AP HUG Unit 1
4.6(5)
4.6(5)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
garth's AP HUG CED Notes converted into flashcards.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
reference maps
maps designed for people to refer to for general information about places. The two pain types are physical and political
2
New cards
thematic maps
maps used as a communication tool - they tell us how human activities are distributed. (statistical map)
3
New cards
Cartogram map
a map where the geometry of regions is distorted in order to display information
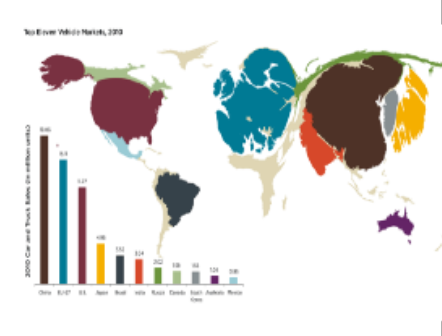
4
New cards
Choropleth Map
a map that uses differences in shading, coloring, or the placing of symbols to display data
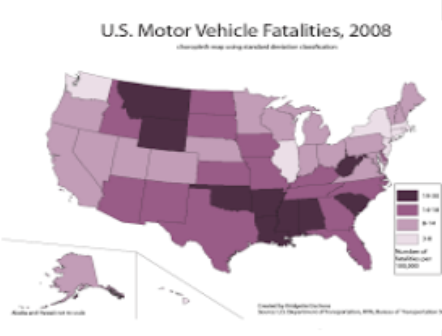
5
New cards
Dot Density Map
a map that shows geographic phenomenon by placing dots on the map..
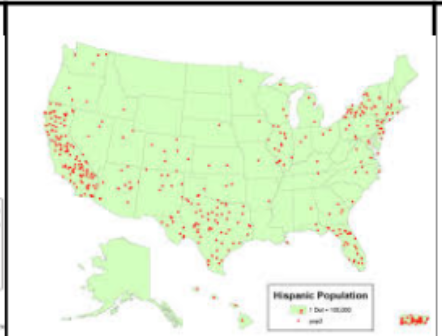
6
New cards
Isoline Map
a map that has lines drawn on to connect data points of the same value.
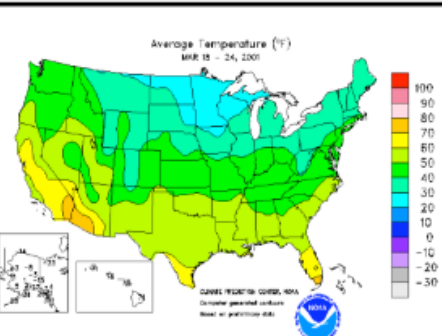
7
New cards
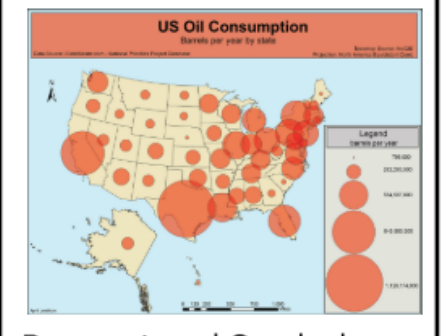
Proportional Symbol Map
a type of thematic map that uses symbols of varying sizes to show data clusters
8
New cards
Absolute Location
The exact coordinates of a place (latitudal and longitudal location)
9
New cards
Relative Location
the location of a place in relation to other things
10
New cards
Absolute Direction
The cardinal directions (North/East/South/West)
11
New cards
Relative Direction
Left/Right/Up/Down
12
New cards
Clustering
A spatial pattern where data is grouped and bunched together
13
New cards
Dispersal
A spatial pattern where data looks to be distributed over a wide area.
14
New cards
Elevation
A measure of how high or low a place is in relation to the sea level.
15
New cards
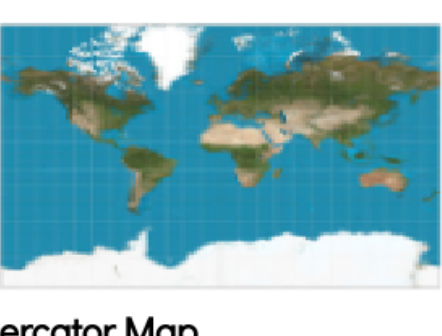
Mercator Map
A map that has greatly distorted poles, but keeps the shape and direction of countries constant.
