cancer clinical pharmacy 6.5
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
clinical cancer 1,2,3 6.5 /
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what is cancer?
process by which abnormal cells divide uncontrollably e.g. hyperplasia
with the ability to invade nearby tissues - only cancer does this
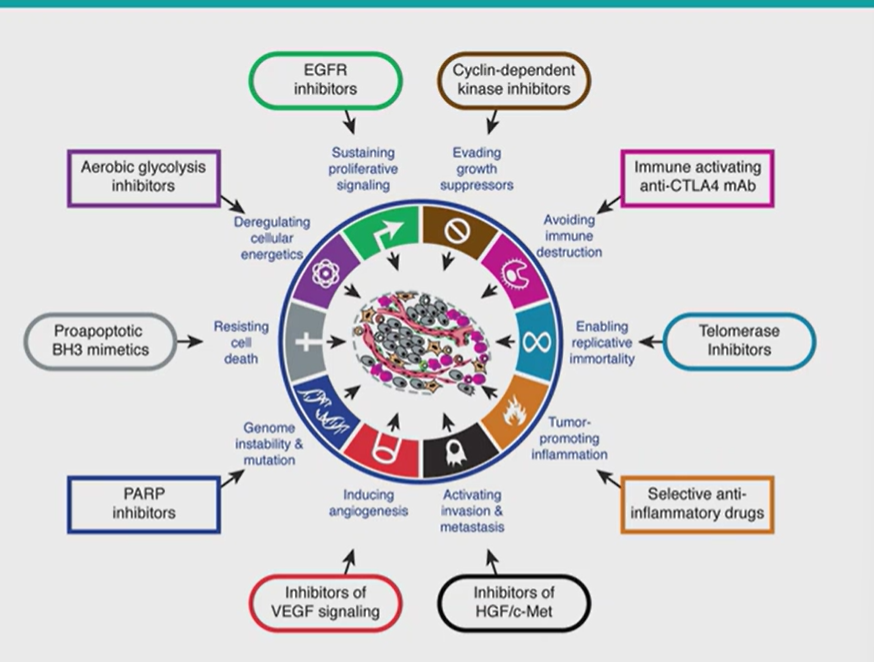
what are the attributes of cancer?
look at the attributes of cancer
we can target this - drug treatment
what is a carcinoma?
it is a cancer which begins in the epithelial tissues
epithelial tissues line all the organs of the body and body cavities
e.g. skin, chest, abdomen, lungs
how are carcinomas named?
based on the type of epithelial cell they affect
what are the names of the types of carcinomas - what tissue do they effect?
squamous cell carcinoma
flat cells covering surface of membranes e.g. skin, throat, oesophagus
adenocarcinoma
affect glandular cells called adenomatous cells. glandular cells produce fluids/mucous to lubricate passages e.g. GI tract lining
transitional cell carcinoma
affect cells in the transitional epithelium - cells which expand e.g. lining of bladder
basal cell carcinoma
found in deepest layer of skin cells - in basal layer
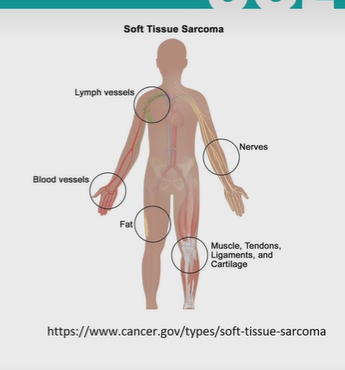
what are sarcomas?
bone or soft tissue- 89%
soft tissue: nerve, blood vessels, lymph vessels, muscle, tendons, ligaments, cartilage
peaks in adolescents during growth spurt
not common - 5,300 each year
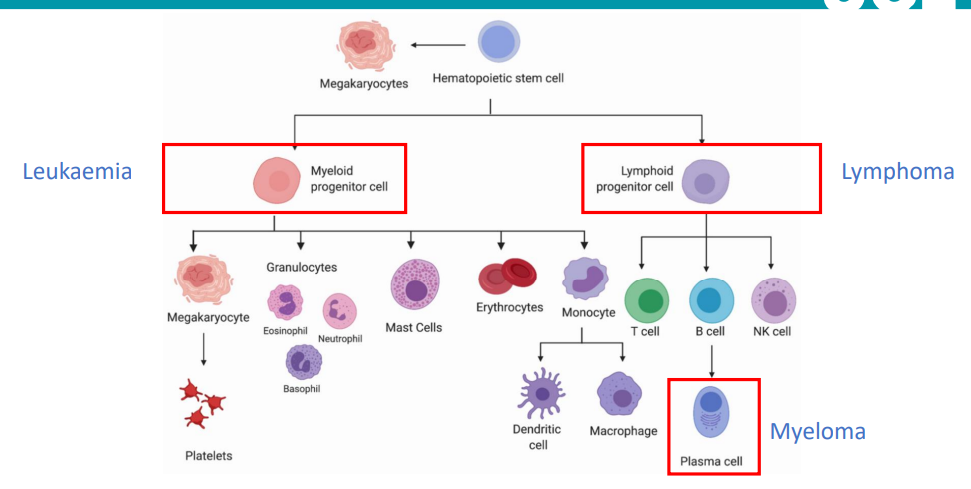
