"Chapter 10- Gross and Microscopic Anatomy of the Arterial System"
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
right axillary artery
gives off branches that supply the axilla, shoulder girdle, and thoracic wall.
Arteries: carry oxygenated blood away from the heart and typically rich in oxygen
carry oxygenated blood away from the heart and typically rich in oxygen
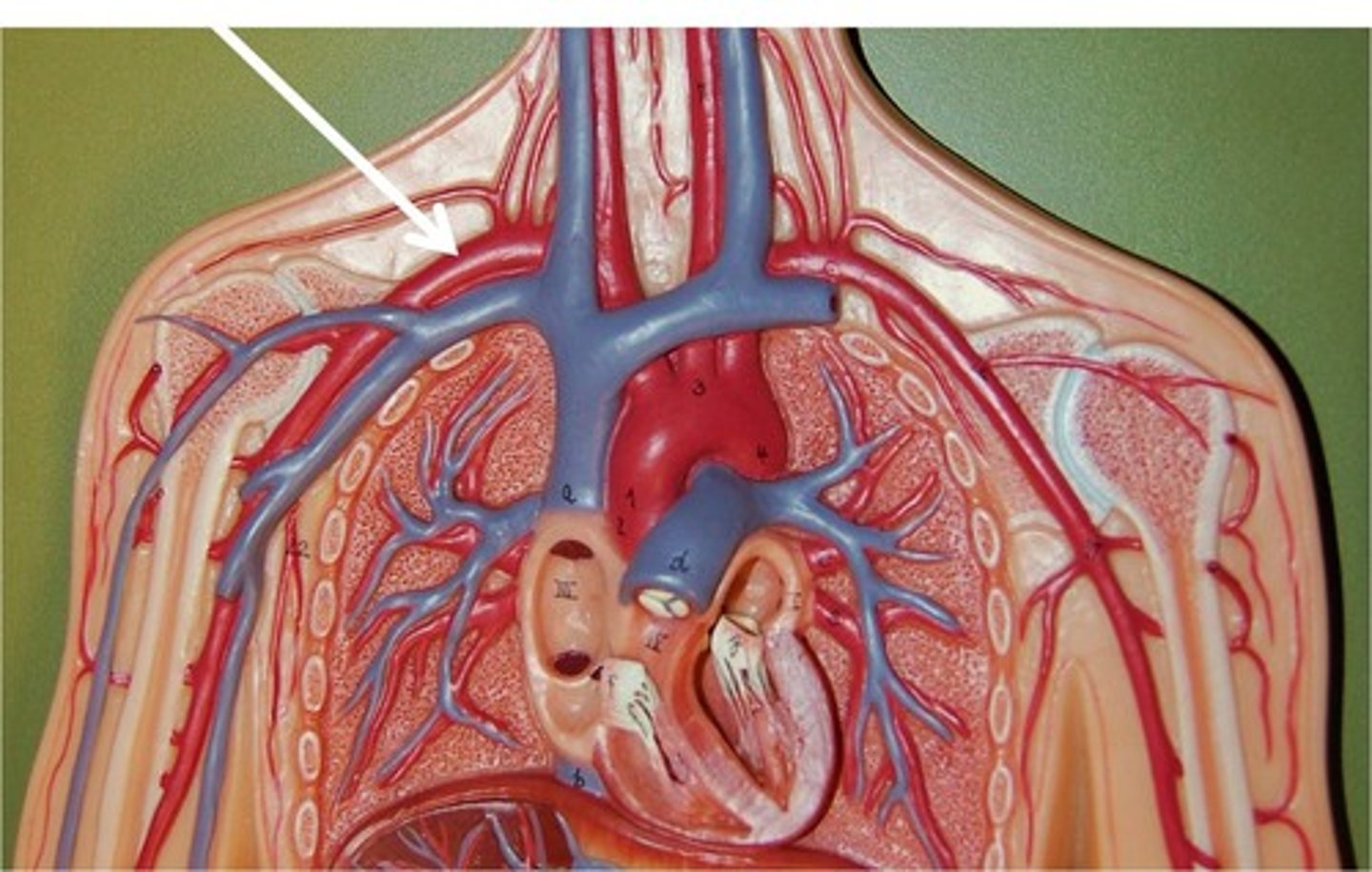
brachiocephalic trunk
takes blood to the right side of the head, neck, and upper limb by branching into the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery.
anterior cerebral artery
supplying the frontal and parietal lobes of the cerebrum
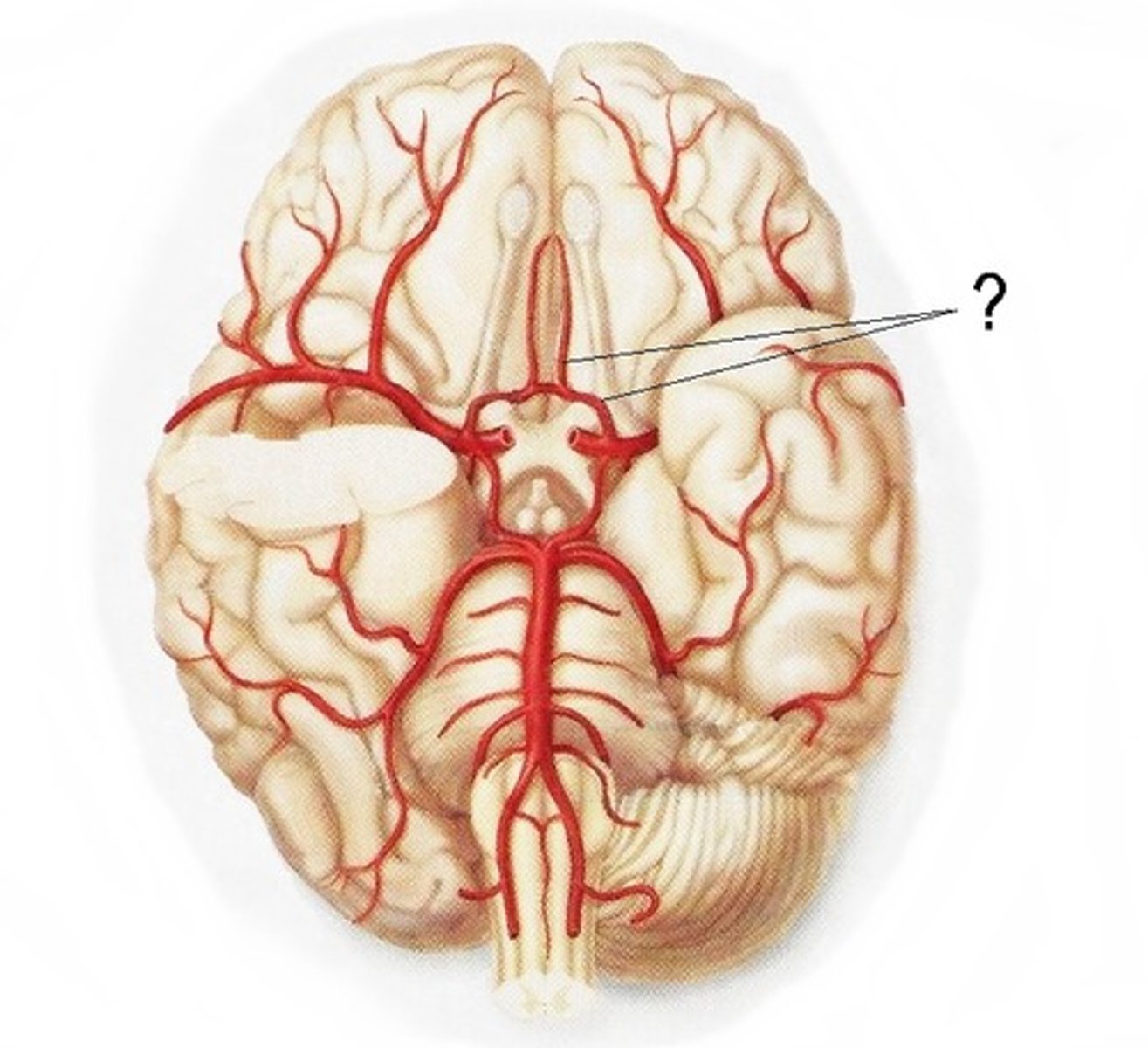
middle cerebral artery
supplying the lateral cerebrum
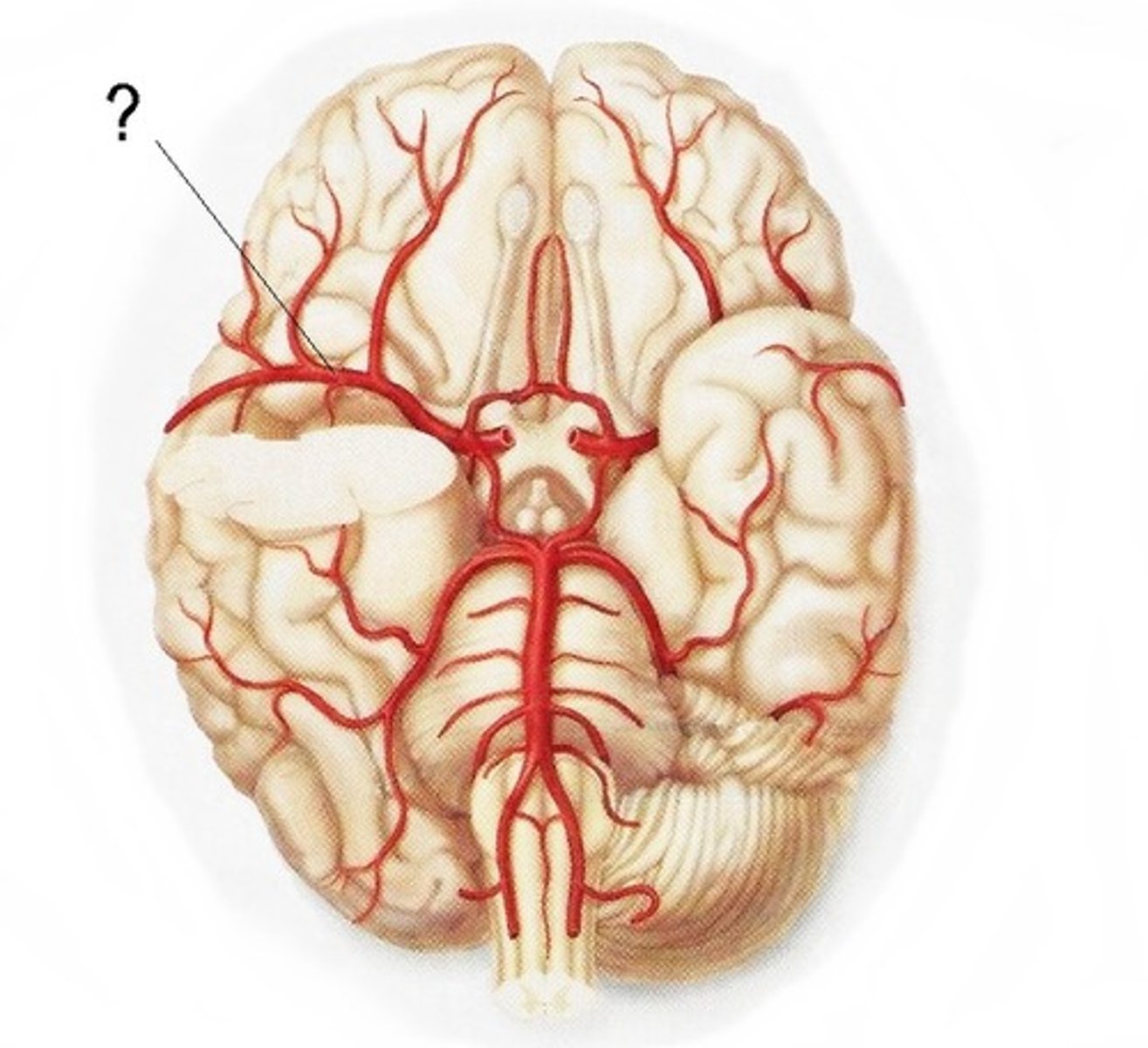
cerebral arterial circle (circle of willis)
opening formed at the base of the brain with anterior and middle cerebral arteries.

internal carotid artery (cut)
Takes blood to the brain, passing through the carotid canal
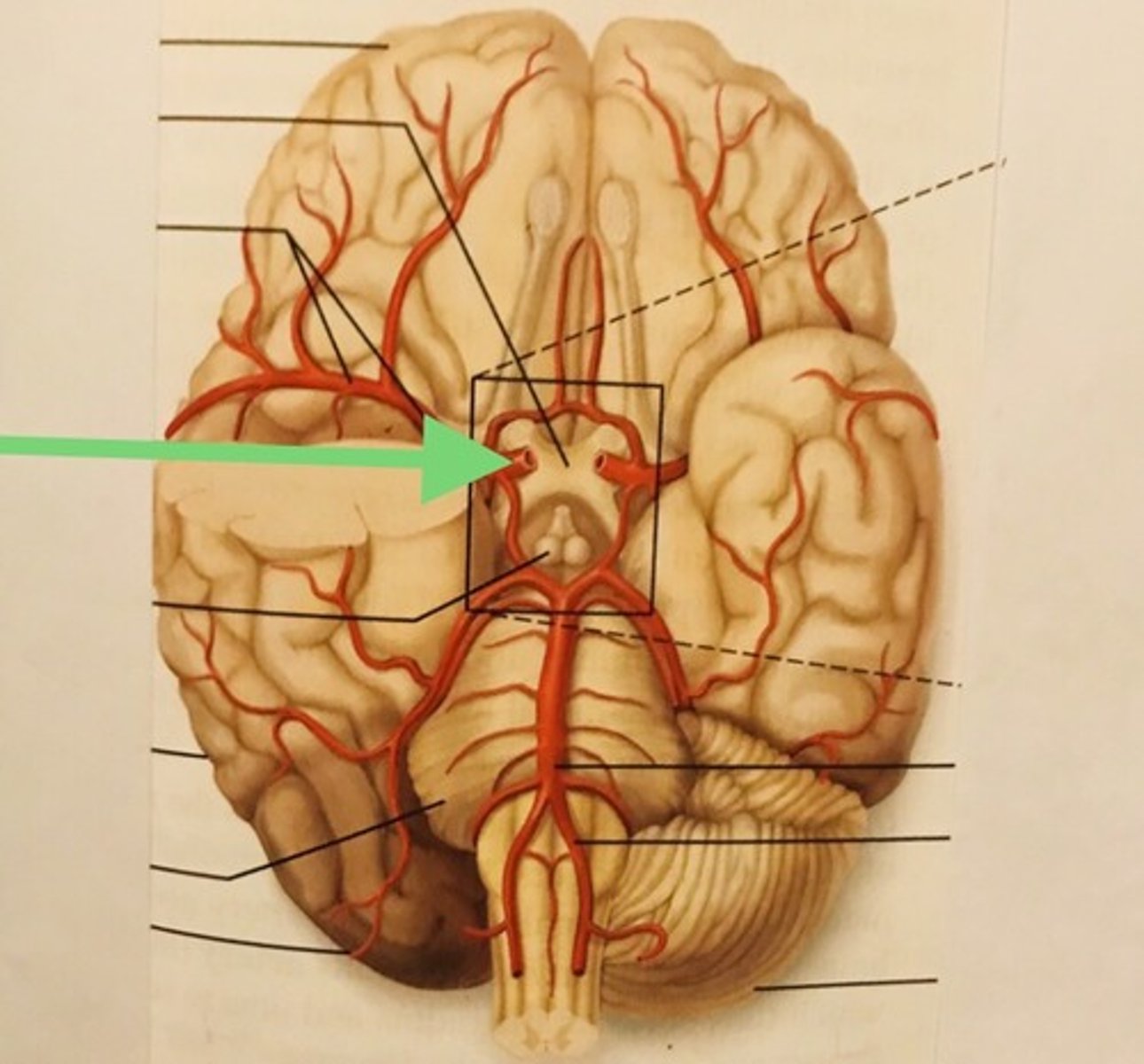
basilar artery
gives off branches to supply the cerebellum and the brain stem.
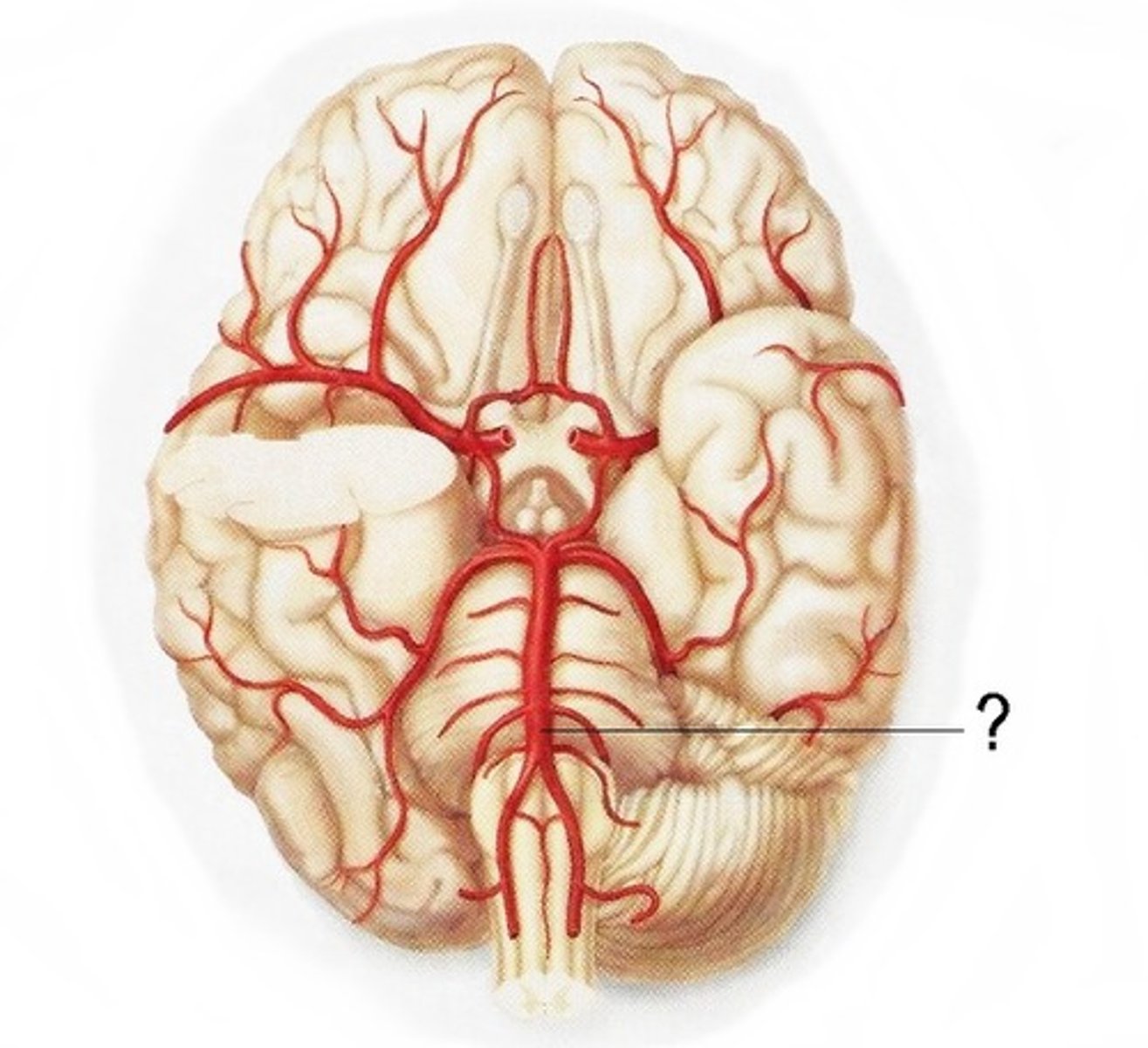
vertebral artery
Supplies blood to the spinal column and brain.
