Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
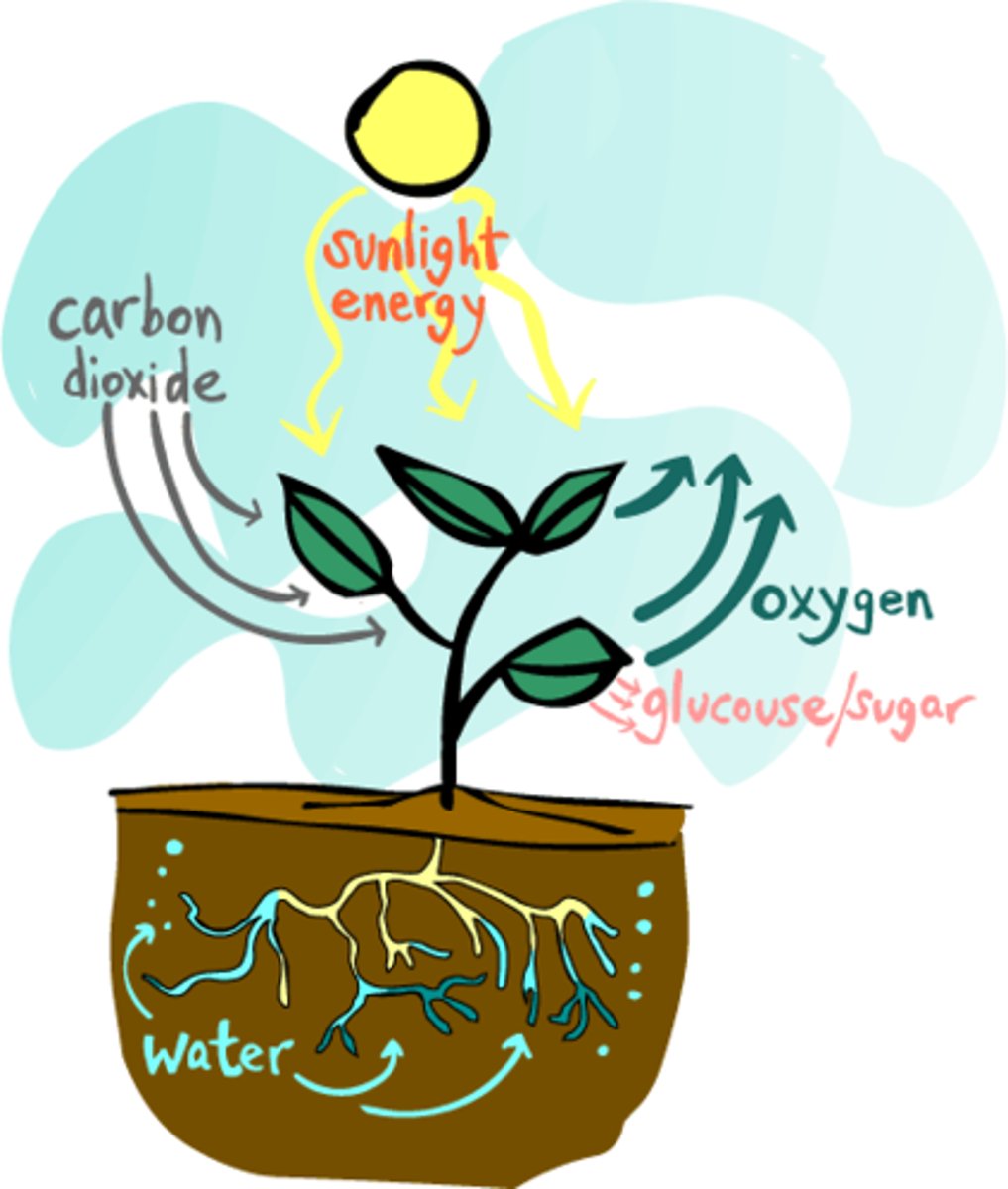
photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy, Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars (glucose)
autotroph
An organism that makes its own food

pigment
light-absorbing molecule

chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis

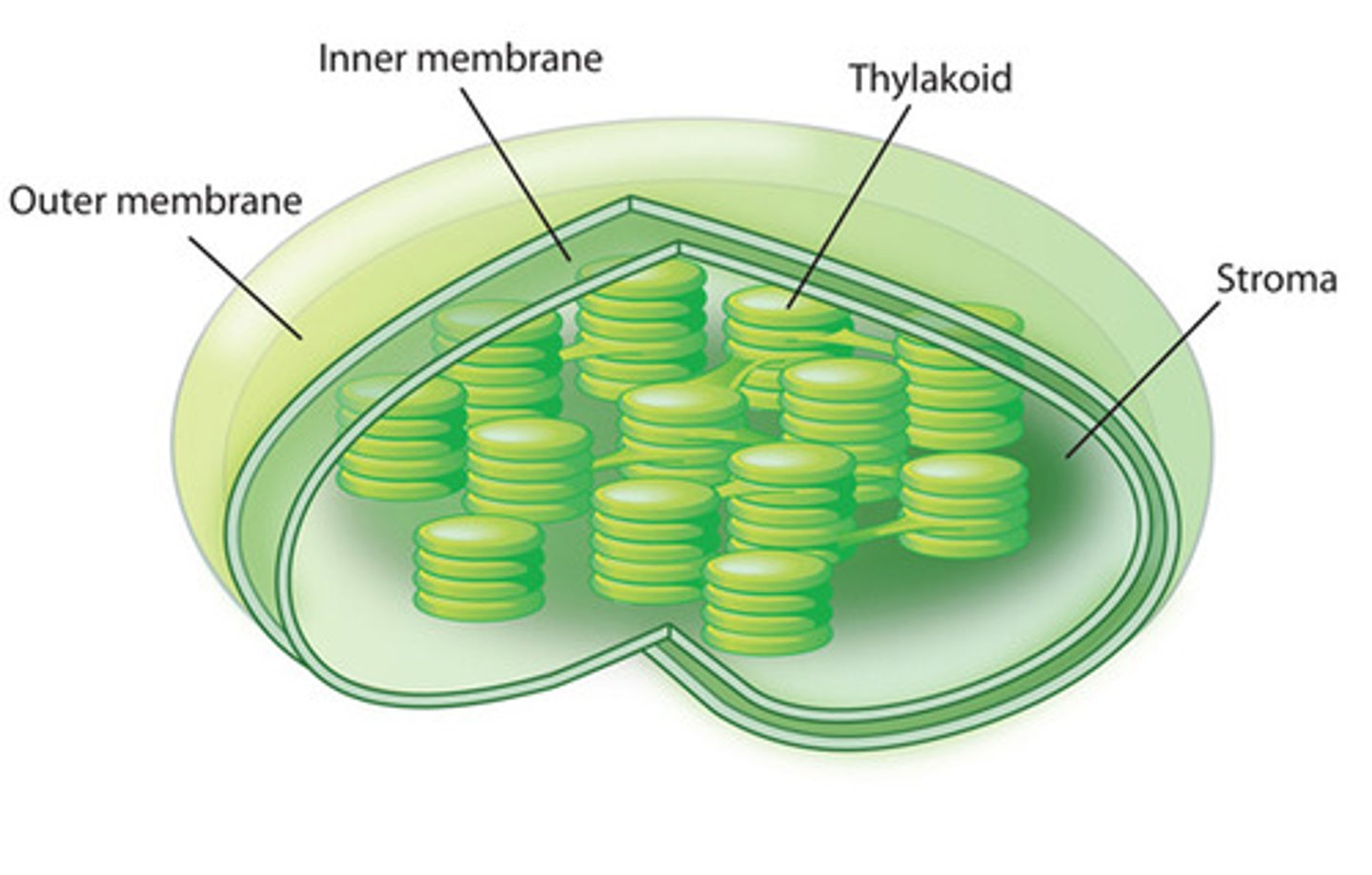
chloroplasts
Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell, site of photosynthesis
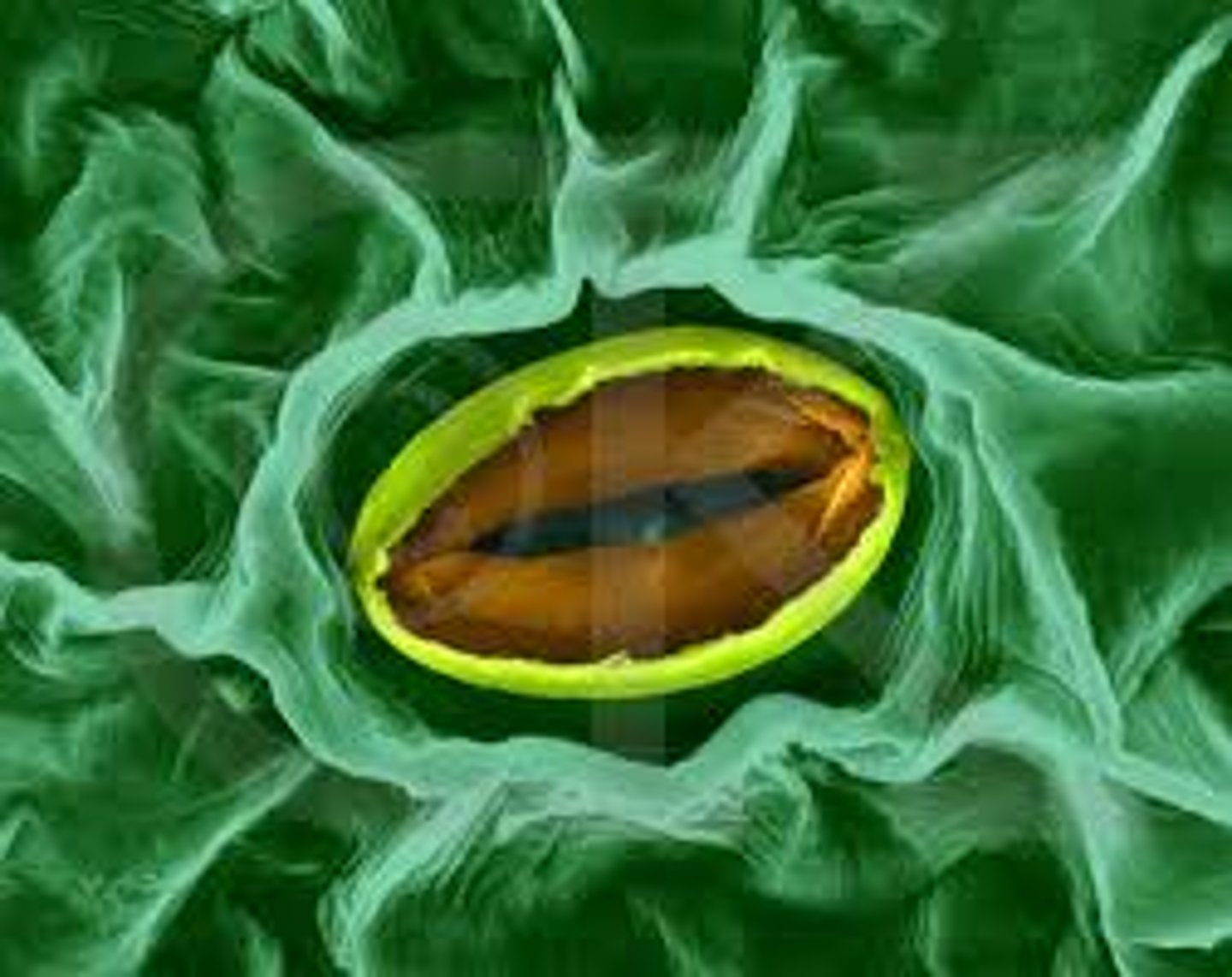
stoma / stomata
the small openings on the undersides of most leaves through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
carbon dioxide
