E.3 Esophageal Cancer
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is the five year survival rate?
less than 20%
The majority of esophageal cancers are:
adenocarcinoma (from glands lining the esophagus)
Incidence is higher in:
men
increases w/ age 70-84 yrs
What is the prognosis?
Poor b/c usually not diagnosed until is advanced
Risk factors include:
barrett's metaplasia (GERD), smoking, excessive alcohol, obesity.
Injury to esophageal mucosa is the greatest risk
Achalasia
Delayed emptying of the lower esophagus and associated w/ squamous cell cancer.
where are most of the tumors located?
Middle and lower portion of the esophagus.
Appear as ulcerations, may penetrate the muscular layer and extend outside the wall.
What is the most common symptom of esophageal cancer?
progressive dysphagia - may be described as substernal feeling with food not passing
occurs first with meat, then w/ soft foods and eventually with liquids
Later s/sx include:
pain (substernal, epigastric, or back and can radiate to neck, jaw, ears, and shoulders).
Increases w/ swallowing
Weight loss without trying
regurgitation of contents with blood flecks
Hemorrhages if cancer erodes into the aorta
Perforation w/fistula formation into lung or trachea
The tumor may cause obstruction in later stages
if the tumor is in the upper third of the esophagus what s/sx are common?
sore throat, choking, and hoarseness
How does it spread?
via lymph system
Where does the cancer most commonly spread?
liver and lungs