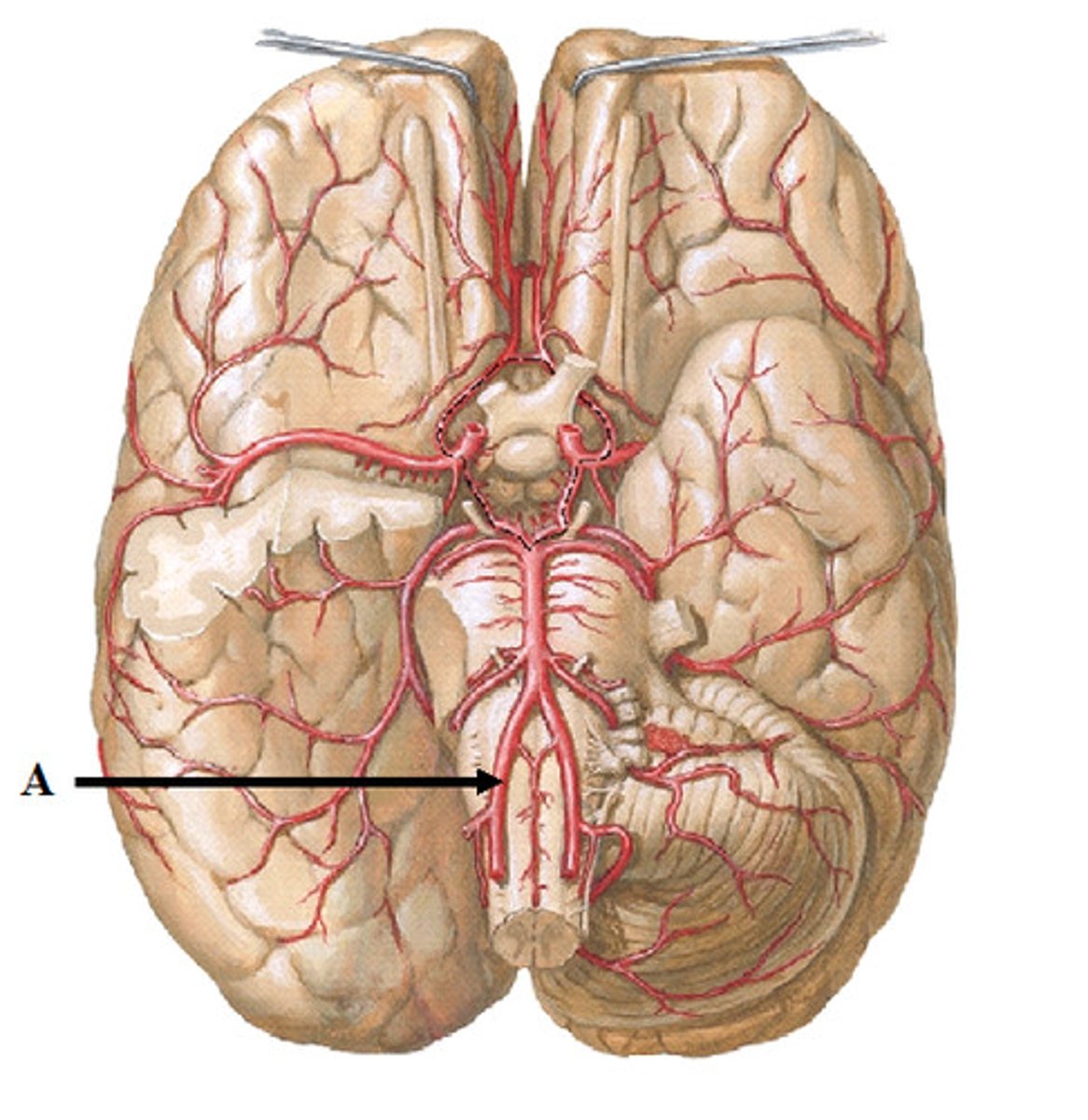
external carotid artery
give off branches that supplies blood to the neck, esophagus, pharynx, larynx, jaw, and face.
internal carotid artery
enters the skull through the carotid canal in the temporal bone and splits off into three branches; takes blood to the brain and eyes.
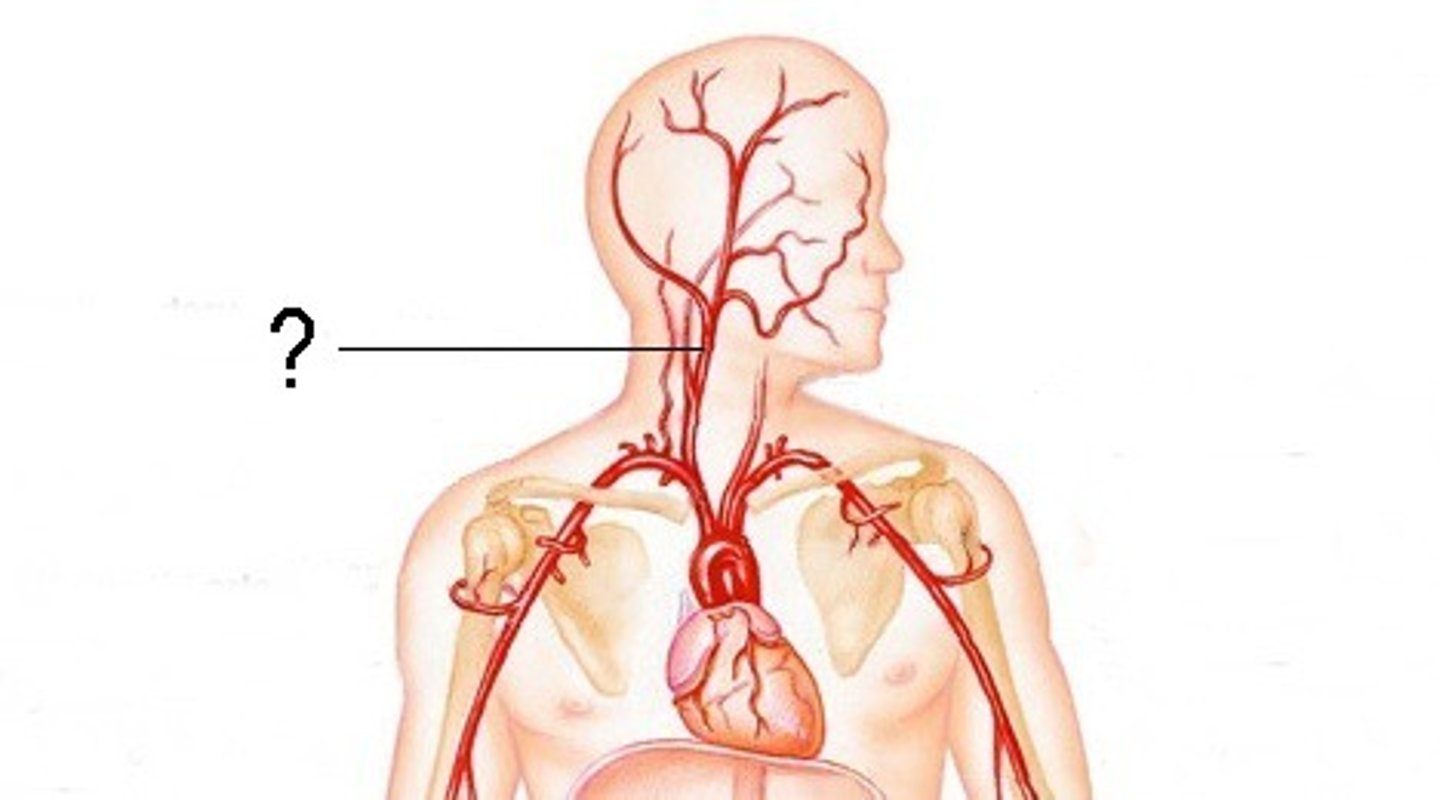
left common carotid artery
takes blood to the left side of the head and neck. It branches directly from the aortic arch and travels upward.
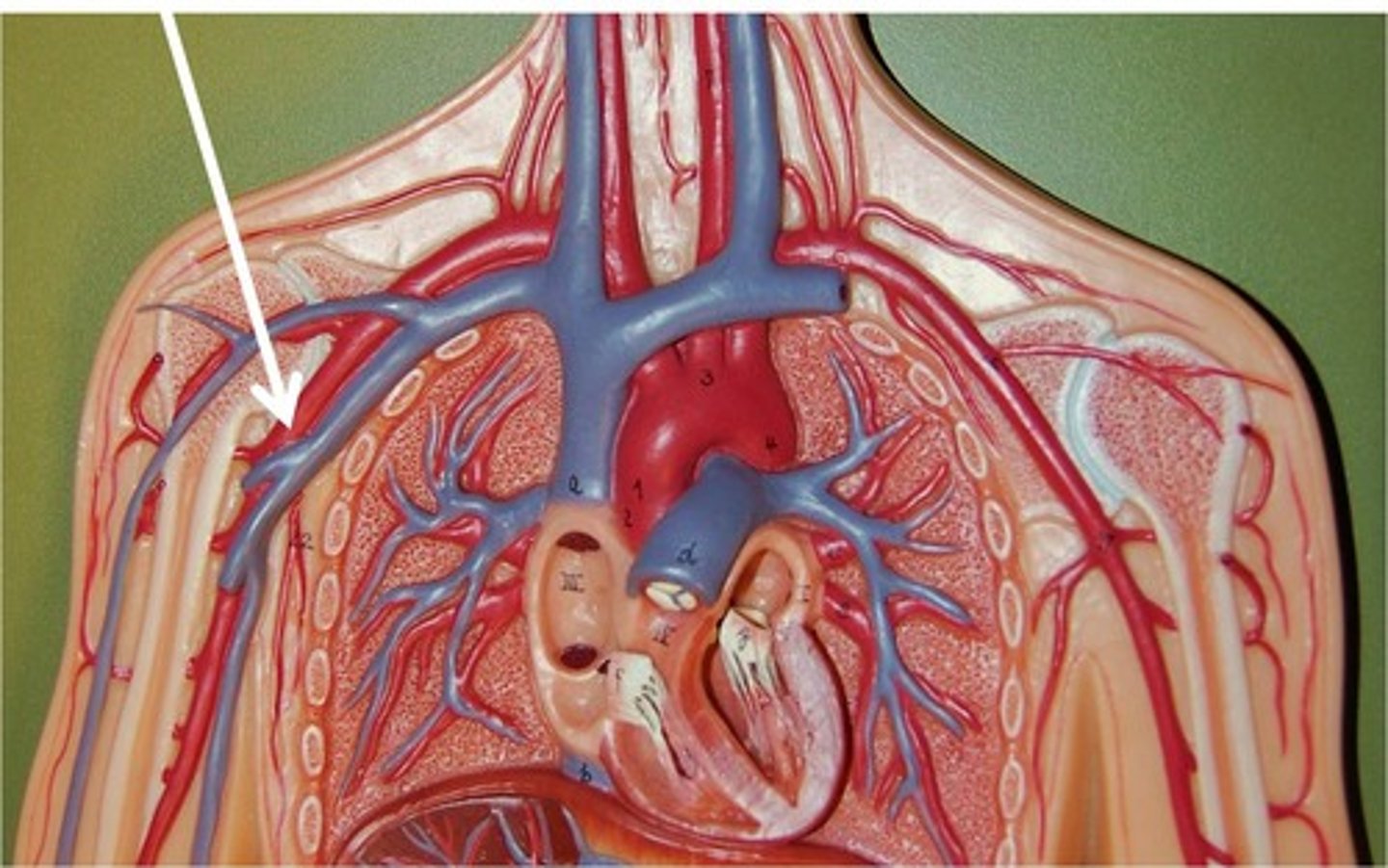
internal thoracic artery
It branches from the subclavian artery and supplies blood to the intercostal spaces, pericardium, and anterior wall of the chest.
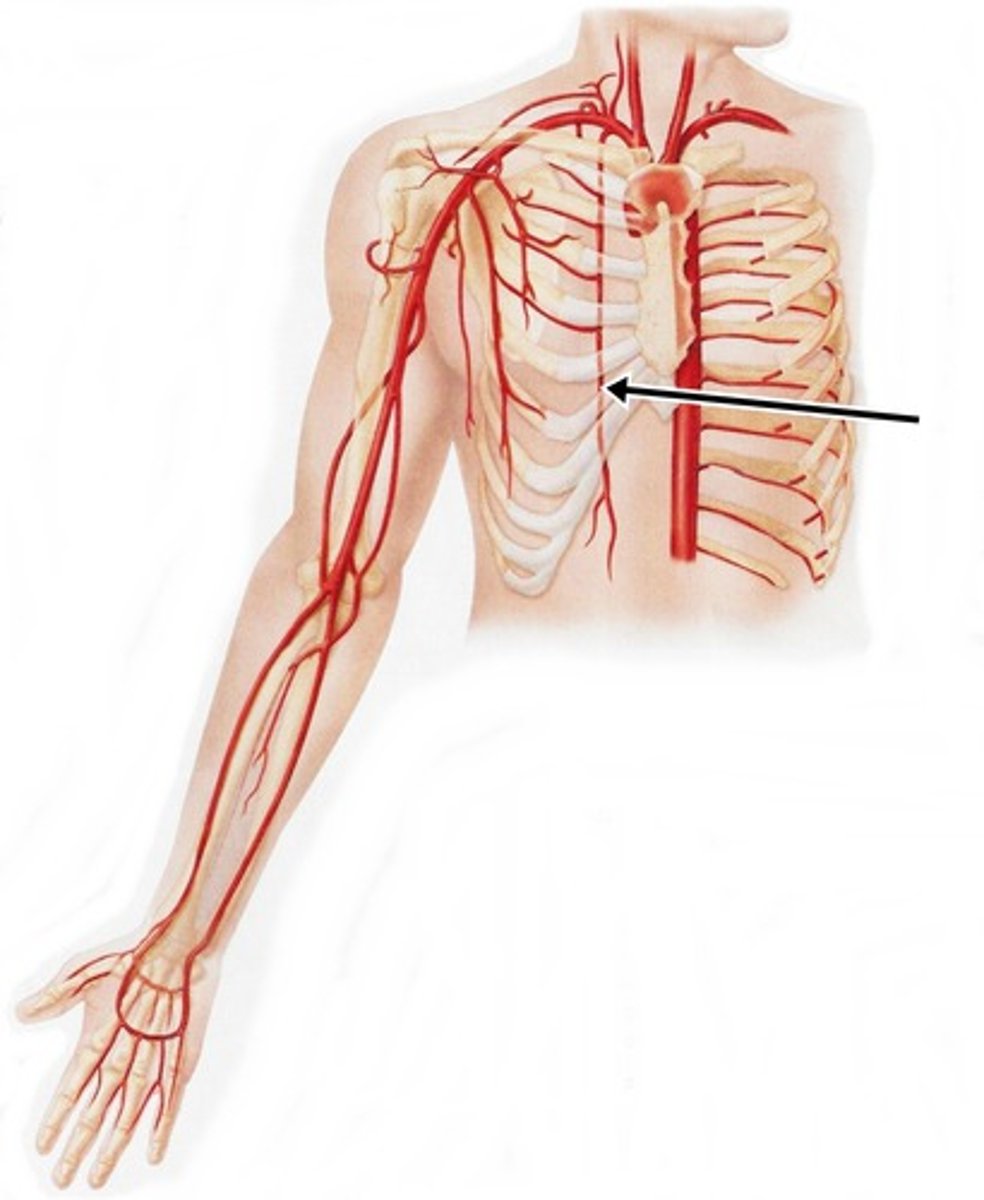
left subclavian artery
Third branch of the aortic arch that provides blood to the left upper limb, shoulder, and parts of the head and thorax
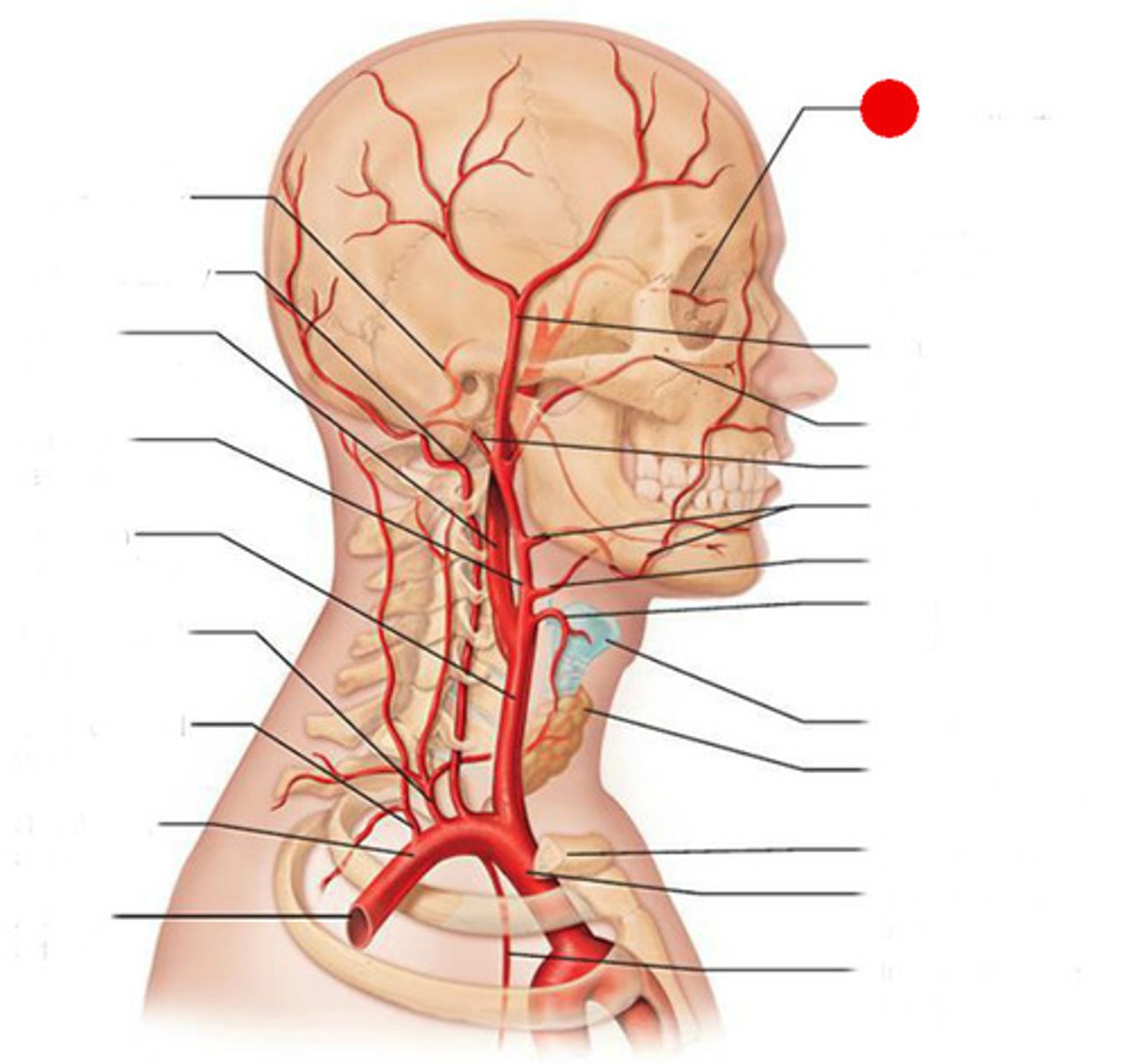
ophthalmic artery
supplies blood to the eyes
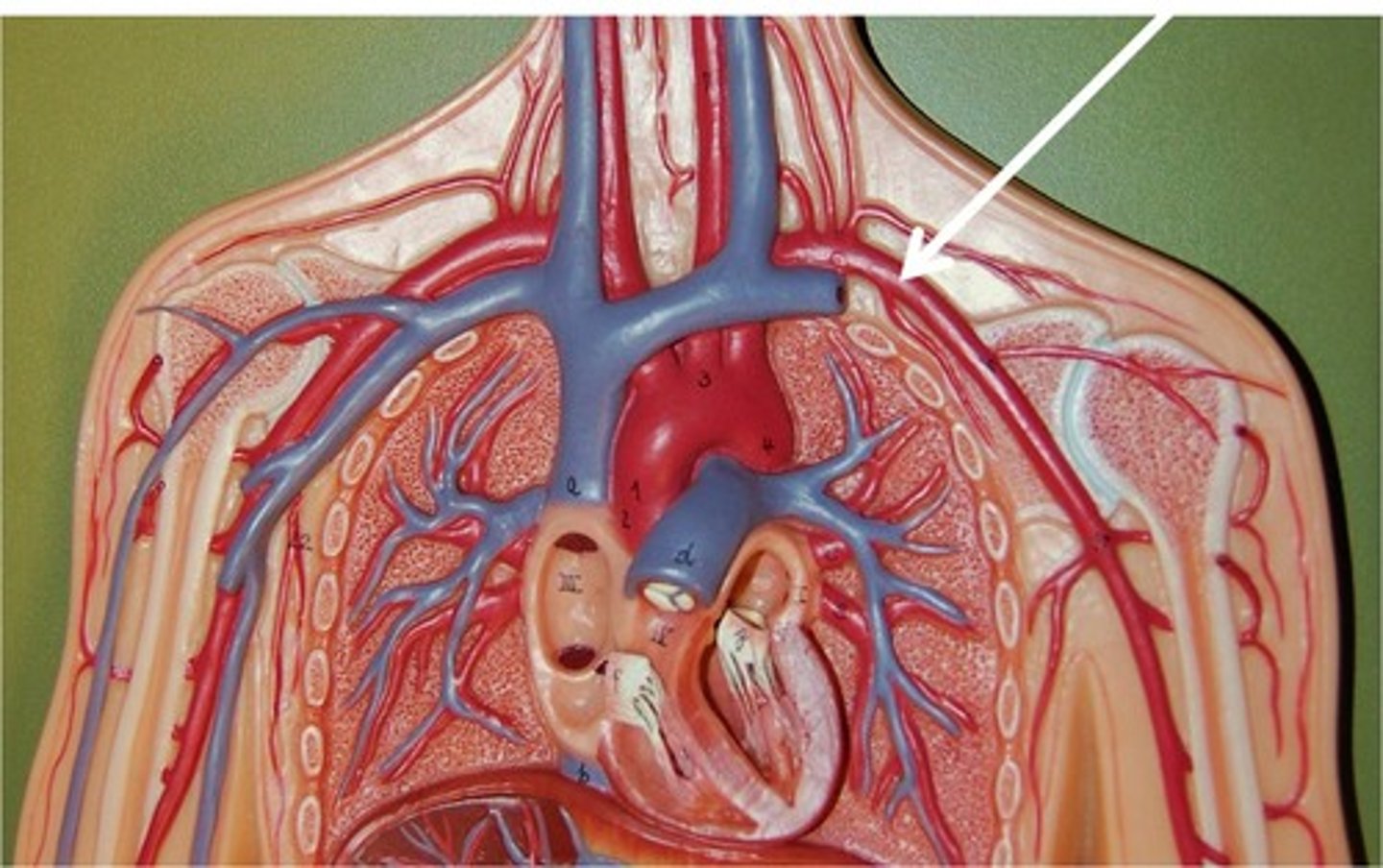
right common carotid artery
branches off from the brachiocephalic trunk and travels upward on the right side of the neck. Is a major blood vessel that supplies blood to the head and neck.
right subclavian artery
The second artery to arise from the right brachiocephalic trunk. It supplies blood to the cervical vertebrae and right forelimb.
