AP Biology Unit 4 Cell Communication and Signal Transduction
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Endocrine system
Secretes hormones into blood from ductless glands that coordinate slower but longer-acting responses
Paracrine
Signals act on cells near the secreting cell
Local regulators
Chemical signals that travel over short distances due to diffusion
Autocrine
Signals act on the secreting cell itself (usually for apoptosis)
Pheromones
Chemical signals that are released from the body and are used to communicate with other individuals
Type I diabetes mellitus
An autoimmune disorder in which the immune system destroys pancreatic beta cells (usually develops while you're young)
Type II diabetes mellitus
Involves insulin deficiency or reduced response of target cells due to change in insulin receptors (due to being overweight and not exercising)
Hormone
A regulatory substance produced in an organism and transported in tissue fluids such as blood or sap to stimulate specific cells or tissues into action.
Negative Feedback
The diminution or counteraction of an effect by its own influence on the process giving rise to it, as when a high level of a particular hormone in the blood may inhibit further secretion of that hormone, or where the result of a certain action may inhibit further performance of that action.
Plant growth regulator
Organic compounds other than nutrients (like hormones that affect plant growth.
tropism
A growth response that results in the curvature of whole plant organs toward or away from stimuli owing to differential rates of cell elongation.
phototropism
Growth of a plant shoot toward or away from light.
action potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
cyclin
a regulatory protein whose concentration fluctuates cyclically depending if the cell needs to divide or not. If the cell receives growth signals, then it will produce more cyclins

cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk)
a protein kinase that is only active when attached to a particular cyclin--> drives the cell cycle forward when activated. Can be inactivated by cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors

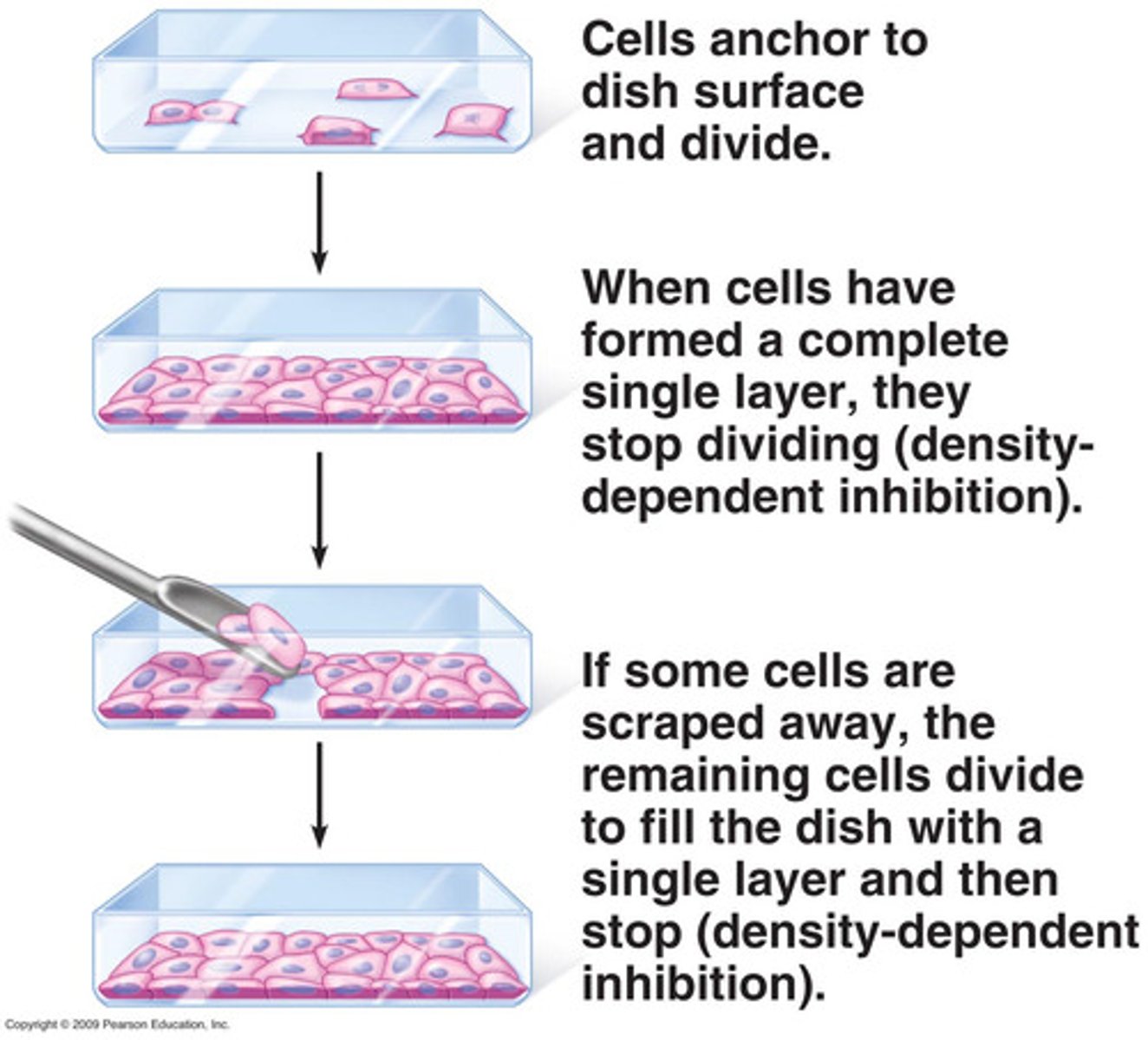
density-dependent inhibition
the phenomenon observed in normal animal cells that causes them to stop dividing when they come into contact with one another