What are the dx studies for esophageal cancer?
Endoscopic biopsy (for definite dx)
Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)
Esophagram (Barium swallow)
Barium swallow shows:
narrowing at the tumor site
What is the gold standard for Barrett's esophagus?
EGD
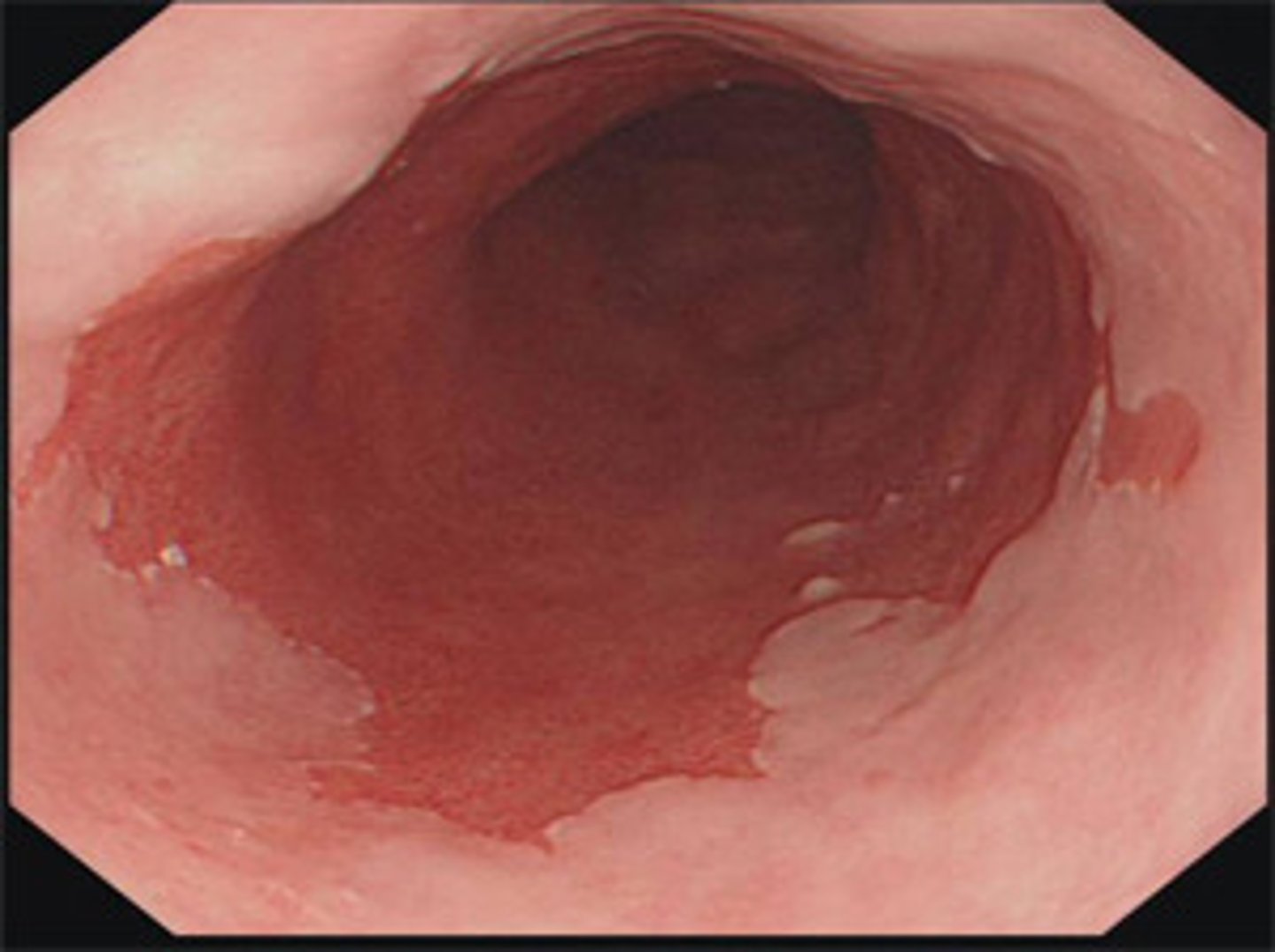
Albumin and Pre-albumin tell us...
about the patients nutritional status and how well they are absorbing nutrients
An endoscopic biopsy is done to...
make a definitive diagnosis of carcinoma by identifying malignant cells
Endoscopic ultrasonography is important to..
stage esophageal cancer
what are the tx options for esophageal cancer?
Depends on location, invasion, and metastases
Best results: multimodal approach
pre-surgery radiation and chemo
surgery resection
esophageal dilation and stenting
Why would radiation and chemo want to be done before surgery?
if you take the esophagus out first, the surgery is going to cause more complications due to the shortening of the esophagus than radiation and chemo would
Radiation and chemo are administered for...
palliation of sx (e.g. dysphagia) and to increase survival
combination drugs are normally used
Esophagectomy is the..
remove all or part of the esophagus and replaced with a dacron graft
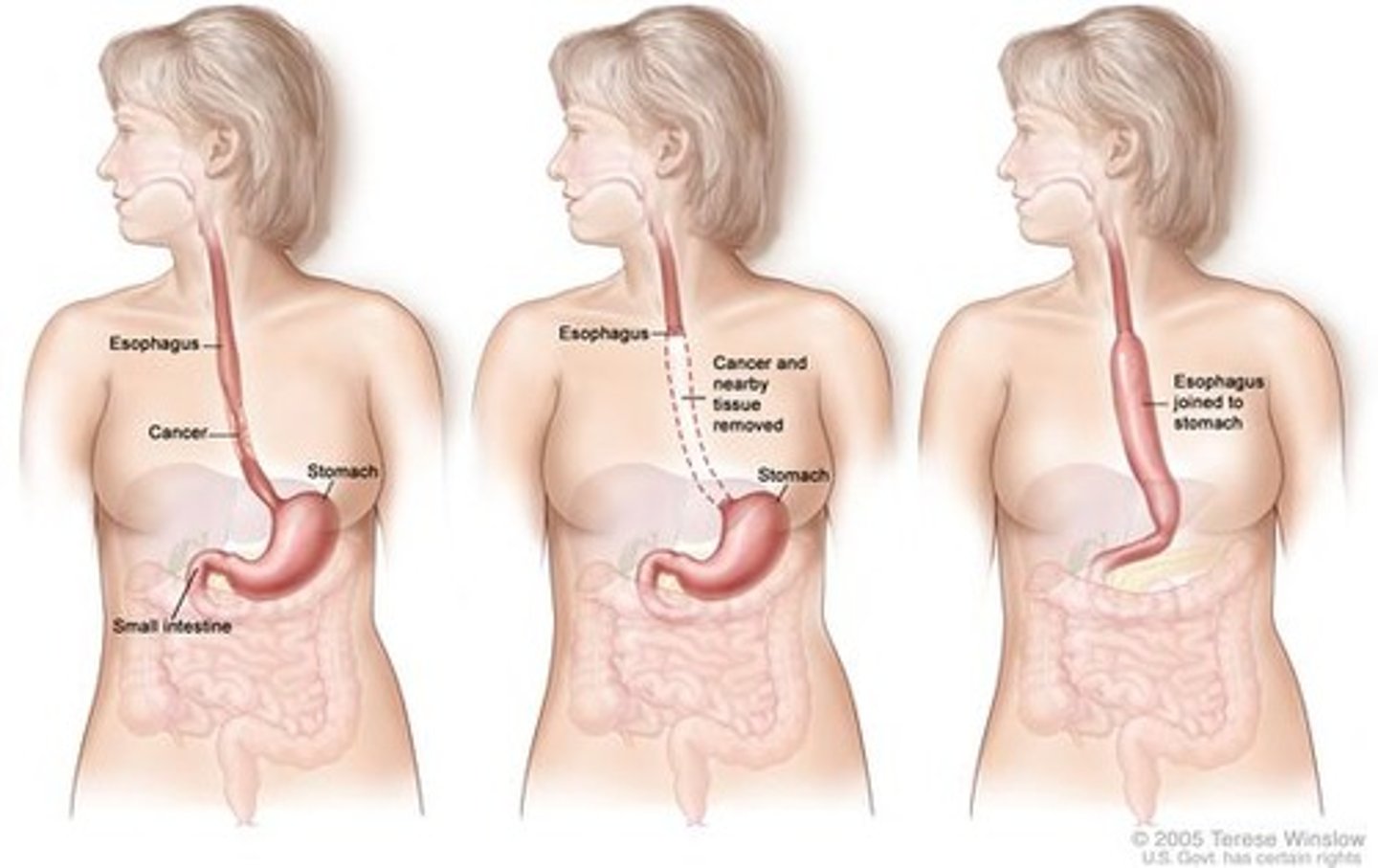
esophagogastrostomy -
resection of a portion of the esophagus and anastomosis of the remaining part to the stomach
Esophagoenterostomy -