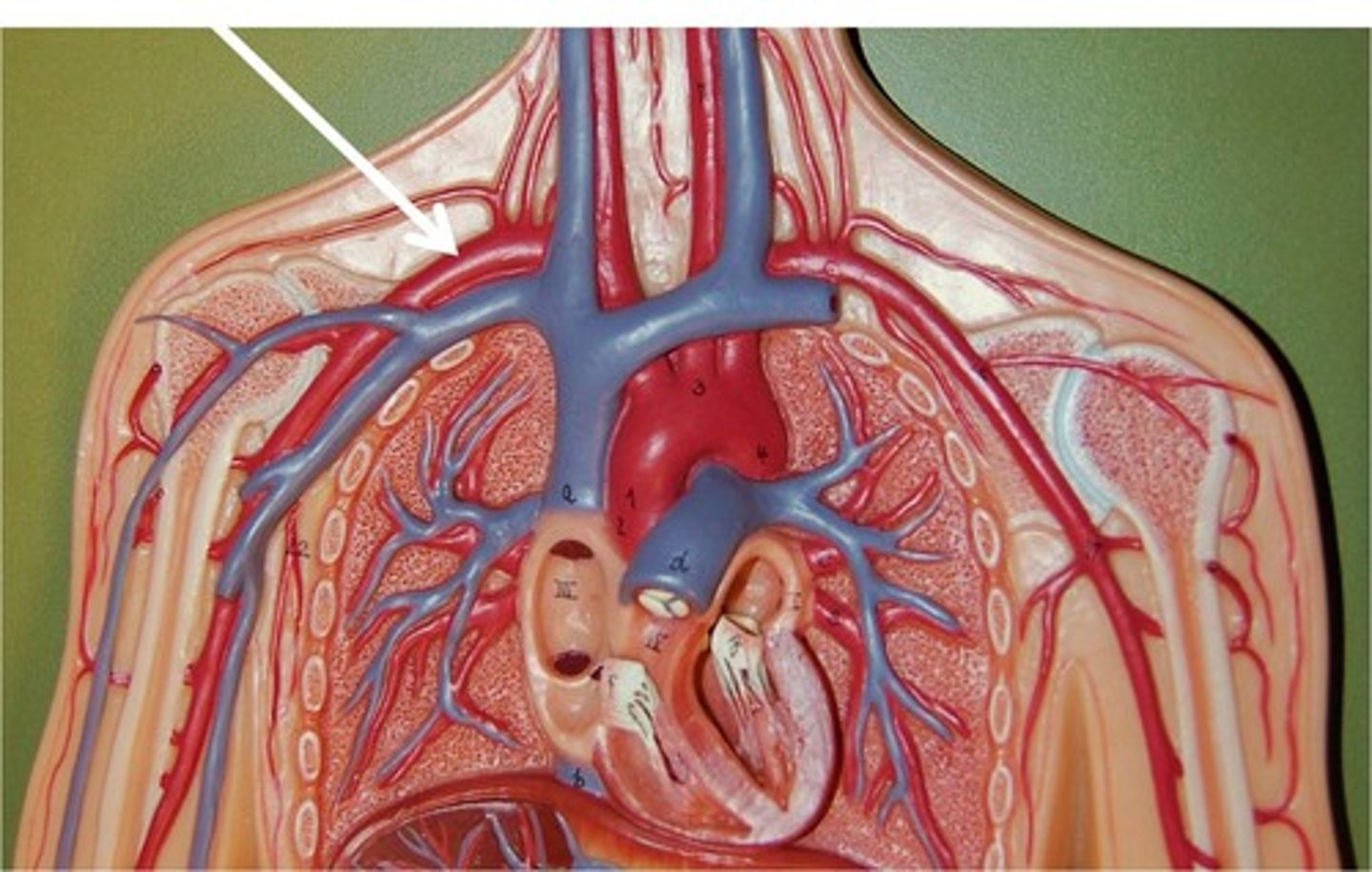
Right vertebral artery
supplies blood to the brain and spinal cord. It is one of the two vertebral arteries, the other being on the left side. It branches from the first part of the right subclavian artery.
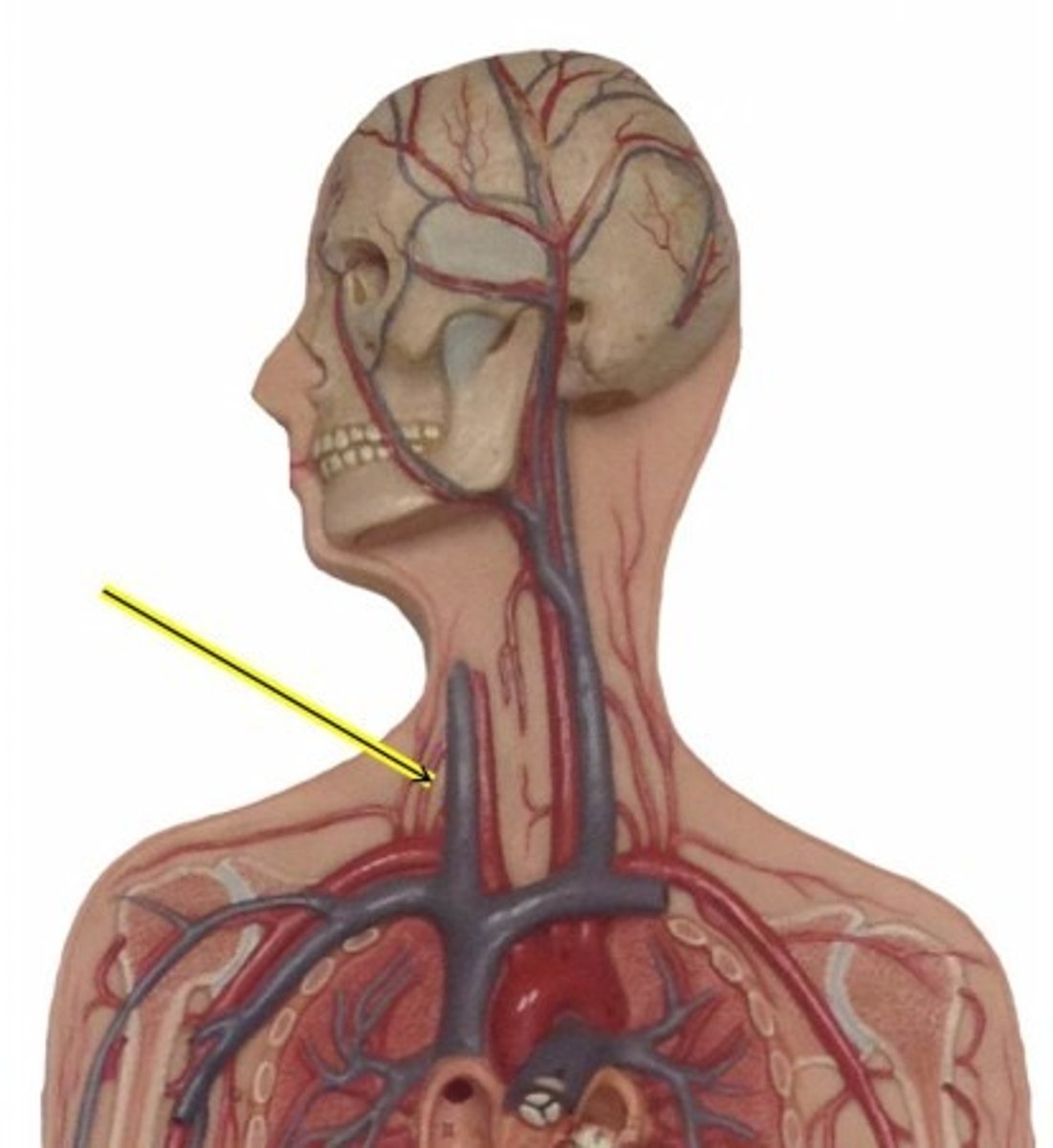
Left vertebral artery
is one of the two vertebral arteries that provide blood to the posterior part of the brain and the spinal cord.
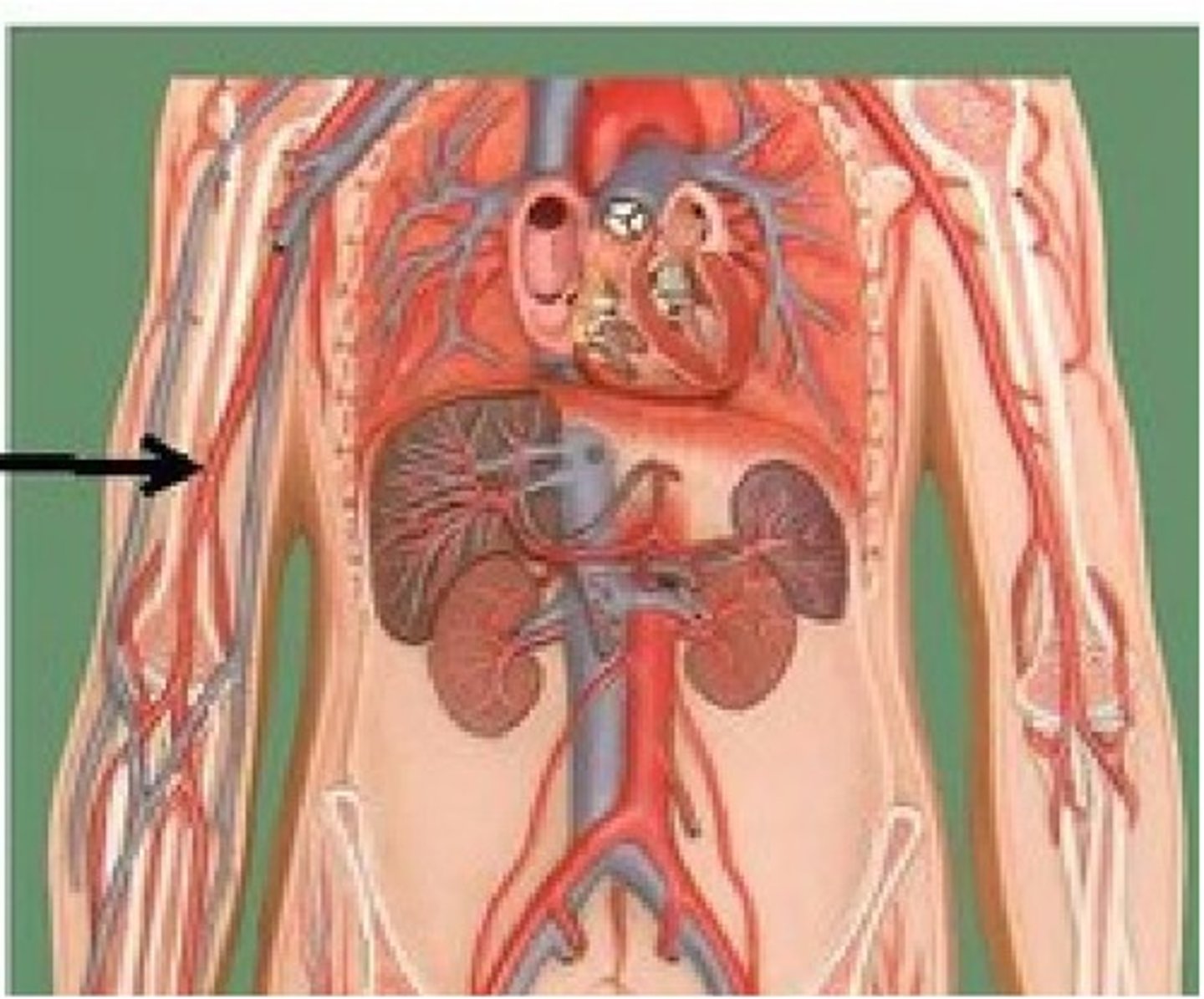
right brachial artery
provides blood to the arm, forearm, and hand. It is the continuation of the right axillary artery.
palmer arch
delivers blood to the metacarpal arteries of the hand
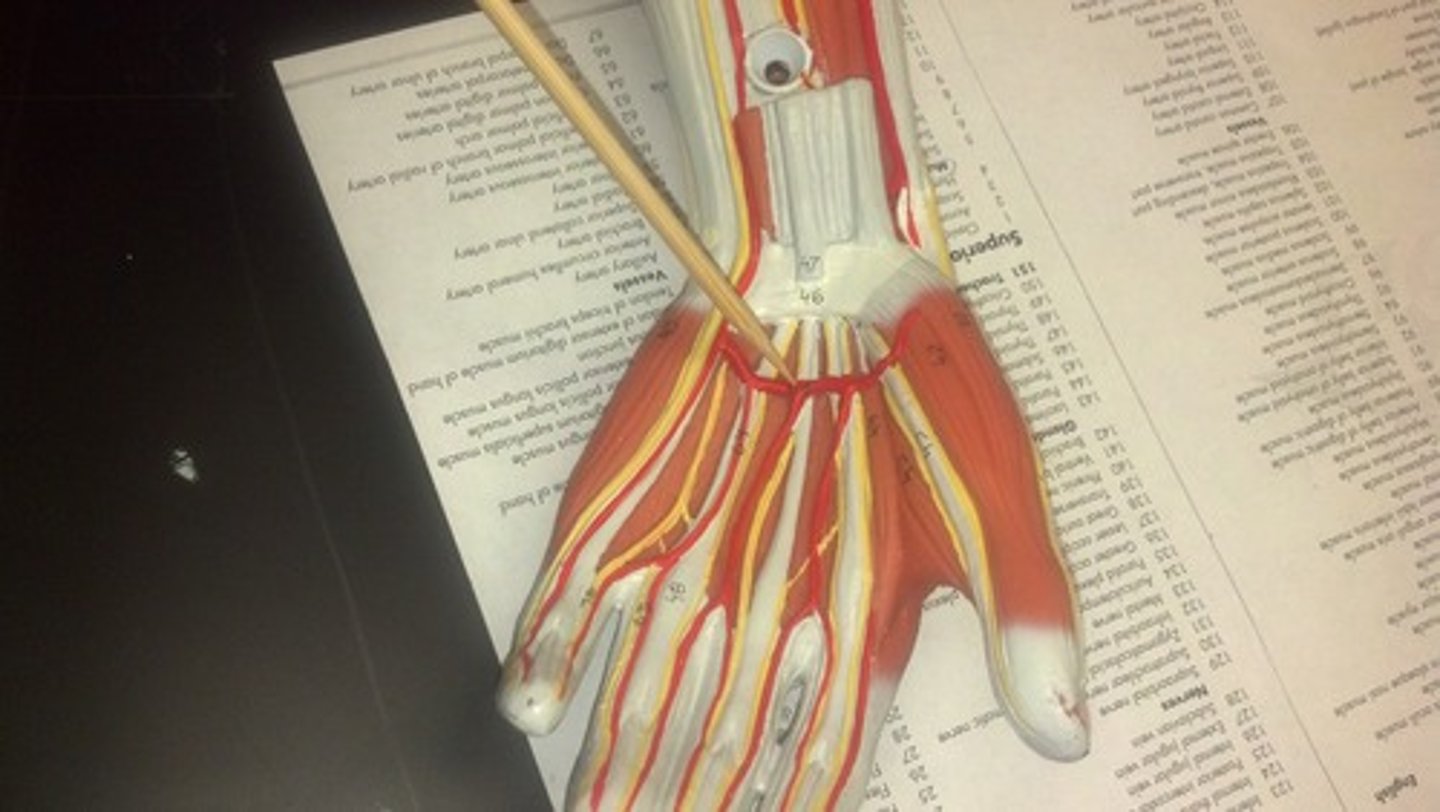
digital arteries (hand)
emerge from palmer arch to supply blood to the fingers
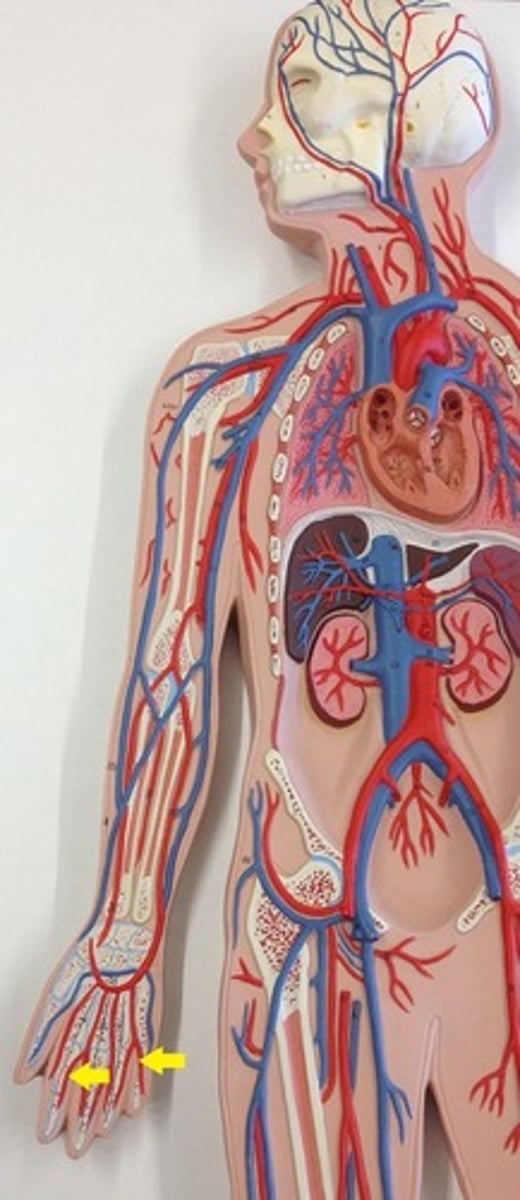