how are blood cancers categorised?
hematopoetitic stem cells make all components of blood
based on which progenitor cell has a mutation
myeloid - leukaemia
lymphoid - lymphoma
under lymphoma is plasma - myeloma
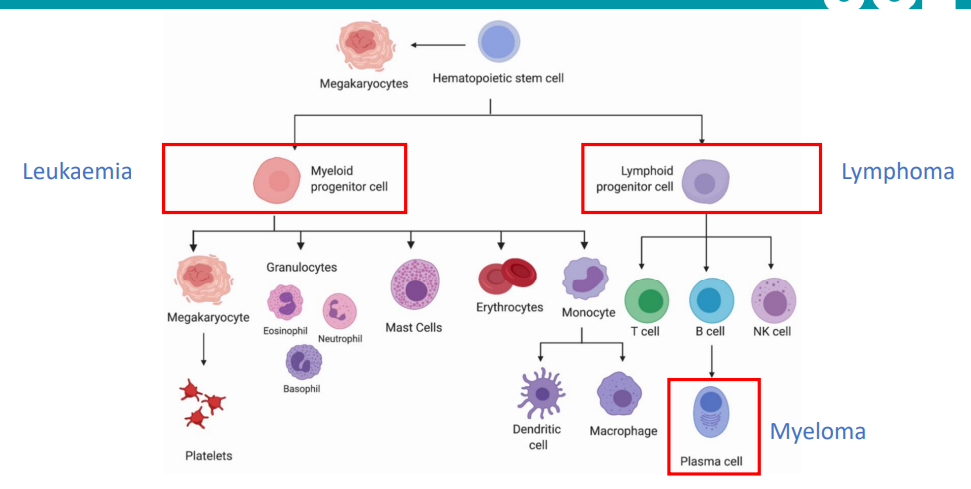
what is the issue with a mutation in the hematopoetic stem cell?
if there is a mutation in the myeloid progenitor cell it means all other cells in the path will be affected - not normal
how many people have cancer each year?
20 million
10 million die
33% because of smoking
what are WHO’s 4 pillars approached to cancer?
Prevention
early detection e.g. screening - can reduce it by 1/3
diagnosis and treatment
palliative care
what are common risks for cancer- for preventable cases
tobacco
infections e.g. HOV, viral hepatitis B
alcohol
obesity
air pollution
40% of cancers are preventable which is why public health is important
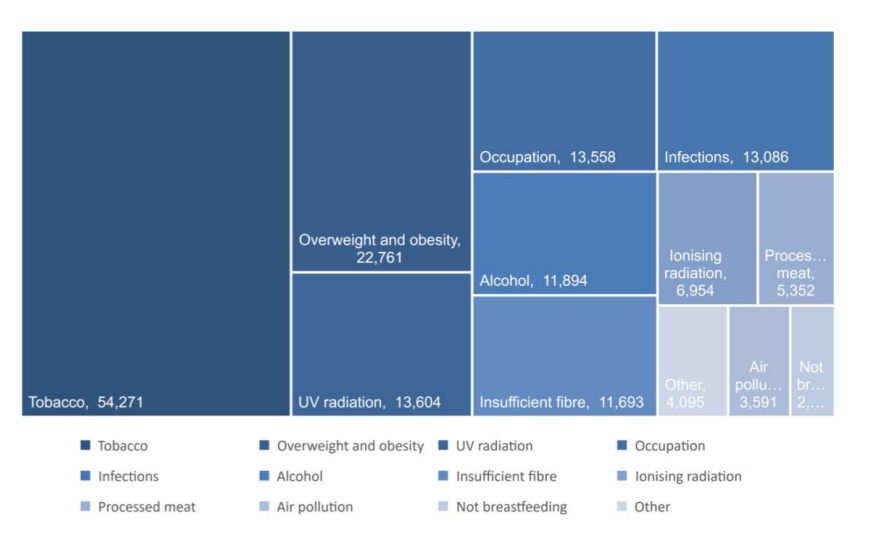
cancer stats in UK
approx 385,000 new cases of cancer in the UK per year
1 person every 2 minutes
nearly half diagnosed at stage 3 or 4 (metastasized)
breast, prostate, lung, bowel most common - make up nearly half of cancers in Uk
men can also have breast cancer!!
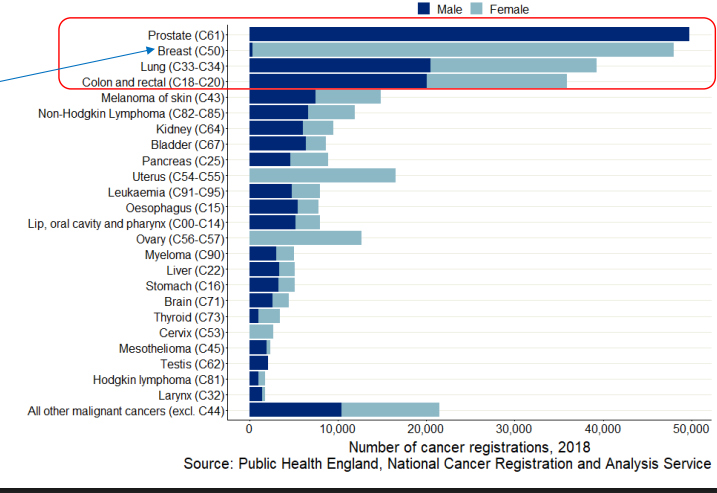
how common is breast cancer?
15% of cases each year in the UK
1 in 7 women
75% survive after 10 years of diagnosis
23% are preventable
8% linked to obesity
8% linked to alcohol consumption
genetic risk- BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene 45-60% risk by age 70