growth factor
a protein that must be present in the extracellular environment for growth and normal development of certain types of cells; a local regulator that acts on nearby cells to stimulate cell proliferation and differentiation
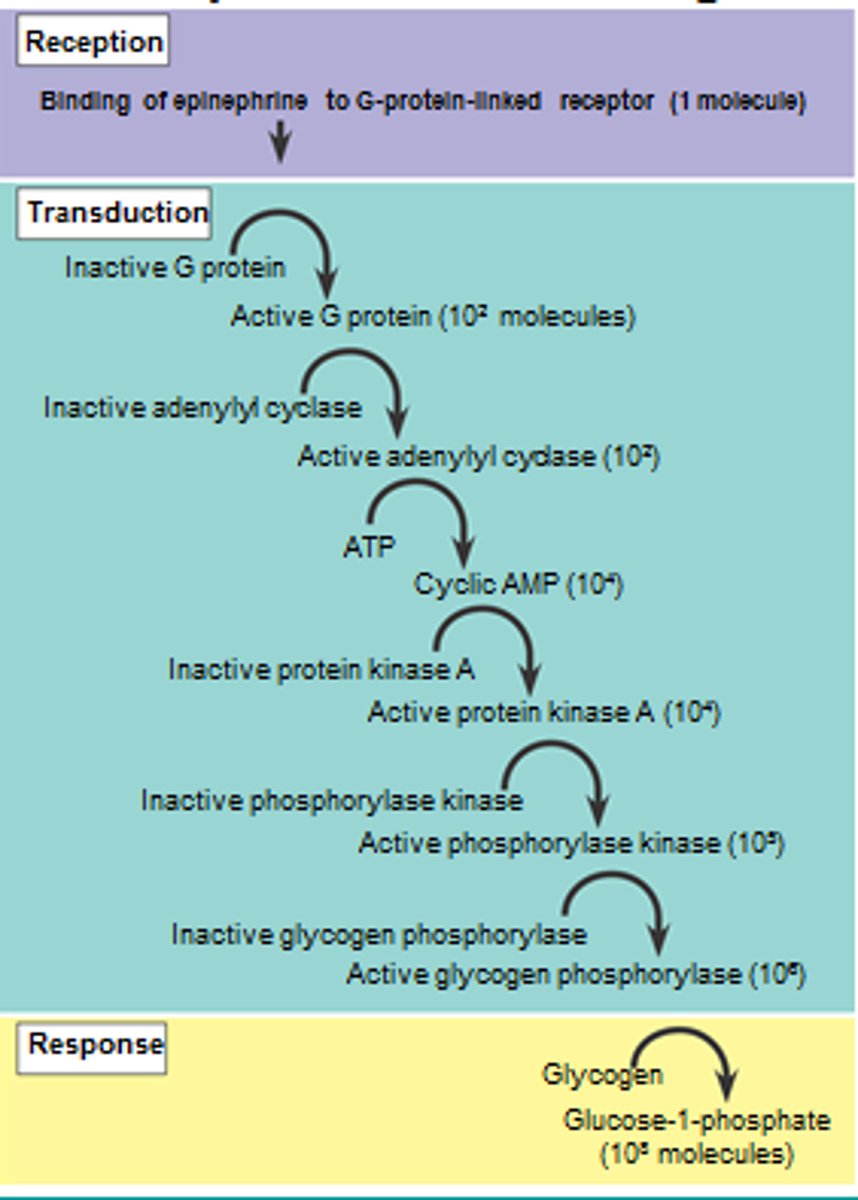
amplification
The strengthening of stimulus energy during transduction.
apoptosis
A program of controlled cell suicide, which is brought about by signals that trigger the activation of a cascade of suicide proteins in the cell destined to die.
epinephrine
water soluble ligand molecule; A catecholamine that, when secreted by the adrenal medulla, mediates "fight-or-flight" responses to short-term stresses; also released by some neurons as a neurotransmitter; also known as adrenaline.
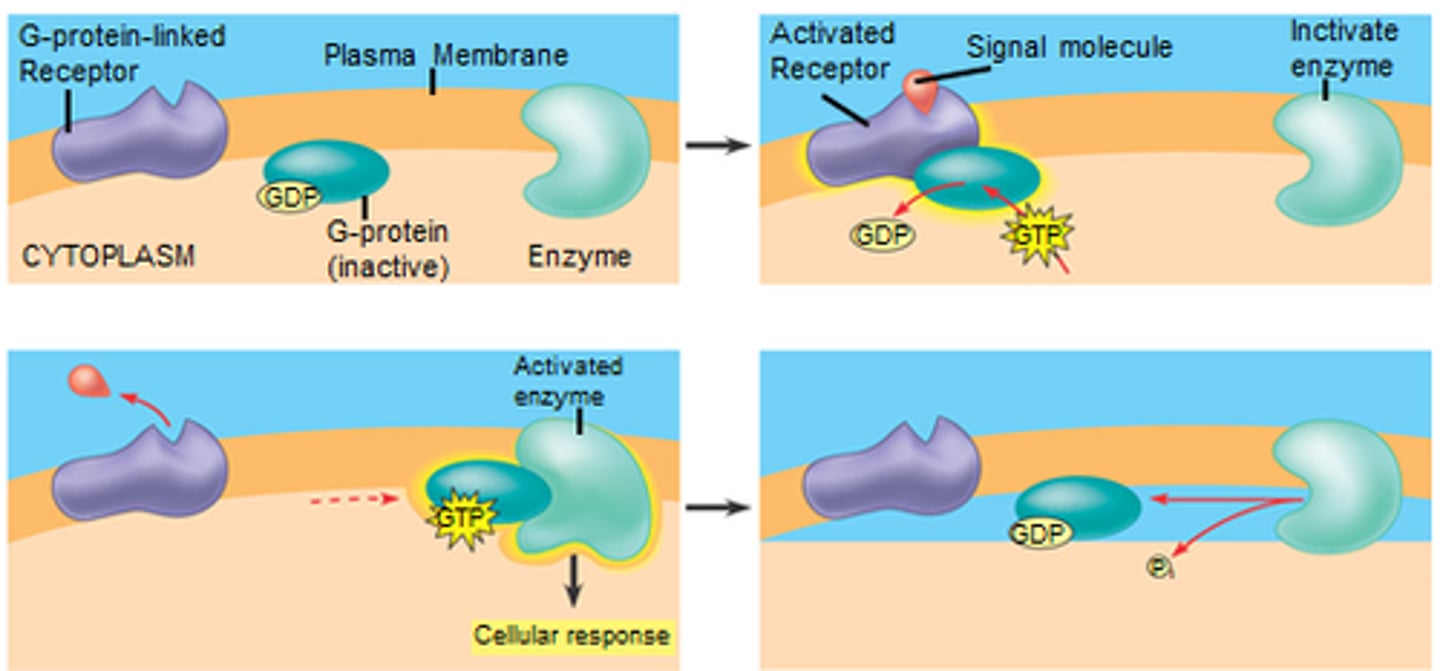
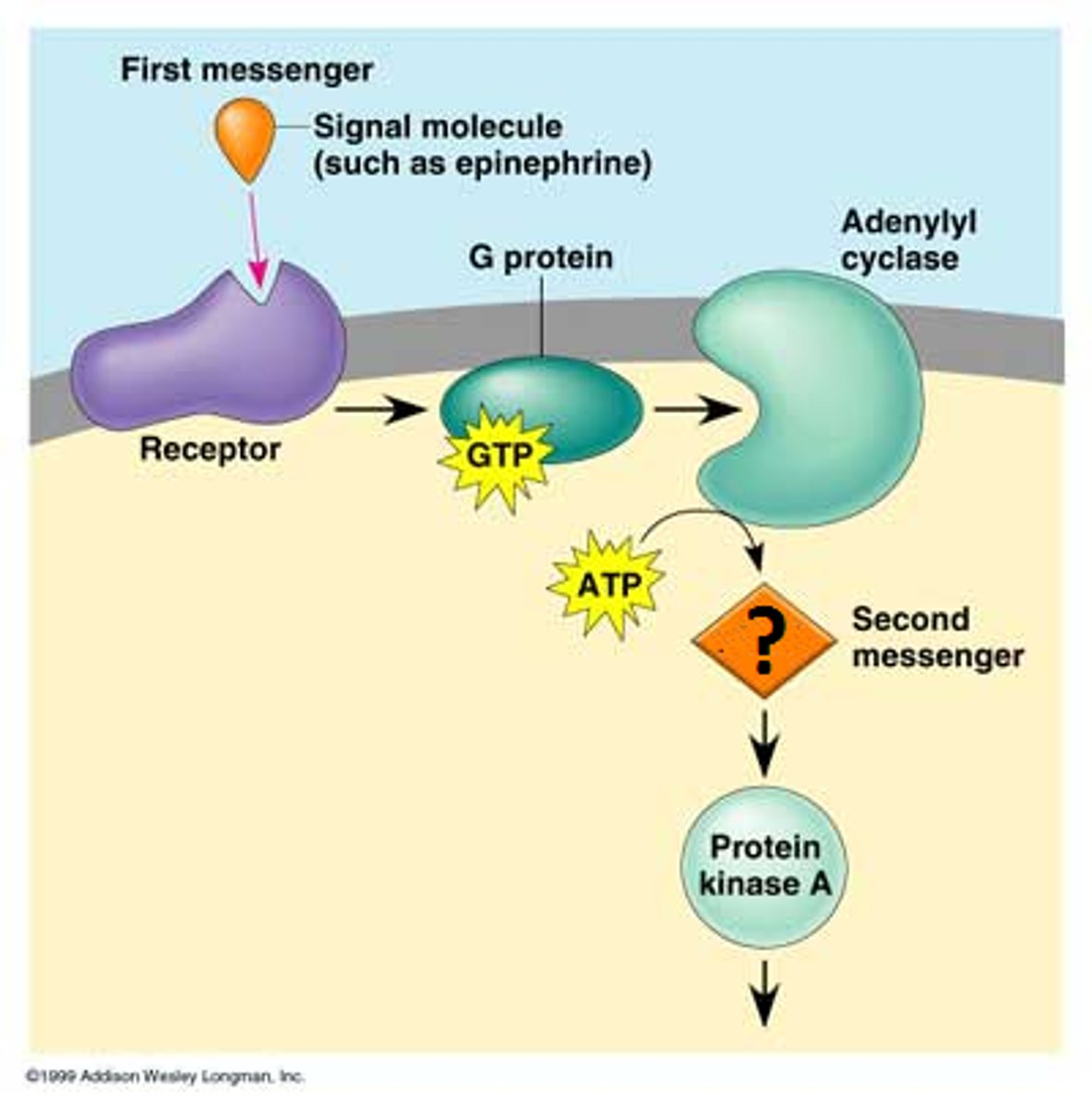
G protein
A GTP-binding protein that relays signals from a plasma membrane signal receptor, known as a G protein-coupled receptor, to other signal transduction proteins inside the cell.
gap junction
A type of intercellular junction in animals that allows the passage of materials between cells.

glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch. Breakdown of this molecule into glucose for release into the bloodstream is controlled by the Gprotein signaling pathway
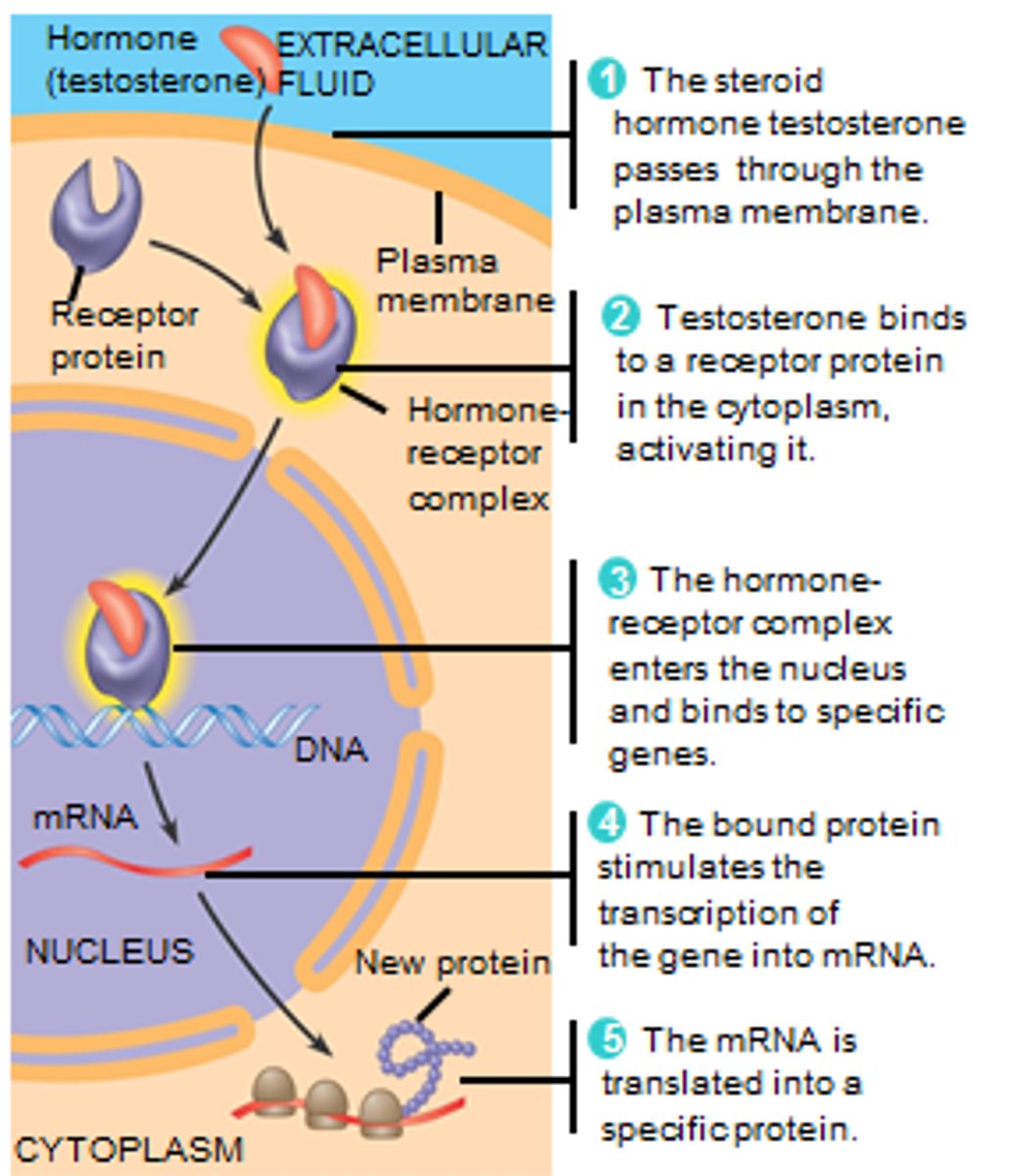
ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to another molecule; often first step in cell communication. Hydro-philic ligands typically do not enter cell. Hydro-phobic ligands (such as steroids) do enter the cell.
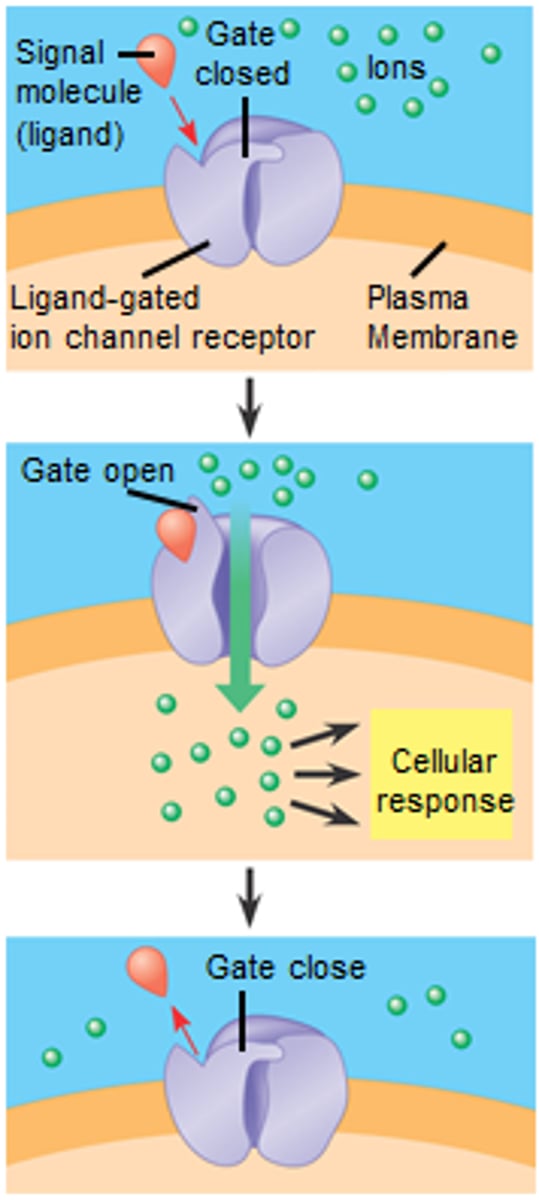
ligand-gated ion channel
A protein pore in cellular membranes that opens or closes in response to A signaling chemical (its ligand), allowing or blocking the flow of specific ions.