resection of a portion esophagus and anastamosis of a segment of the colon to the remaining portion
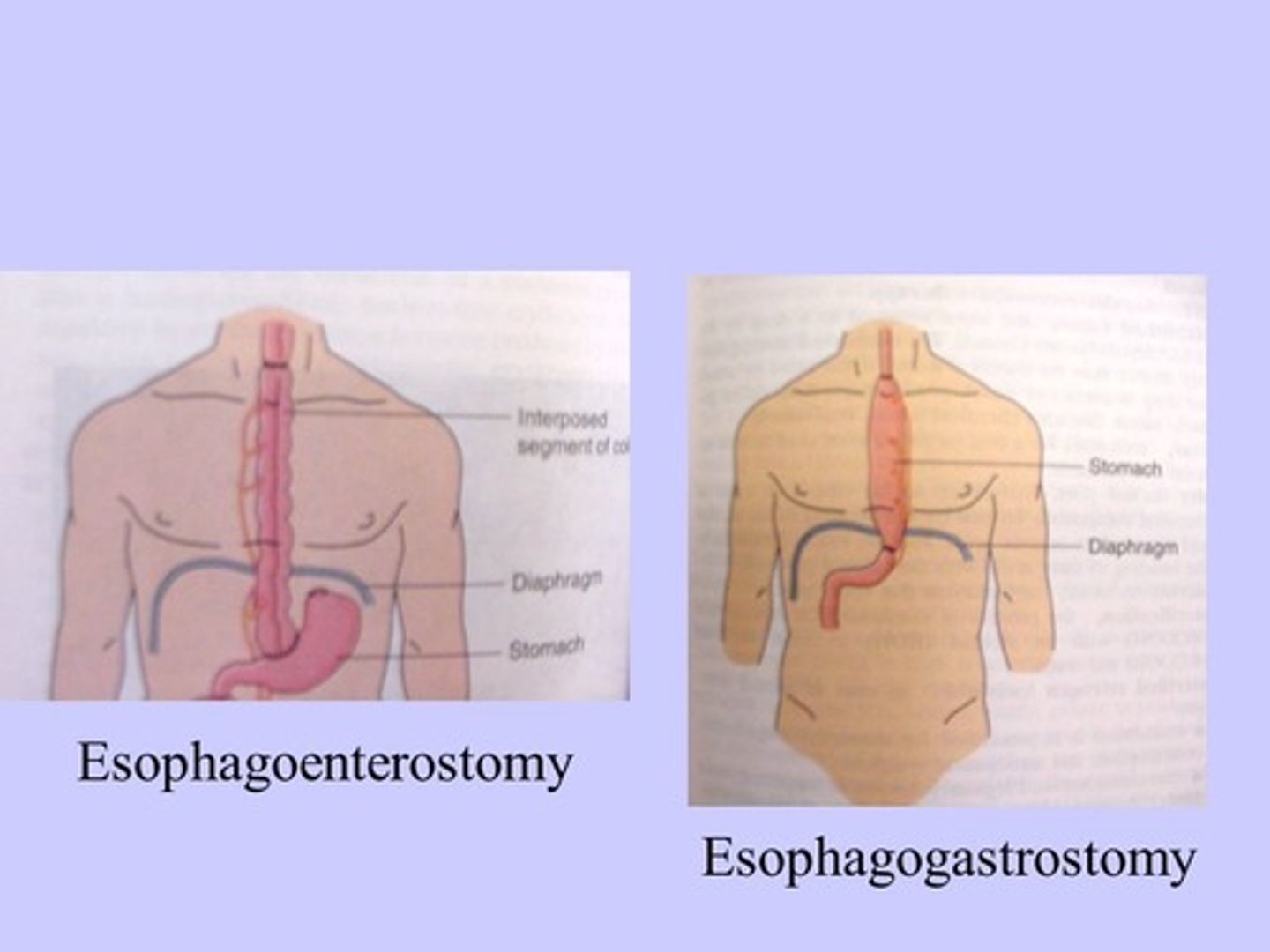
Dilation and stenting is done as..
palliative care to restore the swallowing function and maintain nutrition and hydration.
Allows liquid & food to pass thru stenotic area
stenting is done by:
self expandable metal stents
Stents are placed before surgery to do what?
improve nutrition status
How are these done?
endoscopically
What is photodynamic therapy?
Pt receives IV injection (Porfimer Na =photofrin)
Light is directed to the tumor using fiber passed thru endoscope
Light reacts w/photofrin and destroys cancer cells
Avoid direct sunlight up to 4 weeks after procedure
what are three complications of esophageal resection?
severe dumping syndrome
acid would reflux into the esophagus
malnutrition
What are the six components of post surgical care for esophageal cancer to pay attention too?
NG tube (DO NOT MANIPULATE)
Respiratory (mantain airway)
Semi-fowlers position (b/c aspiration & reflux)
IV fluids
Pain management
Nutritional support
The NGT is in place to do what two things? what do you have to know about it?
drain bloody discharge (may occur for 8-12 hrs before changing to a yellow greenish) and promotes bowl rest until everything heals
** DO NOT reposition the NG tube at any time
Why should be the respiratory status be monitored and what should be done?
surgery was just done near the airway
deep breathing and turning every two hours; incentive spirometry
What will their diet be like?