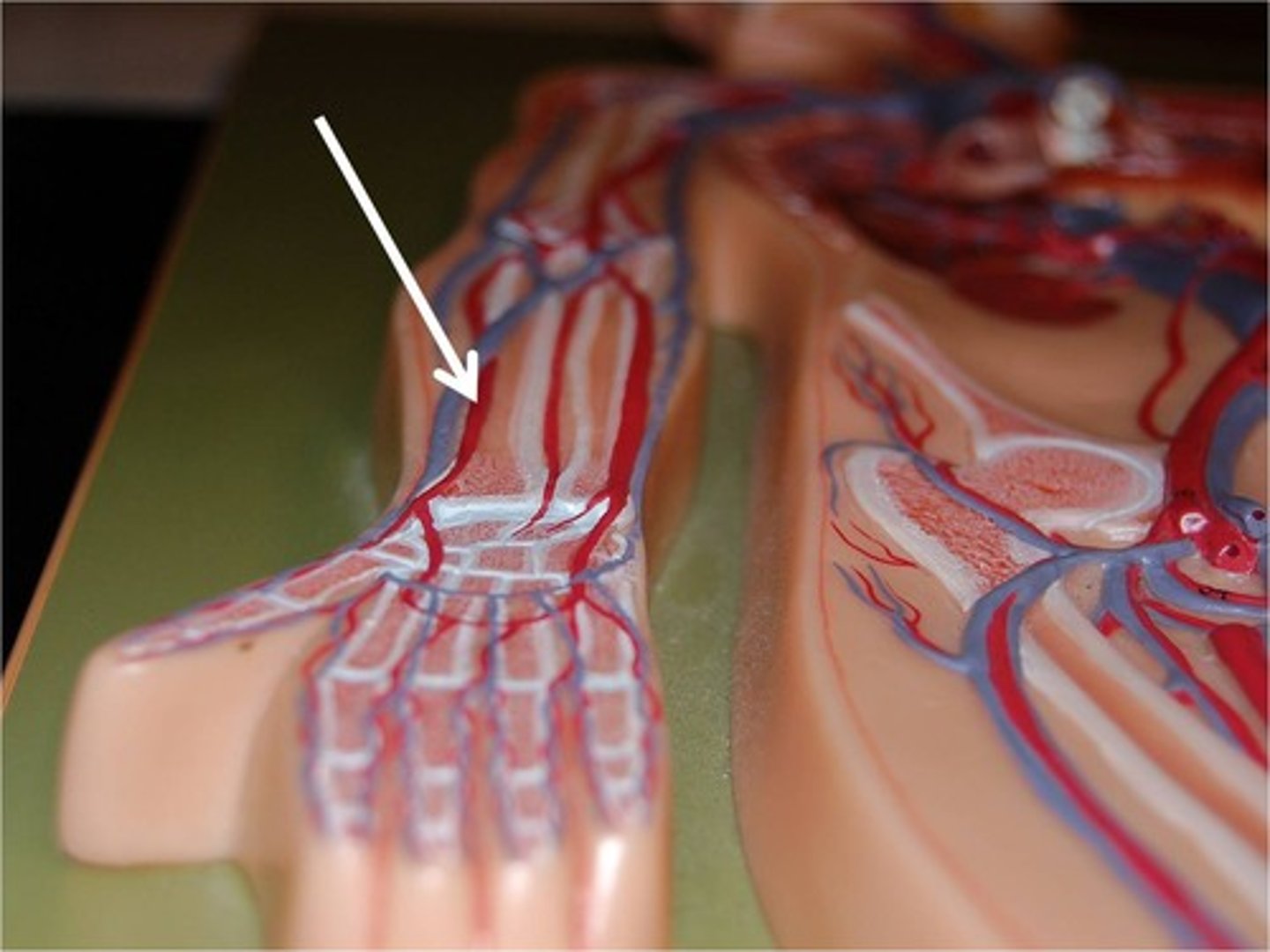
Right radial arteries
supplies blood to the forearm, wrist and hand
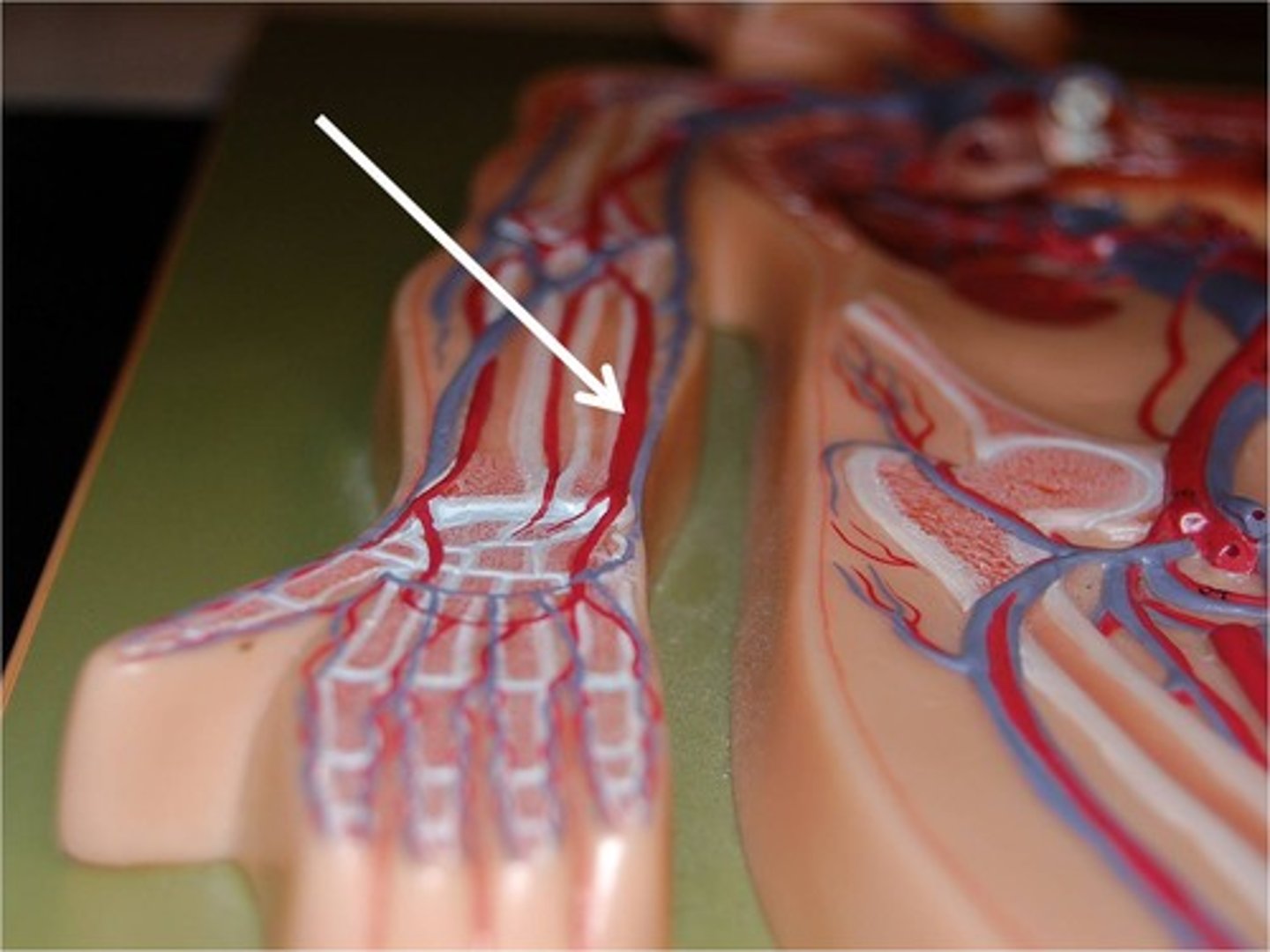
right ulnar arteries
supplies blood to the forearm, wrist and hand, fusing with the radial arteries at the wrist to form the palmer arches.
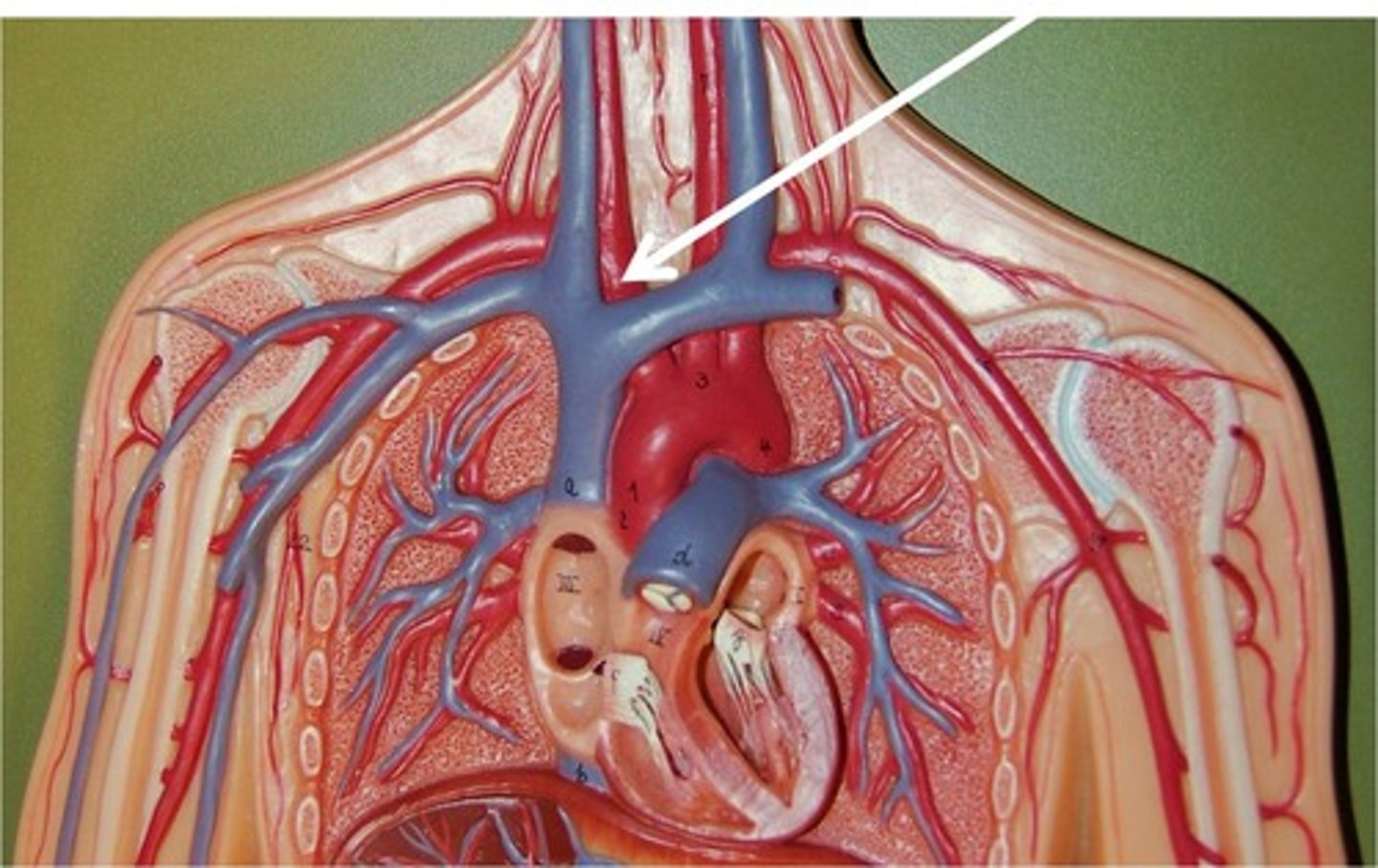
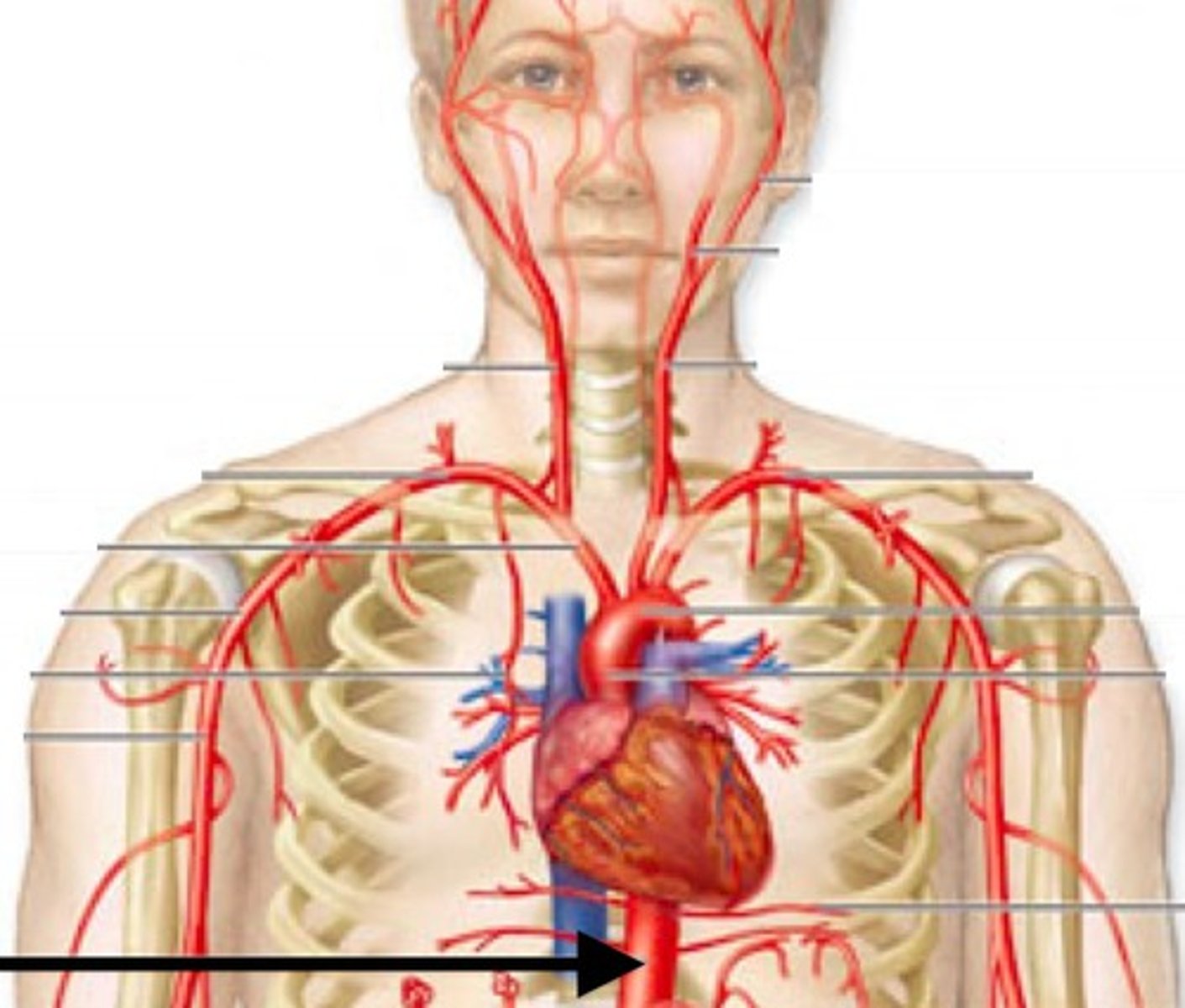
aorta
Largest artery in the body. Superior portion of the left ventricle. Artery carrying blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
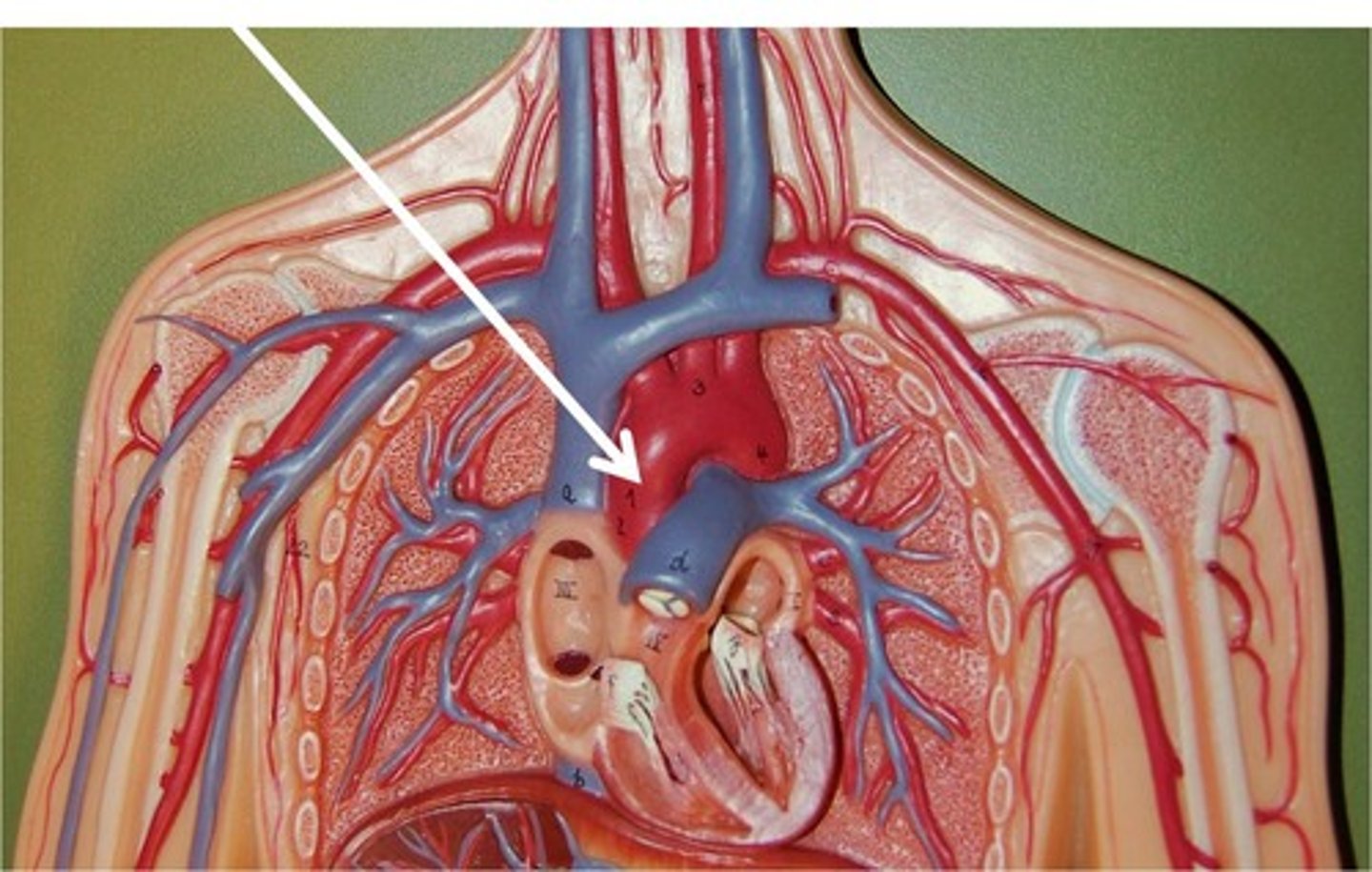
ascending aorta
the ascending part of the aorta as it emerges from the left ventricle; carries blood to parts of the body above the heart
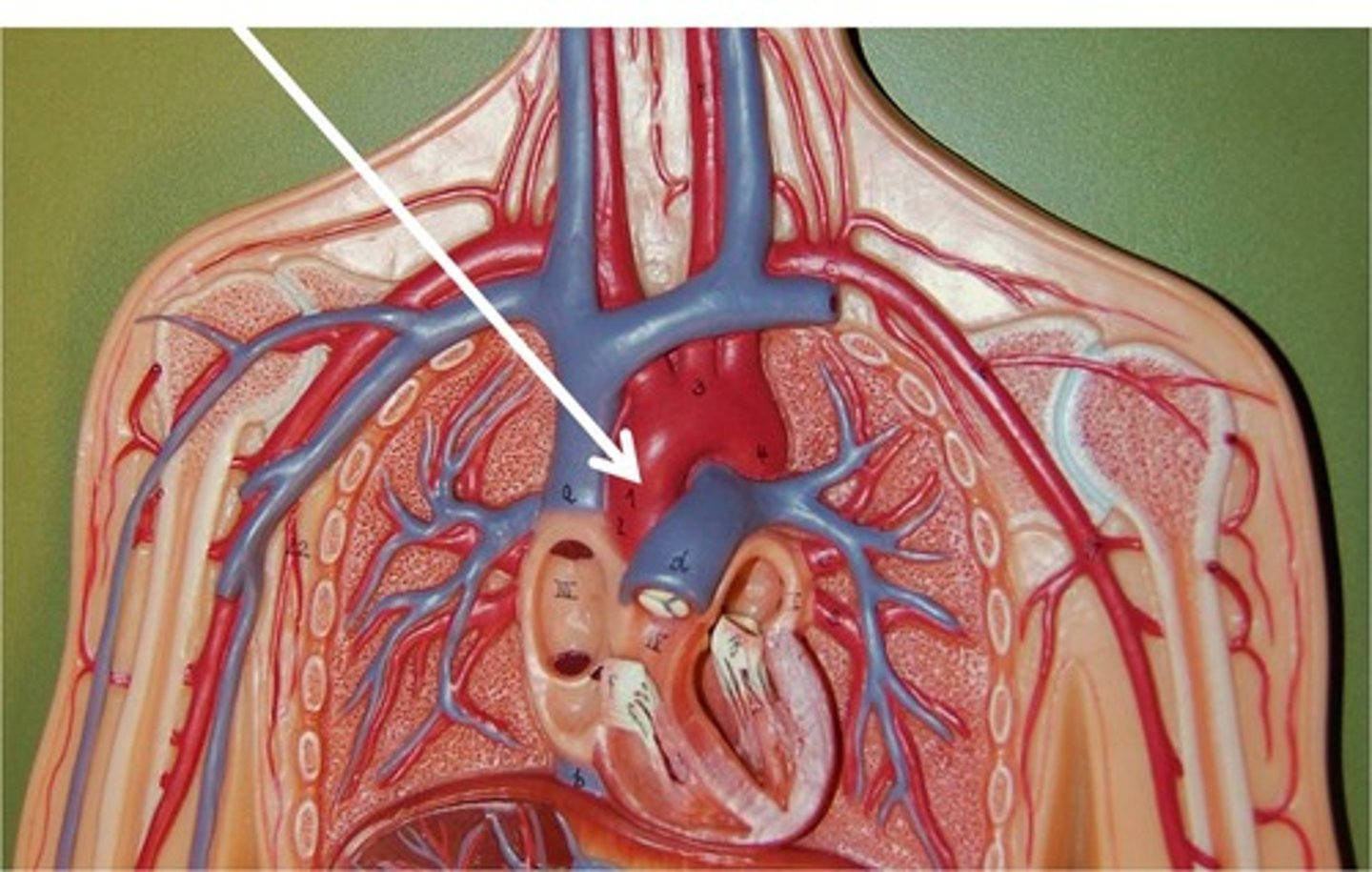
aortic arch
a curved blood vessel (apart of aorta) from which arteries branch to the head and neck.
