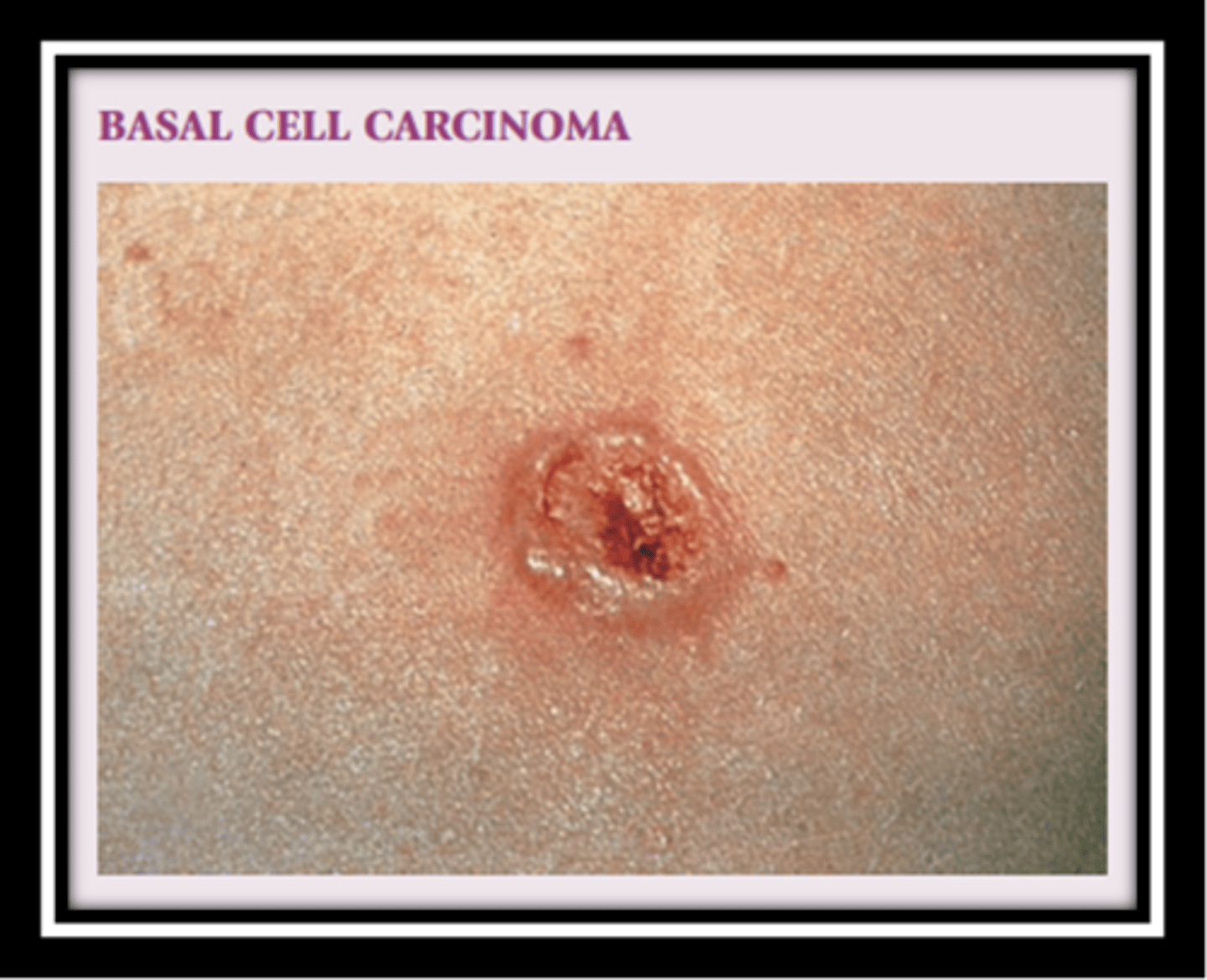
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Slow-growing and locally invasive
Translucent (pearly)papule or nodule with a depressed center and rolled edges
Caused by the sun
Most common cutaneous malignancy
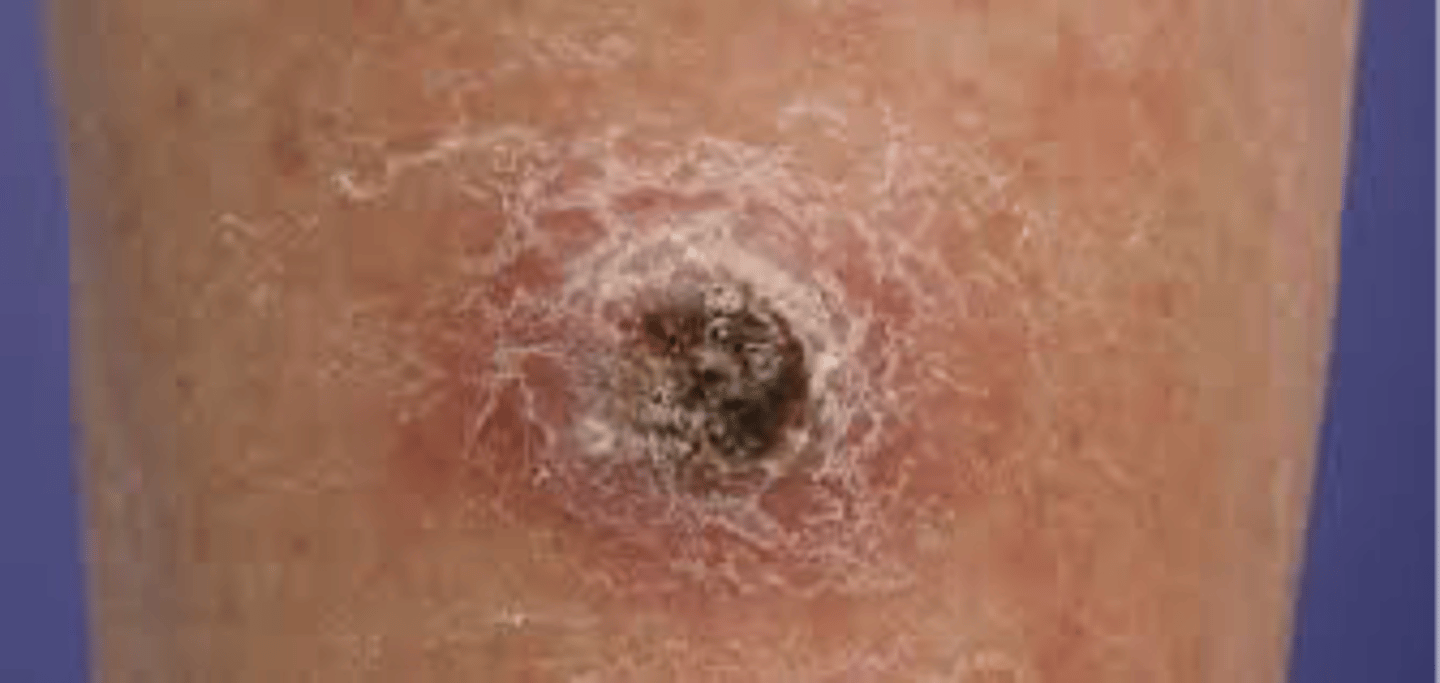
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Grows slightly quicker and more aggressively than a BCC
Looks firmer, redder, sometimes more ulcerated
Caused by the sun exposure
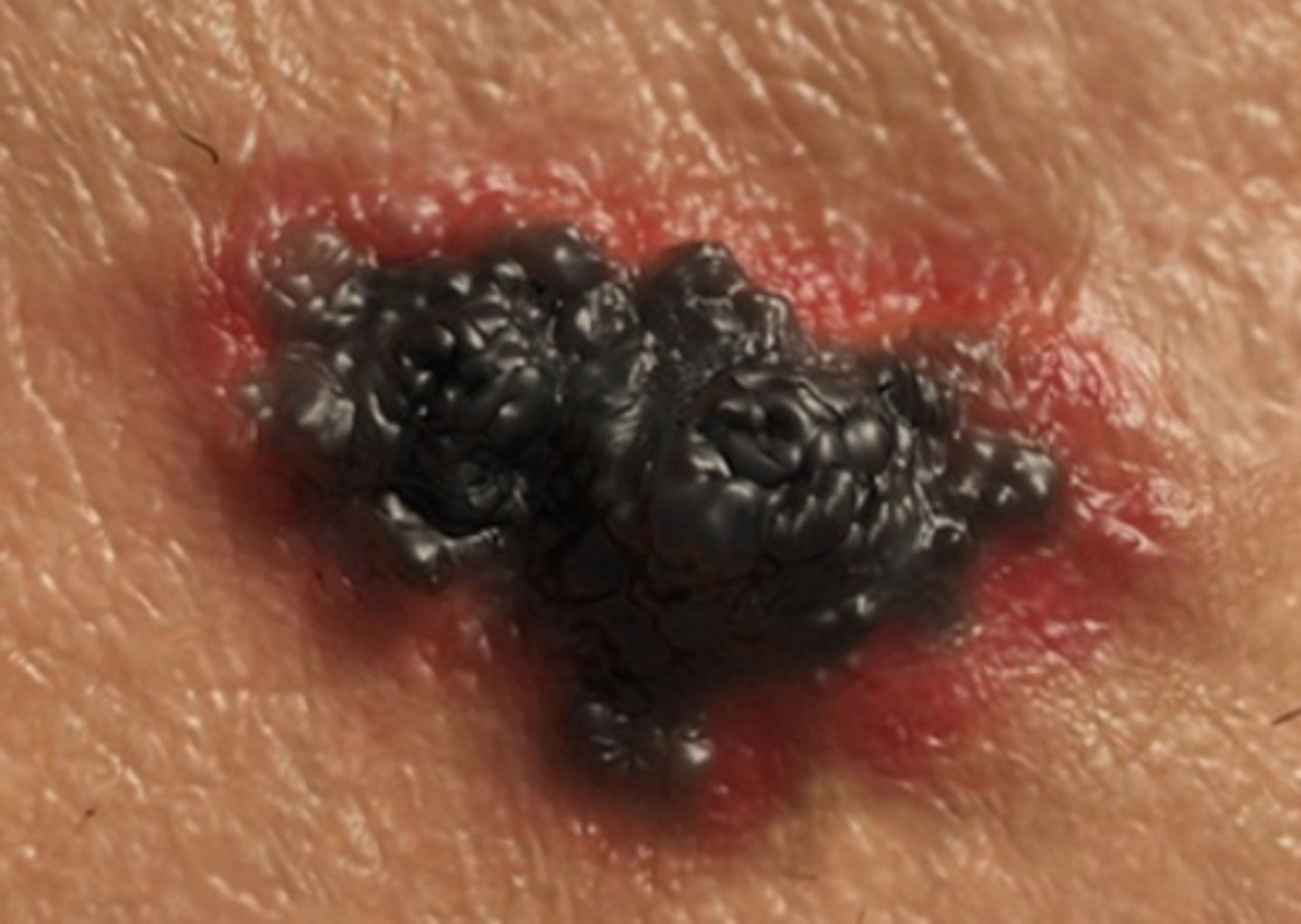
malignant melanoma
Most deadly skin cancer
Develops in melanocytes
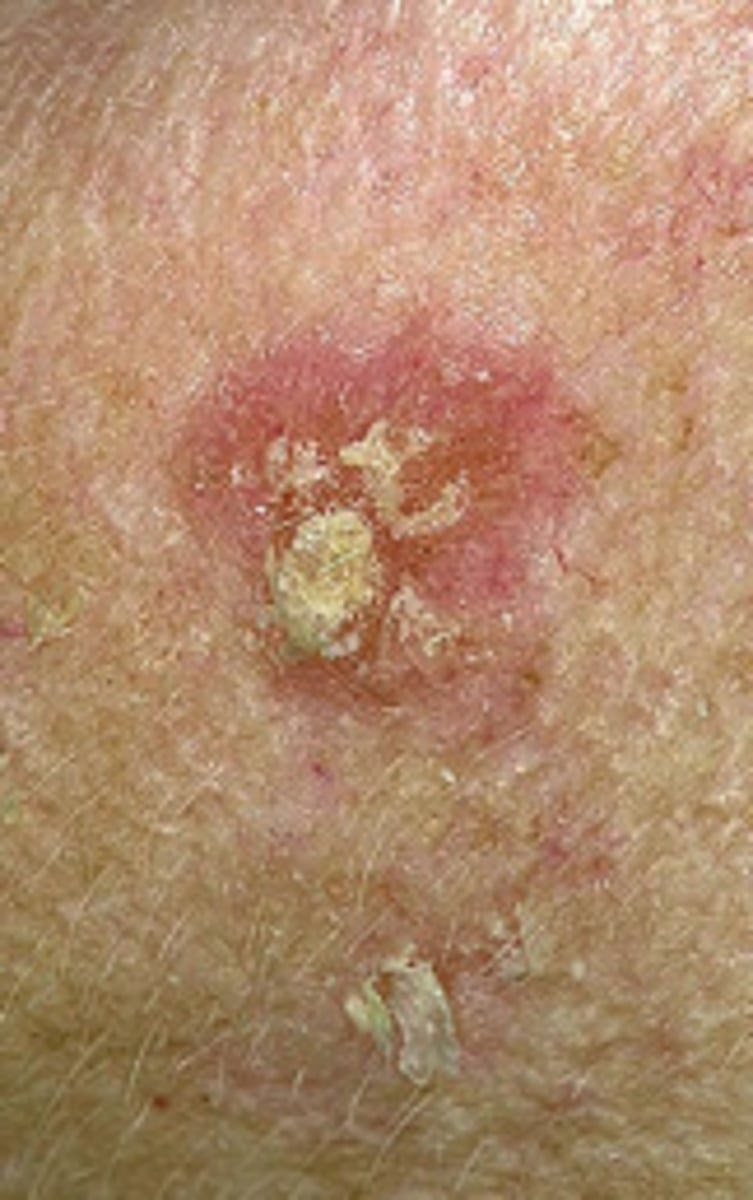
Pre-cancerous Lesions
Actinic Keratosis:
Superficial flattened erythematous papules covered by a dry scale
May be round or irregular
Pink or tan
Vary in size
Most common premalignant skin lesion
Responsible for 60% of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Common Benign Neoplasm