CO2, gas that is a reactant of photosynthesis and a waste product of cellular respiration
oxygen
product of photosynthesis, reactant in cellular respiration
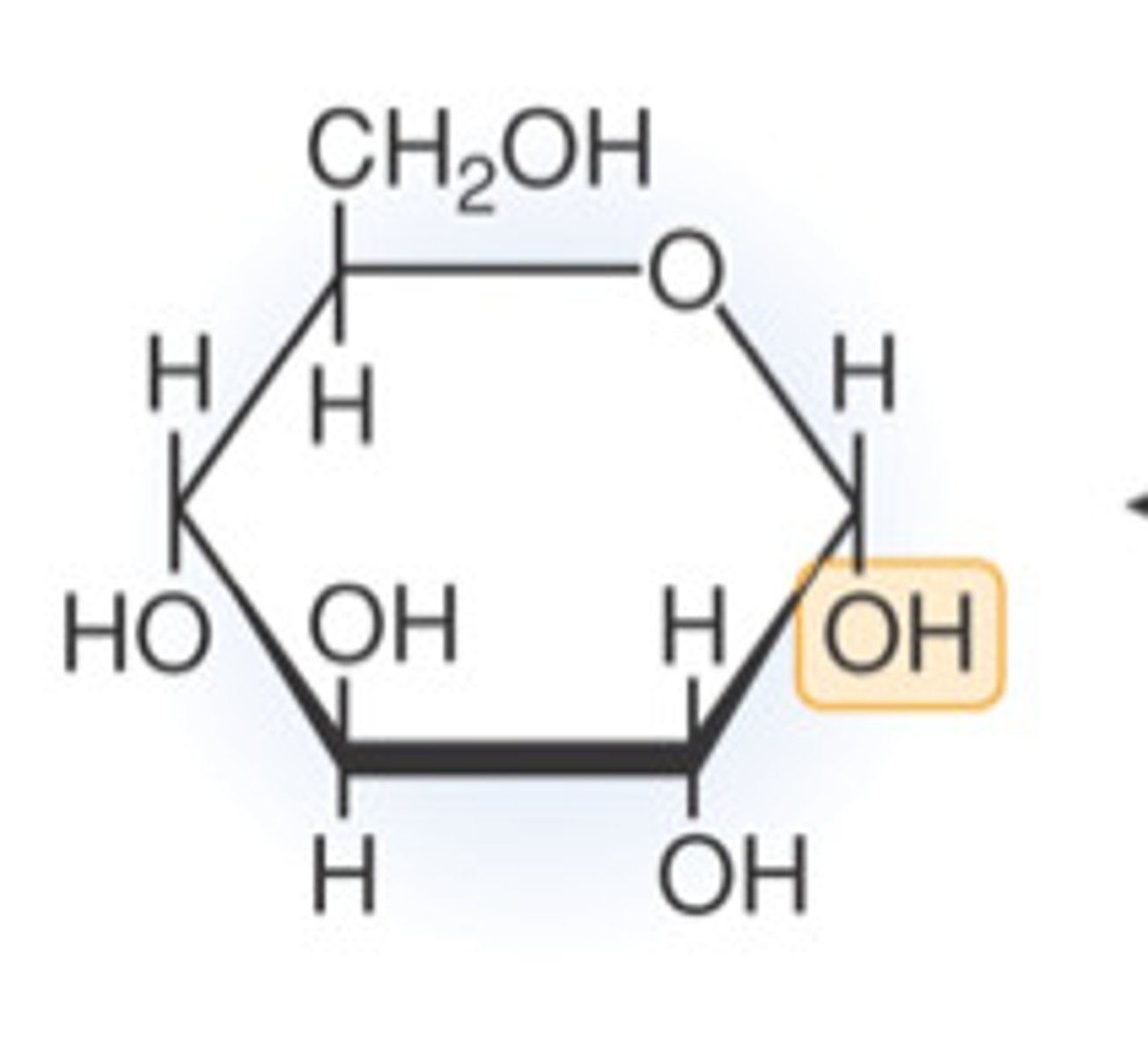
glucose
A simple sugar that is an important source of energy, product of photosynthesis
photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight ---> C6 H12 O6 + 6O2