how common is prostate cancer?
14% of all NEW cases
1 in 6 men
78% survive 10 years or more
no significant risk factors so don’t know how many cases are preventable
often asymptomatic, lots have it without knowing

how common is lung cancer?
13% of new cancers
2nd most common for both men and women
10% survive after 10yrs
79% of cases are preventable
72% by smoking
5% by ionising radiation
workplace exposure e.g. asbestos and air pollution

how common is bowel cancer?
11% new cases
3rd most common in both men and women
53% of patients survive after 10 years
54% of cases are preventable
28% by eating too little fibre
13% obesity
6% excessive alcohol consumption
7% smoking

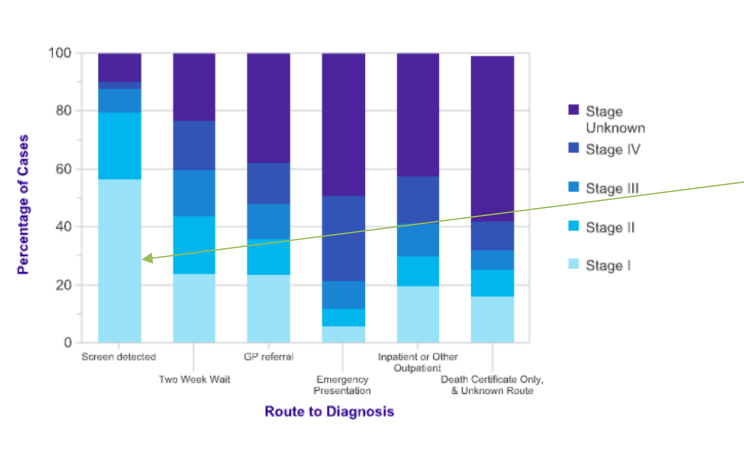
prognosis by stage
risk of cure after 1 year depending on stage of cancer

why is screening good
early diagnosis before symptoms appear
means catching at earlier stages
what are common warning signs of cancer
can see that most of these symptoms are not just associated with cancer

what are common tests used for initial diagnosis?
blood tests - FBC, LFTs, U&Es, bone profile, tumour markers
often during initial investigation to narrow down issue
biopsy - mass, lymph node,
x-ray - chest e.g. lung
ultrasound - breast, gynaecological masses
these are the most accessible initial testing
what are more complex tests used for diagnosis?
Computerised Tomography CT - 3D image using X-ray of chosen area
positron emission tomography PET - patient injected with radio-labelled fluorodeoxyglucose 18F-FDG to identify metabolically active areas of the body (cancer cells as they will use up more glucose then other cells)
PET-CT combination
what are tumour markers
can support diagnosis
PSA - protein specific antigen for prostate cancer
CA125 - ovarian
CA15-3 breast
CA19-9 pancreas or bild duct cancer
CEA carcioembryonic antigen - bowel cancer
if you have one of these tumour markers, it doesnt mean you have the cancer