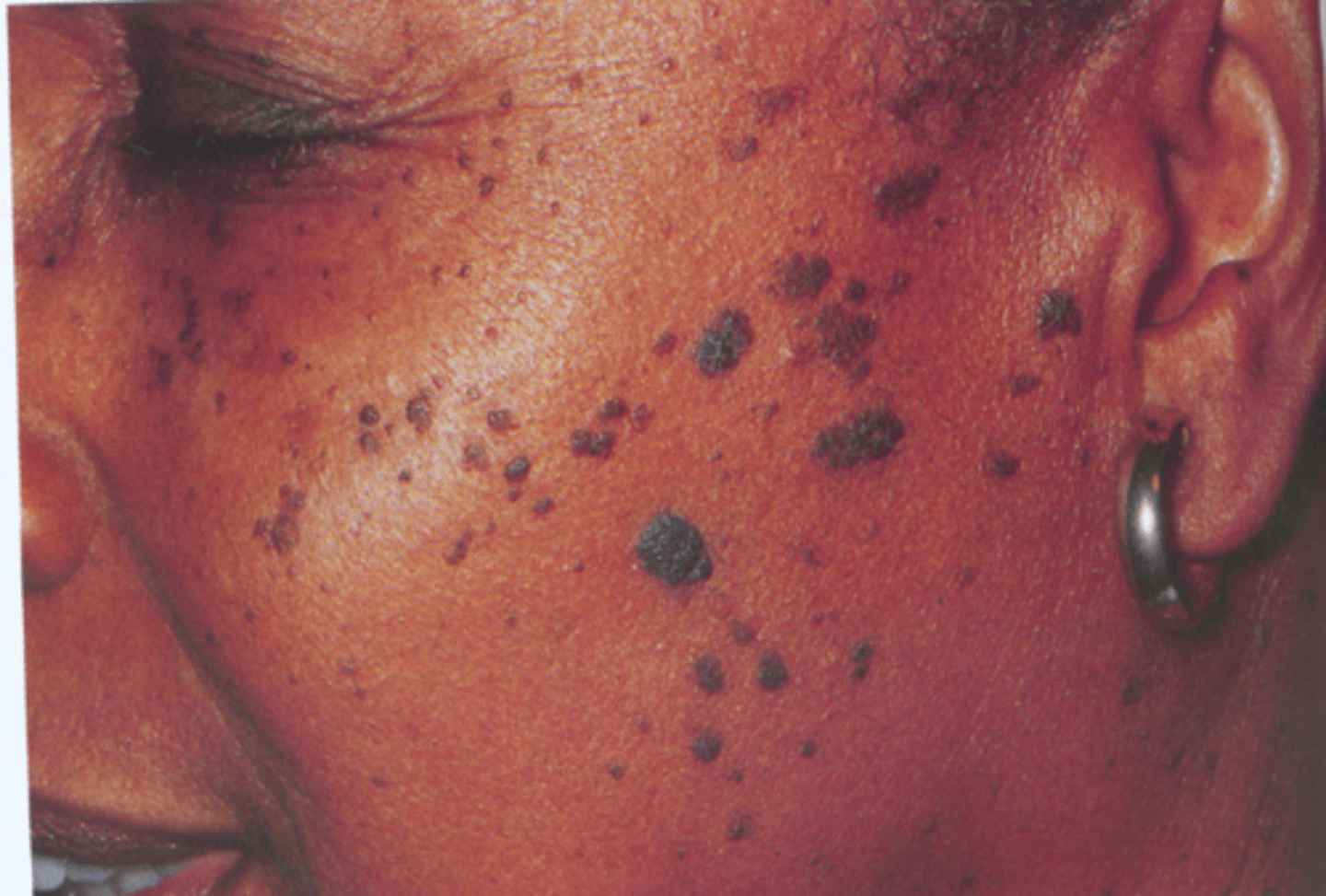
Seborrheic Keratosis
- Brown, raised, "stuck on" lesions
- "Velvety"
Age Related Skin Changes
- Epidermal thinning (atrophy)
- Changes in melanocytes
- Reduced elasticity
- Blood vessels become more fragile: Causes easy bleeding and bruising
- Sebaceous glands produce less oil: Dryer skin
- Sweat glands produce less sweat: Not as easily able to regulate temperature
- Subcutaneous fat layer (insulation and padding) thins: More prone to getting more injuries with trauma and ulcers
What is the translucent part of the nail called?
Nail plate
What is the part of the nail that is covered by the proximal nail fold?
Nail root
What supports the nail and contains blood vessels?
Nail bed
What is the thick layer of epithelium at the base of the nail called?
Cuticle
What is the white half moon at the base of the nail called?
Lunula
What are the lateral folds of the nail referred to as?
