Prostate Gland and Seminal Vesicles
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
how is the prostate located to the rectum
anterior
how is the prostate located to the bladder
inferior
Normal size of the prostate
3.5 cm × 2.5 cm 4 cm
What are the zones of the prostate
peripheral zone
central zone
transitional zone
posterior and lateral to distal prostatic urethra
largest zone
peripheral zone
extends from the base of the prostate to the verumontanum and surrounds the ejaculatory ducts
central zone
located on both sides of the proximal urethra
smallest zone
transitional zone
reservoir for sperm
joins vas deferens to form ejaculatory ducts
seminal vesicles
How does the seminal vesicles lie to the prostate
superior
normal length of the seminal vesicles
5cm
normal diameter of the seminal vesicles
<1cm
enter base of the prostate
pass through the prostatic portion of the urethra at the verumontanum
ejaculatory duct
runs from neck of bladder through prostate to the base of the penis
urethra
Normal PSA level
<30mL
sonographic appearance of the prostate
homogeneous, medium level echo parenchyma
smooth contour
well defined walls
calfications common in older men
Sonographic appearance of seminal vesicles
hypoechoic ovoid structures superior to gland
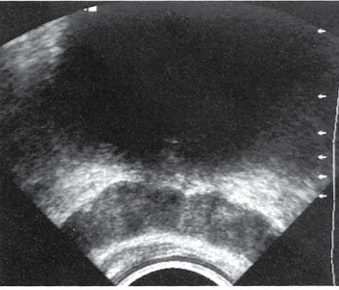
seminal vesicles
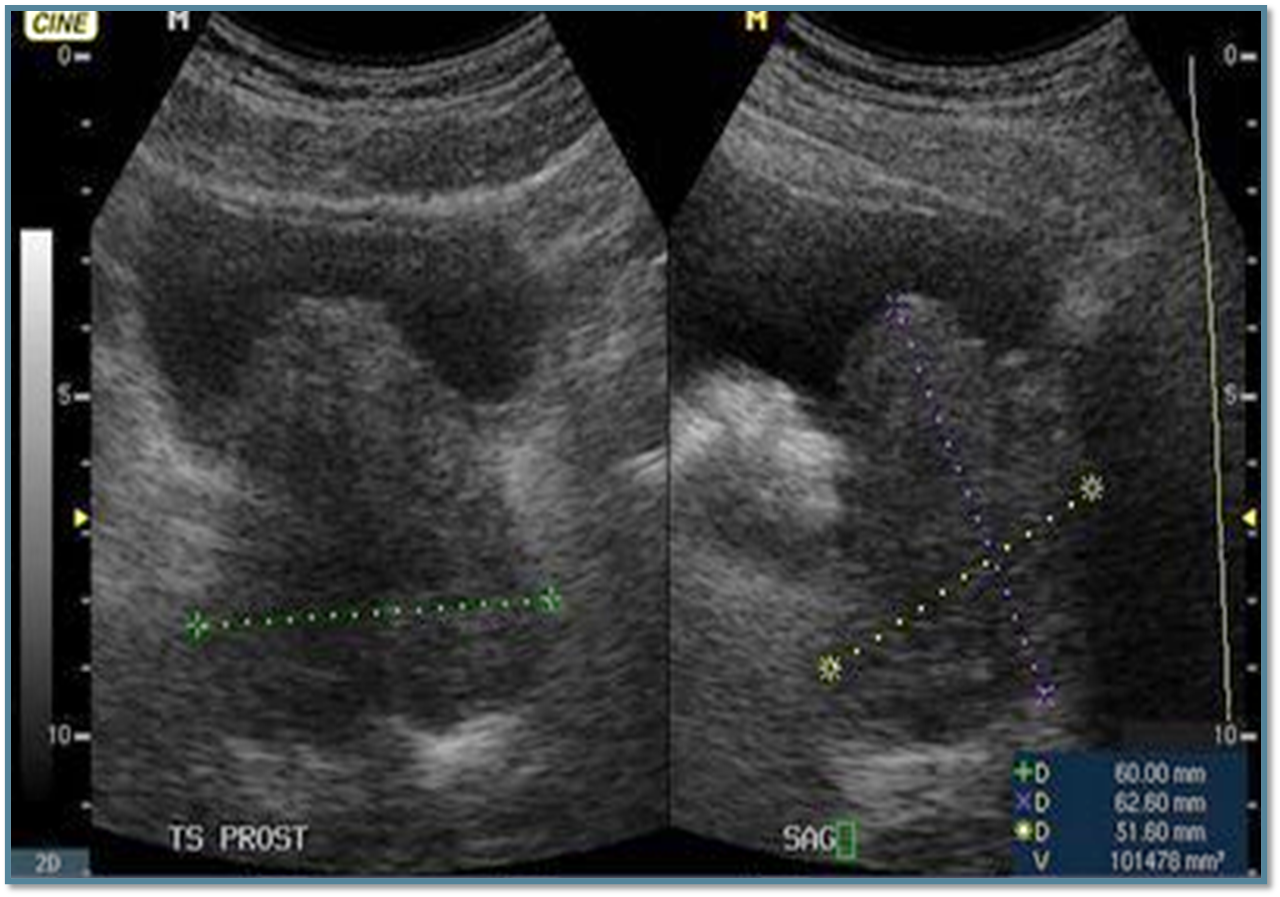
benign prostate hyperplasia
common in older men
metastasizes to the bone
hematuria
bloody semen
black pain
adenocarcinoma
transitional zone naturally enlarges with age
