AP Biology - Unit 1: Elements of Life
1/15
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Organic Compounds
Compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen
Carbon
Has four valence electrons
Can form single, double, and triple covalent bonds
Can create long chains or rings
Hydrocarbons
Organic molecules consisting only of hydrogen and carbon that can create the foundation of more complex molecules
Carbon Skeleton
The carbon framework that forms the backbone of organic molecules
Length
Branching
Double Bond Positions
Rings
Carbon Chain
A connected sequence of carbon atoms that forms the backbone of many organic molecules
Ring
A cyclic arrangement of carbon atoms in a molecule
Branching
Side chains that branch off the main carbon chain, affecting shape and properties
Functional Group
Specific groups of atoms attached to a carbon skeleton that participate in chemical reactions
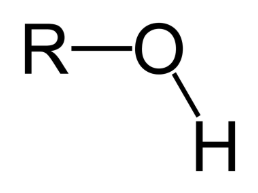
Hydroxyl Group
The -OH group (found in alcohols)
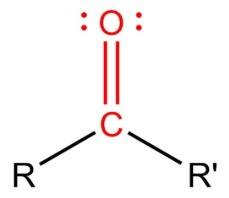
Carbonyl Group
The C=O group (found in aldehydes and ketones)
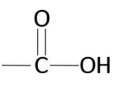
Carboxyl Group
The -COOH group (acidic functional group found in acids)
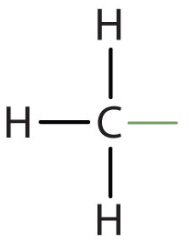
Methyl Group
The -CH3 group (a common alkyl substituent)
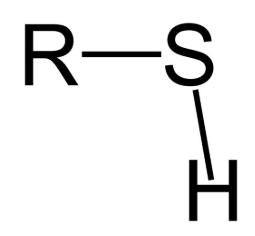
Sulfhydryl Group
The -SH group (found in cysteine: can form disulfide bonds)
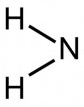
Amino Group
The -NH2 group (foundational for amino acids and amines)
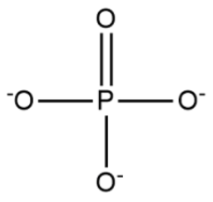
Phosphate Group
The -OPO3 group (found in glycerol phosphate and nucleic acids: important in energy transfer and backbone chemistry)
Covalent Bonds
Bonds created by sharing electrons between atoms
Single (sharing one e- )
Double (sharing two e- )
Triple (sharing three e- )