B3.1 Gas exchange in leaves
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Adaptations of the leaves for gas exchange
-thin leaves
-many stomata
-waxy cuticle
-epidermis
- Spongy mesophyll
- Air spaces
-veins
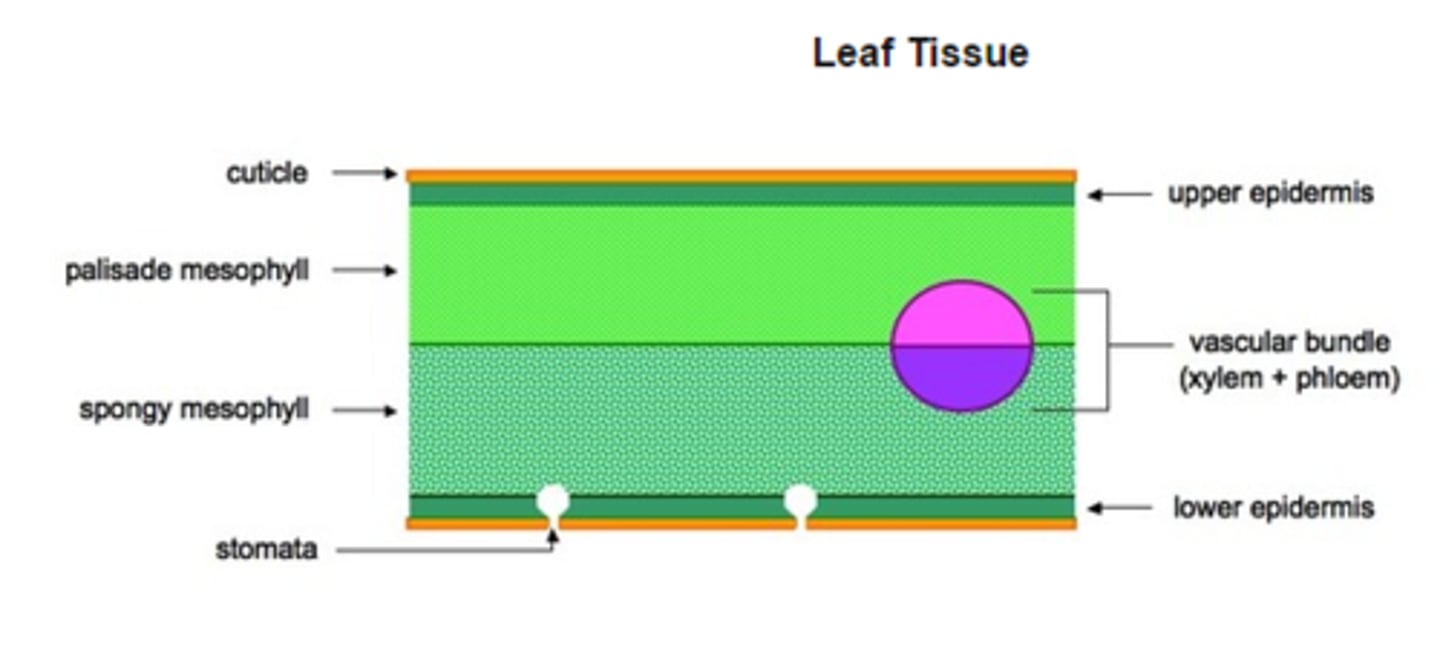
Thin leaves
large surface area across which gases can diffuse into and out of the leaf
waxy cuticle
It is hydrophobic, so water cannot penetrate easily. Waterproof barrier preventing water loss and dehydration
Stomata
Pores surrounded by guard cell that allow diffusion of gases in and out of the leaf.
- They are mainly open during the day, but when this happens, water is lost.
- They close at night.
- Guard cells, by changing their shape can close and open the stomata
Epidermis
Contains stomata
Air spaces
Allow gases to diffuse from one part of the leaf to another
Spongy mesophyll
Contains many air spaces
Veins (Vascular bundle)
Transport water and substances from the roots to the leaves. Veins are made of xylem and phloem tissue
Xylem
Transports water and dissolved minerals
Phloem
Transports sugar and amino acids
How do xylem and phloem transport substances?
capillary action: cohesion (between water molecules) and adhesion (between walls and other molecules)
Plan diagram of a leaf
What happens when leafs recieve more sun?
Thicker palisade mesophyll layer (more chloroplasts in this area)
Transpiration
the loss of water vapour through the leaves, stems, and other above-ground parts of the plant.
Maintains a constant water movement within the plant
Where does transpiration occur?
through the stomata
What factors affect transpiration?
Light, temperature, humidity, wind
Temperature effect on transpiration
Higher-> higher
The higher the temperature, the more kinetic energy water molecules have, and so the faster they evaporate and diffuse out of the stomata.
Light effect on transpiration
Higher-> higher
When light intensity is higher, guard cells cause the stomata to open wider to allow more carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf for photosynthesis.
This means that more water evaporates from the plant.
Wind effect on transpiration
Higher-> Higher
The higher the wind speed, the faster water molecules are moved away from the leaf once transpiration has occurred. This maintains a steep concentration gradient.