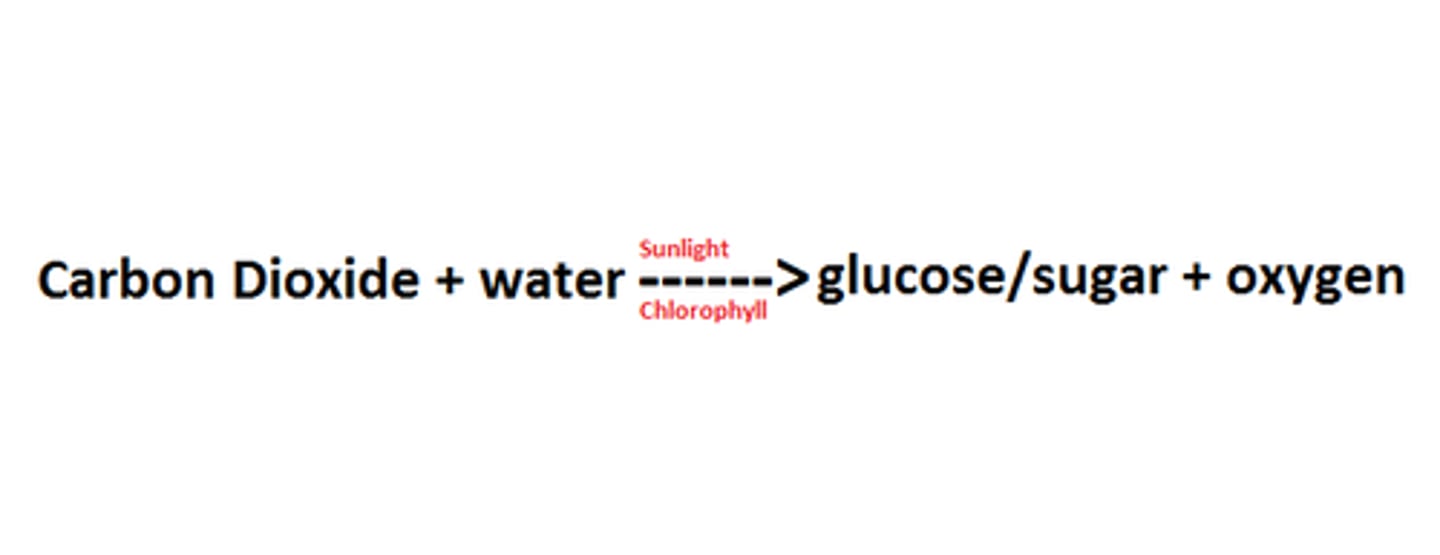
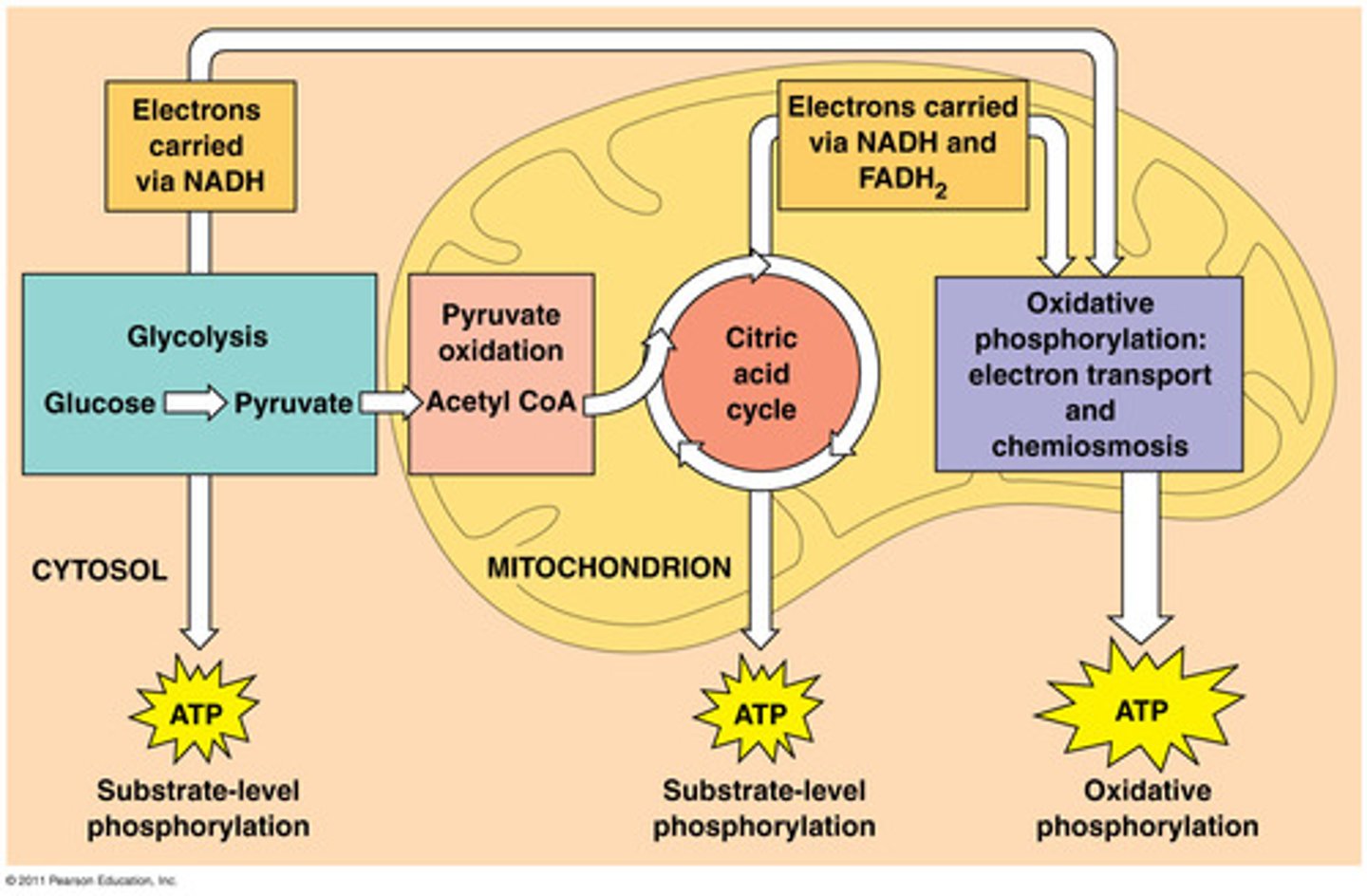
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O2 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (ATP)

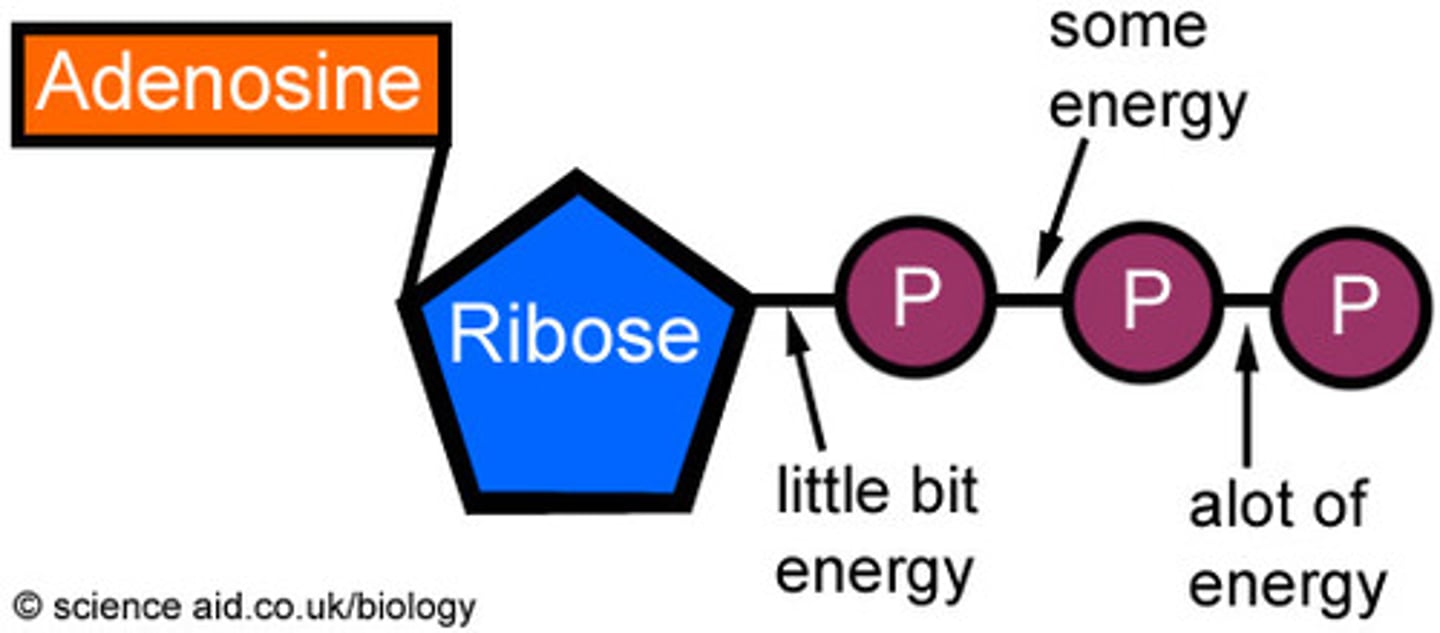
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production, where most of cellular respiration takes place