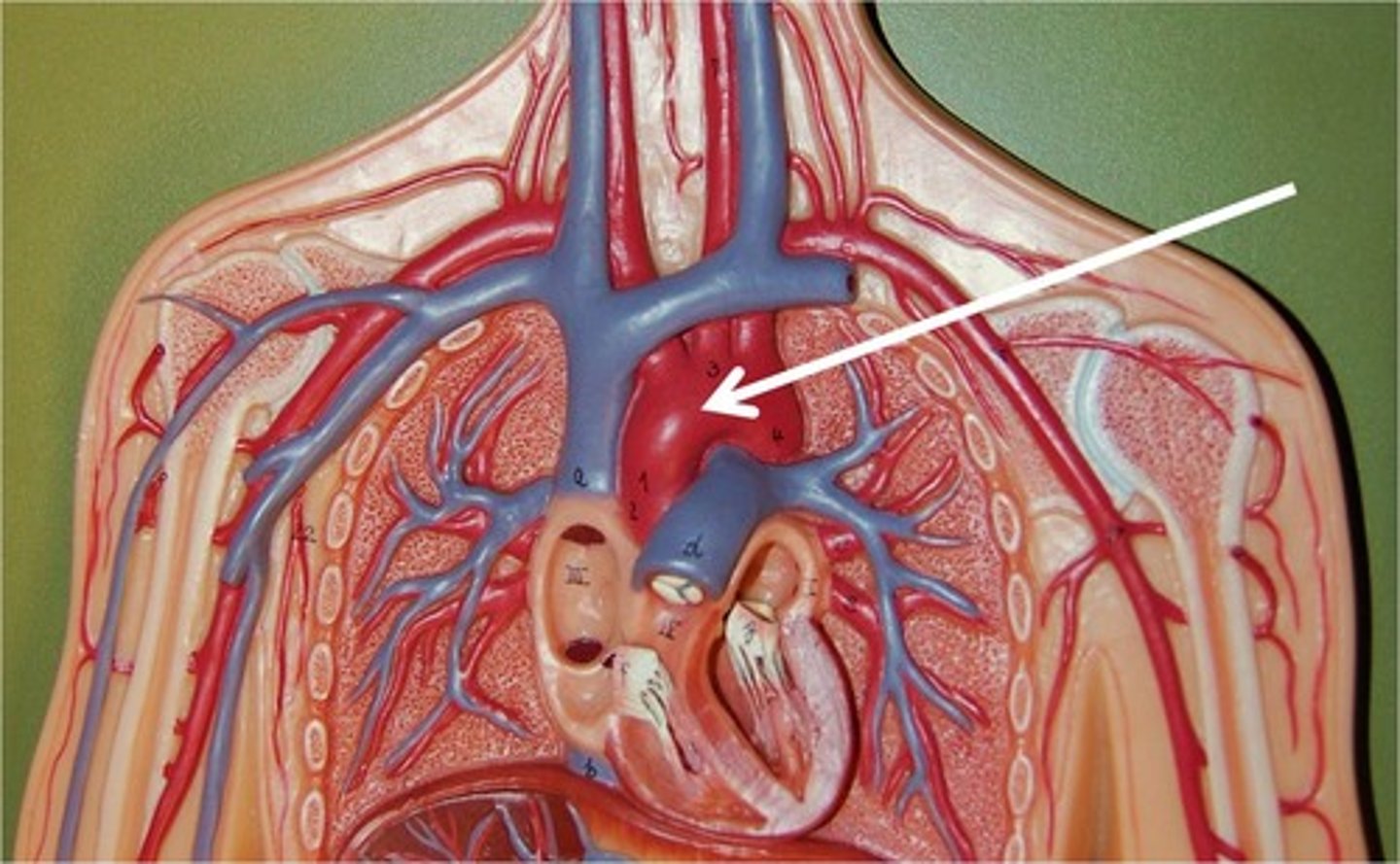
descending aorta
the descending part of the aorta that branches into the thoracic and abdominal aorta. supplies blood to the abdominal organs and lower limbs
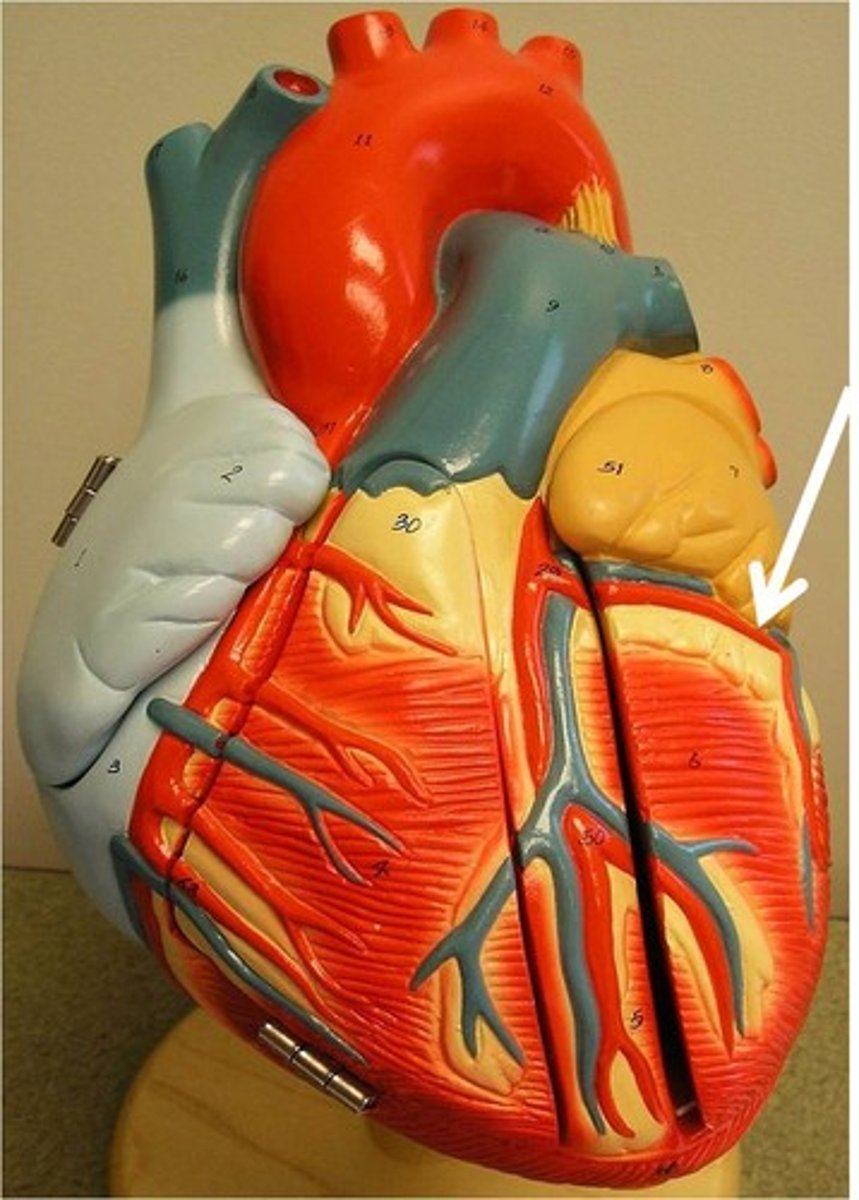
right coronary artery
supplies to the right atrium, right ventricle, sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) node
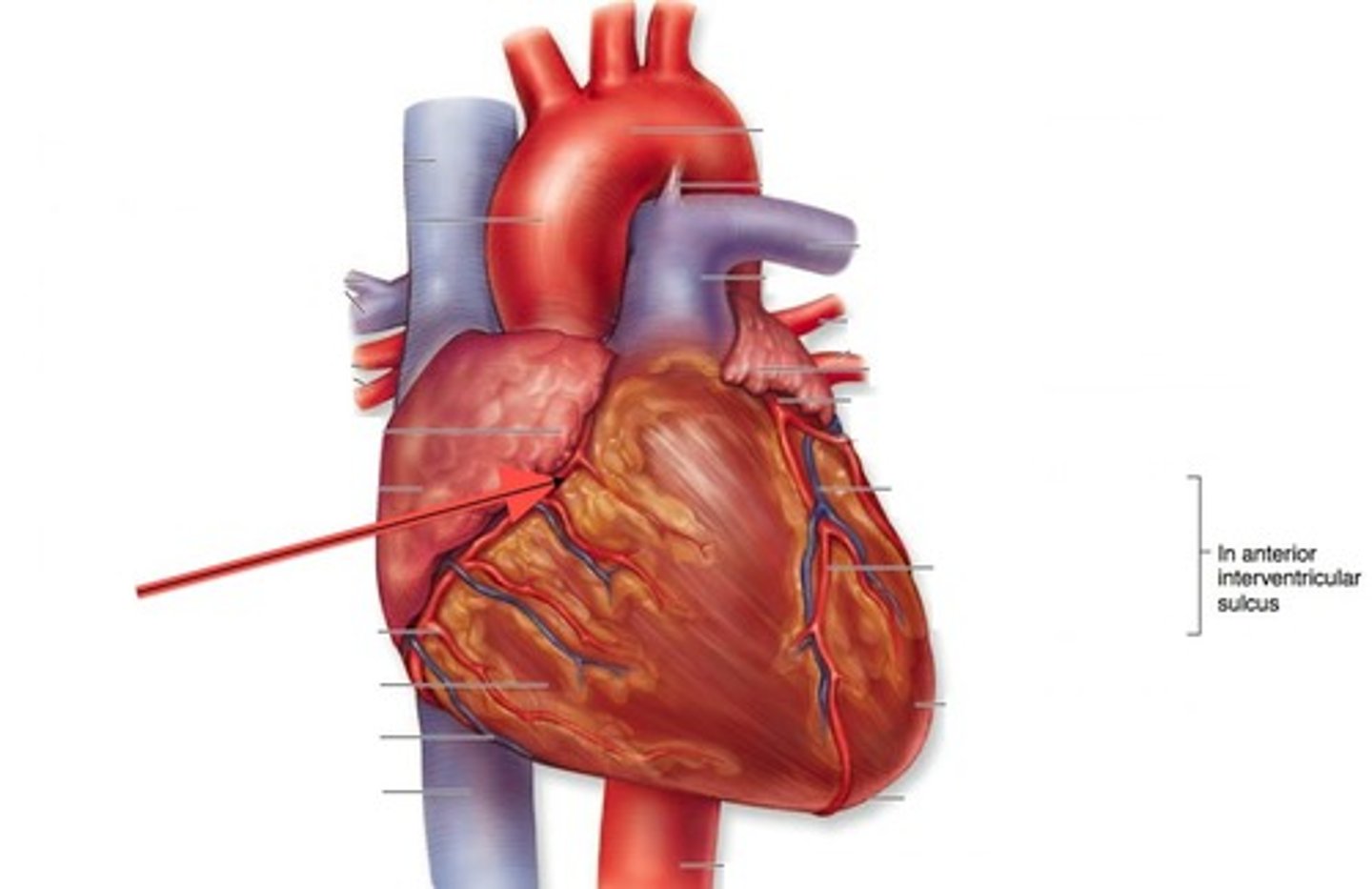
left coronary artery
supplies blood to the left ventricle, left atrium, and interventricular septum
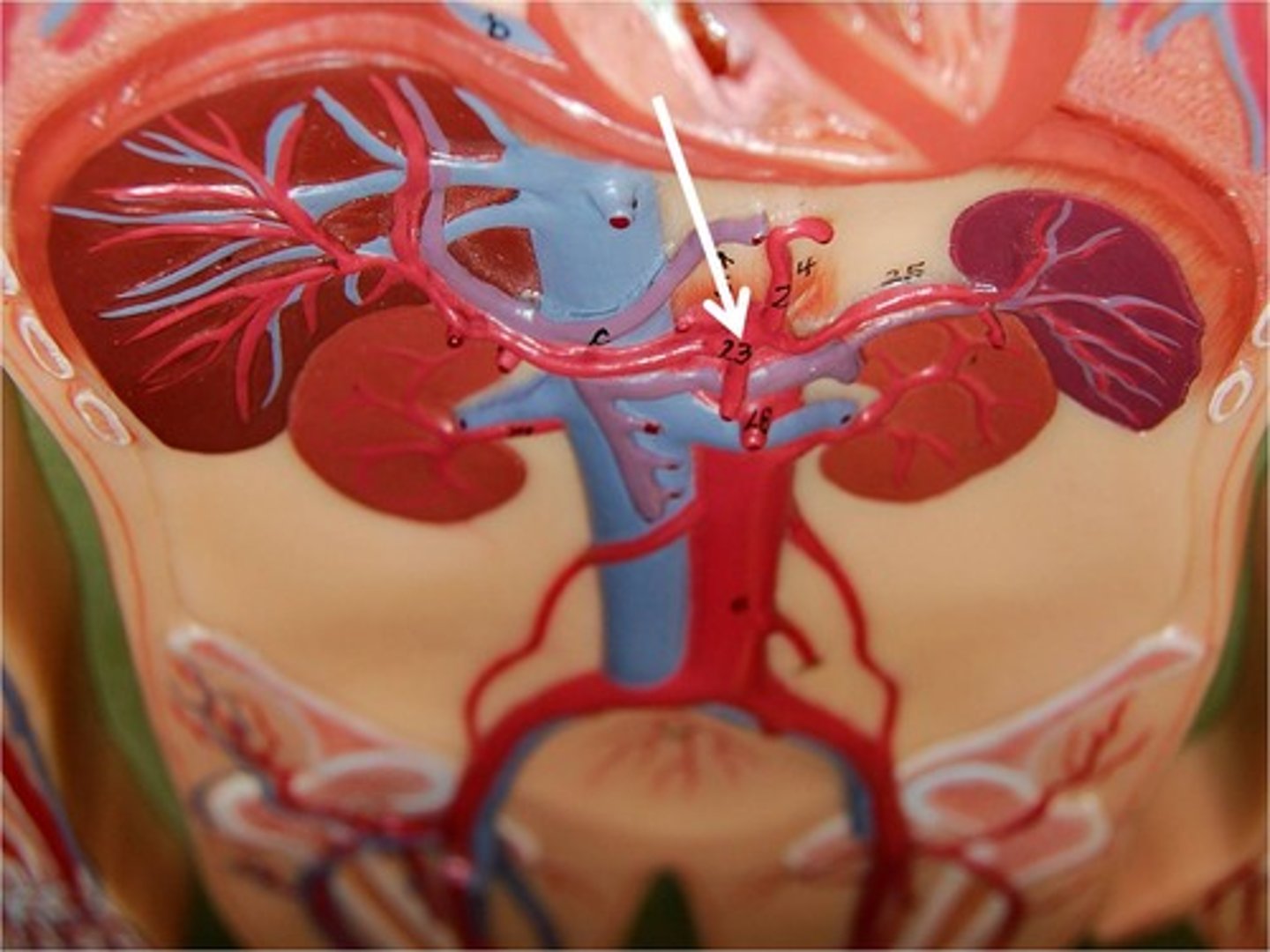
celiac trunk
Large unpaired branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies the liver, stomach, and spleen.
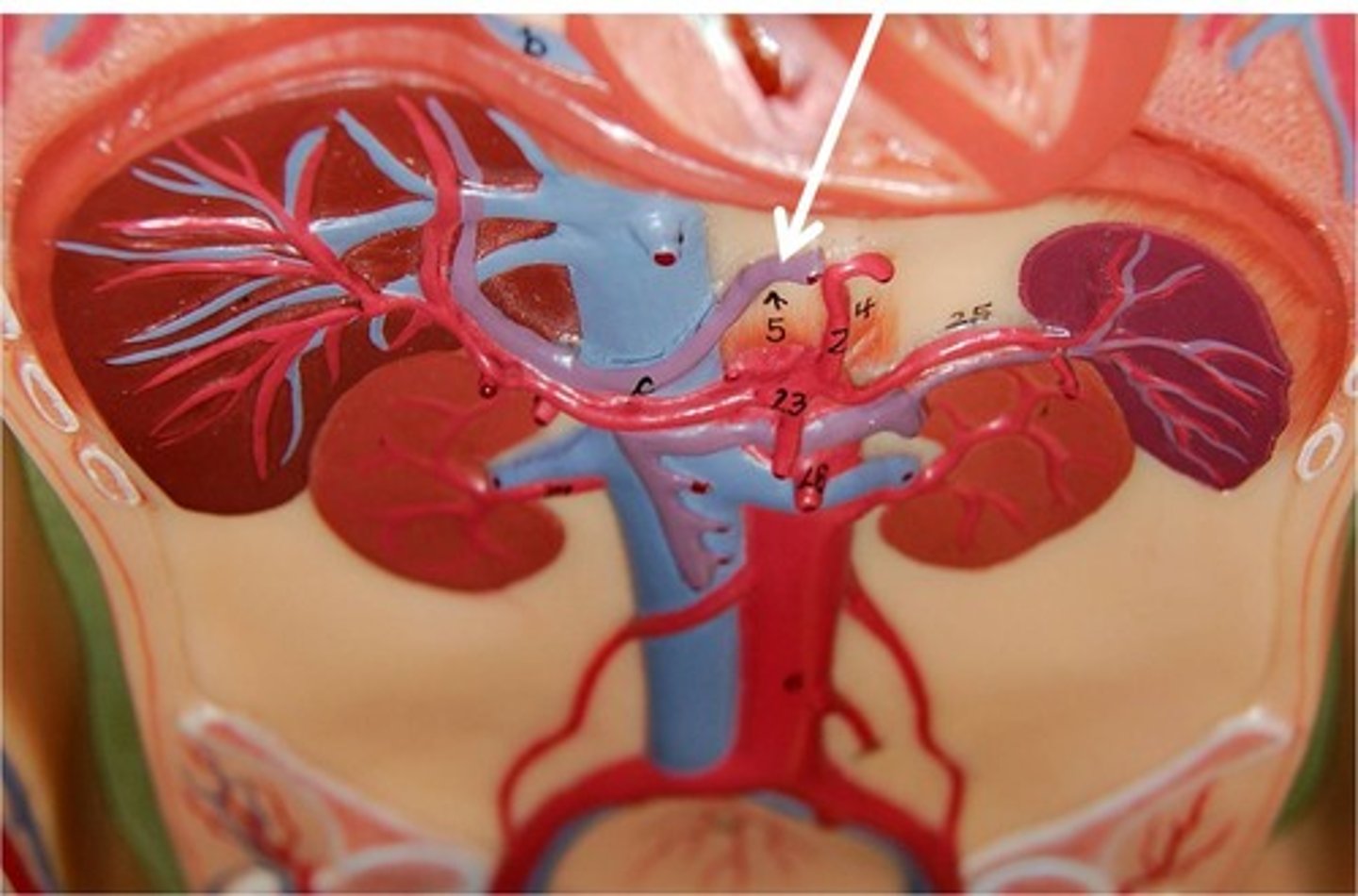
left gastric artery
supplies to the stomach and esophagus
common hepatic artery
supplies blood to the liver, gallbladder, stomach, duodenum, and pancreas.