impedes urine flow, frequency, and urgency
benign prostate hyperplasia
sonographic findings of benign prostate hyperplasia
enlargment
hypoechoic to hyperechoic
cystic areas and calcifications
nodules
20-30mL
sonographic findings of adenocarcinoma
hypervascular
70% mass in PZ
definable hypoechoic lesions
isoechoic bulge in capsule
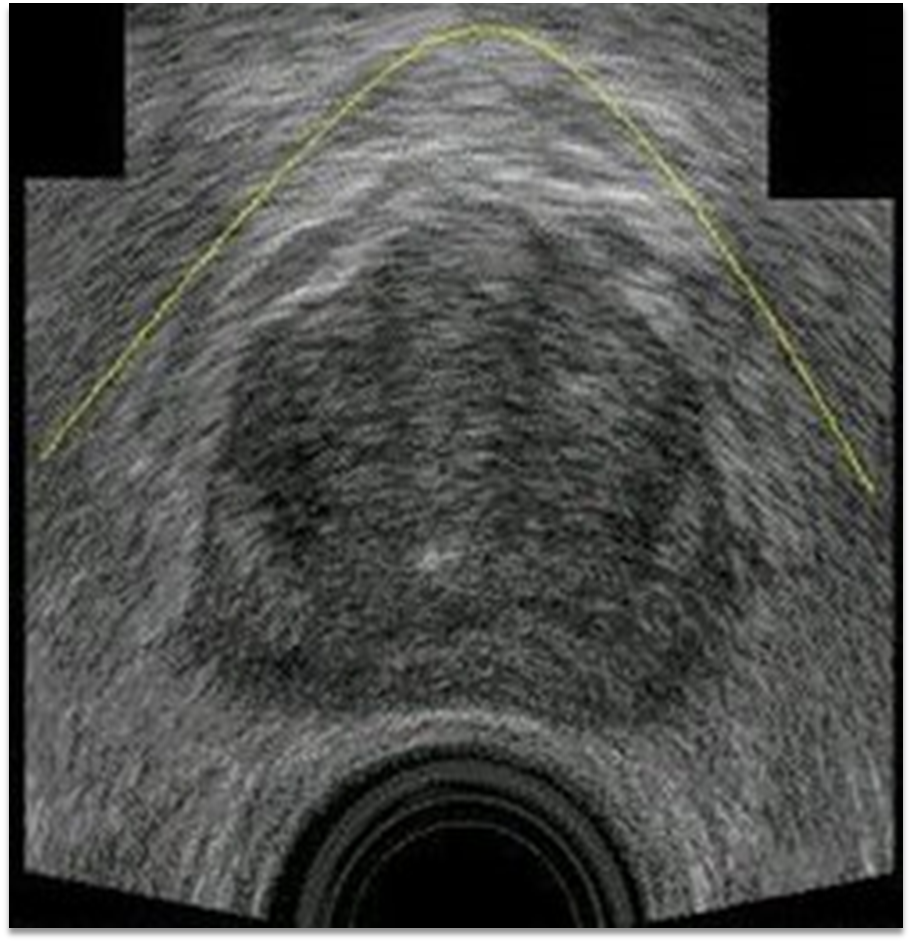
adenocarcinoma
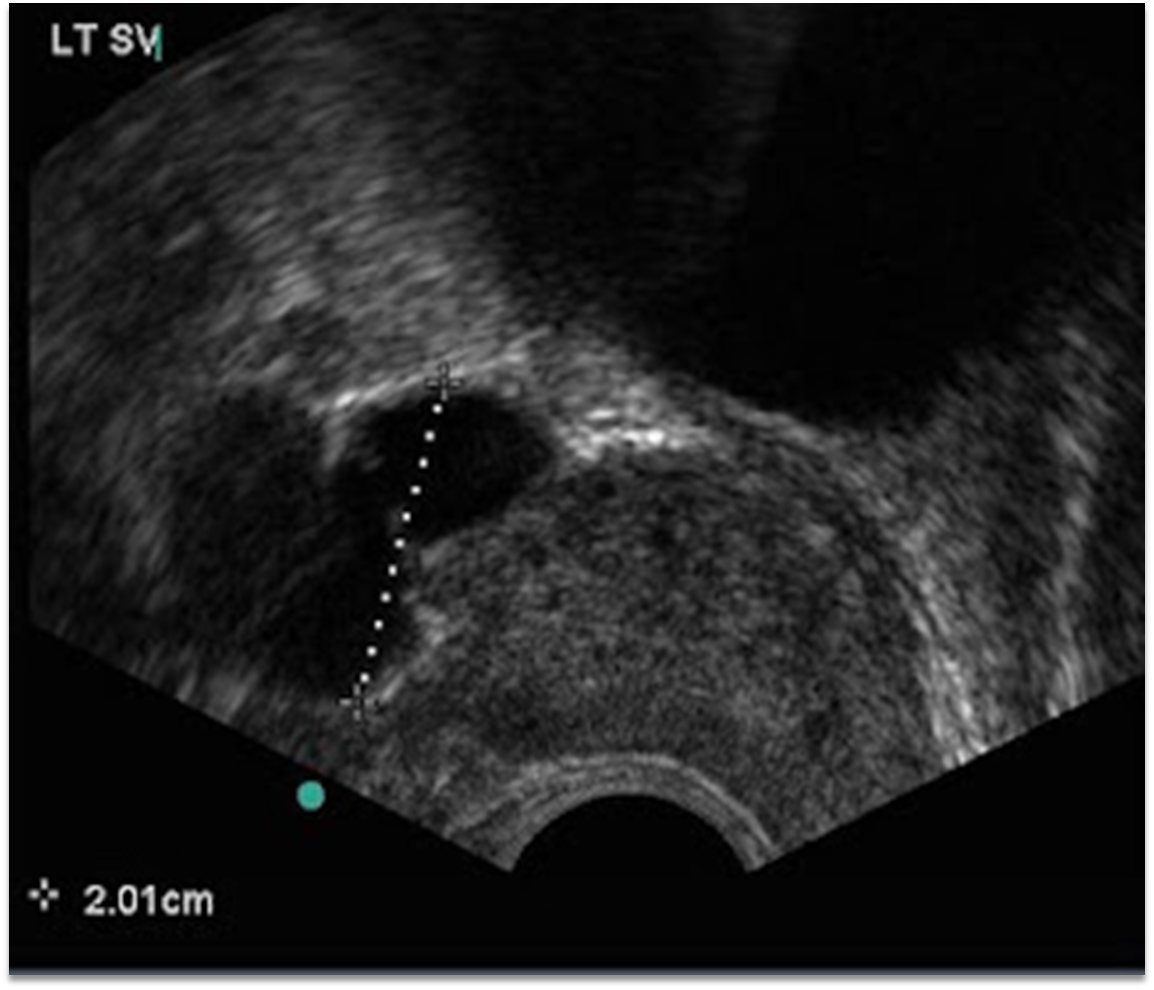
dilation of seminal vesicle
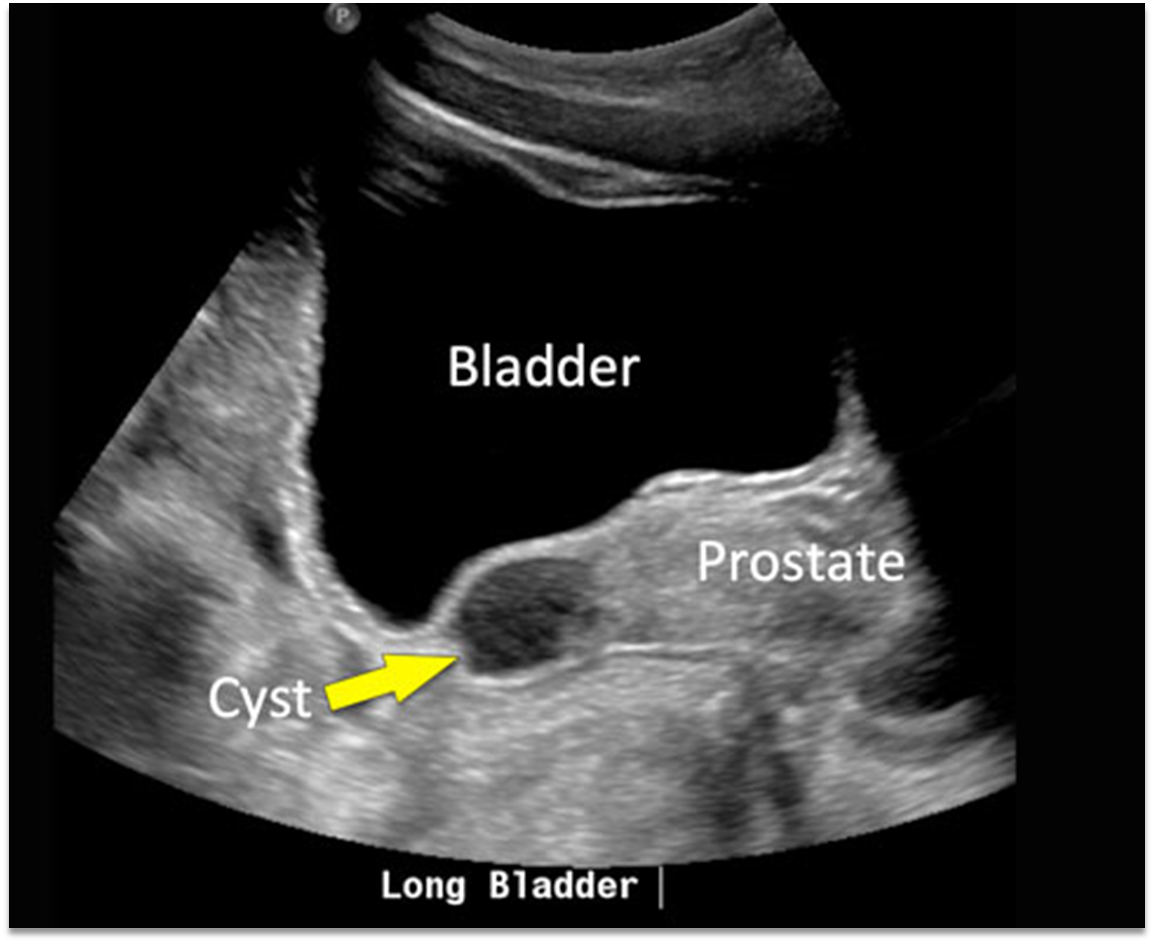
cyst of seminal vesicle