thylakoid membrane
membrane in a chloroplast where the light reactions of photosynthesis occur
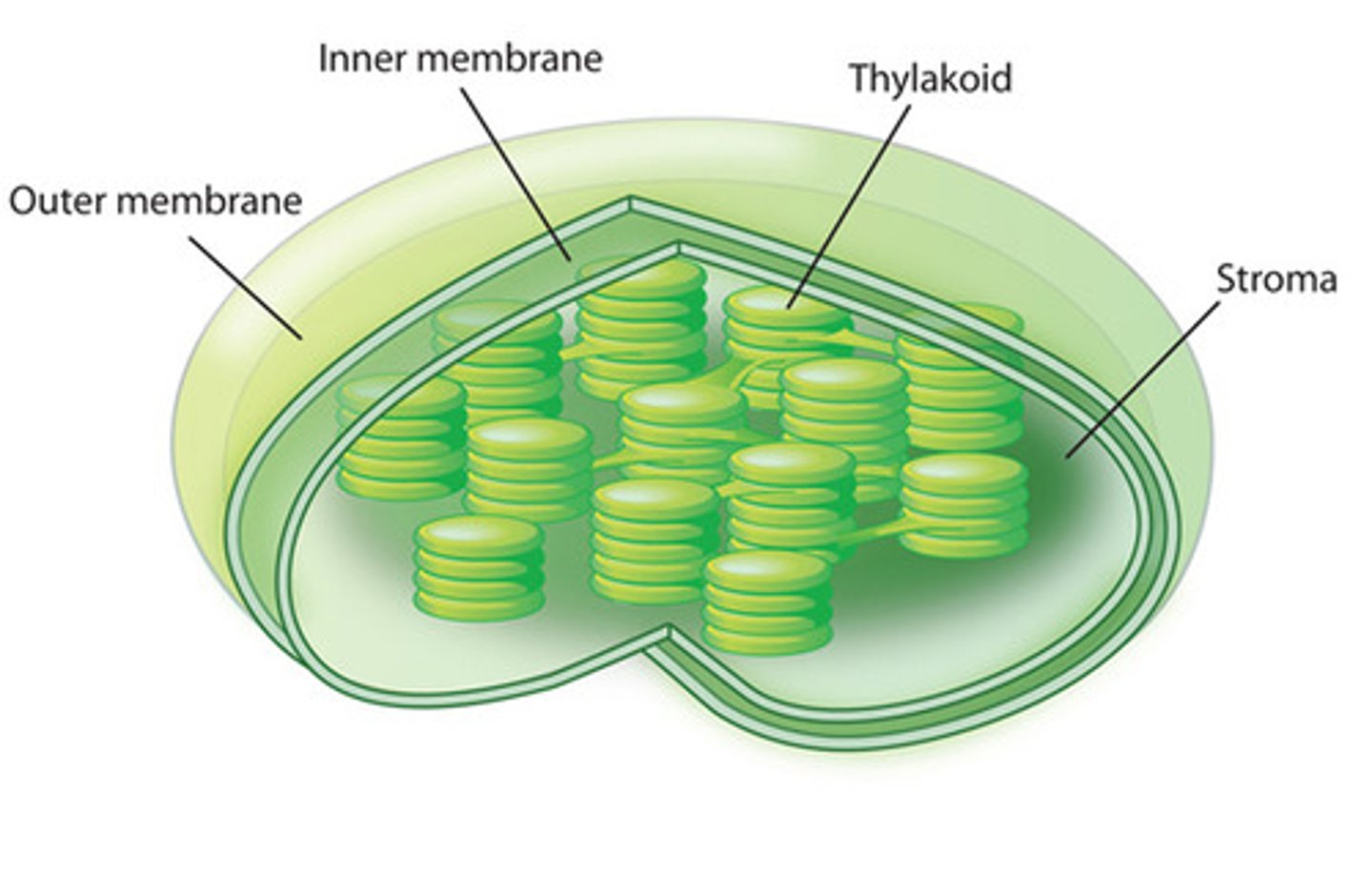
Stroma
The fluid of the chloroplast surrounding the thylakoid membrane; where the dark reactions occur, production of glucose.
Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food.

Cytoplasm/Cytosol
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended. Where chemical reactions occur.
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid.

Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
The third stage of cellular respiration, occurring within the inner membrane of the mitochondria, in which most of the ATP is formed.
alcoholic fermentation
the anaerobic process by which yeasts and other microorganisms break down sugars to form carbon dioxide and ethanol
lactic acid fermentation
Anaerobic series of reactions that convert glucose to lactic acid, in some bacteria and animal cells.
aerobic
requires oxygen
Anaerobic
without oxygen