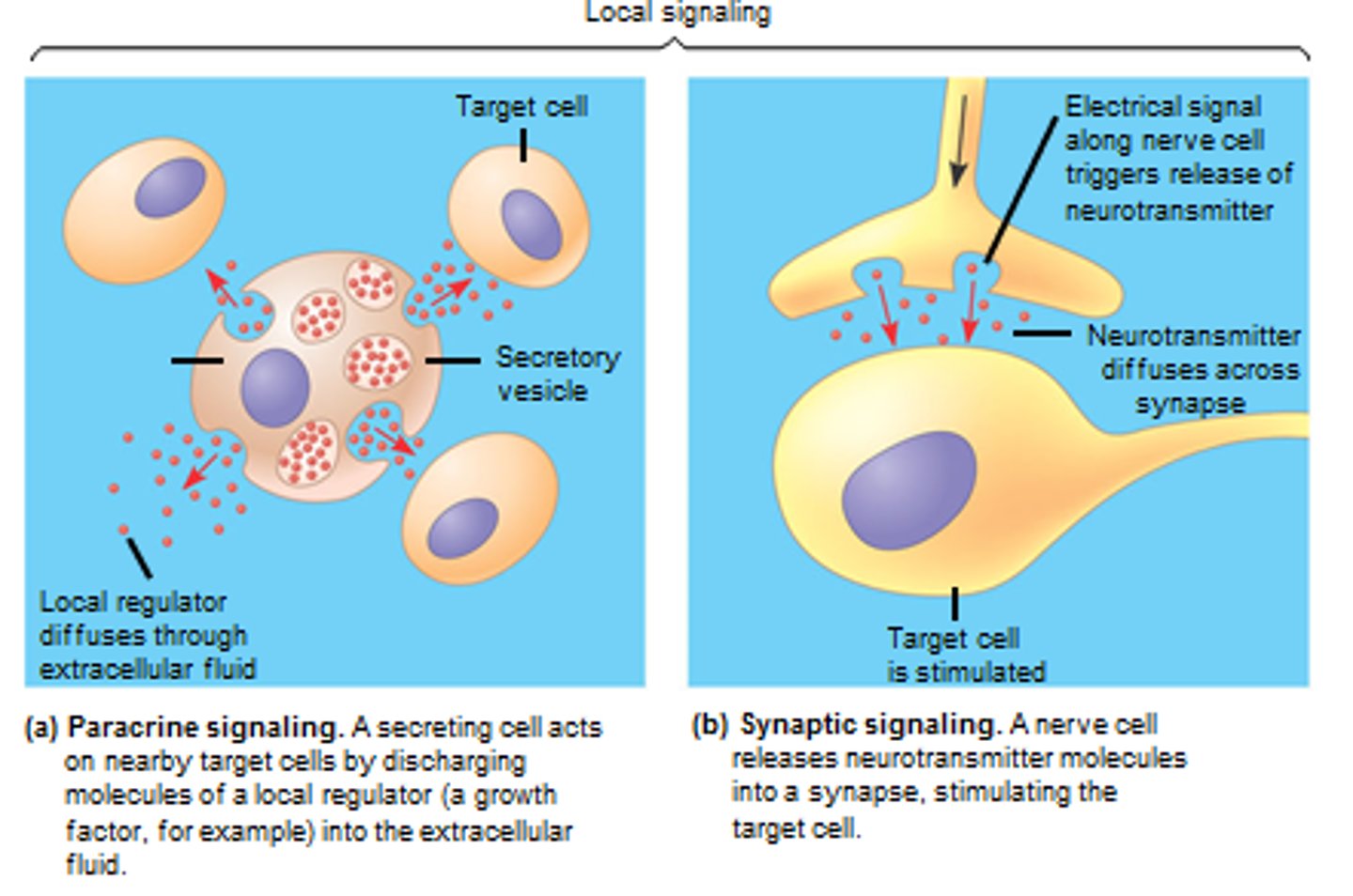
local regulator
A secreted molecule that influences cells near where it is secreted. Used in paracrine and synaptic signaling.
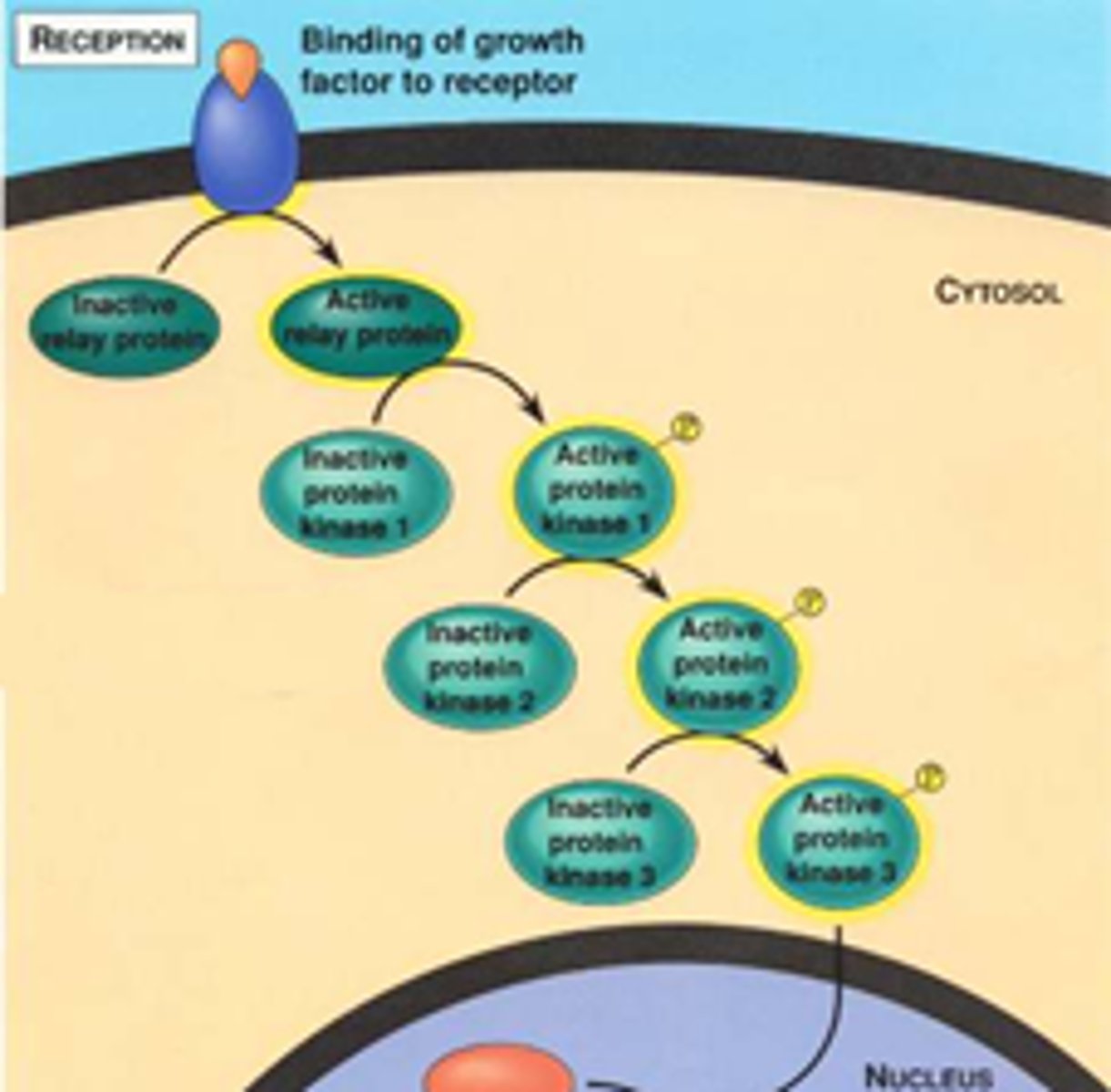
protein kinase
An enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein, thus phosphorylating the protein (and turning it on to create a cellular response).
protein phosphatase
An enzyme that removes phosphate groups from (dephosphorylates) proteins, often functioning to reverse the effect of a protein kinase. (An off switch for the protein)
second messenger
A small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecule or ion, such as a calcium ion (Ca2+) or cyclic AMP, that relays a signal to a cell's interior in response to a signaling molecule bound by a signal receptor protein.
transcription factor
A regulatory protein that binds to DNA and affects transcription of specific genes. The hormone-receptor complex becomes a transcription factor in the steroid transduction pathway.