Paronychial edge
What is the intersection between the nail and the skin on the finger called?
Hyponychium
Nail examination Inspect for:
◦Shape and Size
◦Brittleness
◦Hemorrhages
◦Lines and grooves
◦Clubbing - COPD commonly have this
◦Pitting
◦Masses/Lesions
◦Pigmentation within the nail bed - possible skin cancer under nail bed
◦Trauma
Nail exam
Palpate for texture and consistency
Capillary Refill < 2 seconds
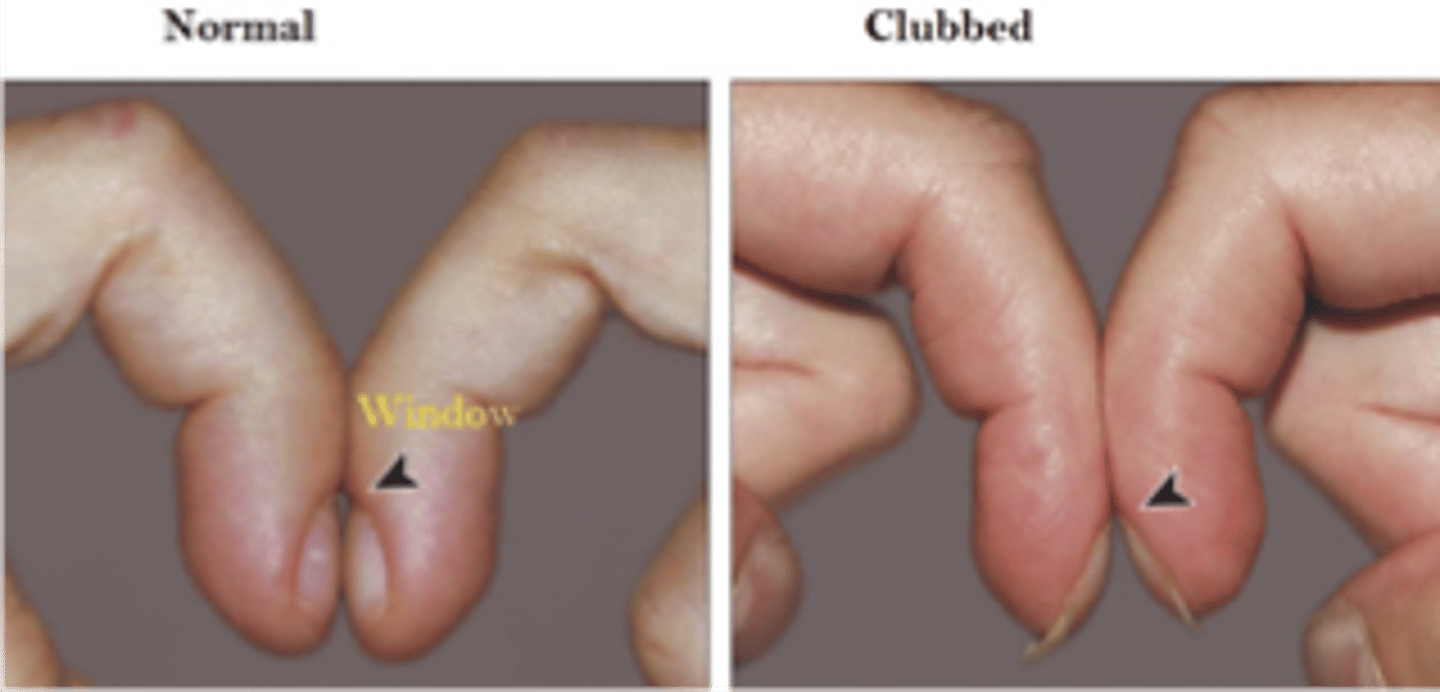
Clubbing
◦The distal phalanx of each finger is rounded and bulbous
- commonly seen in pts with underlying lung issues
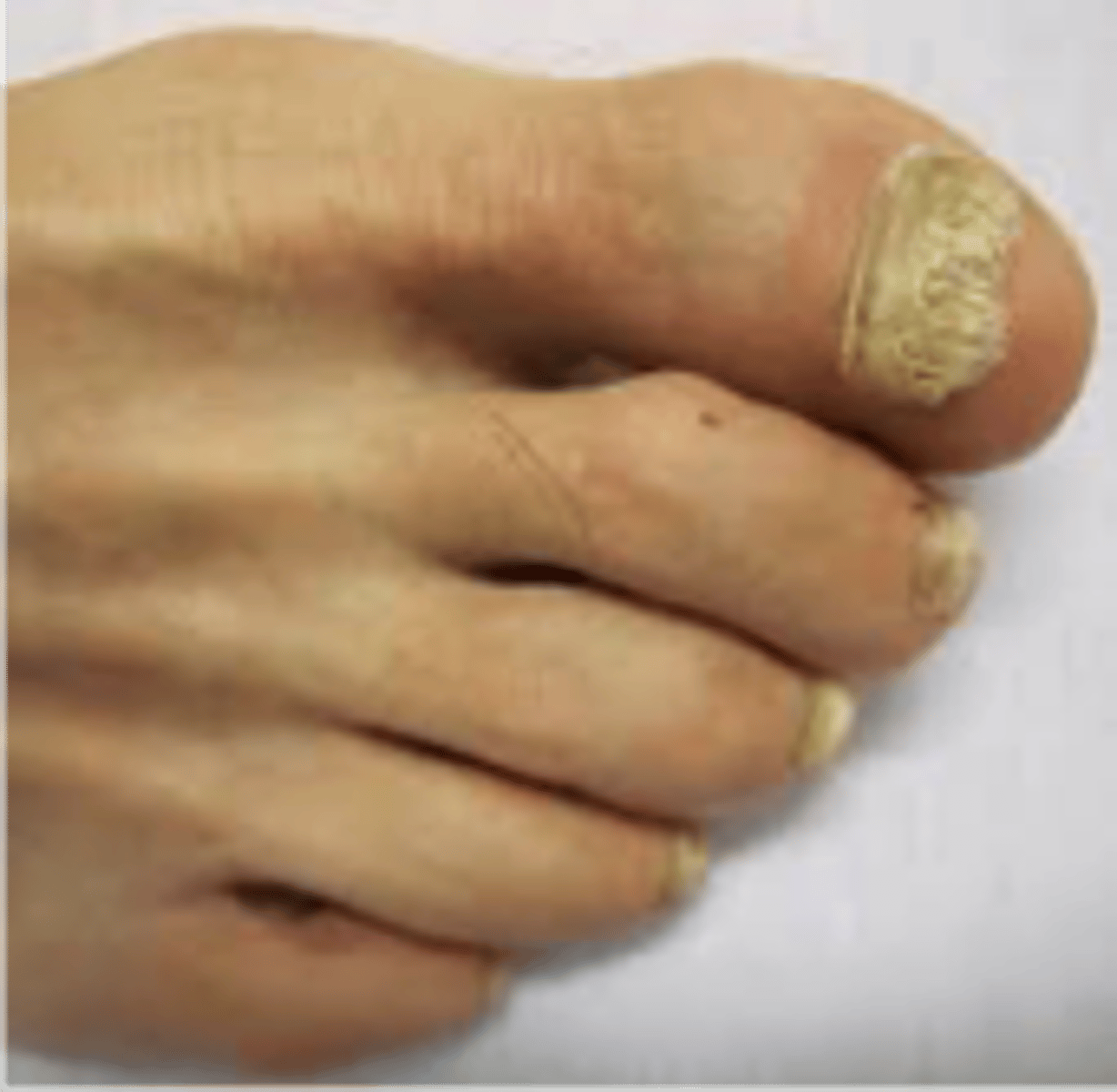
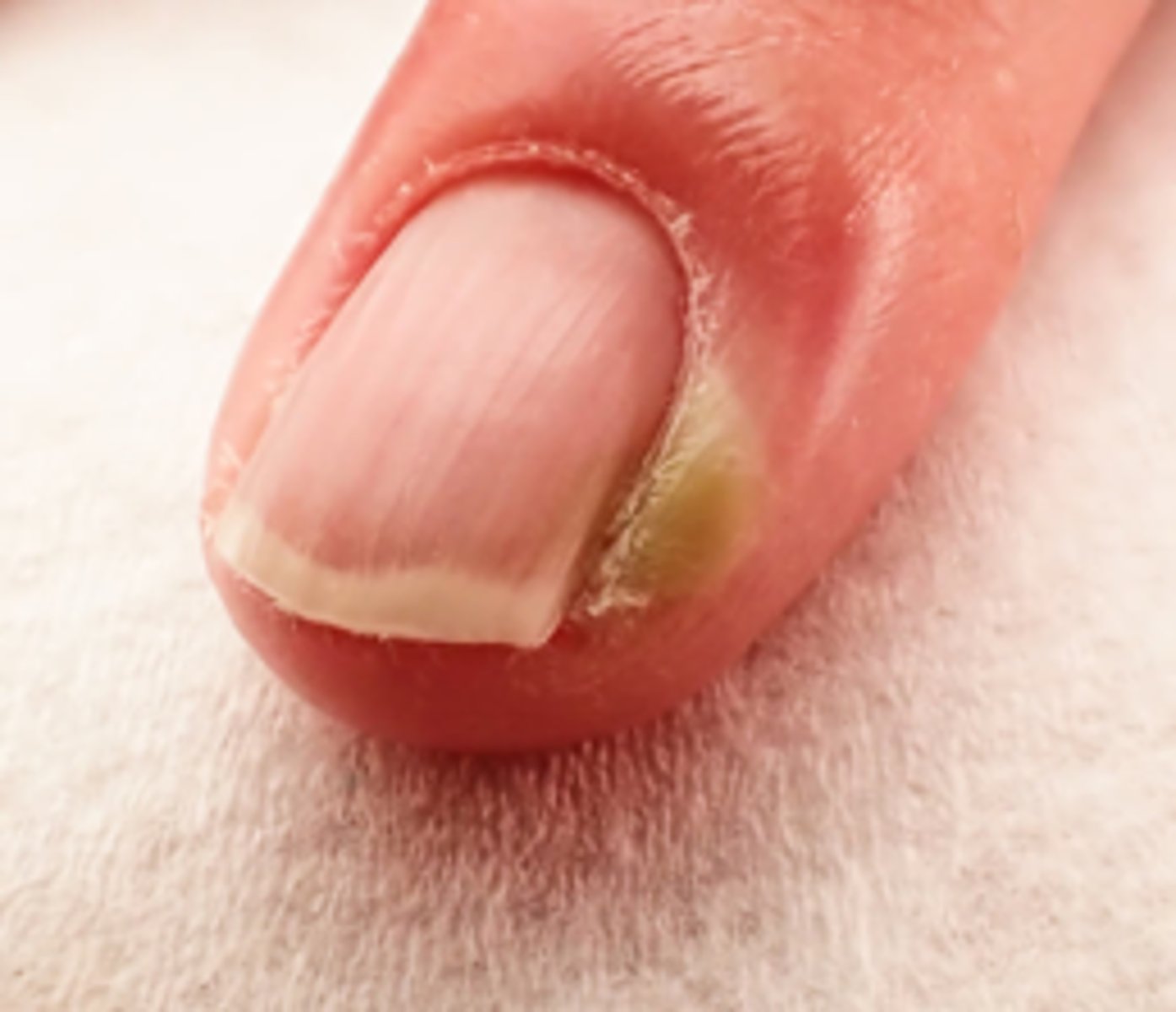
Onychomycosis
◦Thickened yellow hypertrophic nail growth due to fungal infection
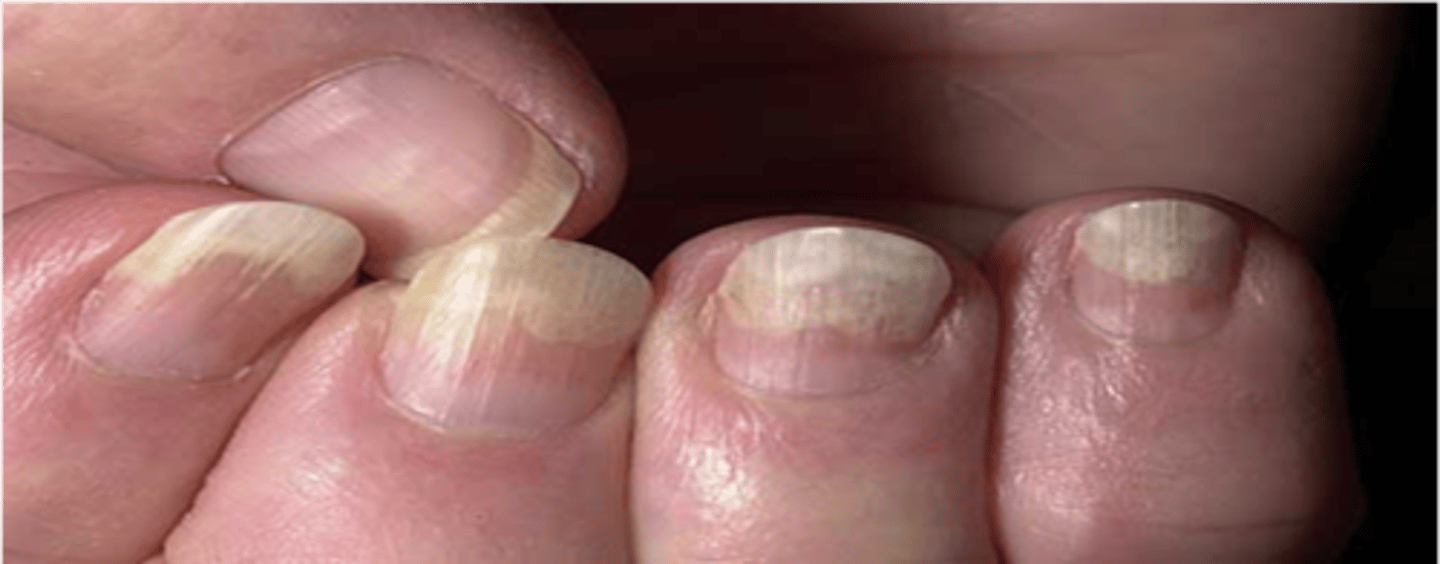
Onycholysis
◦Painless separation of the nail plate from the nail bed
Paronychia
◦Inflammation and infection of the soft tissue of the nail (paronychia area) around the proximal and lateral nail folds