16
New cards
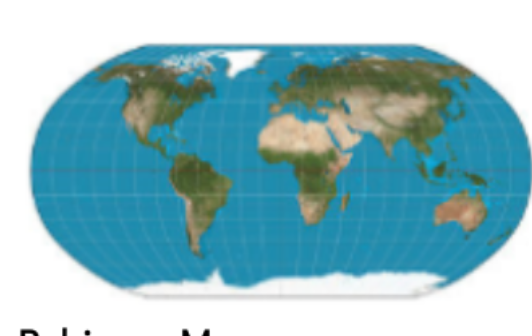
Robinson Map
A map with rounded edges where everything is slightly distorted
17
New cards
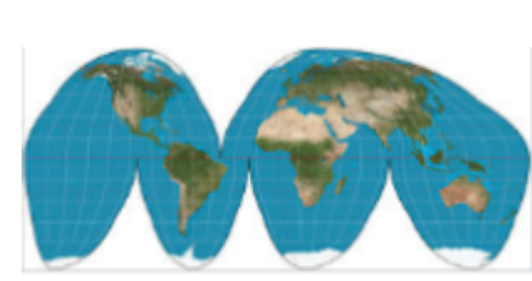
Goode-Homolosine Projection
A map projection that distorts direction and distance, but keeps size and shape accurate.
18
New cards
Gall Peters
A map that distorts the size of countries (especially near the equator)
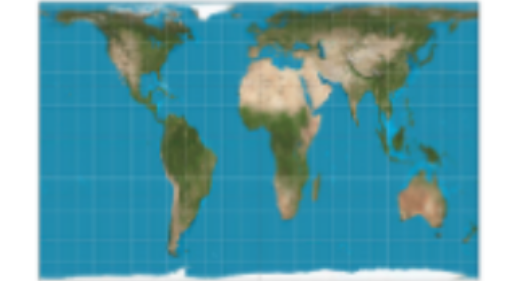
19
New cards
Geospatial Data
all information on a landscape (including physical features and human activities)
20
New cards
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
a computer system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on Earth’s surface
21
New cards
Geographic Positioning Systems (GPS)
A system that uses data from satellites to pinpoint a location on Earth and help people find their way to a destination.
22
New cards
Remote Sensing
the process of taking pictures of Earth’s surface from satellites (or, earlier, airplanes) to provide a greater understanding of Earth’s geography
23
New cards
Census Data
An official count of all individuals in a population in the USA, happens every ten years.
24
New cards
Space
Extent of an area (can be in a relative or absolute sense)
25
New cards
Distance Decay
a geographical term that describes the effect of distance on spatial interactions
26
New cards
Time-Space Compression
the increasing sense of connectivity that seems to be bringing people closer together
27
New cards
Pattern
The geometric or regular arrangement of something in an area
28
New cards
Spatial Information
_____ _________ can come from written accounts in the form of field observations, media reports, travel narratives, policy documents, personal interviews, landscape analysis, and photographic interpretation.
29
New cards
Sustainability
the goal of the human race reaching equilibrium with the environment; meeting the needs of the present without risking the resources of the future
30
New cards
Natural Resources
physical material constituting part of Earth that people need and value
31
New cards
Environmental Determinism
How the physical environment caused, or determined, social development. The belief that the prosperity of a community is determined by its physical environment.
32
New cards
Environmental Possibilism
The belief that (while the physical environment can limit some human actions) humans have the ability to adjust to their environment
33
New cards
Scale
The relationship between the distance onf the ground and the corresponding distance on a specific map. **How zoomed in is the map? What are you looking at?**
34
New cards
Scale of Analysis
At what scale is the **data** being displayed? (Looking at a map of America and seeing data about individual states)
35
New cards
Region
a place larger than a point and smaller than a planet that is grouped together because of a measurable or perceived common feature
36
New cards
Formal Region
A region based off quantitative data -- all government areas are ____ ____s because they share a government (ex. Wisconsin)
37
New cards
Functional Region
a region based around a node or focal point -- terrestrial radio broadcasts are an example of this.
38
New cards
Vernacular (Perceptual) Region
an area that shares a common qualitative characteristic, it’s only a region because people believe it’s a region (The American Midwest)