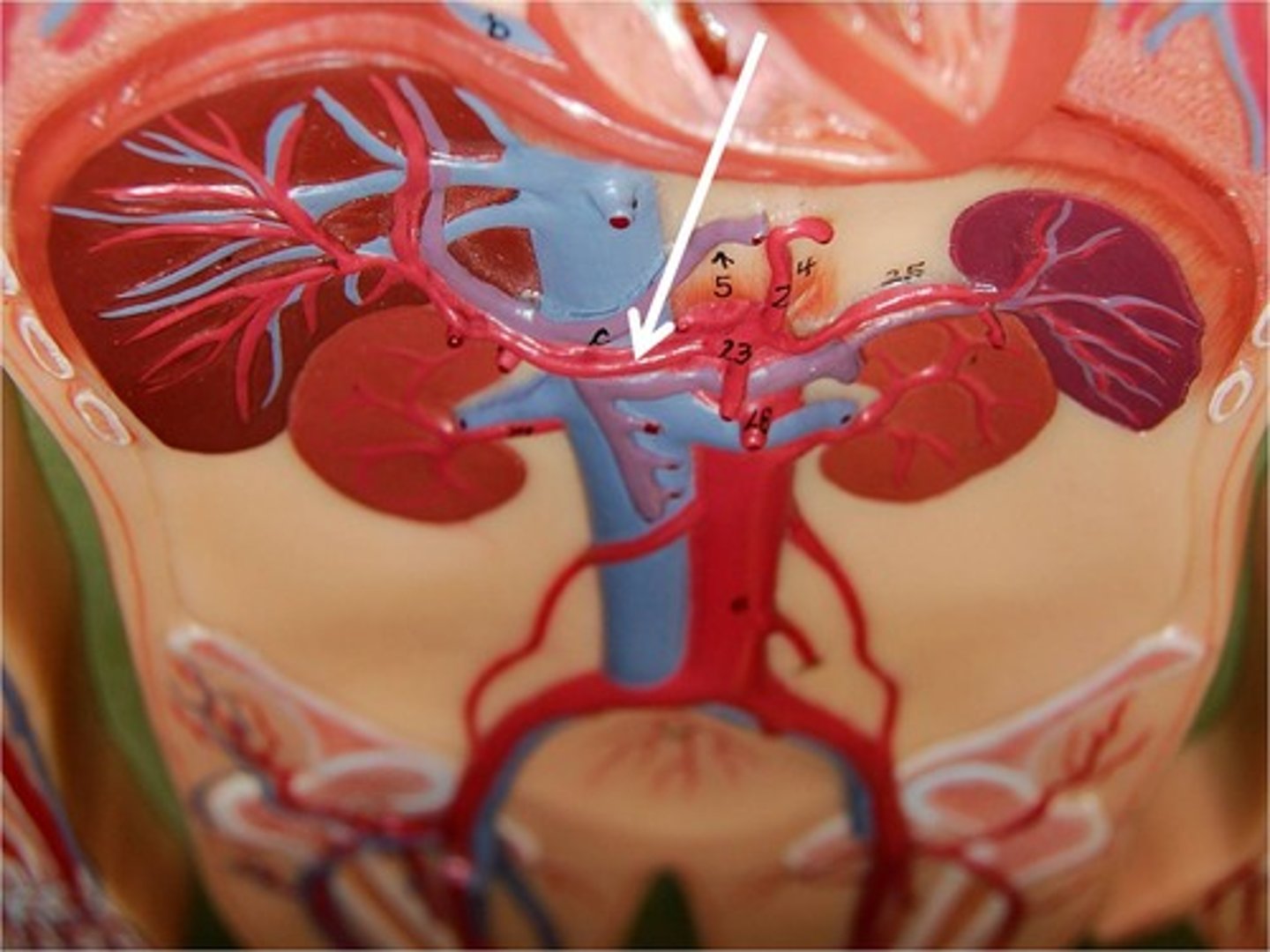
splenic artery
supplies the spleen, but also stomach and pancreas.
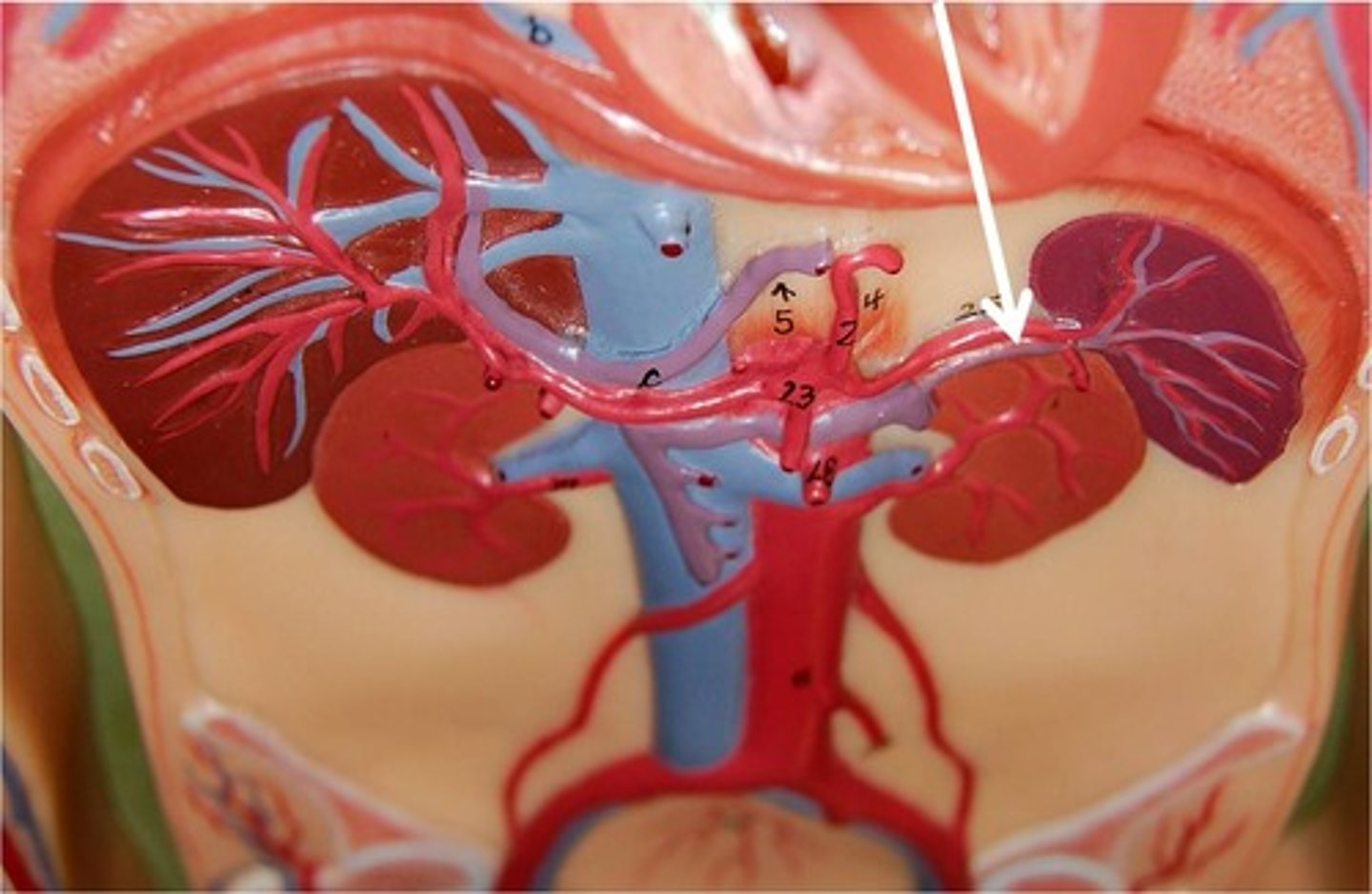
superior mesenteric artery
supplies almost all of the small intestine as well as much of the large intestine
left and right renal arteries
carry blood to the kidneys
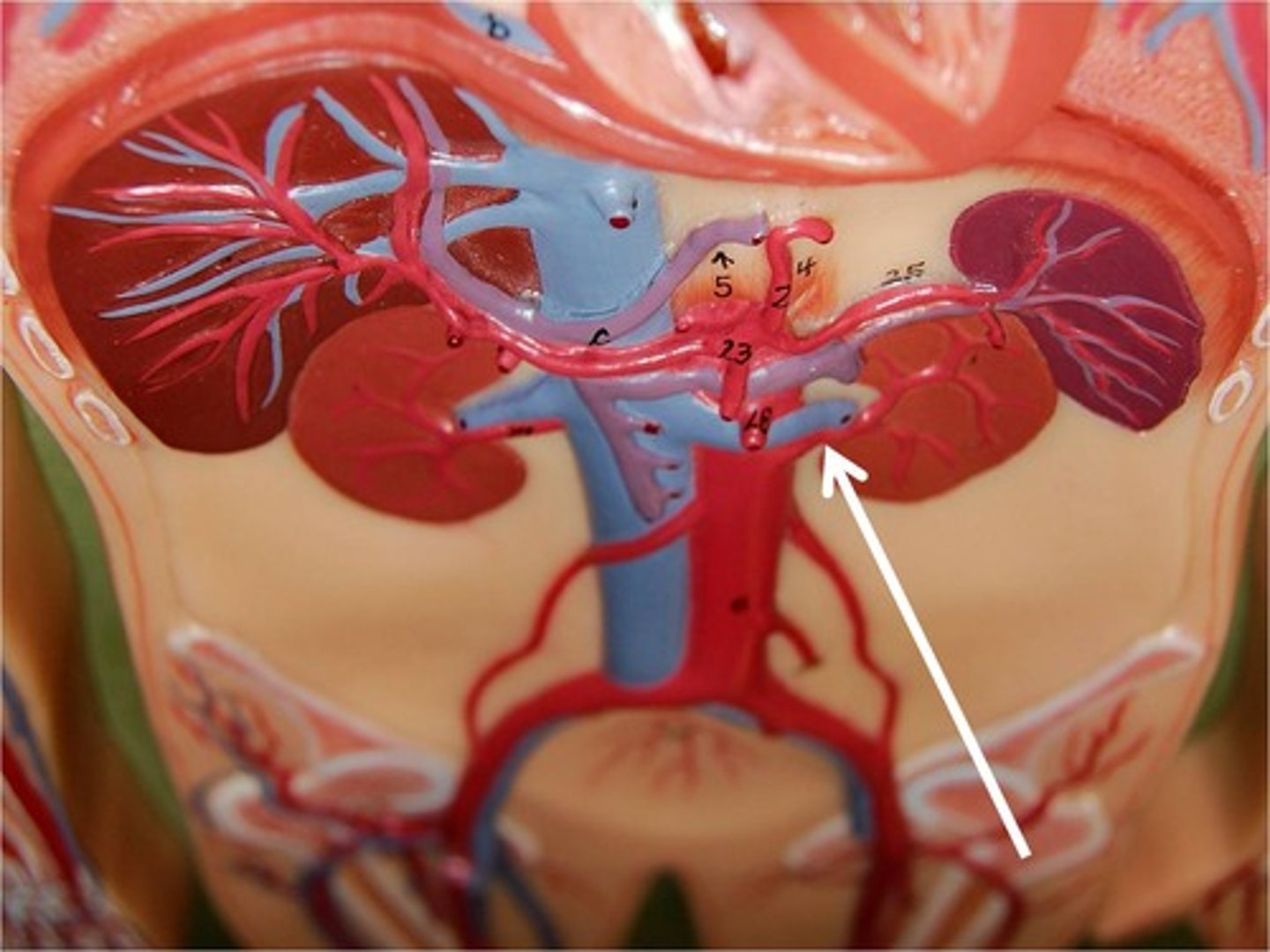
inferior mesenteric artery
Supplies blood to distal large intestine.
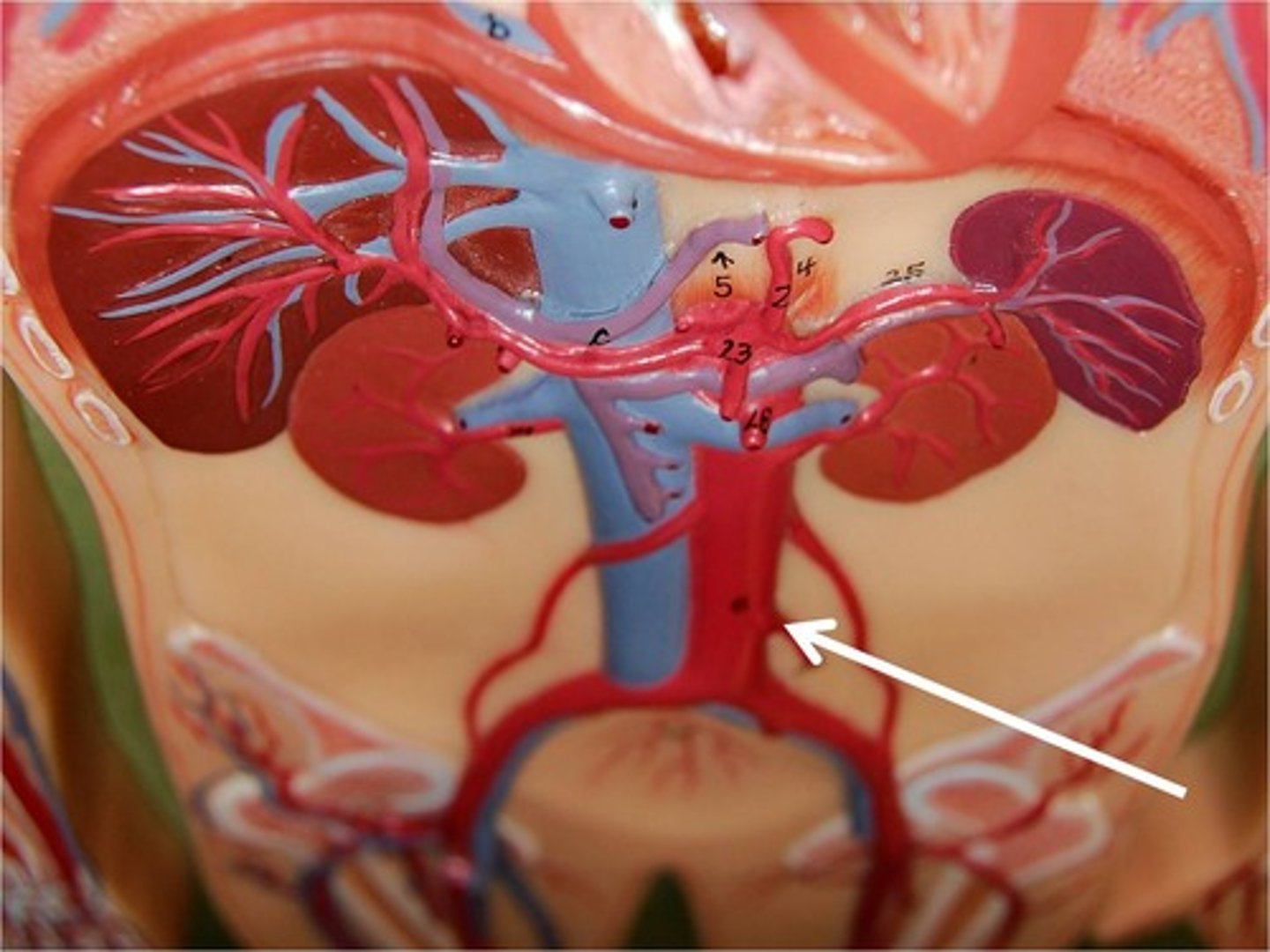
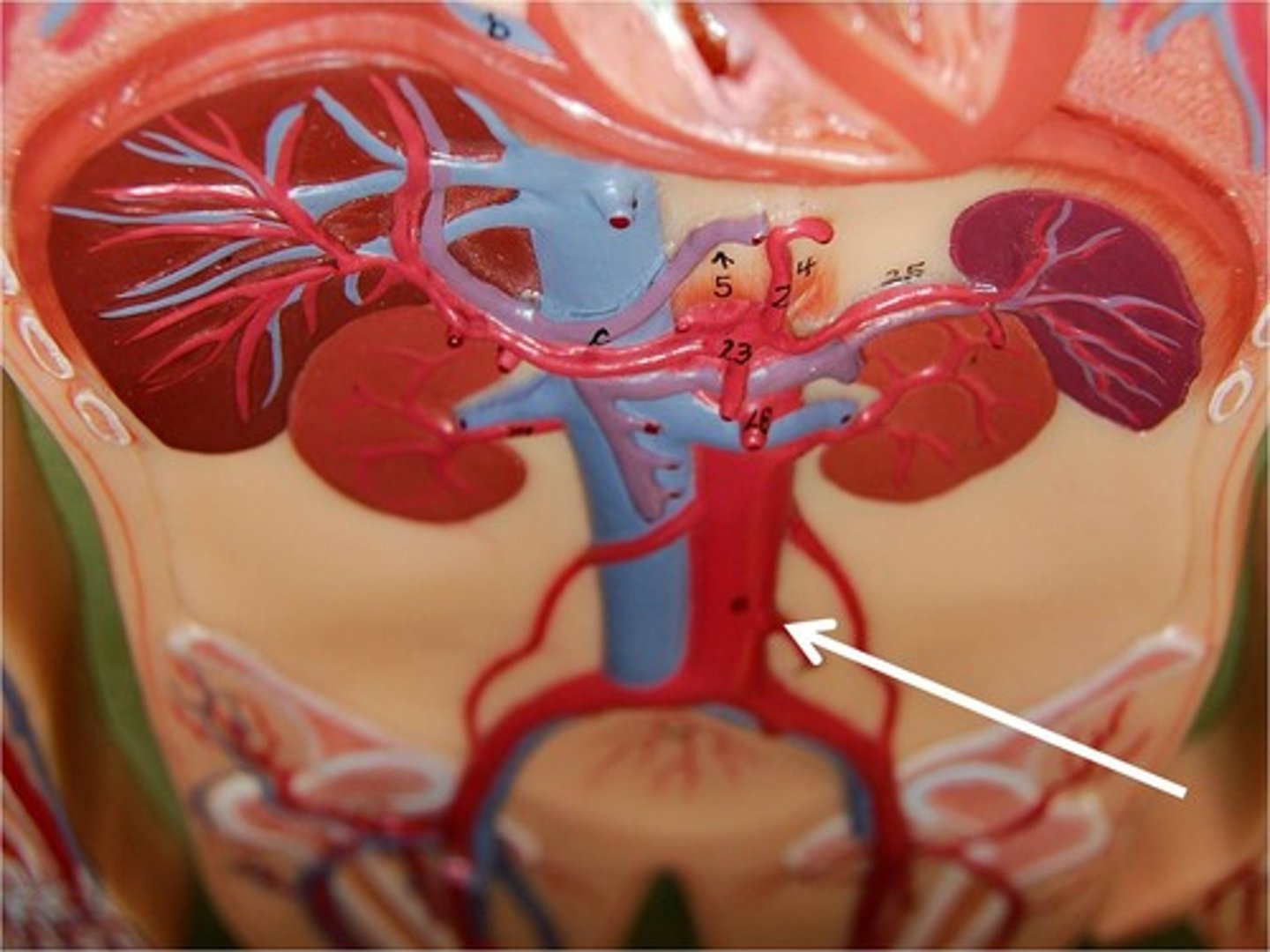
Left and right gonadal arteries
-Ovarian arteries in females serve the ovaries, uterine, tubes and uterus
-Testicular arteries in males serve the testes and scrotum
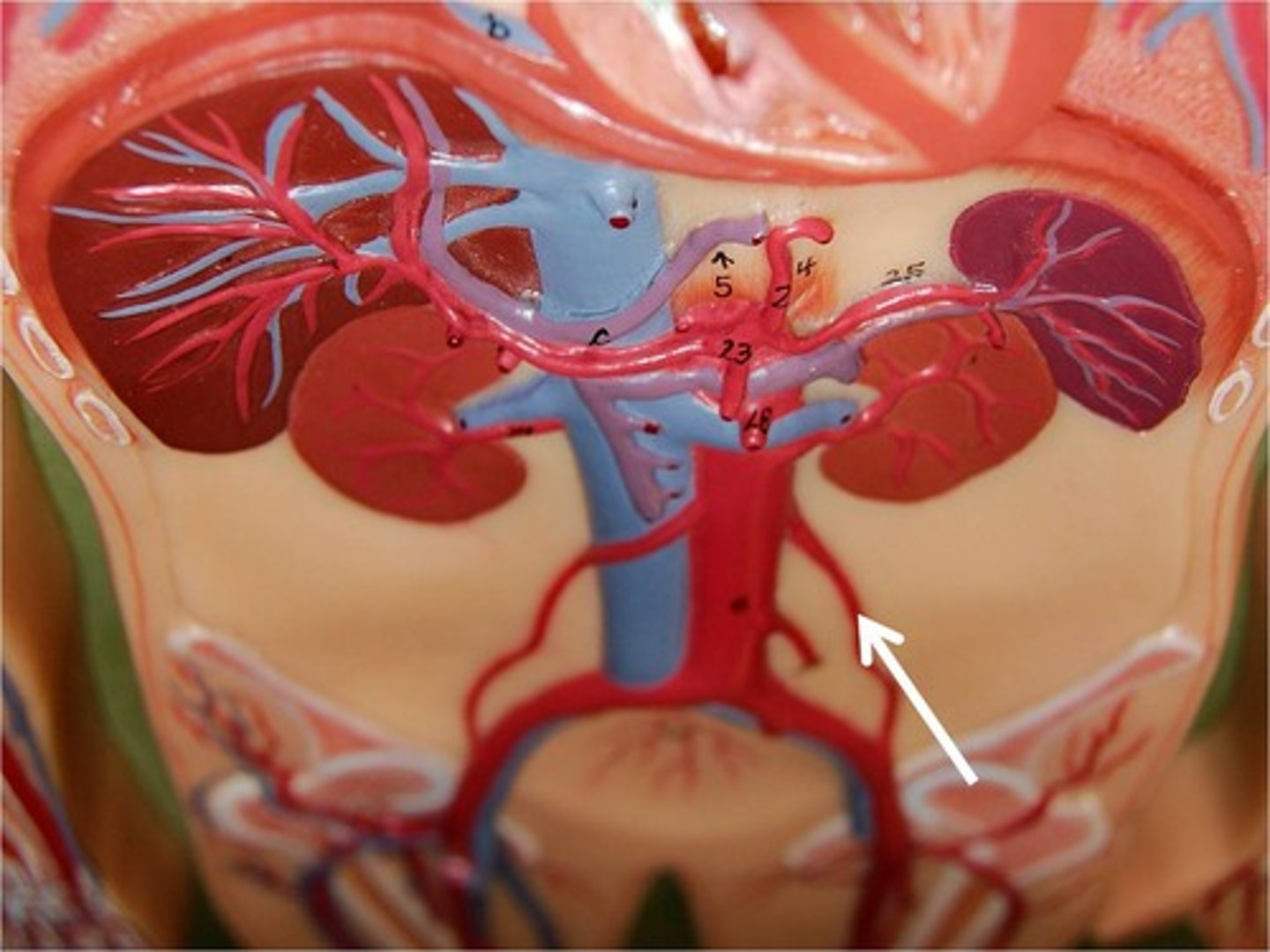
left and right common iliac arteries
take blood to the lower abdomen, pelvis, and legs.