◦Folds become erythematous, swollen, tender (infected)
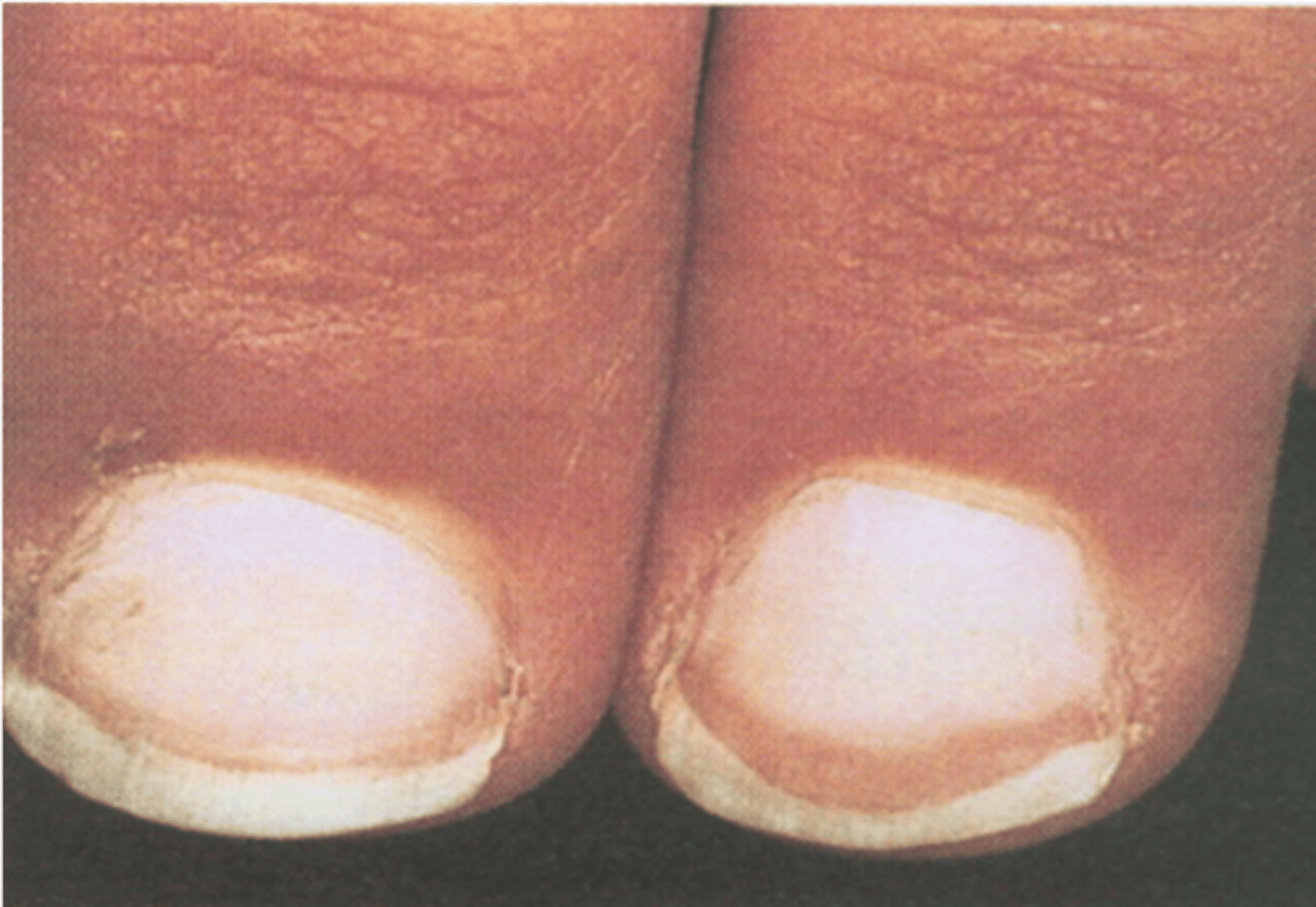
Terry's Nails
◦Mostly whitish with a band of reddish brown, seen in aging, cirrhosis, CHF, diabetes
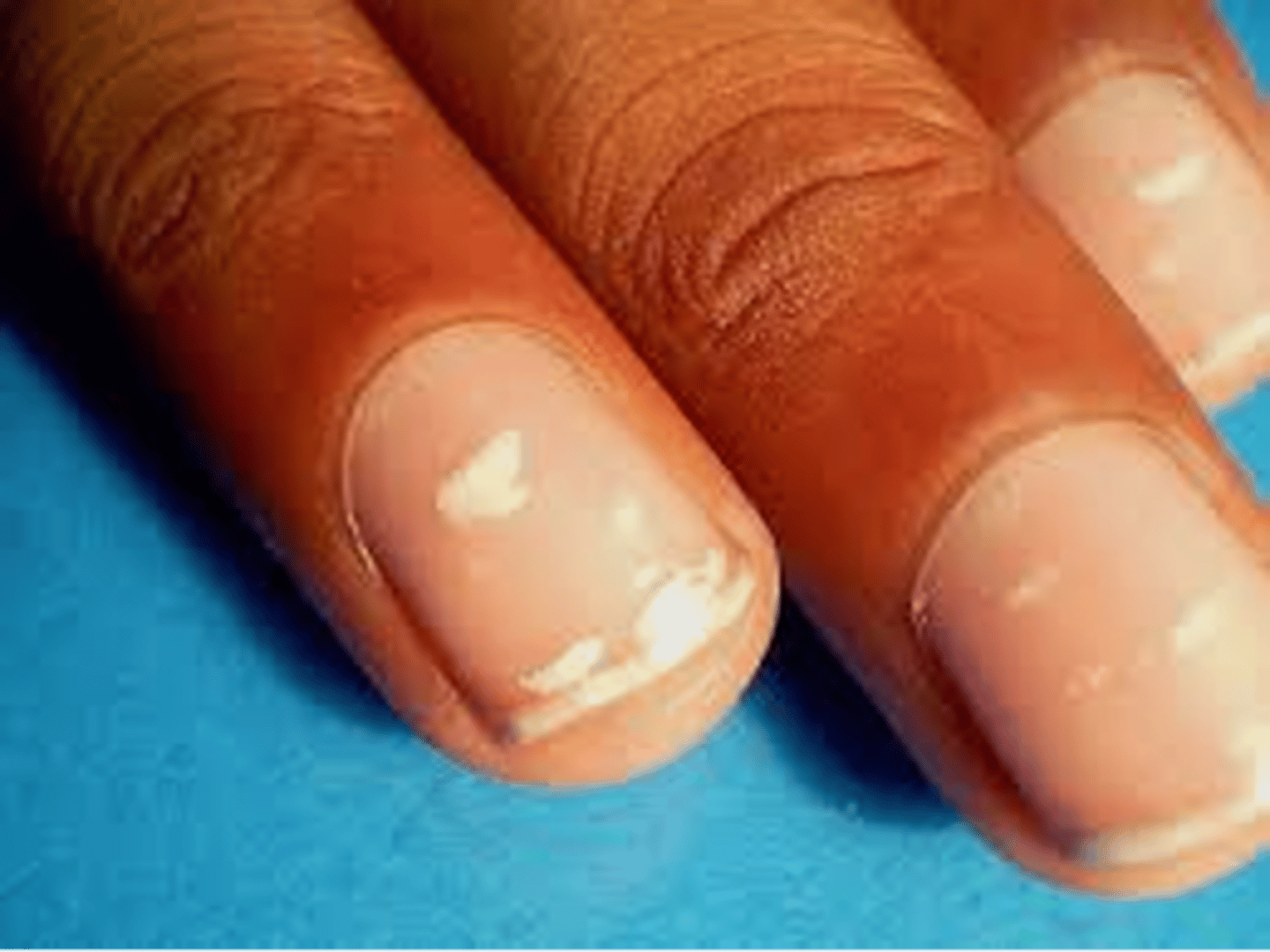
Leukonychia
◦White color changes of the nail
◦Partial or complete
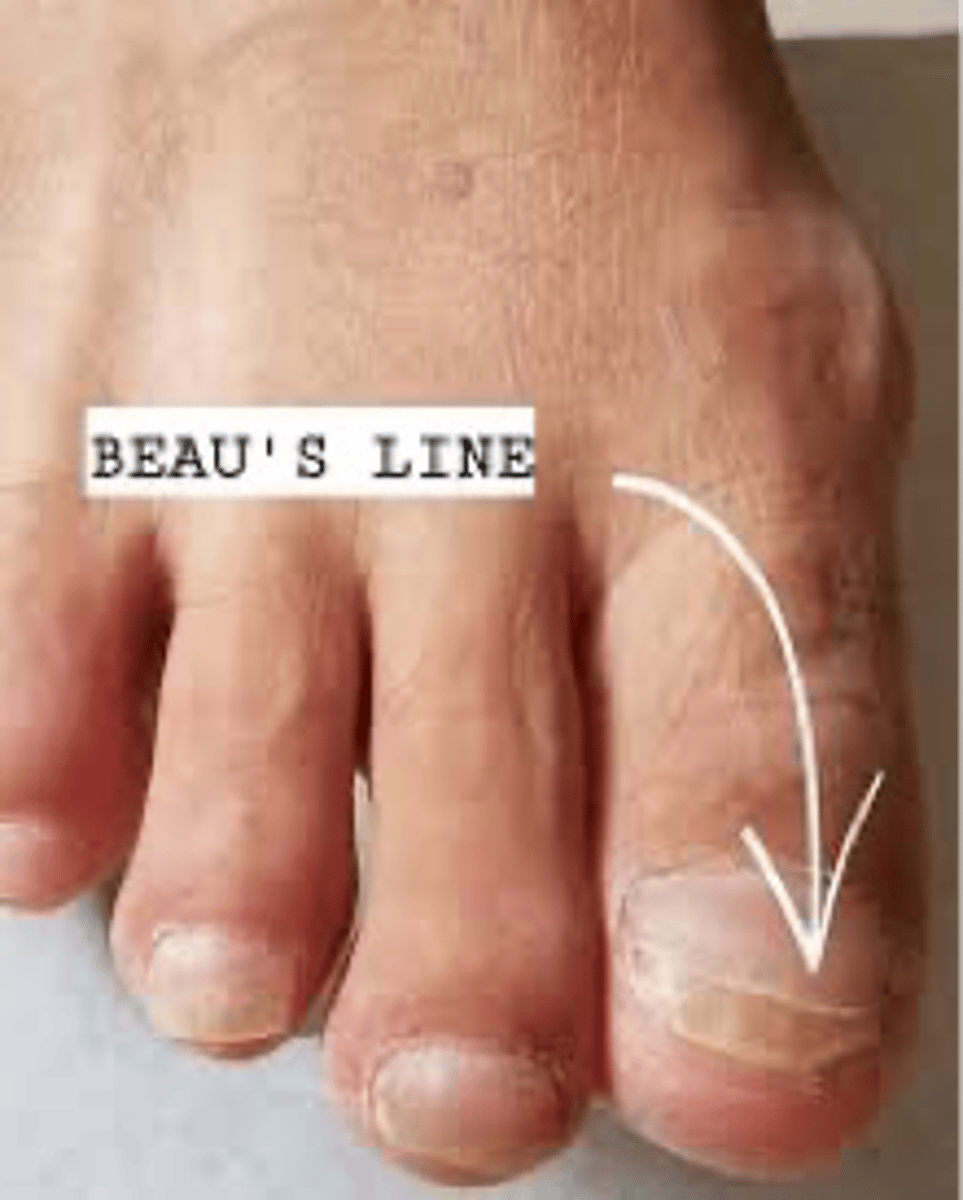
Beau's Lines
◦Transverse depressions in the nails associated with acute or severe illness
◦Grow out with time
Pitted nails
◦Psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis
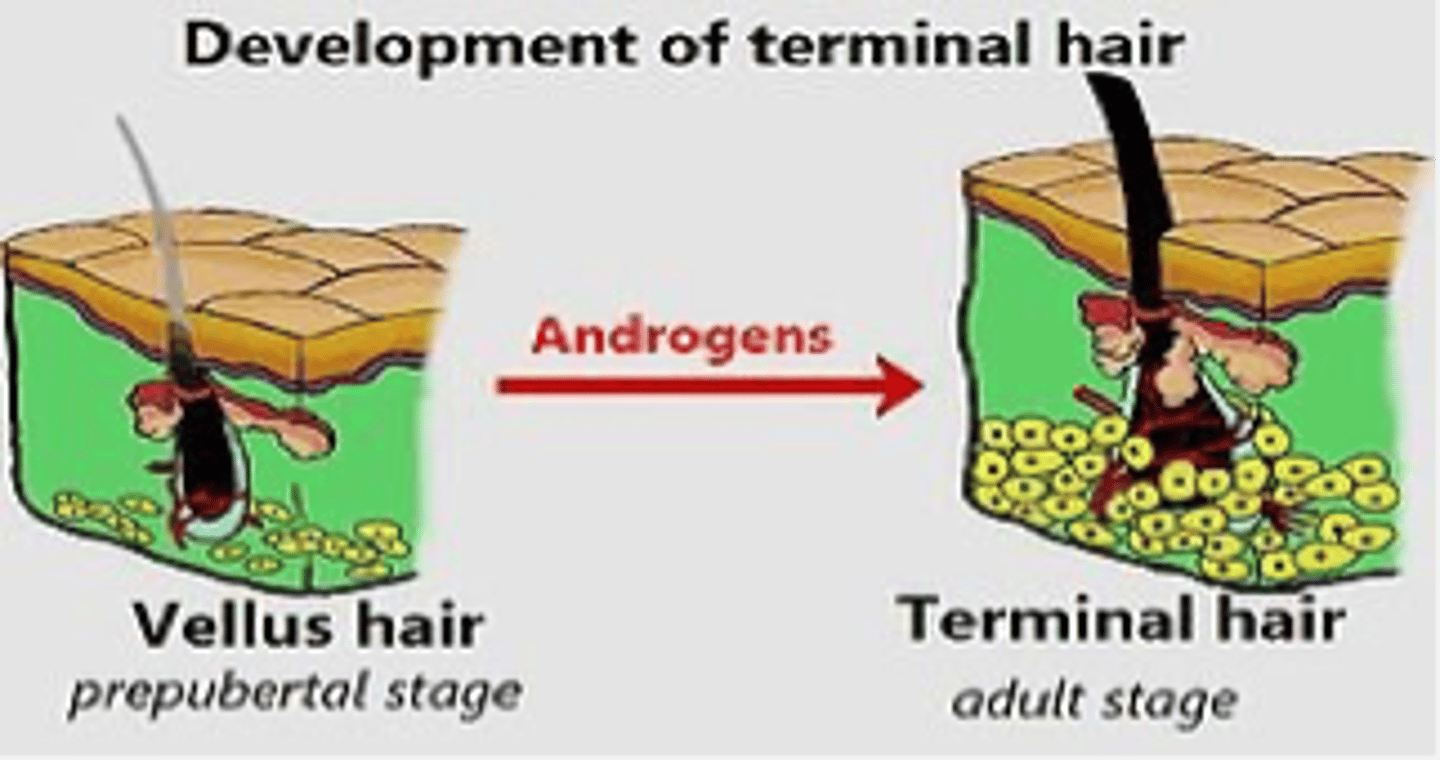
Hair Types
Two Types of Hair:
Vellus
- Aka Peach fuzz
- Short, fine, unpigmented, inconspicuous
Terminal
- Coarse, thicker, more conspicuous, pigmented
- Mature hair
Hair Anatomy
ØHair follicles: contain papilla that provides nutrients
ØArrector pili muscle- smooth muscle hair is attached to