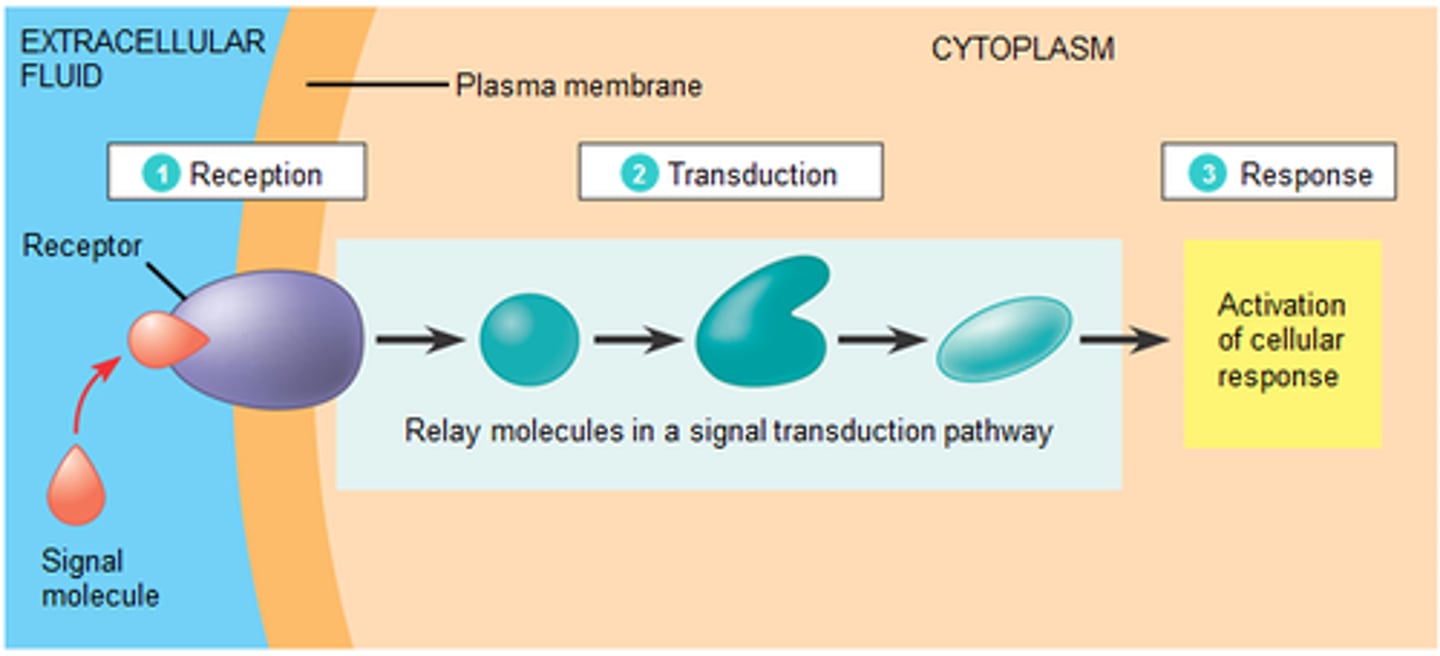
three stages of cell communication
reception - receptor responds to binding of ligand molecule; transduction - translation and amplification of message; response - activation of cellular response
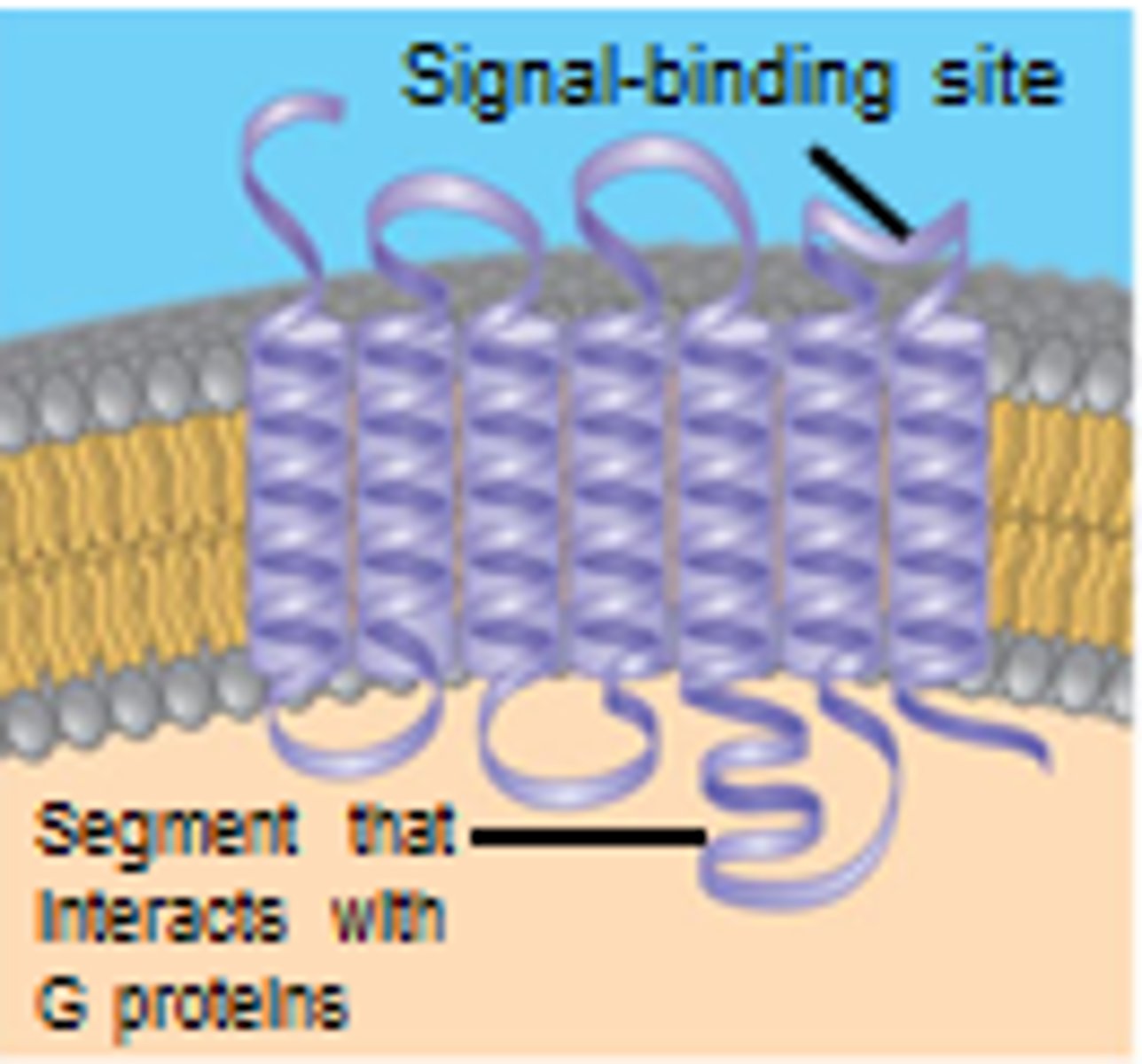
g-linked protein receptor
receives message for g-linked protein signaling pathway. Consists of seven alpha helices that span the plasma membrane. Changes shape when ligand molecule binds.