Humidity effect on transpiration
Higher-> Lower
Increasing humidity decreases the rate of transpiration. This is because there is a high concentration of water vapour in the air which reduces the concentration gradient.
Stomatal density
Number of stomata in a particular unit of area in a leaf or another plant region/organ
How to calculate stomatal density
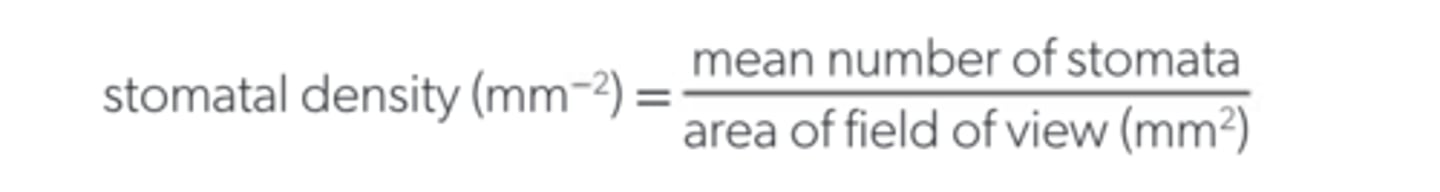
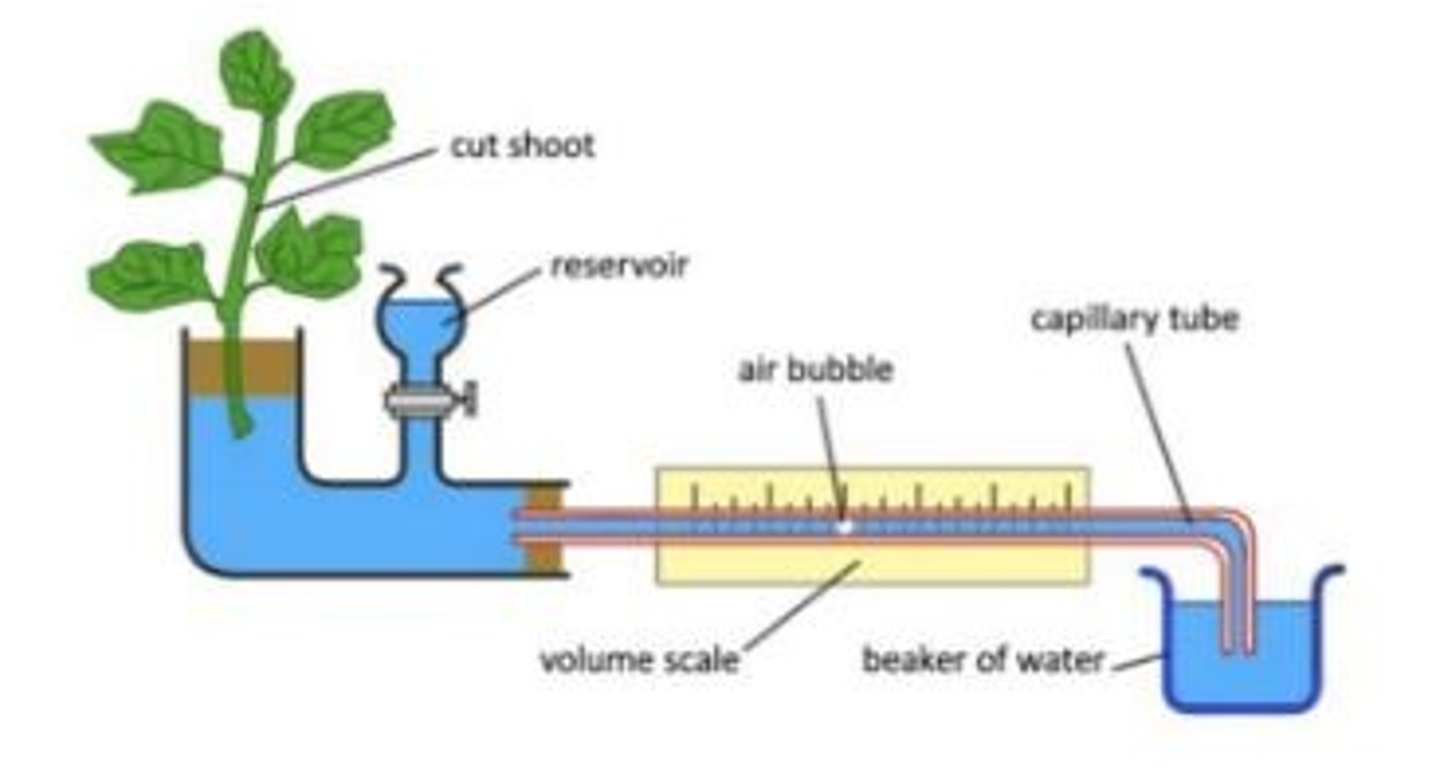
How to measure transpiration
Potometer
Potometer
Work by looking at how much water is being taken up by a plant, using a volume scale and an air bubble.
the air bubble moves towards the plant when it is taking up water (more transpiration)