Hair inspection
Inspect and Note:
◦Hair quantity
◦Hair distribution
◦Hair texture
◦Hair color
◦Loss of hair
Scalp and Hair
- Inspect the scalp for any lesions, rashes, scaling, etc.
- Feel for any lumps or bumps
- Hair Texture
- Oily
- Brittle
- Dandruff
Hirsutism
Common in PCOS where more androgen hormones are produces.
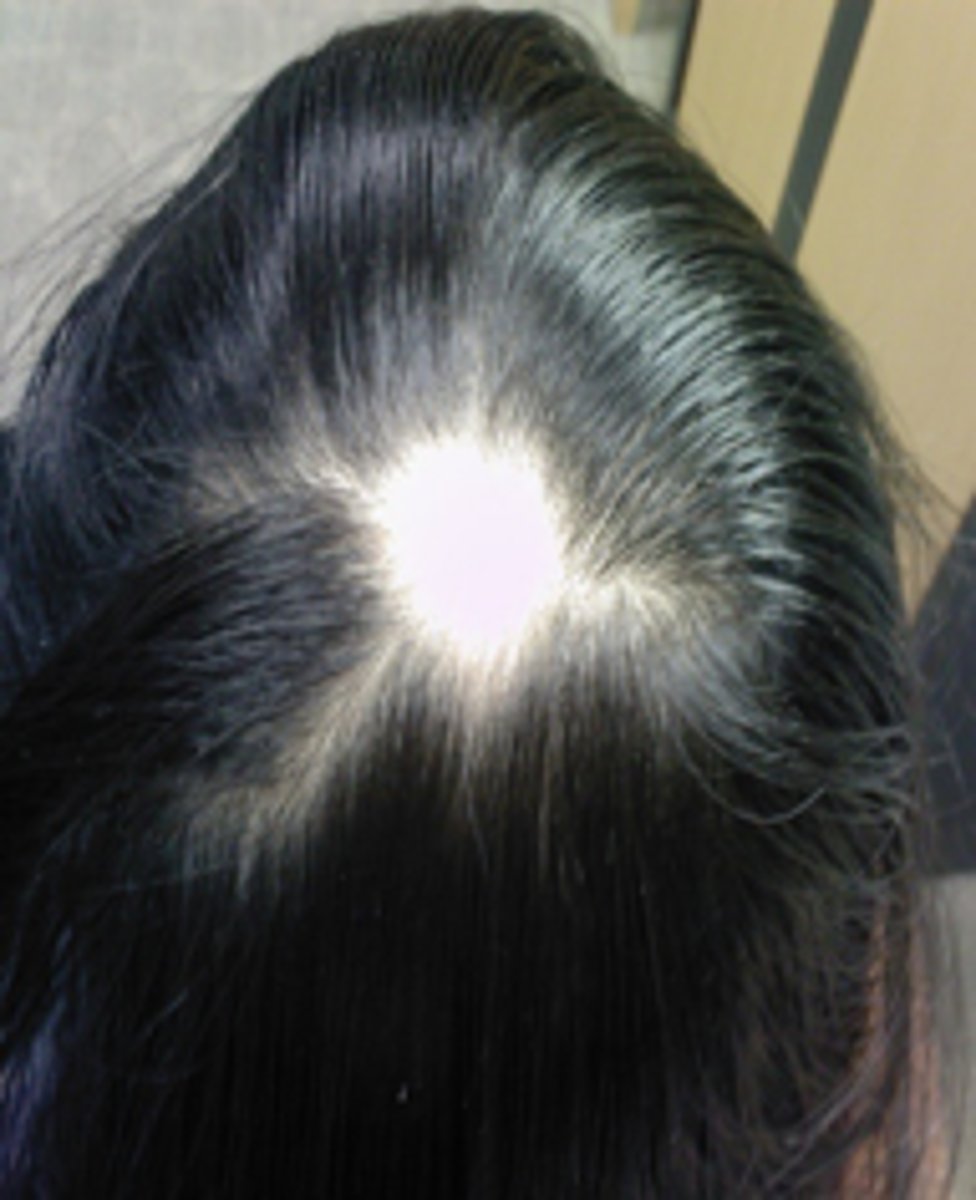
Alopecia Areata-
"spot baldness"
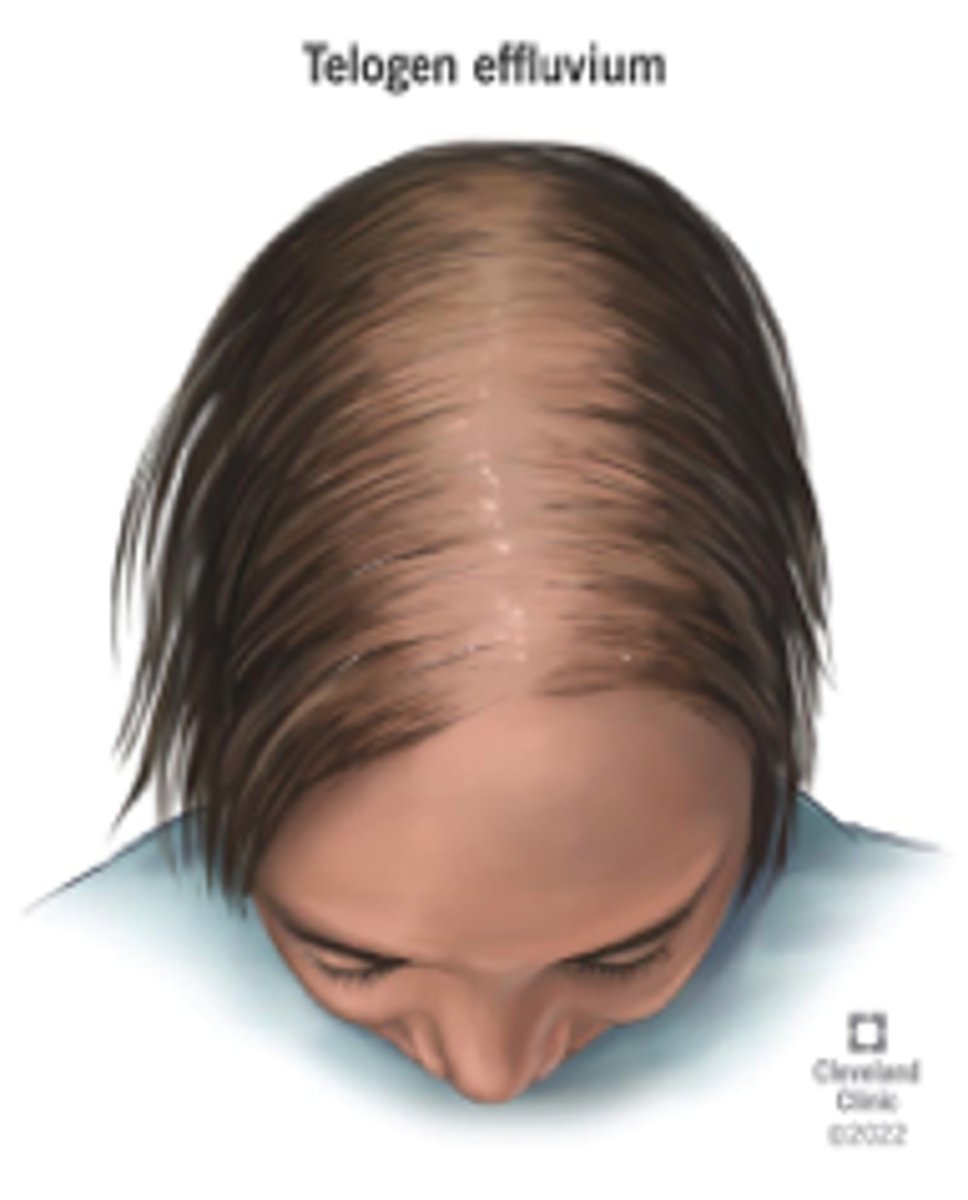
Telogen Effluvium-
uniformed hair thinning
Trichotillomania
"hair pulling disorder"
Male Pattern Baldness
Androgen related
General Survey
oBegins at the opening moments of the encounter and is before you conduct your physical examination
oSimple observations play an important role in the general survey of the patient
oPay attention to how the patient walks, how the patient is dressed, the tone of the patient's voice, etc.
oNarrow in on and greater appreciate any of these findings as you start the assessment and PE