signal transduction pathway
The process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted into a specific cellular response.
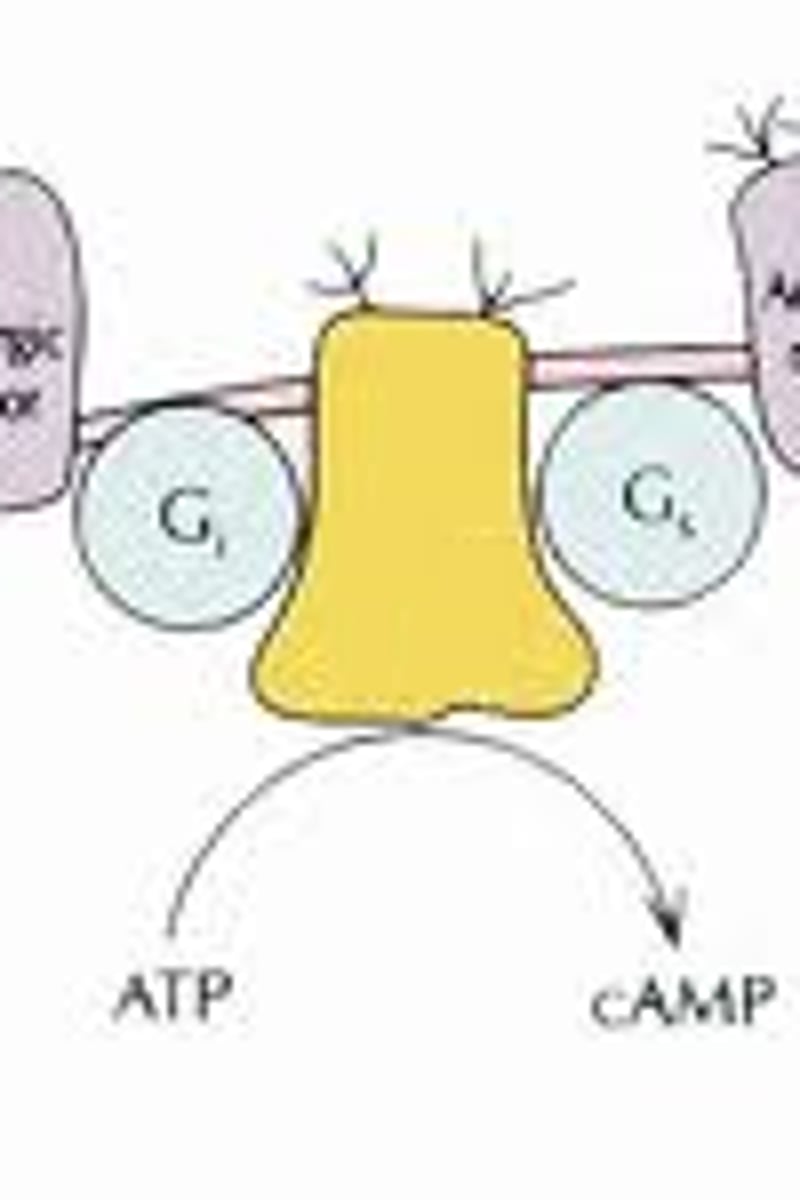
adenylyl cyclase
Converts ATP to cyclic AMP in response to an extracellular signal.
reception
The target cell's detection of a signal molecule coming from outside the cell.