TPN; once they are ready to eat they will have smaller, bland meals, more throughout the day
30-60 mL of fluids an hour with progression to small, frequent, bland meals
If TPN leaks into the mediastinum, what s/sx would be present?
pain, increased temperature, dyspnea
What is post-op nutritional care?
sit up-right
eat 6-8 meals per day w/ fluid
manage diarrhea
What is an important lab value to monitor? why?
calcium - hypercalcemia
the body is not absorbing calcium because the stomach is not secreting the stuff needed to absorb it; abnormal production of PTH
How should we monitor for a GI bleed?
check the stool for bright red blood, if they are vomiting blood, H&H will drop, fatigue, O2 drops
To prevent hypovolemic?
assess BUN and creatinine
assess BP
Administer IV fluids
How often should incentive spirometry be done?
every hour 10x
Why is oral care essential post op and how often should it be done?
what specific liquid helps?
4x a day
prevent infection; the mouth is a passageway to the esophagus so you want to keep it as germ free as possible
milk of magnesia helps to remove crust format n
Chemo
single or combine
Carboplatin + paclitaxel, cisplatin + 5FU
ECF
DCF
cisplatin w/ capecitabine + oxaliplatin w/ either 5FU or calpecitabine
Single: bleomycin, mitomycin, methotrexate, vinorelbine (Navelbine), topotecan, and irinotecan (Camptosar)
Target Tx
targets HER 2 protein in the esophagus (this helps cancer grow) if there is too much.
Trastuzamab
Ramucirumab