oSome characteristics include body habitus, posture, mood and alertness, facial coloration, dentition and conditioning of the tongue and gingiva, color of the nail beds and muscle bulk
- helps make a decision as to whether or not the patient is sick or not
General Appearance
oApparent state of health
oLevel of consciousness
oSigns of distress
oSkin color and obvious lesions/rashes
oDress, grooming and personal hygiene
oFacial expressions
oBody odors
oPosture, gait and motor skills
What are common causes of fatigue/weakness?
Infection, hypothyroidism, anemia, nutritional deficiency, cancer, chronic cardiometabolic disease.
What is the difference between weakness and fatigue?
Weakness refers to loss of muscle power, while fatigue is a general sense of tiredness.
What should be assessed when a patient presents with fatigue/weakness?
A full history and detailed questions about the patient's situation.
What does rapid/acute weight change suggest?
Changes in body fluids.
What is weight gain?
When caloric intake exceeds caloric expenditure over time.
What can contribute to weight gain?
Medications such as antidepressants, OCPs, insulin, and steroids.
What is clinically significant weight loss?
A loss of more than 5% of usual body weight over 6 months.
What are some causes of significant weight loss?
Diabetes, hyperthyroidism, HIV/AIDS, cancer, eating disorders, drug use, cigarette smoking, medications, physical disability.
What should be assessed in a patient with weight loss?
The patient's dietary and caloric intake.
What is one of the most common complaints in patients?
Pain.
What are the two types of pain?
Acute pain and chronic pain.
How is pain sometimes regarded in clinical settings?
As a fifth vital sign.
oFevers, chills and night sweats
oFever --> abnormal elevation in body temperature
oDid they actually measure their temperature? Do they really have a fever or they just feel like they have a fever?
oDistinguish between patient having the chills and patient actually shivering
oFeeling cold and shivering --> rising temperature while feeling hot and sweating --> falling temperature
oMenopause, Tuberculosis, Cancer can cause night sweats
oSystemic infection like sepsis can cause shivering chills
oCertain medications like Tylenol, NSAIDs, steroids can mask a fever
oImportant to inquire about travel (especially outside the US), sick contacts, medications, etc.
Causes of weight gain
hypothyroidism, metabolic syndrome, Cushing's syndrome, medications, binge eating disorder
Causes of weight loss
include cancer, DM, hyperthyroidism, depression, eating disorders (Anorexia Nervosa), diuresis
BMI calculation
BMI: (Weight (lbs) x 700 / height (inches) / height (inches))
BMI: Weight (kg) / height (m^2)