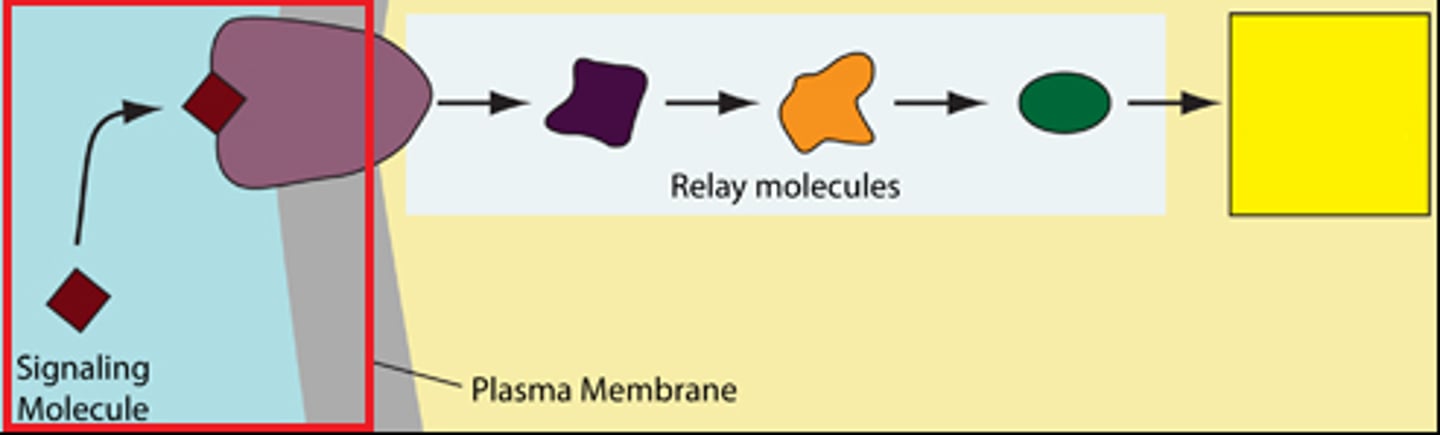
transduction
The binding of the signal molecule changes the receptor protein in some way.
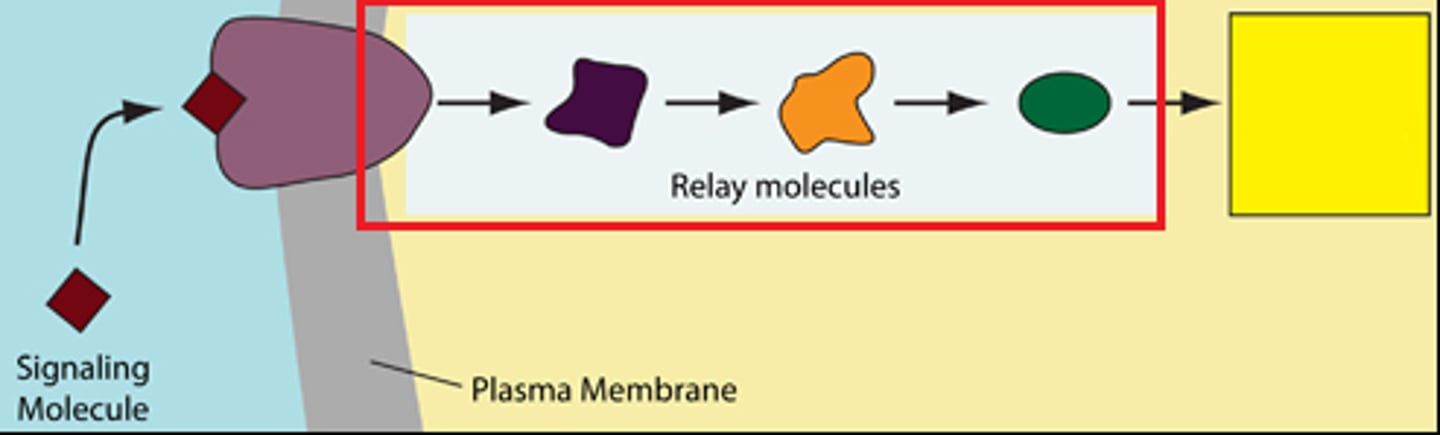
response
The transduced signal finally triggers a specific cellular response.
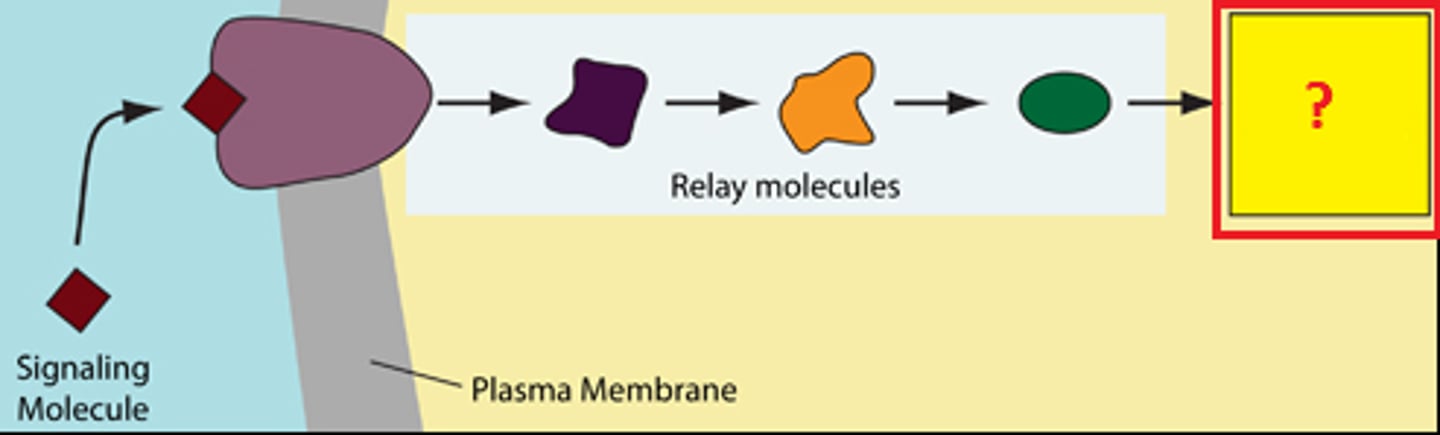
juxtacrine signaling
Type of cell to cell signalling in multicellular organisms that requires close contact (AKA contact-dependent signalling)
synaptic signalling
Type of signalling that occurs over a very short distance called a synapse such as between 2 neurons.
cAMP
Common second messenger which is a derivative of ATP and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms
positive feedback
A process in which the end products of an action cause more of that action to occur (for example: blood clotting, labor during childbirth)
effector
A molecule that binds to a protein and affects the function of that protein.
stimulus
An object, event, or factor capable of inciting a physiological response.
set point
The ideal or target value of a physiological variable.
receptor
A specialized molecular component within or on the surface of a cell that detects and responds to a specific signal.
disease
A abnormal condition of an organism which interrupts the normal bodily functions