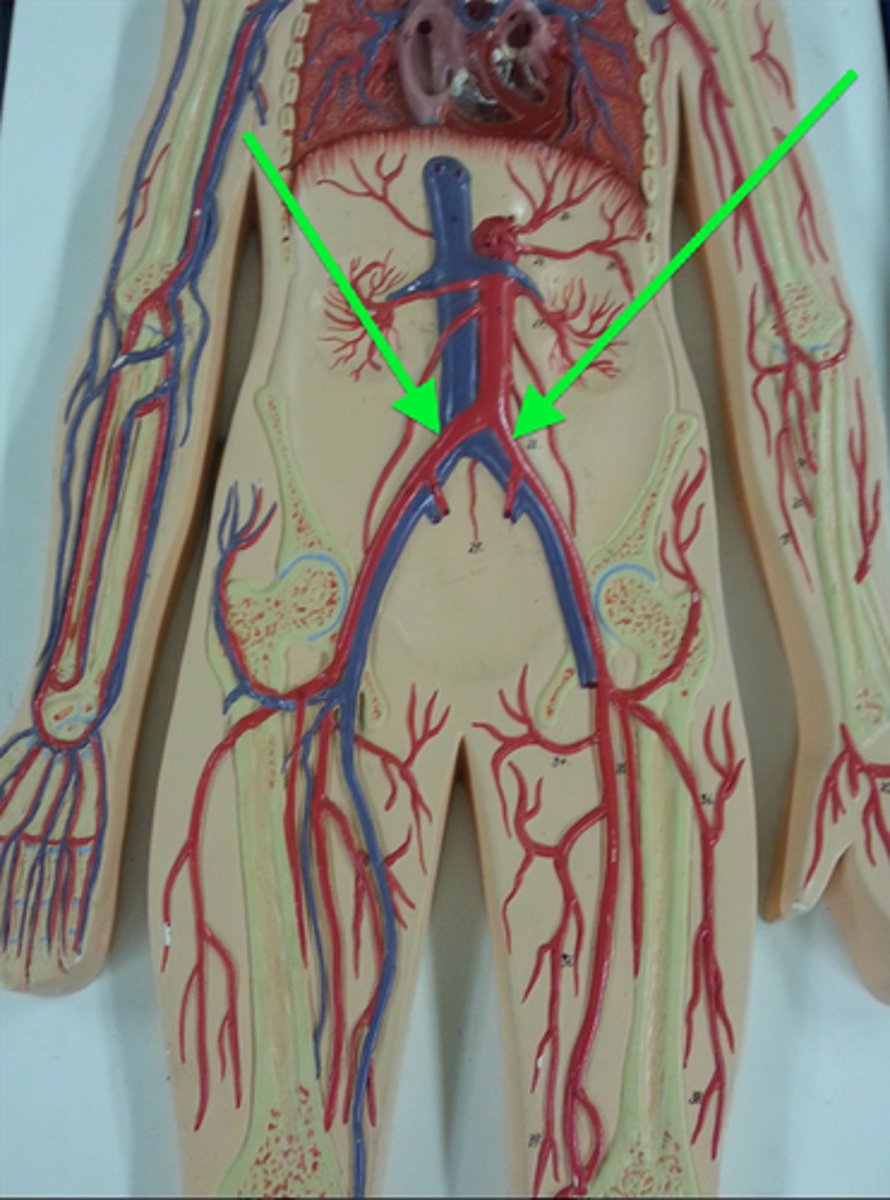
external iliac arteries
supplies blood to the lower limbs. They branch from the common iliac arteries and enter the thigh and become the femoral artery.
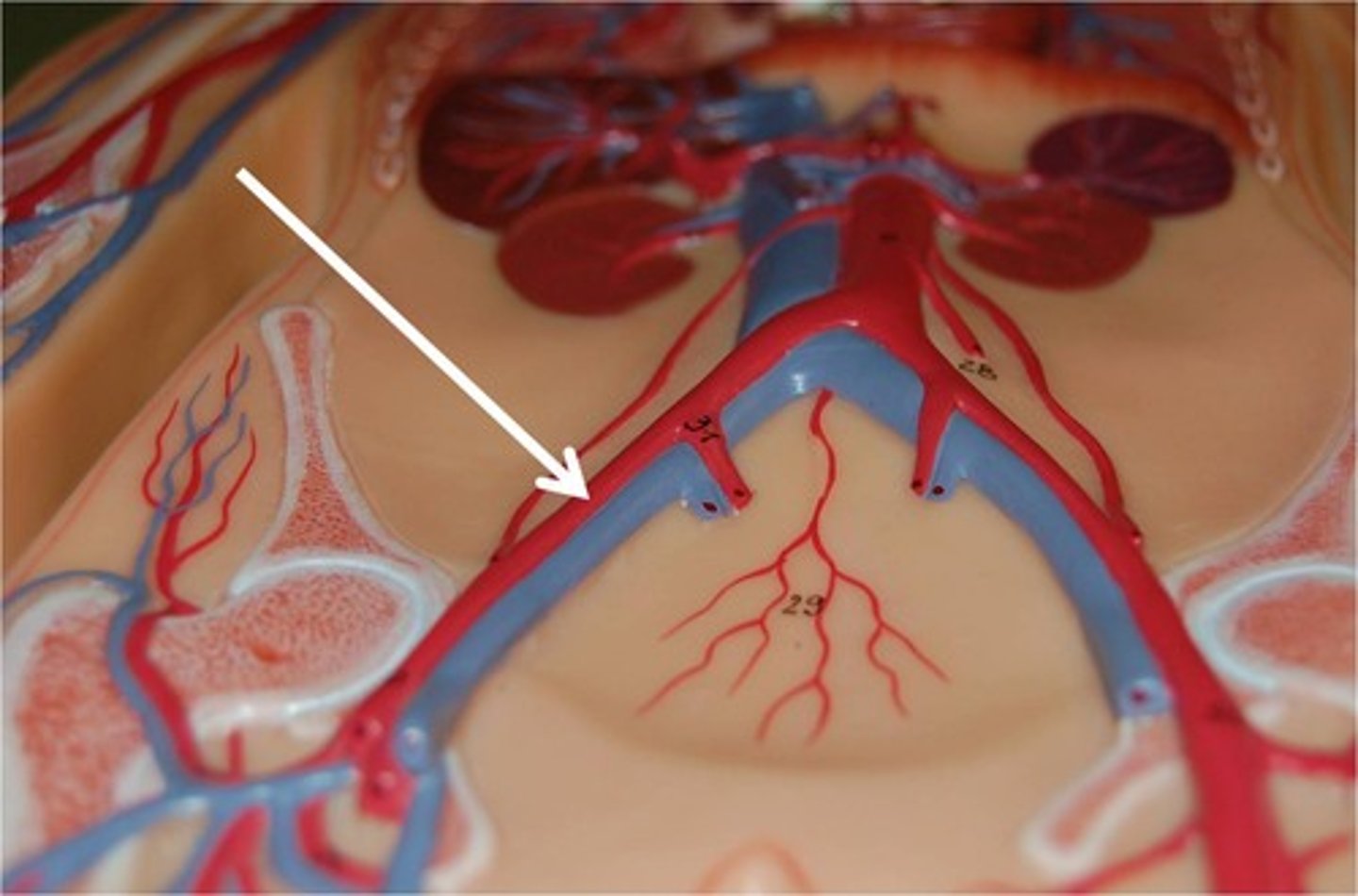
internal iliac arteries
supplies blood to the pelvic walls and pelvic organs
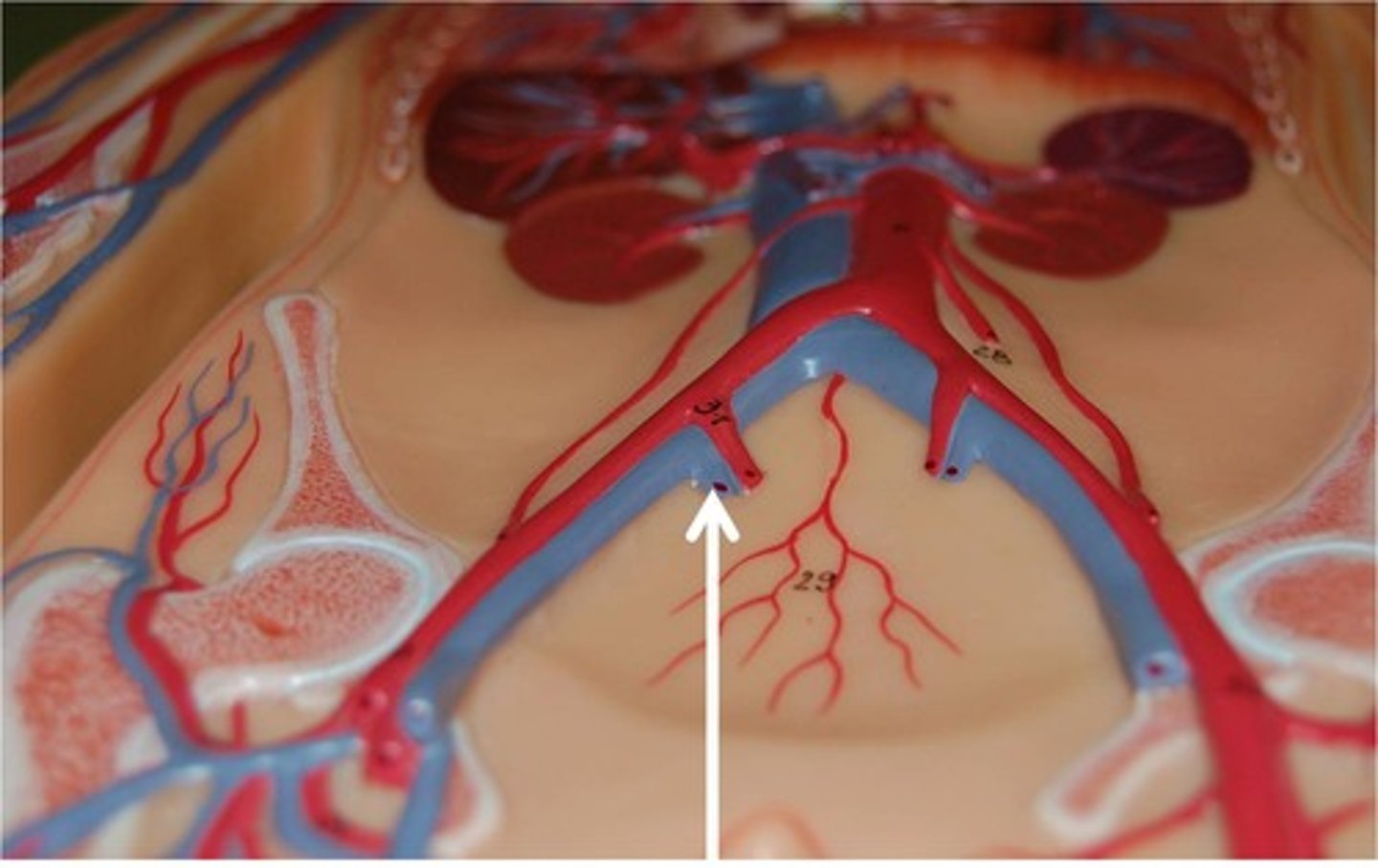
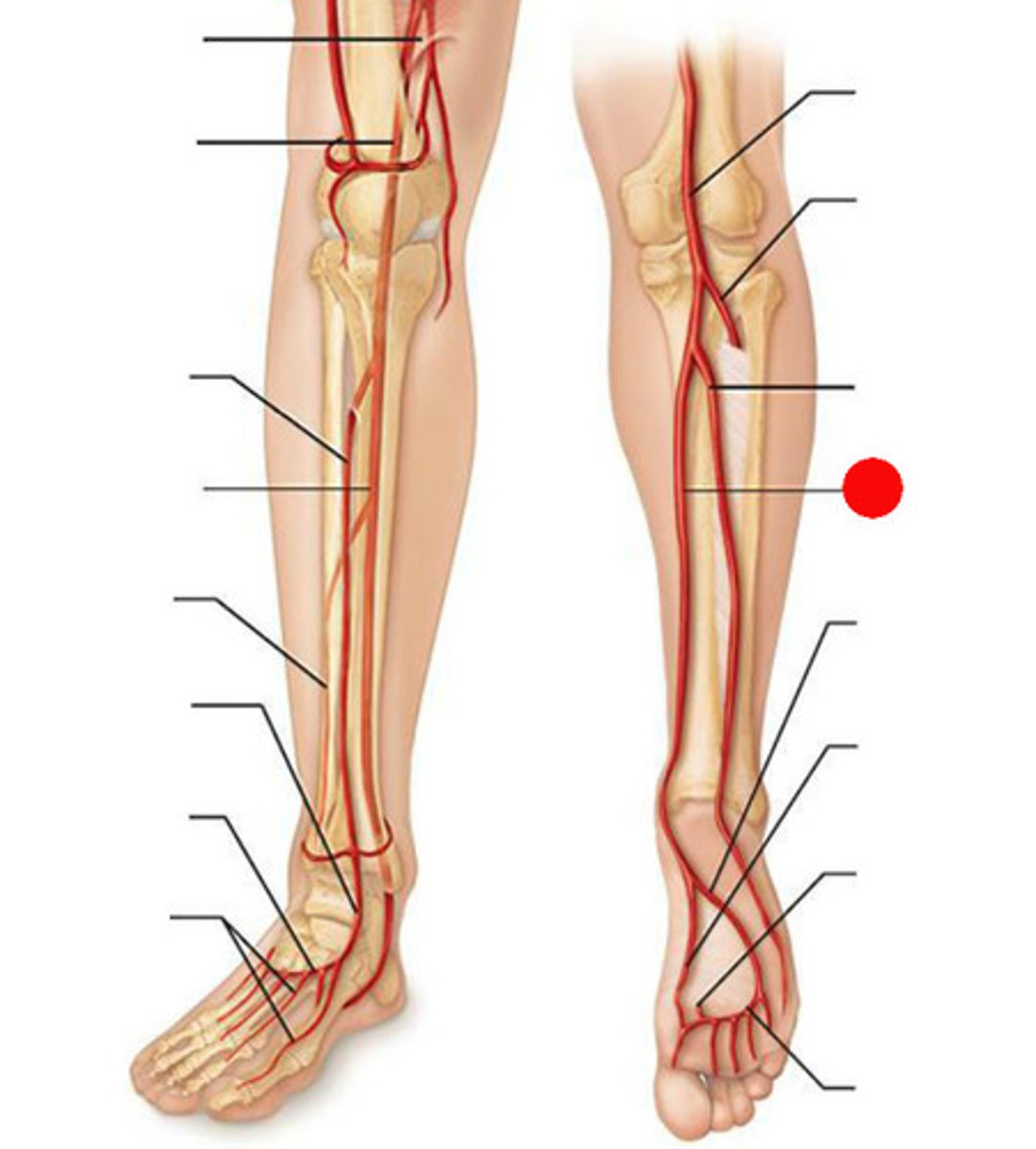
anterior tibial artery
supplies blood to the lower leg muscles and foot. This artery continues to the foot where it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery.
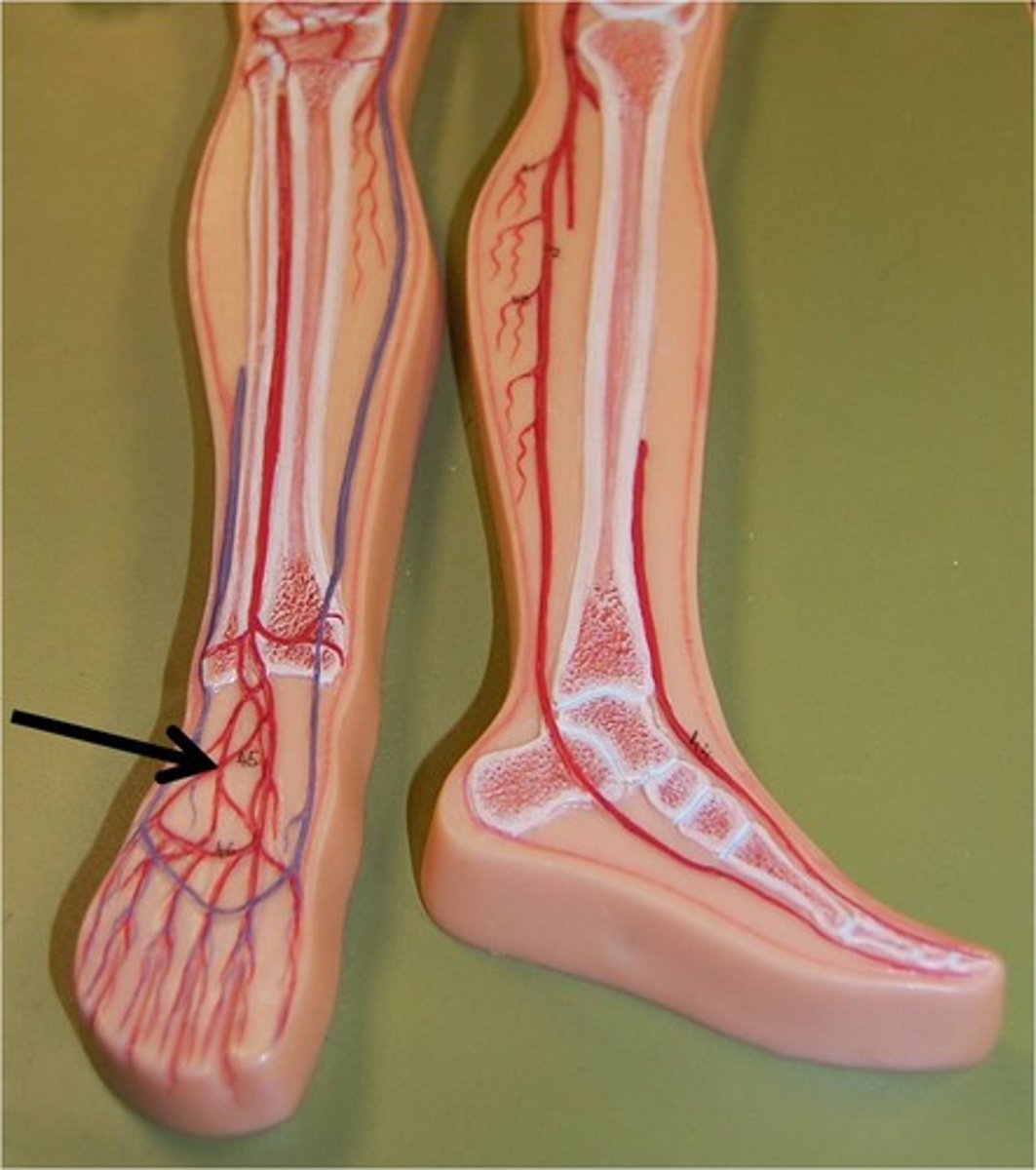
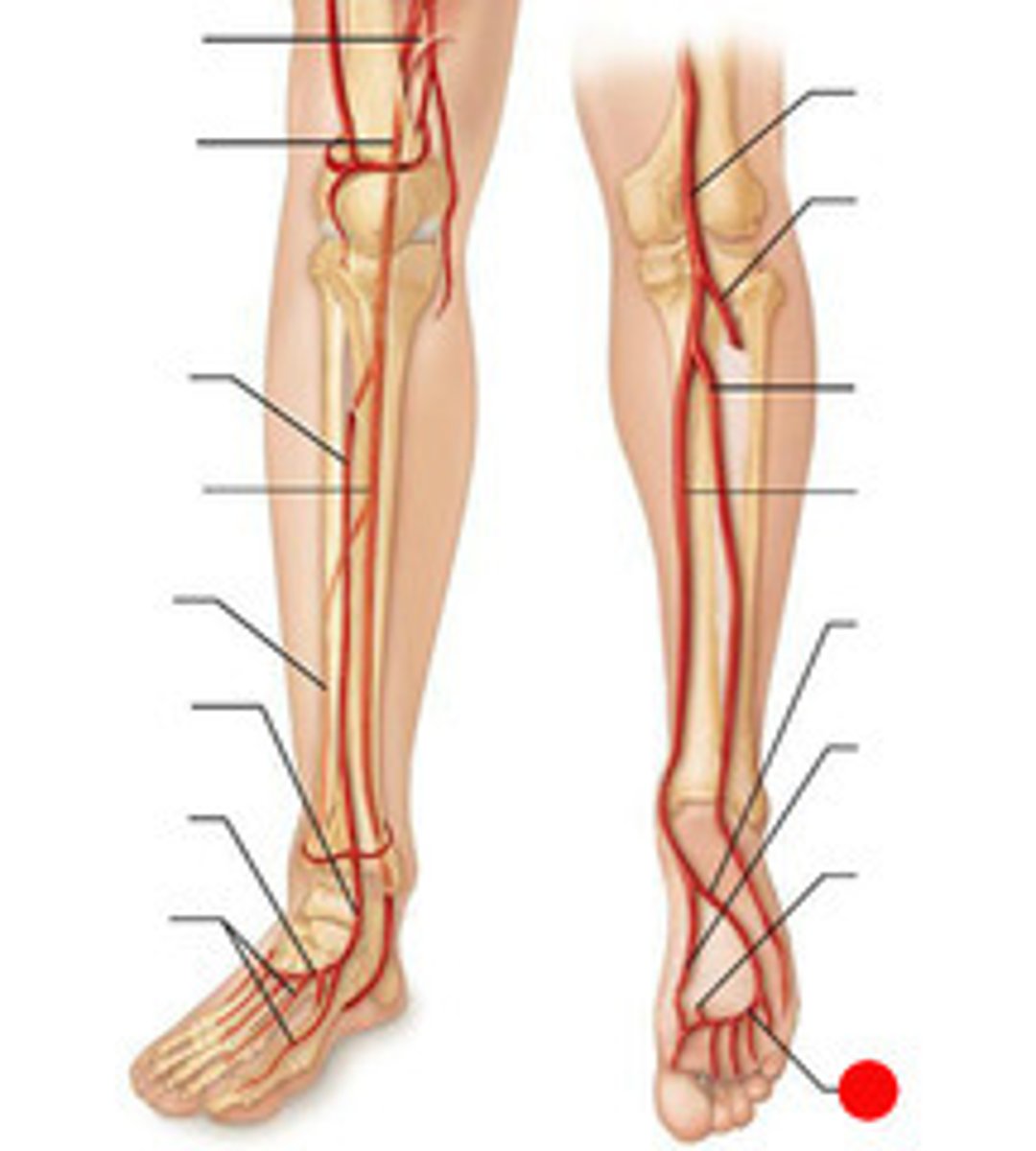
digital arteries (foot)
extend from the plantar arch and supply the toes

dorsalis pedis artery
it supplies to the ankle and the dorsal foot
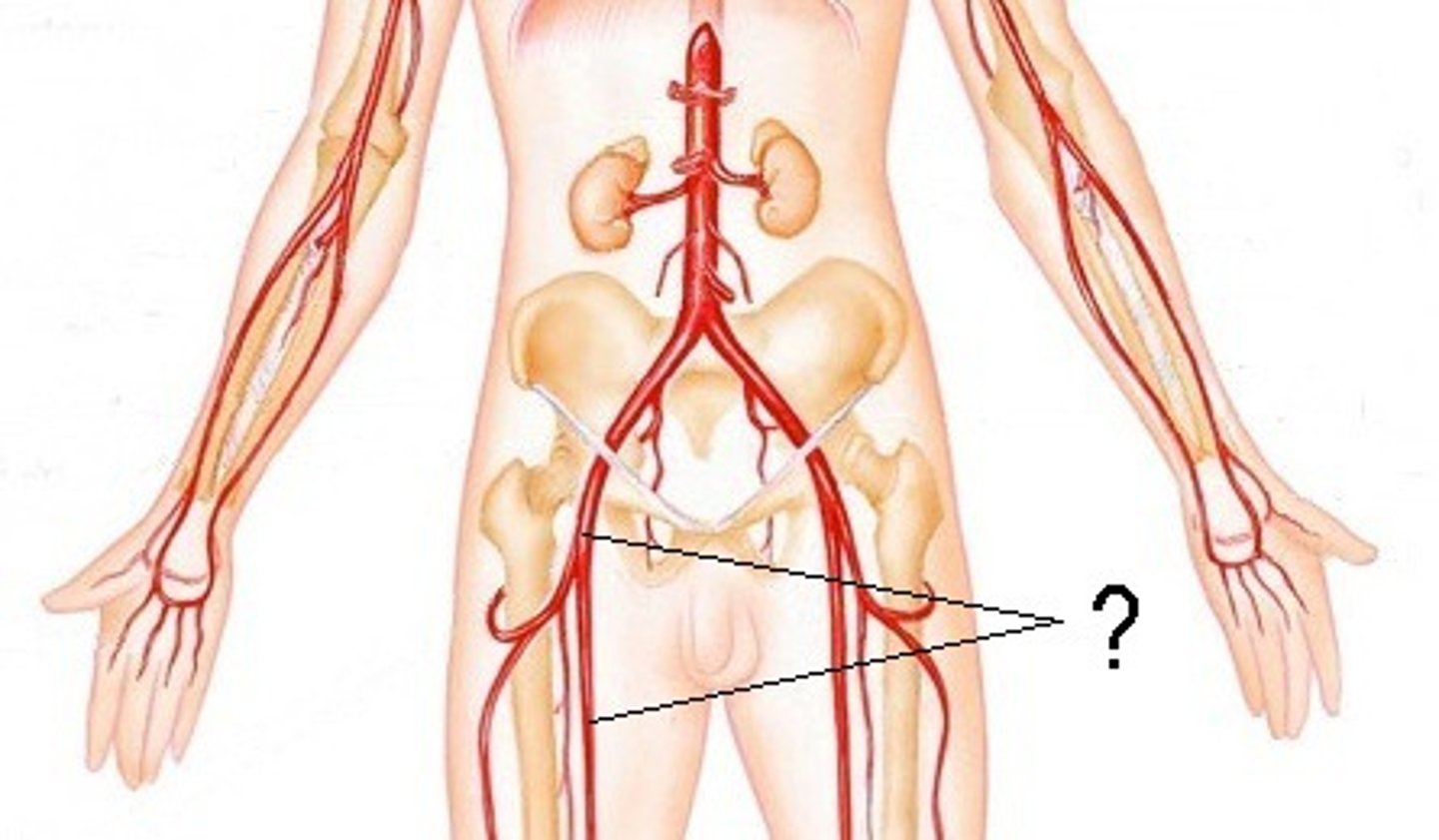
femoral artery
gives off branches that serves the muscles of the thigh
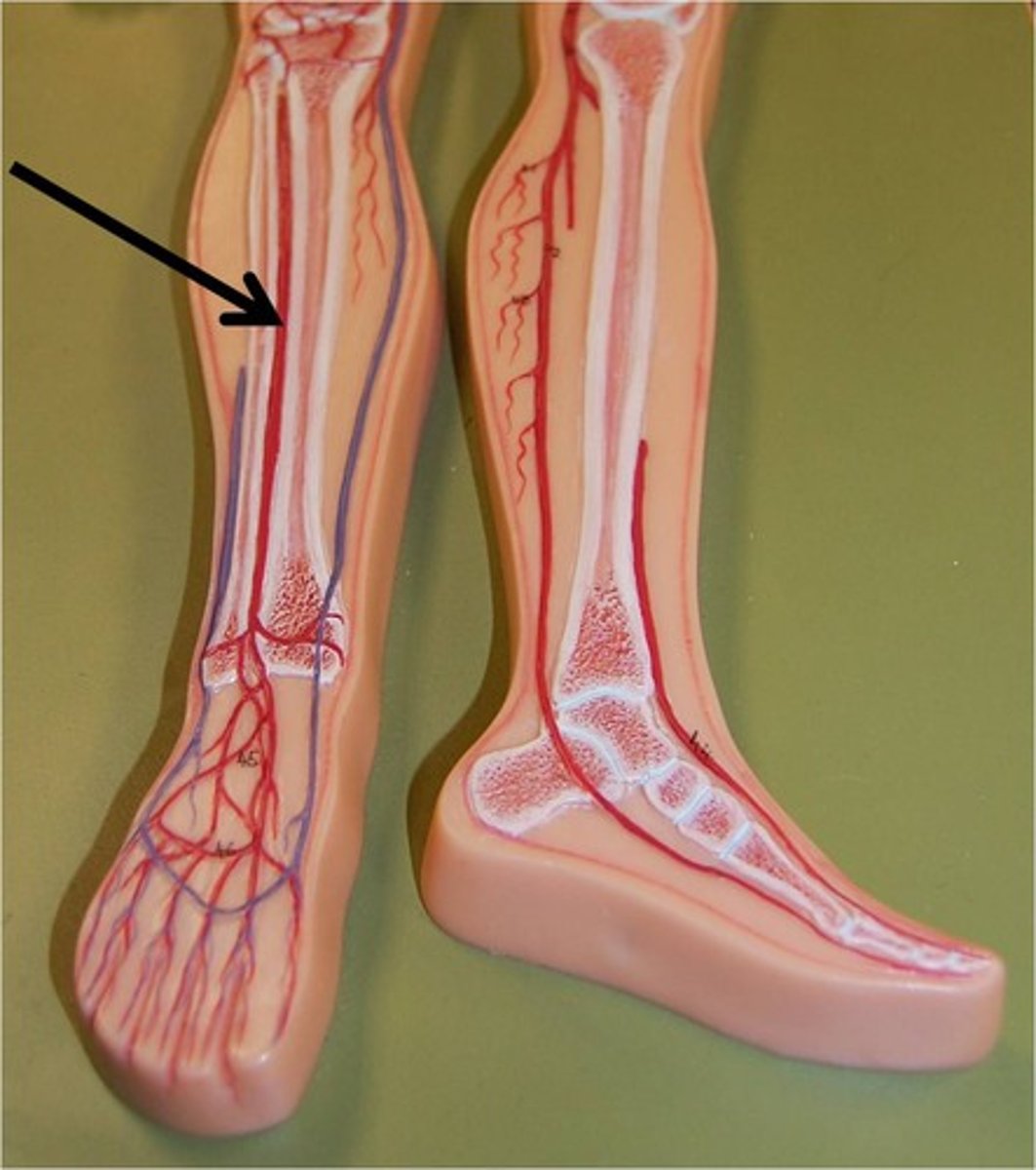
fibular artery
supplies blood to the lateral leg
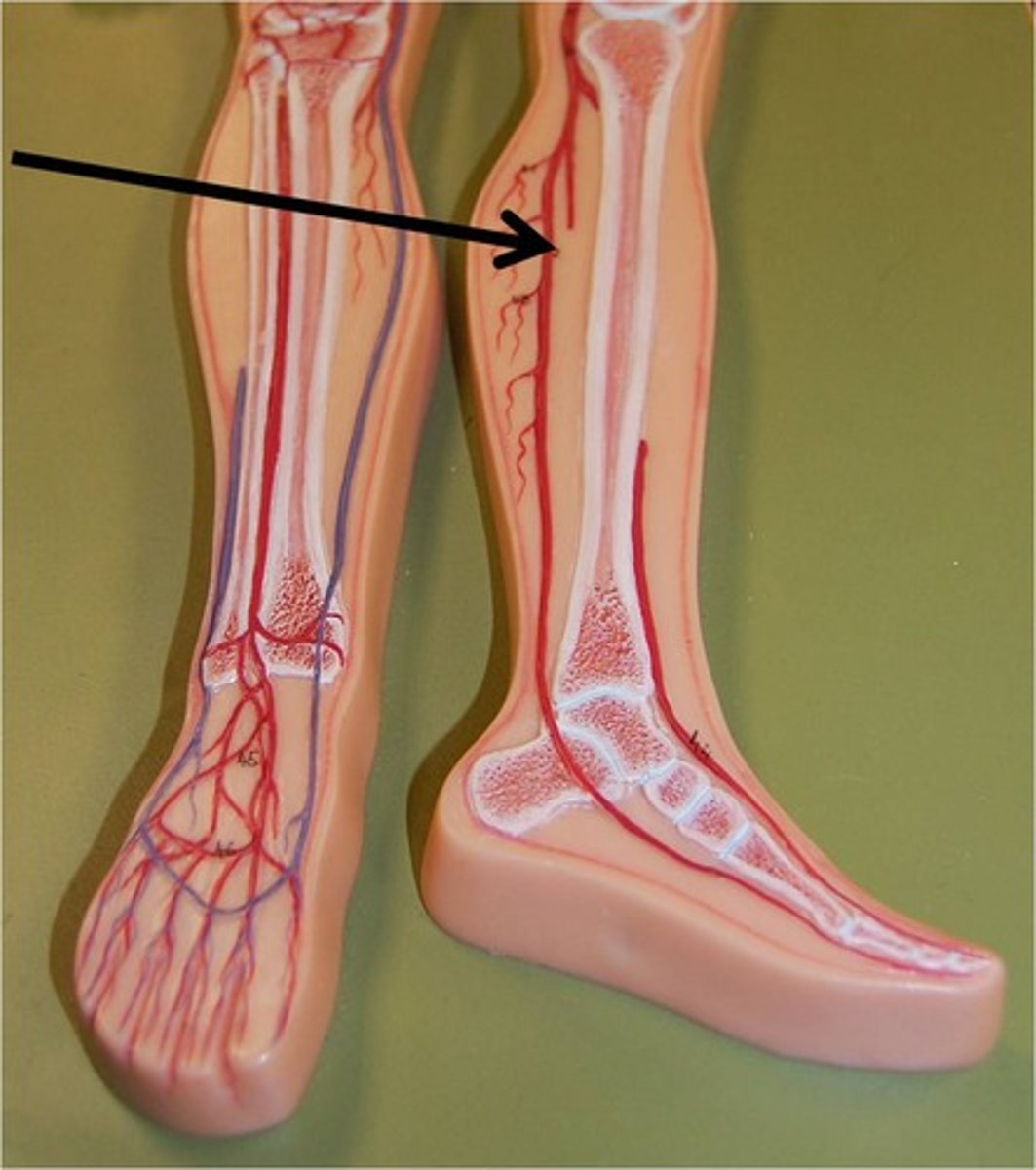
plantar arch
supplies blood to the planter foot
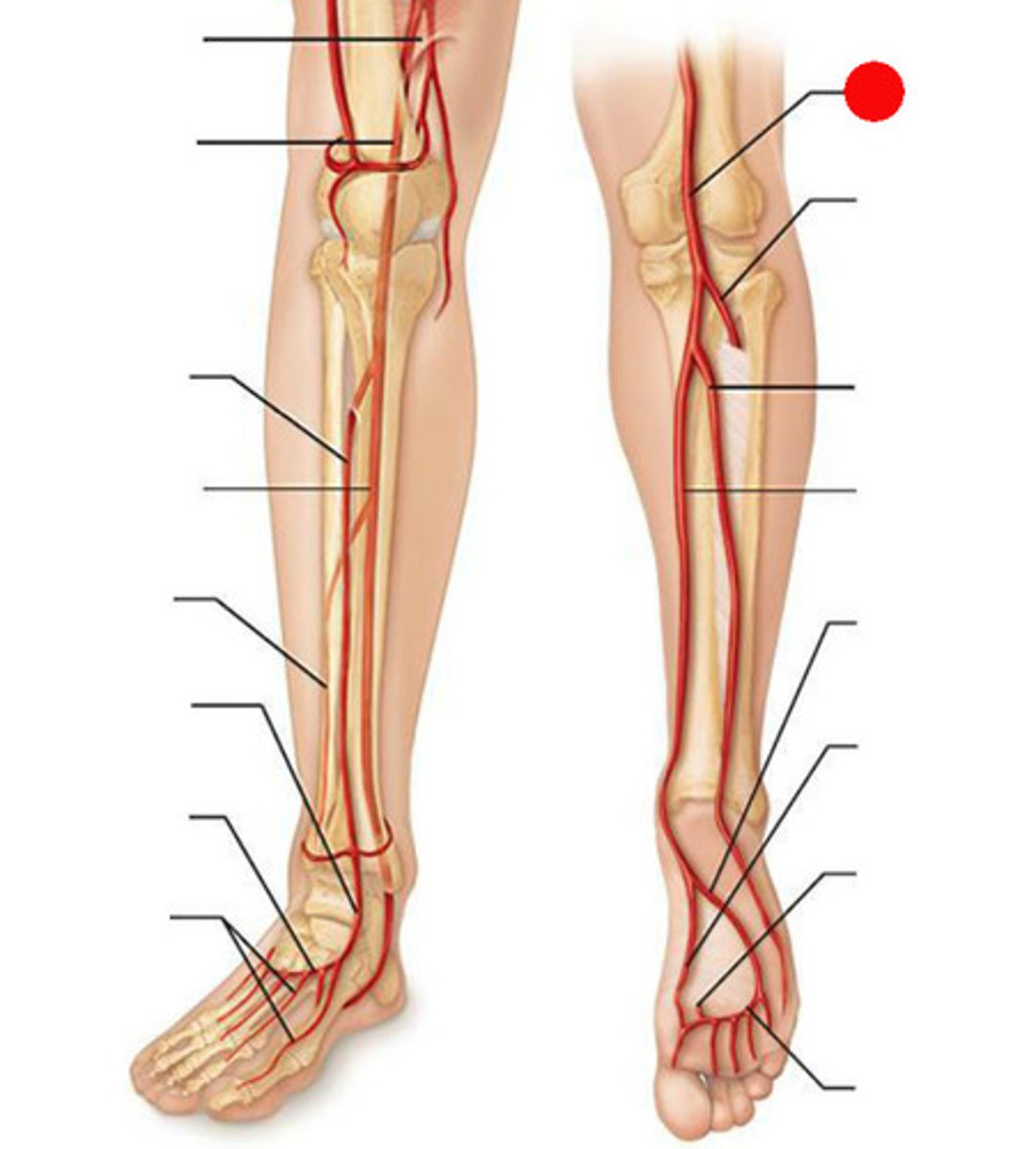
popliteal artery
gives off branches that supply the knee region; divides into two separate arteries known as the anterior tibial artery and the posterior tibial artery.
posterior tibial artery
forms the medial and lateral planter arches which supplies blood to the plantar foot.